Microbiology chapter 2 The molecules of life
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Atoms are…
Basic units of matter
Neutrons
Uncharged found in nucleus
Protons
Positively charged found in nucleus
Electrons
Negatively charged, Found in shells around nucleus
Atomic number is
Number of protons
Atomic mass
Number of protons and neutrons
Isotopes
Atoms with the same atomic number but different mass numbers
How many different types of bonds can form and what are they?
3 Covanlent, Ionic, Hydrogenn
Ionic bonds
Formed by atoms gaining or losing electrons, strongest of bonds
Covalent bonds
Formed when atoms share electrons, a weaker bond
Hydrogen bonds
Atoms bond with a hydrogen generally a weak bond
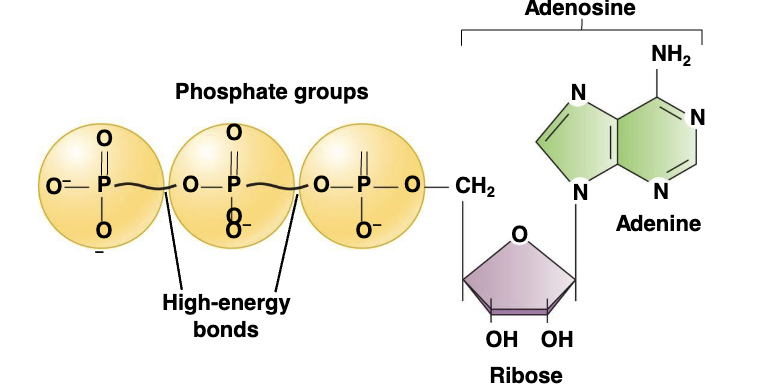
Adenosine triphosphate
(ATP) Energy supplier of the cell
4 major classes of Macromolecules
Proteins
Carbohydrates
Nucleic acids
Lipids
Roles of proteins
Catalysis
transport
movement
cellular framework
cellular response
gene expression
Which macromolecule is more than half of a cells dry weight
Proteins
Building blocks of proteins are —--
Amino acids
How many amino acids are found in proteins
20
what holds amino acids together
Peptide bonds
What determines a protein’s shape
Amino acid sequence
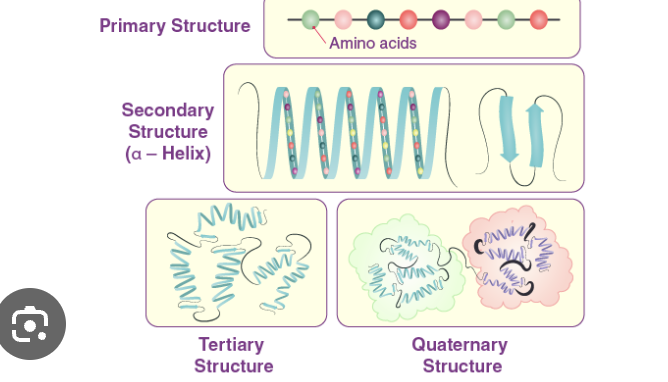
Protein structure levels….
Primary - chain of amino acids
Secondary structure - helix or sheet
Tertiary - 3D
Quaternary - complete protein
What happens when a protein denatures
It becomes inactive; loses its shape
What causes protein denaturation
High temperature, extreme pH and harsh solvents
Carbohydrates are a source of what?
Energy and carbon source
What is the general formula or ratio of a carbohydrate?
General formula (CH2O)n
Ratio 1:2:1 Carbon:Hydrogen:Oxygen
What is a monosaccharide and examples
A single unit carbohydrate
Eg: Glucose, Fructose, Mannose, Galactose
What is a Disaccharide?
Two monosaccharides joined by a covalent bond
Sucrose
Glucose + Fructose
Lactose
Glucose + Galactose
Maltose
Glucose + Glucose
Polysaccharides and examples
Chains of monosaccharides
• Often made from glucose
Eg:
• Cellulose
• Starch
• Glycogen
• Dextran
Nucleic acid
Carries genetic information in sequence of nucleotides
Types - DNA or RNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
RNA
Ribonucleic acid
Two classes of nuceotides
Purines or Pyrmidines
Purines
Adenine (A), Guanine (G)
Pyrimidines
Cytosine ( C ), Thymine (T), Uracil (U only in RNA)
A bonds to ?
T: A bonds to T
C bonds to ?
G: C bonds to G