#7 Habitat selection I
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Habitat
The area where an animal or group of animal lives, including all resources and interactions, both biotic and abiotic, that affect survival and reproduction
the sum total of the environmental factors, food, cover, and water, that a given species needs to survive and reproduce in a given area
What are the 5 scales habitat is described at?
Broadest scale
Region
Habitat
Local habitat
Microhabitat
Broadest scale
Biome/ entire ecoregion of continents
A ton of variation within that area
Coarse, general ecological patterns
May describe a species’ entire distribution or an entire biome
Region
More specific ecological patterns
Area use/patch selection
Home to a species’ home range or one or more populations
Habitat (scale)
Part or all of a population, but rarely entire species’ range
Even more specificity (tides, weather, vegetative community)
The level we tend to perceive things at
Local habitat
Specific sub-set of an area where the species can occur
Where certain stages occur at
Microhabitat
A “habitat within a habitat” that possesses different or unique characteristics
“A nest site”
Why do they choose to nest here opposed to other areas in the same location
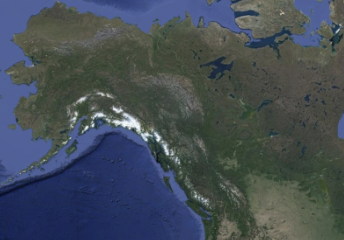
Which habitat scale is this at?
Broadest scale
EX: Nearctic boreal wetlands
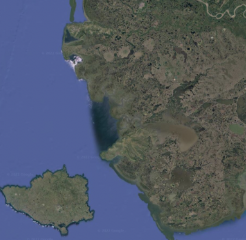
Which habitat scale is this at?
Region
EX: Yukon-Kuskokwim delta wetlands

Which habitat scale is this at?
Habitat
EX: Yukon delta estuarine marsh
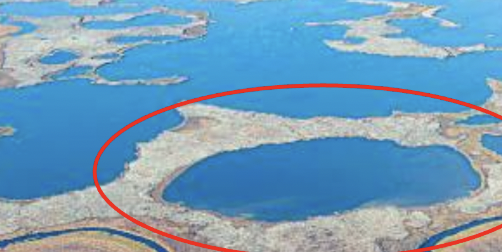
Which habitat scale is this at?
Local habitat
EX: this pothole marsh

Which habitat scale is this at?
Microhabitat
EX: This specific patch of tundra grasses, forbes, and lichens on the edge of this pothole
What are some Habitat characteristics you should look at, and what are the differing scales?
Vegetation:
thousands of hectares
Water level management:
hundreds of hectares
Fine-scale microhabitats:
square meters
How do we measure the + and - of a habitat use?
by looking at and measure the Welfare factors and the Decimating factors
What are some Welfare factors?
accessibility of food, water, and shelter
What are some Decimating factors?
predation, disease/parasites, dangerous weather, human interference, etc.
Competition
Social factors
Habitat change/stability (long term)
How do you Identify habitat types?
Often vegetation is the dominant factor in how we categorize habitat
Cattails?
Habitat for Marsh wrens, dragonflies, waterfowl, and fish
Is it fair to call “cattails” a habitat type?
It depends on the scale of habitat you need to look at
yes → microhabitat
no → anything broader
Habitat quality
the ability of a habitat to provide conditions and resources appropriate for individual and/or population persistence
What do we measure when we are interested in a certain habitat and what other factors in the environment affect it?
Quality*
Pollution
Diversity
size/connectivity
Productivity
Reproductive success**
What are 2 other big types of habitat quality?
Resource provision
Source/sink dynamics
Why is Resource provision a big type of habitat quality?
Production/density of food or other welfare factor
Ability to provide for the needs of resident animals
Change in biomass
lead to a relationship between the amount of food in an area
how good the quality of the environment is for them
Why is Source/sink dynamics a big type of habitat quality?
Areas that are growing = high quality
Failing to reproduce/dieing off = sink = poor quality
Quality assessed by rates of population growth in a given habitat
Underlying assumption– higher quality habitat supports more beavers
Can be helpful in identifying important population strongholds
What is one method to measure habitat quality?
Wetland Rapid Assessment Technique (WRAP)
Developed to produce a single number to assess wetland ‘quality’
Highly generalized, but this can cause drawbacks to applicability!
Many sub-models and different approaches, (California has CRAM)
What are some pros of the Wetland Rapid Assessment Technique?
Compare other habitat and wetlands to see which one to conserve
Works on a larger scale
Wetlands quality across broader scales
What are some cons of the Wetland Rapid Assessment Technique?
The more specialized the wetland becomes the harder it is to assess it
Habitats are also rapidly changing
The technique is too generalized
Habitat use
Where animals/ populations are found
What do we want to seek to understand about habitat use?
mechanisms for selection
Pursue welfare factor?
Avoid decimating factors?
Limited or rare resources
Availability of resources can flip the selection of habitat that is utilized
What does SLOSS stand for, and how is it related to habitat use?
Single Large Or Several Small
refers to a conservation debate about whether one large habitat or several small habitats is better for biodiversity and habitat support
What is one correlation regarding SLOSS and wetlands?
Small wetlands appear to accumulate rare and endemic species faster
though studies are mixed by taxon
Habitat selection
The process by which organisms select habitat across available areas relative to use
Operates across scales
Can be dictated by radically different needs
How does habitat use differ from habitat selection?
Use
refers to where animals are actually found or distributed across habitat types
Selection
Use relative to availability
indicates whether animals are choosing certain types more than expected by chance
What is the underlying assumption of habitat selection theory?
That animals select habitats in a way that increases their fitness — meaning survival and reproduction
Habitat “preference”
an inference made from observed habitat selection — it's the idea of what animals might “like” or favor among available options
Will to use the place
Why is the term "habitat preference" considered imprecise?
often implies cognitive choice (what animals want), which is hard to prove and measure.
selection is more objective and testable
Does habitat selection imply animals are consciously choosing habitat?
Not necessarily.
While preference may imply cognitive choice
Selection can occur through innate behavior (genetically driven) or learned behavior (from experience)
without conscious decision-making