dna modification stuff
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
1
New cards
hyperacetylated histones
associated with _ transcribed genes
_ is responsible
associated with _ transcribed genes
_ is responsible
actively, histone acetyltransferase
2
New cards
acetylation modifes _ residues of the histone, which is a positively charged on the negatively charged DNA backbone
lysine
3
New cards
_ can function over long distances on chromatin
enhancers
4
New cards
_ specifically block such promiscuous enhancer behavior
insulator proteins
5
New cards
promiscuous enhancement is blocked by _
insulator proteins
6
New cards
enhancer-blocking insulators prevent _
enhancer activation
7
New cards
_ prevent enhancer activation
enhancer-blocking insulators
8
New cards
insulator proteins insulate various _ from the activation by various enhancers
promoters
9
New cards
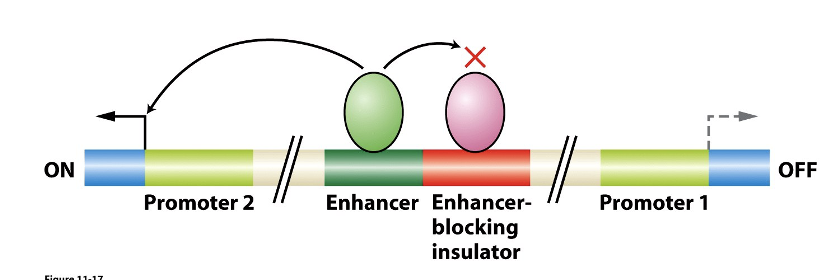
enhancer with enhancer binding protein bound to it
evolved to control promoter 2, but other nearby promoters like promoter 1 can be activated by that enhancer
_ prevents promiscuous activation of promoters by an enhancer - prevents folding so the enhancer can’t activate another promoter
evolved to control promoter 2, but other nearby promoters like promoter 1 can be activated by that enhancer
_ prevents promiscuous activation of promoters by an enhancer - prevents folding so the enhancer can’t activate another promoter
enhancer blocking insulator
10
New cards
enhancers interact with proteins that promote assembly of the _
transcription initiation complex
11
New cards
_ interact with proteins that promote assembly of the transcription initiation complex
enhancers
12
New cards
enhancer activity can be blocked by _
insulators
13
New cards
_ activity can be blocked by insulators
enhancer
14
New cards
enhancers can also recruit proteins that modify _ structure
chromatin
15
New cards
_ can also recruit proteins that modify chromatin structure
enhancers
16
New cards
enhancers can also recruit proteins that modify chromatin structure:
_ of histones
_ of histones
_ of DNA
_ of histones
_ of histones
_ of DNA
acetylation, methylation, methylation
17
New cards
enhancers can also recruit proteins that modify chromatin structure:
acetylation of _
methylation of _
methylation of _
acetylation of _
methylation of _
methylation of _
histones, histones, DNA
18
New cards
_ fundamental regulatory modifications of histones - fundamental because we understand best because they were the first discovered:
_ and _ of histones
_ and _ of histones
two, acetylation, methylation
19
New cards
_ are the fundamental proteins of nucleosomes and fundamental to the formation of chromatin
histones
20
New cards
histones are the fundamental proteins of _ and fundamental to the formation of _
nucleosomes, chromatin
21
New cards
_ and _ have direct impact on the activation of genes
acetylation of histones, methylation of histones
22
New cards
methylated DNA tends to be _
inactive
23
New cards
methylation of DNA drives the chromatin into an _ structure (_ instead of _)
inactive, heterochromatin, euchromatin
24
New cards
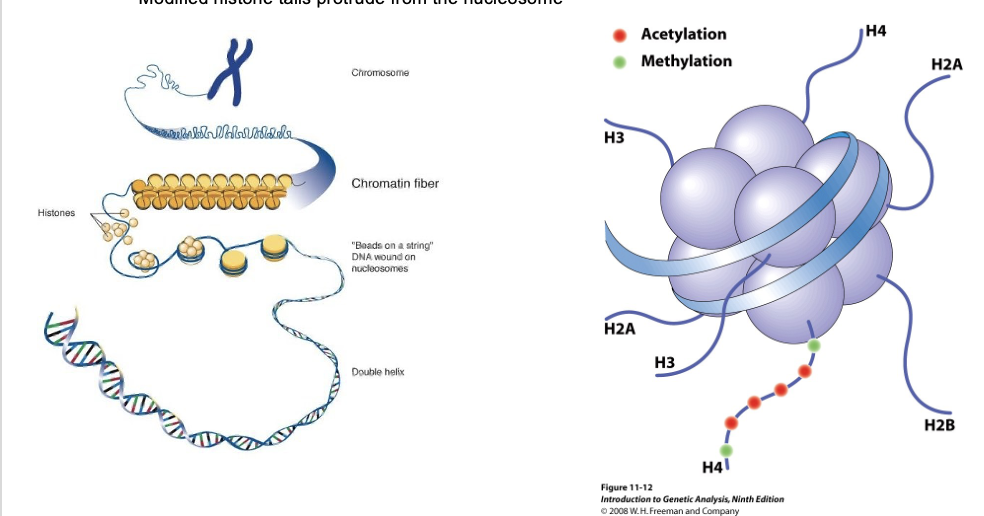
the histones form the nucleosome complex, DNA is wound around, the _ of the different histones projects out away from core of histones, makes the _ region available for modification
amino terminus, amino terminal
25
New cards
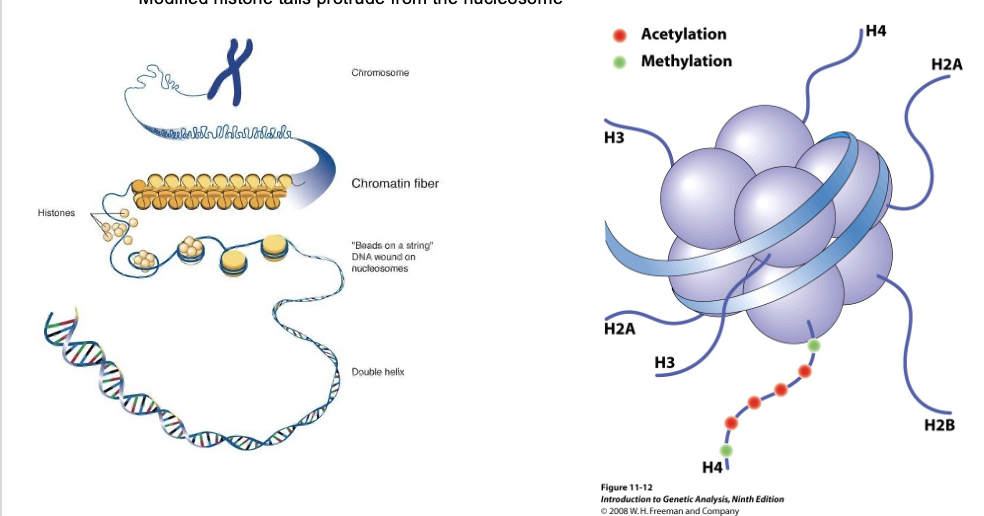
_ of the different histones are critical for methylation and acetylation
amino terminal tails
26
New cards
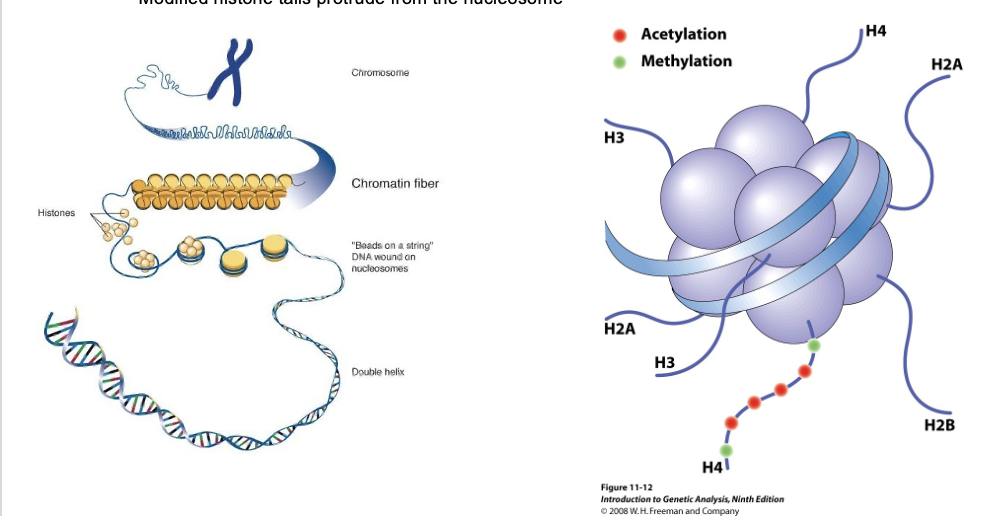
modified _ protrude from the nucleosome
histone tails
27
New cards
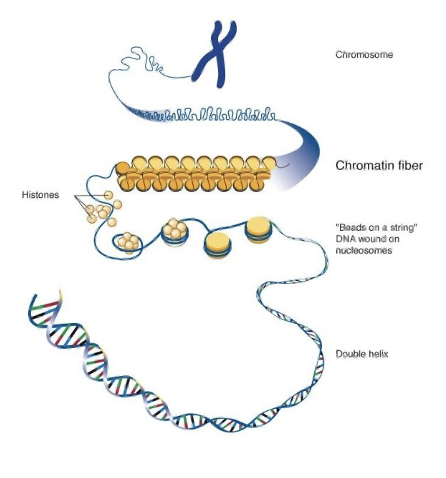
the beads on a string represent _ wound around nucleosomes
DNA
28
New cards
chromatin remodeling exposes _
regulatory sequences
29
New cards
_ exposes regulatory sequences
chromatin remodeling
30
New cards
_ modifies histone lysine residues which are positively charged
acetylation
31
New cards
acetylation modifies histone _ residues which are positively charged
lysine
32
New cards
acetylation modifies histone lysine residues which are _ charged
positively
33
New cards
DNA is _ charged
negatively
34
New cards
modifications either increase the affinity of the histones to DNA, in which case they _ the activity of genes in that region
or _ the interaction of histones with the DNA - allows nucleosomes to be shoved around by enzymes
or _ the interaction of histones with the DNA - allows nucleosomes to be shoved around by enzymes
inhibit, loosen
35
New cards
a promoter element wound tightly around the nucleosome complex is _
modifications of nucleosome complex can allow nucleosome to be pushed out of way/become exposed so it can become _
modifications of nucleosome complex can allow nucleosome to be pushed out of way/become exposed so it can become _
inactive, active
36
New cards
one of the first modifications observed was acetylation of the _ residues in the amino terminal tail of the histones
lysine
37
New cards
one of the first modifications observed was acetylation of the lysine residues in the _ of the histones
amino terminal tail
38
New cards
acetylation of DNA drives the _ of the chromatin - drives into a _ formation, which is _
relaxation, euchromatin, active
39
New cards
_ of DNA drives the relaxation of the chromatin - drives into a euchromatin formation, which is active
acetylation
40
New cards
acetylation means lysine is no longer _, it _ the hold of that particular nucleosome on the DNA, makes it able to form _ structure and accessible to _
charged, relaxes, euchromatin, transcription
41
New cards
_ means lysine is no longer charged, it relaxes the hold of that particular nucleosome on the DNA, makes it able to form euchromatin structure and accessible to transcription
acetylation
42
New cards
_ allows DNA to pack tightly and prevents transcription
deacetylation
43
New cards
deacetylation allows DNA to pack tightly and prevents _
transcription
44
New cards
_ lysine binds tightly to the negatively charged DNA backbone
unmodified
45
New cards
_ histones
associated with actively transcribed genes
histone acetyltransferases responsible
associated with actively transcribed genes
histone acetyltransferases responsible
hyperacetylated
46
New cards
_ histones
associated with inactive genes
histone deacetylases
associated with inactive genes
histone deacetylases
hypoacetylated
47
New cards
hypoacetylated histones
associated with _ genes
uses _
associated with _ genes
uses _
inactive, histone deacetylase
48
New cards
_ neutralizes the positive charge of lysine, reducing the affinity for the negatively charged DNA backbone
acetylation
49
New cards
acetylationn eutralizes the positive charge of _, reducing the affinity for the negatively charged DNA backbone
lysine
50
New cards
histone _ uses histone acetyltransferase (HAT) and produces open chromatin or euchromatin
acetylation
51
New cards
histone acetylation uses _ and produces _ chromatin or _
histone acetyltransferase (HAT), open, euchromatin
52
New cards
histone _ uses histone deacetylases and produces closed chromatin or heterochromatin
deacetylation
53
New cards
histone deacetylation uses _ and produces _ chromatin or _
histone deacetylases, closed, heterochromatin
54
New cards
depending upon which _ you modify in histones, can either have methylation inhibit transcription or active transcription
amino acid
55
New cards
methylation of lysine _ on histone _ correlates with active transcription
4, 3
56
New cards
methylation of lysine 4 on histone 3 correlates with _ transcription
active
57
New cards
methylation of lysine _ of histone _ correlates with inactive regions of chromatin
9, 3
58
New cards
methylation of lysine 9 of histone 3 correlates with _ regions of chromatin
inactive
59
New cards
methylated cytosine is associated with _ chromatin
inactive
60
New cards
association of lysine 9 methylated histones with DNA promotes recruits enzymes that methylate _, which locks down the chromatin into heterochromatin state
cytosine
61
New cards
the methylation of _ locks down the chromatin into a heterochromatin state
cytosine
62
New cards
without methylation of cytosine, histones and DNA are _ accessible to transcription, the chromatin is _ or _, and the gene is switched _
more, active, open, on
63
New cards
with methylation of cytosine, the DNA and histone are _ accessible to transcription, the chromatin is _ or _, and the gene is switched _
less, condensed, closed, off
64
New cards
the function of the _ is to recruit RNA polymerase and drive expression of the gene
promoter
65
New cards
_ drive local concentration of cytosine residues
CpG islands
66
New cards
local runs of CpG dinucleotides are frequently found in the _ of eukaryotic genes
promoters
67
New cards
local runs of _ are frequently found in the promoters of eukaryotic genes
CpG dinucleotides
68
New cards
local runs of CpG dinucleotides are frequently found in the promoters of _ genes
eukaryotic
69
New cards
CpG islands:
the _ residues are a frequent target of methylation - to silence genes
the _ residues are a frequent target of methylation - to silence genes
cytosine
70
New cards
CpG islands:
the cytosine residues are a frequent target of _ - to silence genes
the cytosine residues are a frequent target of _ - to silence genes
methylation
71
New cards
eukaryotes _
sequence on one strange that is C followed by G with phosphate in between
on other strand, have C followed by a G with phosphate in between
drives a local concentration of cytosine residues
sequence on one strange that is C followed by G with phosphate in between
on other strand, have C followed by a G with phosphate in between
drives a local concentration of cytosine residues
CpG islands
72
New cards
73
New cards
there is a mechanism to maintain methylated DNA during replication - maintain methylation states from _ to _ cell
important in development during first trimester where a single cell becomes an embryo through cell division
important in development during first trimester where a single cell becomes an embryo through cell division
parent, daughter
74
New cards
the two big phases of pregnancy:
first trimester - rapid cell _ with development, lay down tissues and organs
rest of pregnancy - _
first trimester - rapid cell _ with development, lay down tissues and organs
rest of pregnancy - _
division, growth
75
New cards
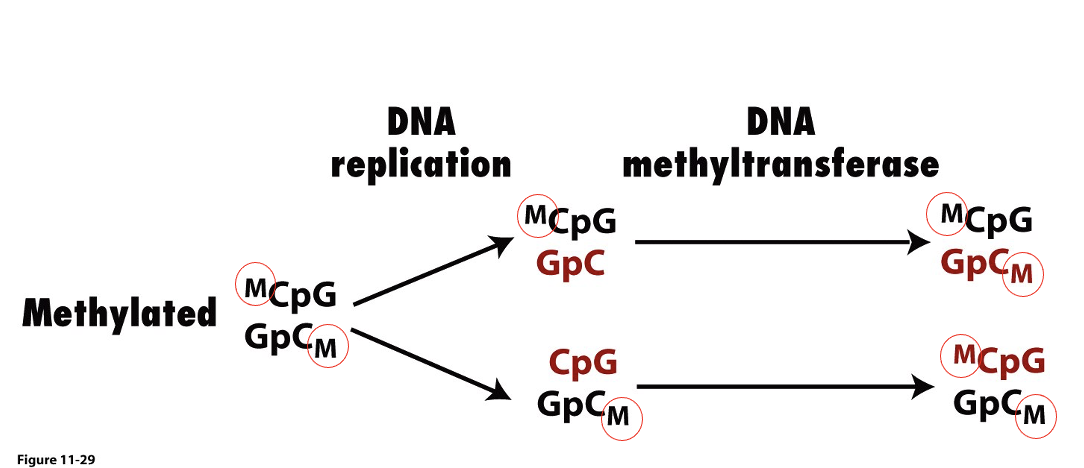
during replication of methylated DNA, the new chromatin _ methylated because can’t incorporate methylated C into DNA
is not
76
New cards
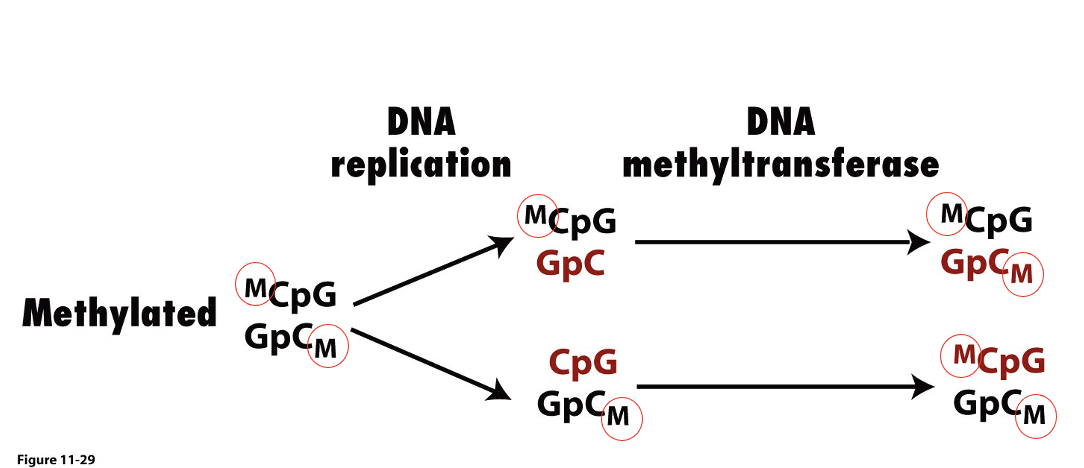
if the chromatin in the cell undergoes changes in methylation of the DNA during development, it _ maintained
applies to Dutch famine embryos
applies to Dutch famine embryos
is
77
New cards
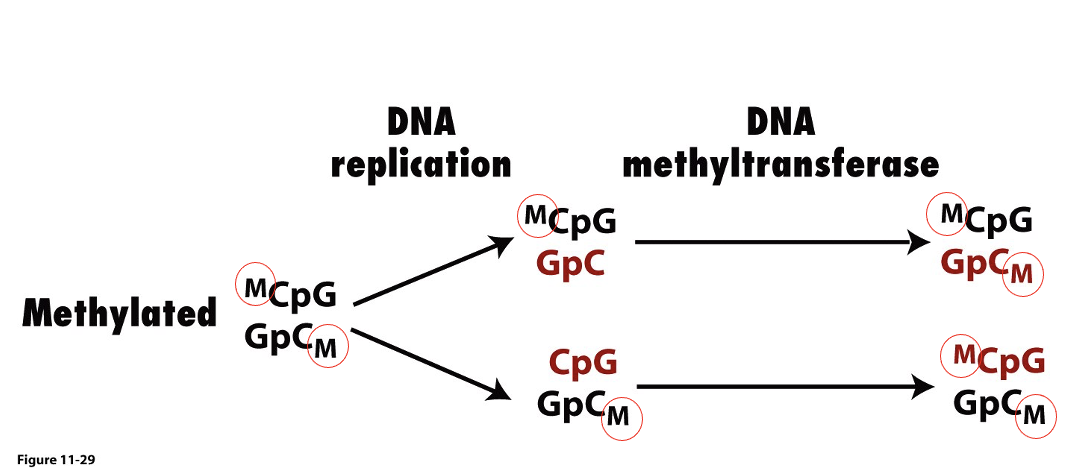
when the cell undergoes division, new chromatin _ methylated because can’t incorporate methylated cytosine into DNA
is not
78
New cards
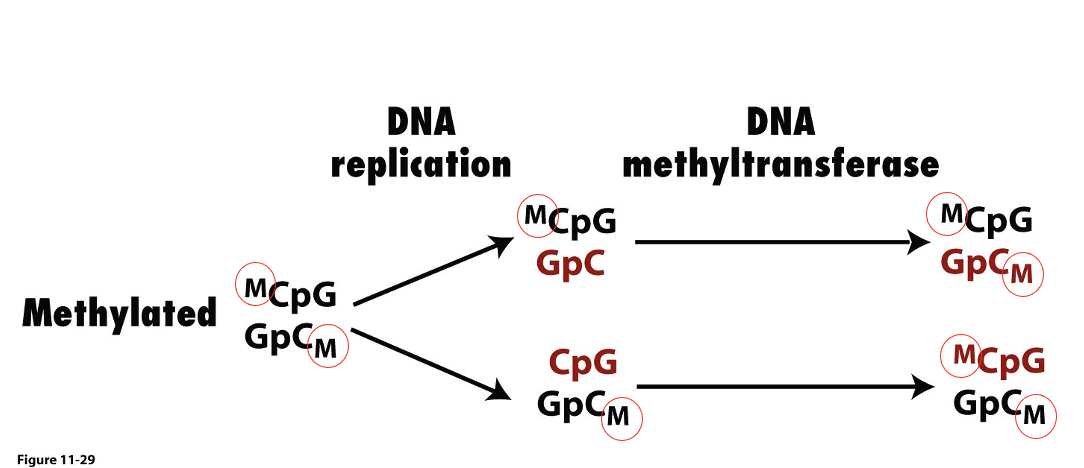
in cell division, the parent strand has a _ that recruits enzymes to methylate the daughter strand cytosine
methyl signal
79
New cards
histones in the nucleosomes:
histone modifications can be _ using a similar mechanism to DNA methylation replication - modifications in the parent cell _ passed on in the daughter cell
histone modifications can be _ using a similar mechanism to DNA methylation replication - modifications in the parent cell _ passed on in the daughter cell
maintained, can be
80
New cards
dna methylation across generations
_ gene - affects coat color
mixture of yellow and black pigment (gray color) = _ gene
yellow mice w/o black pigment, obese mice = _ gene
_ gene - affects coat color
mixture of yellow and black pigment (gray color) = _ gene
yellow mice w/o black pigment, obese mice = _ gene
agouti, wild type, dominant mutated
81
New cards
dominant mutation of agouti gene has significant effect on _ and _
coat color, energy storage
82
New cards
dominant mutated agouti gene mice become particularly obese if feed a _ diet - if provide this as control diet to mother, progeny are _ and _
if add _ to the diet, drives synthesis of _ which is a methyl donor, in the mutant mice, reverts to the wild-type phenotype
if add _ to the diet, drives synthesis of _ which is a methyl donor, in the mutant mice, reverts to the wild-type phenotype
high fat, obese, yellow, folate, adenosylmethionine
83
New cards
agouti gene in wild type form, end up with a _ mouse
normal gray
84
New cards
agouti gene plays a large role in establishing hair follicle pigments and typically becomes _ in the adult (wild-type)
develop coat color properly, but they don’t become obese unless agouti gene continues to be _
develop coat color properly, but they don’t become obese unless agouti gene continues to be _
inactivated, expressed
85
New cards
if provide mother with plenty of folate in diet, drives the synthesis of _
the promoter of the agouti gene in developing embryos becomes _, preventing the development of _
the promoter of the agouti gene in developing embryos becomes _, preventing the development of _
adenosylmethionine, methylated, obesity
86
New cards
need of the male for reproduction is to
pass on genome to next generation
87
New cards
need for female for reproduction:
pass on genome to next generation
has to _ to pass genome to next generation
pass on genome to next generation
has to _ to pass genome to next generation
survive
88
New cards
conflict between male and female during reproduction:
both male and female want to pass genome onto the next generation, but the female has to _
both male and female want to pass genome onto the next generation, but the female has to _
survive
89
New cards
90
New cards
insulin like growth factor 2 is the expressed allele inherited from the _ side
paternal
91
New cards
_ is the expressed allele inherited from the paternal side
insulin like growth factor 2
92
New cards
H19 is the expressed allele inherited from the _ side
maternal
93
New cards
_ is the expressed allele inherited from the maternal side
H19
94
New cards
insulin like growth factor 2 promotes _
growth
95
New cards
for insulin like growth factor 2 to be expressed in the developing embryo, has to be inherited from _, because the allele in _ is inactivated in the gametes
dad, mom
96
New cards
H19 is essential for _ of the embryo
survival
97
New cards
for H19 to be expressed in the developing embryo, it has to be inherited from _, because the allele in _ is inactivated in the gametes
mom, dad
98
New cards
imprinted genes
which of the two alleles that are inherited from mom and dad at fertilization is expressed is a function of _
which of the two alleles that are inherited from mom and dad at fertilization is expressed is a function of _
which parent donated the allele
99
New cards
with imprinted genes, inherit both genes from mom and dad, they are not _, they are on _
sex linked, autosomes
100
New cards
for _ genes, which of the two alleles that are inherited from mom and dad at fertilization is expressed is a function of which parent donated the allele
imprinted