Chronic adaptations to aerobic training - cardiovascular, respiratory and muscular
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
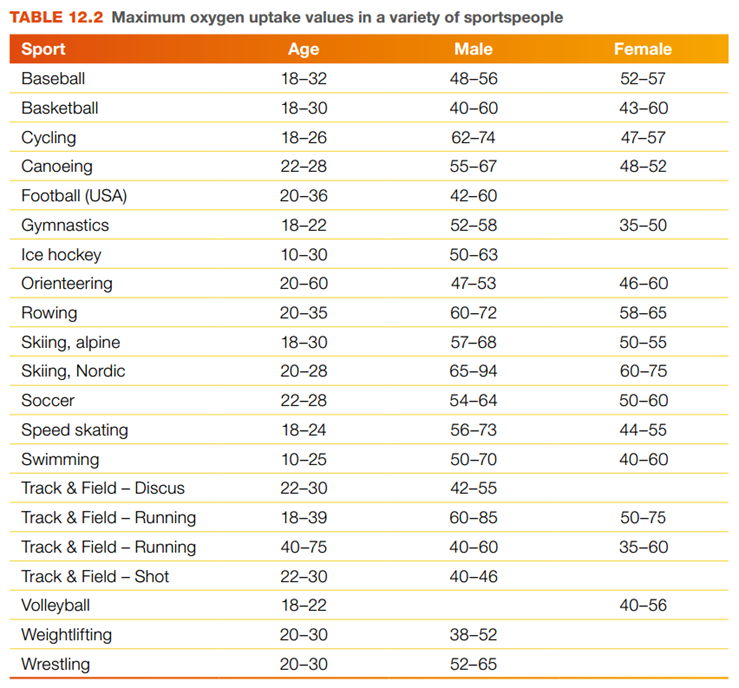
Increased maximal oxygen uptake (VO₂ max)
Aerobic training increases VO₂ max during maximal exercise due to higher cardiac output, red blood cell numbers, A-VO₂ difference, muscle capillarisation, and myoglobin oxygen extraction.
VO₂ max is the maximal oxygen that can be taken in, transported, and utilised to produce ATP.
Increased lactate inflection point (LIP)
Aerobic adaptations improve oxygen delivery and efficiency, raising LIP.
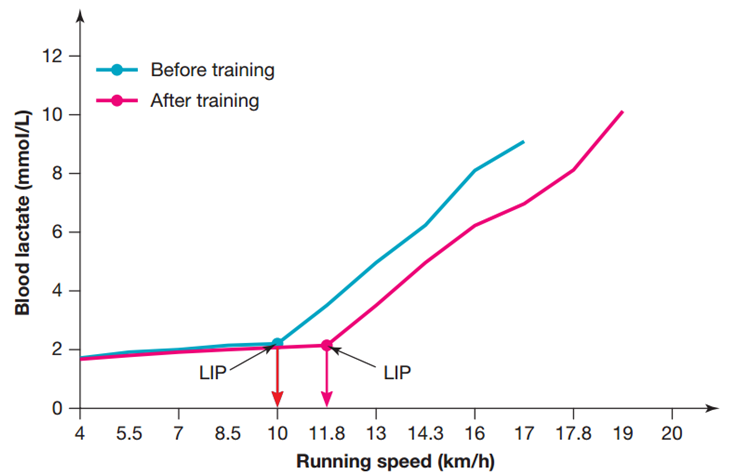
This allows energy to be produced aerobically at higher intensities, reducing reliance on anaerobic glycolysis and delaying fatigue from hydrogen ion accumulation.
Increased VO₂ max
Aerobic training increases the maximum oxygen uptake, allowing more oxygen to be taken in by the respiratory system, transported by the cardiovascular system, and utilised by muscles to produce ATP, improving performance and economy.
Increased lactate inflection point (LIP)
A higher LIP allows the aerobic system to supply energy at higher intensities, delaying reliance on anaerobic glycolysis and reducing fatigue from hydrogen ion accumulation, enabling sustained high-intensity performance.