L31 Immune cells in blood
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key concepts from HUBS 191 Lecture 31 Immunology II
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Components of blood
Plasma and cells (formed elements).
Cells or formed elements 45%
Platelets, white blood cells (leukocytes), and red blood cells.
Plasma 55%
Proteins in cluding antibodies/immunoglobin. Other solutes and water.
Bone marrow stem cells
Source of blood cells (hematopoiesis). Derived from these are myeloid and lymphoid blood cell lineages.
Myeloid lineage
Red blood cells, granulocytes, monocytes, DC, and platelets.
Lymphoid lineage
B and T lymphocytes.
Granulocytes
Neutrophils and mast cells. Neutrophils circulate in blood and can move into tissue during inflammation. Mast cells stay in mucosal membranes.
Neutrophils
75% of all leukocytes, highly phagocytic (eat and kill) numbers increase during infection. Multi-lobed nucleus
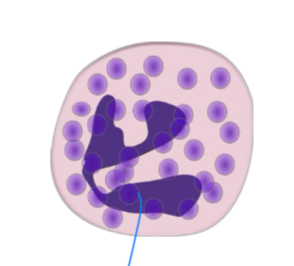
Mast cells
Line mucosal surfaces (not found in blood), release granules that attract leukocytes to areas of tissue damage.
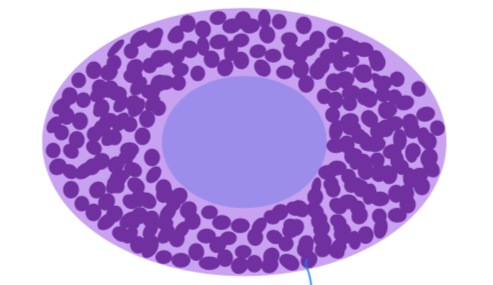
Monocytes
Present in blood, low phagocytosis (engulfing). Can move into tissue at site of inflimmation where they develop into macrophages (high phagocytosis).
Macrophages
Become resident, or move through tissues (migratory). Functions= phagocytosis, release of chemical messengers, showing information about pathogenic microbes to T cells (link innate and adaptive).
DC
Low numbers in blood and tissues, very potent, highly phagocytic, most important cell type to help trigger adaptive immune responses (links innate and adpative).
How cells of immune system move around body
Carried in the blood and lymph nodes, leave blood to enter tissues, lymph in tissues drain into lymph nodes via lymphatic vessels. Can re-enter blood and circulate.
Virus PAMPS
envelope, nucleocapsid, nucleic acid ssRNA and dsDNA.
Bacteria PAMPs
Cell wall (LPS)/endotoxins, lipoteichoic acid. Flagella. Nucleic acid- unmethylated CpG DNA.
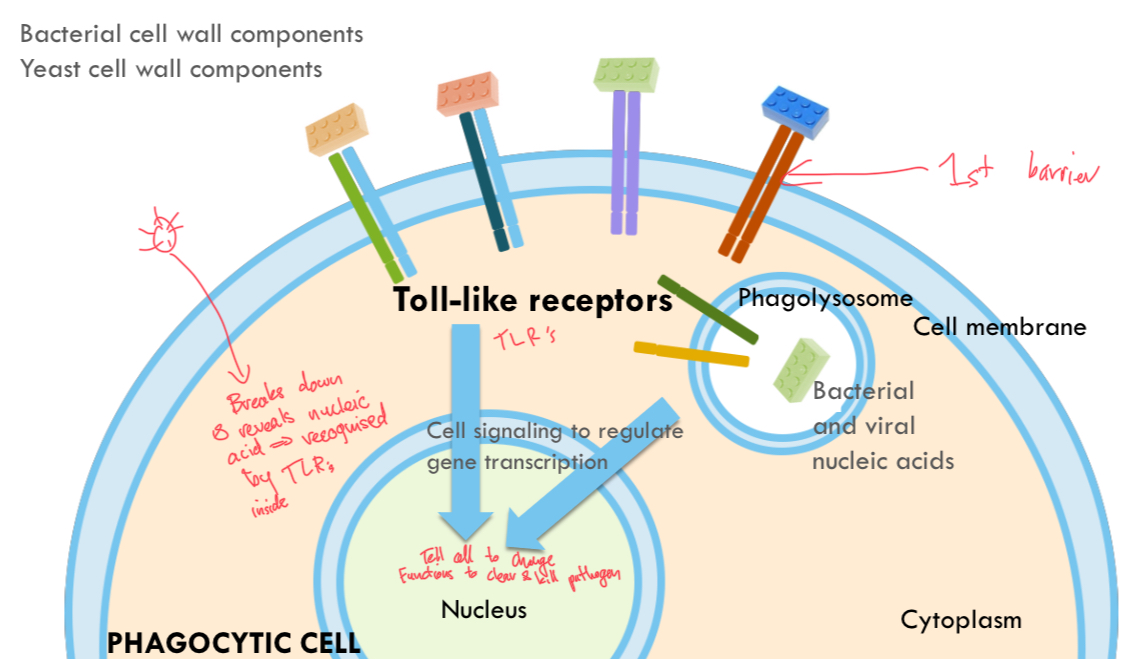
Pattern recognition receptors
Pathogen breaks down revealing nucleic acid (PAMP)= recognised by TLR. Cell signaling to regulate gene transcription, change functions to kill and clear pathogen.
Define fever (pyrexia)
Abnormally high temperature (>37˚C) due to the resetting of the thermostat (hypothalamus) triggered by release of pyrogens (released by cells of the immune system). Phagocytes produce chemical messenger and (IL-1) after ingesting bacteria.
Fever function
It temporarily creates a hostile environment for pathogens and enhance immune function. After pathogen is cleared temp, phagocytosis, and IL-1 decreases to normal.
PAMP
Pathogen associated molecular patterns. What innate immune system recognises to identify pathogen.