Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
anatomy
branch of science concerned with structure of the body
physiology
branch of science that deals with functions of living organisms and their parts
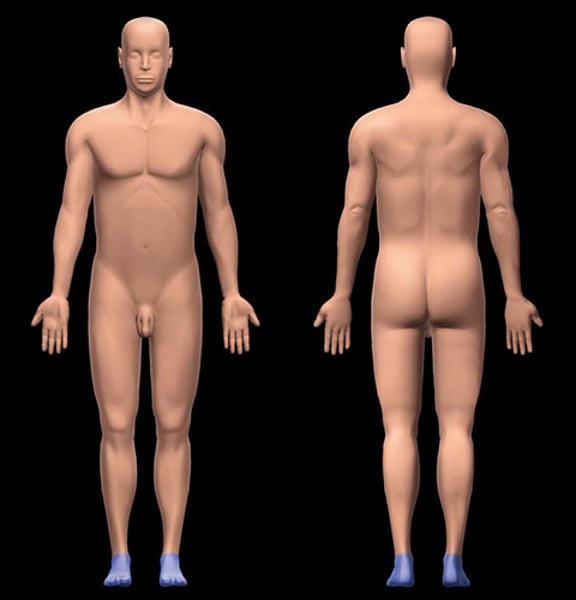
anatomical position
standing straight, facing forward, arms at sides with palms forward
superior
toward the head, upper
inferior
away from head, below
anterior
toward the front, in front of
ventral
What is another term for the anterior part of the body?
posterior
toward the back, behind
dorsal
What is another term for the posterior part of the body?
medial
toward the midline of the body, on the inner side
lateral
away from the midline of the body, on the outer side
proximal
closer to the point of attachment
distal
farther from the point of attachment
superficial
close to surface of body
deep
toward interior of body
axial
making up the main axis of the body (head, neck, trunk)
appendicular
consisting of appendages or limbs
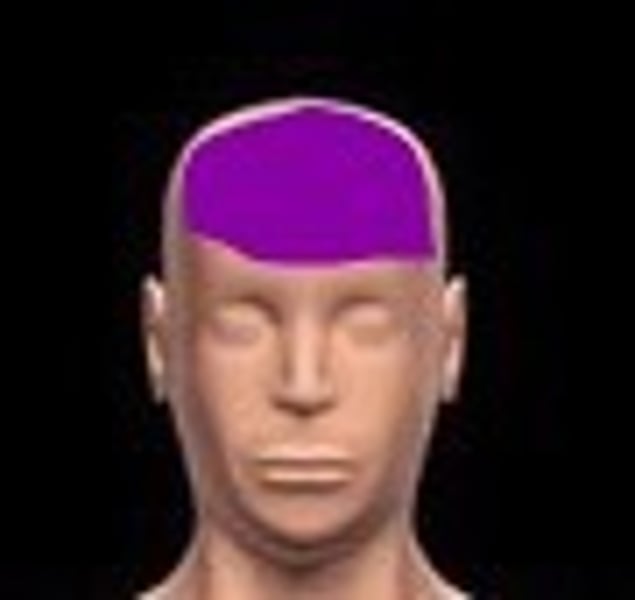
frontal

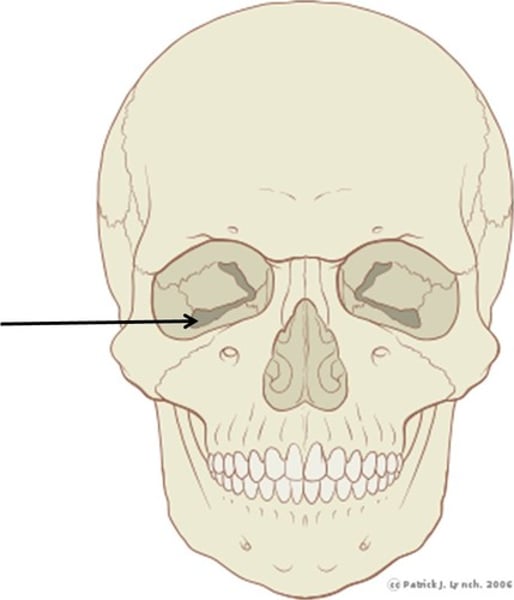
orbital
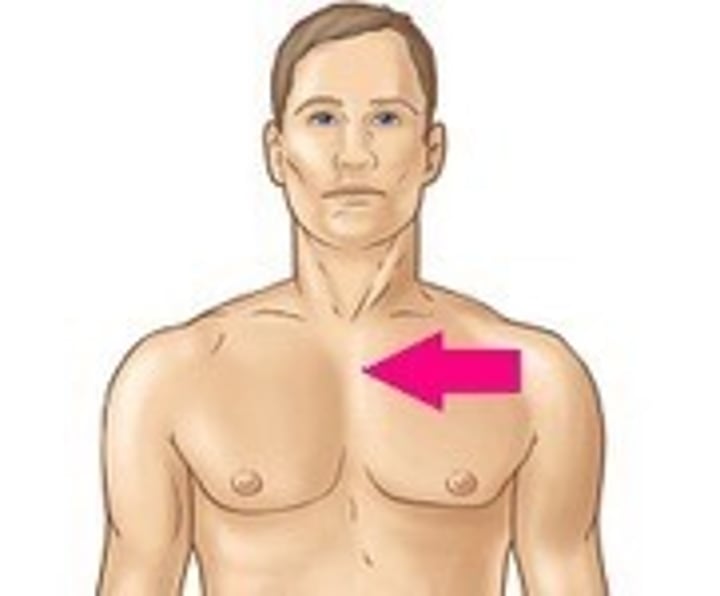
sternal
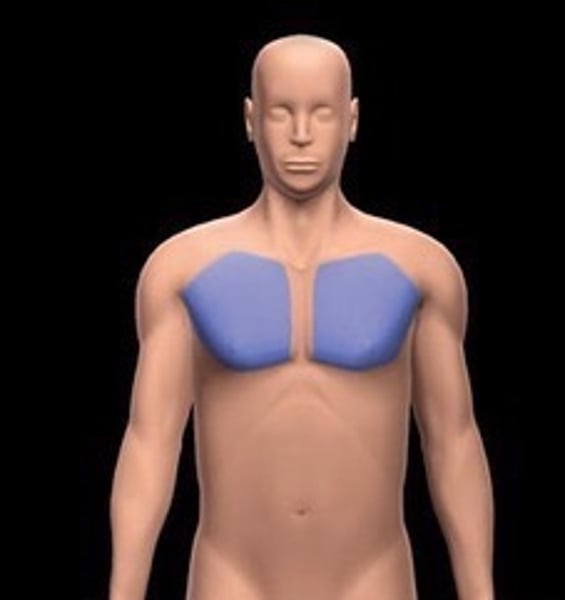
pectoral
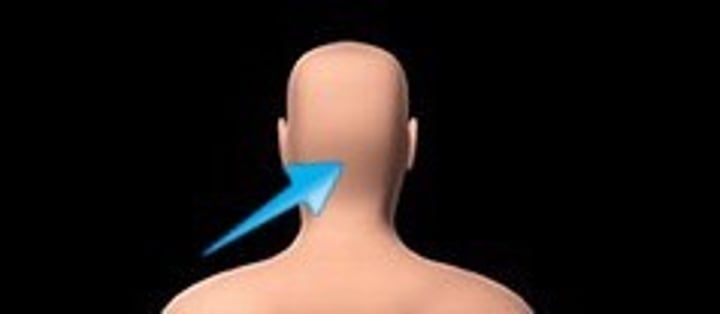
cervical

acromial
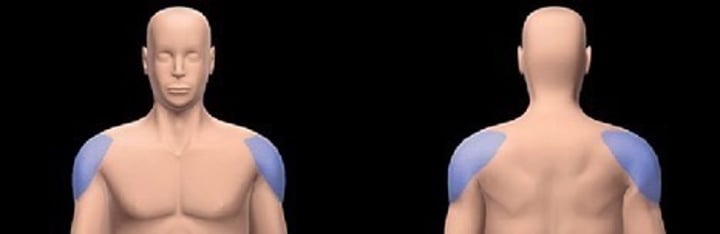
axillary
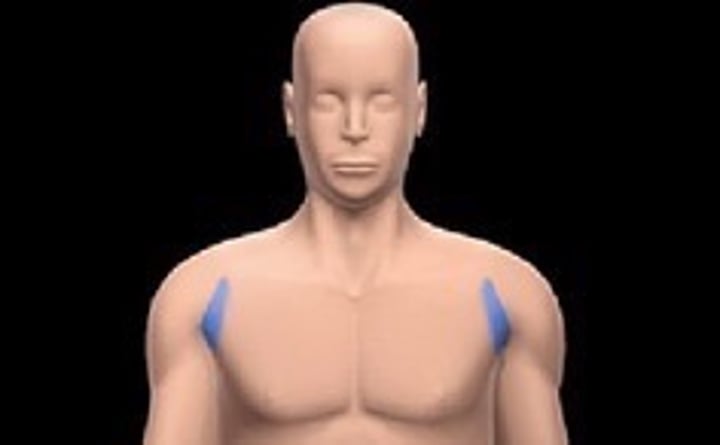
brachial
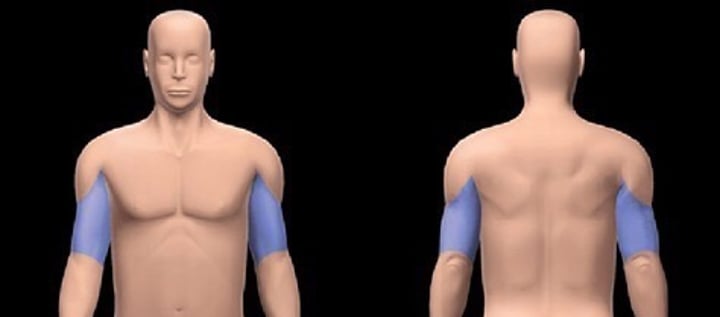
antecubital
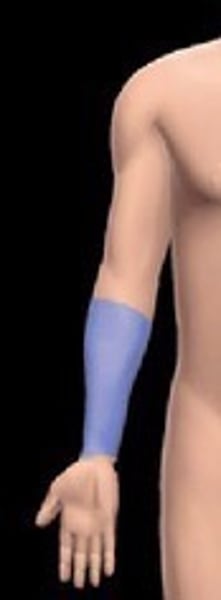
antebrachial
pelvic
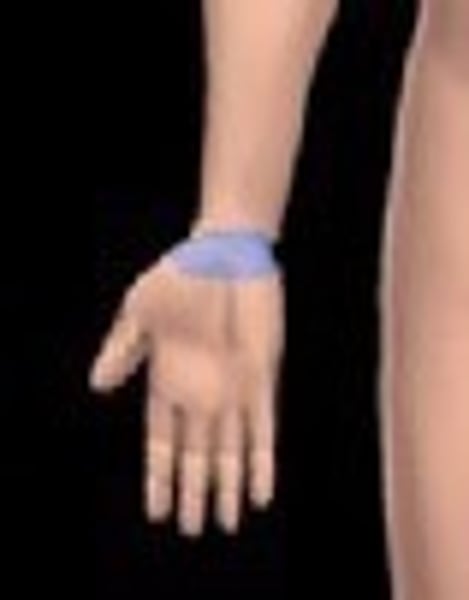
carpal
palmar
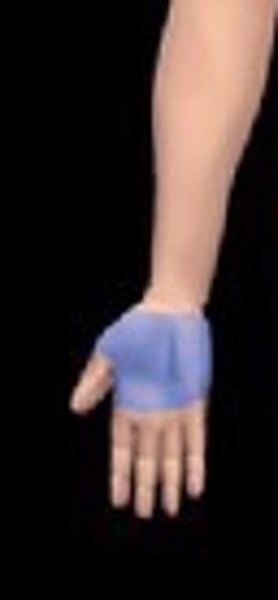
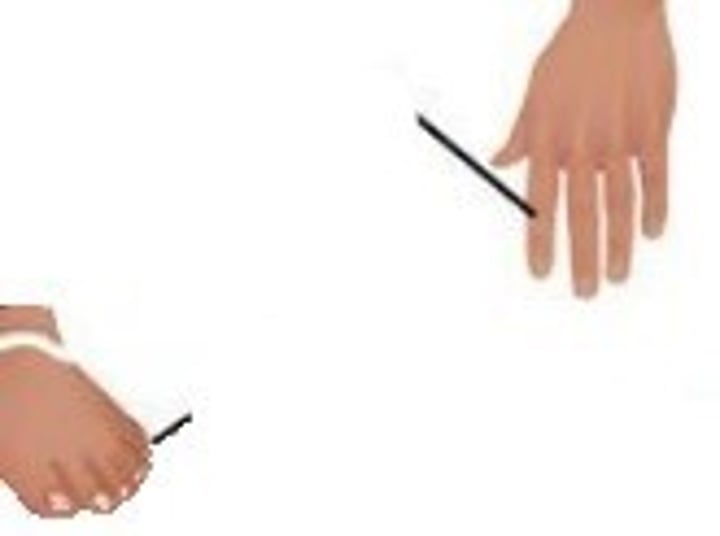
digital

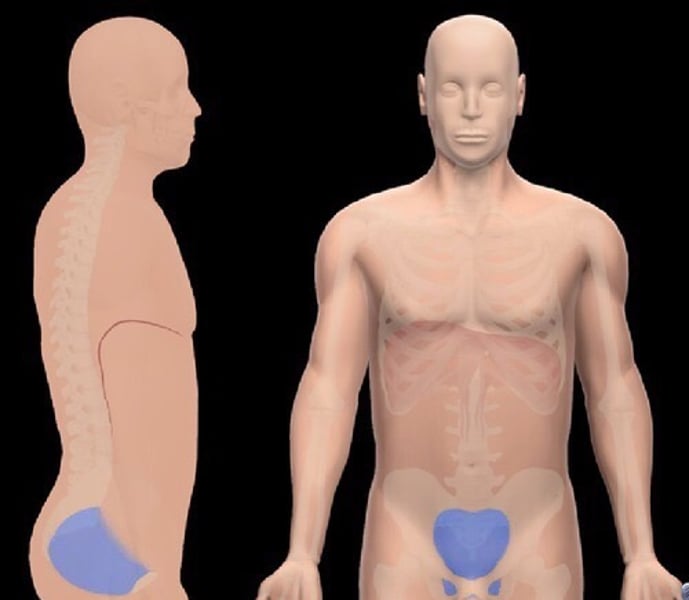
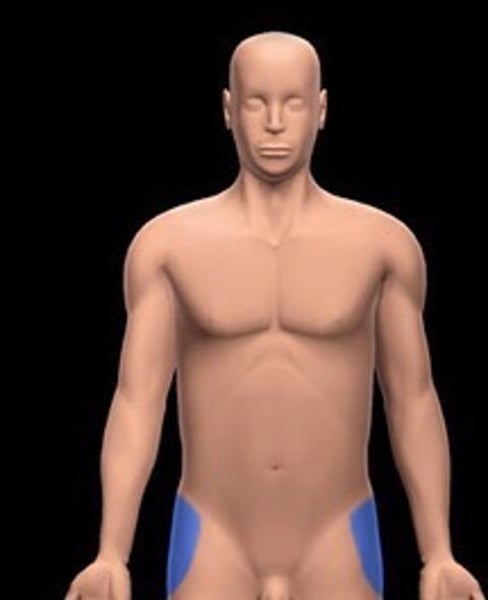
coxal
femoral
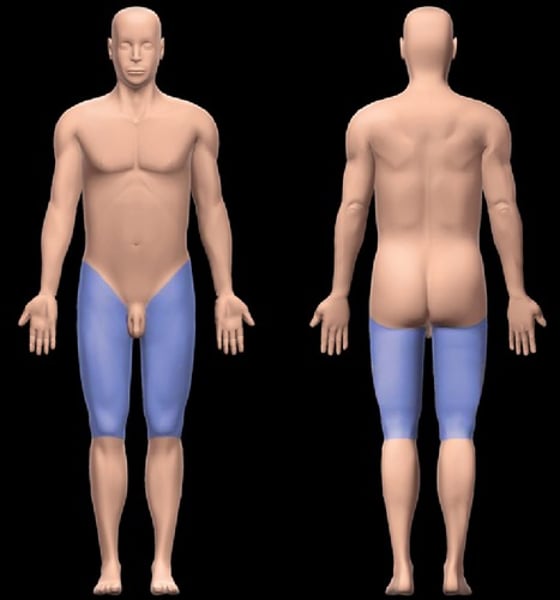
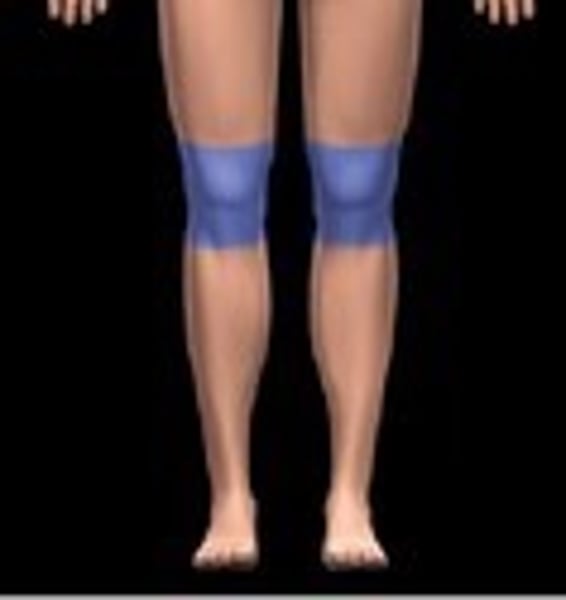
patellar
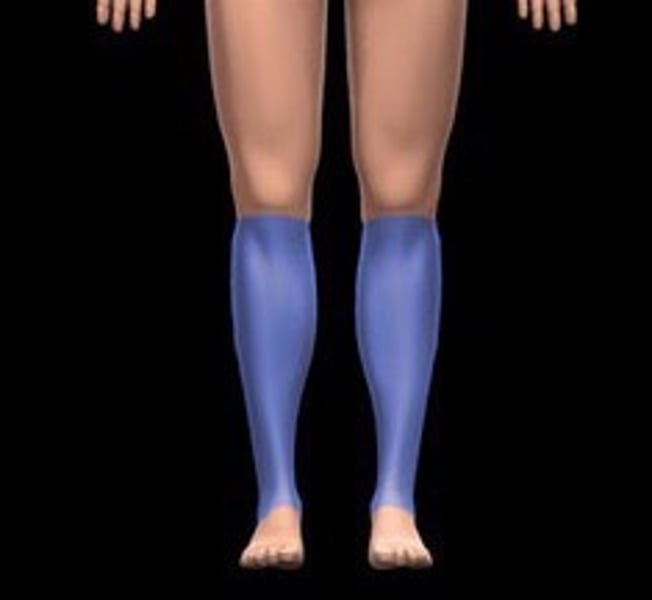
crural
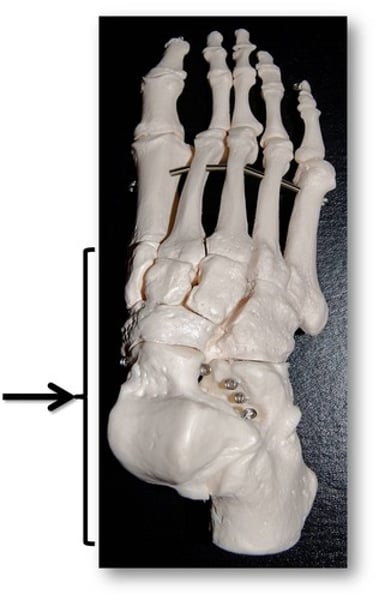
tarsal
cephalic

otic

occipital
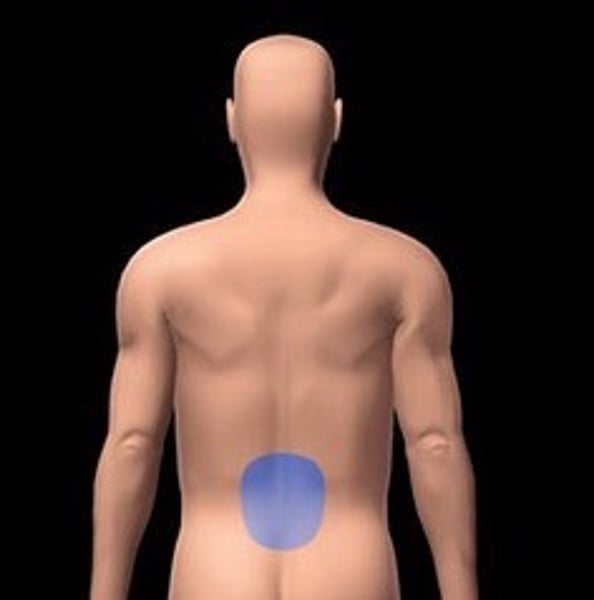
lumbar
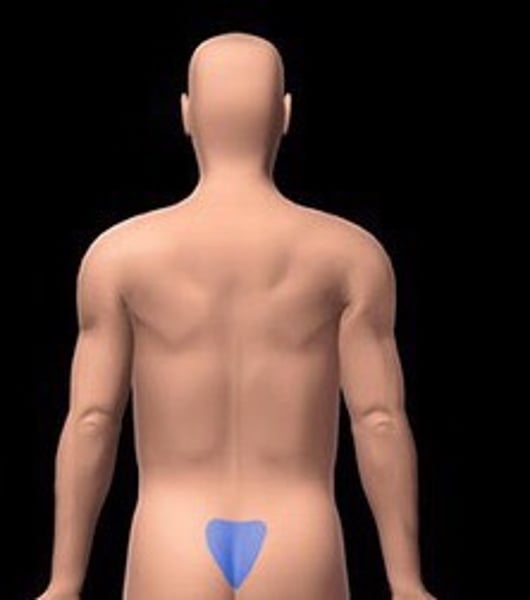
sacral
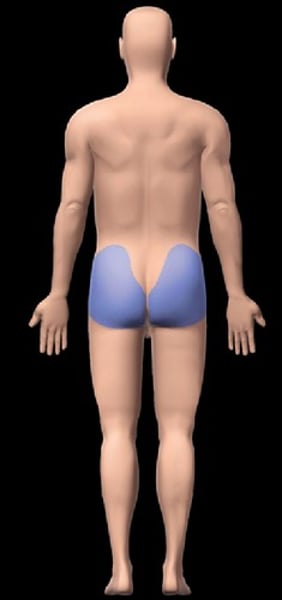
gluteal
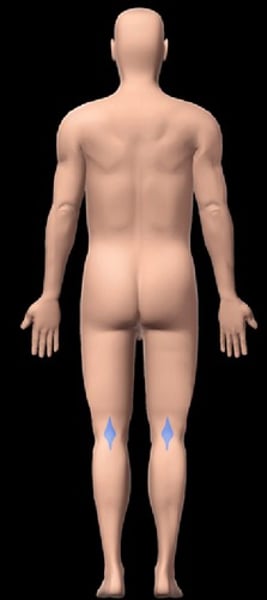
popliteal
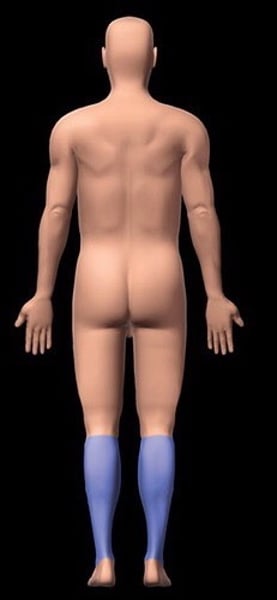
sural
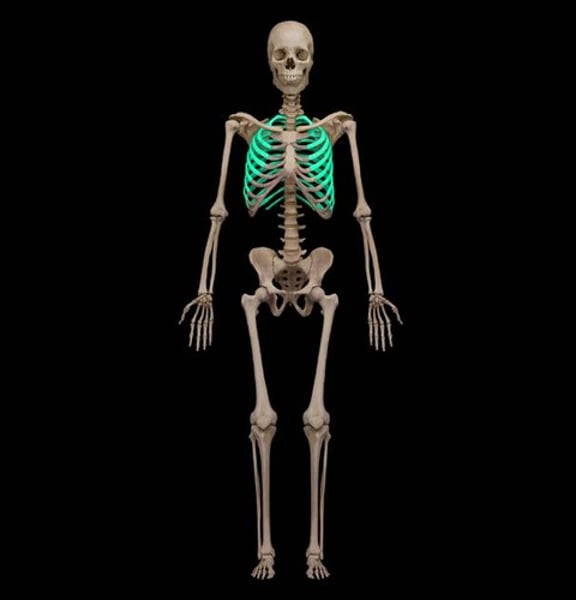
costal
plantar

cubital
pedal
sagittal
vertical plane, dividing into left and right sides
midsagittal
divides equally into right and left halves
parasagittal
divides unequally into right and left sides
transverse
divides into superior and inferior sections
coronal
divides into anterior and posterior sections
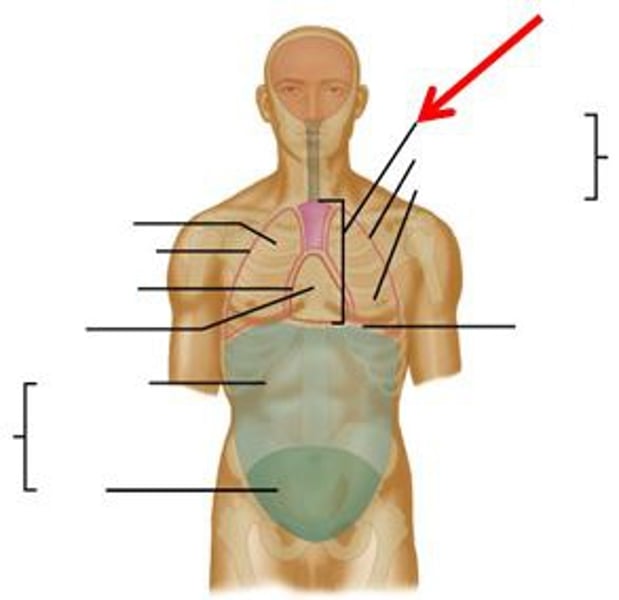
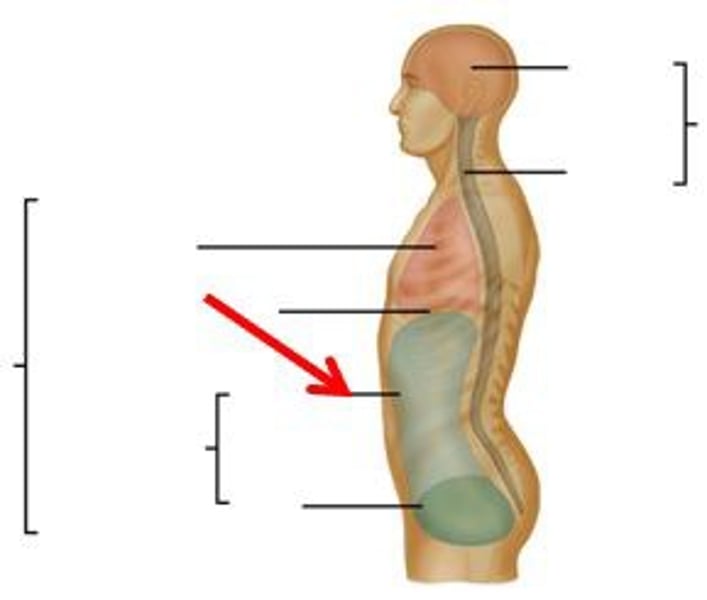
body cavity
major, closed compartment containing internal organs.
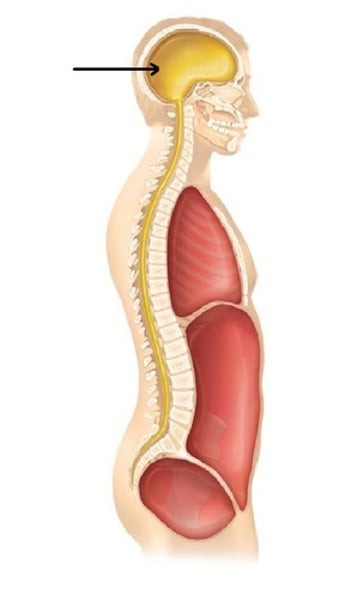
dorsal body cavity
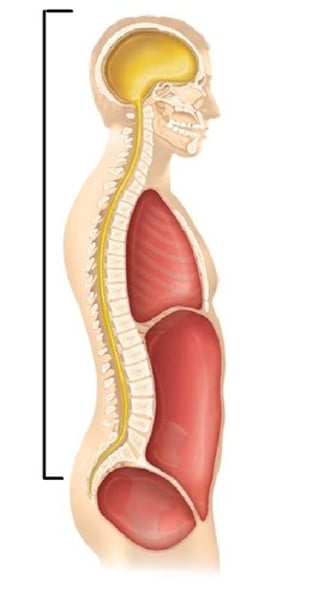
cranial cavity
also includes oral, nasal, orbital, and middle ear cavities
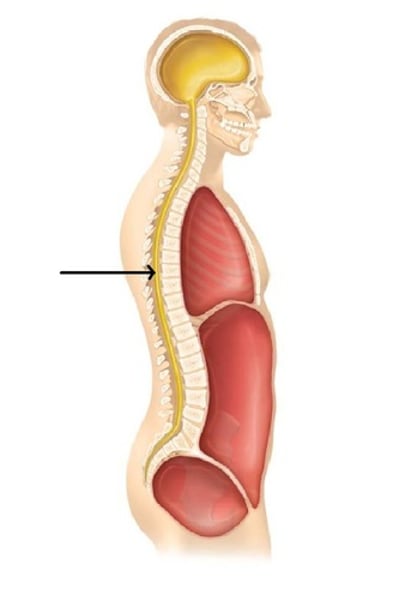
vertebral cavity
contains the spinal cord
ventral body cavity
includes the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
thoracic cavity
surrounds organs of the chest, such as heart and lungs
pleural cavity
houses a lung
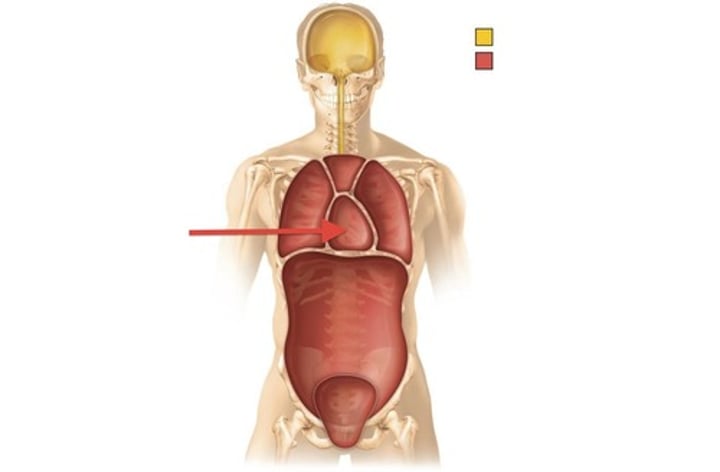
mediastinum
in the center of the thoracic cavity; it contains the pericardial cavity housing the heart, esophagus, and trachea
mediastinum
pleural cavity
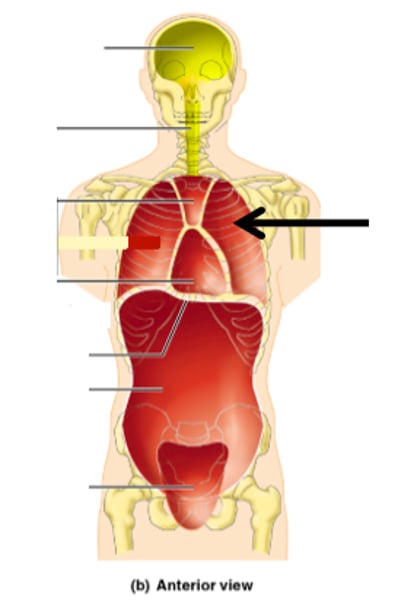
pericardial cavity
ventral body cavity
dorsal body cavity
contains the cranial cavity and vertebral canal (cavity)
abdominopelvic cavity
cavity of the trunk below the diaphragm
abdominal cavity
contains stomach, liver, spleen, intestines, etc...
pelvic cavity
contains bladder, some reproductive organs, rectum...
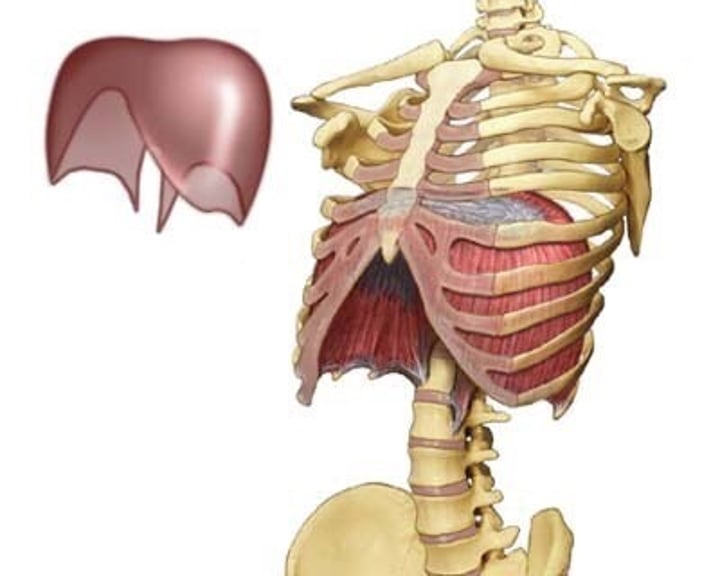
diaphragm
large, dome-shaped muscle separating the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
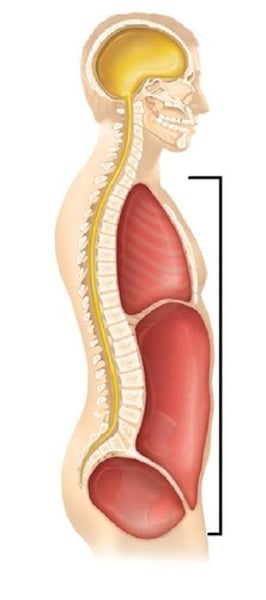
pelvic cavity
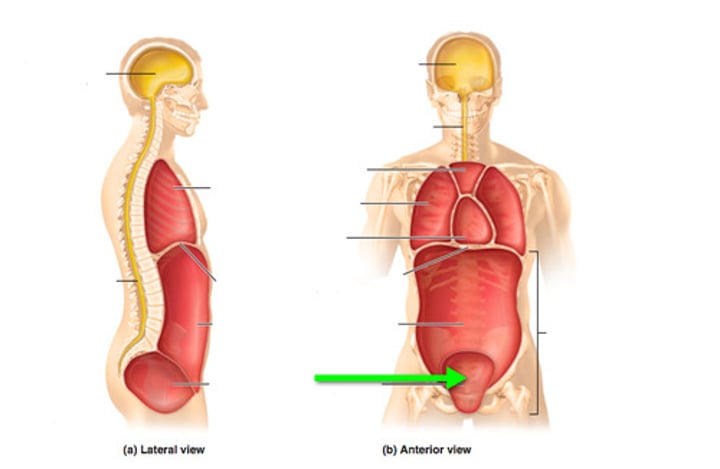
diaphragm
abdominal cavity
characteristics of life
movement, responsiveness, growth, reproduction, respiration, digestion, absorption, circulation, assimilation, excretion
levels of structural organization
atoms > molecules > cells > tissues > organs > organ systems > organisms
metabolism
sum of all chemical reactions that happen in the body
five requirements of life
water, food, oxygen, heat, pressure
homeostasis
dynamic condition in response to changing conditions, maintains a relatively stable environment
negative feedback system
maintains value of condition within normal range
positive feedback system
if change outside of normal occurs, this feedback makes the change greater
receptor
monitors value of a condition, senses changes
control center
establishes set point around which condition is maintained (brain)
effector
can change value of a condition (gland or muscle)
serous fluid
lubricating fluid between the parietal and visceral membranes
visceral pleura
membrane covering the surface of the lungs
visceral pericardium
membrane covering the surface of the heart
parietal pleura
membrane covering the cavity surrounding the lungs
parietal pericardium
membrane covering the cavity surrounding the heart
visceral peritoneum
membrane covering the surface of the abdominal organs
parietal peritoneum
membrane covering the cavity surrounding the abdominal organs
cardiovascular system
consists of the heart and blood vessels, responsible for transporting oxygen and nutrients throughout the body
digestive system
a group of organs including stomach, intestines, and liver working together to convert food into energy and basic nutrients to feed the entire body
endocrine system
glands, like the thyroid and pituitary, that secrete hormones to regulate the body
integumentary system
made of of skin, hair, and nails; protects the body from damage such as loss of water or infection
lymphatic system
contains lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and spleen; it transports fluids from tissues and includes the immune system
muscular system
permits movement of the body, maintains posture, and circulates blood
nervous system
coordinates body activities by transmitting signals throughout the body; contains brain and spinal cord
reproductive system
allows for the production of offspring for the continuation of the species
respiratory system
contains lungs and air passageways to allow for gas exchange
skeletal system
structural system that performs various functions such as, support, protection, and calcium storage