Lesson 1.1 Homeostasis and Endocrine Signaling
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Homeostasis
process of how the body maintains stable internal conditions for optimal health
Major Conytol Systems
Nervous System and Endocrine System
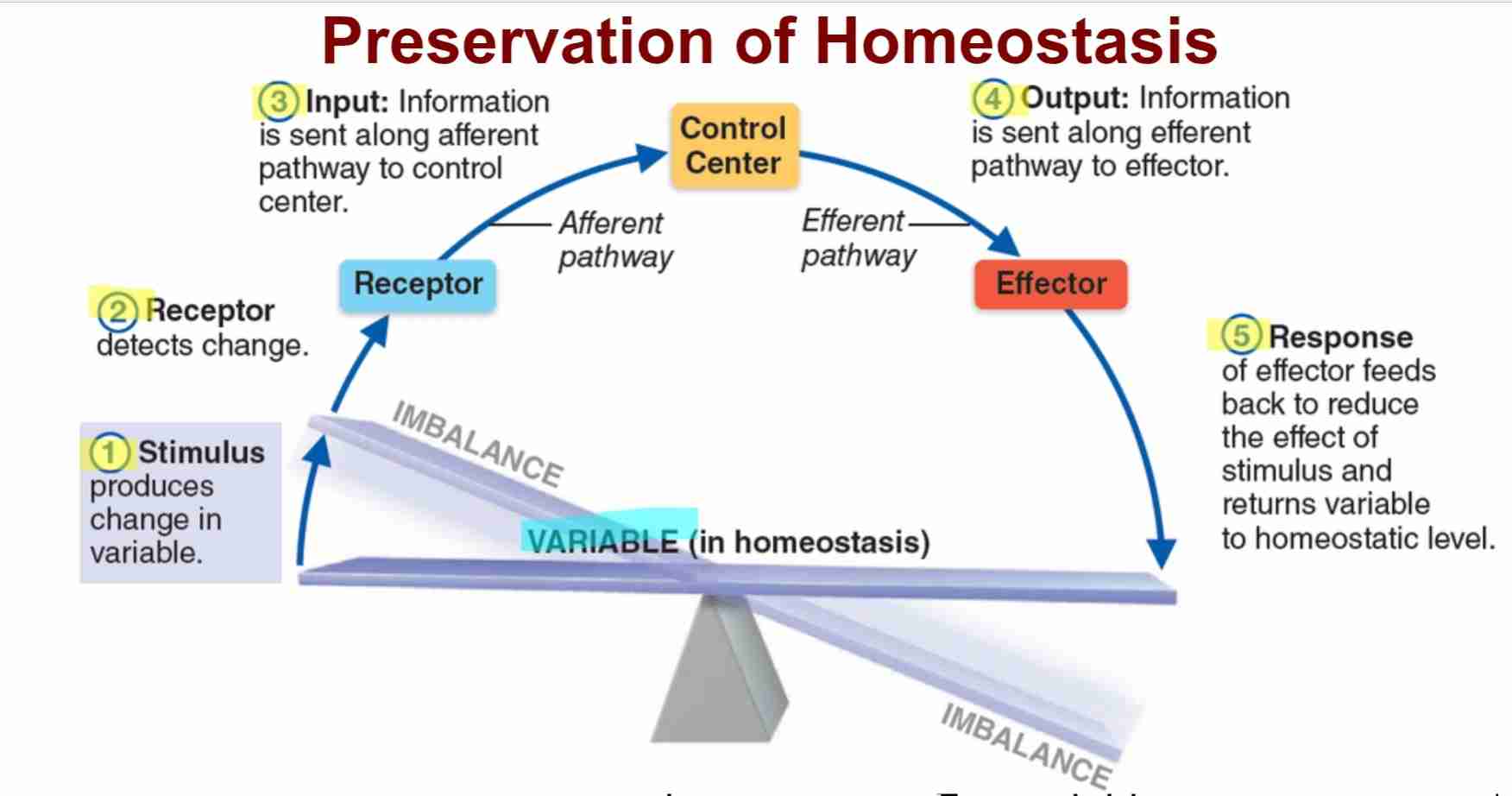
Steps Homeostasis: Stimulus
change in internal or external environment to disrupt body
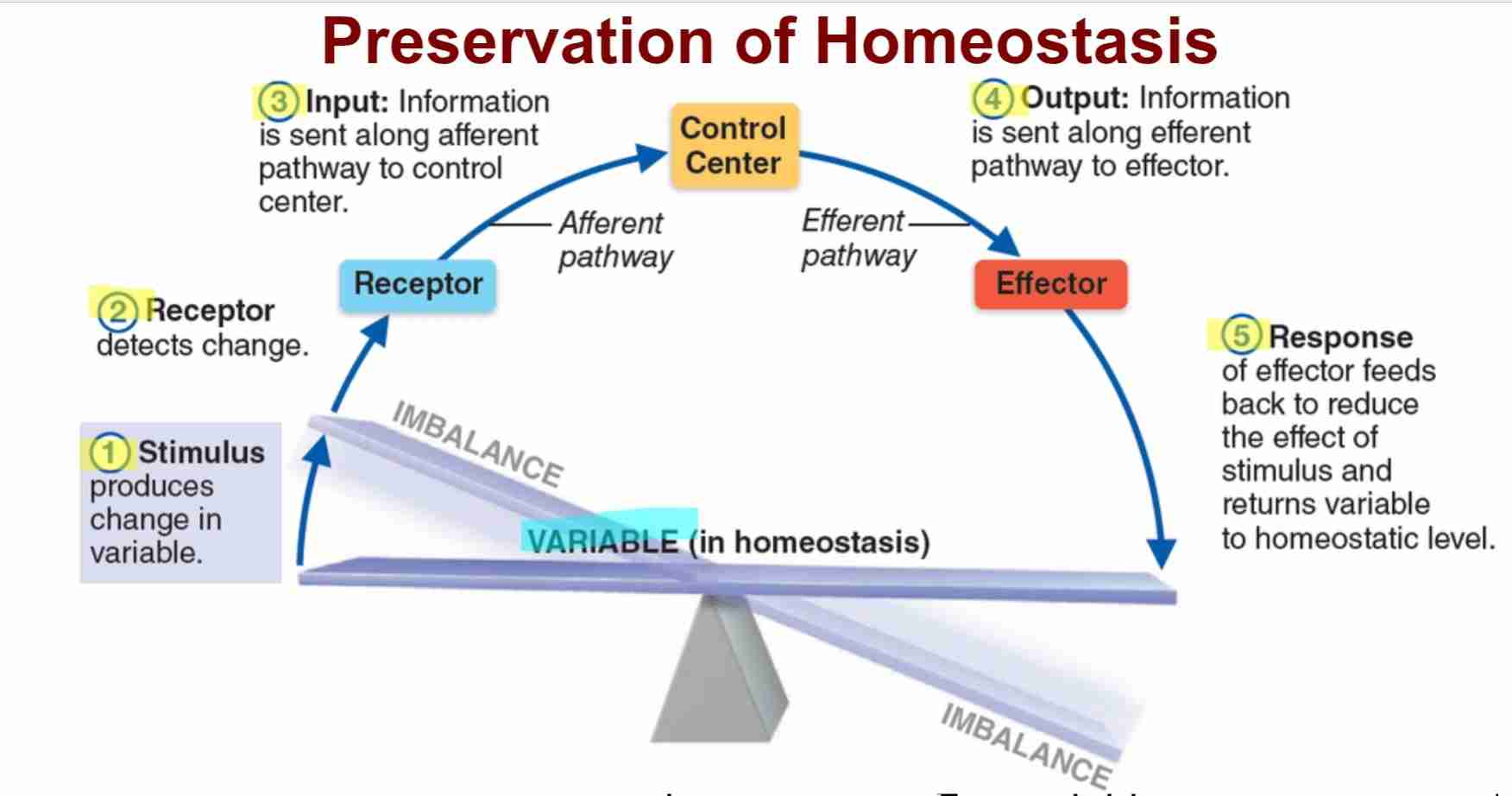
Steps Homeostasis: Receptor
specialized sensor that detects imbalance
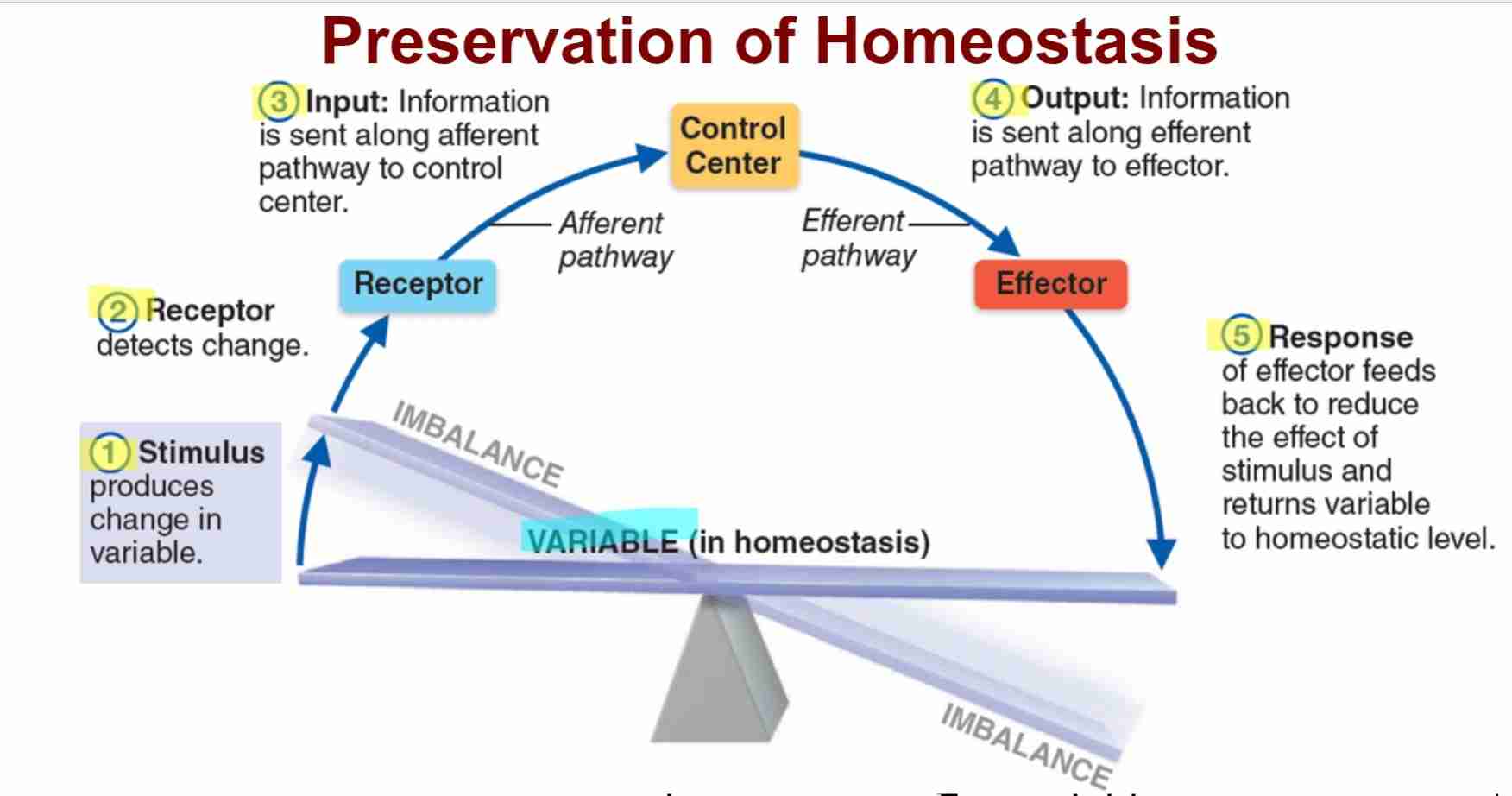
Steps Homeostasis: Input
Information is transmitted to control systems
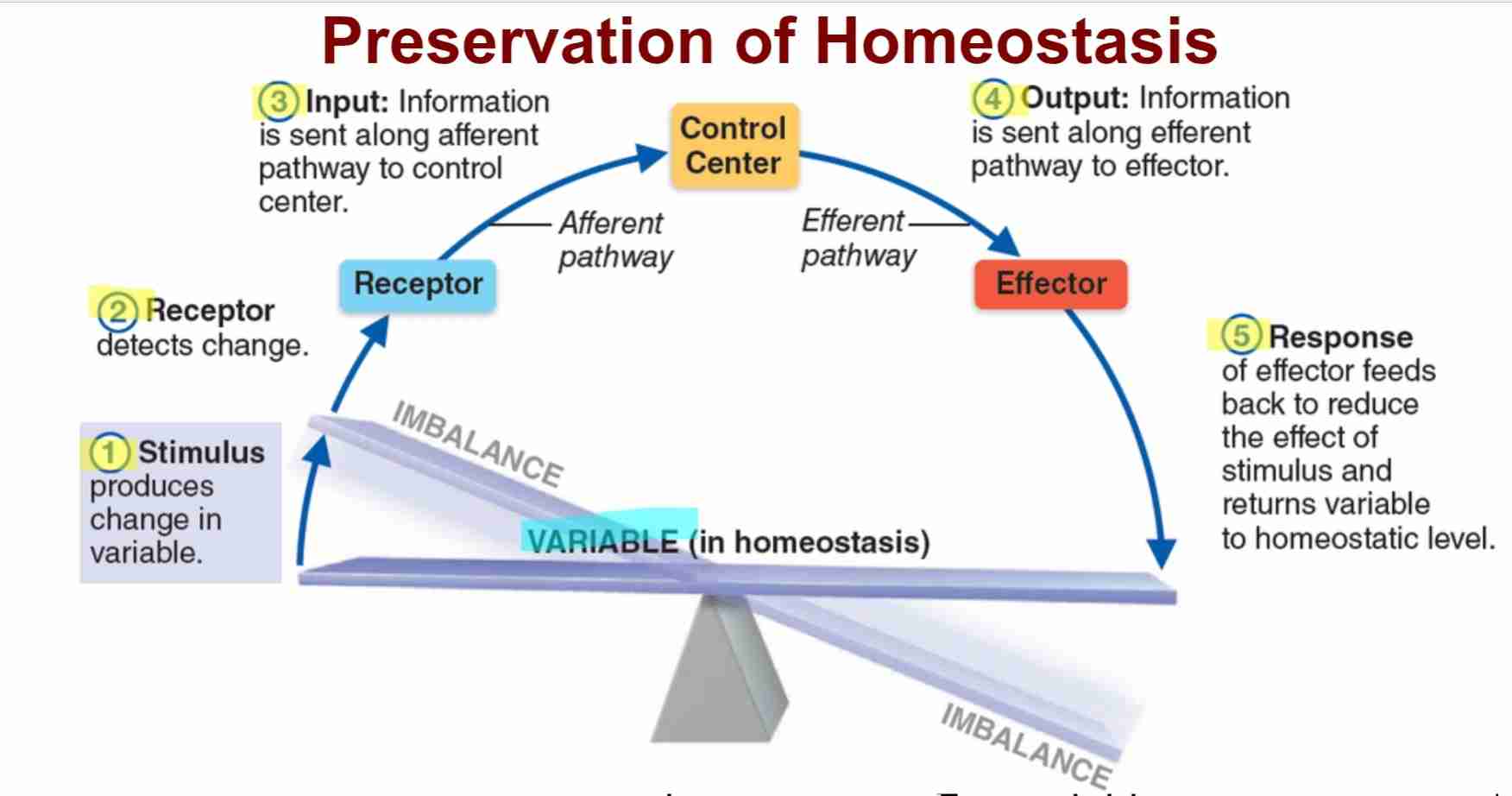
Steps Homeostasis: Output
Information is sent to effectors to correct imbalance
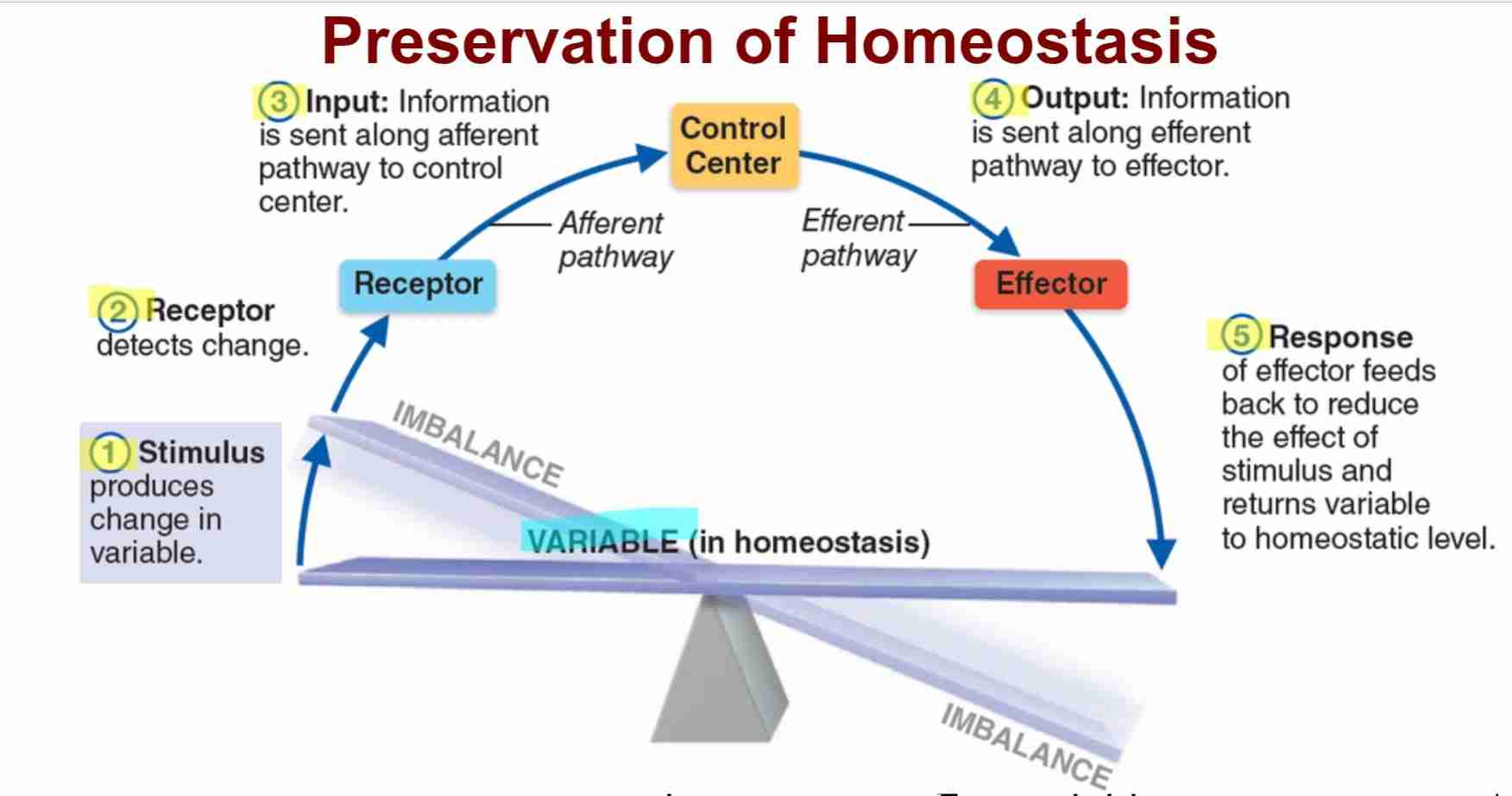
Steps Homeostasis: Reponse
Effector carries out reponse to return body to homeostasis
Nervous: Communicates Via
Electrical Signal (main) + chemical (neurotransmitter)
Nervous: Signal Speed
Fast
Nervous: Signal Persistance
Short
Nervous: Response Speed
Fast
Nervous: Range Affects
Locally
Endocrine: Communicate Via
Chemical (Hormone)
Endocrine: Signal Speed
Slow
Endocrine: Signal Persistance
Long Lasting
Endocrine: Reponse Speed
Slow
Endocrine: Rance Affects
Wide Range
Pineal Gland
Produce melatonin. Regulate sleep wake cycle and circadian rhythmn
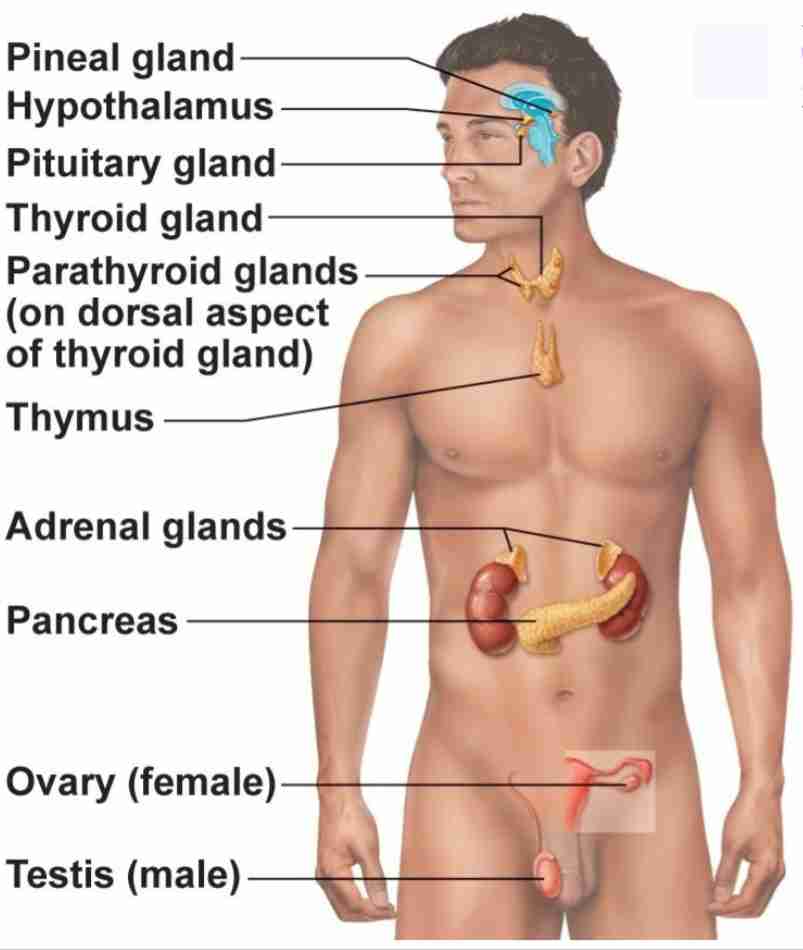
Pituitary Gland
Has anterior and posterior lobes. Regulates many processes in body
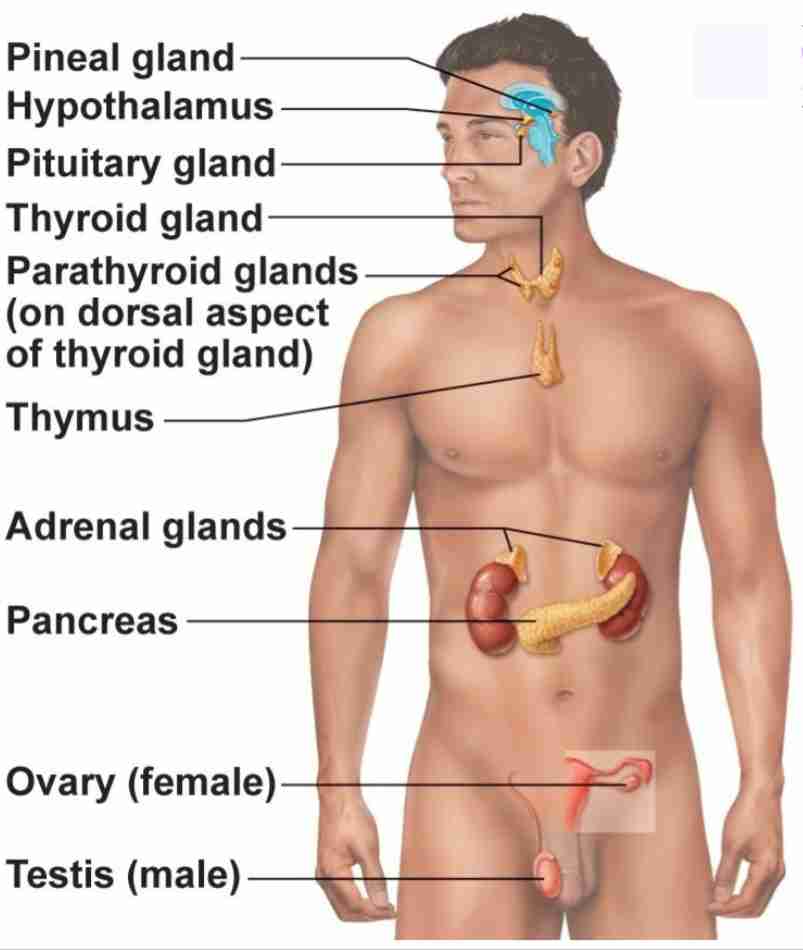
Thyroid Gland
Butterfly shaped gland that regulates metabolic rate
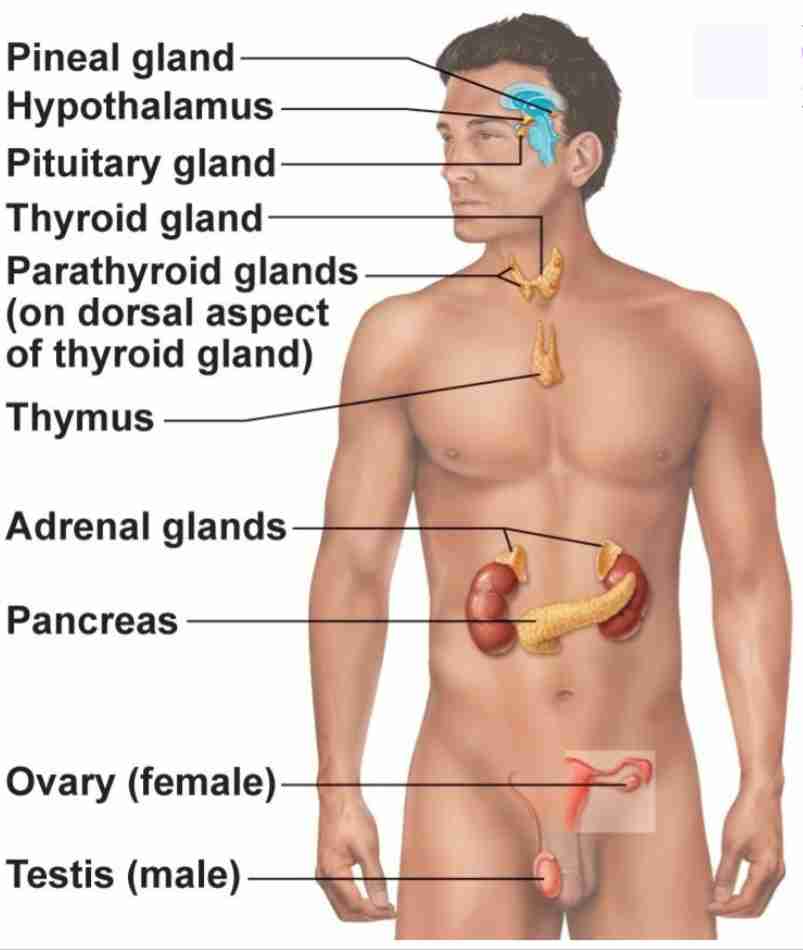
Parathyroid Glands
4 glands behind thyroid gland that regulates calcium levels
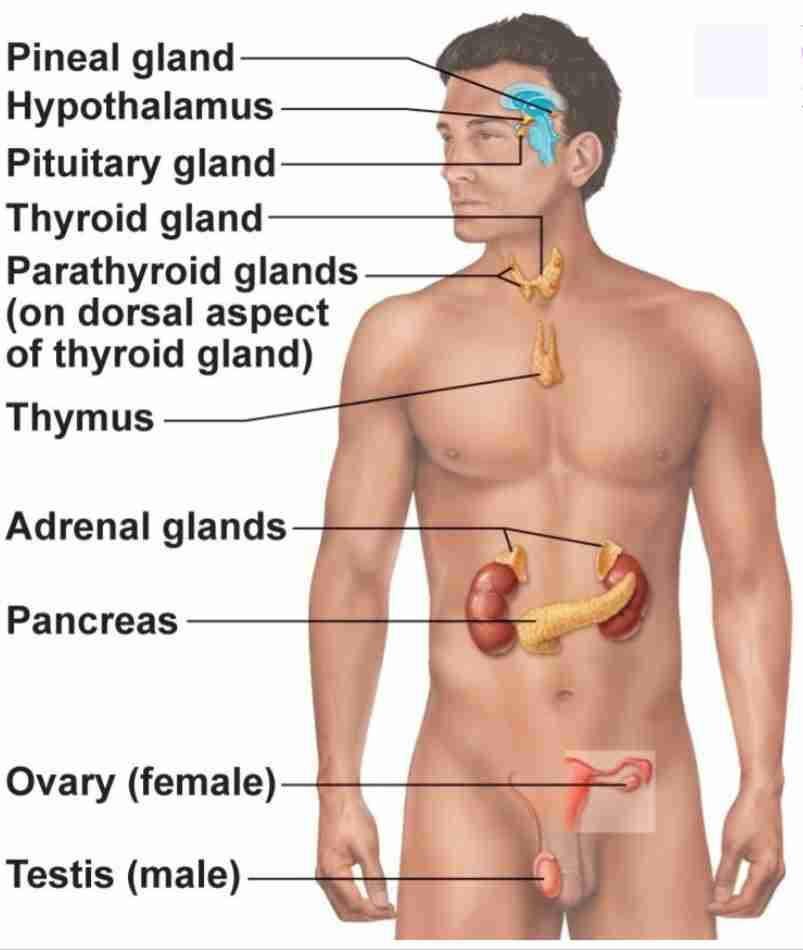
Thymus
regulates immune cell productions (T-cells)
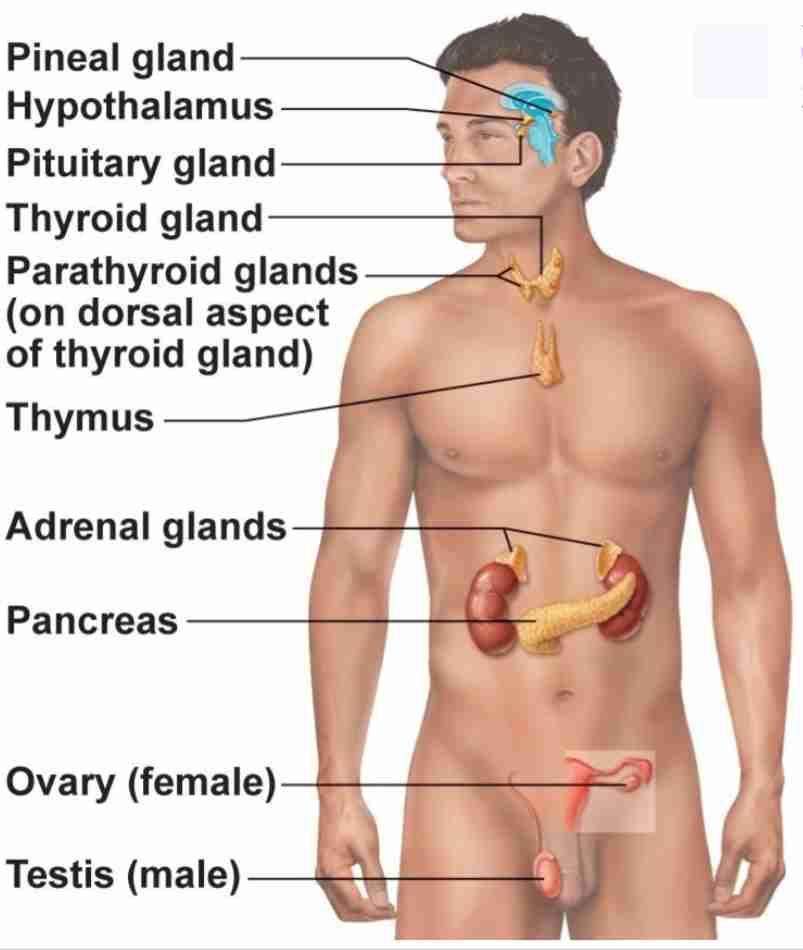
Adrenal Glands
2 glands on top of kidneys that regulate stress response
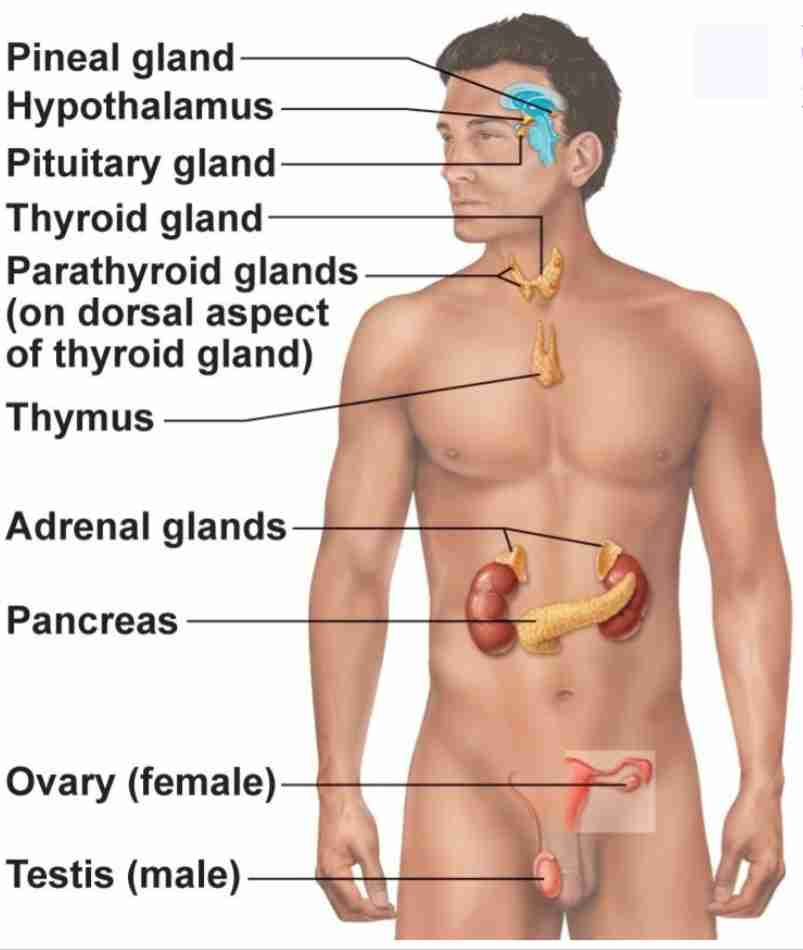
Pancreas
secretes hormones insulin and glucagon to regulate blood glucose levels
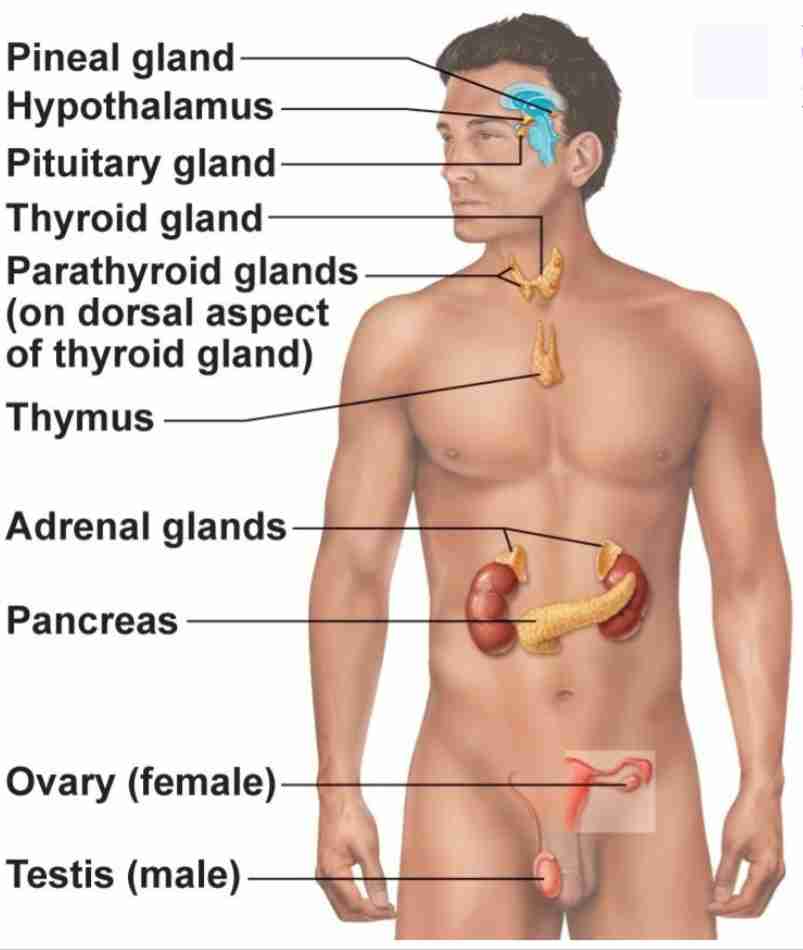
Ovary
2 glands that regulate female reproduction, breast tissue, and childbirth preparation
Testes
2 glands that regulate male reproduction and sperm maturation
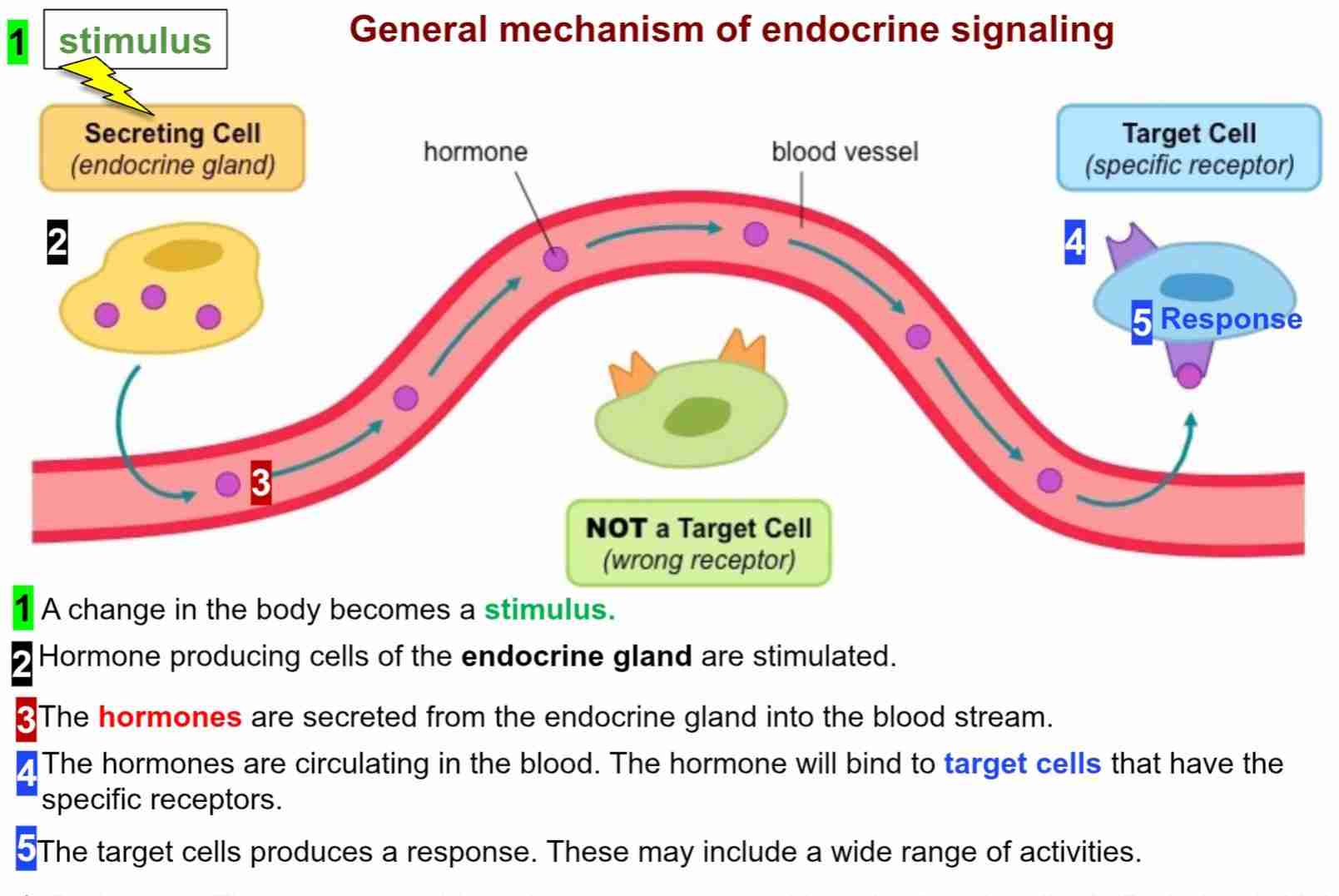
Endocrine Signaling: Draw
Possible Pathologies: Endocrine Gland
No functional Gland
Gland does not receive stimulus
Gland removes
Gland failed to produce enough hormone
Possible Pathologies: Hormone
Too much or little hormone
Imitator hormone in bloodstream
Hormone Mutation
Possible Pathologies: Target Cell + Response
Target cell fails to respond
Target gland missing
Mutation fails to make receptor
Receptor not right shape
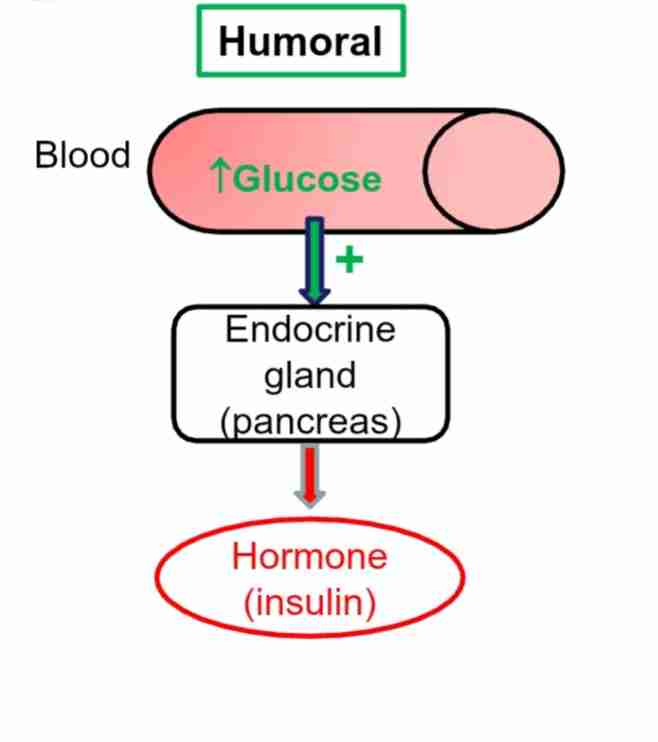
Humoral Stimulus
Type of Endocrine Stimulus: glands reponse to change in blood levels
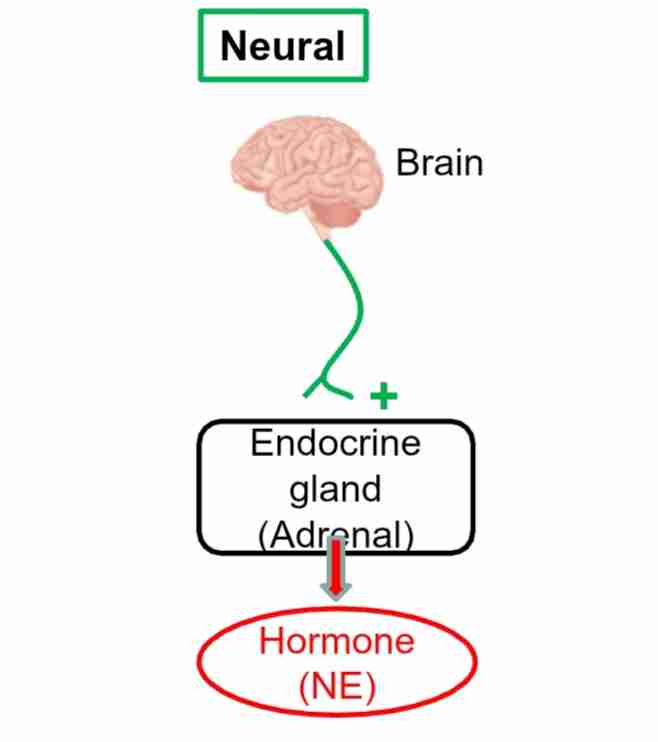
Neural Stimulus
Type of Endocrine Stimulus: Glands release hormones when stimulated by neurons
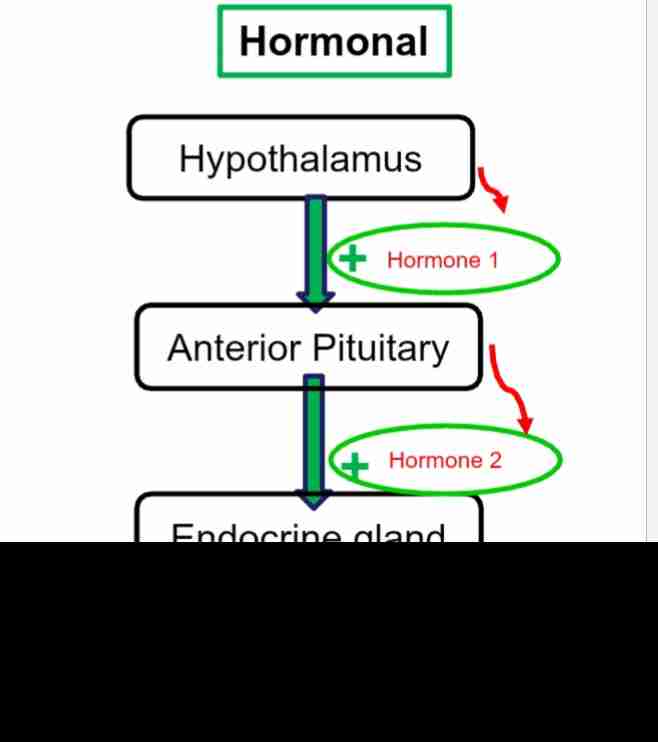
Hormonal Stimulus
Type of Endorcine Stimulus: Gland release hormones when stimulated by another hormone