AP HUG U1 review
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Census
Counts how many people live in each home, sex, age and race to count for every person
Friction of distance
The idea that distance acts as a barrier to interraction
Geographic System
Includes natural, human and environmental factors
Meridian of Longitude
Measures east to west, North pole to the South pole
Parallel of Latitude
Measures north to south, parallel to the equator
Reference Maps
Provide information on the location of features, such as cities or roads
Scale of analysis
The level of detail geography is studied, from local to global
Site
Physical and cultural characteristics of a place
Situation
The location of a place relative to its surroundings
Thematic Maps
Displays spatial patterns of places and uses quantitative data for topics
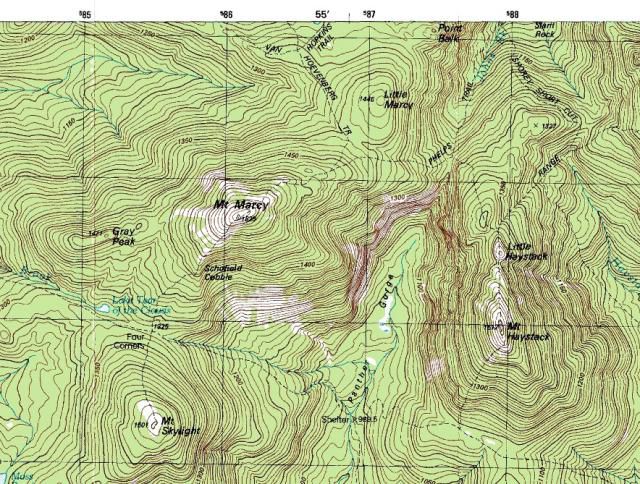
Topographic Maps
A reference map that uses contour lines to display the terrain and elevation changes in an area
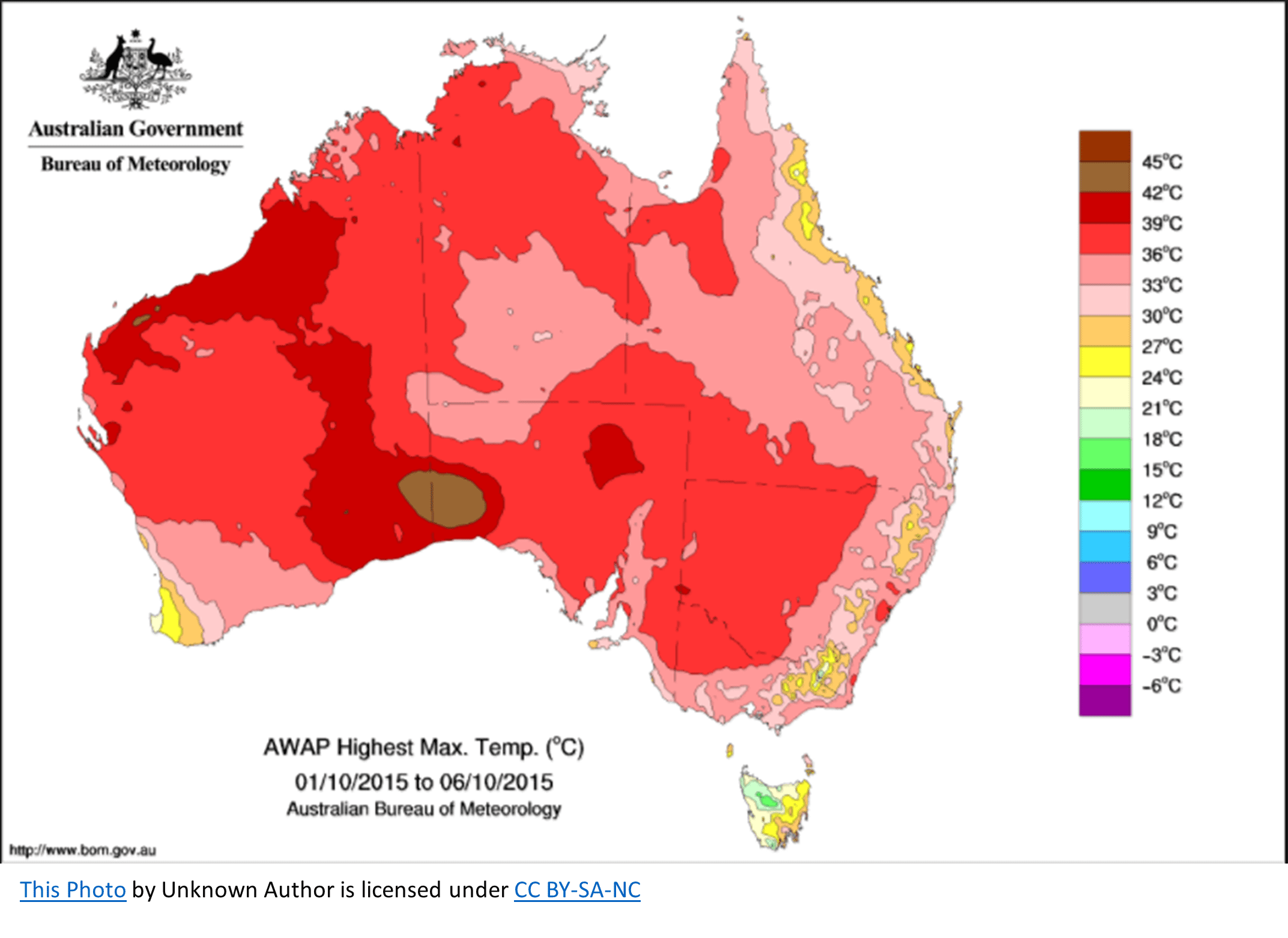
Choropleth map
Displays data by using different colors to show a different quantity of data
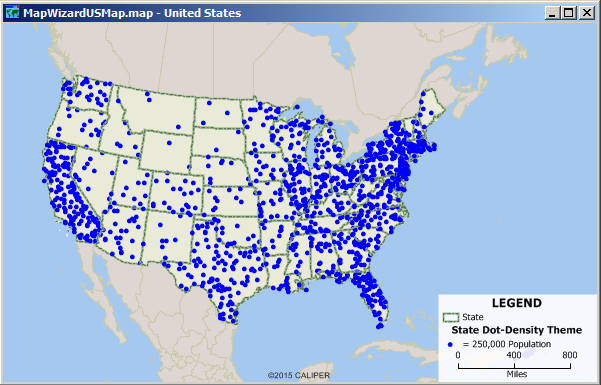
Dot Density
Shows data by placing points on a map where the data is occurring, shows spatial distribution
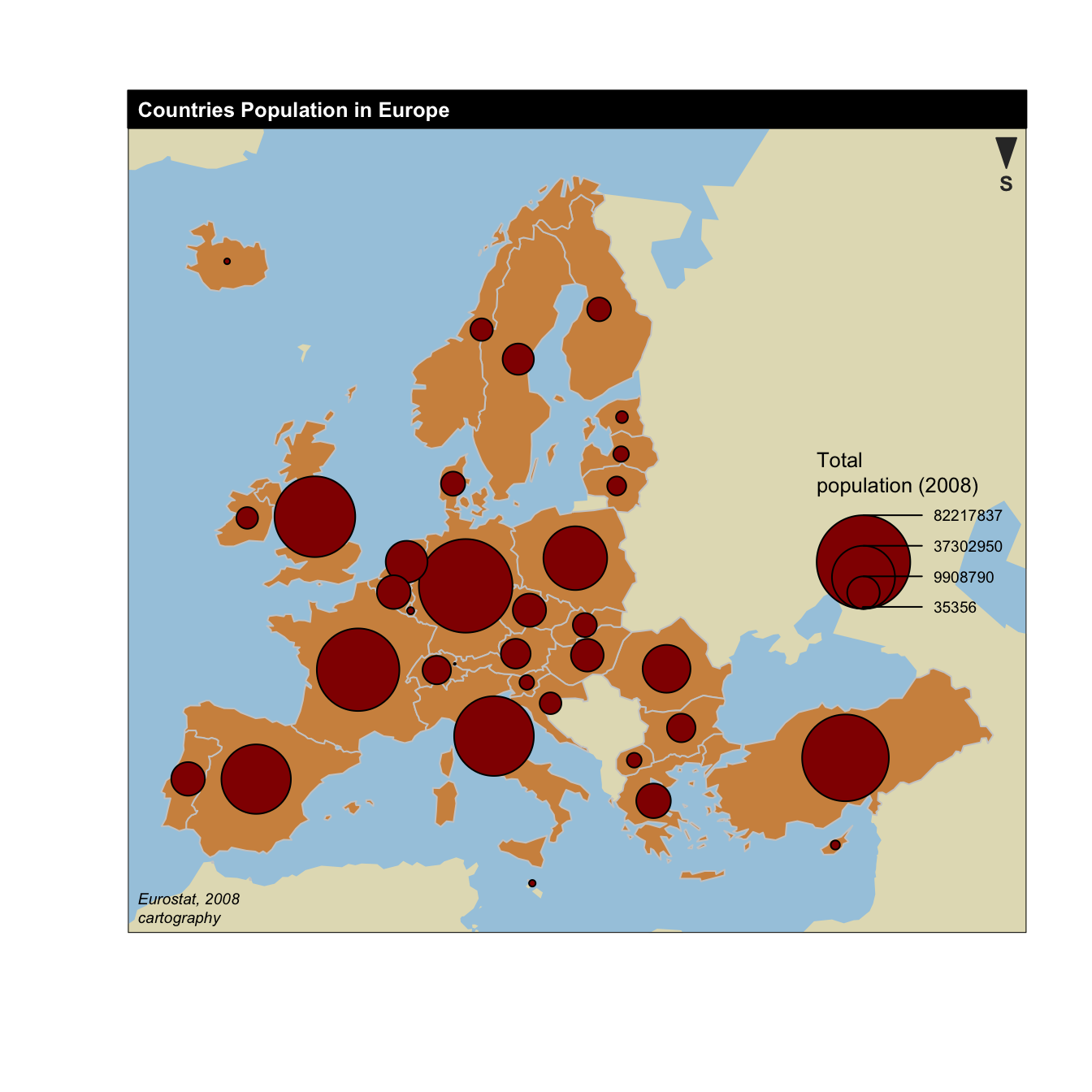
Graduated Symbol
Uses symbols to show the location and amount of data on a map
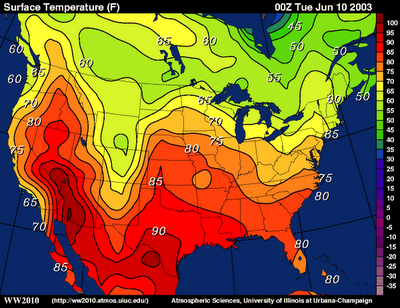
Isoline
Uses lines to connect different areas that have similar or equal amounts of dataC
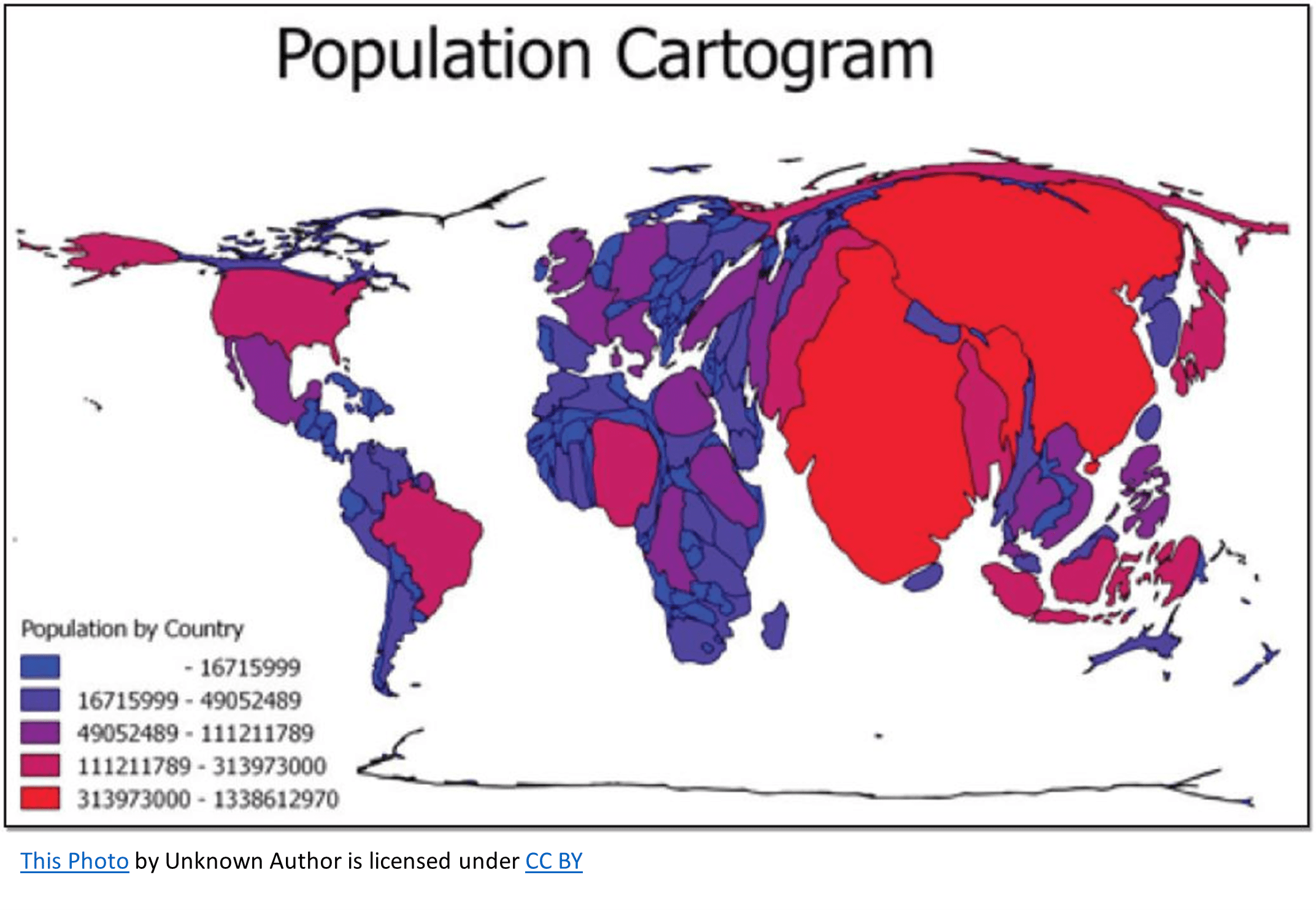
Cartogram
Shows data by the greatest value represented as the largest area
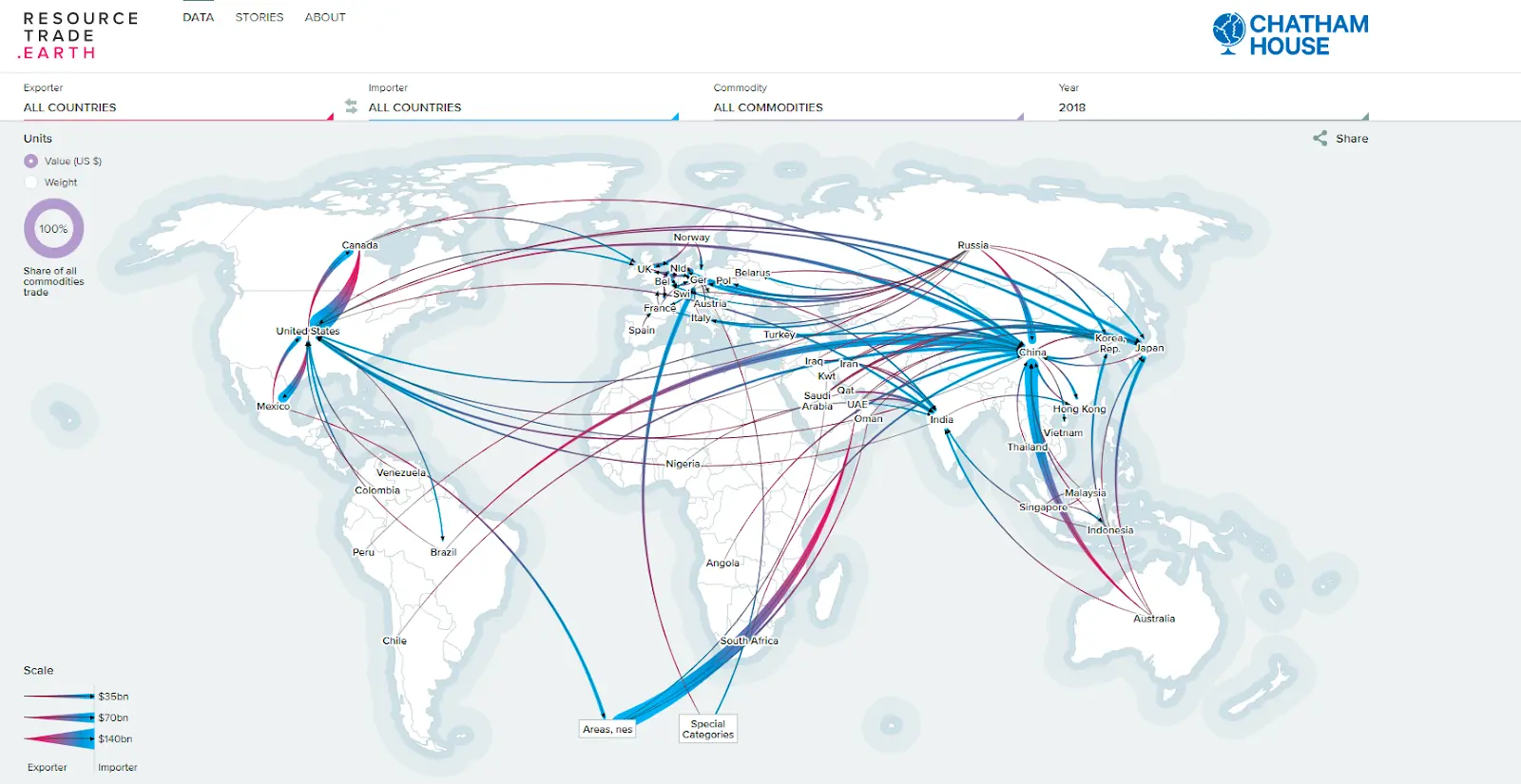
Flow line
Displays the movement of different goods, people, and other things between places
Remote Sensing
A process of collecting information about the Earth’s surface from satellites
GIS
A computer system that can collect, analyze and display geographic data
GPS
Satellites that determine the location of something on Earth’s surface
Absolute location
The exact spot using long and lat
Relative location
Where something is in relation to another object or place
Sense of Place
A strong feeling or perception a person has of a specific location
Time-space compression
The reduction of time it takes for something or someone to get from one place to another
Distance decay
The effect of distance on cultural or spatial interactions
Environmental Determinism
The belief that the physical environment dictates a society’s success
Possibilism
The belief that the environment factors a bit into society but human’s can also change that
Land use concept
How land has been changed to be utilized for a specific purpose
Sub-national scale
City, county, region or census tract
Formal/Uniform Region
Has physical or cultural characteristics
Functional/Nodal Region
An area organized around a center point, like transportation
Vernacular/Perceptual Region
Region exists because people believe it does, like the South
Tobler’s first law of geography
Everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things
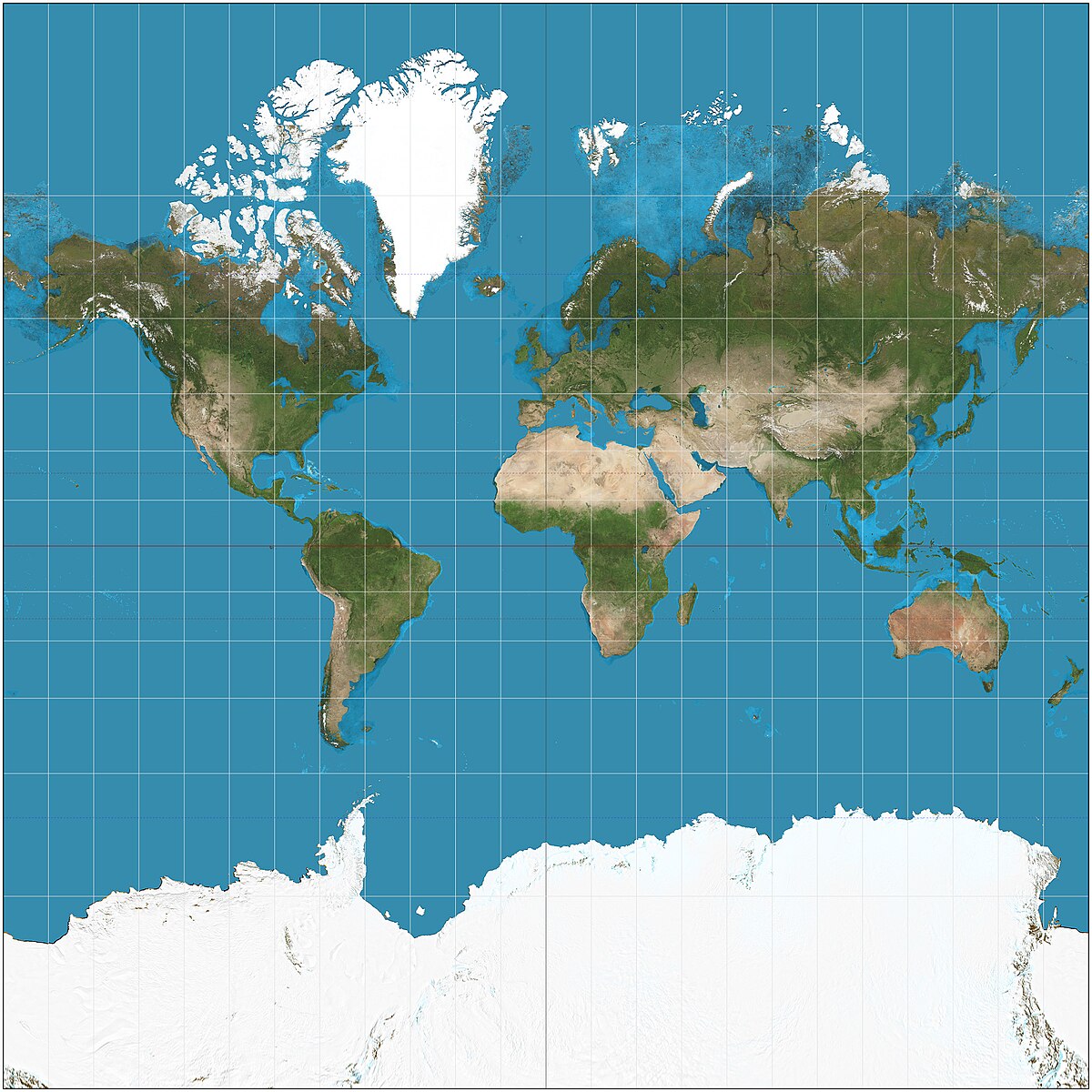
Mercator projection
shows true direction, distorts the shape and size of land masses
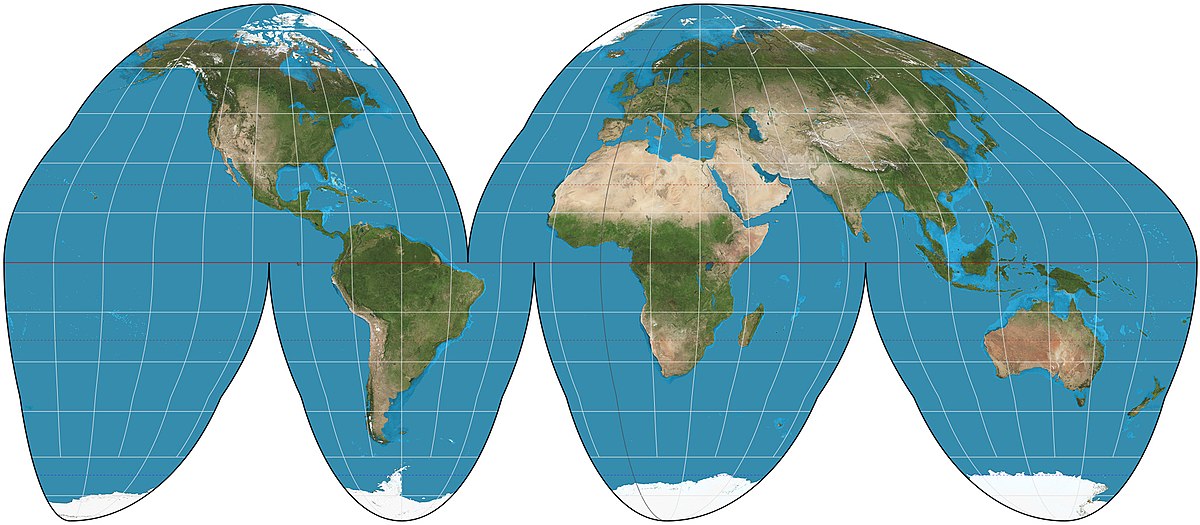
Goode Homolosine projection
Maintains accurate land mass size, minimizes distortion
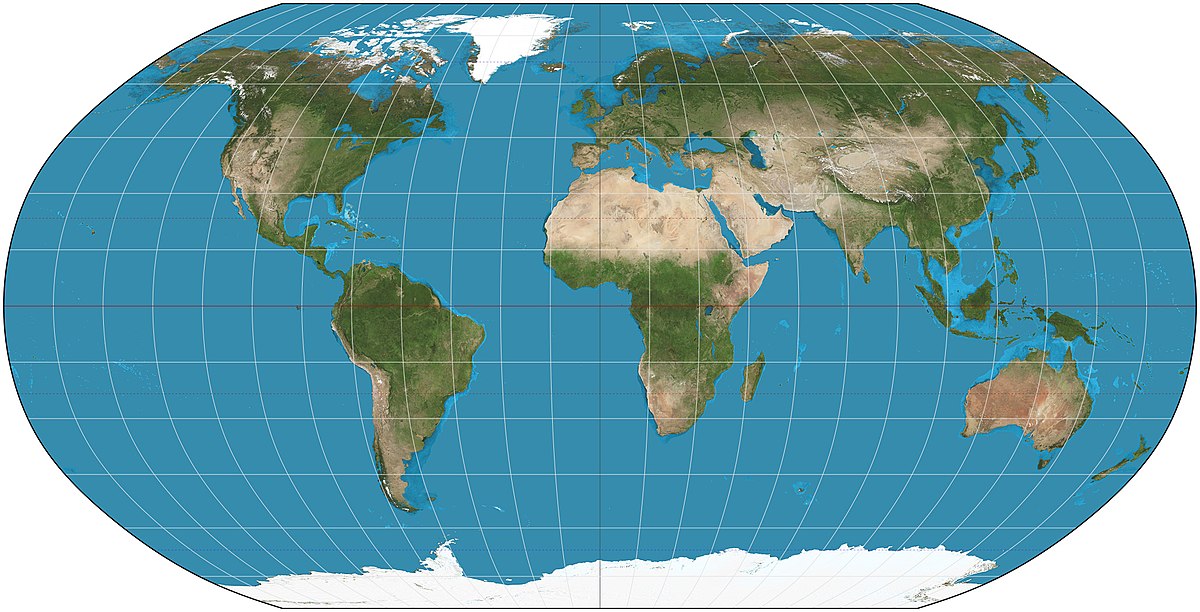
Robinson projection
Distortion near the poles and evenly throughout but preserves the size of land masses
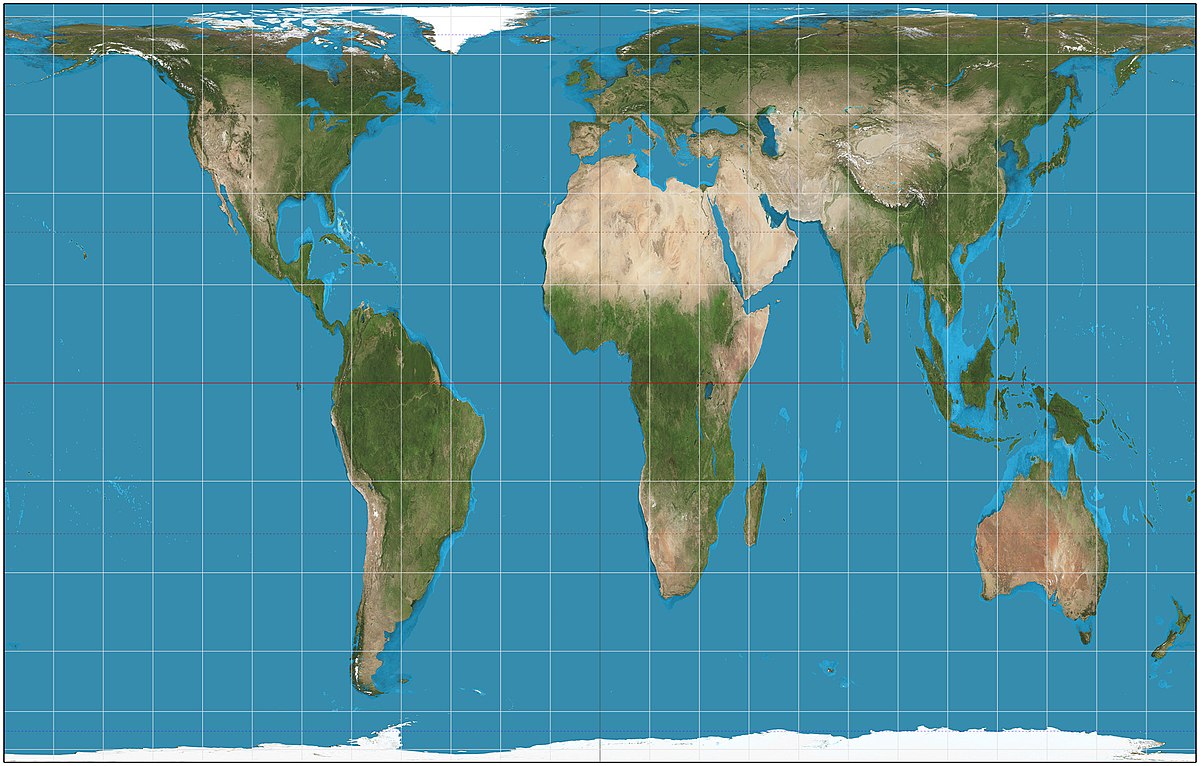
Gall-Peters projection
shows the true size of the earths land masses, distorts direction and shape