EESA10 midterm
1/320
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
321 Terms
Environment
is everything that affects a living organism
Factors of environment that effect human health
Air
Water
Soil
Biota
Manmade environment
(Created by society)
Genetic makeup and environmental factor are
independent risk factors
Models of gene-environment interaction
– Genetic makeup increases exposure to an
environmental risk factor
– Genetic makeup increases susceptibility to an
environmental risk factor
What is Environmental Health? (1)
According to the WHO:
“In its broadest sense, environmental health
comprises those aspects of human health,
disease and injuries that are determined or
influenced by factors in the environment.”
What is Environmental Health? (2)
According to the WHO:
“This includes the study of both the direct and the
indirect pathological effects of various:
❑ Chemical
❑ Biological
❑ Physical (only man-made)
Types of Hazards: Chemical Hazard
Chemicals in air, water, soil and food
Types of Hazards: Biological Hazard
Bacteria, viruses, parasites, allergens, animals such as bees and poisonous snakes
Types of Hazards: Physical Hazard (that are not environmental hazards)
Natural fires, tornados, hurricanes, volcanic eruptions, and earthquakes are not environmental health hazards (they are natural disasters or natural hazards)
Types of Hazards: Physical Hazard (that are environmental health hazards)
Housing, urban development, land use, transportation are environmental health hazards
Types of Hazards: Social or Behavioral Hazards and which are environmental health hazards
Poor diet, smoking, drugs, drinking, poverty are not environmental
health hazards (but the chemicals in a tobacco smoke are – second hand smoke)
Types of Hazards: Genetic Traits
Health risks associated with the chromosomal defect that causes
Down syndrome are not environmental health hazards
The Scope of Environmental Health
Core hazards:
Chemical
Biological
Physical
Hazards that influence core hazards:
genetic traits
social/behavioural
natural disasters
Boundaries are not sharp
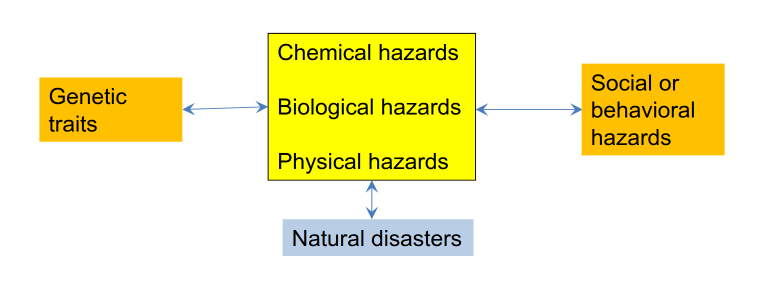
Core concerns of Environmental Health, Focus on
chemical, biological, physical hazards
Core concerns of Environmental Health, Interactions with
genetic traits and with social/behavioral stressors
Core concerns of Environmental Health, Emphasis on
anthropogenic hazards
Core concerns of Environmental Health, Much more than just
pollution
Core concerns of Environmental Health, As branch of public health, the field of environmental health takes a
population perspective
Key Themes of this Course
• We make the world we live in and we live in the
world we make
• People living a modern Western lifestyle create,
use, and dispose of lots of “stuff”
• In an ecosystem, nothing ever goes away
• Therefore, our “stuff” and its byproducts are
transported and transformed, but they do not
disappear
• There has often been a lack of foresight in
adopting new products and technologies
• The natural environment is globally connected;
trade and travel are increasingly globalized
• Global disparities in development and health are
enormous
• Western-style development is not sustainable at
a global scale
Environmental Crisis: Human
Alteration of Earth
Atmosphere: CO2 increased ___ since ____
30% since the beginning of the
Industrial revolution
Environmental Crisis: Human
Alteration of Earth
Hydrosphere:
Geosphere:
Biosphere:
Industrialization:
Overpopulation and Overconsumption:
Hydrosphere: Polluted lake
Geosphere:1/3 to 1/2 of the land surface has
been transformed by human action
Biosphere: Deforestation
Industrialization: Release of chemicals into atomsphere
Overpopulation and Overconsumption: strains resources and leads to environmental degradation, the excessive use of resources beyond what is needed or sustainable, exacerbates the problem by depleting resources and contributing to pollution
____________ is the clearest
indicator of environmental threats to human health
The declining health of other organisms
Decline in number of
frogs (no single
factor is responsible)
Increase UV
Traces of toxic
chemicals
Infections (fungi and
bacteria)
Predators
Environmental Health
Environmental factors are responsible for
25 % of all
preventable diseases
In developing countries ______ infections
are heading the list
In developing countries diarrhea and respiratory infections
are heading the list
Protecting the environment has been a
mainstream of public health practices since 1878
general populations for studying environmental health
rich & poor, African Americans & Hispanic & Whites, Developed & developing countries
New york city study:
African American, Hispanic and low income populations
have been found to have hospitalization and death rate from asthma 3-5 times higher than those for all New York City residence
Chemicals in new york study:
Pollutant, African Americans, Hispanic, Whites
Particulates 16.5 34.0 14.7
Carbon monoxide 46.0 57.1 33.6
Ozone 62.2 71.2 52.5
Sulfur dioxide 12.1 5.7 7.0
Lead 9.2 18.5 6.0
Two case studies on outdoor air pollution:
London smog, Indonesian fires
London case study:
The Great Smog of London in 1952 was a severe air pollution event that impacted the city for five days, from December 5th to 9th. It was caused by a combination of industrial emissions and specific weather conditions that trapped pollutants near ground level. The smog was so dense that it brought the city to a standstill and resulted in thousands of deaths, primarily due to respiratory illnesses, due to sulfure dioxide and smoke
Cause:
The smog was a result of a combination of factors. London's heavy reliance on coal for heating and industrial activities, coupled with a high-pressure weather system that created a temperature inversion (warm air trapping cooler, polluted air near the ground), led to a buildup of pollutants.
Impact:
The smog was incredibly dense, reducing visibility to near zero in many areas. Pedestrians and vehicles struggled to navigate the city, and public transportation was severely disrupted. The event resulted in an estimated 12,000 excess deaths, primarily due to respiratory problems.
Consequences:
The Great Smog led to the passage of the Clean Air Act in 1956, which aimed to reduce air pollution by regulating the use of coal and promoting cleaner energy sources. The event is also considered a turning point in public awareness and government action regarding air pollution
Indonesian fires
Use of fires to clear land for agriculture, due to severe drought of El Nino, resulted in an unprecedented fire episode where more than 9 million hectares of land were burnt in Indonesia. Smoke from the fires hung as a huge blanket over Southeast Asia, covering large cities such as Kuala Lumpur and Singapore, restricting traffic (air, sea and land) and causing a severe health hazard.
Sources of Outdoor Air Pollution types of pollutant sources
Human sources: stationary → factory
Human sources: mobile → transportation
Natural sources: Weather, geological events → Volcanoe erruption
Primary outdoor air pollutants
CO, CO2, SO2, NO, NO2, hydrocarbons, particulates
Secondary outdoor air pollutants
HNO2, HNO3, SO3, H2SO4, H2O2, O3, PANs, most NO3 and SO4 2- salts
Key major sources of major air pollutants from burining fossil fuels
Vehicles gasoline/diesel, Electrical power plants coal or oil, Heating for buildings oil or natural gas, Manufacturing coal oil or natural gas
All burning of fossil fuels produces
CO2, PM
Health Effects of Outdoor Air Pollution
The effects depend on the dose or concentration:
Asthma, Chronic bronchitis, Pulmonary emphysema
Health Effects of Outdoor Air Pollution, Caused or exacerbated by exposure to air pollution
–Lung Cancer
–Heart disease
–Toxic poisoning
–Eye irritation
–Birth defects
Asthma caused by
Particulates and/or SO2 can irritate bronchial passages leading to severe difficulties in breathing
Chronic bronchitis caused by
• Occurs when an excessive amount of mucus is produced in bronchi which
results in a lasting cough
• SO2 and smoking is related to Chronic bronchitis
Pulmonary emphysema caused by
• Weakening of the wall of alveoli, they become enlarged and
loss their resilience
• Shortness of breath is the primary symptom
• NO2 is related to emphysema
Seven common outdoor air pollutants ;
___- air pollutants:
____- air pollutant
• Primary air pollutants
– Particulate matter
– Carbon monoxide
– Nitrogen oxides
– Sulphur oxides
– VOC (Volatile Organic
Compounds)
– Lead
• Secondary air pollutant
– Ground level Ozone
Particulate Matter is:
Particles found in the air (dust, soot, smoke, and liquid droplets)
• Particulates classified by size
• PM10 —respirable
• PM2.5 —“fine” (mostly from combustion)
• Ultrafine particulates
Source of each type of PM:
Natural and mechanical sources → 2.5 to 10 microns
Combustion → 0.1 to < 2.5 microns
diesel combustion → < 0.1 microns
How each PM effects body:
respirable: settle in trachea and bronchi → removed via coughing
fine: reach small airways and aveoli → removed from aveoli
ultrafine: can pass into bloodstream
CO what it is and how it forms:
• Odourless, colourless gas
• Incomplete burning of carbon containing
fuels
• Heaters, woodstoves, gas stoves, fireplaces,
water heaters, automobile exhaust, and
tobacco smoke
• Fetuses, infants, elderly and people with heart
and respiratory illnesses are at high risk for
adverse health effects
What is confused for food poisoning or flu
carbon monoxide poisoning
Health Effects of Carbon Monoxide
• Interferes with the delivery of
oxygen in the blood to the rest of
the body
• Worsen cardiovascular conditions
• Fatigue
• Headache
• Weakness
• Confusion
• Disorientation, loss of coordination
• Nausea, Dizziness, Death
CO prevention
• Never leave a car engine running in a shed or
garage or in any enclosed space
• Proper selection, installation, and
maintenance of appliances
• Correct use of appliances
• Good ventilation
• Use CO detectors
Nitrogen Oxides (NOx), what is and how it forms
• Formed in any type of combustion process
• Involved in formation of ground level ozone
• Forms nitrate particles, and acid aerosols
what outdoor air pollutant forms acid rain and transports over long distances
Nitrate oxides
Sulphur Oxides (SOx), how it forms and how it is contaminant
• Burning of coal and oil, extraction of metals from ore
• SO2 dissolve in water vapour to form acids
• Acids react with other gases and particles and form
sulphates
• Transported over long distances
• Respiratory illnesses, aggravates existing heart and
lung diseases
Sulphur Oxides (SOx)
VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds), what it is and why contaminant
• Variety of organic compounds used as solvent
in industry, automobiles
• Hydrocarbons (HC): methane, butane,
propane
• Some produce photochemical smog
Lead (Pb) (outdoor air pollutant), what it is and why it is contaminant
• Metal
• Vehicles and industrial sources
• Leaded gasoline
• Deposit on soil and water
• Children accidentally can eat soil
• Particularly affects young children
(outdoor air pollutant) Lead is ____, effects are :
• Lead is neurotoxicant
– Effects on
• IQ, cognitive & neurological performance more
broadly
• Cardiovascular mortality, increased lung cancer
risk, kidney toxicity, high blood pressure,
reproductive effects, and oral health impacts
– Heavier burden of exposure on poor,
nonwhite populations
Ozone (O3) equation:
VOC + NOx + Heat + Sunlight = Ozone
O3 formations
• Summertime pollutant, time of the day, seasonal, climate
• Good in stratosphere
• Bad on a ground
• Transported on long distances
O3 effects
• Lung damage (small airways)
• Shortness of breath, chest tightness, coughing and nausea
• Irritate and damaged eyes, nose, sinuses and throat
• Problem for people who exercise outdoors during the
concentration pick
What is smog, types of smog
• Smoke + fog = Smog (first used in 1905 in
England)
• Sulphurous smog- London type of smog or
industrial smog
• Photochemical smog - L.A. type of smog or
brown air
formation of photochemical smog
transportation creates NO, factories and gas stations create carbon dioxide and hydrocarbons. Reactions occur in atmosphere with compounds. Brown smog is formation of Nitric acid, PANs, formaldehyde and other aldehydes and Ozone with solar energy.
indoor air pollution vs outdoor
• Contains 2-5 times higher concentration of hazardous
pollutants than outdoor air
Sick building syndrome definition
– Nonspecific symptoms experienced by occupants
of a building
“Sick building” designation
– A building whose occupants experience such
symptoms
Building-related illness
– Specific diagnosable illness, linked to specific
feature of building
Sick Buildings Syndrome most likely cause is ____ with __ %
Inadequate venting with 53 %
Probable causes of sick building syndrome
Inside source, outside source, microbiological, building material, inadequate venting, unknown
Health effects of Indoor Air Pollution
• Hard to detect by our senses
• Symptoms are similar,
need years to develop
• Headaches, tiredness, dizziness, nausea, itchy nose, scratchy throat
• Asthma
• Cancer
Six Common Indoor Air Pollutants
• Asbestos
• Formaldehyde
• Mold and Moisture
• Secondhand Smoke
• Radon Gas
• Air Dust
Asbestos
• Group of six different
fibrous minerals
• Have separable, long,
strong and flexible
heating resistant fibers
Asbestos in the Environment how it contaminates
• Do not evaporate into air or dissolve in water,
do not break down
• Fibers and particles may remain suspended in
the air and carried long distances
• Not able to move through soil
What abestos is used in
• Used in:
– Building materials (roofing
shingles, ceilings and floor tiles,
paper products, and asbestos
cement products)
– Friction products (automobile
brakes and transmission parts)
– Heat resistant fabrics,
packaging and coatings
How might you be exposed to asbestos?
• In industrialized countries, nearly everyone has
asbestos fibers in their lungs
– Some risk of cancer
• People working in some industries
• People living near these industries
• During demolition work and remodeling
• From drinking water
(natural sources or asbestos
containing cement pipes)
Health Effects of Asbestos in body
- Affect the lungs and the membrane that surrounds the lungs
-Abestosis
- Plaques in the pleural membranes
- Lung cancer, mesothelioma
- Increase risk of getting other types of cancer
(stomach, esophagus, pancreas, kidney)
- Risk increases with smoking
Asbestosis
• Asbestosis- Scar-like tissue, not in
general public
– difficulty breathing,
– often cough,
– heart enlargement
– lead to disability and death
Formaldehyde, what it is and how it forms
• Volatile organic
compound (VOC),
naturally occurring gas,
colourless, and strong
smell
• Becomes a gas at normal
room temperature
• Also released by burning
wood and natural gas, by
automobile and by
cigarettes
Where formaldehyde is used (indoor air pollution)
Glue or adhesives in pressed
wood products (particleboards,
MDF, plywood)
• Preservatives in some paints
and cosmetics
• Coatings that provide
permanent press quality to
fabrics and draperies
• Finish used to coat paper
products
• Certain insulation materials
Health Effects of Formaldehyde
• Allergic reactions
– Watery eyes, burning sensation in the eyes, nose
and throat
– Skin rashes
• Nausea
• Coughing
• Chest tightness
• Asthmatic reactions
• Cancer
• Some people very
sensitive
Mold and Moisture how it forms and where it forms
• Need moisture, does not
need standing water, just
requires high relative air
humidity
– Bathrooms and
kitchens
– Gym areas
– Locker rooms
– Leaky roof areas
– Damp basements
– On or within wood,
paper, carpet and
foods
Mold Health Effects
• Major source of indoor allergens
• Trigger asthma
• Produce Toxins
• Produce Irritants
Mold and Moisture, how to identify and remove
• The way to control indoor mold growth is to
control moisture (maintaining the relative
humidity between 30-60%)
• Often undiscovered
• Produce tiny spores
• Discoloration and odour problems
Second hand smoke contains ___ compounds, __ are carcinogens
Contain 4 000 compounds (CO and Formaldehyde), 40 are carcinogens
A non-smoker exposed to secondhand smoke
has a ___ increased chance of developing lung
cancer
25%
Health Canada estimates that more than ___
non-smokers die from lung cancer each year
because of such exposure
300
• Environmental tobacco smoke (secondhand smoke) effects on adults and children and why concern:
– Adults: heart disease, heart attack, lung cancer,
hearing loss, eyes, nose and throat irritation
– Children: SIDS, asthma, pneumonia, bronchitis,
ear infection and hearing loss
• Smoking is on the rise in less developed
countries
Third hand smoke
smoke that gets on clothing and furniture
Radon Gas, what it is and how it occurs
● Colorless, odorless, tasteless
● Naturally occurring
● Radioactive decay of uranium
● From soil and rock into
basements and lower floors
indoor air
● Dissolved in groundwater,
pumped into wells and then
into homes
● In construction building
blocks
Radon Gas in Buildings, how it occurs and why hazard
– Begins series of rapid breakdowns
– Radon and some progeny are alpha emitters;
lung cancer risk
– Often simple to detect and
remediate
Air Dust, how it occurs and why concern
• Heating and cooling -forced air system
• Dust particles
• Pollen or other debris
• Duct Cleaning Service Providers
cause exposures to :
Dust Mites, Pollen, Mold, Pet Dander, Bacteria / Viruses
Why earth is called Liquid Natural Capital:
• The Earth is a water planet
• Water covers 71% of the Earth’s surface
• Mostly salty water
• No species can live without water
• Sculpting the Earth’s surface
• Moderating climate
• Removing and diluting wastes and pollutants
major environmental concerns of water
Quantity of water, Quality of water
__ % is readily available fresh water
0.014%
most water is in the world at __ %
ocean and saline water at 97.4%
____ % is fresh water in the world with _ % is ice caps
2.6 % with 1.984 % ice caps
Water stress
<1700 cubic meters/year/person
Water scarcity
<1000 cubic meters/year/person
Some areas have lots of water but
the largest rivers are far from agricultural and population centers
Lots of precipitation arrives during a short period but
cannot be collected and stored