EXERCISE 5: PLANT CELL DIVISION
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
interphase and mitosis
cell cycle is divided into two:
Interphase
normal resting cell state
chromatin
In interphase, __________ is undifferentiated.
centromere
In the synthesis of s-phase during the interphase, chromosome is duplicated and consist of 2 sister chromatid joined together by a specific DNA sequence known as _____________.
Mitosis
mechanism that allows the nuclei of cell to split and each daughter cell with a complete set of chromosome
Prophase
first stage of mitosis
chromatids
PROPHASE: When cells divide, chromatin condenses to form chromosomes which split into two identical strands called _________
cytoskeleton
PROPHASE: ___________ begins to disassemble, and the biotic spindle begins to form outside the nucleus at opposite ends of the cell
nuclear envelope
PROPHASE: the ___________________ fragments, and the nucleolus disintegrates
Prophase
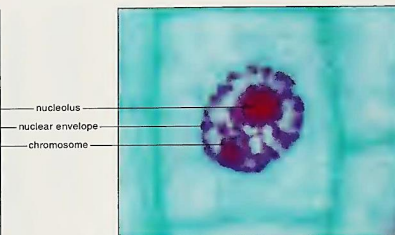
Metaphase
Chromosomes attached to the kinetochore (specialized protein complex) microtubules, begin to align in one plane halfway between the spindle pole, where centromeres are in a plane roughly in the center of the cell.
kinetochore microtubule
METAPHASE: The ___________________________ exert tension on the chromosome, and the entire spindle chromosome complex is now ready for the next event
Metaphase
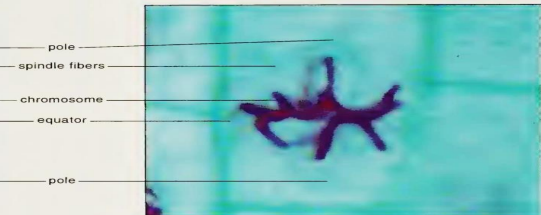
Anaphase
The two halves of each chromosome (sister chromatids) are pulled part by the spindle apparatus and migrate to the opposite spindle post
kinetochore microtubule
The ___________________________________________ shorten as the chromosome are pulled towards the poles while the pole microtubule elongate to assist in the separation
daughter chromosomes
After the chromatids after separated at their centromeres are called
Anaphase
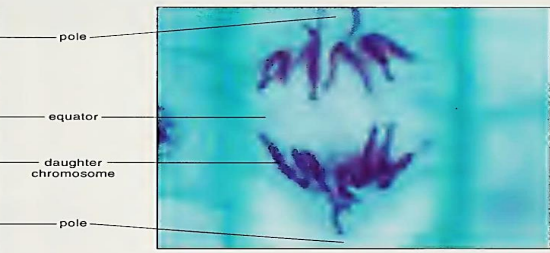
Telophase
daughter chromosome arrive at the spindle pole and are eventually redistributed into chromatin
Cytokinesis
where the cytoplasm is divided by cleavage, also starts sometime in late anaphase and continues through telophase
nuclear membrane
After complete separation of the chromosome and their extrusion to the spindle pole, the ______________ begins to reform around each group of chromosome; nucleoli reappear; many of the spindle fibers disintegrate; and a cell plate forms
2 new daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nuclues
what is formed in mitosis?
ordinary tissue growth
Where is mitosis used?
four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell
result of meiosis
production of gametes and plant spores
where is meiosis applicable?
Meiosis I - Prophase I
parts of the chromatids of the homologous chromosomes break and are exchanged with each other (cross -over)
Crossing-over
results in an exchange of some of the DNA contributed by the two parents, which is the basis for some of the variability seen in the offspring
chiasma
An X-shaped figure called a _____________________ results from each crossover.
Meiosis I - Anaphase I
the nuclear envelope and the nucleolus have disassociated and disappeared, and spindle fibers (microtubules having the appearance of fine threads) are beginning to form.
Meiosis I - Metaphase I
When the chromosomes move to the invisible, circular, plate-like equator, homologous chromosomes are lined up directly opposite one another on each side of the equator
Meiosis I - Anaphase I
the chromatids of each chromosome remain cohered at their centromeres and do not separate from one another. Whole chromosome from each pair migrates to an opposite pole.; They still consist of two chromatids, but only half the total number of chromosomes is at each pole.
Meiosis I - Telophase I
Each cell has one of the replicated chromosome from each homologous pair chromosomes.
Meiosis II - Prophase II
Chromosomes become shorter and thicker, and their two - stranded nature once more becomes apparent
Meiosis II - Metaphase II
The centromeres of the chromosomes become aligned along the equator. New spindles become conspicuous and complete.
Meiosis II - Anaphase II
The centromeres and chromatids of each chromosome separate and migrate to opposite poles
Meiosis II - Telophase II
coils of the chromosomes relax so they become longer and thinner. New nuclear envelopes and nucleoli reappear for each group of chromosomes; The set of chromosomes present in each of the four cells formed by the end constitutes half the original number, and none of the four cells will have exactly the same combination of DNA.