AP Chem Topic #2 Atoms & Beyond
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Democritus
Described the world as made up of tiny indivisible particles called “atomos.”
John Dalton’s theory
Explained the Law of Constant Composition and Law of Conservation of Mass
Law of Multiple Proportions (predicted by Dalton)
When two elements combine to form two or more compounds, the ratio formed from each compound’s mass ratio always yields a fraction. (Elements cannot combine with random compositions. The number of atoms of each element in a compound must be a whole number.)
Dalton’s Atomic Model
All matter consists of tiny, indivisible particles.
J.J. Thomson
Conducted the Cathode Ray Experiment, Discovery of the electron, Plum-pudding atom
Millikan’s oil drop experiment
Determined how much charge an electron has
Becquerel
Discovered that a compound of uranium spontaneously emits high-energy radiation.
Rutherford’s Gold foil experiment
The atom is mostly empty space but has a dense center (nucleus) with positive charge too (Most alpha particles passed the gold foil, but some alpha particles deflected).
Rutherford
Revealed 3 types of radiation: alpha, beta, and gamma.
Chadwick
Discovered the neutron
Atomic number
Number of protons in an atom
Isotopes
Atoms with same atomic number but different mass numbers (same number of protons but different number of neutrons)
Oxyanions
Polyatomic anions containing oxygen that have names ending in either -ate or -ite.
What is an acid?
A substance whose molecules yield hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water.
What is an acid composed of?
An anion connected to enough H+ ions to neutralize or balance the anion’s charge.
Acids containing anions whose names end in -ide are changed to…
hydro + -ic acid
Acids containing anions whose names end in -ate are changed to…
-ic acid
Acids containing anions whose names end in -ite are changed to…
-ous acid
Isomers
Same molecular formulas but different arrangements of atoms.
Electronic structure of an atom
Refers to the arrangement of electrons
Visible light is a form of?
Electromagnetic radiation/radiant energy
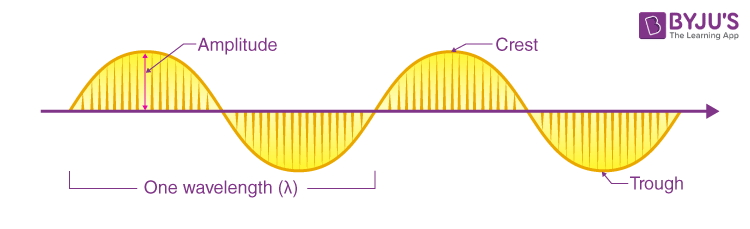
What is electromagnetic radiation?
The emission and transmission of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves.
What is the lowest energy electromagnetic radiation?
Radio waves (Lowest frequency and longest wavelength).
In the EM spectrum, the highest energy to lowest energy is?
Gamma Rays, X-rays, Ultraviolet, Visible, Infrared, Microwaves, Radio waves
What is the highest energy electromagnetic radiation?
Gamma rays (Highest frequency and shortest wavelength).
What are the units of wavelength?
meter or nm
1 nm = what m?
1 × 10-9 m
What are the units of frequency?
Hz-1 or 1 cycle/sec or s-1
Maxwell (1873)
Created equations to propose that visible light consists of electromagnetic waves. Discovered that as you change the temperature/energy, you get “quantized” energy events or colored lights.
Electromagnetic spectrum
A display of the various types of electromagnetic radiation arranged in order of increasing wavelength.
Energy is…
Quantized which means it can occur in discrete packets.
Photons
The energy packets light travels in.
Quanta
Refers to the discrete, indivisible units of energy.
Photoelectric effect
e- are emitted from the surface of a metal when light strikes it.
Quantum
The smallest amount of energy that can be emitted or absorbed as electromagnetic radiation.
When does photoelectric effect occur?
Only occurs if the radiation’s frequency is greater than te threshold frequency of the metal.
Work function
Minimum amount of energy to remove a electron from a metal.
Bright line spectrum
A gas placed in an evacuated tube and subjected to a high voltage produces single colors of light. The spectrum that we see contains radiation of only specific wavelengths.
Photoconductivity
Optical or electrical phenomenon where materials become more electrically conductive due to absorption of EMR —> absorbed light must be sufficient to move e- across the band gap.
Band gap
Gap in energy between the bonding orbitals/valence bands and the anti-bonding orbital/conduction bands.
Doping
Method of increasing conductivity.
Diffraction
When light is scattered from a regular array of points or lines.
The Uncertainty Principle
States that we can’t determine the exact position, direction of motion, and speed of subatomic particles simultaneously.
Aufbau
Electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy with no more than two electrons per orbital.
Pauli’s exclusion principle
No two electrons can fill one orbital with the same spin because they can’t have the same set of four quantum numbers.
Hund’s rule
The lowest energy is attained when the number of electrons with the same spin is maximized (to minimize repulsions).
Paramagnetic
Attracted to a magnetic field, unpaired electrons
Diamagnetic
Not magnetic, paired electrons
Ferromagnetic
Retain magnetism when introduced to and then removal from a magnetic field. The clusters of atoms have their unpaired electrons aligned within a cluster and substance acts as a magnet.