dermatology
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms

ID
Atrophie blanche
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong> allergy–cross sensitivities to griseofulvin </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f6d53c19-cf5d-45c9-921b-52ef035c372b.png)
[...] allergy–cross sensitivities to griseofulvin
Penicillin
[What demographic?]
seldom have tinea pedis or onychomycosis but are prone to eczema
Children
![<p><span>Weeping vesicles on erythematous plaques of acute <strong>[...]</strong> </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8ed2458c-e909-4e87-a1ff-3738417a2bc6.png)
Weeping vesicles on erythematous plaques of acute [...]
neurodermatitis
![<p>Atrophie Blanche</p><ul><li><p>Common skin disorder<br></p><ul><li><p>1-5% normal population</p></li><li><p>38-87% patients with <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>75% patients with recurrent venous leg ulcers </p></li></ul></li><li><p>More frequent in <span>women</span> (4:1 Ratio)</p></li><li><p>Extremely painful ulcers in acute stage</p></li><li><p><strong>mostly lower legs and perimalleolar regions. <br></strong></p></li><li><p>Skin changes permanent<br></p><ul><li><p>White atrophic scars-not painful </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e51577ea-1176-4fcb-a988-02c68b0f40bb.png)
Atrophie Blanche
Common skin disorder
1-5% normal population
38-87% patients with [...]
75% patients with recurrent venous leg ulcers
More frequent in women (4:1 Ratio)
Extremely painful ulcers in acute stage
mostly lower legs and perimalleolar regions.
Skin changes permanent
White atrophic scars-not painful
chronic venous insufficiency
Atrophie Blanche
Common skin disorder
1-5% normal population
38-87% patients with chronic venous insufficiency
75% patients with recurrent venous leg ulcers
More frequent in [what gender?] (4:1 Ratio)
Extremely painful ulcers in acute stage
mostly lower legs and perimalleolar regions.
Skin changes permanent
White atrophic scars-not painful
women
![<p><span>Classical Kaposi’s sarcoma is seen more often in <strong>[what ethnicity?]</strong></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8c7788ed-befa-46b5-86b8-6f660d949bd4.png)
Classical Kaposi’s sarcoma is seen more often in [what ethnicity?]
Mediterranean people
![<p><strong><u>Cutaneous Disease Distribution </u></strong></p><ul><li><p>Arms <br></p><ul><li><p>Flexor: <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>Extensor: <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li><li><p>Legs <br></p><ul><li><p>Flexor: <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>Extensor knee: <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/34385342-4914-4d8e-b5be-1b4790a6429b.png)
Cutaneous Disease Distribution
Arms
Flexor: [...]
Extensor: [...]
Legs
Flexor: [...]
Extensor knee: [...]
atopic dermatitis
psoriasis
atopic dermatitis
psoriasis
![<p><strong><u>Cutaneous Disease Distribution </u></strong></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[Where are these usually found?]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>Tinea pedis</p></li><li><p>onychomycosis</p></li><li><p>pressure keratoses</p></li><li><p>warts </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d6c0c6ef-3768-42d8-ab5e-5236fcefd1ac.png)
Cutaneous Disease Distribution
[Where are these usually found?]
Tinea pedis
onychomycosis
pressure keratoses
warts
Feet
![<p><strong><u>Cutaneous Disease Distribution </u></strong></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[Where are these usually found?]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p>Tinea cruris</p></li><li><p>discharge</p></li><li><p>ulceration </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6e84cdce-0100-46b0-9fc5-769257f21dbe.png)
Cutaneous Disease Distribution
[Where are these usually found?]
Tinea cruris
discharge
ulceration
Groin
![<p><strong><u>Cutaneous Disease Distribution </u></strong></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[Where are these usually found?]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p>Warts</p></li><li><p>paronychia</p></li><li><p>tinea manum</p></li><li><p>punctate keratoderma </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1505173f-9bb6-4b32-beea-0923766b97d9.png)
Cutaneous Disease Distribution
[Where are these usually found?]
Warts
paronychia
tinea manum
punctate keratoderma
Hands
Cutaneous larvae migrans from stepping in [...]
cat feces
![<p>Dermatophytid Reaction</p><ul><li><p>Called <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> when associated with a corresponding infectious process due to bacteria </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/26bd8365-9182-4a26-a574-cddecac1f937.png)
Dermatophytid Reaction
Called [...] when associated with a corresponding infectious process due to bacteria
Bacterid
Duration in days suggests [...] process and cool soaks, sprays or lotion are indicated.
Present for weeks means it is [...] and creams often work best.
Present for months is definitely a [...] condition and may respond better with ointment vehicle
acute
subacute
chronic
Duration in days suggests acute process and cool soaks, sprays or lotion are indicated.
Present for weeks means it is subacute and [...] often work best.
Present for months is definitely a chronic condition and may respond better with [...] vehicle
creams
ointment
![<p><span>Heel pain and paronychia may be <strong>[...]</strong></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7386fc31-49d5-4a76-9f77-3f7780da9b23.png)
Heel pain and paronychia may be [...]
Reiter’s disease
Paronychia is a nail infection that is an often tender bacterial or fungal infection of the hand or foot
Reactive arthritis, formerly known as Reiter's syndrome, is a form of inflammatory arthritis that develops in response to an infection in another part of the body (cross-reactivity).
![<p><span>Lacy white network on buccal mucosa in <strong>[...]</strong></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/73f11485-022d-4349-90a6-835a802b96f1.png)
Lacy white network on buccal mucosa in [...]
lichen planus
![<p><span>Palmar plantar plaques may suggest <strong>[...]</strong> </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6033349e-140c-48d9-9b9d-e8f0dffb6aec.png)
Palmar plantar plaques may suggest [...]
syphilis
![<p><span>Pruritus or generalized itching is worsened by <strong>[...]</strong> in eczemas and anemias </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ee83bcfd-d932-4f8d-871c-5e9b525d172a.png)
Pruritus or generalized itching is worsened by [...] in eczemas and anemias
hot
read the bottom of this slide
![<p><span>Purple plaques or nodules may be <strong>[...]</strong> </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/44081bda-9513-44a7-98b8-b7a593fbf482.png)
Purple plaques or nodules may be [...]
Kaposi’s sarcoma
associated with AIDS
![<p><span>Suspect <strong>[...]</strong> in any bizarre, extensive or surprisingly recurrent skin disease even psoriasis, tinea and onychomycosis </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3c8badaa-ceac-4631-b67b-8628e97f0bd9.png)
Suspect [...] in any bizarre, extensive or surprisingly recurrent skin disease even psoriasis, tinea and onychomycosis
AIDs
![<p><span>Volleyball and basketball can cause <strong>[...]</strong> or <strong>[...]</strong></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/024e4736-b546-44bc-813f-196f847b2455.png)
Volleyball and basketball can cause [...] or [...]
talon noir or black heel
![<p><span>Xerosis (dry skin) & skin cancer is more common in <strong>[What ethnicity?]</strong> </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fbdab86b-67f5-4f73-bcab-914d0fd79bf2.png)
Xerosis (dry skin) & skin cancer is more common in [What ethnicity?]
Celtic people
![<p><span><strong>[What ethnicity?]</strong> have higher incidence of </span><strong>palmar plantar punctate keratodermas (KPPP)</strong></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/380b0b0f-b284-485c-98ba-2435d68b4548.png)
[What ethnicity?] have higher incidence of palmar plantar punctate keratodermas (KPPP)
African American people
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>Genetic predisposition to allergic rhinitis, hay fever, asthma, sensitive skin or urticaria</p></li><li><p>Predisposed to itch or scratch </p></li><li><p>Frequent history of <span>milk allergies</span> as a newborn </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fd03531c-9148-46a2-945f-ff9e36324893.png)
[...]
Genetic predisposition to allergic rhinitis, hay fever, asthma, sensitive skin or urticaria
Predisposed to itch or scratch
Frequent history of milk allergies as a newborn
Atopy of atopic dermatitis
![<p><span>Atopy of atopic dermatitis</span></p><ul><li><p>Genetic predisposition to allergic rhinitis, hay fever, asthma, sensitive skin or urticaria</p></li><li><p>Predisposed to itch or scratch </p></li><li><p>Frequent history of <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> as a newborn </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8a6efe53-72e0-490c-8541-7ee0d76b03cc.png)
Atopy of atopic dermatitis
Genetic predisposition to allergic rhinitis, hay fever, asthma, sensitive skin or urticaria
Predisposed to itch or scratch
Frequent history of [...] as a newborn
milk allergies
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>Secondary skin eruption that is an expression of immune hypersensitivity to a dermatophyte fungal antigen<br></p><ul><li><p>extremely pruritic, erythematous, maculopapular, or papulovesicular eruption occurs 1-2 weeks <span>after</span> primary infection</p></li><li><p>4-5% of patients with dermatophyte infections</p></li><li><p>37% of patients with stasis dermatitis </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a2e244b4-8863-436c-b8cc-121dfda9dc0d.png)
[...]
Secondary skin eruption that is an expression of immune hypersensitivity to a dermatophyte fungal antigen
extremely pruritic, erythematous, maculopapular, or papulovesicular eruption occurs 1-2 weeks after primary infection
4-5% of patients with dermatophyte infections
37% of patients with stasis dermatitis
Dermatophytid Reaction
![<p><span>Dermatophytid Reaction</span></p><ul><li><p>Secondary skin eruption that is an expression of immune hypersensitivity to a dermatophyte fungal antigen<br></p><ul><li><p>extremely pruritic, erythematous, maculopapular, or papulovesicular eruption occurs 1-2 weeks <span><strong>[before or after]</strong></span> primary infection</p></li><li><p>4-5% of patients with dermatophyte infections</p></li><li><p>37% of patients with stasis dermatitis </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/588928d8-5c80-4a8f-84b9-b7e268156b8d.png)
Dermatophytid Reaction
Secondary skin eruption that is an expression of immune hypersensitivity to a dermatophyte fungal antigen
extremely pruritic, erythematous, maculopapular, or papulovesicular eruption occurs 1-2 weeks [before or after] primary infection
4-5% of patients with dermatophyte infections
37% of patients with stasis dermatitis
after
[What demographic often have the following conditions?]:
Solar damage
actinic keratoses
skin cancer
xerosis (dry skin)
nail dystrophies
infection
pressure keratoses
ulcers
Elderly often have:
actinic keratosis is a rough, scaly patch on your skin that develops from years of exposure to the sun
Pressure-related hyperkeratosis occurs as a result of excessive pressure, inflammation or irritation to the skin. When this happens, the skin responds by producing extra layers of keratin to protect the damaged areas of skin
[where would you find the following?]:
Actinic Keratoses
melasma
xanthelasma
spider angiomas
rosacea
acne
peleche
psoriasis
seborrheic dermatitis
Face:
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong> useful to distinguish warts from corns </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/132bfb06-4121-4d28-9254-3363c899efa9.png)
[...] useful to distinguish warts from corns
[...] useful to distinguish warts from corns
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p><ul><li><p>any of several generalized skin disorders due to a genetically caused molecular defect in keratinization process <strong>resulting in retention of keratinocytes rather than normal desquamation</strong> </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3a65c393-6314-4b35-895b-a78c74e5c1df.png)
[...]
any of several generalized skin disorders due to a genetically caused molecular defect in keratinization process resulting in retention of keratinocytes rather than normal desquamation
Ichthyosis
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> grouping: </p><ul><li><p>Lymphangiitis</p></li><li><p>contact dermatitis due to poison ivy</p></li><li><p>shin excoriations from itching xerotic skin </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d14a2a16-e284-4d41-b51a-0bac2ed080d4.png)
[...] grouping:
Lymphangiitis
contact dermatitis due to poison ivy
shin excoriations from itching xerotic skin
Linear
[What demographic] exhibit more
Contact dermatitis
mechanical keratoses
tinea
eczemas
Middle age
![<p><span><strong>[where would you find the following?]</strong></span>: </p><ul><li><p>leukoplakia - precancer</p></li><li><p>Wickham’s striae-lichen planus</p></li><li><p>scrotal tongue - congenital central furrow and lateral transverse grooves</p></li><li><p>Hairy tongue - black hairs of Aspergillus fungus </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/75385a73-fe41-40df-a075-76f8846187fa.png)
[where would you find the following?]:
leukoplakia - precancer
Wickham’s striae-lichen planus
scrotal tongue - congenital central furrow and lateral transverse grooves
Hairy tongue - black hairs of Aspergillus fungus
Oral Cavity
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> can be triggered by</p><ul><li><p>Chlorpromazine</p></li><li><p>griseofulvin</p></li><li><p>tetracycline </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cbea1dbe-dcdb-44a6-a3ee-5c54132b5562.png)
[...] can be triggered by
Chlorpromazine
griseofulvin
tetracycline
Solar urticaria hypersenstivity
Solar urticaria, also known as sun allergy, is a rare allergy to sunlight that causes hives to form on skin that's exposed to the sun
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong> is abnormal dryness of the skin </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a3acd422-1b02-489e-aeb8-5524a2b20ebc.png)
[...] is abnormal dryness of the skin
Xerosis
![<p><span><strong>[What demographic]</strong></span> often have</p><ul><li><p>Verrucae (painful wart) </p></li><li><p>IGTNs (ingrown toenail)</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ee77c712-6bf4-49a5-9c3a-da5d02c9aad3.png)
[What demographic] often have
Verrucae (painful wart)
IGTNs (ingrown toenail)
Young adults
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong> grouping: Lesions in broad bands following dermatome. </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a01c955f-4dbd-4a67-b392-d7a29be5fb79.png)
[...] grouping: Lesions in broad bands following dermatome.
Zosteriform
![<p><span>Silver scaly large plaque of <strong>[...]</strong> </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d50d206b-d297-4227-8fcb-e0a491f84893.png)
Silver scaly large plaque of [...]
psoriais
![<p><span>Hyperkeratotic annular plaques of <strong>[...]</strong>; chronic and pruritic </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7061f500-7f3d-4ca5-8916-4a931b56ab28.png)
Hyperkeratotic annular plaques of [...]; chronic and pruritic
Tinea pedis
![<p>A (max of 5 points) = total area of involvement</p><ul><li><p>1 point – <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> to <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> of nail</p></li><li><p>2 point – <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> to <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> of nail</p></li><li><p>3 point – <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> to <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> of nail</p></li><li><p>4 point – <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> to <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> of nail</p></li><li><p>5 point – <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> of nail </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8ab730f6-8ca2-4a69-b83f-cded5c281f09.png)
A (max of 5 points) = total area of involvement
1 point – [...] to [...] of nail
2 point – [...] to [...] of nail
3 point – [...] to [...] of nail
4 point – [...] to [...] of nail
5 point – [...] of nail
1 to 10%
11 to 25%
26 to 50%
51 to 75%
more than 75%
![<p>Additional 10 points if nail dystrophies are present</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> – <span>longitudinal streaking or patches</span></p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> – <span>Thick nails (> 2 mm)</span> </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9800bcff-3525-40b5-8cd6-8790f6abdf92.png)
Additional 10 points if nail dystrophies are present
[...] – longitudinal streaking or patches
[...] – Thick nails (> 2 mm)
Dermatophytoma
Subungual Hyperkeratosis
Additional 10 points if nail dystrophies are present
Dermatophytoma – [...]
Subungual Hyperkeratosis – [...]
longitudinal streaking or patches
Thick nails (> 2 mm)
Benign nevus or malignant melanoma? Use acronym ABCDE
A = [...]
B = [...]
C = [...]
D = [...]
E = [...]
A = Asymmetry
B = Border irregularity with blurred, notched or ragged edges
C = Color (variation indicates melanoma)
D = Diameter (greater than 6 mm (pencil top eraser) is suspicious)
E = Elevation and Evolution
![<p>Dermoscopy</p><ul><li><p>Survey <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> to the tip of the toes </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0baec0a3-f018-4a60-9bf1-fa893dfdc7d8.png)
Dermoscopy
Survey [...] to the tip of the toes
tibial tubercle
![<p>Dermoscopy</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> has a pigment network (honey combed grid network)</p></li><li><p><span>Dried blood</span> is easily cut away</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/507933b5-c75c-4a52-b4f9-4a4c432683fd.png)
Dermoscopy
[...] has a pigment network (honey combed grid network)
Dried blood is easily cut away
Melanin
![<p>Dermoscopy</p><ul><li><p><span>Melanin</span> has a pigment network (honey combed grid network)</p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> is easily cut away</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/dbf015c0-827b-492c-a096-2f6ae0d5d94c.png)
Dermoscopy
Melanin has a pigment network (honey combed grid network)
[...] is easily cut away
Dried blood
![<p><span>Erosions: usually seen <strong>[where?]</strong></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/969e116f-29ff-4831-8907-0a28cf8bfc0a.png)
Erosions: usually seen [where?]
in between toes
![<p><span>Following occurs more in <strong>[what gender?]</strong>:</span></p><ul><li><p>Vasospastic disorders</p></li><li><p>atrophy blanche</p></li><li><p>stasis dermatitis </p></li><li><p>diabetic dermopathies </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5b0d9ea0-677e-4f84-8a51-93248d8b22d8.png)
Following occurs more in [what gender?]:
Vasospastic disorders
atrophy blanche
stasis dermatitis
diabetic dermopathies
females
Following occurs more in [what gender?]:
Keratoderma blenorrhagicum of Reiter’s
tinea
onychomycosis
males
Keratoderma blenorrhagicum is the most common skin lesion of reactive arthritis or Reiter's sydnrome. Typically these scaly lesions occur on the palms and soles and are thought to be indistinguishable clinically and histologically from pustular psoriasis.
![<p><span>If melanin, what are the 3-point checklist?</span></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c6bf0a00-3f3b-470c-bde8-b7512e41cd65.png)
If melanin, what are the 3-point checklist?
[...]
[...]
[...]
Asymmetry
Atypical network
Blue-white structures
![<p>Interpreting KOH</p><ul><li><p>Mold appear as <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>Candida albicans is characterized by <span>pseduohyphae</span><br></p><ul><li><p>Terminally segmented, shorter rectangular buds </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5eb69243-7e4f-483e-8505-ea485250d64d.png)
Interpreting KOH
Mold appear as [...]
Candida albicans is characterized by pseduohyphae
Terminally segmented, shorter rectangular buds
very large flat ribbons (aerial hyphae)
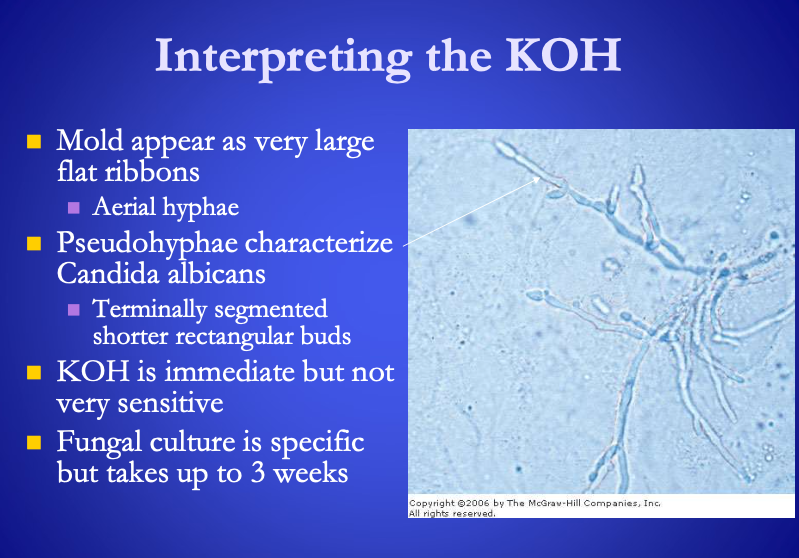
Interpreting KOH
Mold appear as very large flat ribbons (aerial hyphae)
Candida albicans is characterized by [...]
Terminally segmented, shorter rectangular buds
pseduohyphae
![<p>KOH wet mount Artifacts</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> – mosaic pattern</p></li><li><p><span>Air bubbles</span> – dark outline & central clear space </p></li><li><p>KOH crystals are long and thin</p></li><li><p>Cotton fibers are large, long rough tipped stalks</p></li><li><p>Synthetic fibers are smooth long and curving</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0be7c176-c9e8-4b23-9c6b-019e6720e138.png)
KOH wet mount Artifacts
[...] – mosaic pattern
Air bubbles – dark outline & central clear space
KOH crystals are long and thin
Cotton fibers are large, long rough tipped stalks
Synthetic fibers are smooth long and curving
Lipids
![<p>KOH wet mount Artifacts</p><ul><li><p><span>Lipids</span> – mosaic pattern</p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> – dark outline & central clear space </p></li><li><p>KOH crystals are long and thin</p></li><li><p>Cotton fibers are large, long rough tipped stalks</p></li><li><p>Synthetic fibers are smooth long and curving</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/961093c1-c8a0-4f56-8594-c80e5a94293c.png)
KOH wet mount Artifacts
Lipids – mosaic pattern
[...] – dark outline & central clear space
KOH crystals are long and thin
Cotton fibers are large, long rough tipped stalks
Synthetic fibers are smooth long and curving
Air bubbles
KOH wet mount Diagnostic Techniques
Procedure
Apply 2 drops of either [...] or [...]
Let stand for 5 to 10 mins
Cover slip and observe with reduced light on low power
Scan for thick scales of keratin
Diagnostic narrow segmented branching hyphae of dermatophyte
Resembles pearls on a string
Chlorozol black E fungal stain or 20% KOH and DMSO
KOH wet mount Diagnostic Techniques
Procedure
Apply 2 drops of either Chlorozol black E fungal stain or 20% KOH and DMSO
Let stand for 5 to 10 mins
Cover slip and observe with reduced light on low power
Scan for thick scales of keratin
Diagnostic [...] branching hyphae of dermatophyte
Resembles [...]
narrow segmented
pearls on a string
![<p>Onychomycosis Severity Index (OSI)</p><ul><li><p>Index to quantify progression of nail fungal treatment</p></li><li><p>Maximum of <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> points</p></li><li><p>OSI = <span><strong>[...]</strong></span>*<span><strong>[...]</strong></span> (<span><strong>[...]</strong></span>) </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e559331e-49cb-4338-936f-894c13c2bab2.png)
Onychomycosis Severity Index (OSI)
Index to quantify progression of nail fungal treatment
Maximum of [...] points
OSI = [...]*[...] ([...])
35
OSI = (A)*(P) (+10?)
![<p>OSI related to onychomycosis</p><ul><li><p>Mild: <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> to <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> points</p></li><li><p>Moderate: <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> to <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> points</p></li><li><p>Severe: <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> to <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> points </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b89675ce-05d3-4260-89cb-91fd5d6bc6f0.png)
OSI related to onychomycosis
Mild: [...] to [...] points
Moderate: [...] to [...] points
Severe: [...] to [...] points
Mild: 1 to 5 points
Moderate: 6 to 15 points
Severe: 16 to 35 points
![<p>P (max of 5 points) = proximity to nail matrix</p><ul><li><p>1 point – <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>2 point – <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>3 point – <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>4 point – <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>5 points – <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3cbc4b62-b817-4ad4-8baf-3c3f6e3a7b53.png)
P (max of 5 points) = proximity to nail matrix
1 point – [...]
2 point – [...]
3 point – [...]
4 point – [...]
5 points – [...]
1 point – Distal rectangle
2 point – Rectangle #2
3 point – Rectangle #3
4 point – Rectangle #4
5 points – Lunula
![<p><span>Past medical history of hyperuricemia, gout or allopurinol or cholchicine suggest: </span></p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/929b9aae-e5a8-448a-a6cd-b87a916d1425.png)
Past medical history of hyperuricemia, gout or allopurinol or cholchicine suggest:
[...]
Tophaceous nodules tumors and ulcers
Hyperuricemia is an excess of uric acid in the blood
Allopurinol is used to treat gout or kidney stones, and to decrease levels of uric acid in certain cancer patients
Colchicine is an oral drug used to treat or prevent gout symptoms
![<p><span>Past medical history of <strong>[what might cause the following?]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>Cutaneous somatization disorder</p></li><li><p>neurodermatitis</p></li><li><p>lichen simplex chronicus </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c7cfefd2-9c4f-4203-ac31-a831d4cbcb98.png)
Past medical history of [what might cause the following?]
Cutaneous somatization disorder
neurodermatitis
lichen simplex chronicus
Anxiety and obsessive compulsive behavior
unexplained cutaneous sensory syndromes especially the cutaneous dysesthesias associated with pain, numbness and pruritus; traumatic memories in post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) which are experienced on a sensory level as 'body memories' and may present as local or generalized pruritic states
Neurodermatitis is a skin condition characterized by chronic itching or scaling (can be triggered by anxiety)
Lichen simplex chronicus (LSC) is a localized, well-circumscribed area of thickened skin (lichenification) resulting from repeated rubbing, itching, and scratching of the skin.
![<p><span>Past medical history of <strong>[of what might suggest the following?]</strong> </span></p><ul><li><p>pyoderma gangrenosum ulcers </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/56f424e9-f4fe-422c-9eb6-80a1639e7f85.png)
Past medical history of [of what might suggest the following?]
pyoderma gangrenosum ulcers
Crohn’s ileitis
Crohn ileitis: Inflammation of the ileum due to Crohn's disease
Pyoderma gangrenosum (pie-o-DUR-muh gang-ruh-NO-sum) is a rare condition that causes large, painful sores (ulcers) to develop on your skin, most often on your legs
![<p><span>Past medical history of <strong>[what might indicate the following?]</strong> </span></p><ul><li><p>dermopathy</p></li><li><p>necrobiosis lipoidica</p></li><li><p>paronychia </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e5f03608-0e8b-4a3d-9822-441ca681cc43.png)
Past medical history of [what might indicate the following?]
dermopathy
necrobiosis lipoidica
paronychia
Diabetes Mellitus
Dermopathy is a skin condition that develops as a result of changes to the blood vessels that supply the skin. Dermopathy appears as a shiny round or oval lesion of thin skin over the front lower parts of the lower legs
Necrobiosis lipoidica is a rare granulomatous skin disorder which can affect the shin of insulin-dependent diabetics
If you have diabetes, there's a risk that paronychia could spread to deeper tissues and bones, or into the bloodstream and other parts of the body
![<p><span>Past medical history of <strong>[what?]</strong>:</span></p><ul><li><p>tinea pedis</p></li><li><p>atopic eczema</p></li><li><p>disordered plantar dermatoglyphic </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ac41e4f4-45c7-405b-b7c4-e33bca9d7b6d.png)
Past medical history of [what?]:
tinea pedis
atopic eczema
disordered plantar dermatoglyphic
down syndrome
![<p><span>Past medical history of <strong>[what might cause the following?]</strong>:</span></p><ul><li><p>hyper sensitivity to pain or clothing</p></li><li><p>chronic fatigue</p></li><li><p>disordered sleep </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/610e8b56-a3a8-4764-83a5-5730ef24d9d7.png)
Past medical history of [what might cause the following?]:
hyper sensitivity to pain or clothing
chronic fatigue
disordered sleep
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain accompanied by fatigue, sleep, memory and mood issues
![<p><span>Past Medical History of <strong>[what?]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>hemorrhagic pressure keratoses</p></li><li><p>vasculitic ulcers </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/26ddfe1c-7029-436a-86fc-f82b5e490be6.png)
Past Medical History of [what?]
hemorrhagic pressure keratoses
vasculitic ulcers
Rheumatoid arthritis
Vasculitic ulcers are known to be more resistant to treatment and also more painful than ulcers of other aetiologies [10, 11, 14-17]. It has also been shown that patients with RA
Pedal Skin Temperature
Diabetic neuropathy
In early stages, [...]
In late stages, [...]
temperature increases with loss of sympathetic tone
temperature decreases
Pedal Skin Temperature
Normal day temperature: [...] deg C or [...] deg F
Normal night temperature: [...] deg C or [...] deg F
30 deg C or 86 deg F
34 deg C or 93.2 deg F
Pedal Skin Temperature
Normal: [...] deg F
Active psoriasis: [...] deg F
Parkinson’s disease: [...] deg F
86 deg F
95 deg F
71.5 deg F
Pedal Skin Temperature
Peripheral Arterial Disease – compare extremities
Normal side – [...] deg F
Affected side – [...] deg F
84 deg F
72 deg F
![<p><span>Scales: implies <strong>[...]</strong> </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/528ff886-0345-4025-aeea-b86f5c0abe50.png)
Scales: implies [...]
shedding
![<p>Scars: changes in skin texture due to injury</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> often occur in acne</p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> hoped for after a success verrucae curettage</p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> elevated </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/68777598-2f81-48f0-bd98-12e57d011c7d.png)
Scars: changes in skin texture due to injury
[...] often occur in acne
[...] hoped for after a success verrucae curettage
[...] elevated
Soft scars
Flat scares
Hypertrophic scars
A curettage procedure involves an incision into the epidermal and dermal layers surrounding the verrucae (wart) lesion followed by the use of a curette
![<p>Shape and arrangement clues</p><ul><li><p>Linear like scratches in <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>Target or iris lesions in <span>erythema multiforme</span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e185f043-e434-45bf-b6be-9a0ec9fc0e8b.png)
Shape and arrangement clues
Linear like scratches in [...]
Target or iris lesions in erythema multiforme
poison ivy lesions
![<p>Shape and arrangement clues</p><ul><li><p>Linear like scratches in <span>poison ivy lesions</span></p></li><li><p>Target or iris lesions in <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/601fd1cc-d528-4ffb-8a73-47bf884a3a60.png)
Shape and arrangement clues
Linear like scratches in poison ivy lesions
Target or iris lesions in [...]
erythema multiforme
![<p>Shape and arrangement clues</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> lesions in: </p><ul><li><p>tinea</p></li><li><p>psoriasis</p></li><li><p>drug eruptions</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Zoster form vesicles and bullae in dermatomal pattern unilaterally point to <span>Herpes Zoster or shingles</span> </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fbdce843-2ef8-4900-b806-d890ce2fa7fe.png)
Shape and arrangement clues
[...] lesions in:
tinea
psoriasis
drug eruptions
Zoster form vesicles and bullae in dermatomal pattern unilaterally point to Herpes Zoster or shingles
Annular or ring shaped
![<p>Shape and arrangement clues</p><ul><li><p><span>Annular or ring shaped</span> lesions in: </p><ul><li><p>tinea</p></li><li><p>psoriasis</p></li><li><p>drug eruptions</p></li></ul></li><li><p>Zoster form vesicles and bullae in dermatomal pattern unilaterally point to <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a82f2646-32e1-45e5-9293-bd5be6f96347.png)
Shape and arrangement clues
Annular or ring shaped lesions in:
tinea
psoriasis
drug eruptions
Zoster form vesicles and bullae in dermatomal pattern unilaterally point to [...]
Herpes Zoster or shingles
![<p>Types of Pedal Melanoma</p><ol><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> (most common)</p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li></ol><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e4b04ad5-5692-4043-8116-1b3b905ec088.png)
Types of Pedal Melanoma
[...]
[...]
[...] (most common)
[...]
Superficial spreading
Nodular
Acral lentiginous (most common)
Subungual Melanoma
What does NLDOCAT stand for?
N = [...]
L = [...]
D = [...]
O = [...]
C = [...]
A = [...]
T = [...]
N = Nature
L = Location
D = Duration
O = Onset
C = Course
A = Attributes
T = Treatment
![<p><span>What does the MEASURE acronym stand for? </span></p><ul><li><p>M = <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>E = <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>A = <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>S = <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>U = <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li><li><p>R = <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>E = <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e0a76e8f-b608-41c8-88a1-fd32652c1e7f.png)
What does the MEASURE acronym stand for?
M = [...]
E = [...]
A = [...]
S = [...]
U = [...]
R = [...]
E = [...]
M = Measure
E = Exudate
A = Appearence
S = Suffering
U = Undermining
R = Re-evaluation
E = Edge
![<p>Wood’s light examination</p><ul><li><p>Examples<br></p><ul><li><p>Detects <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> florescence of Corynebacteria minuitissium in erythrasma</p></li><li><p>Pseudomonas glows <span>white to yellow</span></p></li><li><p>Urine glows <span>orange to pink</span></p></li><li><p>Microsporum in tinea capititis glows <span>yellow to green</span></p></li><li><p>Trichophytons <span>do not glow</span></p></li><li><p>Tinea verisicolor and patches of tuberous sclerosis <span>do not glow</span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/65acd58a-b739-4686-b626-a1a9aa8c1bb4.png)
Wood’s light examination
Examples
Detects [...] florescence of Corynebacteria minuitissium in erythrasma
Pseudomonas glows white to yellow
Urine glows orange to pink
Microsporum in tinea capititis glows yellow to green
Trichophytons do not glow
Tinea verisicolor and patches of tuberous sclerosis do not glow
coral-red
![<p>Wood’s light examination</p><ul><li><p>Examples<br></p><ul><li><p>Detects <span>coral-red</span> florescence of Corynebacteria minuitissium in erythrasma</p></li><li><p>Pseudomonas glows <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>Urine glows <span>orange to pink</span></p></li><li><p>Microsporum in tinea capititis glows <span>yellow to green</span></p></li><li><p>Trichophytons <span>do not glow</span></p></li><li><p>Tinea verisicolor and patches of tuberous sclerosis <span>do not glow</span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d009c418-3790-4071-bd8d-e096293b75b9.png)
Wood’s light examination
Examples
Detects coral-red florescence of Corynebacteria minuitissium in erythrasma
Pseudomonas glows [...]
Urine glows orange to pink
Microsporum in tinea capititis glows yellow to green
Trichophytons do not glow
Tinea verisicolor and patches of tuberous sclerosis do not glow
white to yellow
![<p>Wood’s light examination</p><ul><li><p>Examples<br></p><ul><li><p>Detects <span>coral-red</span> florescence of Corynebacteria minuitissium in erythrasma</p></li><li><p>Pseudomonas glows <span>white to yellow</span></p></li><li><p>Urine glows <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>Microsporum in tinea capititis glows <span>yellow to green</span></p></li><li><p>Trichophytons <span>do not glow</span></p></li><li><p>Tinea verisicolor and patches of tuberous sclerosis <span>do not glow</span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/dfbf350d-bb8e-4ba0-89b1-169ce569b49b.png)
Wood’s light examination
Examples
Detects coral-red florescence of Corynebacteria minuitissium in erythrasma
Pseudomonas glows white to yellow
Urine glows [...]
Microsporum in tinea capititis glows yellow to green
Trichophytons do not glow
Tinea verisicolor and patches of tuberous sclerosis do not glow
orange to pink
![<p>Wood’s light examination</p><ul><li><p>Examples<br></p><ul><li><p>Detects <span>coral-red</span> florescence of Corynebacteria minuitissium in erythrasma</p></li><li><p>Pseudomonas glows <span>white to yellow</span></p></li><li><p>Urine glows <span>orange to pink</span></p></li><li><p>Microsporum in tinea capititis glows <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>Trichophytons <span>do not glow</span></p></li><li><p>Tinea verisicolor and patches of tuberous sclerosis <span>do not glow</span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f1605c1d-8e75-4cd7-b1be-e76b54843f16.png)
Wood’s light examination
Examples
Detects coral-red florescence of Corynebacteria minuitissium in erythrasma
Pseudomonas glows white to yellow
Urine glows orange to pink
Microsporum in tinea capititis glows [...]
Trichophytons do not glow
Tinea verisicolor and patches of tuberous sclerosis do not glow
yellow to green
![<p>Wood’s light examination</p><ul><li><p>Examples<br></p><ul><li><p>Detects <span>coral-red</span> florescence of Corynebacteria minuitissium in erythrasma</p></li><li><p>Pseudomonas glows <span>white to yellow</span></p></li><li><p>Urine glows <span>orange to pink</span></p></li><li><p>Microsporum in tinea capititis glows <span>yellow to green</span></p></li><li><p>Trichophytons <span><strong>[glows..?]</strong></span></p></li><li><p>Tinea verisicolor and patches of tuberous sclerosis <span><strong>[glows..?]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/afde78d7-b571-49a1-bff3-e611aebb2fda.png)
Wood’s light examination
Examples
Detects coral-red florescence of Corynebacteria minuitissium in erythrasma
Pseudomonas glows white to yellow
Urine glows orange to pink
Microsporum in tinea capititis glows yellow to green
Trichophytons [glows..?]
Tinea verisicolor and patches of tuberous sclerosis [glows..?]
do not glow
do not glow
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>Autoimmune mediated hair loss that progressively attacks hair follicles</p></li><li><p>May progress to <span>alopecia universalis</span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1ff0c7ab-860f-4def-bf47-7d042499edf3.png)
[...]
Autoimmune mediated hair loss that progressively attacks hair follicles
May progress to alopecia universalis
Alopecia Areata
![<p><span>Alopecia Areata</span></p><ul><li><p>Autoimmune mediated hair loss that progressively attacks hair follicles</p></li><li><p>May progress to <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d5eae3f9-cd07-4a14-870b-994cad1650ca.png)
Alopecia Areata
Autoimmune mediated hair loss that progressively attacks hair follicles
May progress to [...]
alopecia universalis
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> </p><ul><li><p>autosomal dominant</p></li><li><p>Male pattern baldness</p></li><li><p>In women, diffuse thinning on the crown </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/929b3b17-9e39-4438-a68d-b485b7ba66ea.png)
[...]
autosomal dominant
Male pattern baldness
In women, diffuse thinning on the crown
Androgen alopecia
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong>: arranged in a circle or ring shape </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/520349d3-1b70-4b60-b8df-ece04c7e7427.png)
[...]: arranged in a circle or ring shape
Annular
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong>: arranged in arcs or portions of a circle </span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4b0588f1-5d32-4bcf-a848-83c1e5deeaa1.png)
[...]: arranged in arcs or portions of a circle
Arciform
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span>: depression in contour of skin</p><ul><li><p><span>Corticosteroid injections</span> within the subcutaneous fat layer can cause atrophy </p></li><li><p>Is a secondary lesion</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b1fcf996-e16c-406a-9905-a66cb11548af.png)
[...]: depression in contour of skin
Corticosteroid injections within the subcutaneous fat layer can cause atrophy
Is a secondary lesion
Atrophy
![<p><span>Atrophy</span>: depression in contour of skin</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> within the subcutaneous fat layer can cause atrophy </p></li><li><p>Is a secondary lesion</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/96958883-d65a-41ce-8d1b-9f458103663b.png)
Atrophy: depression in contour of skin
[...] within the subcutaneous fat layer can cause atrophy
Is a secondary lesion
Corticosteroid injections
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> of Psoriasis</p><ul><li><p><strong>Pinpoint bleeding </strong>upon forcible removal of a scale of psoriasis</p></li><li><p>Psoriasis is a skin disorder that causes skin cells to multiply up to 10 times faster than normal</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7c740549-a6f2-45a8-b77c-0bdf564cd42b.png)
[...] of Psoriasis
Pinpoint bleeding upon forcible removal of a scale of psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin disorder that causes skin cells to multiply up to 10 times faster than normal
Auspitz’s Sign
![<p><span><strong>[Benign or melanoma?]</strong></span></p><ul><li><p>Homogenous</p></li><li><p>Parallel pattern</p></li><li><p>Pigmented network</p></li><li><p>Cobblestone pattern</p></li><li><p>Pigmented globules</p></li><li><p>Starburst pattern </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3ec0843c-28da-400b-85ff-1598a621f300.png)
[Benign or melanoma?]
Homogenous
Parallel pattern
Pigmented network
Cobblestone pattern
Pigmented globules
Starburst pattern
Benign criteria
[...] can occasionally stain apocrine sweat (bible)
Blood pigments
[...] stains the skin yellow if there is dietary excess
Carotene
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong>: dried blood or pus</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/01b38834-23d3-4d4f-be36-4af384ffe0c8.png)
[...]: dried blood or pus
Crusts
![<p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span> – checking for blanching of a skin lesion</p><ul><li><p>Blanching (turning pale) suggest <span>vascular</span> lesion like telangectasia or erythema</p></li><li><p>No blanching if pigmented or purpuric (rash of purple spots) because that’s due to extravascular changes </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/738cb3ba-4cdb-45d9-99ba-db9e9f761282.png)
[...] – checking for blanching of a skin lesion
Blanching (turning pale) suggest vascular lesion like telangectasia or erythema
No blanching if pigmented or purpuric (rash of purple spots) because that’s due to extravascular changes
Diascop
![<p><span>Diascopy</span> – checking for blanching of a skin lesion</p><ul><li><p>Blanching (turning pale) suggest <span><strong>[...]</strong></span> lesion like telangectasia or erythema</p></li><li><p>No blanching if pigmented or purpuric (rash of purple spots) because that’s due to extravascular changes </p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7e142b55-d0f3-4c48-870d-d14e297cf785.png)
Diascopy – checking for blanching of a skin lesion
Blanching (turning pale) suggest [...] lesion like telangectasia or erythema
No blanching if pigmented or purpuric (rash of purple spots) because that’s due to extravascular changes
vascular