Magnetism and Electromagnetism
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are the two types of magnetic pole?
North (seeking) pole
South (seeking) pole.
Where are magnetic forces stronger?
The poles of a magnet.
What happens to like and unlike poles?
Like poles repel- north pole will repel a north poll etc
Unlike (opposite) poles attract- north pole will attract a south pole of another magnet.
What is a magnetic field?
The region around a magnet, where a force acts on another magnet of magnetic material (e.g. iron, steel, nicker cobalt)
What does the strength of a magnetic field depend on?
The distance from the magnet- strongest at poles.
What are permanent magnets?
Magnets that produce their own magnetic field.
What are induced magnets?
Magnets that become a magnet when placed in a magnetic field.
What do the arrows on fields lines do?
Always run from north to south.
Show direction of the force that would act on a north pole placed at that point.
What is the flux density?
The density of the field lines. Indicates the strength of the field at that point- closer together lines, higher flux density
What happens if the flux density is higher?
The stronger the field and the greater force that would be felt by another magnet.
What does a magnetic compass align with?
The Earth’s magnetic field- always points to the magnetic north.
How can you use a magnetic compass to plot the field around a bar magnet?
Place bar magnet on piece of paper.
Place compass at one end of the magnet.
On paper, mark where point of the compass needle is.
Move the compass so tail of needle is at the point that has just been marked.
On paper, mark new point where needle is.
Repeat and connect marks until full field is plotted.
What happens when a current flows in a conducting wire?
A magnetic field is produced around the wire.
What does the direction of the field lines depend on?
The direction of the current.
How can you find the direction of the field lines using the right hand grip method?
Grip wire in right hand, with thumb pointing in direction of the current.
Fingers curled around the wire will point in direction that field lines should be drawn.
What does the strength of the magnetic field depend on?
Size of current and distance from wire.
What is a solenoid?
Formed when a wire is looped into a cylindrical coil.
What does shaping a wire into a solenoid do?
Increases strength of magnetic field, creating strong uniform field inside solenoid.
How can you increase magnetic field strength?
Add an iron core to create an electromagnet.
How does a solenoid increase magnetic field strength?
Concentrates longer piece of wire into smaller area.
Looped shape means that magnetic field lines around the wire are all in the same direction.
How can you use the right hand grip method to find the north pole of a solenoid?
Hold solenoid in right hand with your fingers following direction the current flows.
Thumb will point to north pole of solenoid.
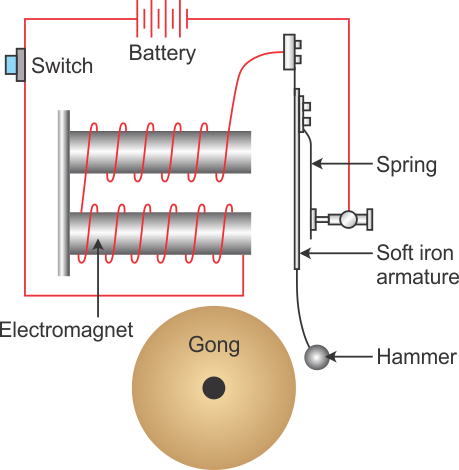
How does an electrical bell work?
When switch is pushed, electromagnet is magnetised.
Electromagnet attacks the armature.
Hammer strikes gong and breaks circuit.
Armature springs back, completing circuit again and remagnetising the electromagnet.
Cycle repeats for as long as button remains pushed.