MBHS Unit 4: Social Psych and Personality
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
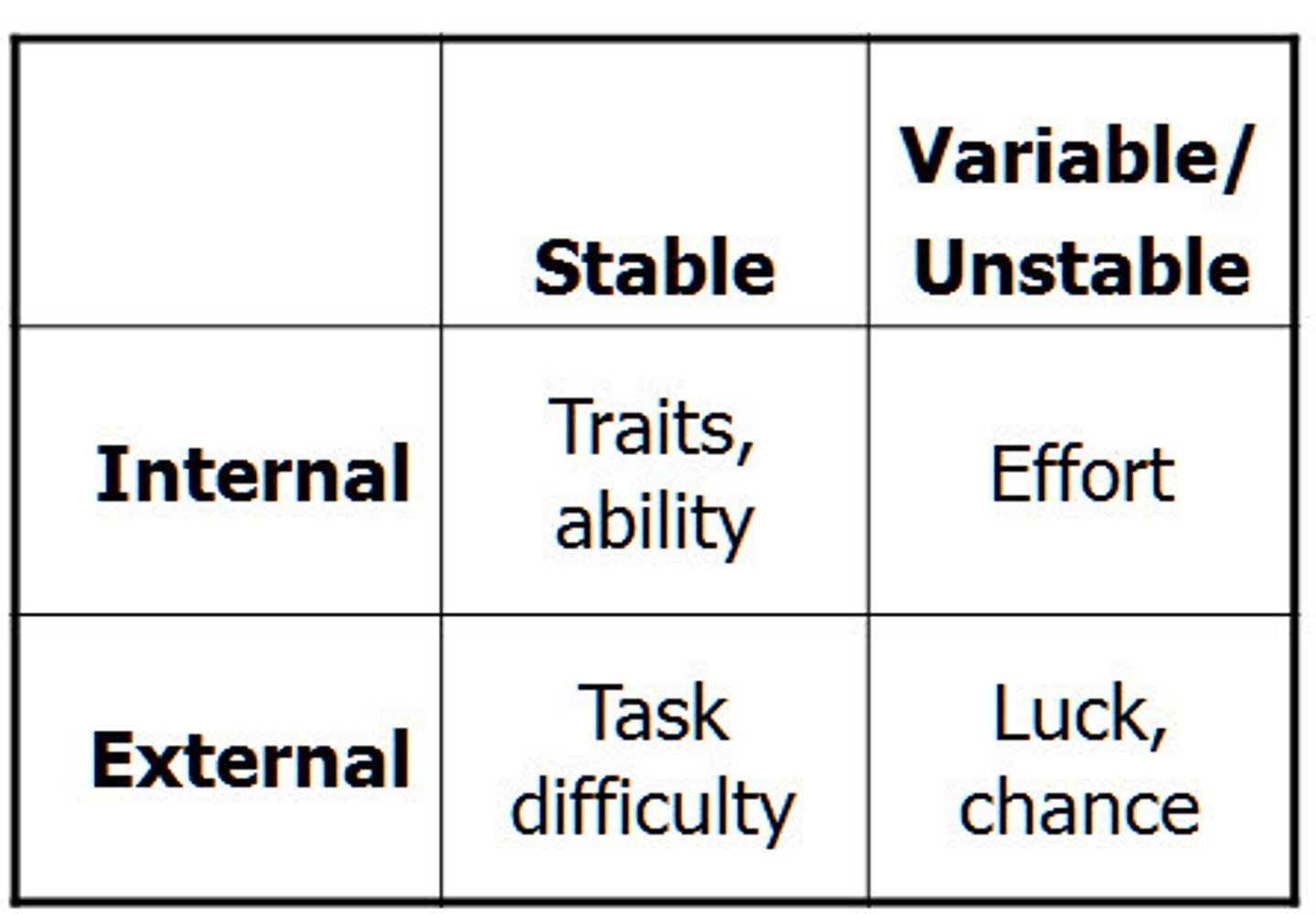
attribution theory
the theory that we explain someone's behavior by crediting either the situation or the person's disposition
dispositional attribution
attributing behavior to the person's disposition and traits

cognitive dissonance
unpleasant mental experience of tension resulting from two conflicting thoughts or beliefs

central route persuasion
occurs when interested people focus on the arguments and respond with favorable thoughts

peripheral route persuasion
occurs when people are influenced by incidental cues, such as a speaker's attractiveness

reciprocity norm
an expectation that people will help, not hurt, those who have helped them

social facilitation
stronger responses on simple or well-learned tasks in the presence of others
false consensus effect
the tendency to overestimate the extent to which others share our beliefs and behaviors

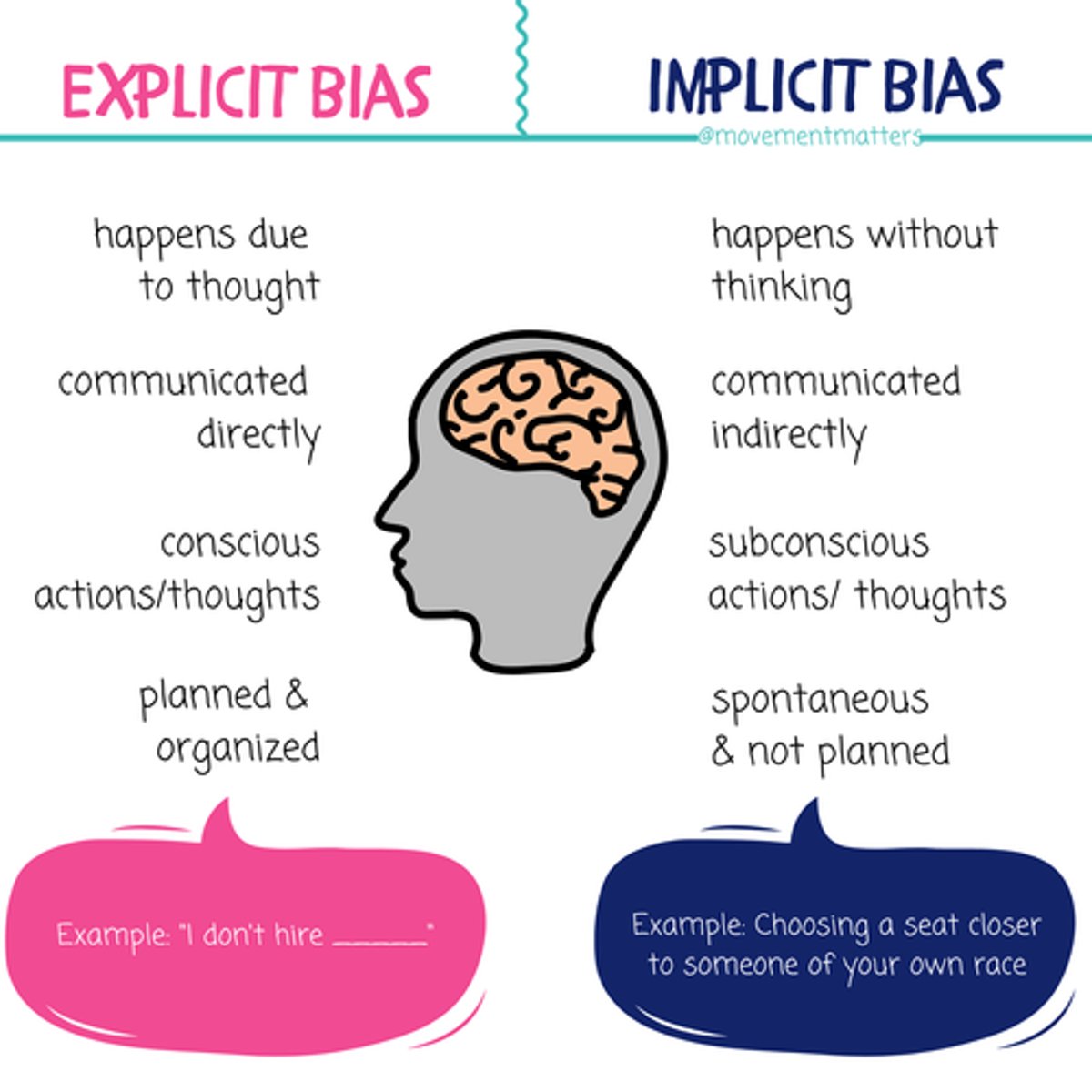
implicit bias
attitudes or stereotypes that affect our understanding, actions, and decisions in an unconscious manner
explicit bias
attitudes or beliefs that one endorses at a conscious level
altruism
unselfish regard for the welfare of others

humanistic theory of personality
theories of motivation which focus on human potential and the drive to be the best a person can be
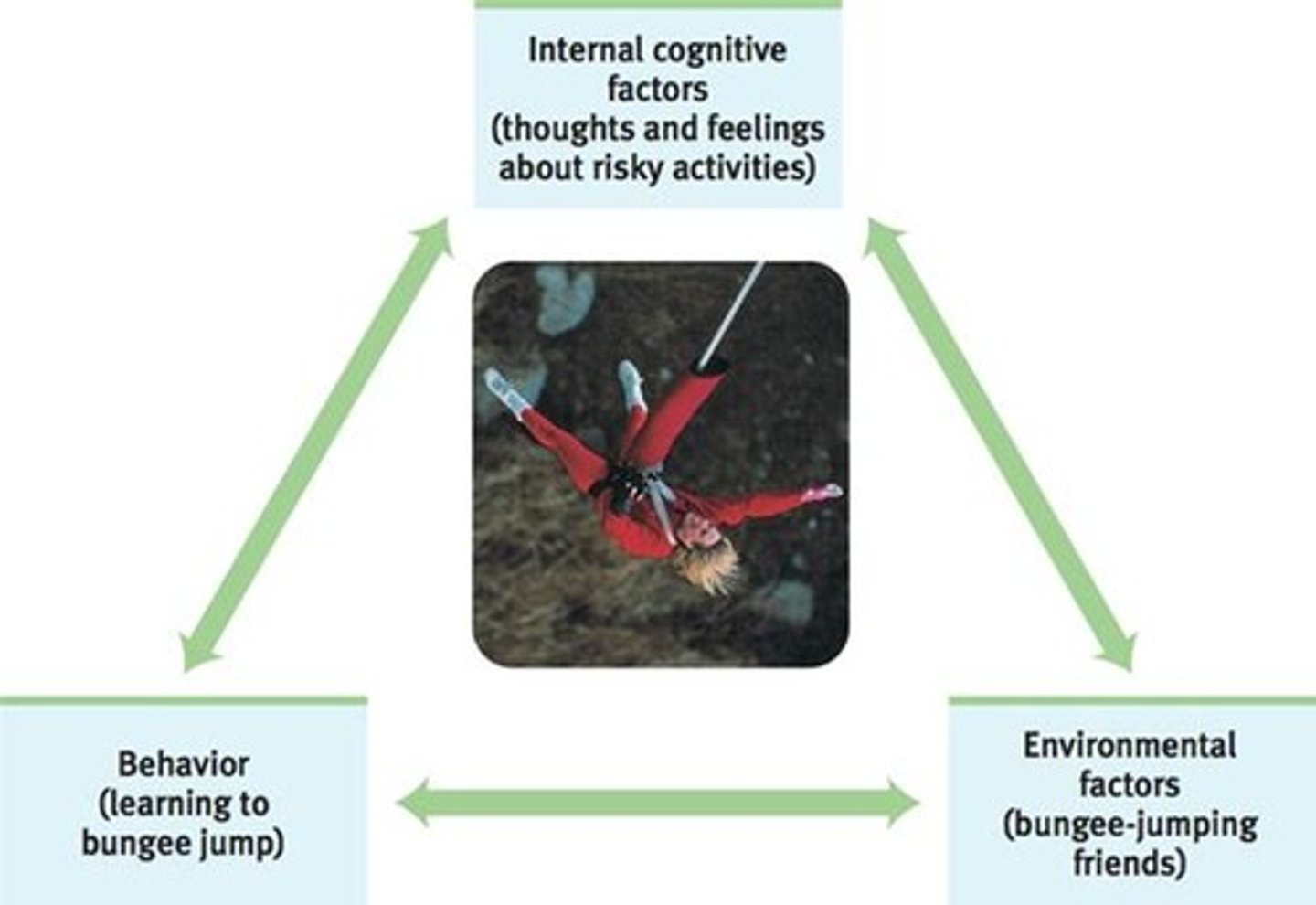
reciprocal determinism
the interacting influences of behavior, internal cognition, and environment
regression (defense mechanism)
A person goes back to an earlier or less mature state or behavior
Repression (defense mechanism)
Banishes anxiety-arousing wishes and feelings from consciousness

conscientiousness
how dependable, responsible, achievement-oriented, and persistent one is

neuroticism (emotional stability)
calm or anxious, secure or insecure, self-satisfied or self-pitying

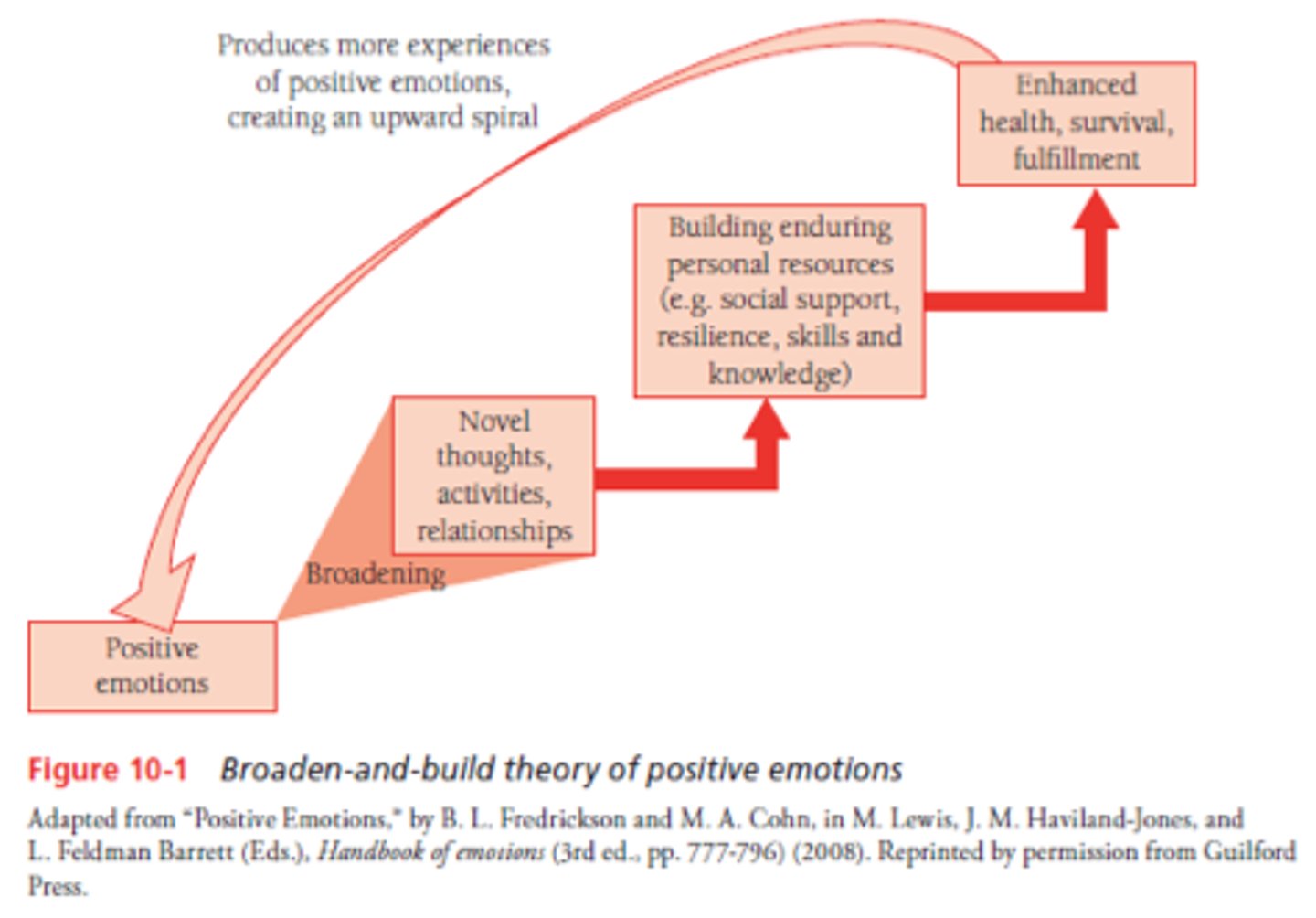
broaden and build theory of emotion
a positive psychology theory that suggests that positive emotions can help people build skills and resources over time