Cognitive exam 3 Visual Imagery
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
visual imagery
“seeing” in the absence of a visual stimulus, visual imagery may involve visual information in working memory or long term memory
LTM: how many drawers are there in ur kitchen
WM: B to heart example
more important notes
• some people have exceptional visual imagery abilities
ex: albert einsten, thots in a stream of pictures
• visual imagery can be used to recall landmarks or imagine alternative routes during spatial navigation
ex: “what other route can I take”
• visual imagery can be used to plan future actions
ex: planning room layout
• visual imagery can be used to improve memory
ex: picturing a tree growing out of a boat to remember the word pair “boat–tree.”
• visual imagery can help when reasoning and problem solving
ex: weird riddle abt the son/father
• visual imagery can help when reasoning and problem solving
ex: which glass needs to be tilted more to pour water
imagery vs. perception
• visual imagery is less vivid than perception
• visual imagery is effortful and fragile, whereas perception is automatic and stable
perception you instantly recognize a red apple on a table without trying—it’s stable and detailed because it’s based on sensory input
Visual imagery, on the other hand, is internally generated—you’re imagining something (like a red apple) without seeing it.
ex: Looking at a tree gives you a rich, continuous perception. Imagining that same tree takes mental effort and the image may blur or fade quickly.
• visual imagery can be confused with perception
ex: You might think you saw your friend put their keys on the counter when you actually just imagined it happening—this is a source monitoring error, where your brain confuses imagined events with real ones.
• visual imagery can prime perception
ex: when you imagine the same object you'll later see (image-same task), you're faster and more accurate at recognizing it because the visual system is pre-activated.
spatial representation (imagery and perception)
different parts of an image correspond to specific locations in space
• perception definitely uses spatial representation (and this is not controversial)
• imagery may also use spatial representation
mental scanning: we create mental images and then scan them in our mind
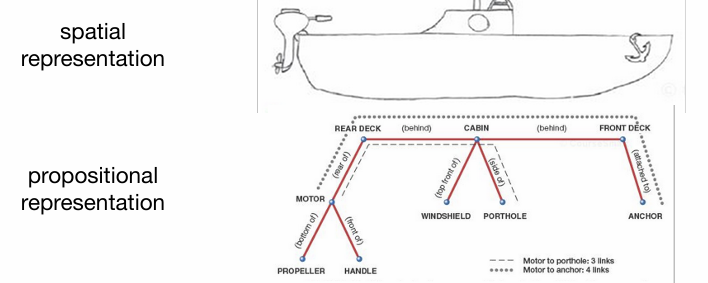
ex: takes longer to imagine finding part of an image that is further away (motor) from the point of focus (anchor)
ex: takes longer to find part of an image that is further away (mountain) from the point of focus (tree)
mental rotation: takes longer to imagine rotating an image that is further away from the original image
symbolic distance effect: we detect more details when we are closer to a stimulus
detect more details when we imagine viewing a closer (larger) stimulus
ex: elephant and rabbit (does it have whiskers
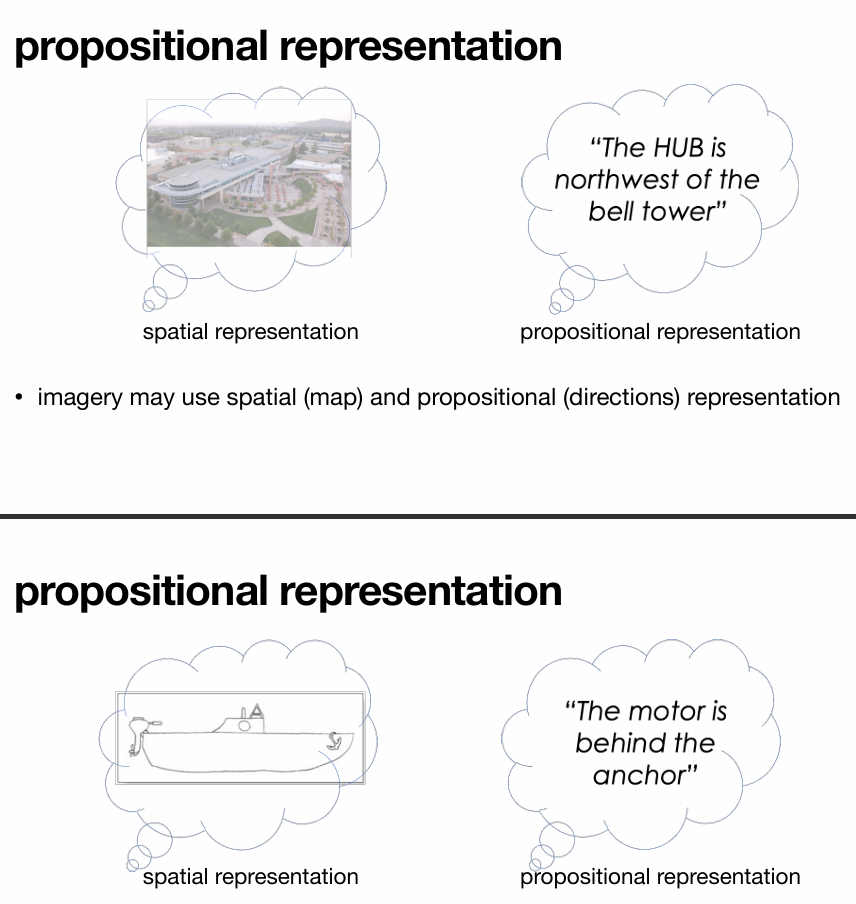
propositional representation
linguistic aspect compared to spatial
• imagery may use spatial (map) and propositional (directions) representation
propositional representation: semantic networks
takes longer to imagine finding parts of an image that are further away in a semantic network
pegword technique
“hang” to-be-remembered words to “pegs” of concrete nouns that you use to create images
ex:
1 = bun → imagine a bun soaked in milk
2 = shoe → cracked eggs in a shoe
3 = tree → apples hanging from a tree
Uses visual memory and elaborative encoding to create strong mental associations. The fixed pegword list provides a structured retrieval cue, making it easier to recall the correct order of items.