Objectives I and II
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is the role of DNA in protein synthesis?
DNA stores the genetic code, a sequence of nucleotide bases that provides instructions for the primary structure of proteins.
What is the role of mRNA in protein synthesis?
mRNA carries the transcribed genetic code from DNA to the ribosome, where it is translated into a polypeptide.
What is the role of rRNA in protein synthesis?
rRNA is a structural and catalytic component of the ribosome; it forms the peptidyl transferase center for peptide bond formation.
What is the role of tRNA in protein synthesis?
tRNA reads the codons on mRNA via its anticodon and brings the correct amino acid for incorporation into the polypeptide.
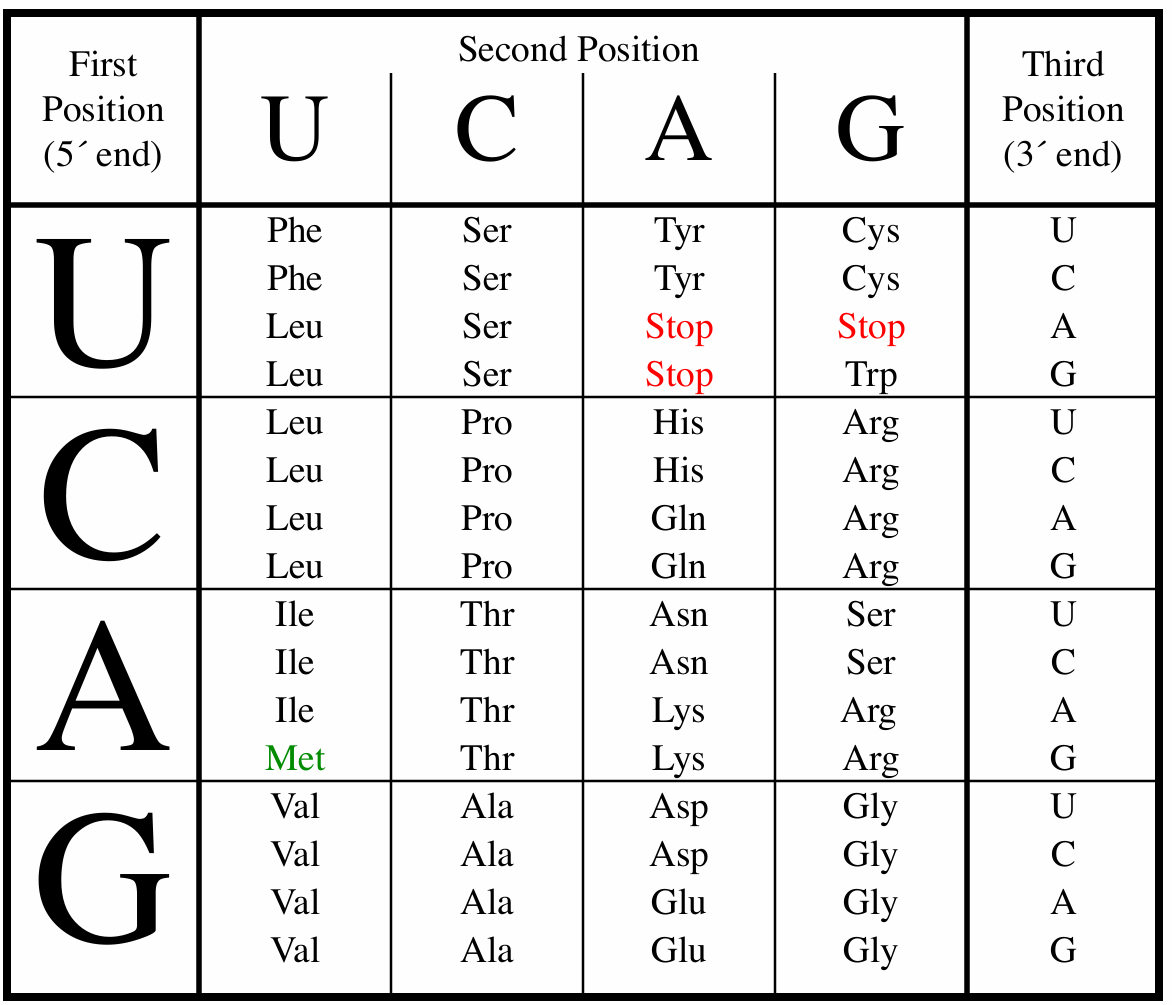
What is the genetic code?
A set of triplet nucleotide sequences (codons) on mRNA that specify amino acids during protein synthesis.
Why is the genetic code considered simple and elegant?
It uses only 4 nucleotides to code for 20 amino acids via 64 codons, is almost universal, and has built-in redundancy.
What is a codon?
A sequence of three nucleotides on mRNA that specifies an amino acid or stop signal in protein synthesis.
What is meant by 'degenerate' in the context of the genetic code?
Multiple codons can specify the same amino acid, reducing the effect of mutations.
What does 'punctuationless' mean regarding the genetic code?
Codons are read continuously without any separating markers or “commas.”
What does it mean that the code is 'non-overlapping'?
Each nucleotide is part of only one codon; codons are read one at a time.
What does it mean that the genetic code is 'universal'?
The same codon-amino acid relationships are used by almost all organisms.
What are synonymous codons?
Codons that differ in sequence but specify the same amino acid.
What are termination or nonsense codons?
Codons that signal the end of translation: UAA (Ochre), UAG (Amber), UGA (Opal).
What is the initiation codon?
AUG, which codes for methionine and sets the reading frame.
What is a reading frame?
The sequential triplet grouping of nucleotides that determines how codons are read.
What is a silent mutation?
A change in a nucleotide that does not change the amino acid due to code degeneracy
What is a missense mutation?
A nucleotide change that substitutes one amino acid for another
What is a nonsense mutation?
A mutation that converts a codon for an amino acid into a stop codon.
What is a frameshift mutation?
An insertion or deletion that changes the reading frame, usually resulting in a nonfunctional protein.
How do you read and translate the genetic code using a codon table?
Locate the first base on the left, the second base on the top, and the third on the right to find the corresponding amino acid.