UNIT 9 FLASHCARDS
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/24
Last updated 12:46 PM on 5/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
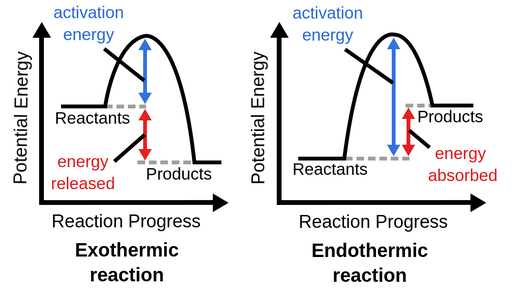
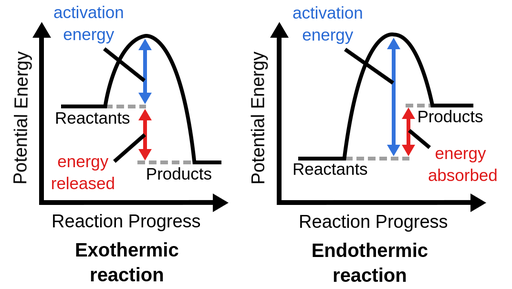
activation energy
the amount of energy needed for a reaction to begin
2
New cards
calorimeter
an insulated container used to determine the amount of energy exchanged during a chemical reaction or physical process
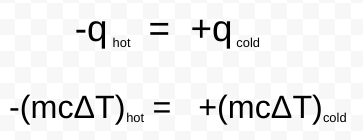
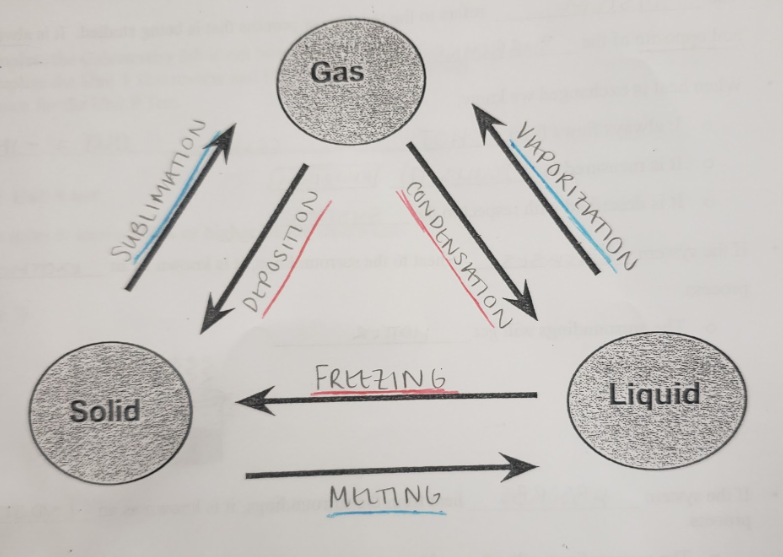
3
New cards
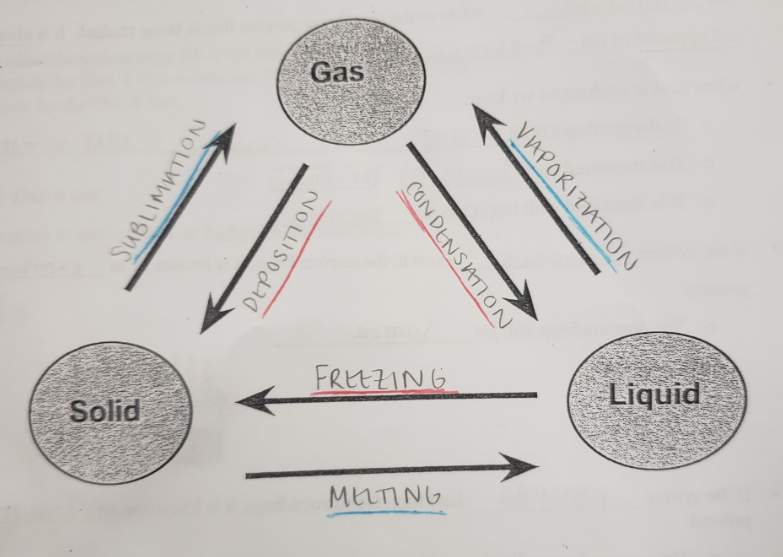
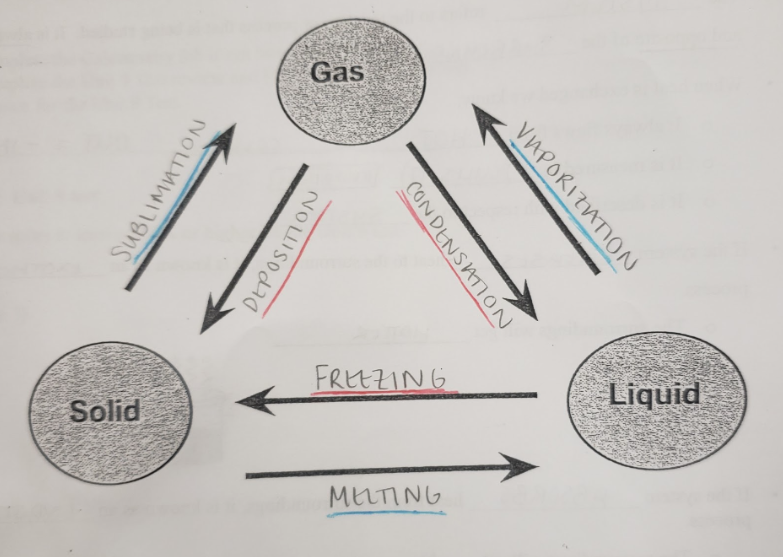
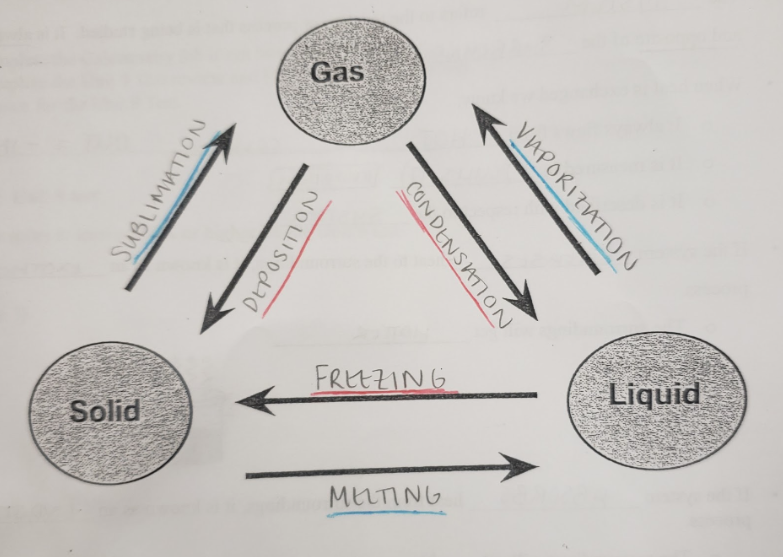
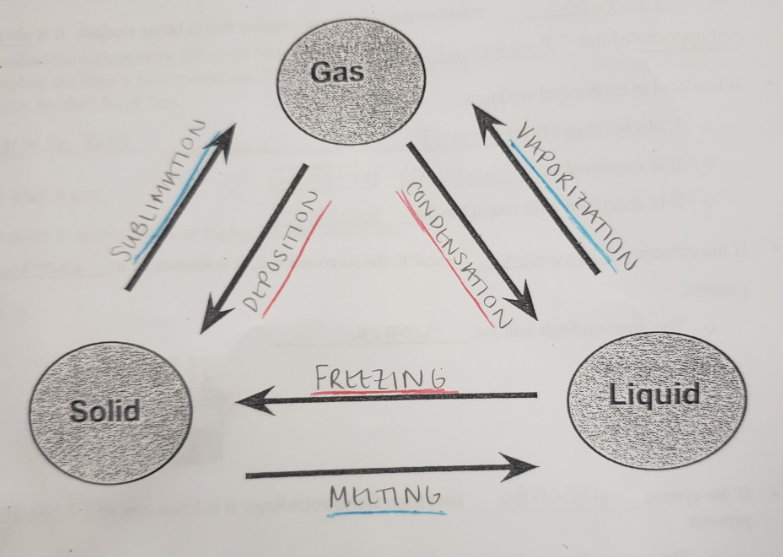
condensation
the transition of gaseous particles to liquid particles through a decrease in temperature
4
New cards
deposition
the transition of gaseous particles to solid particles through a decrease in temperature
5
New cards
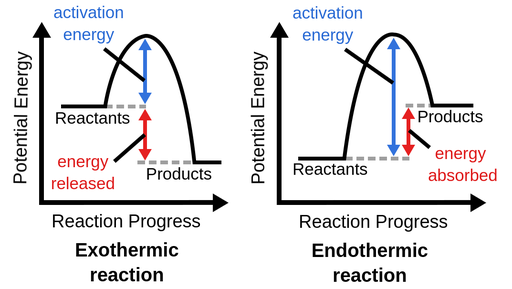
endothermic
a reaction in which energy is absorbed as heat from the surroundings
6
New cards
energy diagram
graph which shows the changes in enthalpy that occur during the progress of a reaction
7
New cards
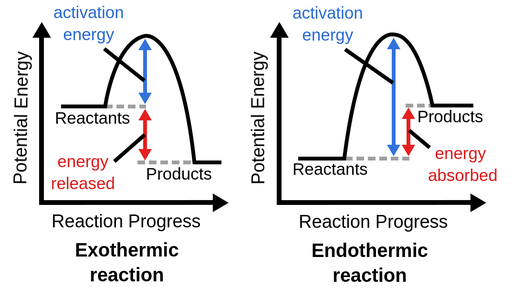
enthalpy
the amount of heat exchanged between reactants and products during a chemical reaction
8
New cards
entropy
the measure of dispersal or randomness of particles in a system

9
New cards
exothermic
a reaction in which energy is released as heat to the surroundings
10
New cards
freezing
the transition of liquid particles to solid particles through a decrease in temperature
11
New cards
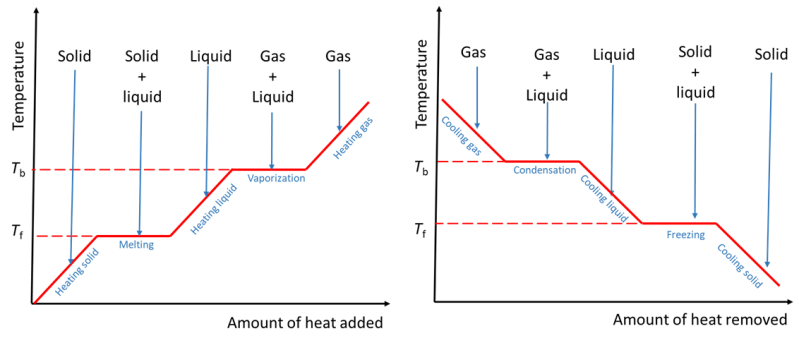
heating curve
graphically shows the phase changes that occur with an increase in temperature
12
New cards
heat of fusion
the amount of energy required to melt on more of solid
13
New cards
heat of vaporization
the amount of energy required to boil one more of a liquid
14
New cards
joule
the SI unit used to measure heat or energy
15
New cards
law of conservation of energy
states that energy cannot be created nor destroyed
16
New cards
melting
the transition of solid particles to liquid particles through an increase in temperature
17
New cards
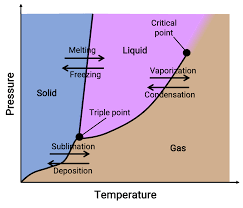
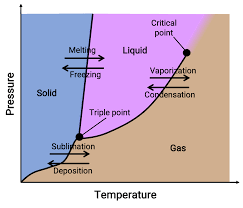
phase diagram
graph that shows the phases of a substance under different conditions of pressure and temperature
18
New cards
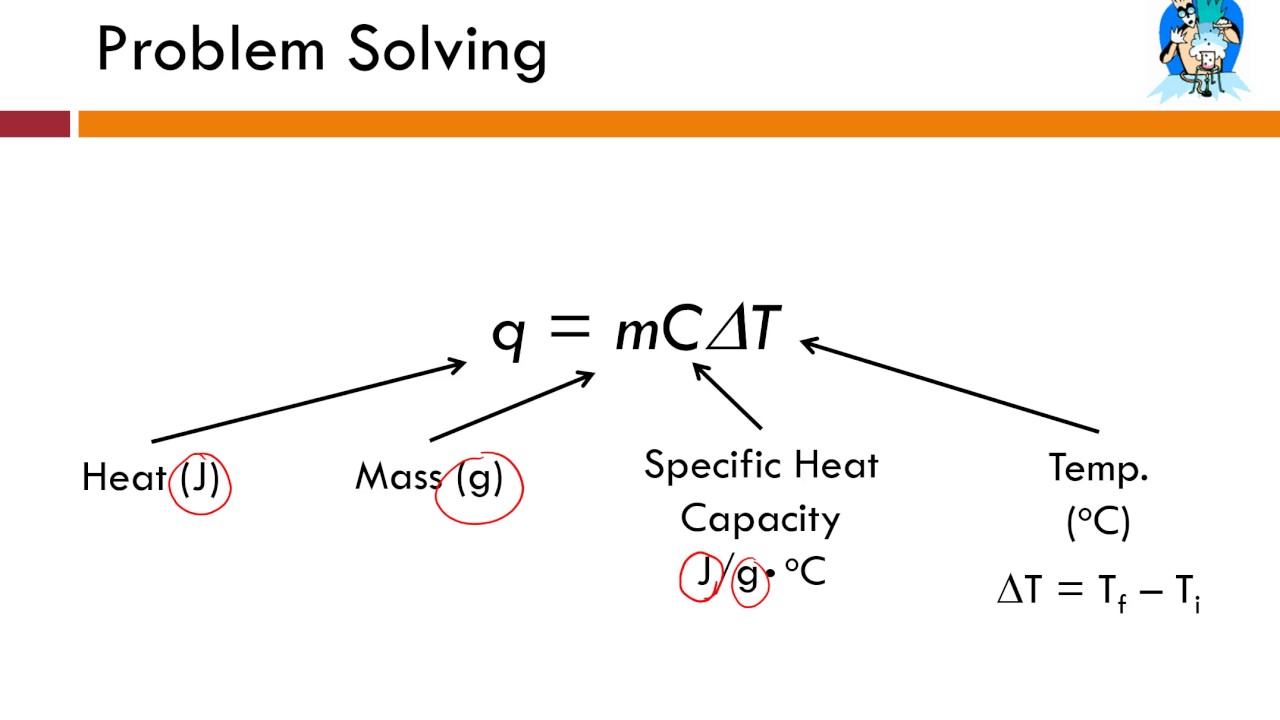
specific heat
the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by 1°C
19
New cards
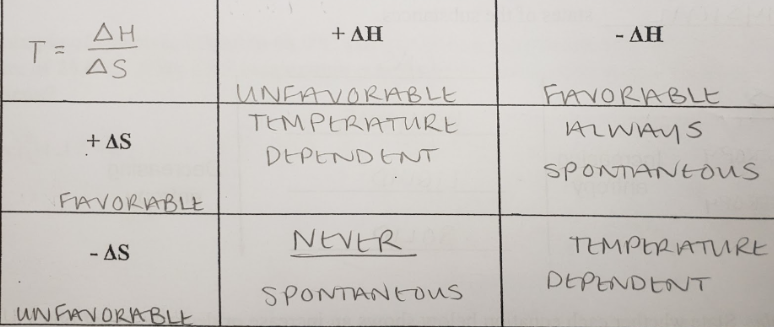
spontaneous
a reaction or process that can occur without outside intervention
20
New cards
sublimation
the transition of solid particles to gaseous particles through an increase in temperature
21
New cards
system
refers to the reaction or process being observed
22
New cards
thermochemistry
the study of energy exchanges during reactions or processes
23
New cards
transition state
an intermediate structure during the course of a reaction which is no longer reactant but not yet product
24
New cards
triple point
the conditions at which all three phases of matter exist at the same time
25
New cards
vaporization
the transition of liquid particles to gaseous particles through an increase in temperature