CP MCAT
1/35
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
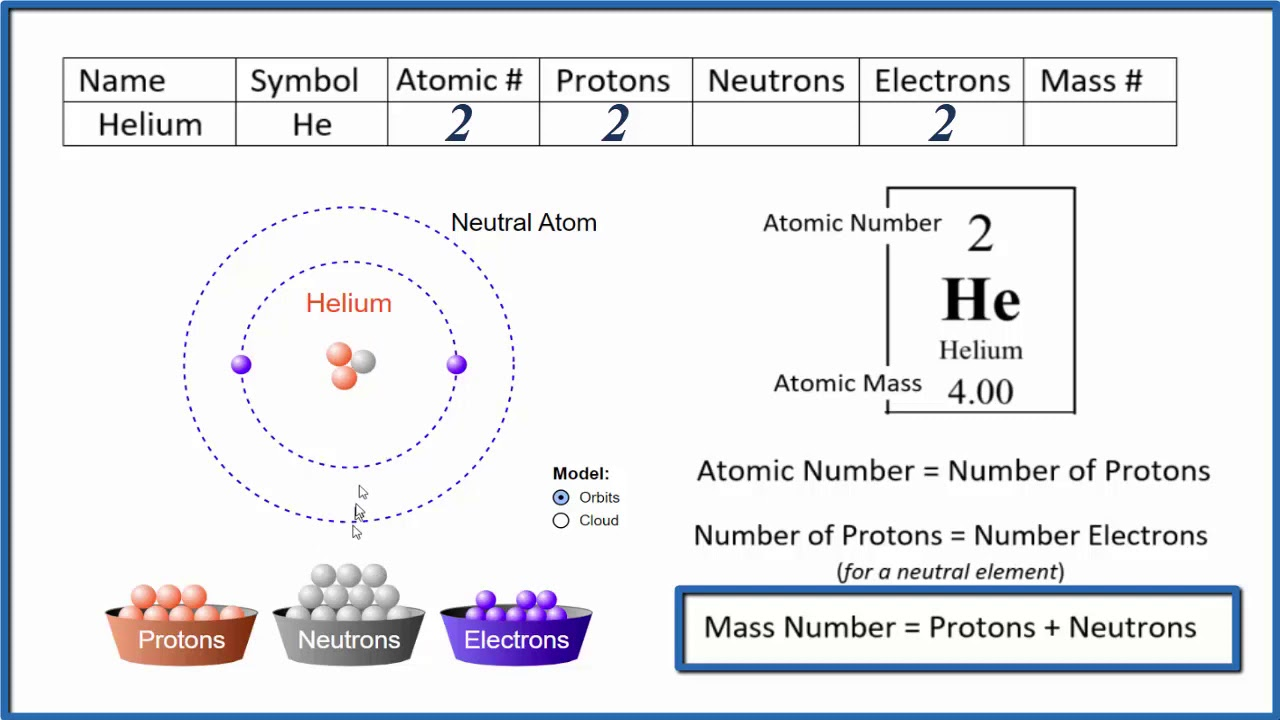
Protons, Neutrons and Electrons
Atomic Mass = (Number of protons) + (Number of neutrons)
Number of neutrons = ( Atomic Mass) - Number of Protons
Number of Electrons = Equivalent to the number of protons Except when the atom is charged
If the Atom (ion) is positively charged, the number of electrons is found by subtracting the charge number from the proton number and vice versa.
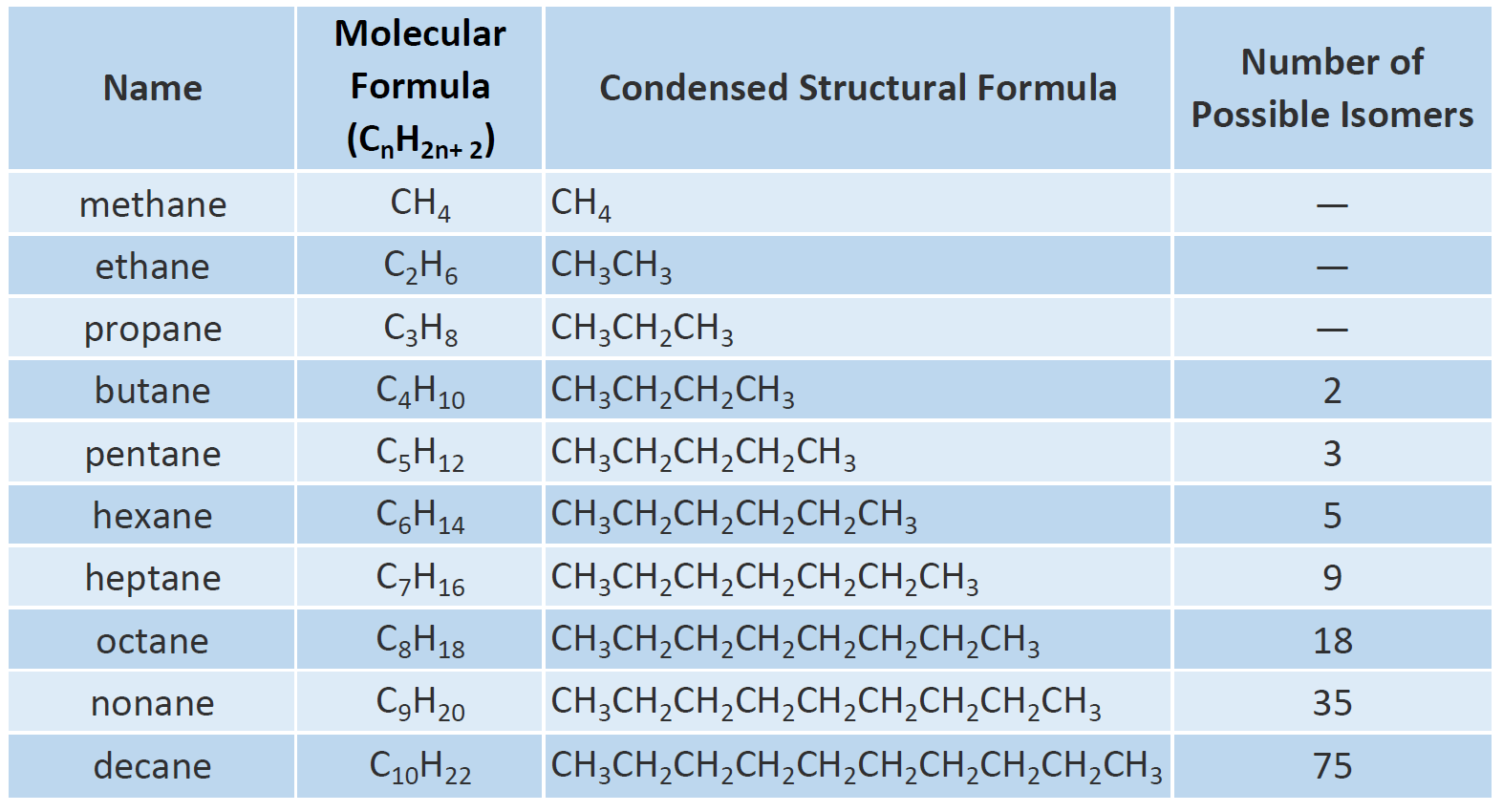
Alkanes
MNEMONIC:
Me Eats Peanut Butter; Paul Has Had Only Nine Donuts
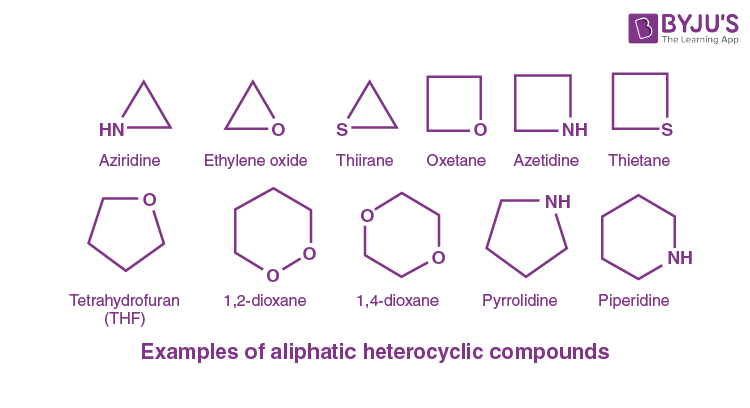
Heterocyclic Compounds
At least one carbon atom is replaced by one of heteroatoms
Heteroatoms are: O, N and S

Matrix Pre-fixes
Avogado’’s Number
1 mole = 6.02 × 1023 molecules
Any time you’re given a mass (or number of moles) of a substance and you’re asked to determine the number of individual ions/atoms/molecules, you’re gonna need Avogadro’s number
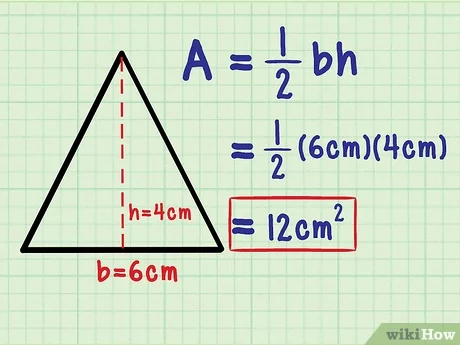
Area of a triangle
Formula: A= ½ bh
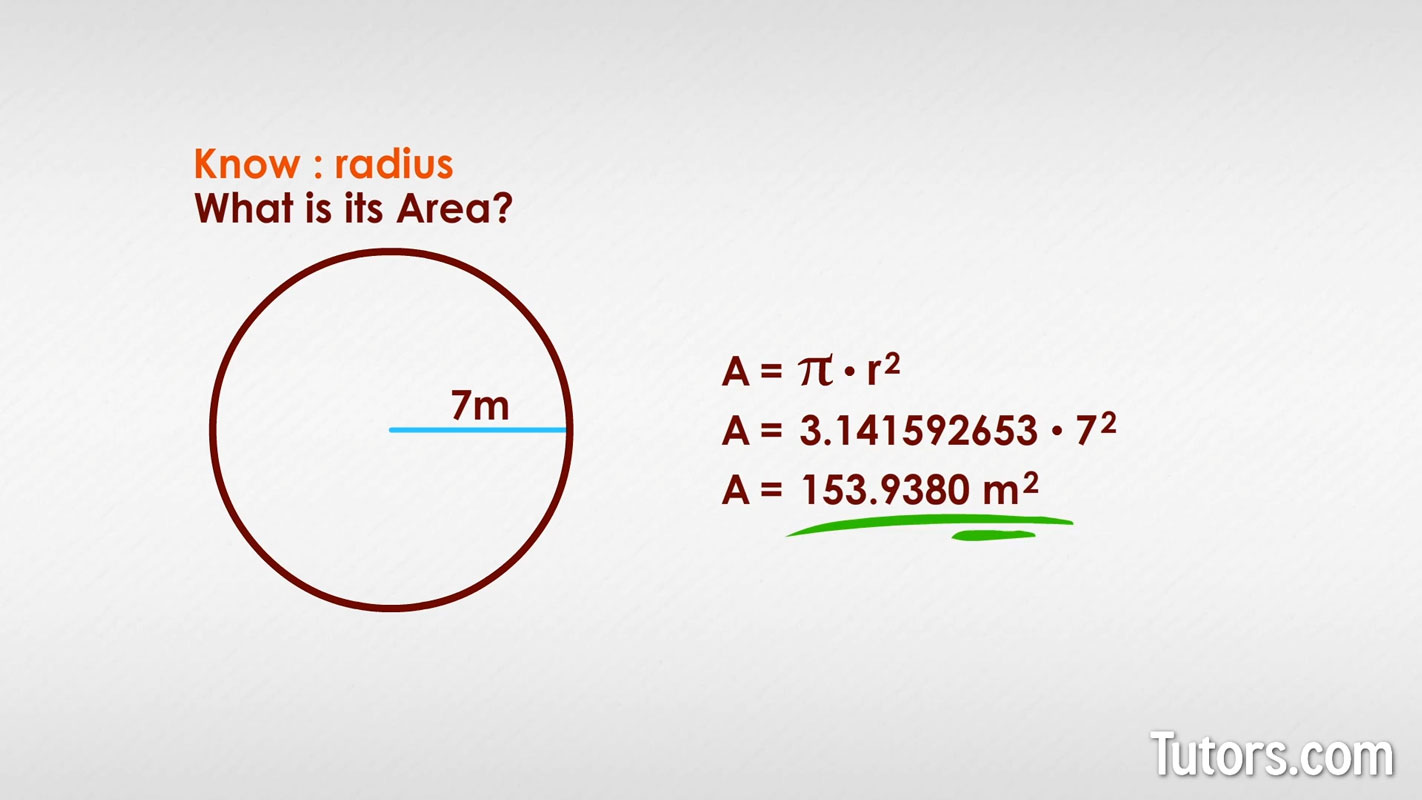
Area of a circle
Naming M
An agonist
Activates a receptor to perform its biochemical function.
Antagonist
Blocks the biochemical function of the protein it binds to.
Placebo
Catalyst
stereoisomerism
Count chiral Chiral centers then use 2n
n = chiral centers
Molar solubility ( S)
Unsaturated Solution
Saturated Solution
Supersaturated Solution
Maximum concentration of a solute that can dissolve in a solution
Unsaturated Solution
You have not dissolved as much solute in the solution as you possibly can so current concentration is less than molar solubility
Saturated Solution
Supersaturated Solution
Solubility product constant (Ksp)
Unsaturated Solution
Q < Ksp
Saturated Solution
Q = Ksp
Supersaturated Solution
Q < Ksp
Action Potential
Inside of an axon will always be negative (-70 )
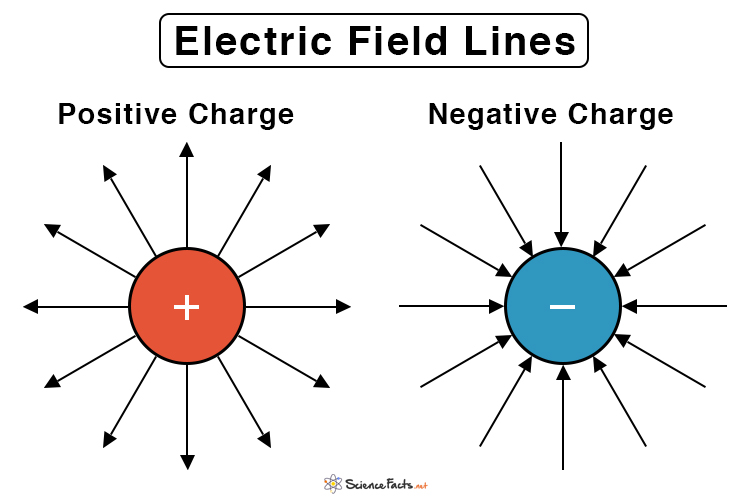
knowing that if we connect this to electrical filed lines they Always move towards the negative
Electrical Field lines
Always move towards the negative
Myelin Sheath function
insulate the axon from the surroundings
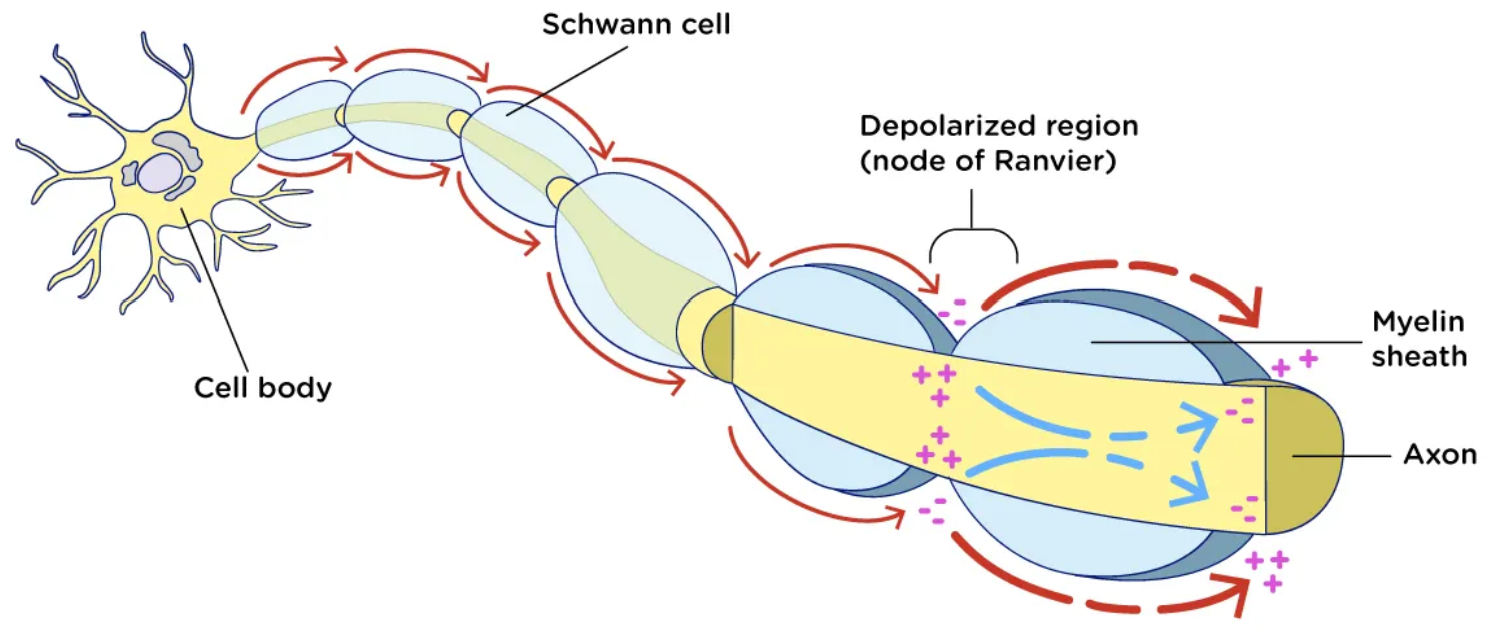
Schwann cells
Glial cells that form the myelin sheath on axons outside the brain
Oligo
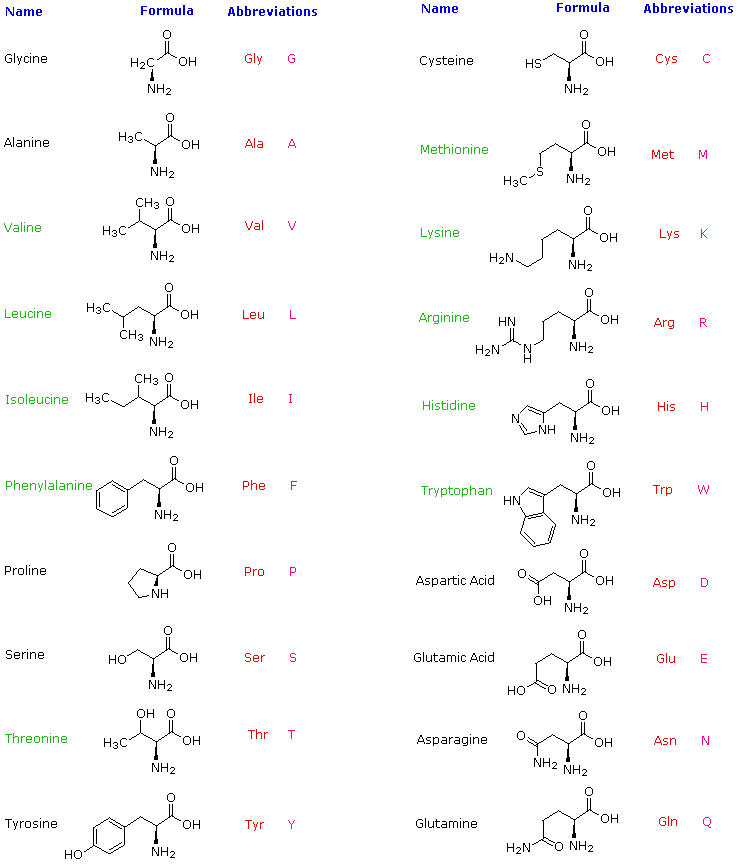
Know Amino Acids
Atomic number
Determines how big an atom is
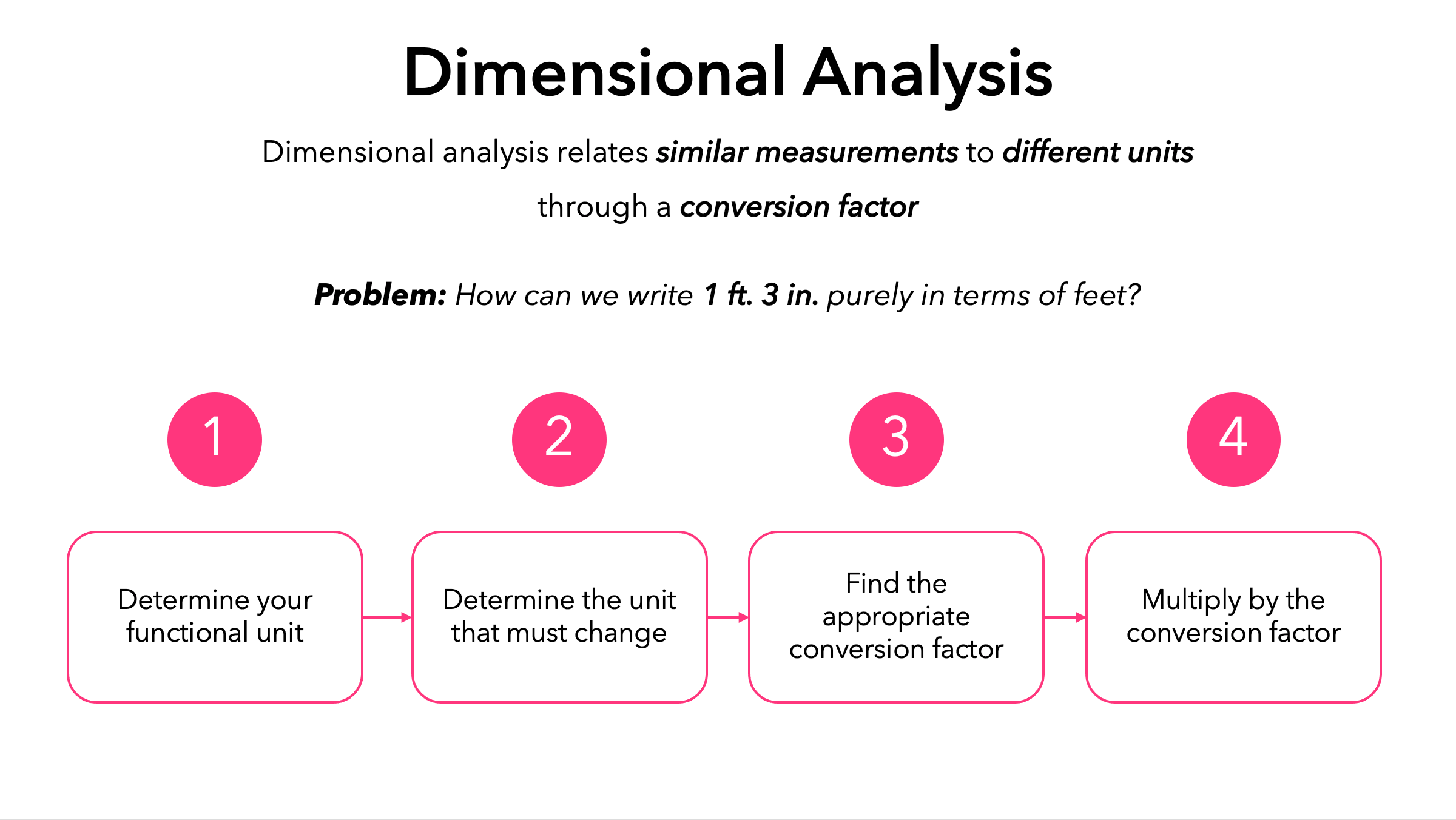
Dimensional Analysis
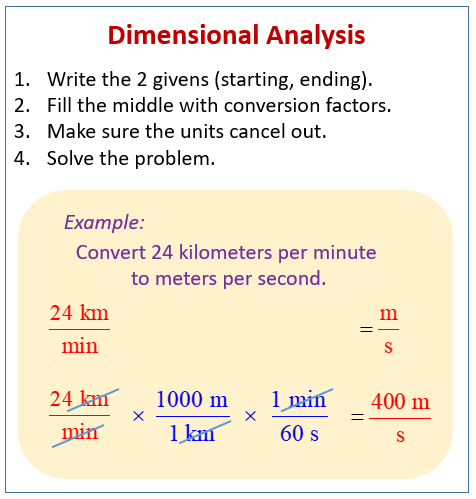
Current formula
The potential is accounted for here, and if we multiply the resistance per unit length by the length over which that resistance occurs, we would have the total resistance. I=V/R and both variables needed to calculate current are accounted for. This is our golden ticket to another point on the chem/phys section.
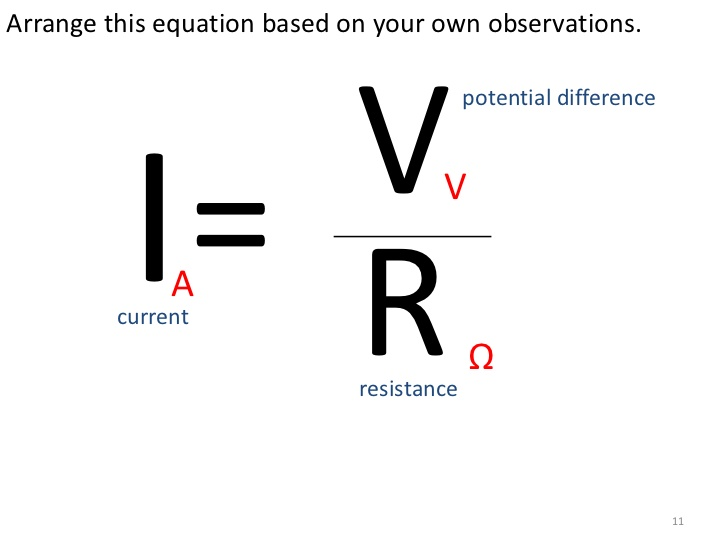
Calculate PH
Logs in MCAT
Strong Acids Vs Weak Acids
Strong Bases vs Weak Bases
Two additional compounds were studied: NO2(OH) dissolved in water and produced an acidic solution, and Ni(OH)2 dissolved only in an acidic solution. What type of compounds were these?
NO2(OH) is an oxyacid and Ni(OH)2 is a base
Explanation: Let’s use that information and look at these compounds one at a time NO2(OH) dissolved in water and produced an acidic solution –> well, if it produced an acidic solution, it should be an oxyacid. Ni(OH)2 dissolved only in an acidic solution –> unlike the NO2(OH), Ni(OH)2 did not produce an acidic solution, it dissolved in an acidic solution. We know that acids dissolve in bases, and bases dissolve in acids due to the common ion effect, so if Ni(OH)2 dissolved in an acid, it is a base.
Strong Acids completely dissolve in water
Ions/ charged
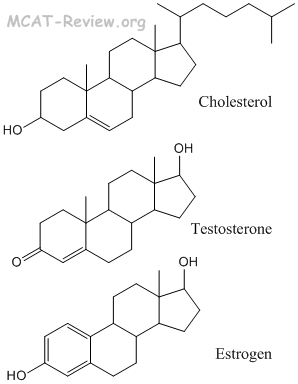
Pre-cursor of Steroid Hormones
What is the concentration of Cl– ions in a 0.1 M solution of calcium chloride?
The formula for calcium chloride is CaCl2 and it produces twice as many Cl− ions as Ca2+ ions in solution when it dissolves.
CaCl2 ⇌ Ca + Cl
Balance the equation
Monosachride
Disachride
Reducing Sugar
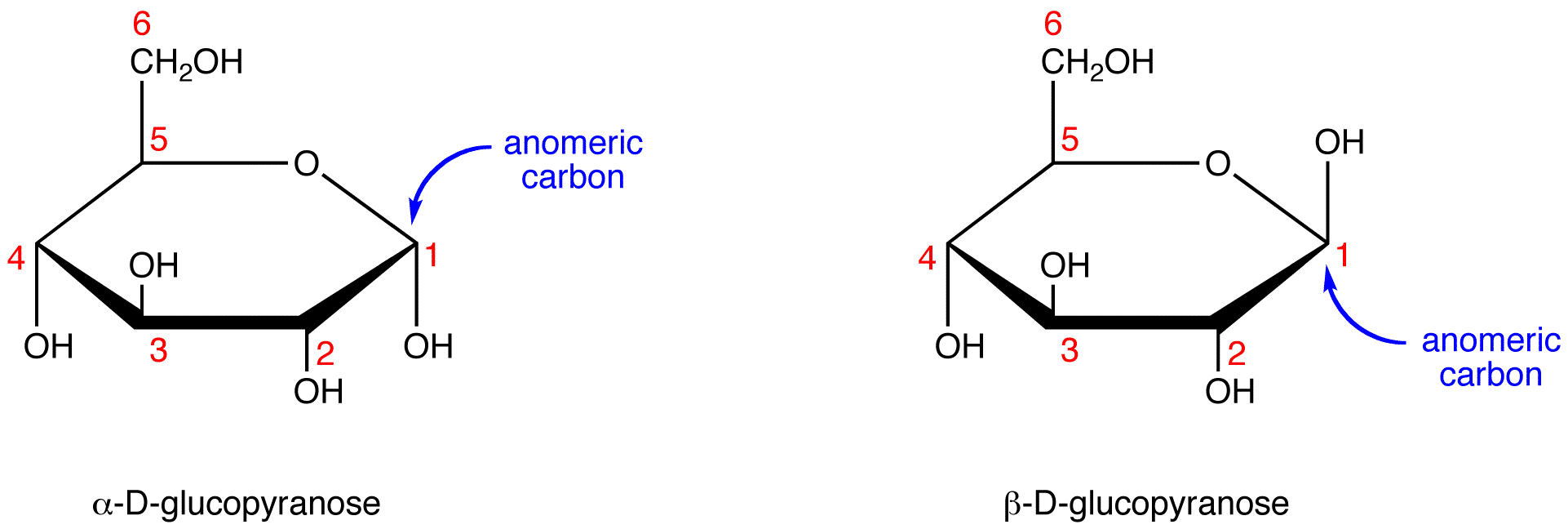
A sugar that has anomeric carbon
Net charge of the peptide