Macromolecules: Carbohydrates
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is dehydration synthesis
2 monomers come together to create a polymer, releasing a water molecule in the process
Hydrolysis
breaking a polymer apart by consuming a water molecule
What are glycosidic bonds?
COVALENT bonds between monosaccharides
Carbohydrate function
- gives structure to plant and bacteria cell walls
- makes up chitin
- major source of energy
What is the name of the monomer and polymer
Monomer: monosaccharide
Polymer: polysaccharide
what is the 1, 2, 1 ratio?
C, H, O has a ratio of 1, 2, 1
EX. C6H12O6
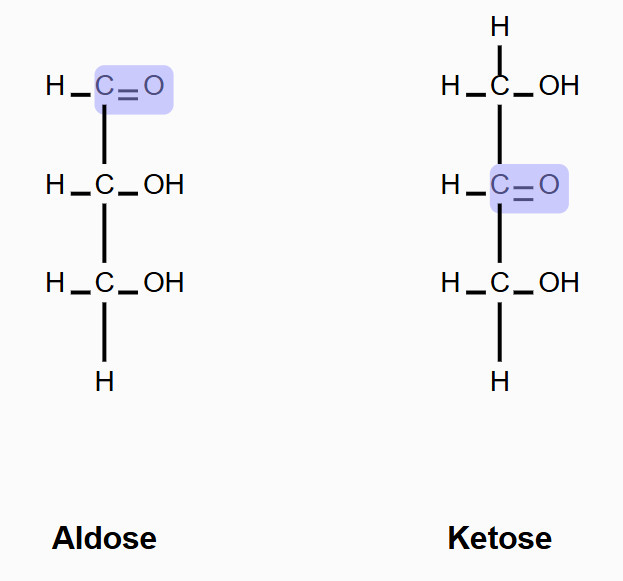
Aldose vs Ketose
aldose: carbonyl group at the end
Ketose: carbonyl group in the middle
Types of Monosaccharides
- Glucose: energy for cells
- Galactose: found in milk
- Fructose: found in fruit
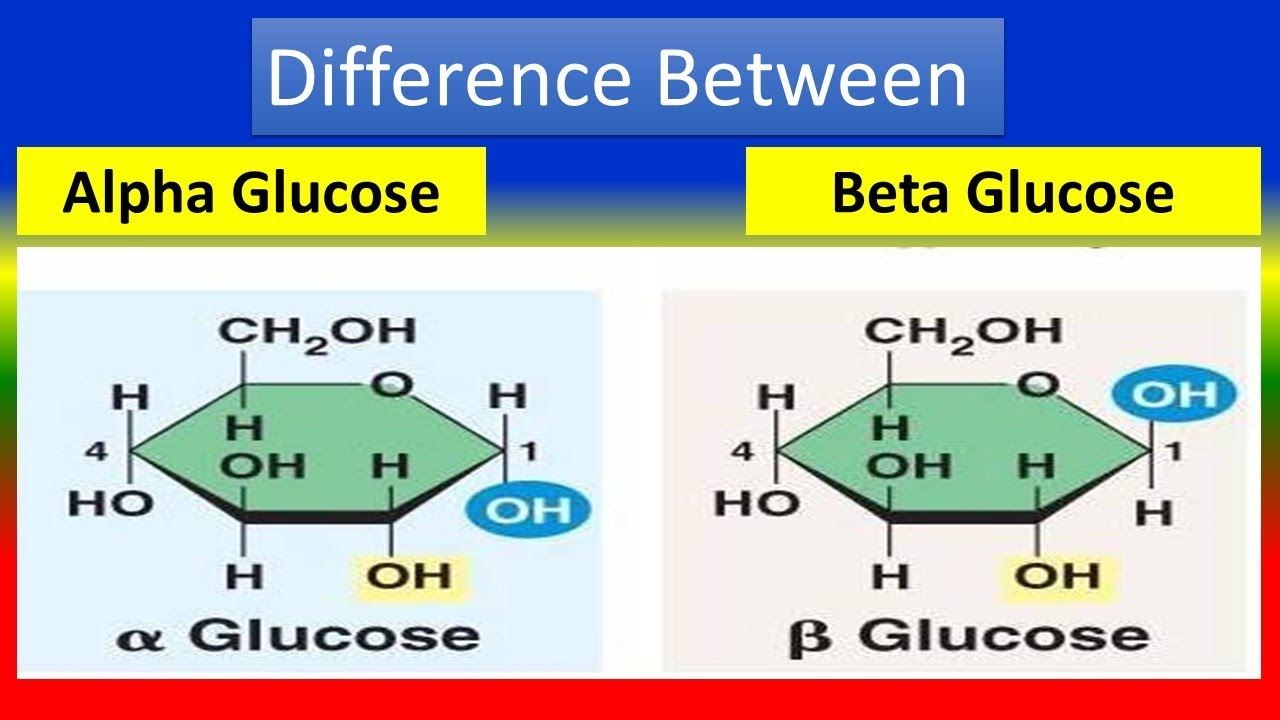
Two forms of Glucose
stereoisomer
B - glucose: -OH at the top
a - glucose: -OH at the bottom
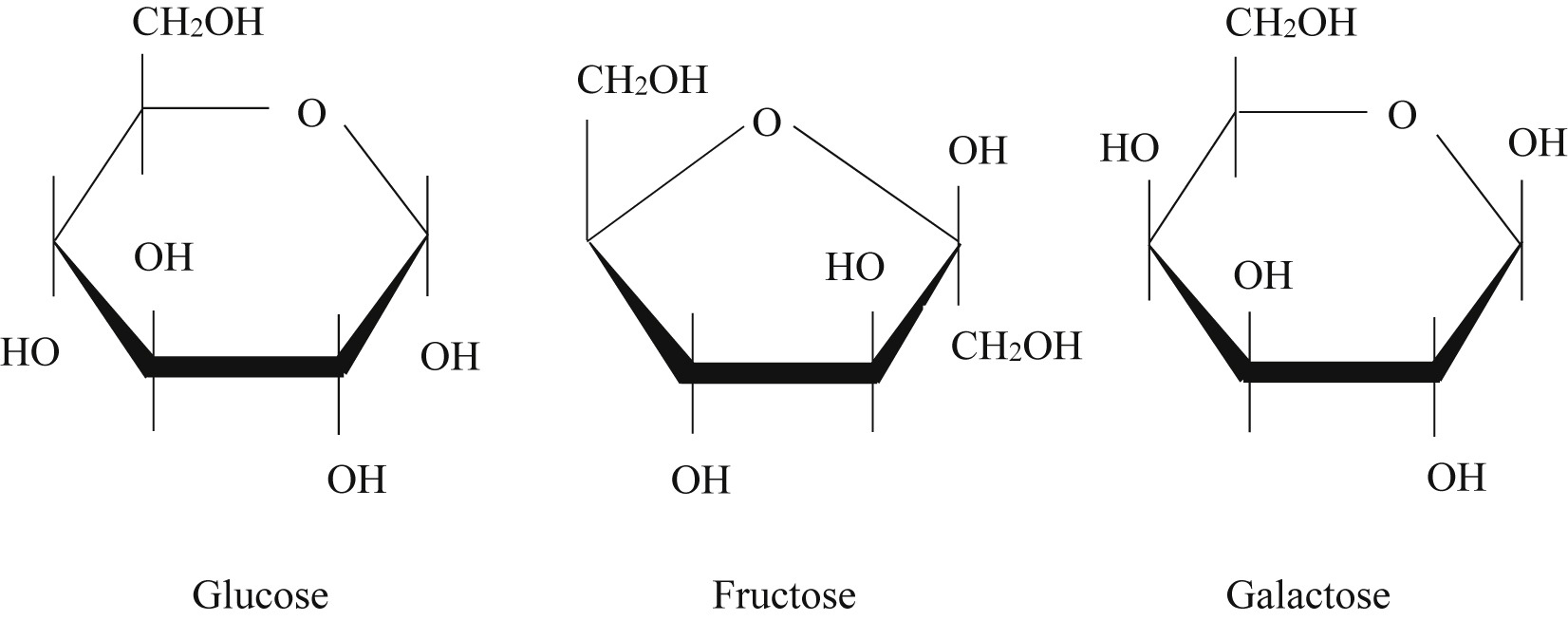
Differentiating between glucose, galactose, and fructose
Glucose and galactose are stereoisomers
Glucose: -OH on the bottom left
Galactose: -OH on top left
Fructose: has carbonyl group, literally looks diff than glucose and galactose
Types of Disaccharides
Maltose: beer
Lactose: milk
Sucrose: table sugar
Maltose is made of…
glucose - glucose
Lactose is made of…
Glucose - galactose
Sucrose is made of…
glucose - fructose
Types of Polysaccharides
- Starch
- Glycogen
- Cellulose
Starch characteristics
branched
- can be 1, 4, or 1, 6 glycosidic bond
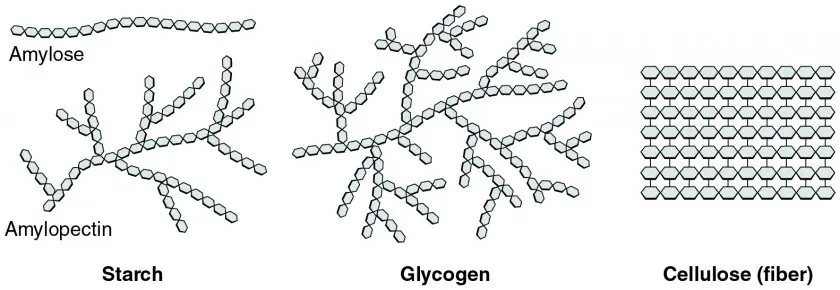
Glycogen characteristics
highly branched
- can be 1, 4 or 1, 6 glycosidic bond
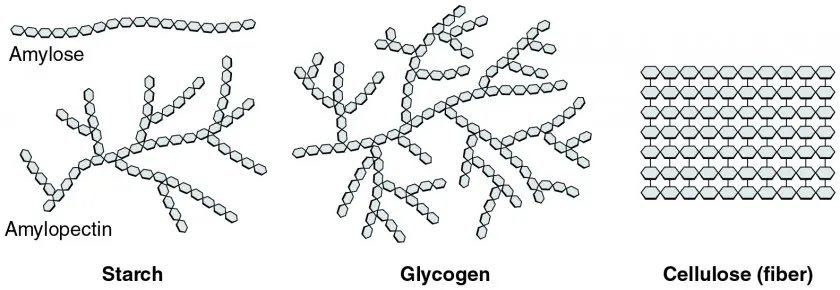
Cellulose characteristics
- linear
- only 1, 4 glycosidic bond (this creates that linear formation)