Topic 13- Reproduction II (Female)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What are the functions of the female reproductive system?
Egg production, receives penis and sperm, nourishes embryo, lactation.
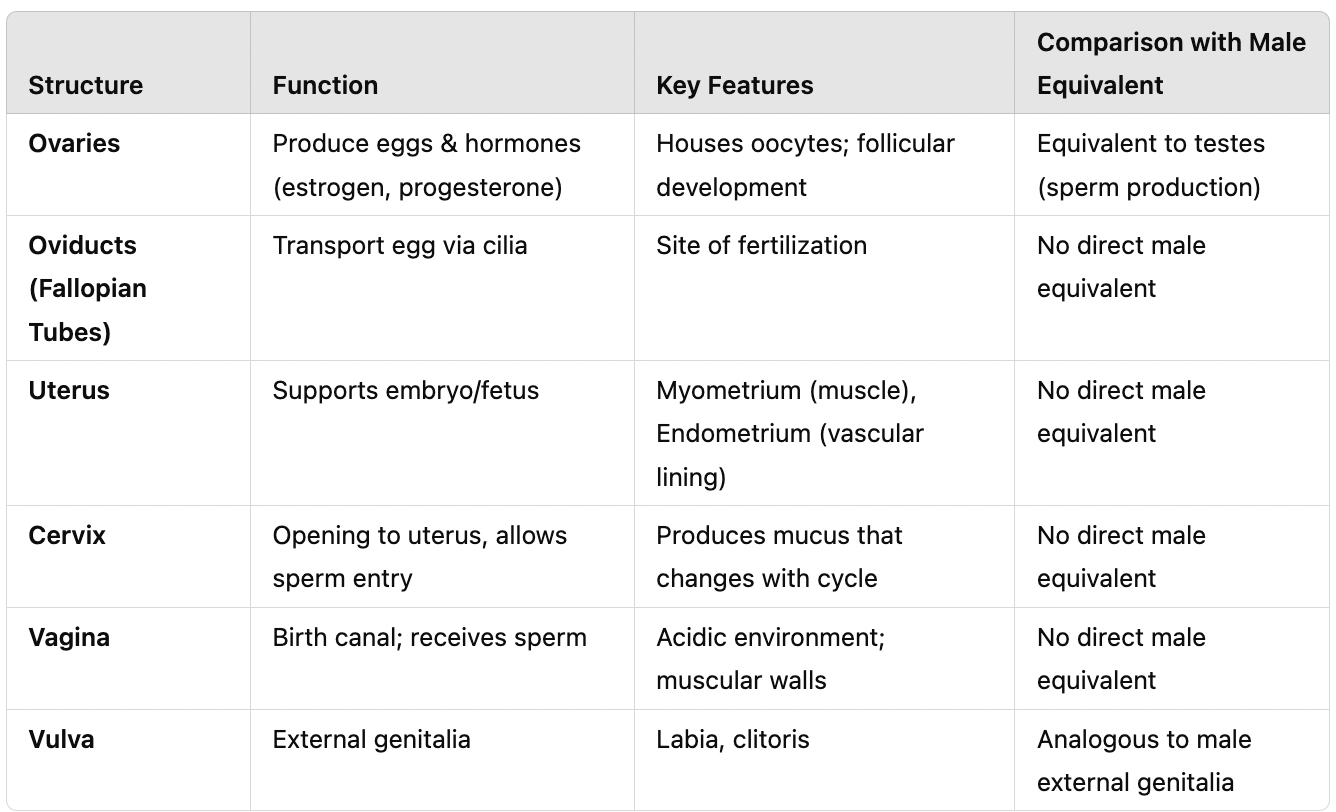
What are the primary female reproductive structures?
Ovaries, oviducts (fallopian tubes), uterus, cervix, vagina, vulva.
What hormones are produced by the ovaries?
Estradiol and progesterone.
What is the function of the oviducts (fallopian tubes)?
Transports the secondary oocyte, aided by cilia.
What are the two main layers of the uterus?
Myometrium: Smooth muscle responsible for contractions. Endometrium: Contains blood vessels, glands, and tissues.
What is the function of the cervix?
A small opening at the bottom of the uterus that allows sperm entry.
What is the function of the vagina?
Acts as the birth canal and receives sperm during intercourse.
What is the vulva?
The external female genitalia.
What is oogenesis?
The process of egg development in females.
How does meiosis function in oogenesis?
A diploid (2n) cell undergoes meiosis to produce four haploid cells, but only one egg survives; the others become polar bodies.
What happens to oocytes before birth?
Primordial germ cells divide into oogonia. Primary oocytes begin meiosis I but stop at prophase I. At birth, there are 1-2 million oocytes, but only 200,000 remain at puberty.
What happens to oocytes at puberty?
Each month, 6-12 follicles begin to mature, but only one completes development. Primary oocyte finishes meiosis I, forming one secondary oocyte and a polar body. The secondary oocyte starts meiosis II but stops at metaphase II.
What triggers ovulation?
An LH surge.
What happens if fertilization does not occur?
The secondary oocyte degenerates and is expelled during menstruation.
What happens if fertilization occurs?
The secondary oocyte completes meiosis II, forming an ovum and a second polar body.
What are the three phases of the menstrual cycle?
Follicular Phase (Days 1-13) – Follicle matures, endometrial lining thickens. Ovulation (Day 14) – Egg is released due to LH surge. Luteal Phase (Days 15-28) – Corpus luteum secretes progesterone, preparing for pregnancy.
What happens during the follicular phase?
Day 1-5 (Menstrual Flow): Endometrial lining sheds. Day 6-13 (Proliferative Phase): Endometrial lining thickens, follicle grows.
What happens during ovulation (Day 14)?
LH surge causes release of secondary oocyte. Oocyte is coated in the zona pellucida and follicle cells.
What happens during the luteal phase (Days 15-28)?
Corpus luteum forms, secreting progesterone and estrogen. If no pregnancy occurs, hormone levels drop, and menstruation begins again.
What are the two key female reproductive hormones?
Estrogen (Estradiol): Produced by follicle cells and corpus luteum; stimulates endometrial growth. Progesterone: Produced by the corpus luteum; maintains the uterine lining.
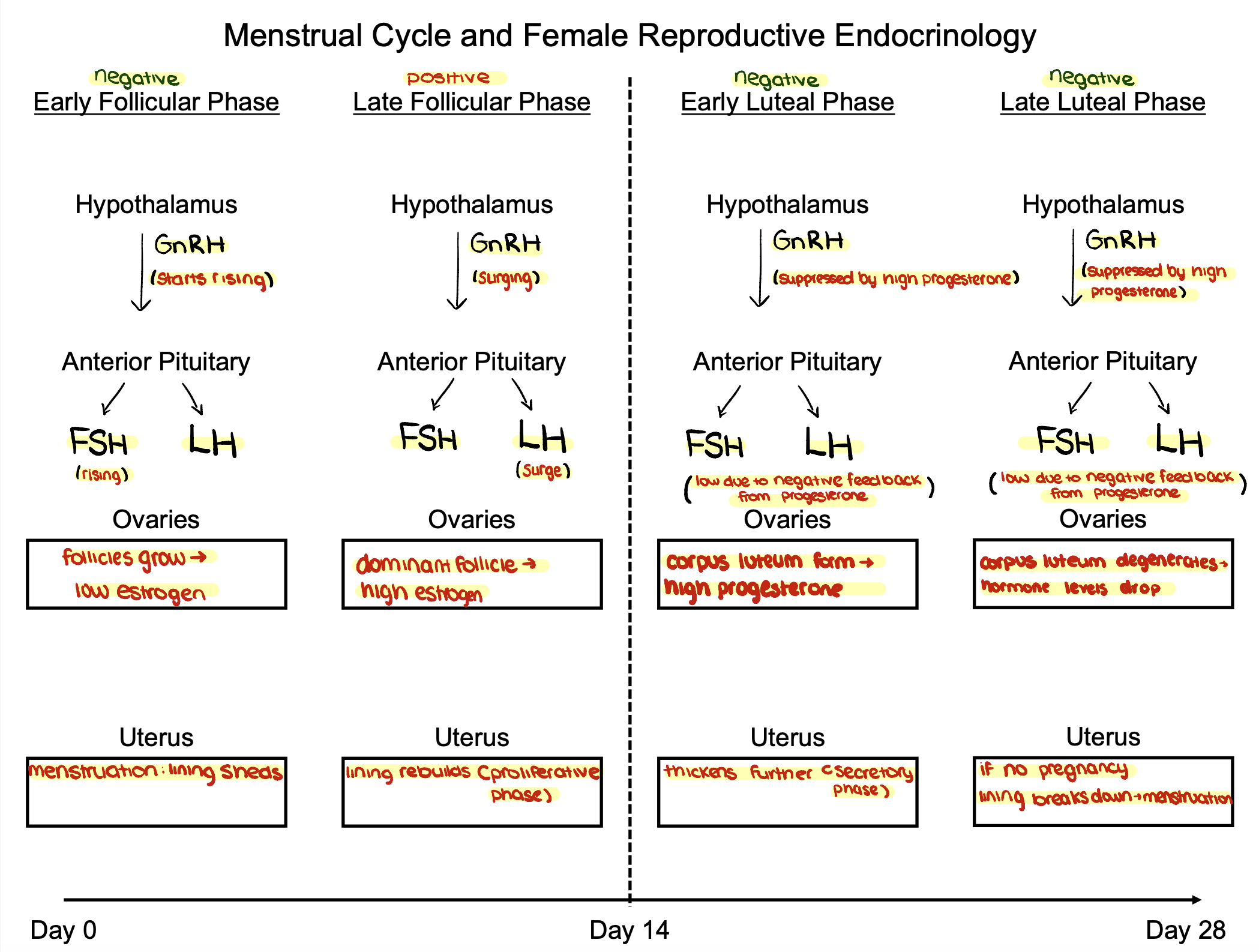
How does hormone regulation affect the menstrual cycle?
High estradiol, low progesterone → Stimulates the hypothalamus. High estradiol, high progesterone → Inhibits the hypothalamus.
What happens in the early follicular phase (Days 1-5)?
Anterior pituitary releases FSH & LH. Follicle secretes a little estradiol. Negative feedback on the anterior pituitary due to low estrogen and progesterone.
What happens in the late follicular phase (Days 5-13)?
Follicles grow, increasing estradiol but keeping progesterone low. Positive feedback leads to an LH surge (Day 13).
What happens during ovulation (Day 14)?
1 day after LH surge, secondary oocyte is released. High estradiol, low progesterone → Increases GnRH, which increases LH and FSH.
What happens in the luteal phase (Days 15-28)?
Follicle tissue becomes the corpus luteum, secreting progesterone and estradiol. Negative feedback inhibits the hypothalamus, preventing another egg release. If no pregnancy occurs, LH and FSH drop, corpus luteum degenerates, and cycle restarts.
What are the main phases of the ovarian cycle?
Follicular Phase – Follicle matures, estrogen increases. Ovulation – Secondary oocyte is released. Luteal Phase – Corpus luteum forms, secreting progesterone.
What are the main phases of the uterine cycle?
Menstrual Phase – Endometrial lining sheds. Proliferative Phase – Endometrium thickens. Secretory Phase – Endometrium is maintained for implantation.
How do the ovarian and uterine cycles interact?
Follicular phase aligns with the proliferative phase. Ovulation occurs at the midpoint. Luteal phase aligns with the secretory phase. If no fertilization occurs, hormone levels drop, triggering menstruation.
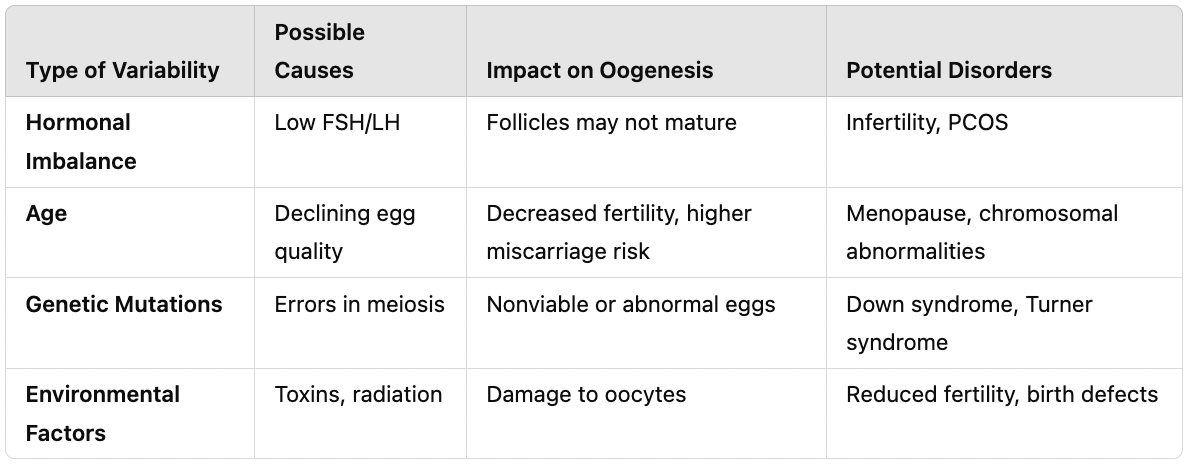
What happens if there is a hormonal imbalance in the menstrual cycle?
Low estrogen/progesterone → Irregular or absent periods. Excess estrogen → PCOS, thickened endometrium. Low progesterone → Failure to maintain pregnancy.
How does stress affect the menstrual cycle?
Increased cortisol can disrupt ovulation and delay menstruation.
What are the effects of aging on oogenesis?
Declining egg quality reduces fertility. Increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities (e.g., Down syndrome).
How do environmental factors impact female reproduction?
Toxins, radiation, and malnutrition can reduce fertility and increase birth defects.
Compare and contrast female reproductive structures in terms of function and key features, as well as compare them to male equivalents. (ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix, vagina, vulva)
Sequence oogenesis in 6 steps

Hypothesize and diagnose the impact of variability on oogenesis, including possible causes, impact on oogenesis, and potential disorders.
Sequence the menstrual cycle in three phases

Hypothesize and diagnose the impact of variability on the menstrual cycle in terms of the causes, implications for the menstrual cycle, and their related conditions. (hormonal changes, stress, nutritional deficiency, and medical conditions)
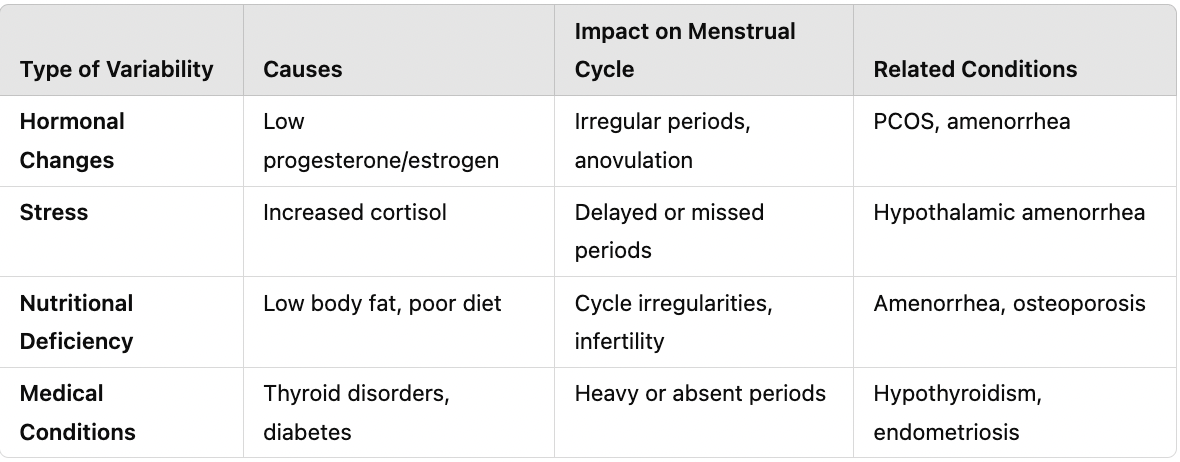
Sequence female endocrinology and include if there are no pregnancies. (hormones involved and effects)
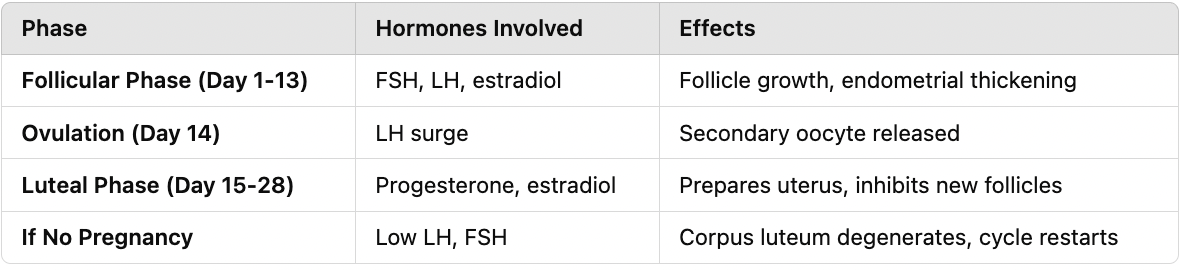
Hypothesize and diagnose the impact of variability on female endocrinology and reproductive cycles in terms of causes, effects on reproduction, and potential disorders. (high estrogen, low estrogen, low progesterone, high cortisol)
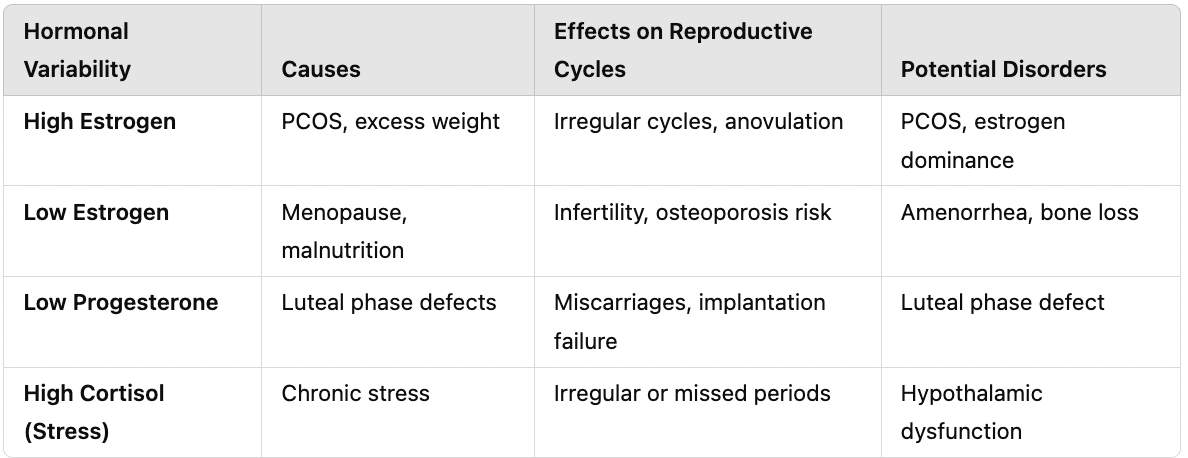
Compare and contrast the ovarian and uterine cycle in terms of phases, key events, and hormonal control.
Fill out the organizer for the female reproductive system. (feedback mechanisms, hormones and their amount, function, and other details)