Endocrinology: Thyroid, Adrenal, Pancreas, and Calcium Regulation
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is included in the peripheral glands?
Thyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas and parathyroid glands
What is the primary function of the thyroid gland?
To synthesize and secrete thyroid hormones, T3 and T4, which regulate metabolism.
What are the two main hormones produced by the thyroid gland?
Tetraiodothyronine (T4 or thyroxine) and Tri-iodothyronine (T3).
What are lumen filled with?
Colloid
How is thyroid hormone stored in the thyroid gland?
Thyroid hormones are stored in the colloid of follicles as thyroglobulin until needed.
What is the chief constituent of colloid?
Thyroglobulin
What do C cells secrete?
Calcitonin, a peptide hormone
What process allows the secretion of T3 and T4 from the thyroid gland?
Follicular cells phagocytize thyroglobulin-laden colloid, and lysosomes break it down to release T3 and T4.
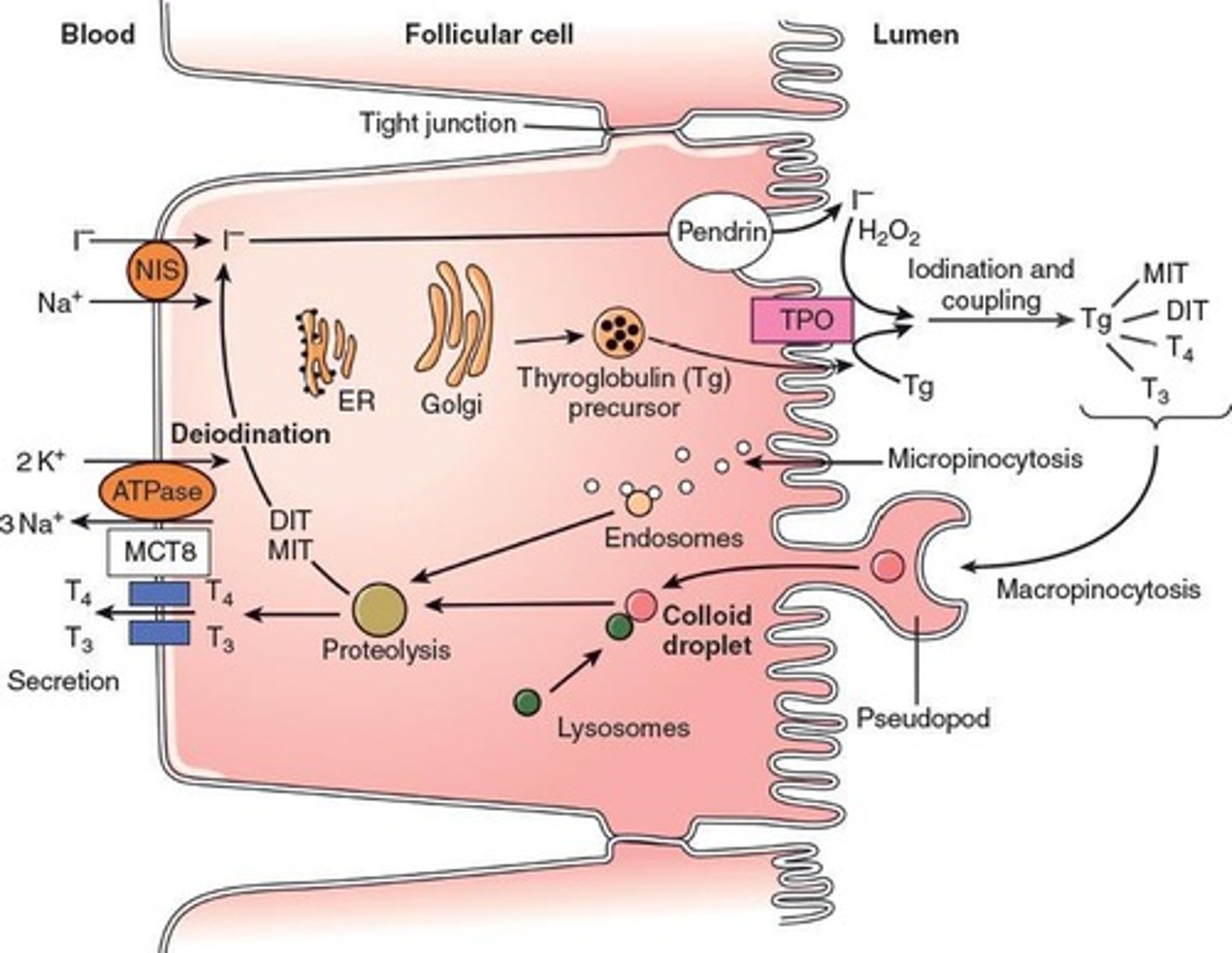
How is iodide captured from blood and transferred into colloid?
Thyroid captures iodide and it's transferred by iodide trap (pump), a symporter driven by Na concentration.
What oxidizes iodide?
Thyroperoxidase
What does coupling of MIT and DIT yield?
T3
What does coupling of DIT and DIT yield?
T4
How are T3 and T4 transported in the blood?
By thyroxine binding globulin (TBG)
Which thyroid hormone is secreted more and which is more powerful?
T4 is secreted more (about 90% of what is secreted is T4) but T3 is 10x more powerful
What is the major biologically active form of thyroid hormone?
T3
What physiological effects do thyroid hormones have on the heart?
They increase heart rate, force of contraction, cardiac output (partly due to catecholamine response)
What physiological effects to thyroid hormones on growth and the nervous system?
They stimulate secretion of GH and increases production of IGF-1 by the liver. They are essential for normal growth and normal development of the nervous system and CNS function
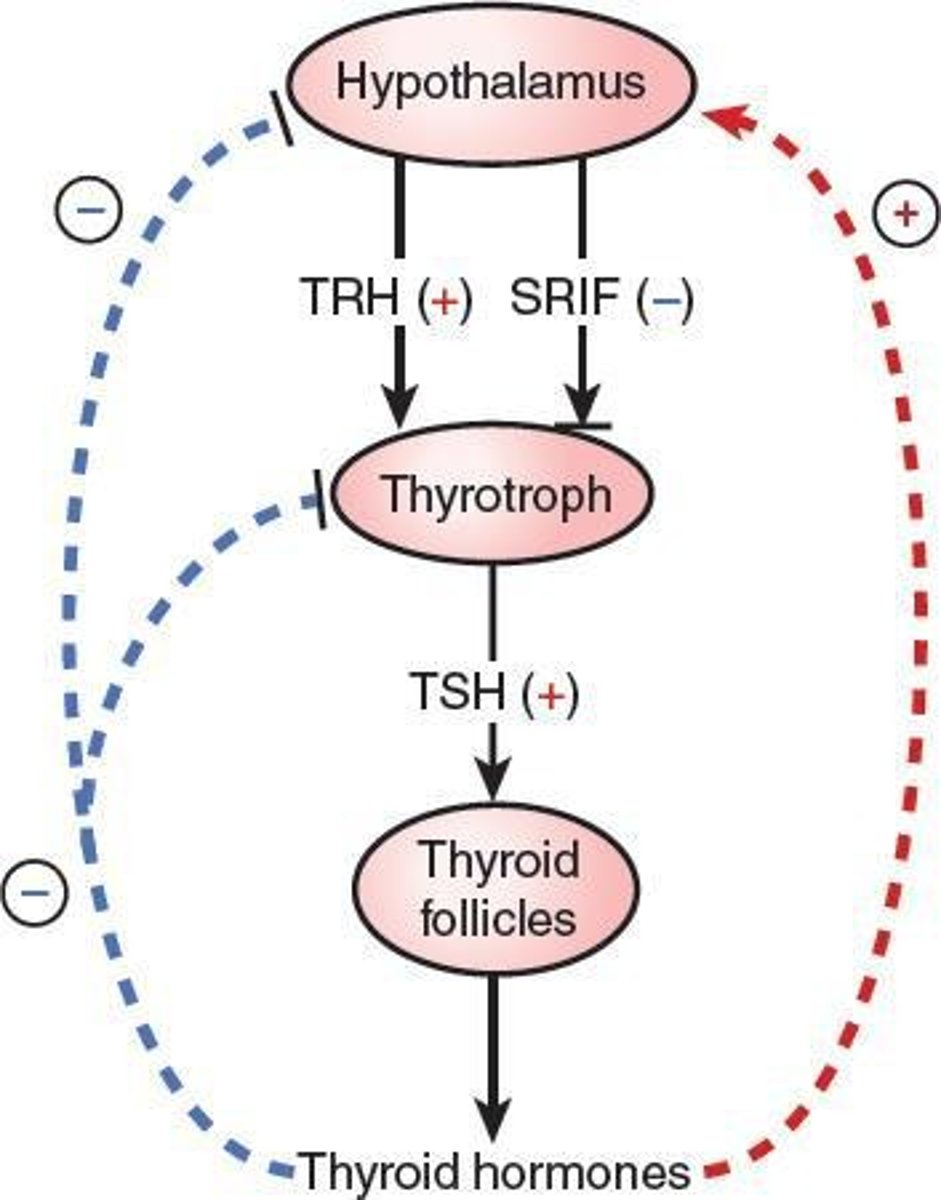
What regulates the secretion of thyroid hormones?
The hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis, primarily through negative feedback involving TRH and TSH.
What are the symptoms of hypothyroidism?
Reduced basal metabolic rate, cold intolerance, weight gain, fatigue, slow pulse, and poor mental response.
What are common causes of hypothyroidism?
Primary failure of thyroid gland, secondary to a deficiency of TRH, inadequate dietary supply of iodine
What is a common cause of hyperthyroidism?
Graves' disease, an autoimmune disorder that produces thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins.
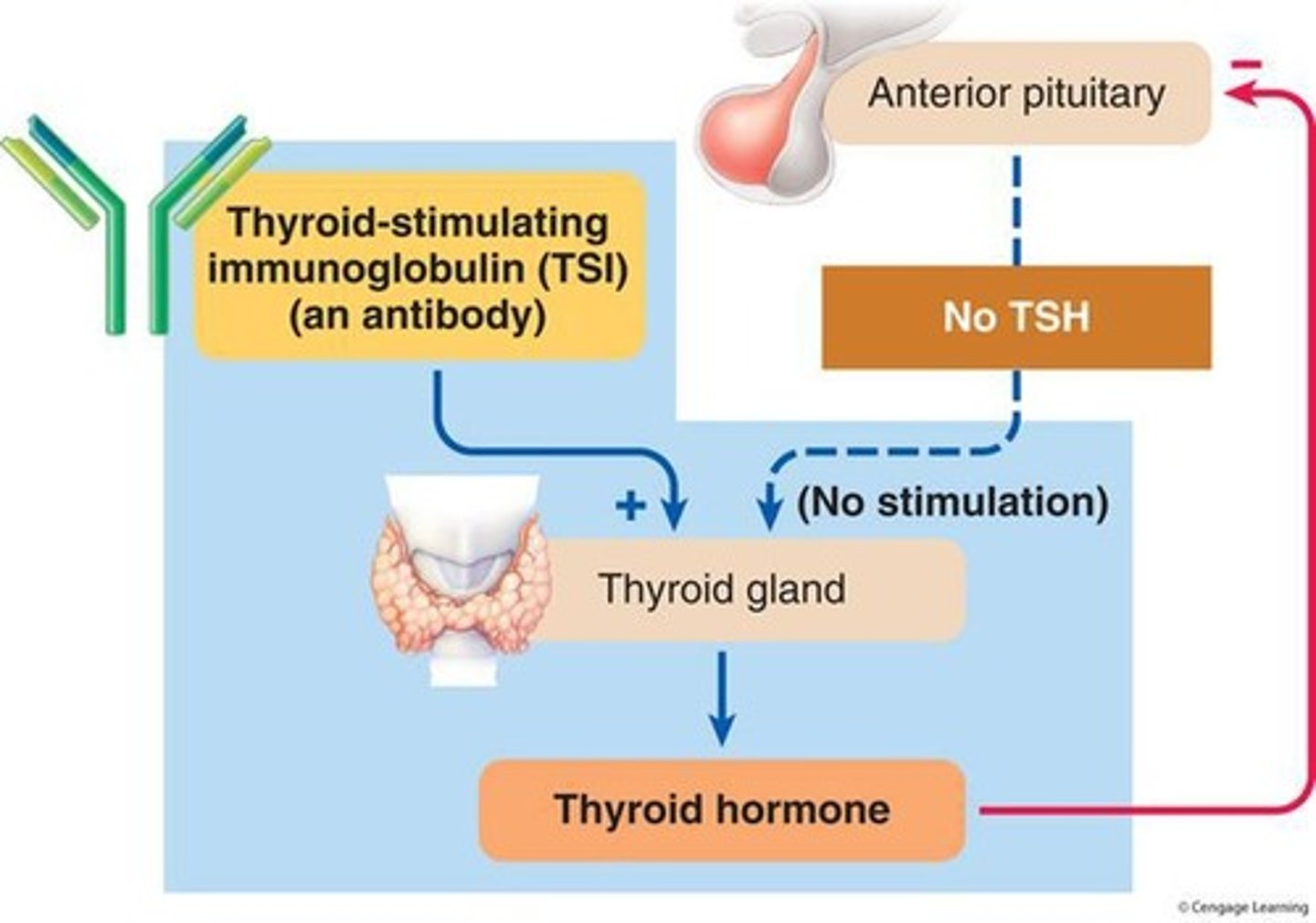
What is a goiter and what causes it?
A goiter is an enlarged thyroid gland caused by excessive stimulation from TSI or TSH.
What are the two main parts of the adrenal glands?
The adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla.
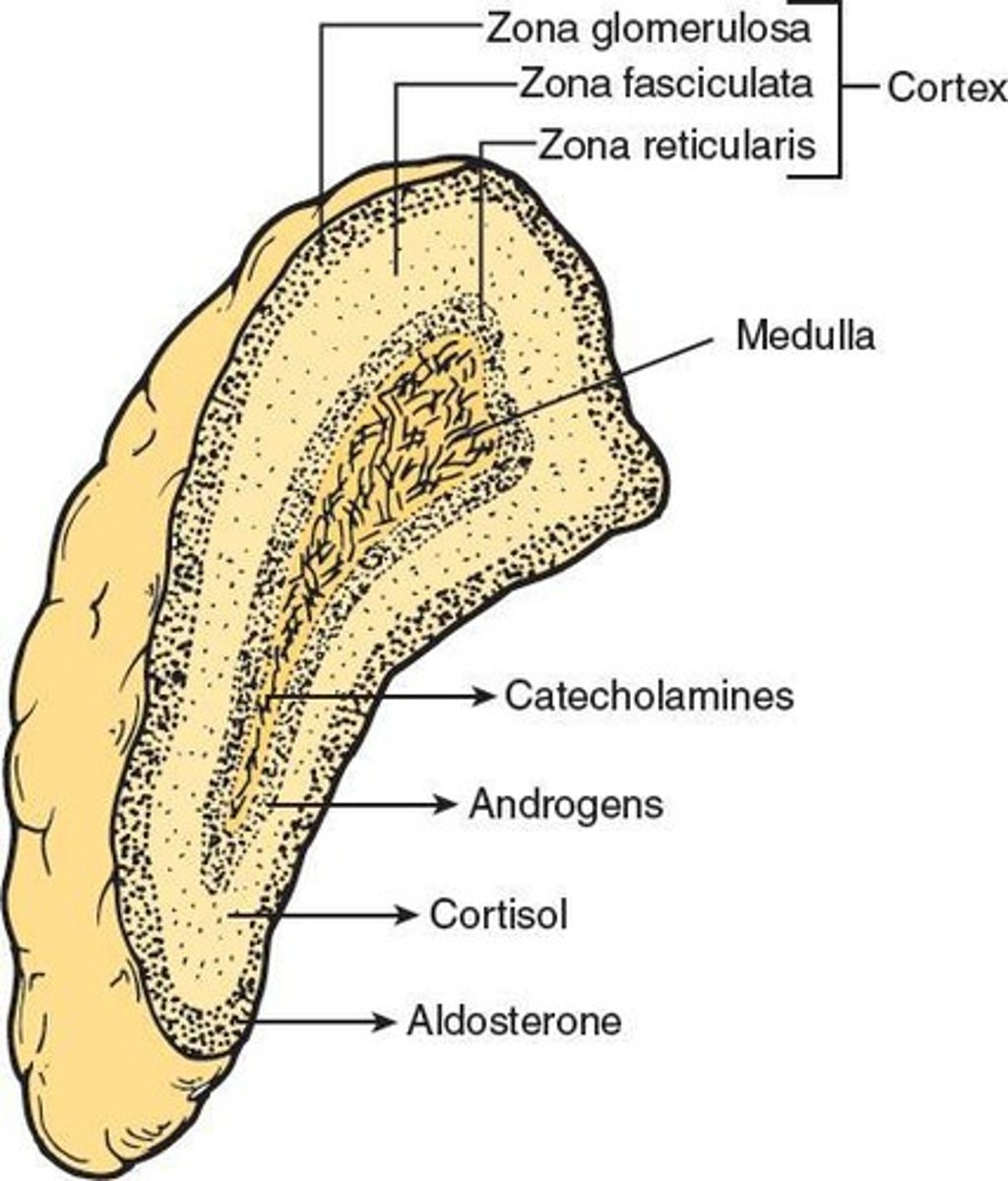
What hormones are secreted by the adrenal cortex?
Steroid hormones like mineralocorticoids (mainly aldosterone), glucocorticoids (primarily cortisol) and sex hormones (male and female)
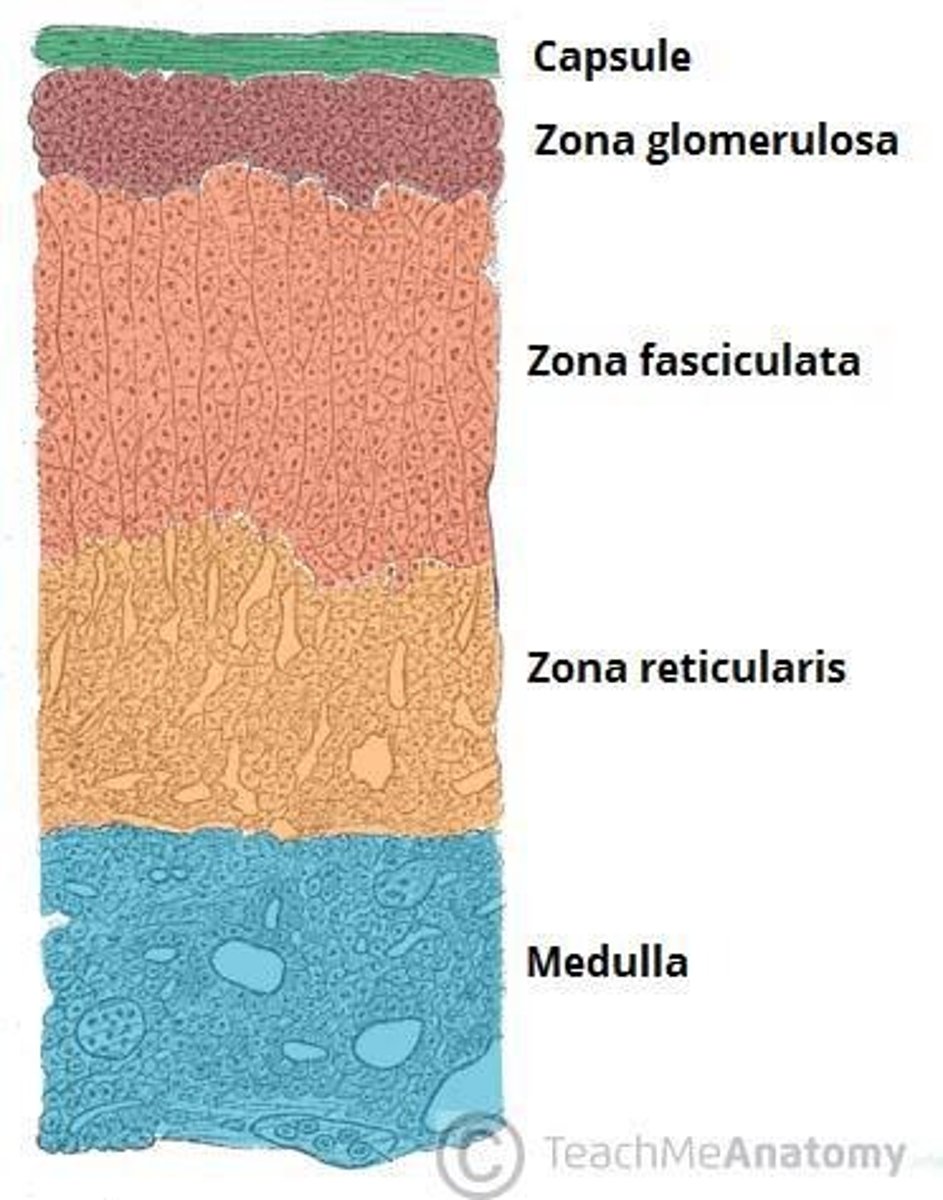
What is the function of mineralocorticoids?
Influence mineral balance, specifically Na and K balance
What is the function of glucocorticoids?
Plays a major role in glucose metabolism as well as in protein and lipid metabolism as well as adaptation to stress
What is the most abundant and physiologically important sex hormone?
DHEA, an androgen male "sex" hormone
What are adrenocortical hormones derived from?
Cholesterol
Where is the principal action site of aldosterone?
Distal and collecting tubules of the nephron
What is the primary role of cortisol?
Helps the body adapt to stress and stimulates hepatic gluconeogenesis. It converts non-carb sources into carbs and increases blood glucose, particularly important to the brain.
How does cortisol impact glucose uptake?
It inhibits glucose uptake by tissues, but not the brain. It maintains a ready supply of glucose for the brain.
What is the negative feedback mechanism regulating cortisol secretion?
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) from the hypothalamus stimulates adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) from the pituitary, which in turn stimulates cortisol secretion from the adrenal cortex.
What is the function of the adrenal medulla?
To secrete catecholamines, such as epinephrine and norepinephrine, which are involved in the stress response.
What is the role of chromaffin cells in the adrenal medulla?
They release epinephrine and norepinephrine directly into the blood.
What percentage of adrenomedullary catecholamine output is epinephrine?
80%.
Where on the adrenal medulla is epinephrine released?
Only on sympathetic stimulation of the adrenal medulla
What is metabolism?
All the chemical reactions that occur within the cells of the body
What is anabolism?
The synthesis of larger organic macromolecules from small organic subunits, requiring ATP energy.
What is catabolism?
The breakdown of large, energy-rich organic molecules within cells to yield energy for ATP production.
What is gluconeogenesis and its consequence?
Amino acids → glucose. Increases blood glucose
What is the primary role of the liver in metabolic states?
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels and conducting metabolic interconversions. Its metabolic fuel correlated is carbs.
What is the primary role of adipose tissue in metabolic states?
Primary energy storage site, important for regulating fatty acid levels in the blood. Its metabolic fuel correlated is fat.
What is the primary role of muscle in metabolic states?
Primary site of amino acid storage. Its metabolic fuel correlated is protein
What are the Islets of Langerhans?
Clusters of cells in the pancreas that produce hormones like insulin and glucagon.
What is the function of pancreatic beta cells?
They synthesize and secrete insulin, which regulates blood glucose levels. Also site of amylin
What is the function of amylin?
Works in CNS to enhance satiety, delay gastric emptying and suppress secretion of glucagon.
What is the role of insulin?
An anabolic hormone that maintains proper blood glucose homeostasis
What stimulates insulin secretion?
An increase in blood glucose concentration
What are the 4 primary effects of carbohydrates?
1.Facilitates glucose transport into most cells, 2.Stimulates glycogenesis (production of glycogen), 3.Inhibits glycogenolysis (breakdown of glycogen), 4.Inhibits gluconeogenesis (conversion of amino acids into glucose)
What is the difference between type I and type II diabetes?
Type I diabetes is characterized by autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing cells in early childhood (lack of insulin secretion), while type II involves insulin resistance (will have normal or increased insulin secretion)
What are the long term consequences of DM?
1.Cardiovascular lesions, 2.Lesions in kidneys and eyes, 3.Impaired delivery of blood to extremities, 4.Degenerative lesions in nerves
What is the most common cause of premature death in diabetics?
Cardiovascular lesions
What is the leading cause of kidney failure and blindness in the US?
Lesions in kidneys and eyes caused by DM complications/
What is the role of glucagon?
To increase blood glucose levels by promoting glycogen breakdown in the liver.
What is the immediate effect of PTH?
To promote transfer of Ca from bone fluid into plasma