Dermatology Unit
1/132
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PA 201: Intro to Medicine
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
What are the functions of the skin?
Covers the entire body,
Provides protection
Regulates body temperature
Sensory organ
Produces Vitamin D
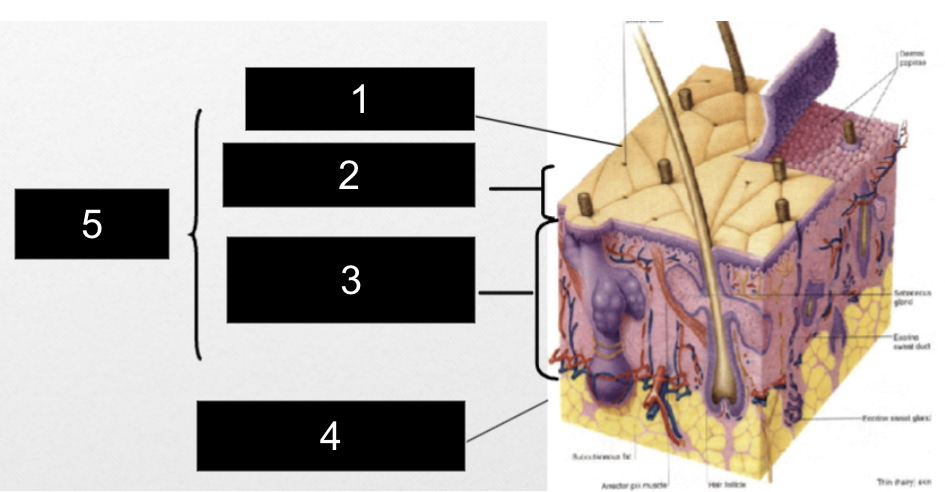
What is #1?
Epidermis
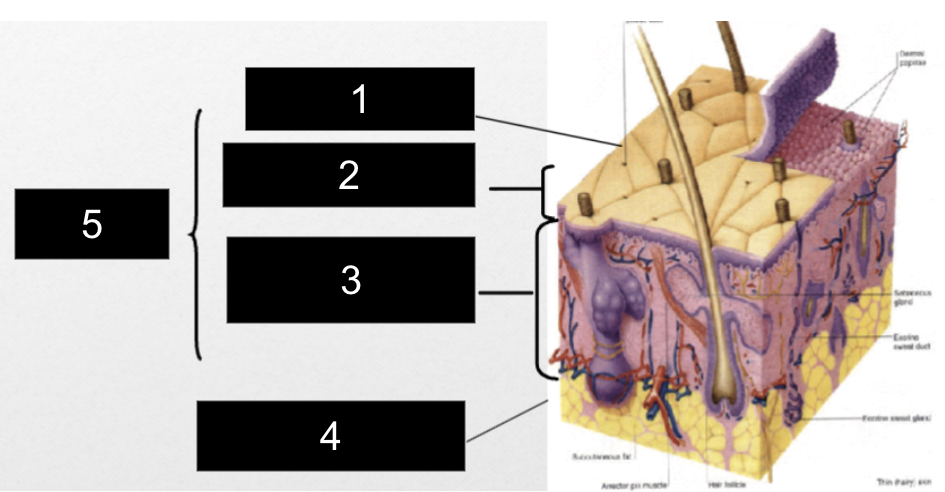
What is #2?
Papillary Layer
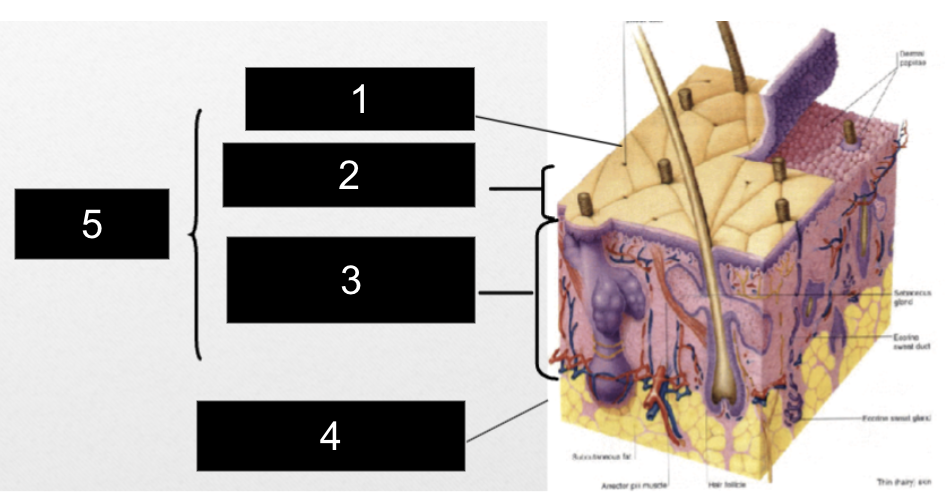
What is #3?
Reticular Layer
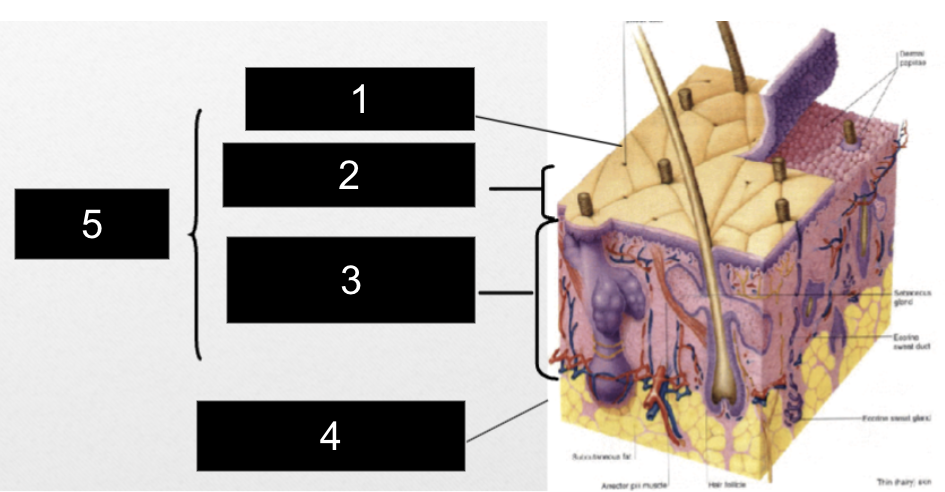
What is #4?
Subcutaneous Layer
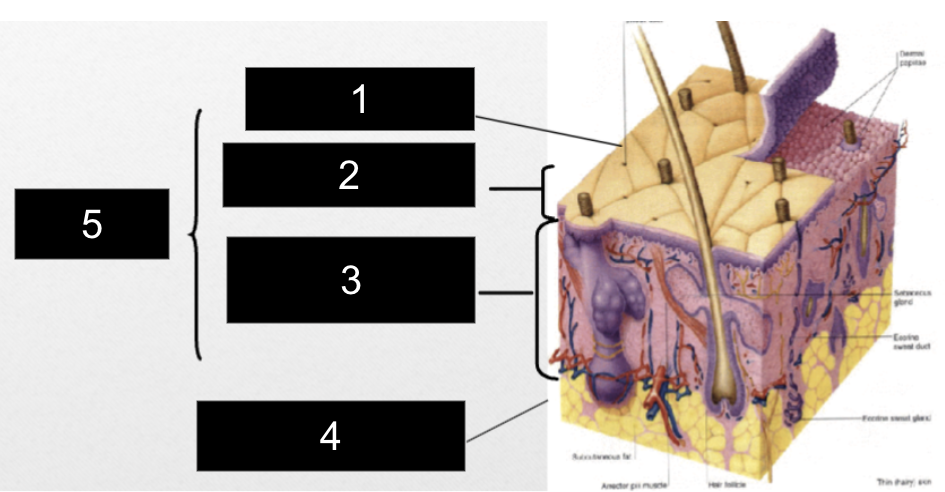
What is #5?
Dermis
Keratinocyte
produces keratin, a protein in hair, skin, nails
Melanocyte
produces skin pigment melanin when exposed to sunlight, shields against UV radiation, determines skin color
Langerhans Cells
macrophages that initiate immune response, provides defense against environmental foreign proteins
Merkel Cells
touch receptors, found at junction of epidermis and dermis
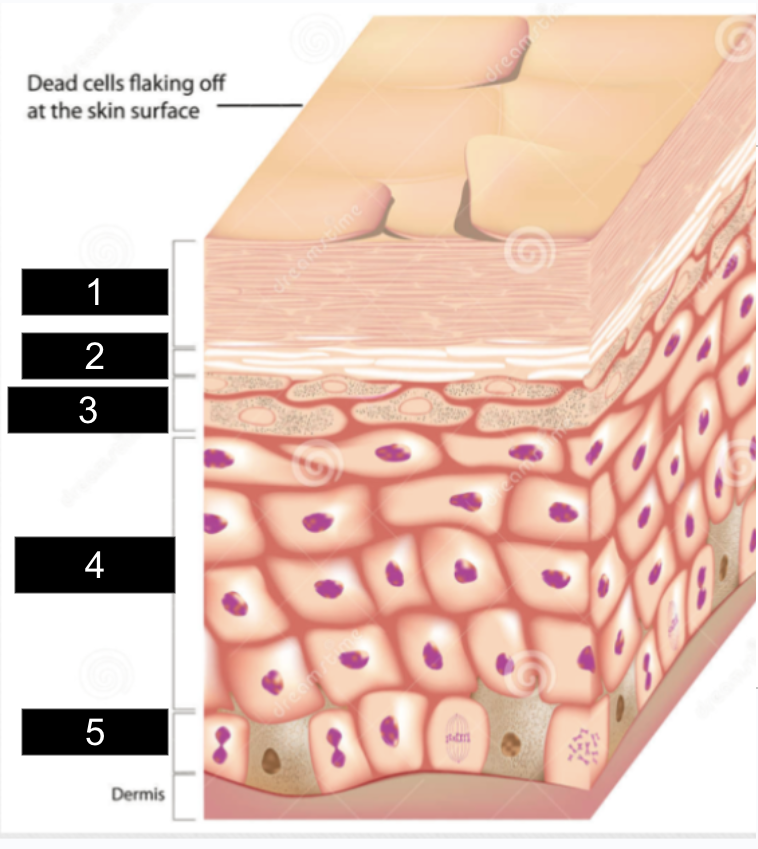
What is #1?
stratum corneum
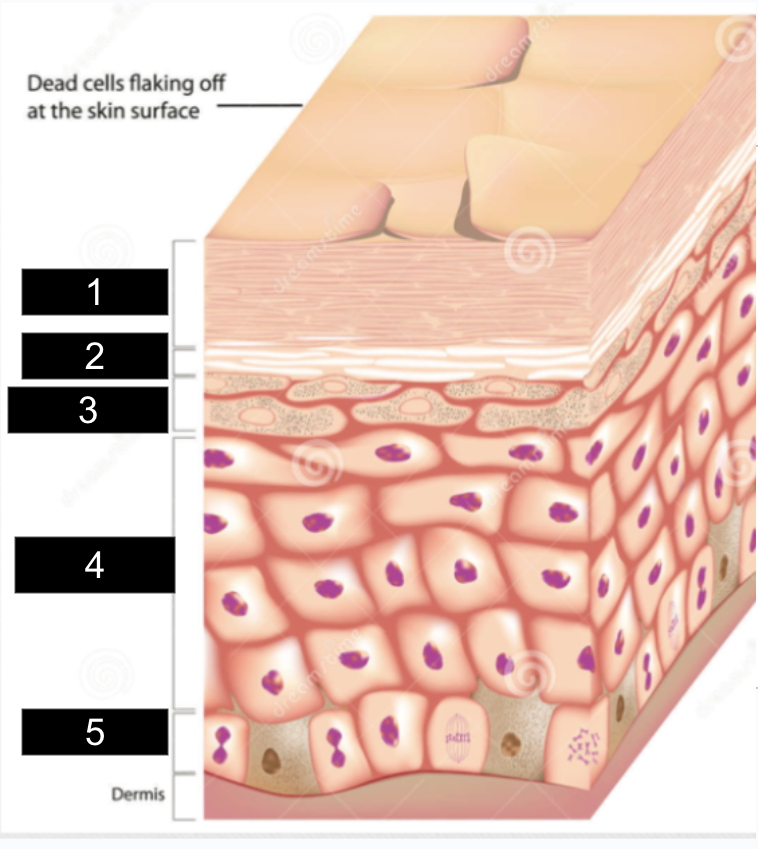
What is #2?
stratum lucidum
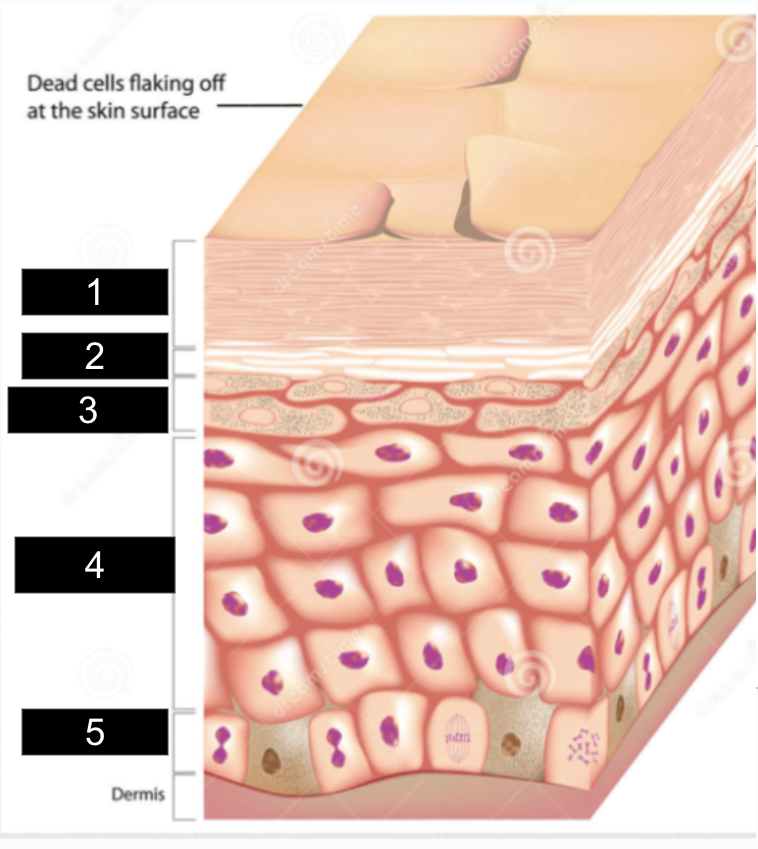
What is #3?
stratum granulosum
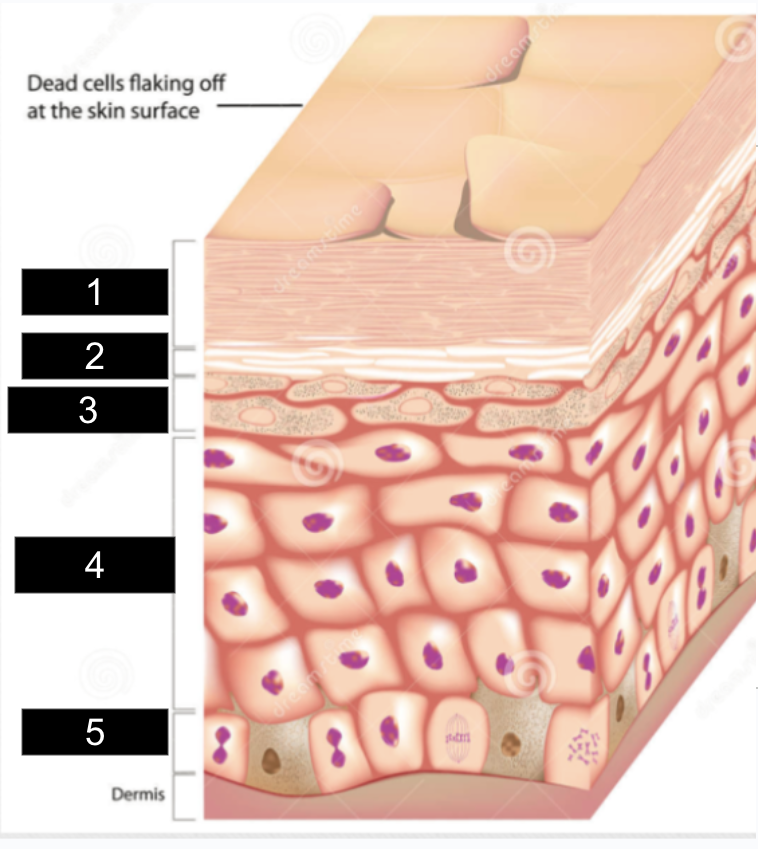
What is #4?
stratum spinosum
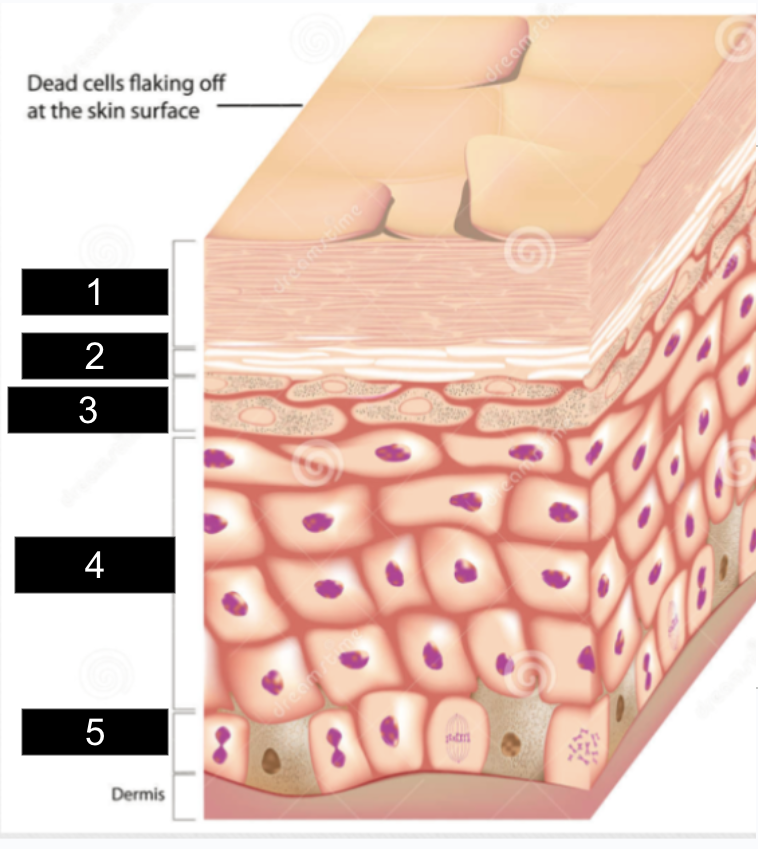
What is #5?
stratum basale
Dermis
thickest section of skin,
made of collagen/elastin fibers
rich in blood vessels, lymphatics, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, nerves, has hair follicles
What are the two layers of the dermis?
papillary layer and reticular layer
Papillary layer
directly under epidermis, has capillaries and neurons
Reticular layer
makes up 80% of dermal layer, has collagen bundles, hair follicles, and sweat glands
Subcutaneous
layer of fat/connective tissue with larger blood vessels and nerves
important with regulation of skin/body temp
Lesion
any pathological change in the skin
Primary lesion
develop from previously healthy skin
Secondary lesion
develop from primary lesions
Types of primary skin lesions
macule, patch,
papule, nodule,
tumor, plaque,
vesicle, pustule,
bulla/cyst, wheal,
petechiae/purpura,
ecchymosis, telangiectasia
Macule (v)
flat, non-palpable, <2cm
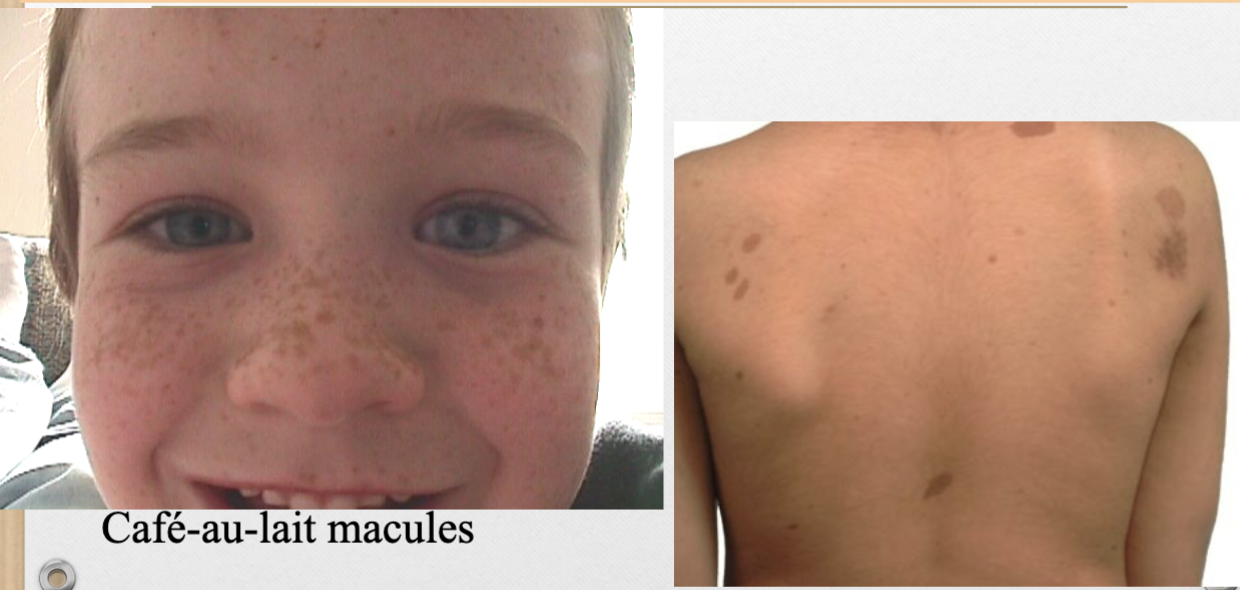
ex. freckles
Macule (p)
Patch (v)
>2cm with color different than surrounding skin
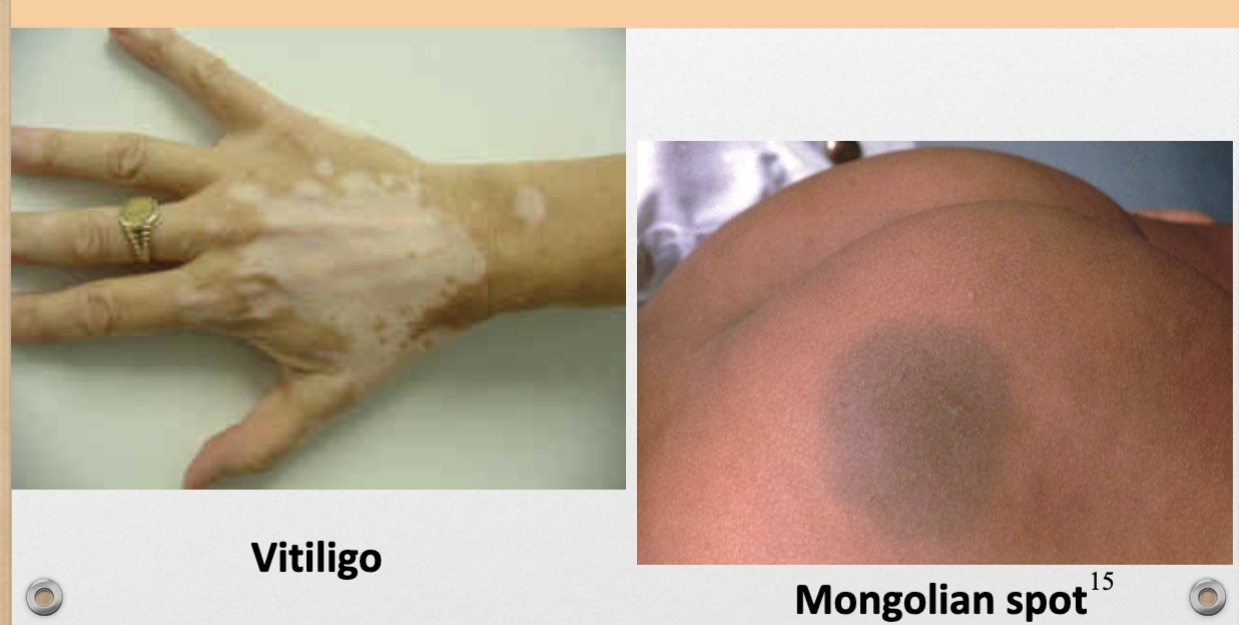
ex. vitiligo, mongolian spot
Patch (p)
Papule (v)
<1cm, raised, palpable
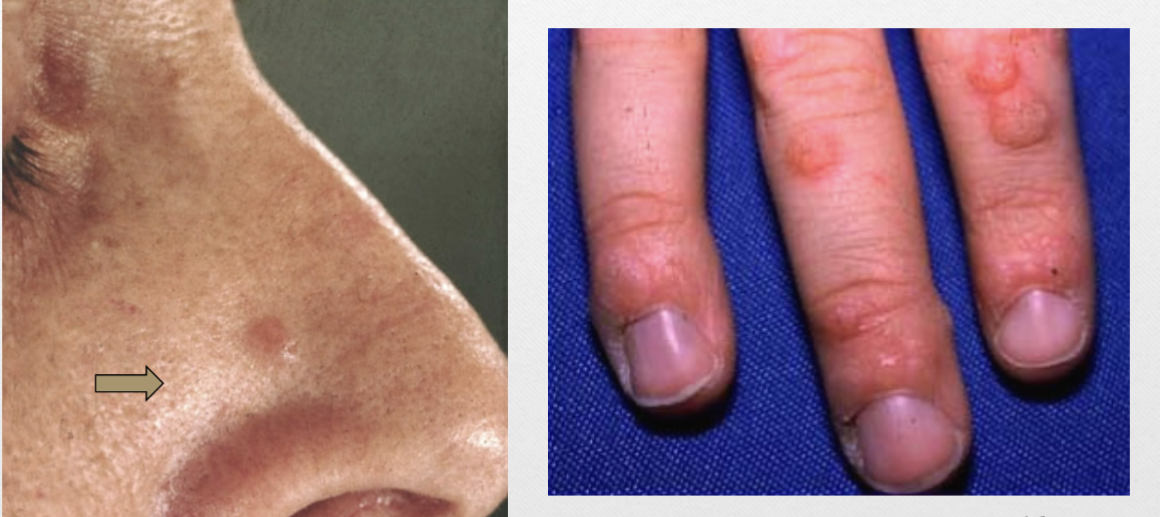
ex. wart (verruca vulgaris)
Papule (p)
Nodule (v)
1-5cm, firm lesion, palpable
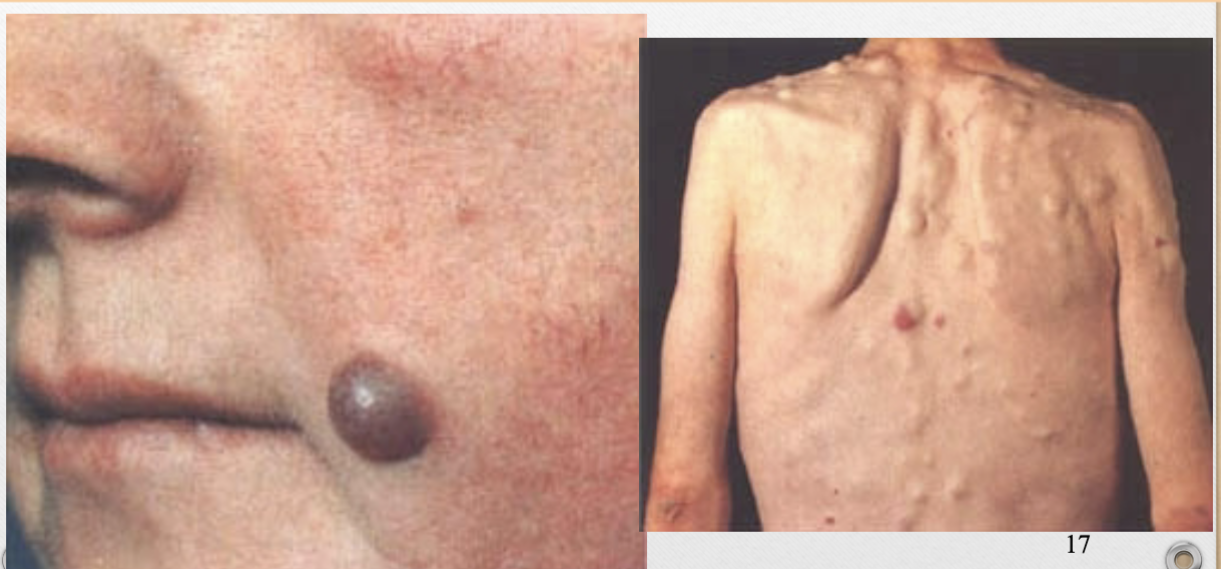
ex. mole
Nodule (p)
Tumor (v)
>5cm, solid raised lesion
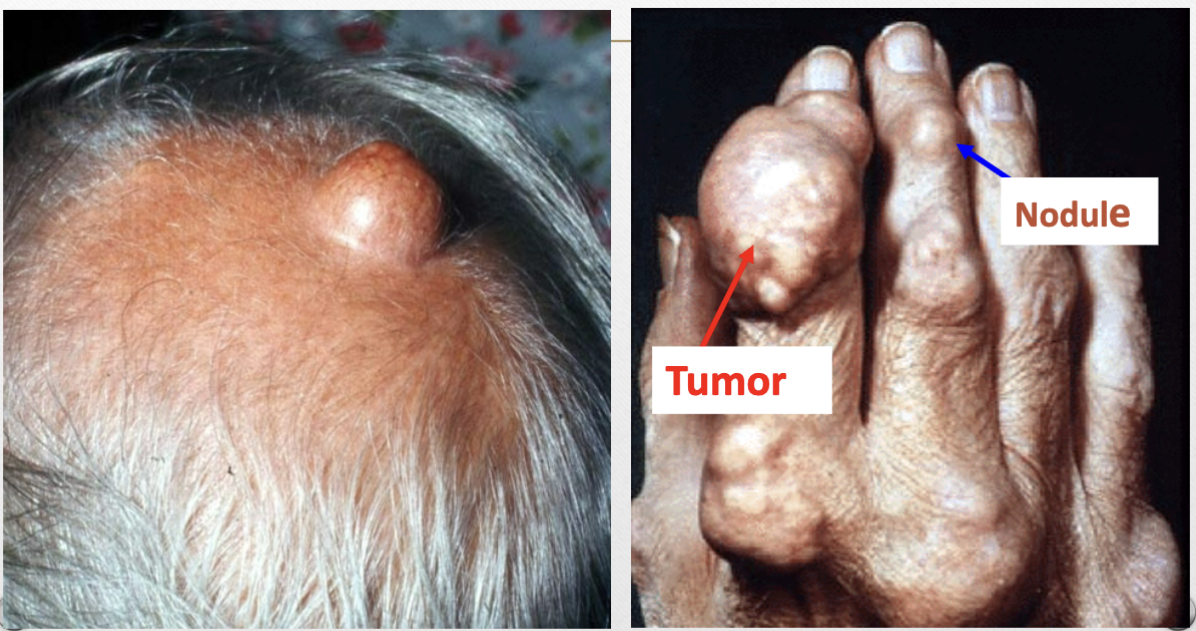
Tumor (p)
Plaque
>1cm, raised but flat-topped, confluence of papules
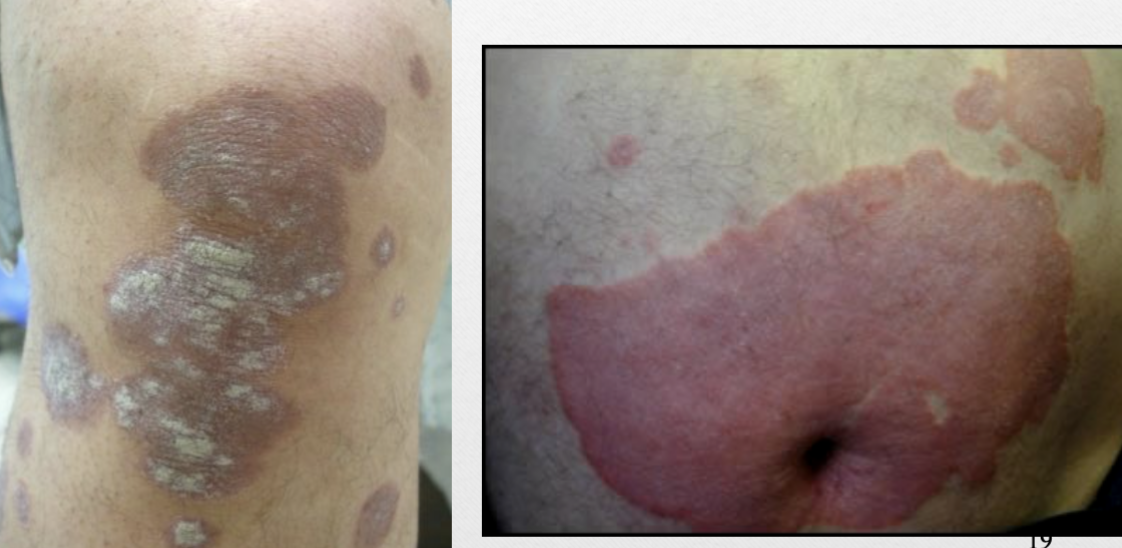
ex. psoriasis
Plaque (p)
Vesicle
<1cm, thin-walled, fluid-filled (serum, blood, lymph) lesion
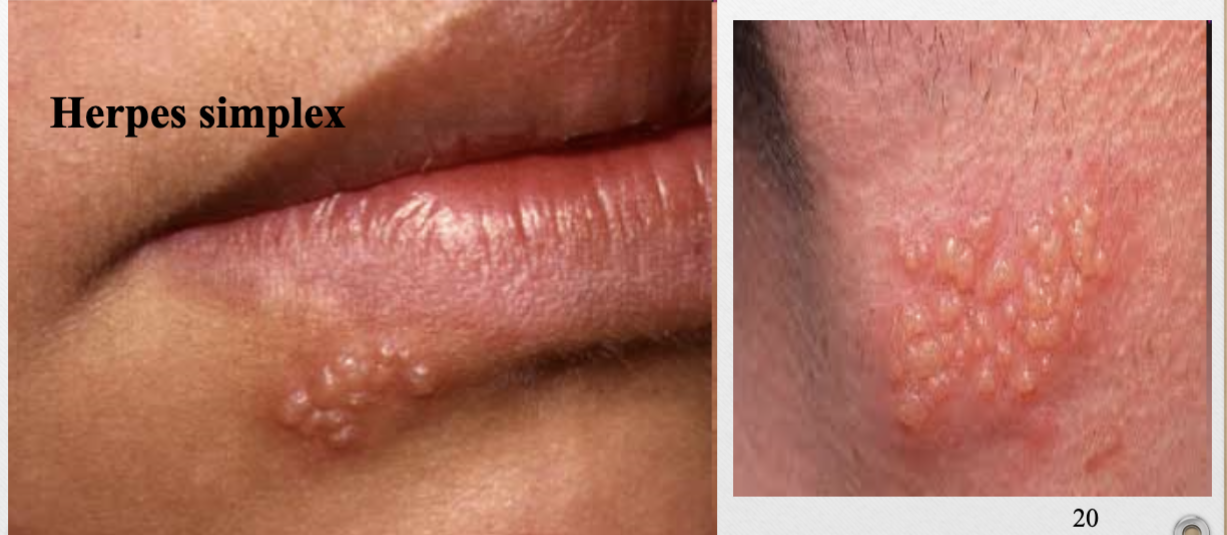
ex. cold sore (herpes simplex)
Vesicle (p)
Bulla (v)
>1cm, fluid-filled lesion
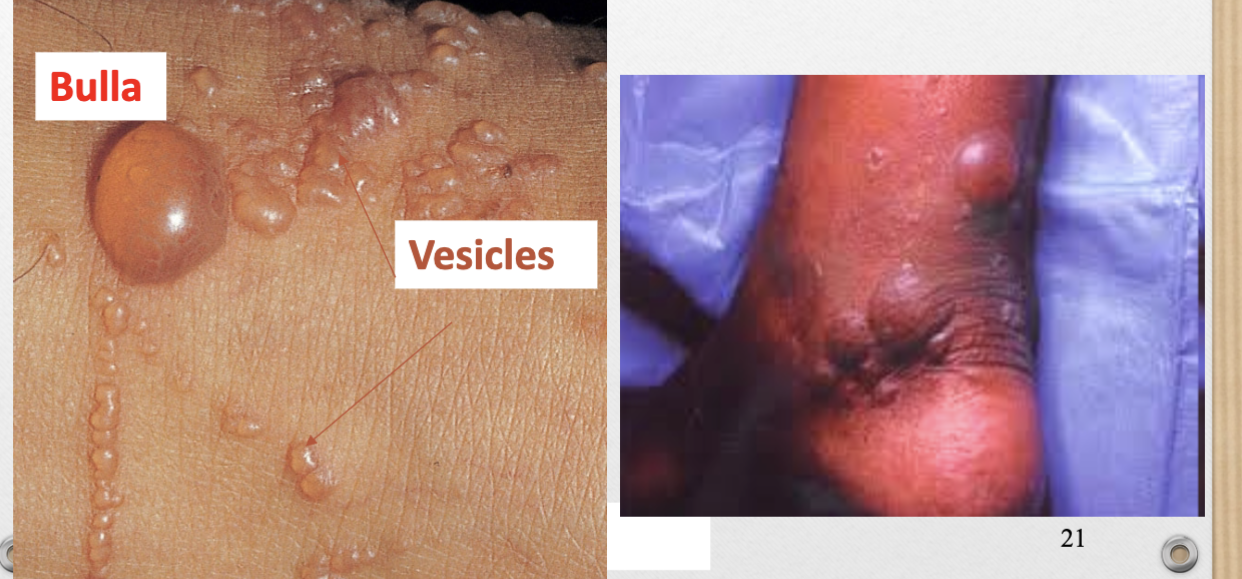
ex. from burns
Bulla (p)
Pustule (v)
raised lesion with purulent exudate
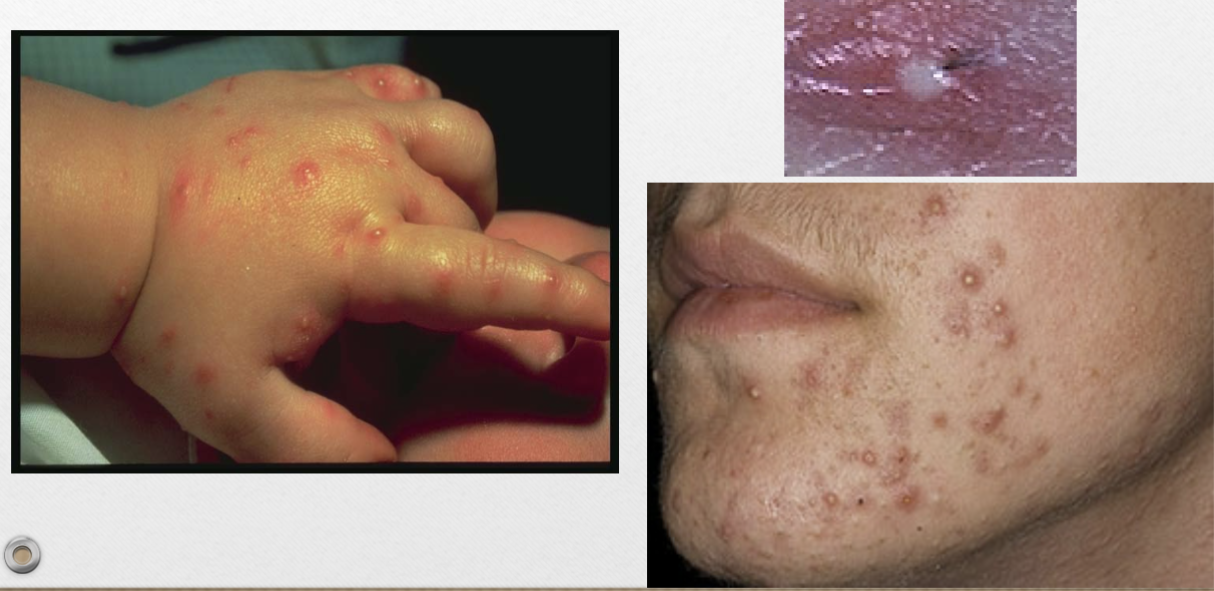
ex. acne, clogged pores
Pustule (p)
Cyst (v)
soft, raised lesion filled with semisolid/liquid material
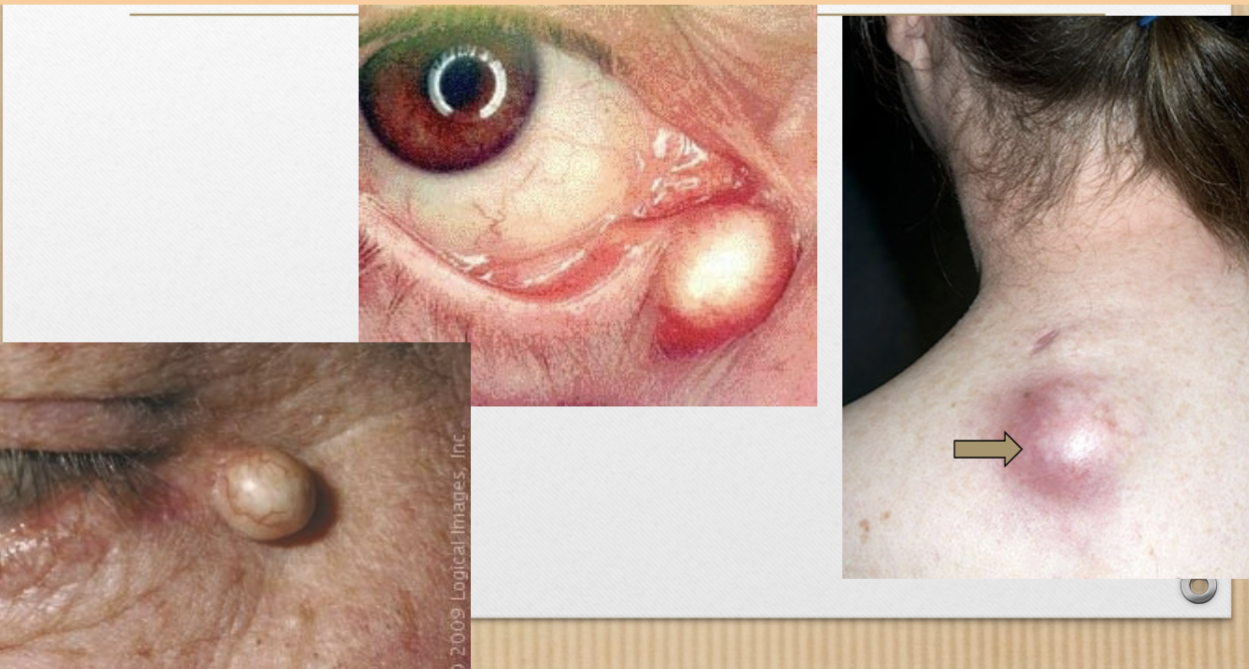
Cyst (p)
Wheal (v)
raised, flat-topped, transient edematous papule or plaque
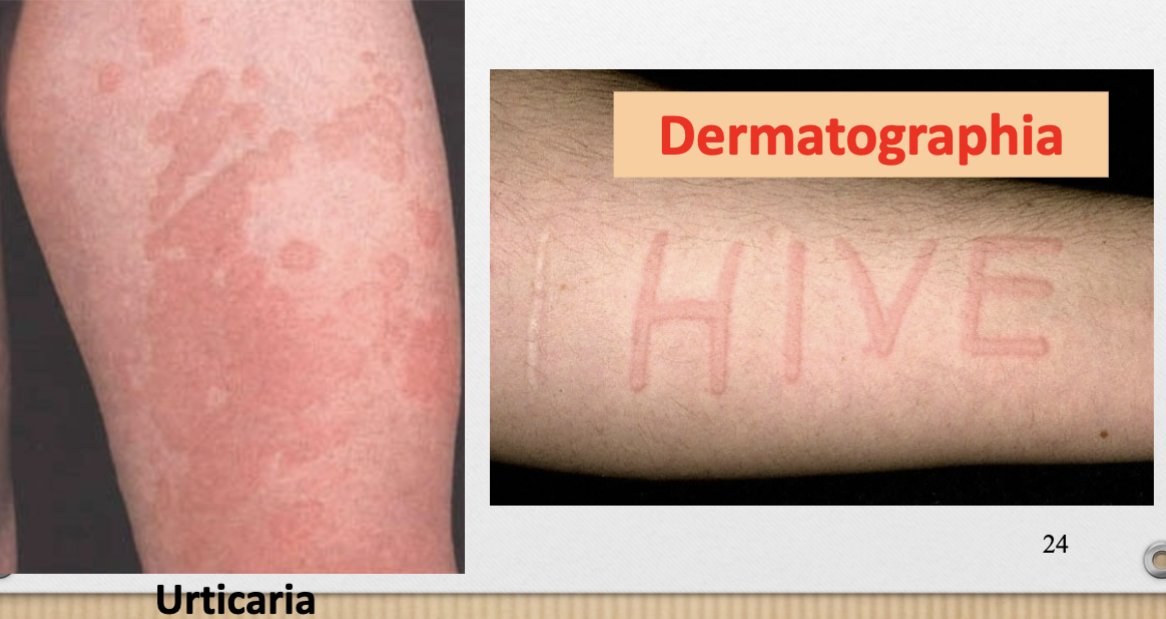
ex. urticaria, dermatographia (hive)
Wheal (p)
Petechiae (v)
tiny, circumscribed deposits of blood that don’t blanch (color doesn’t disappear when pressed)
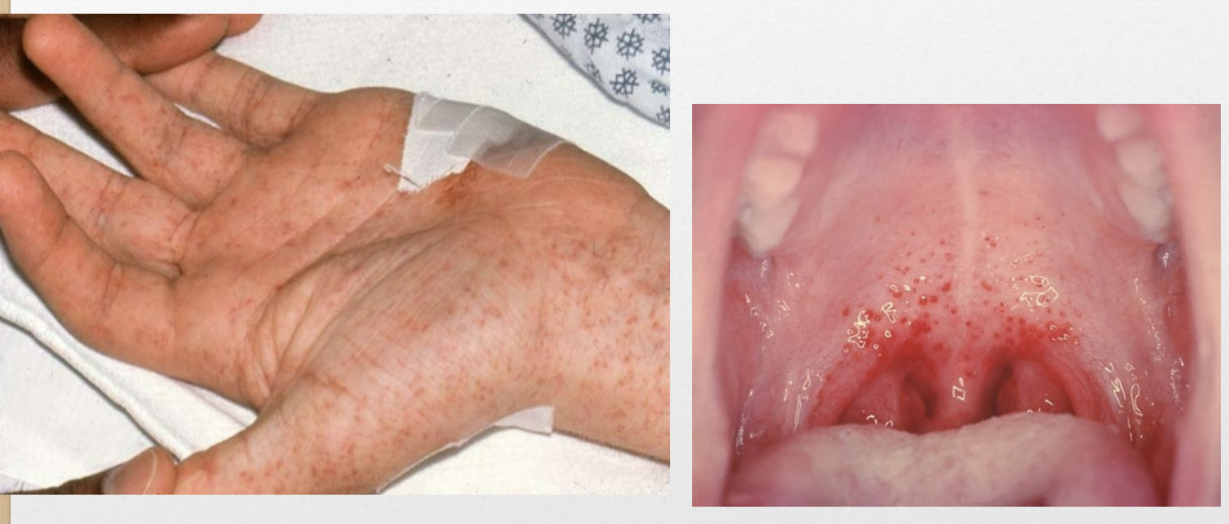
Petechiae (p)
Ecchymosis (v)
larger areas of blood deposits under the skin
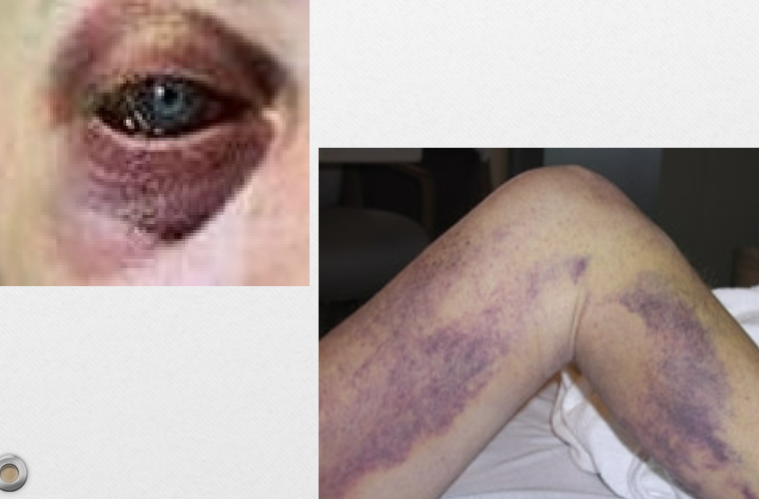
ex. bruise
Ecchymosis (p)
Purapura (v)
bleeding disorder producing ecchymosis or petechiae
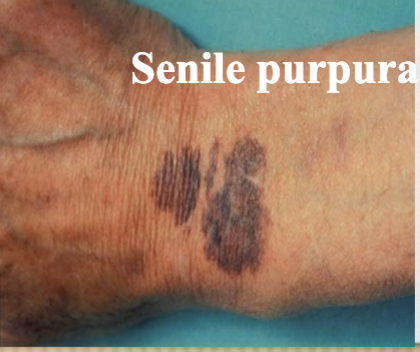
Purpura (p)
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura (v)
self-limiting hypersensitivity vasculitis with lesions of lower abdomen, butt, legs
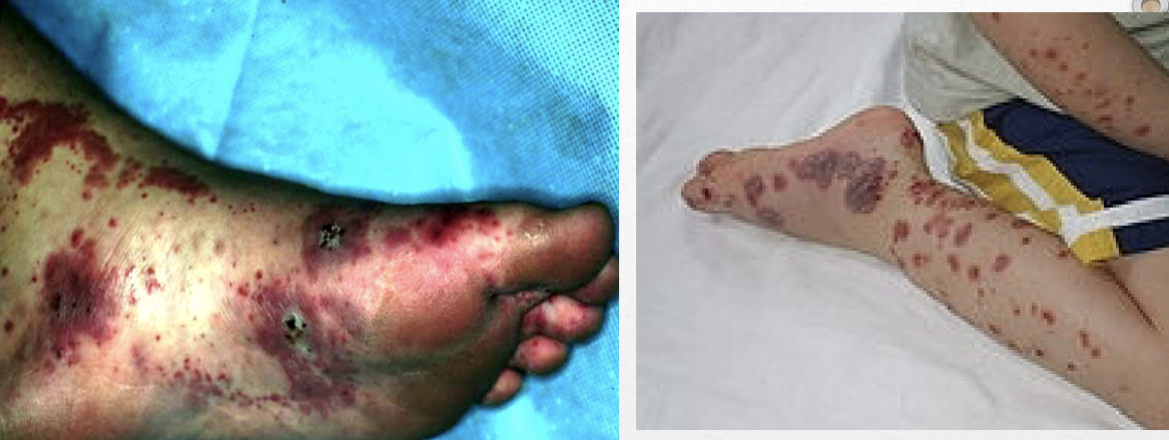
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Telangiectasia (v)
dilated superficial blood vessels
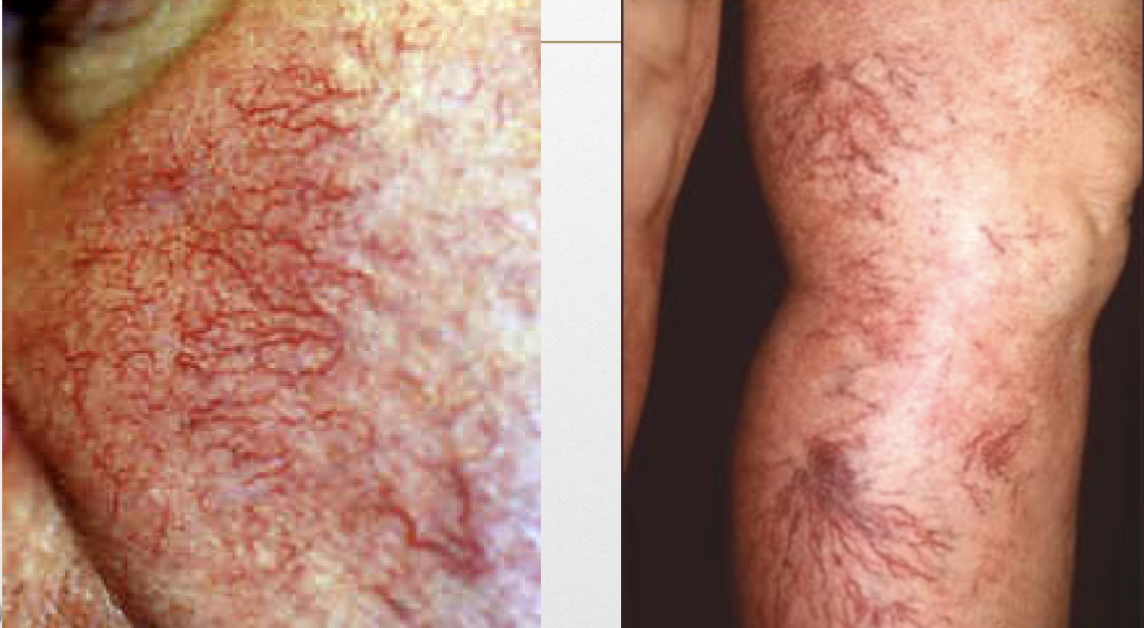
Telangiectasia (p)
Types of secondary lesions
scales, crusts, ulcer,
erosion, fissure,
excoriations, lichenification,
scar, keloid, atrophy
Scales (v)
dead epidermal cells produced by abnormal keratinization/shedding
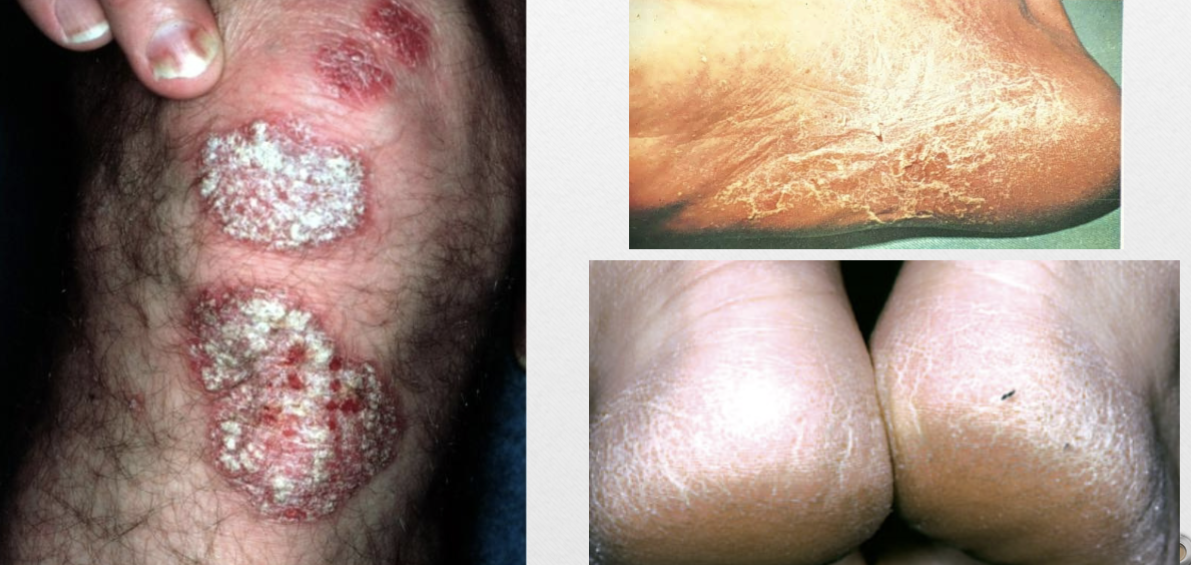
Scales (p)
Crusts (v)
collection of dried serum/ cellular debris
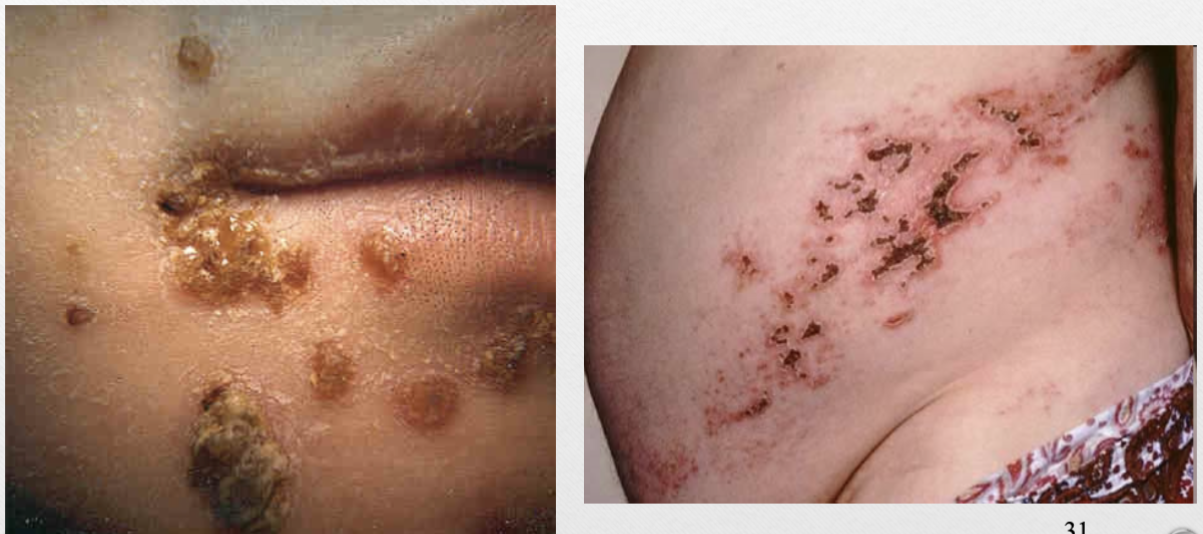
ex. scab
Crusts (p)
Ulcer (v)
open lesion of skin/mucus membrane with loss of epidermis and upper papillary layer, usually heals with a scar
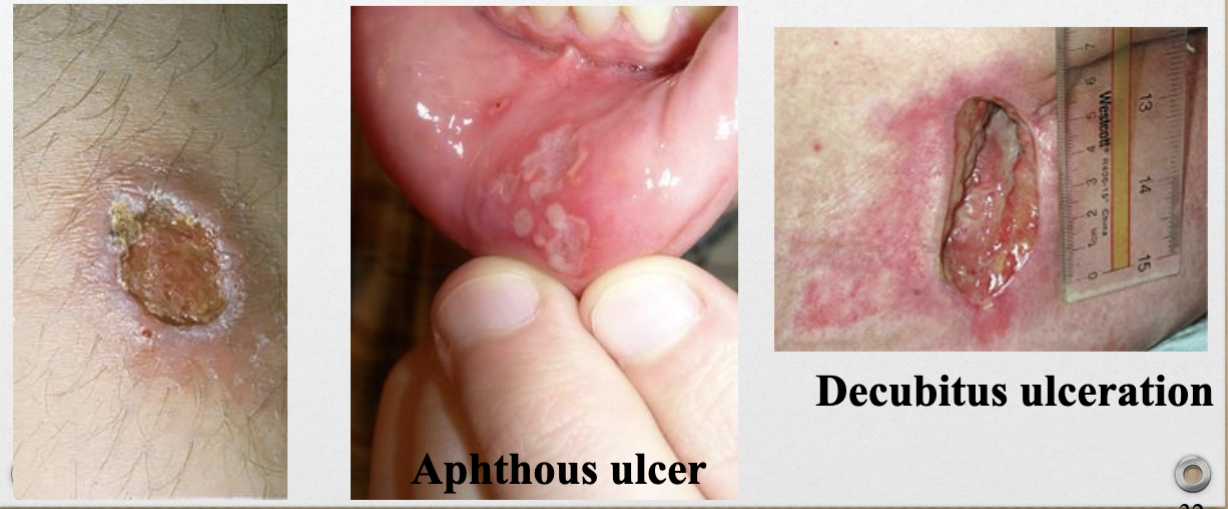
ex. aphthous ulcer, decubitus ulcer
Ulcer (p)
Erosion (v)
loss of epidermis, superficial
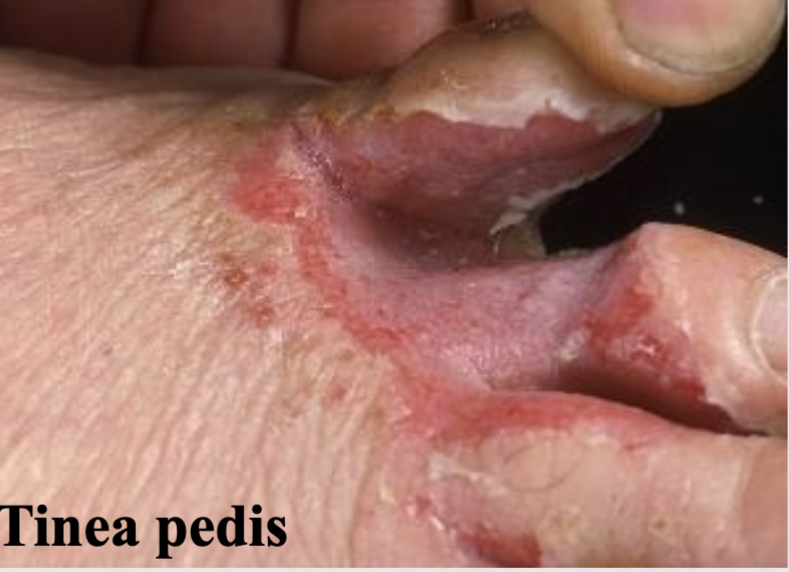
ex. tinea pedis (athletes’ foot)
Erosion (p)
Fissure (v)
linear ulcer or crack-like lesion
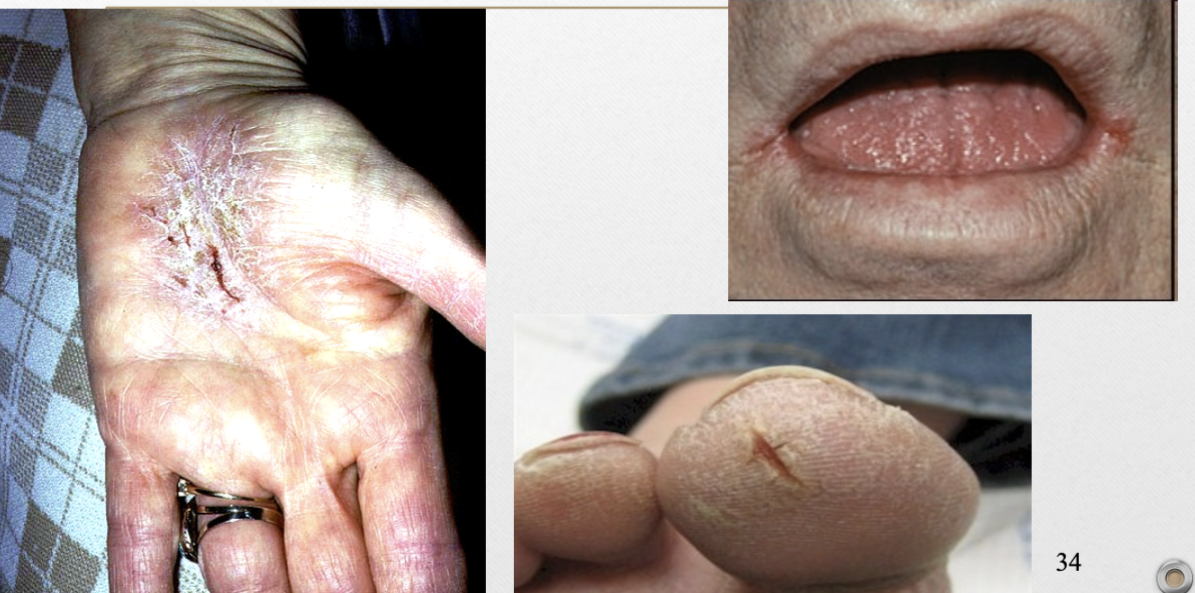
Fissure (p)
Excoriations (v)
linear abrasion of epidermis, self-inflicted by scratching
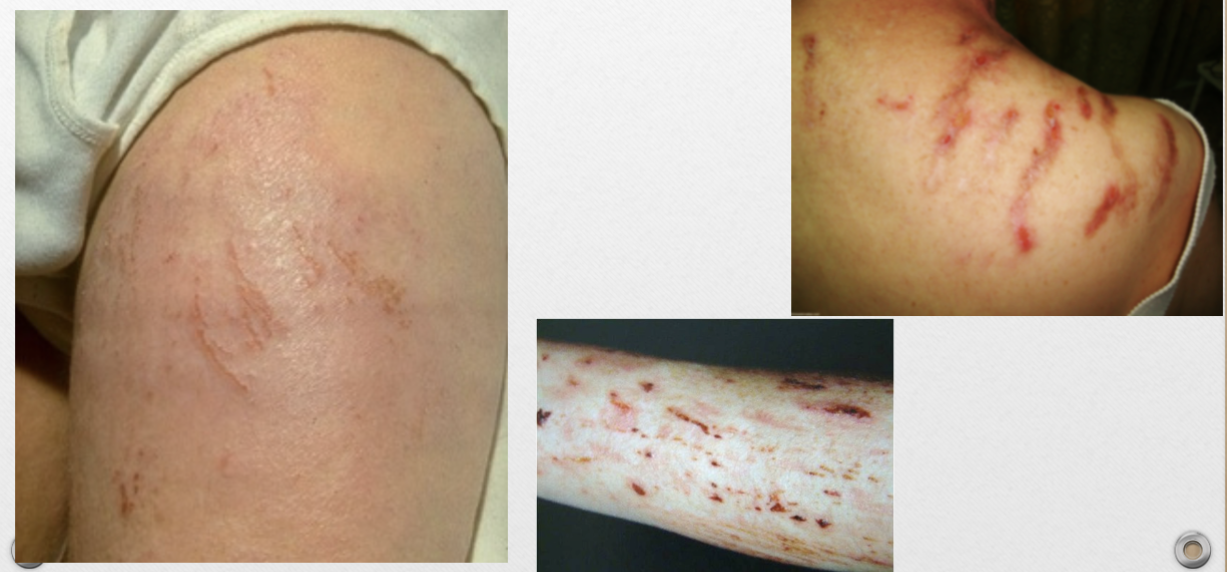
Excoriations (p)
Lichenification (v)
thickened area of skin from chronic scratching/rubbing
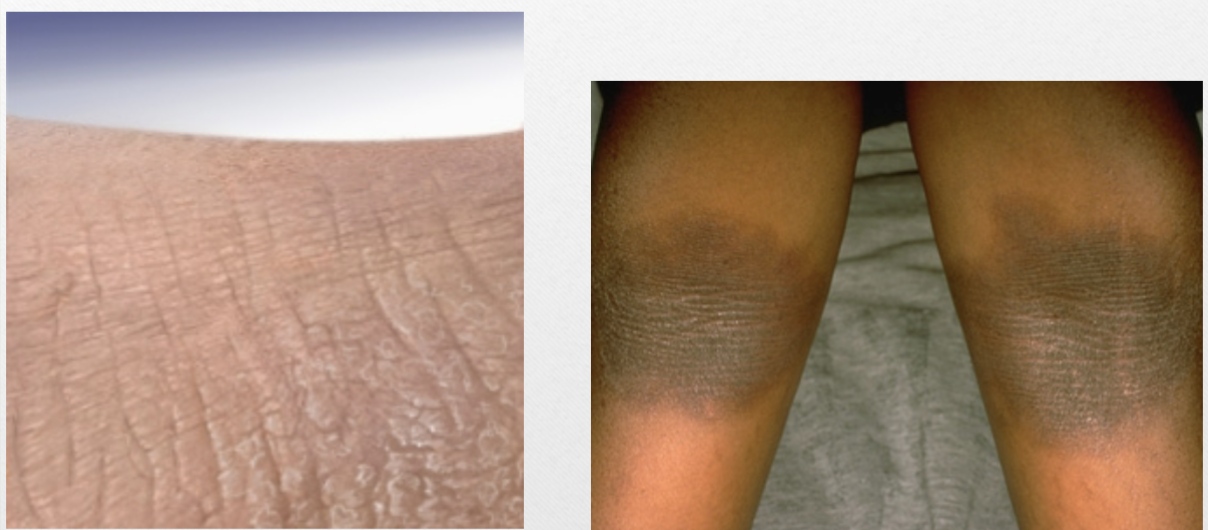
Lichenification (p)
Scar (v)
change in skin from trauma/inflammation
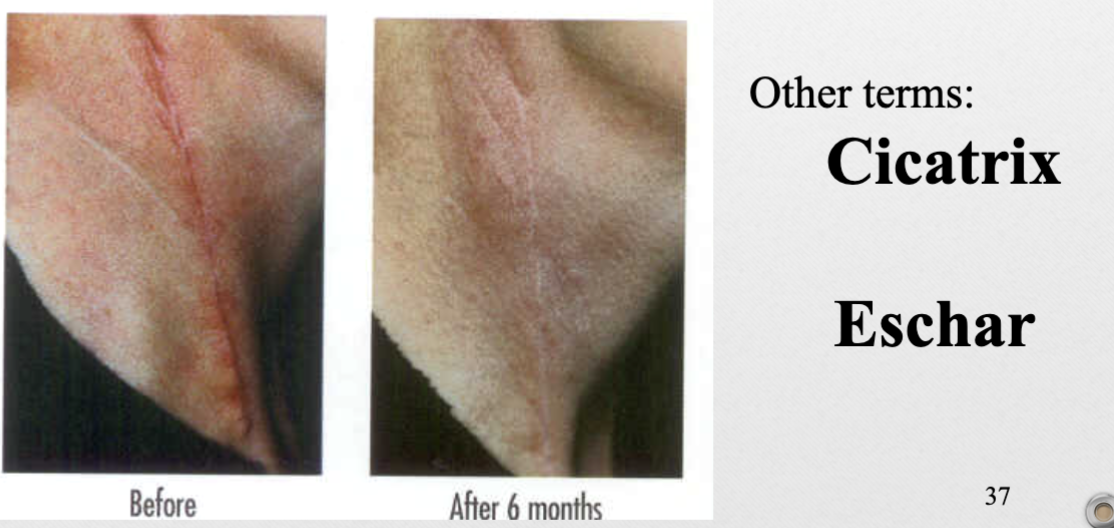
ex. cicatrix, eschar
Scar (p)
Keloid (v)
hypertrophied scars
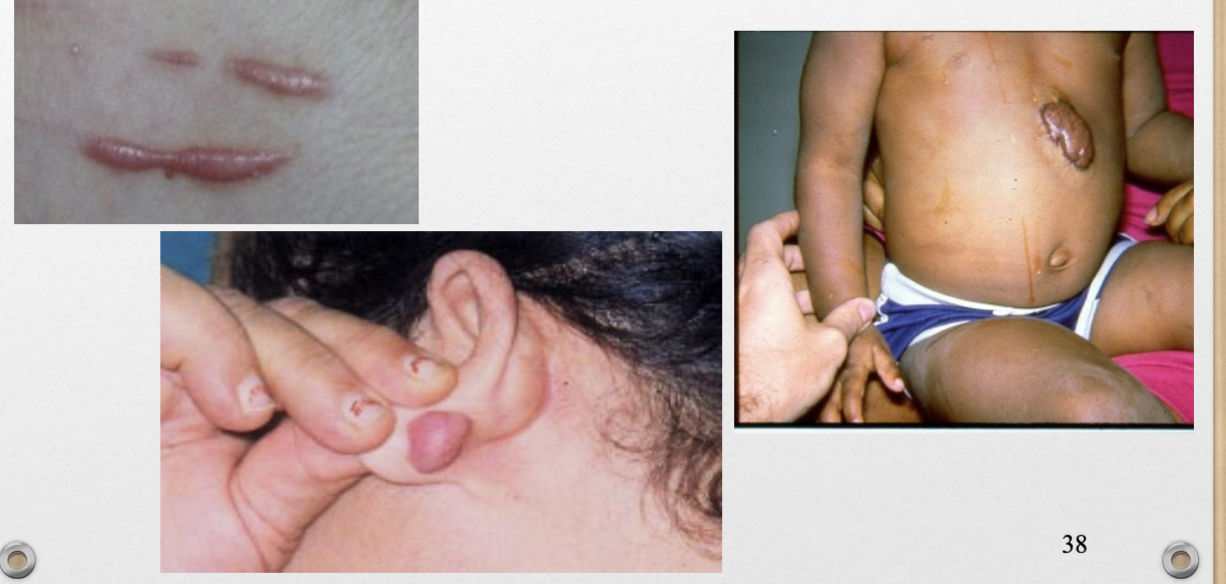
Keloid (p)
Atrophy (v)
loss of normal skin texture with thinning/wrinkling
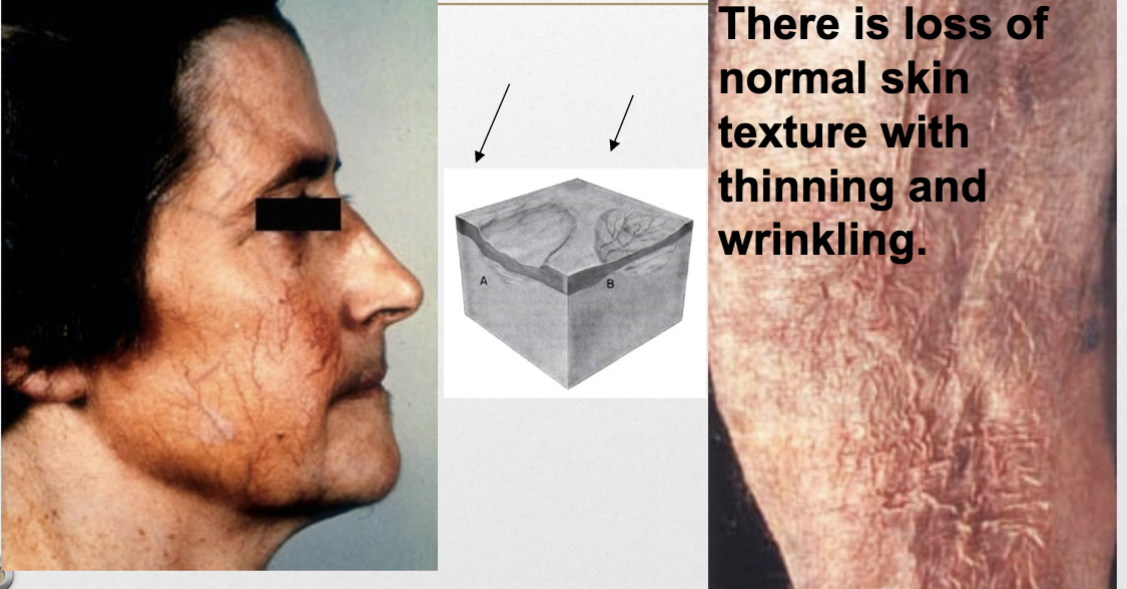
Atrophy (p)
8 parts of description/examination of a lesion
quantity- how many
type- primary/secondary
shape- round, oval, irregular, umbilicated (indent), annular (ring-shaped)
color- erythematous, pale, cyanotic, violaceous (purple from blood), brown
arrangement- linear, annular, confluent (merge)
distribution of pattern- generalized (all over), isolated (single/few), localized (many in one spot), intertriginous (in skin folds/rubs), symmetrical, dermatomal (along nerve, on one side only)
margination- well or ill defined
size- measure
What is the difference between arrangement and distribution of pattern?
arrangement-how lesions are in relation to each other
distribution- where lesions are on the body
Impetigo
most common bacterial infection in children, superficial
caused by Staph aureus or Strep pyogenes
contagious, autoinoculable (spreads), painless
Non- Bullous Impetigo
70% of cases, usually where there was previous skin trauma/disorder
primary- small vesicles/pustules
secondary- rupture/ turn into honey-colored crusts with erythematous base
confluent on nose, cheeks, lips, chin
risk factors- contact sports, poor hygiene, crowded living conditions, hot/humid weather
more contagious, can have mild regional lymphadenopathy
Bullous Impetigo
superficial fragile bullae, rupture/ drain clear-yellow fluid
spreads to face, trunk, extremities, butt (perineal region in infants)
occurs on previously normal skin, not as contagious
Impetigo treatment
localized- topical mupirocin (Bactroban) to affected area TID x 10 days or retapamulin (Altabax)
widespread- oral cephalexin (Keflex) 500mg BID/ 250mg QID (kids dose by weight) or doxycycline (Vibramycin) 100mg BID
Cellulitis
acute, diffuse, spreading infection of dermis/sub-q tissue
caused by Staph aureus or Strep pyogenes
red, hot, tender area of skin, progresses over time
can occur at any age, most often elderly, concerning in diabetics
symptoms- pain in area, fever, chills (all progressive), watch for septicemia
Cellulitis Treatment
Systemic antibiotics
less severe- oral cephalexin (Keflex) 250mg QID/ 500mg BID x 5-10 days or dicloxacillin (Dynapen) 250mg QID x 5-10 days, Bactrim if suspected MRSA
severe- IV ceftriaxone (Rocephin), levofloxacin (Levaquin), nafcillin (Unipen)
Erysipelas
AKA St. Anthony’s Fire
edematous, spreading, well circumscribed, hot, erythematous area, w/ or w/o bullae
superficial form of cellulitis, on central face
caused by Group-A beta-hemolytic Strep
symptoms- pain, fever, chills, rash (after others)
rash starts as bright red spot, progresses to clearly demarcated, glistening, smooth, red plaque
Erysipelas treatment
urgent, can cause death from systemic toxicity
IV antibiotics for first 48 hrs- Penicillin G
oral antibiotics x 7 days- Pen VK 250mg QID, Dicloxacillin 250mg QID, Cephalexin 250mg QID
Folliculitis
inflammatory process of hair follicle from infection, chemical irritation, physical irritation
caused by Staph, trauma, scratching, shaving
Pseudo follicilitis
foreign body reaction when hair curves into skin after being cut against growth pattern
Folliculitis treatment
antibacterial soap, warm wet dressing
localized- Bactroban ointment TID x 5 days
extensive/spreading- oral antibiotics
Hot Tub Folliculitis
start 1-4 days after being in hot tub, may resolve spontaneously
caused by Pseudomonas
treatment- ciprofloxacin (Cipro) 500mg BID x 5 days
Abscess
localized collection of pus, intensely painful, red, tender, indurated
caused by Staph aureus if on trunk, extremities, head, neck, in axillae, or by organisms found in stool if on butt, inguinal/perineal area
will progress to a point/head, may drain spontaneously
Abscess
warm compress to cause head/point, then incision, drain, pack
oral antibiotics- cephalexin (Keflex) 500mg BID or 250mg QID
Furuncle abscess
abscess involving hair follicle and surrounding tissue, uncomfortable, maybe painful
caused by Staph aureus
found on neck, breasts, face, butt
Carbuncle abscess
collection of furuncles connected subcutaneously, uncommon
found on back of the neck, may have fever
MRSA (Methicillin Resistant Staph Aureus)
resistant to β-lactam antibiotics, macrolides, quinolones, clindamycin, sometimes Bactrim
can be hospital or community required, latter becoming increasingly common
risk factors- close skin-skin contact with cuts/abrasions, crowded living conditions, poor hygiene
MRSA treatment
Bactrim if possible or IV vancomycin or Zyvox
MRSA prevention
susceptible groups add 1/4c bleach to bathwater 1-2 x week
document people with colonized MRSA in nares (1%), treat with Bactroban ointment BID x 5 days
Warts
caused by HPV, 12 high-risk cancer strains
Common warts- 16, 18 (70%), Genital Warts 6, 11
6 types- common, periungual, flat, filiform, plantar, genital
Common warts
aka verruca vulgaris, most common on hands and knees
dome-shaped with irregular surfaces
spread by skin-skin contact, contact with contaminated surfaces, autoinoculation
common in kids