Plant Biology Test 1
1/200
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
201 Terms
Why are plants important?
Eat them
Medicines
Oxygen
Building material
Support ecosystems
Supporting tourism
Decoration
Paper
Clothing
Scientific research
Scents
Wood (fuel)
Shade
Animal feed
Dyes
Poisons
Protection from natural disasters
aesthetic/flowers
Heterotrophs
gain energy by consuming other organic material from other organisms/sources
EX. animals, fungi, some single celled organisms
Autotrophs
self-feeding organisms that can make their own food from inorganic substances
EX. plants use sunlight, CO2, and water to produce carbohydrates
Roots
hold the plant in place, absorb water from the soil
Stem
support for above-ground plant parts
Leaves
the main plant organ to gather sunlight for photosynthesis
What is the flow of water?
Soil → Roots → Stem → Leaves → Atmosphere
Cuticle
a waxy material to educe water loss from leaves and impacts gas exchange
Epidermis
outermost covering (layer of cells) on a plant
Stomata
openings in the epidermis of leaves for gas exchange
the size of stomata is controlled by a pair of guard cells
Vascular System
composed of xylem and phloem
NOT FOUND IN ALL PLANTS!
Xylem
transports water up
Phloem
transports nutrients to the plant body
Meristems
structures that maintain the ability to produce new cells, responsible for a plant’s continual growth
Apical meristem
found at the tips of roots and shoots
contains primary growth = increase in length/height
associated with lateral meristems
Lateral meristems
composed of cork cambium and vascular cambium
secondary growth = increase in girth/diameter
Plant categories
ancestor of land plants → green algae
Bryophytes
moss, liverworts, hornworts (non vascular so no X or P)
Ferns and Fern Allies
vascular, reproduce only with spores
Gymnosperms
vascular, produce with seeds (cones)
naked seeds
cycads
conifers
gnetophytes
ginkgo - only has one species!
Angiosperms
flowering plants (vascular, reproduce with seeds)
enclosed seeds (fruits)
Cell Theory
All living things are made up of at least one cell.
Cells come from pre-existing cells.
A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in organisms’
Metabolism occurs inside cells.
Cells have DNA that can be passed from the parent cell to daughter cells.
Robert Hooke
1600s
coined the term cell
Schleiden
botanist
discovered that all plants are made of cells
Schwann
zoologist
discovered that all animals are made of cells
Virchow
pathologist
discovered that cells come from other cells
Prokaryotes
lacks a nucleus
archaea (archaebacteria) and bacteria (eubacteria)
circular DNA
lack of membrane-bound organelles
smaller (1-10 micrometers)
Eukaryotes
have a nucleus
plants, animals, fungi, and protists
linear DNA
have membrane-bound organelles
larger (5-100 micrometers
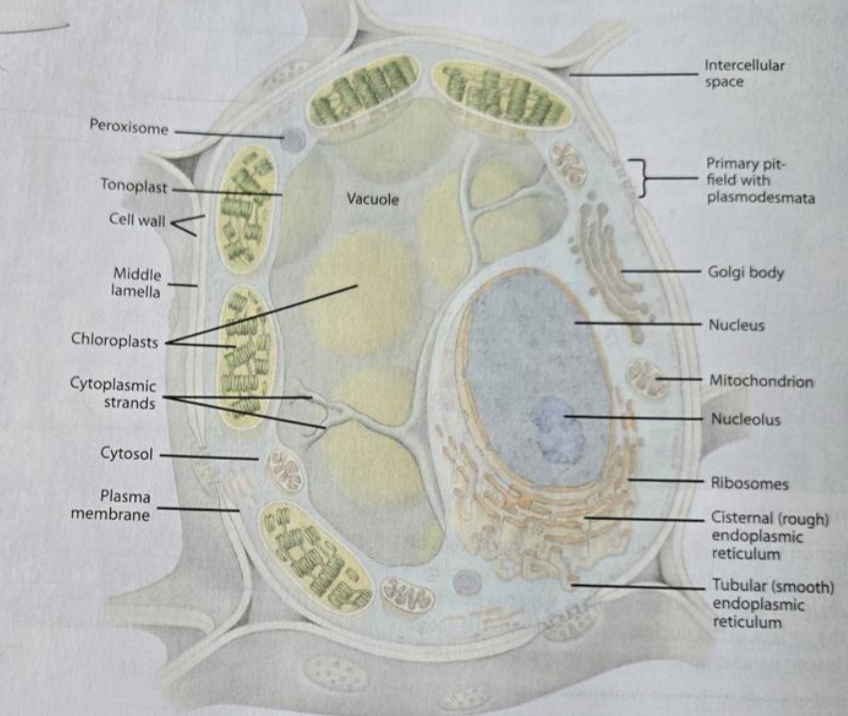
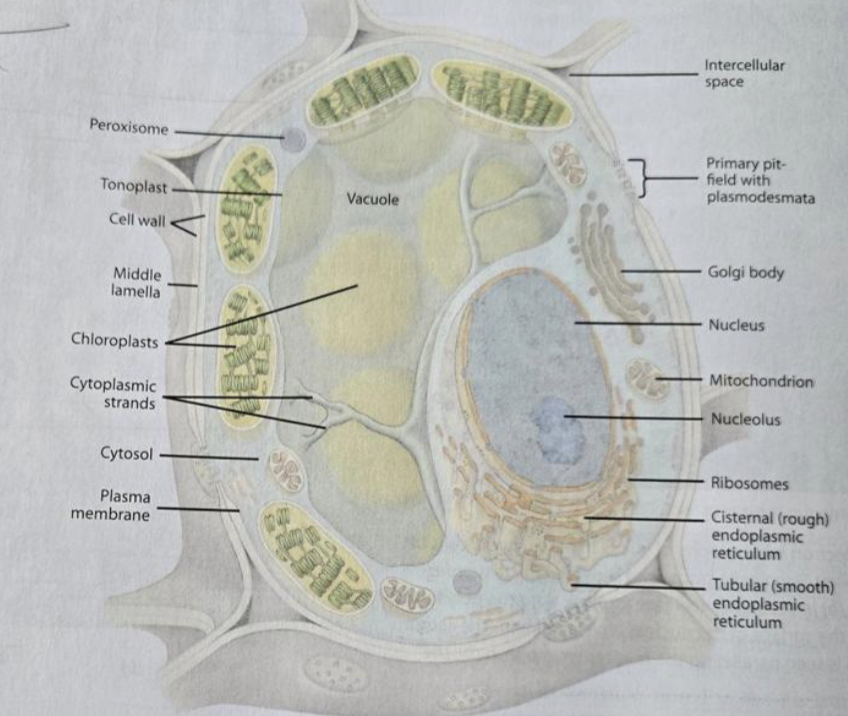
Cell wall
provides strength to the plant cell (mostly cellulose)
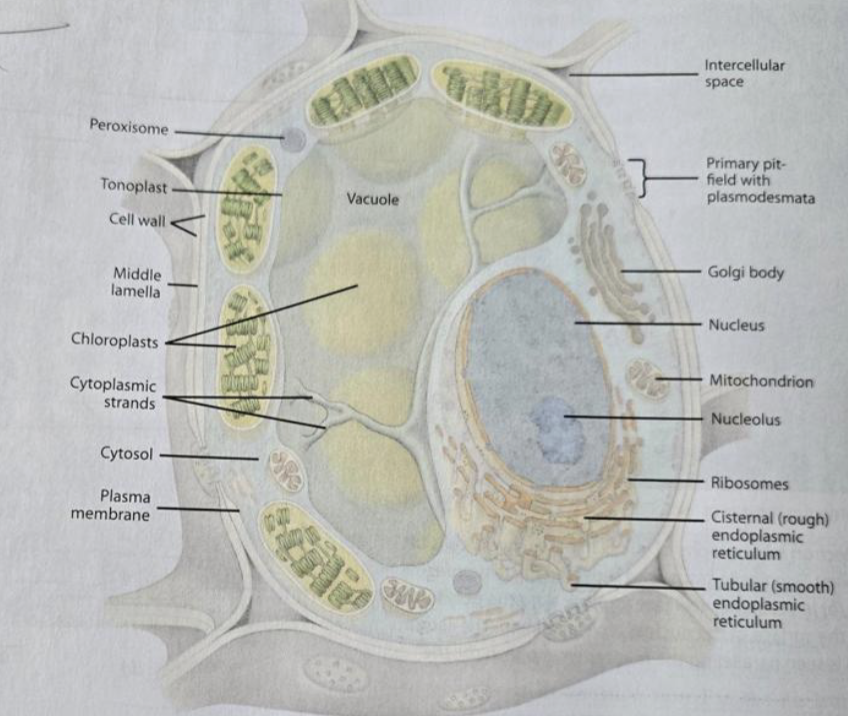
Protoplast
plant cell components without the cell wall
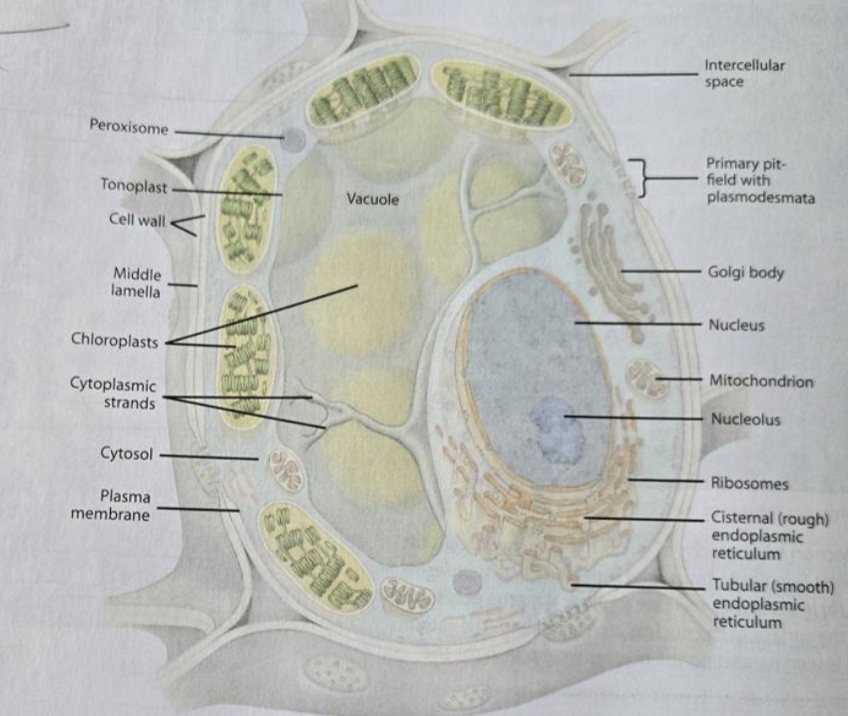
Cytoplasm
space outside the nucleus (organelles and cytosol)
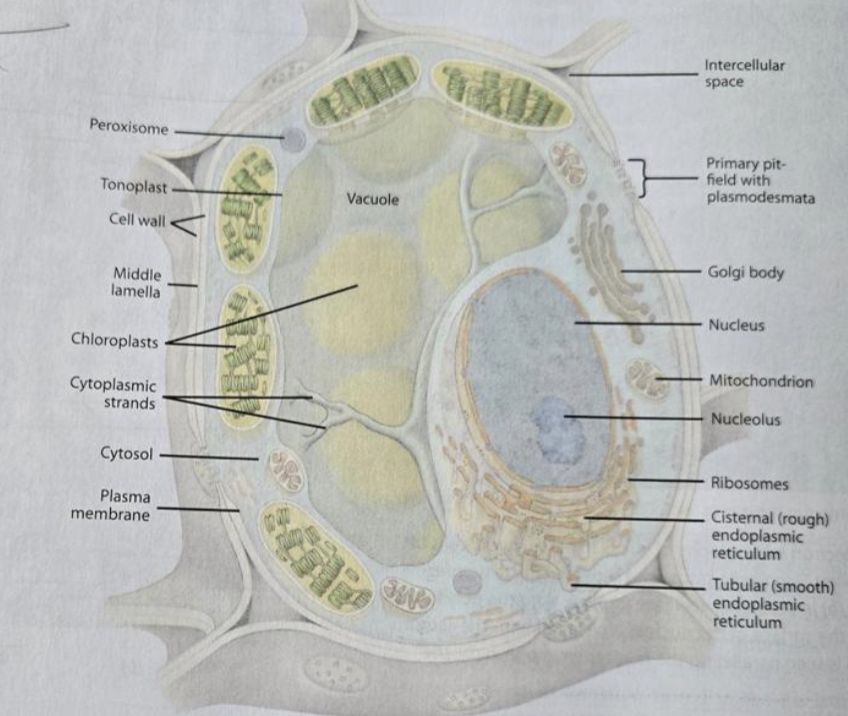
Cytosol
fluid/liquid component of the cytoplasm
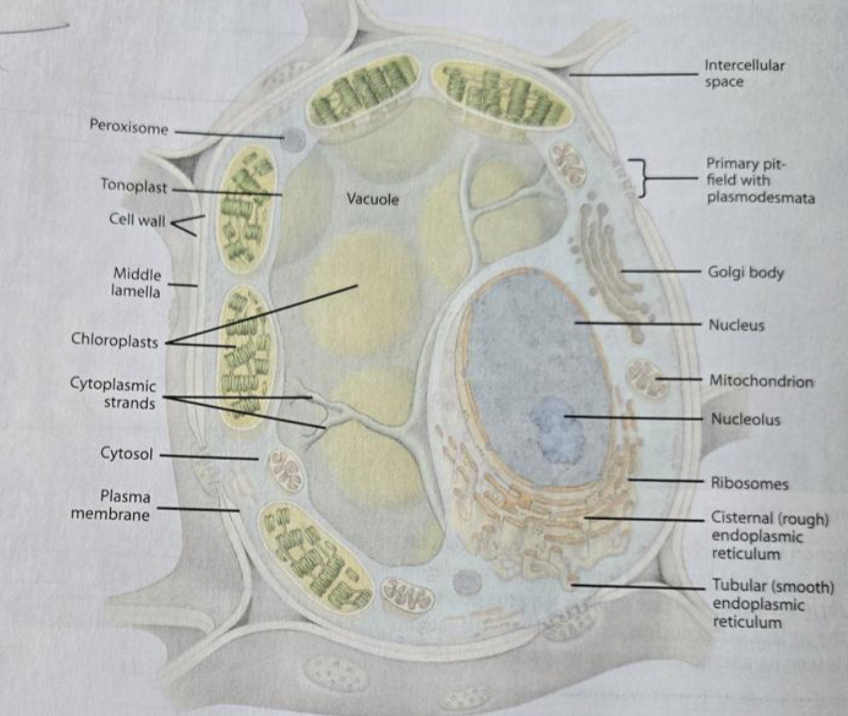
Plasma membrane
semi-permeable structure surrounding the cytoplasm
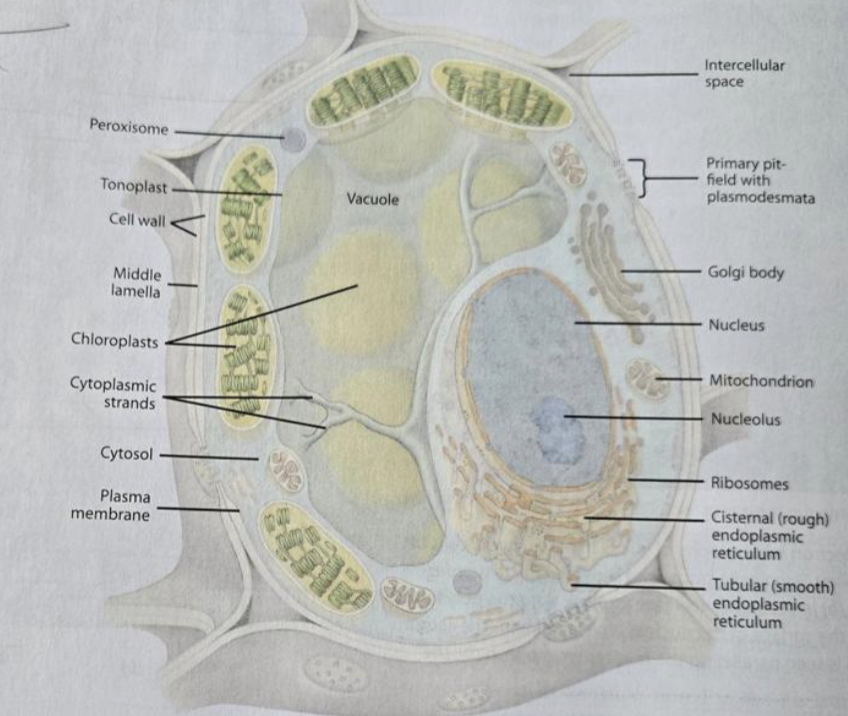
Nucleus
the nuclear genome, nucleolus, has a nuclear envelope with pires
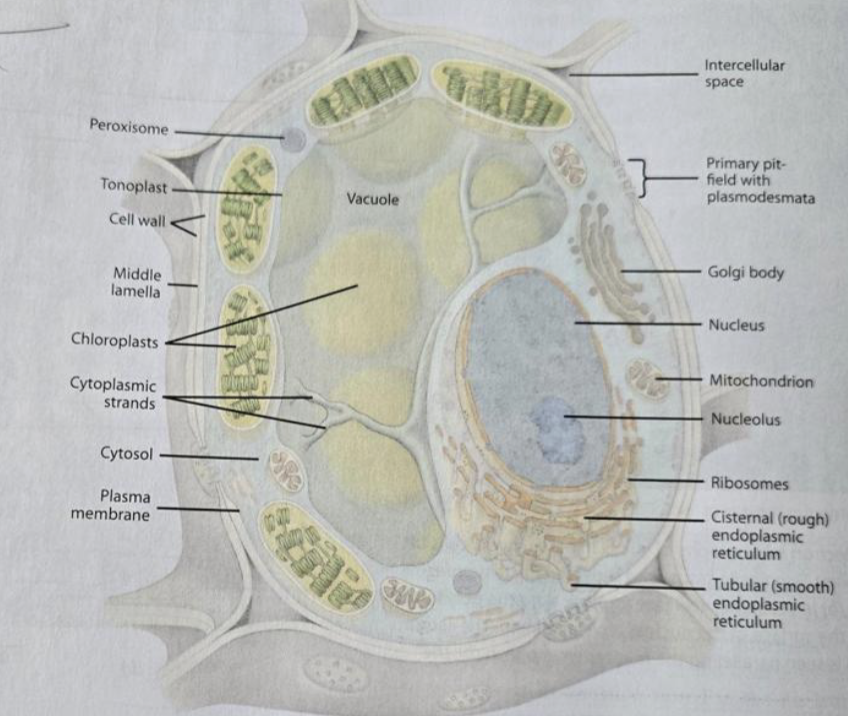
Ribosomes
made of rRNA and protein, attached to the rough ER or free-floating in the cytoplasm
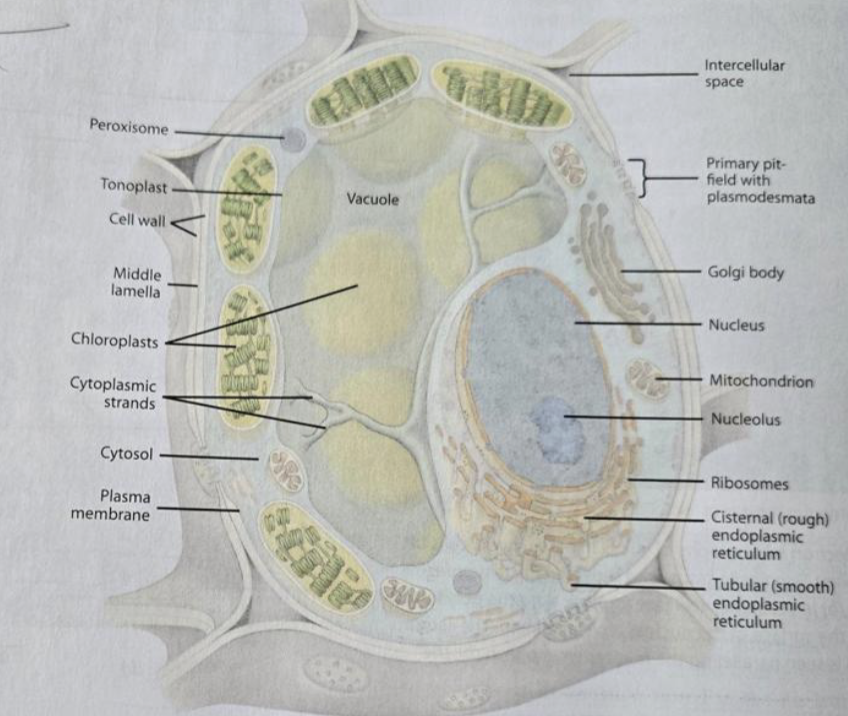
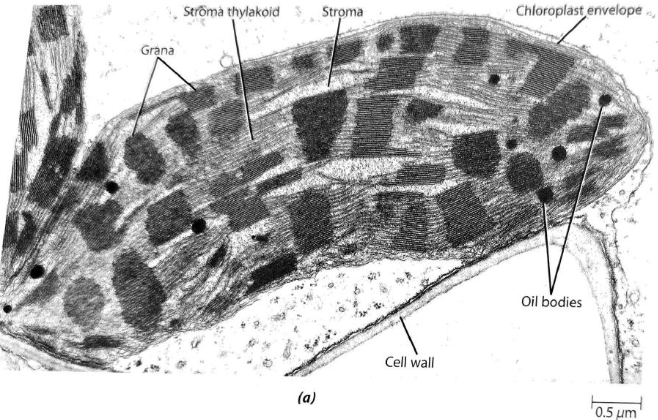
Plastids
double-membraned, reproduced by binary fission
Chloroplast
consists of thylakoid, granum, and stroma
own DNA and ribosomes
photosynthesis
bright
In ____ light, chloroplasts line the walls of plant cells.
dim
In ____ light, the chloroplasts line up horizontally to get as much light as they can.
Thylakoid
disc-shaped sacs
Granum
one stack of thylakoids
Stroma
fluid within the chloroplast
Chromoplast
contain yellow, red, and orange pigments
Leucoplast
lacks pigments and has little structure
EX. amyloplast - store starch
Proplastid
found in meristematic areas, an undifferentiated plastid
Mitochondria
can fuse and divide, have their own DNA and ribosomes, double-membraned, and cristae
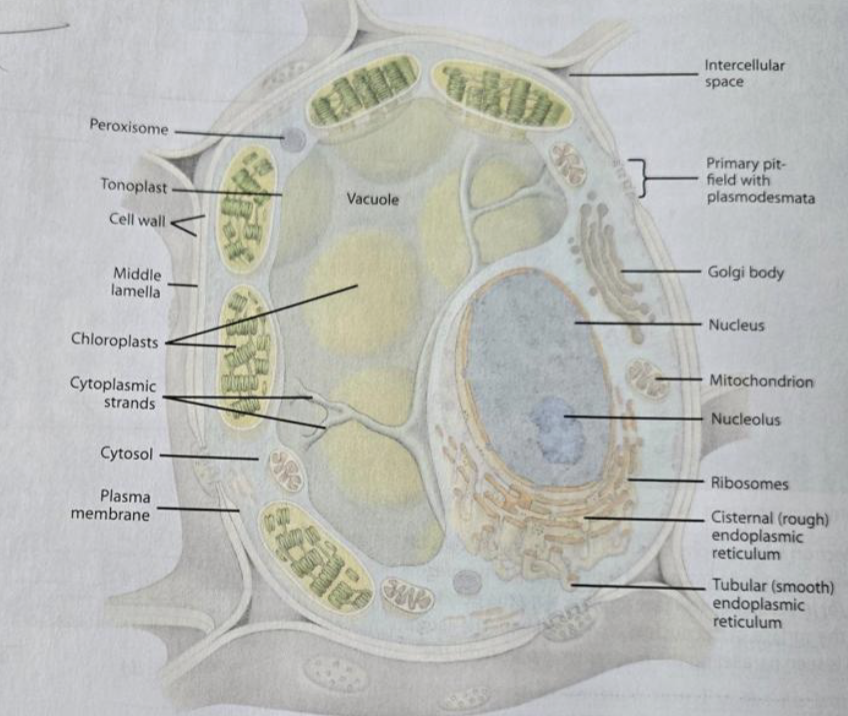
Cellular respiration
makes ATP; the number of mitochondria per cell depends on energy needs
Vacuole
surrounded by the tonoplast, the appearance differed based on whether the cell was mature or immature; contains cell sap
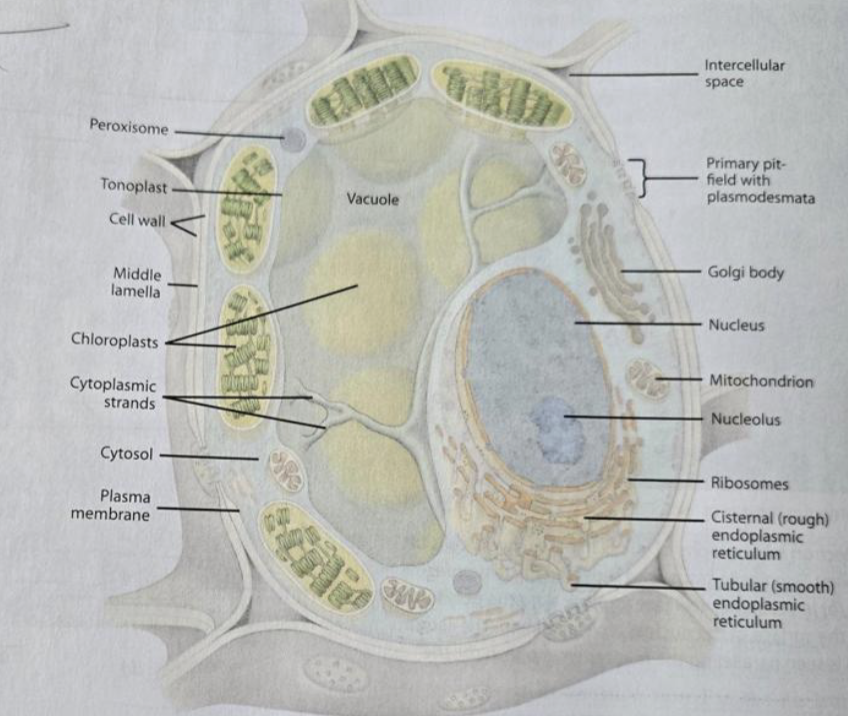
Rough ER
has ribosomes attached
the purpose is to make proteins
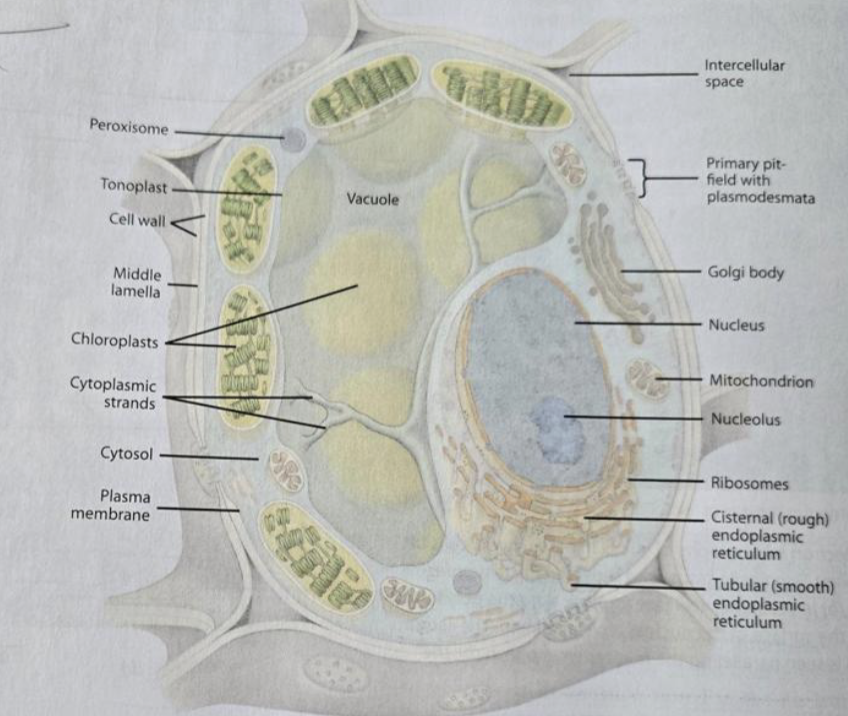
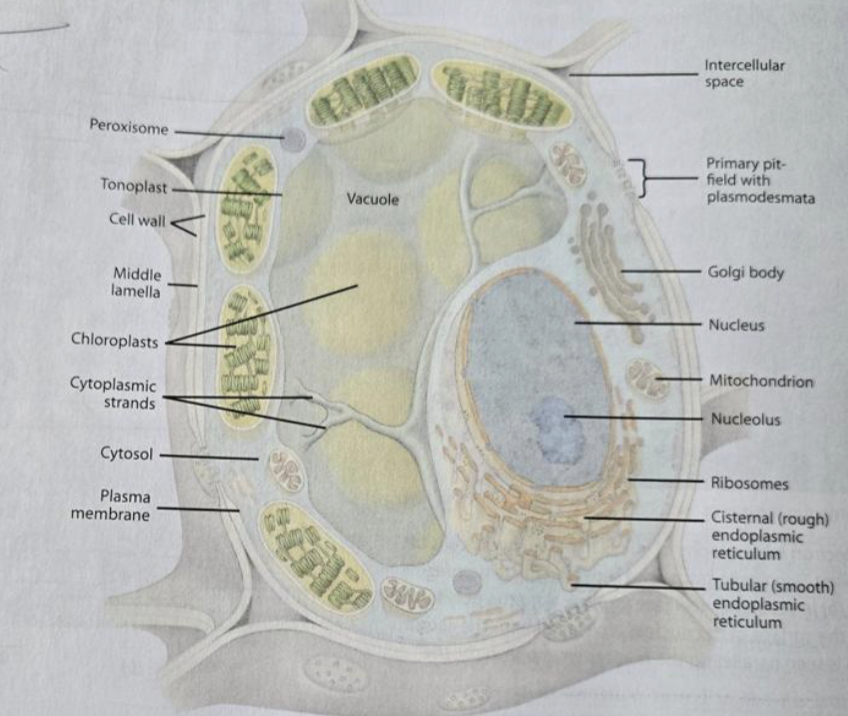
Smooth ER
no ribosomes
the purpose is to make lipids
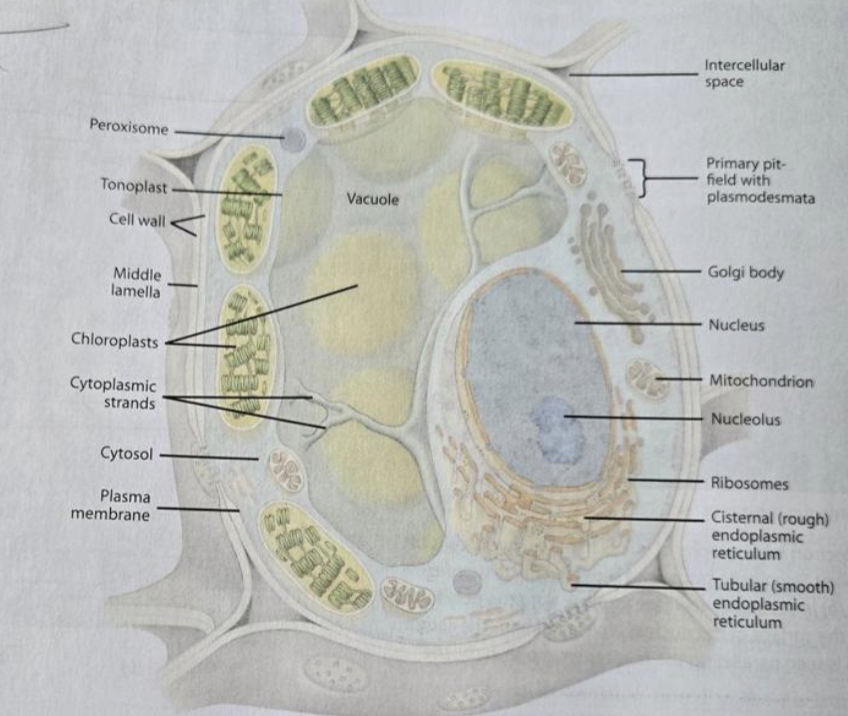
Golgi
synthesizing, processing, and secreting certain polysaccharides and glycoproteins
Cytoskeleton
network of proteins found in the cytosol
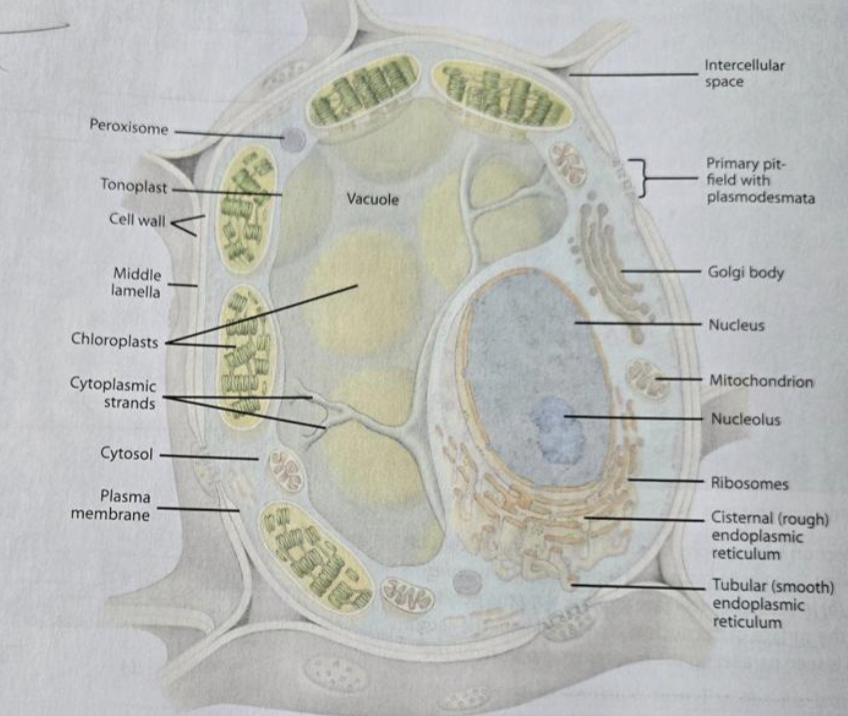
Mictrotubules
forming a spindle, cell wall growing
Actin filaments
movement of organelles
Plasmodesmata
openings in the primary cell wall for communication, lined with the plasma membrane
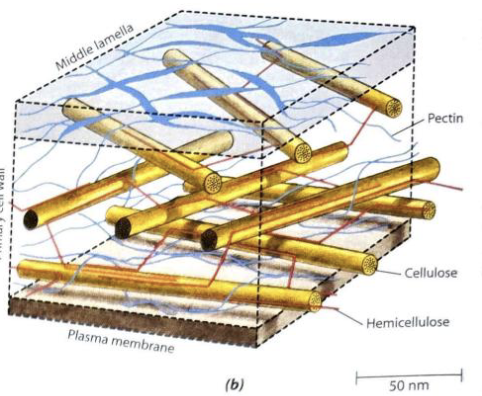
Cell wall
found in plant cells
prevents the cell from bursting
controls the size and shape
defense
mostly made of cellulose
Primary cell wall
found in all plant cells
Hemicellulose
connected to cellulose microfibrils to control how much the cell wall can expand
Pectin
a hydrophilic polysaccharide that makes up the primary cell wall and the middle lamella, allows for expansion
Glycoprotein
protein with carbohydrate attached
Lignin
adds strength to the cell wall
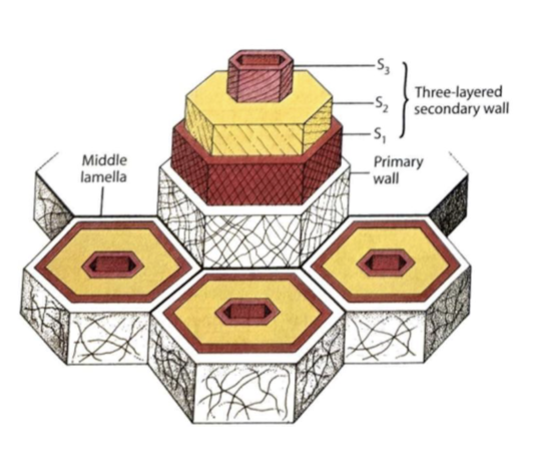
Secondary cell wall
found in some plant cells
laid down toward the inside of the primary cell wall
Middle lamella
connect nearby plant cells, mostly protein
3
The middle lamella is laid down in ___ layers.
S1, S2, S3
What are the three layers of the middle lamella?
S1
What layer is closest to the primary cell wall?
cellulose
There is a higher percentage of ____ in the secondary cell wall than the primary cell wall.
primary cell wall
The ______ ___ ___ is produced before and while the plant cell is still growing.
thin; plasmodesmata
The primary cell wall has ___ areas in which ________ can be found.
Expansins
cell wall proteins that act to loosen the cell wall
Cellulose synthase
found in the plasma membrane
UDP-glucose
substrate acted by the cellulose synthase
Cellulose microfibril
is produced by cellulose synthase, linking UDP-glucose molecules together
The cellulose microfibril is extruded on the other surface of the plasma membrane.
Embryogenesis
process of embryo formation
establish a body plan → apical-basal and radial
Zygote
in the embryo sac inside the ovule
Division I
asymmetrical division
helps set up the apical-basal axis
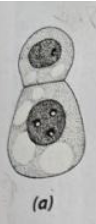
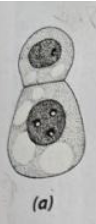
top cell
The ___ ___ also known as the apical cell is responsible for the mature embryo
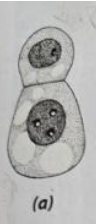
bottom cell; suspensor
The ______ ___ also known as the basal cell produces the ______, which hods the embryo at the micropyle (opening in the ovule where the pollen tube entered)
embryo proper
For the other division, the ____ ____ (undifferentiated) is at the top.
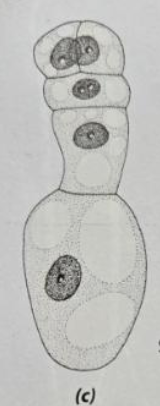
basal cell
For the other division, the ___ ___ produces the suspensor
3; apical meristems
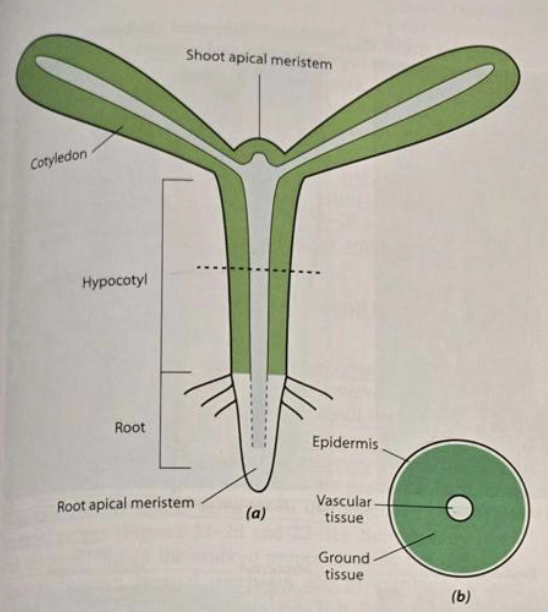
There are ___ primary meristems associate with primary growth. These are derived from ______ ______ (shoot,root).
Protoderm
becomes the epidermis
Ground
becomes the ground tissue
Procambium
becomes vascular tissue (xylem and phloem)
Globular stage
sphere-like embryo proper, cotyledons. These have not developed yet
Heart stage
cotyledons (seed leaves) develop in eudicots → 2 seed leaves/cotyledons
Torpedo stage
cotyledons lengthen along with the axis
shoot and root apical meristems
embryonic root (eventually)
eudicots
In ____, the shoot apical meristem is between the two cotyledons.
monocots
In ____, the shoot apical meristem is on one side of the cotyledon and is enclosed by a covering from the base of the cotyledon.
mature embroyo
shoot apical meristem and root apical meristem at opposite ends
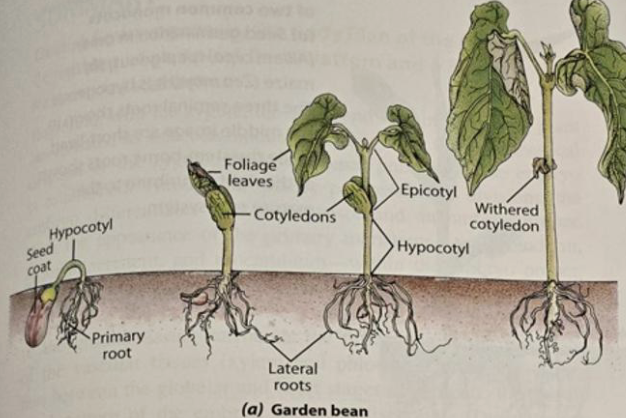
Hypocotyl
stem-like structure below cotyledons
Epicotyl
stem-like structure above the cotyledons
1
Monocots have __ cotyledon
cleoptile
Plumule is protected by the ____.
coleorhiza
Radicle is protected by the _____.
coat; integuments
All seeds have a seed ___ developed from the ______ of the ovule.
Hilum
scar left on the seed coat after the seed separates from the ovary wall.
nutrient; dries; hardens; metabolism
What occurs during seed maturation?
_____ accumulation
seed ____
seed coat ____
little ______.
Seed germination
the embryo resumes growth
internal and external factors
water (imbibition)
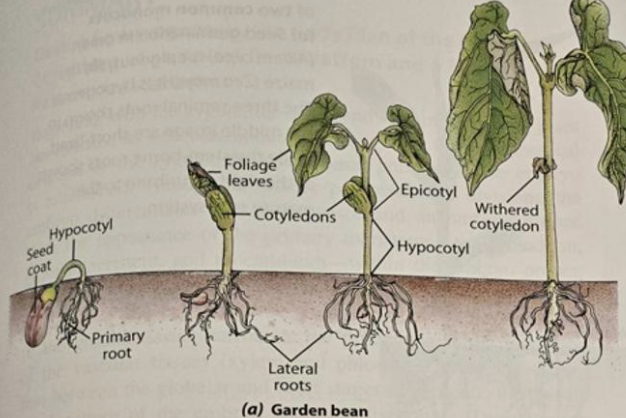
embryonic
In seed germination (step 1), ____ root growth occurs.