SCB 204 - Midterm Exam
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Previous quizzes 1-3 + Study guide topics 1-15 (from lectures 16-18)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
True or false: The nervous system functions to form consciousness, personality, learning and memory.
True
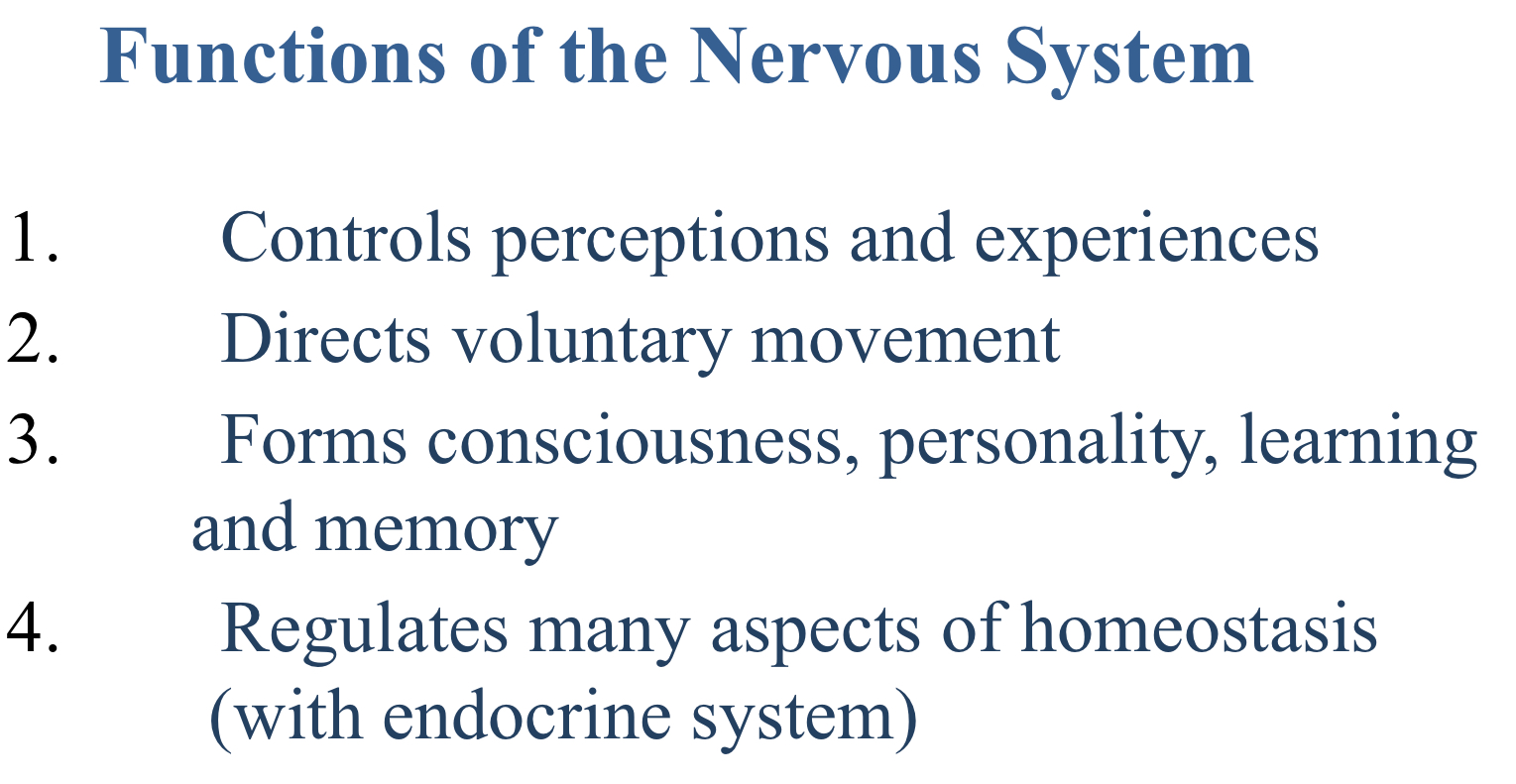
Which function of the nervous system analyzes and interprets information in preparation for appropriate response?
Integrative
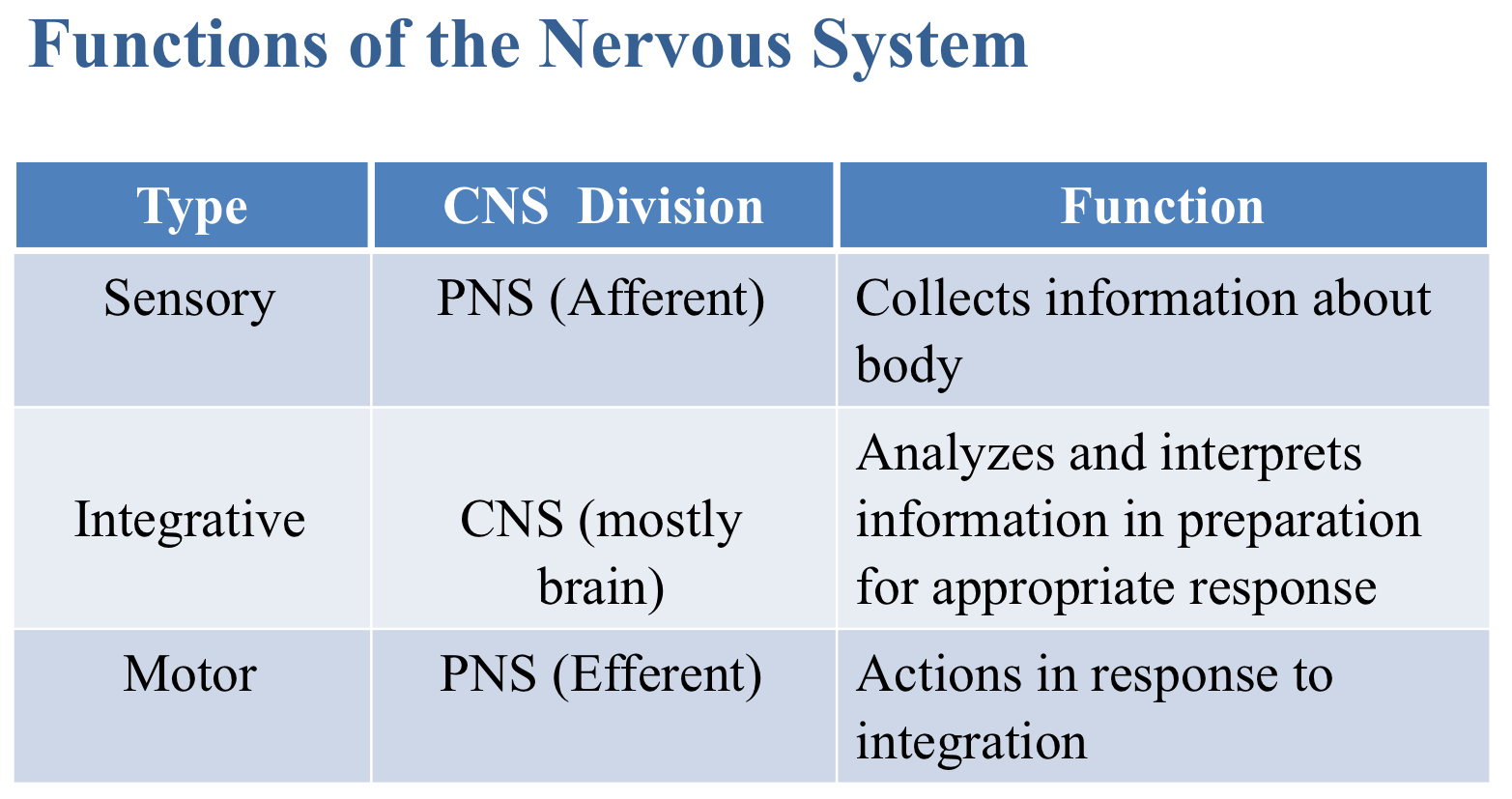
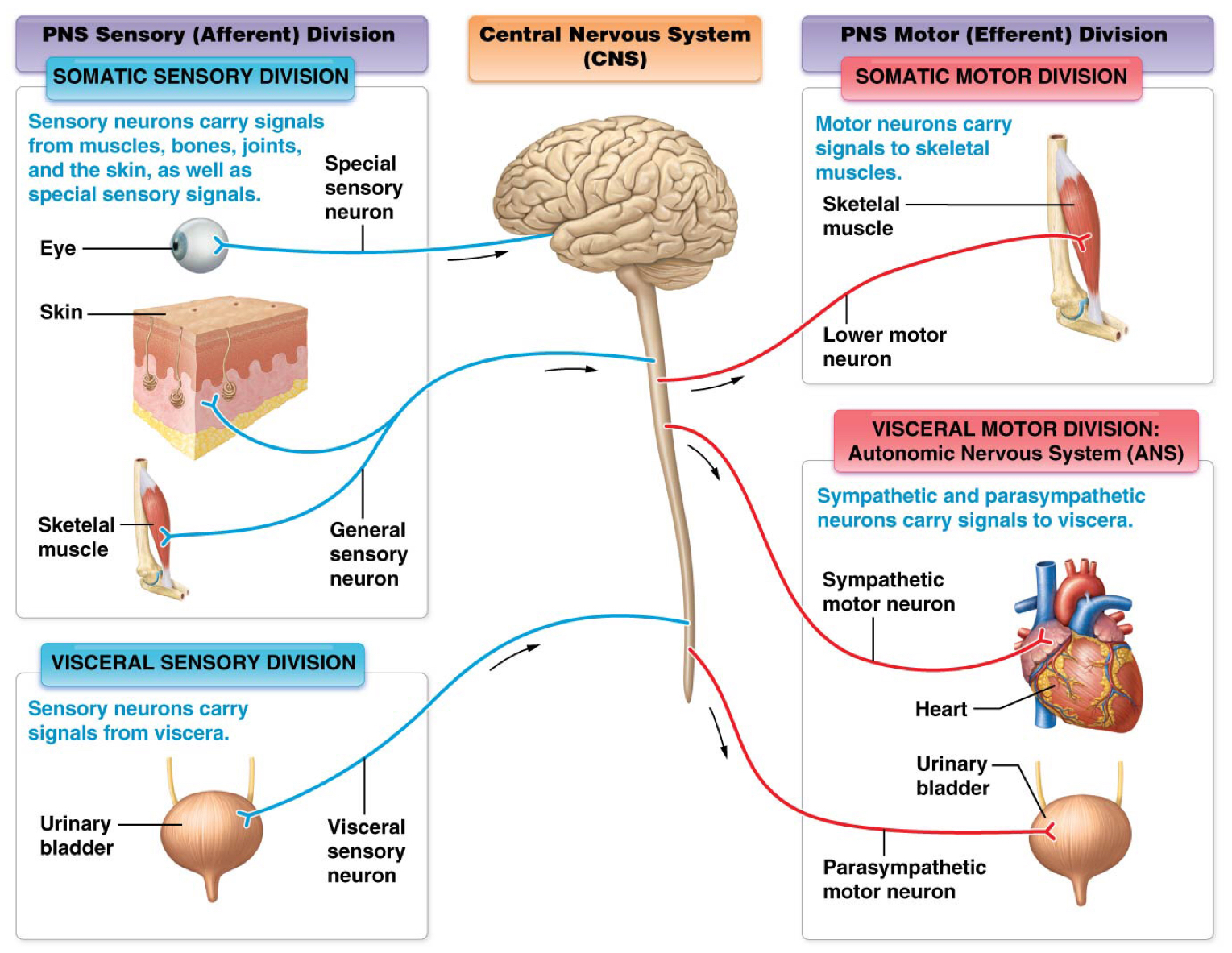
Which division of the nervous system is composed of neurons that signals from organs such as heart, lungs, intestines, kidneys and urinary bladder?
Visceral sensory division
True or false: Dendrites send information to other cells.
False
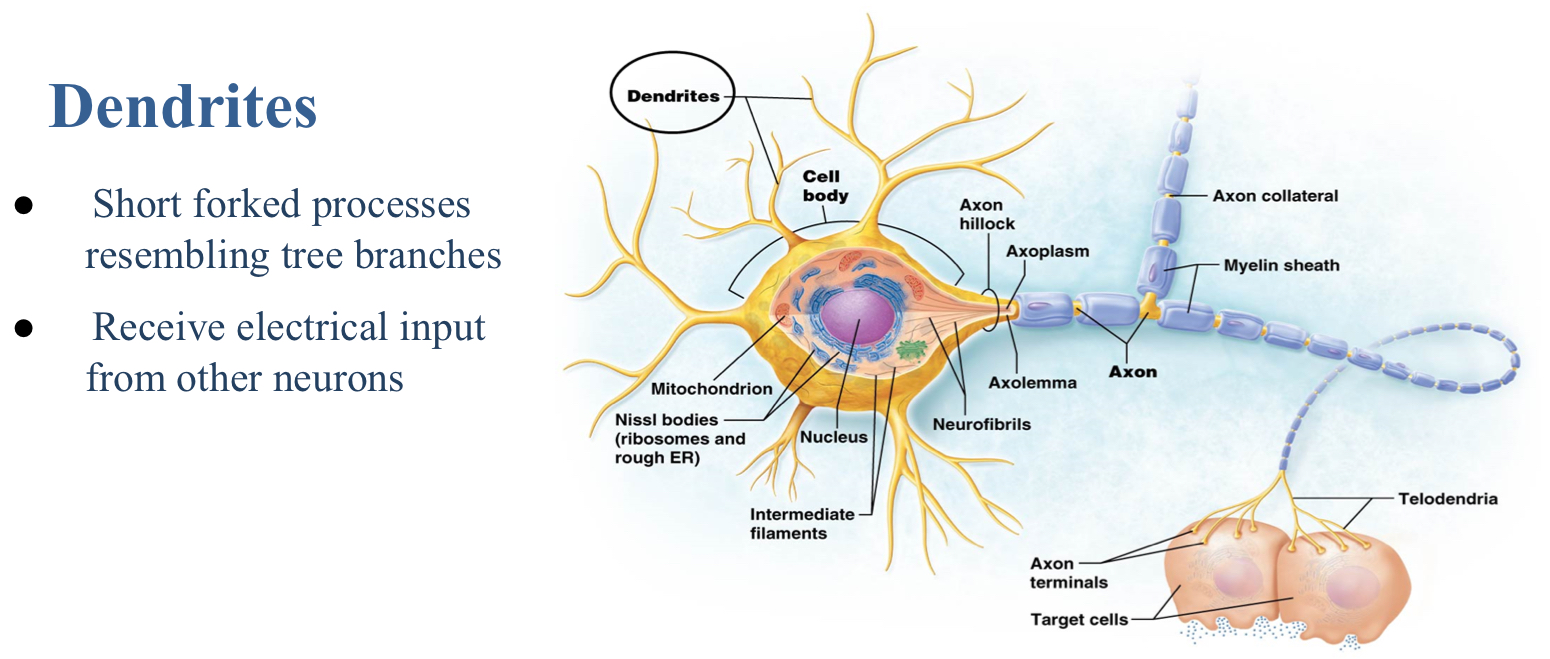
Which is the secretory region of a neuron?
Axon terminals
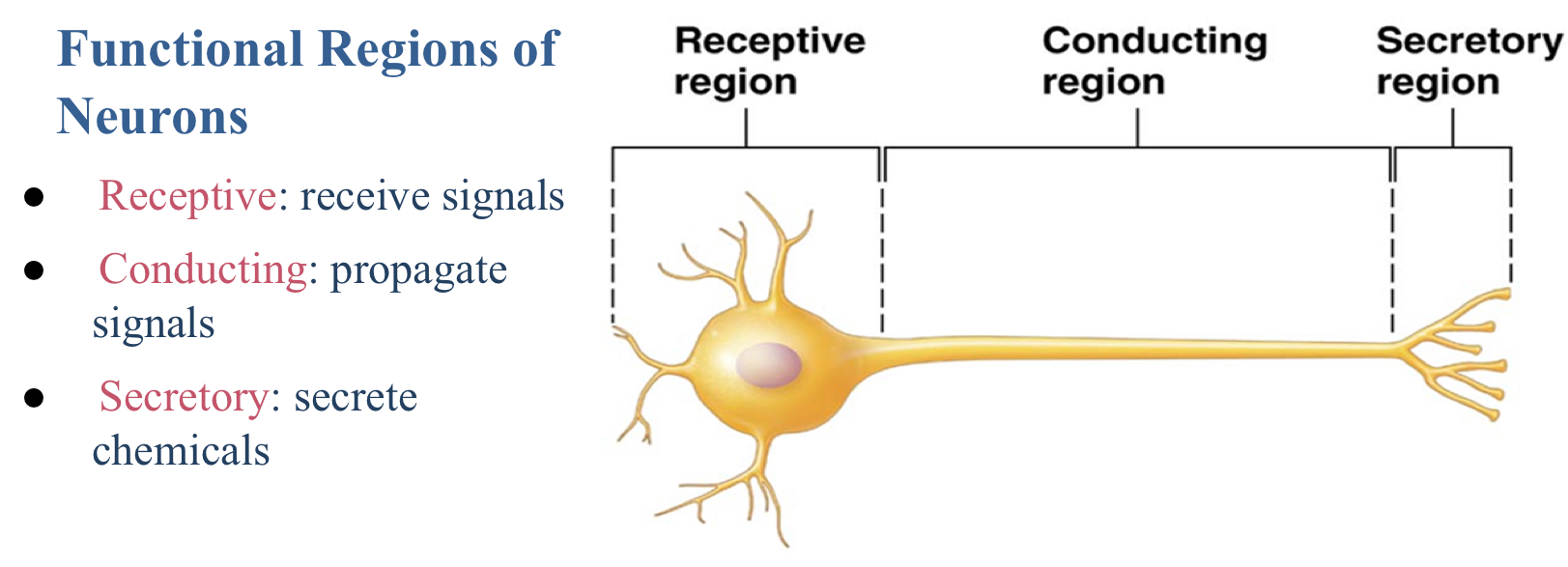
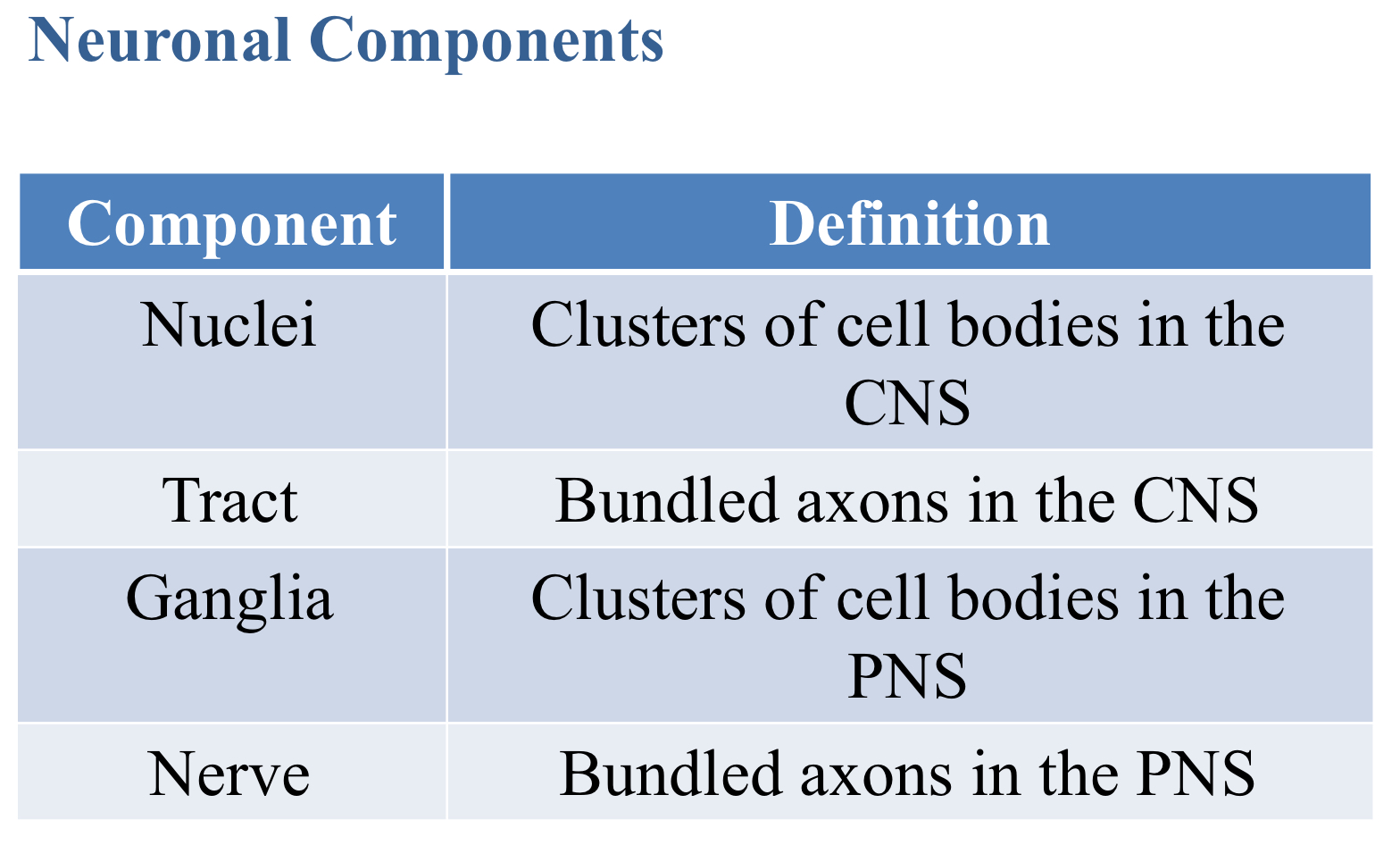
Which are bundled axons in the CNS?
Tract
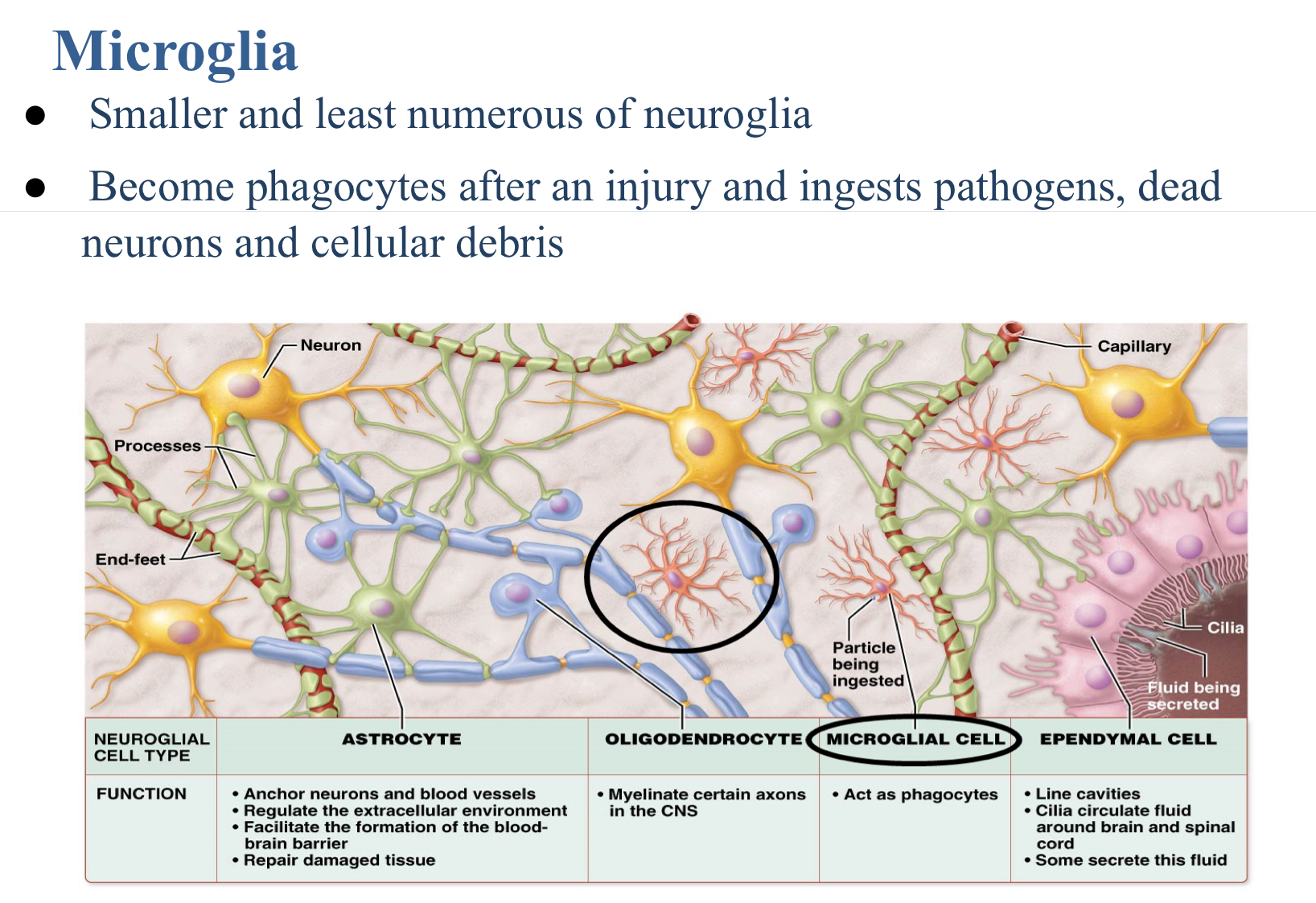
Which neuroglia cell becomes phagocytes after an injury and ingests pathogens, dead neurons and cellular debris?
Microglia
Which type of gated channel will open in response to a chemical that binds to the channel?
A ligand-gated channel
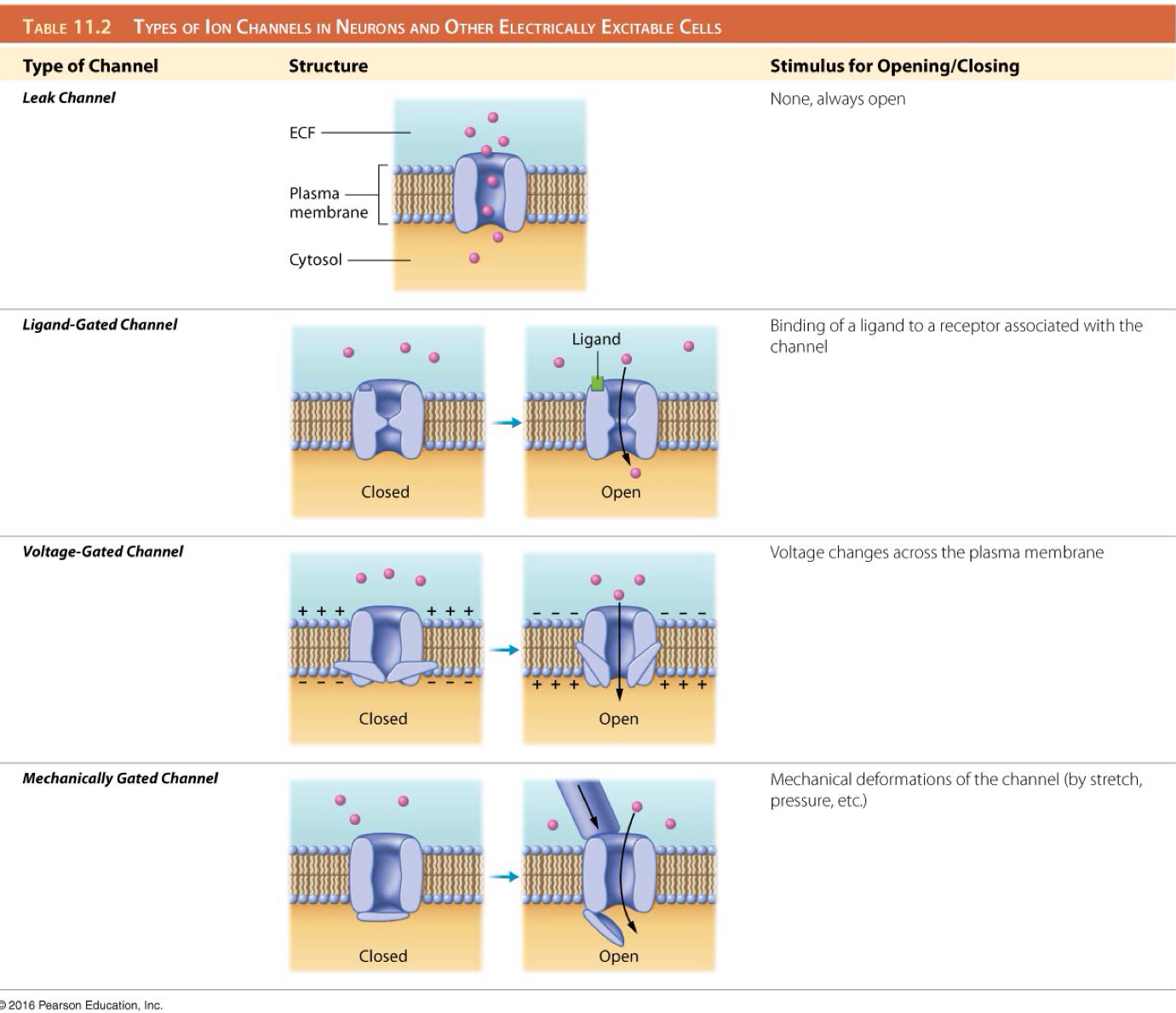
True or false: Both the electrical and concentration gradient for potassium favors its movement out of the cell.
False
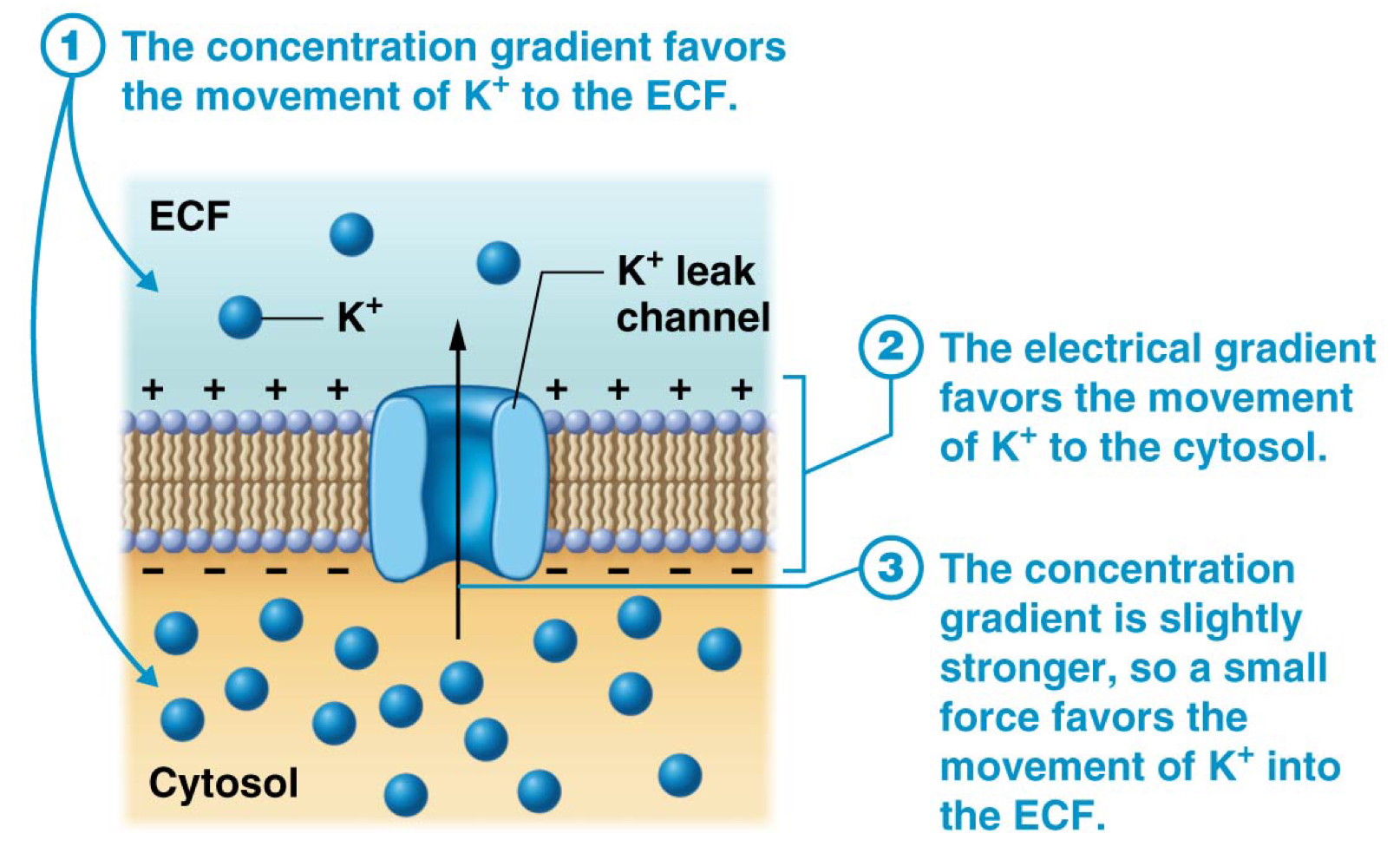
True or false: The movement of negatively charged ions through a ligand gated channel will cause a hyperpolarization.
True
All are correct about local potentials EXCEPT?
A. All or none
B. Graded
C. Decremental
D. Reversible
A. All or none

True or false: A local potential will always produce an action potential.
False
True or false: In the absolute refractory period no additional stimulation no matter how strong can produce an additional action potential.
True
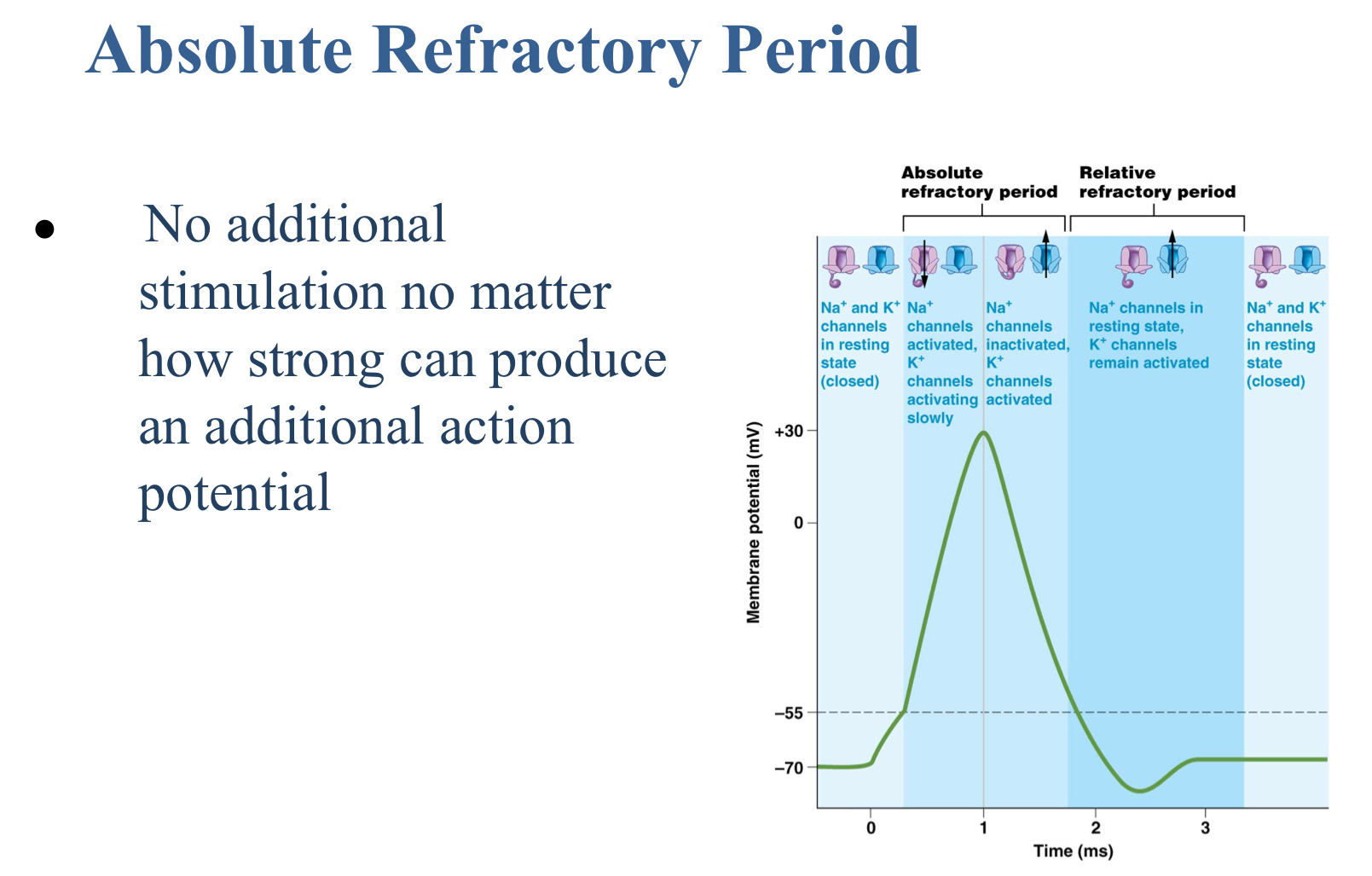
Which ion is involved in repolarization?
Potassium
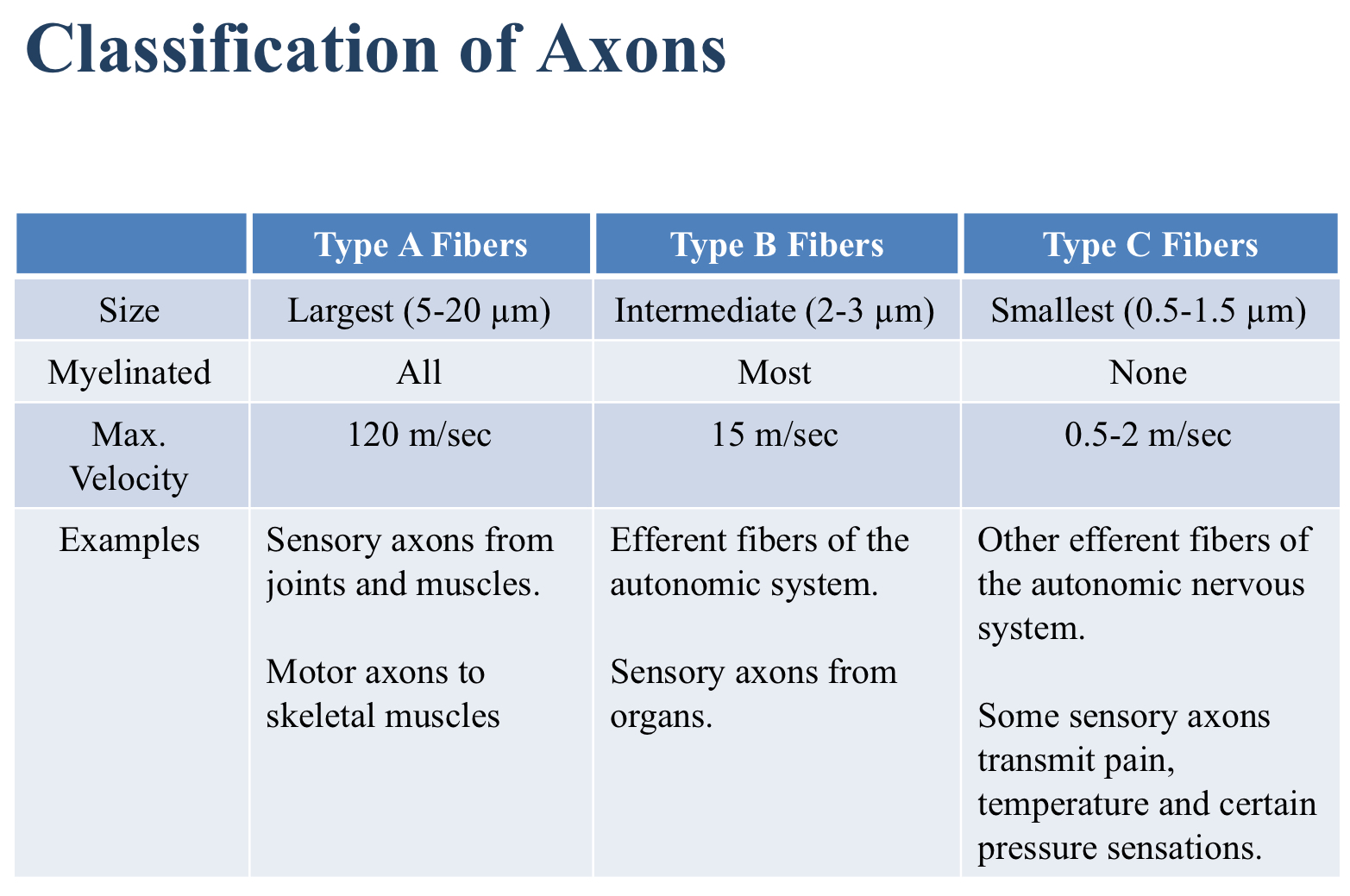
Which is a correct statement about the classification of axons?
A. Type A fibers have the smallest diameter
B. Type C fibers have the fastest conduction speed
C. Type C fibers are all unmyelinated
D. Type B fibers are all myelinated
C. Type C fibers are all unmyelinated
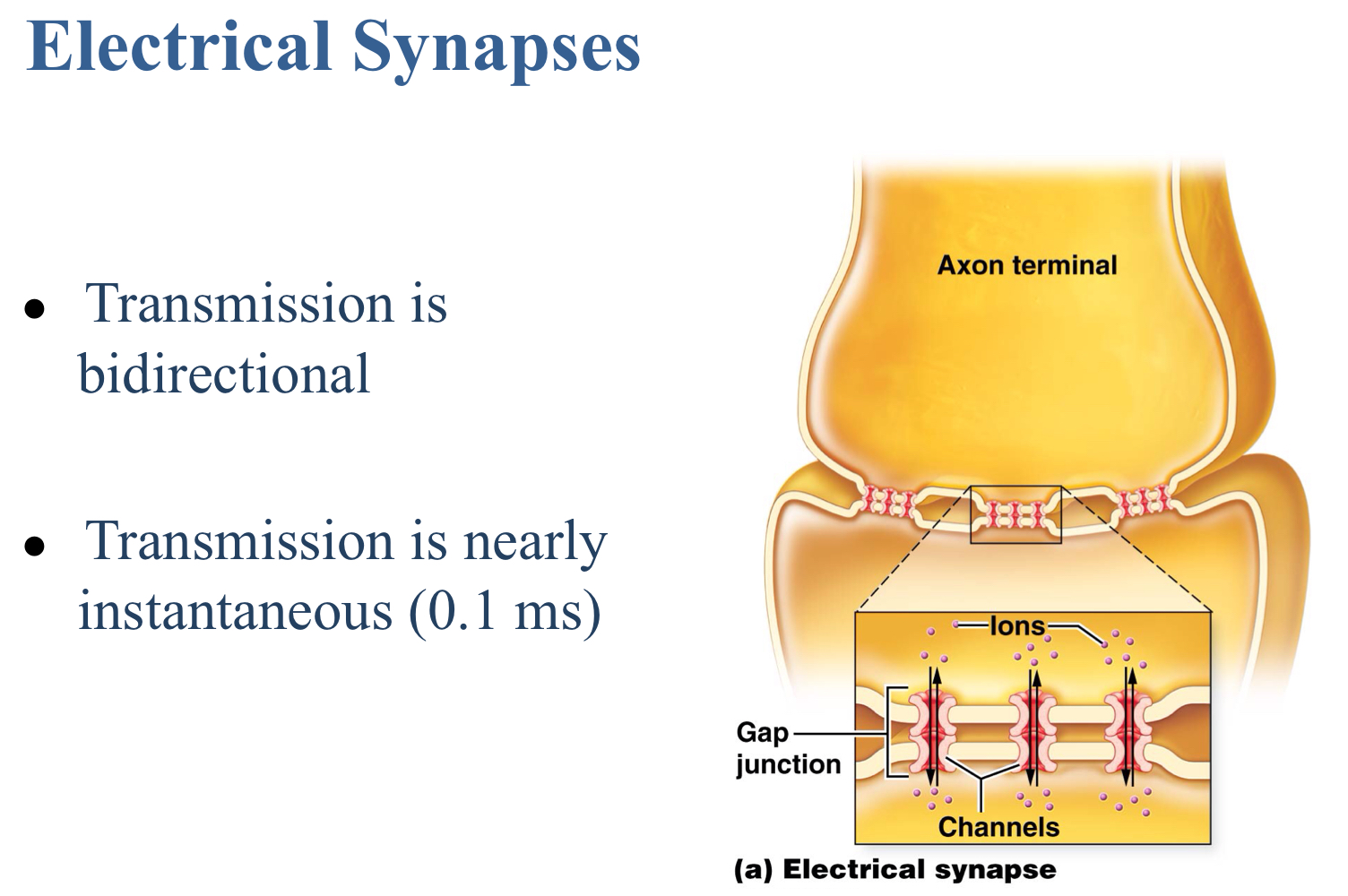
True or false: The transmission of an electrical synapse is bidirectional.
True
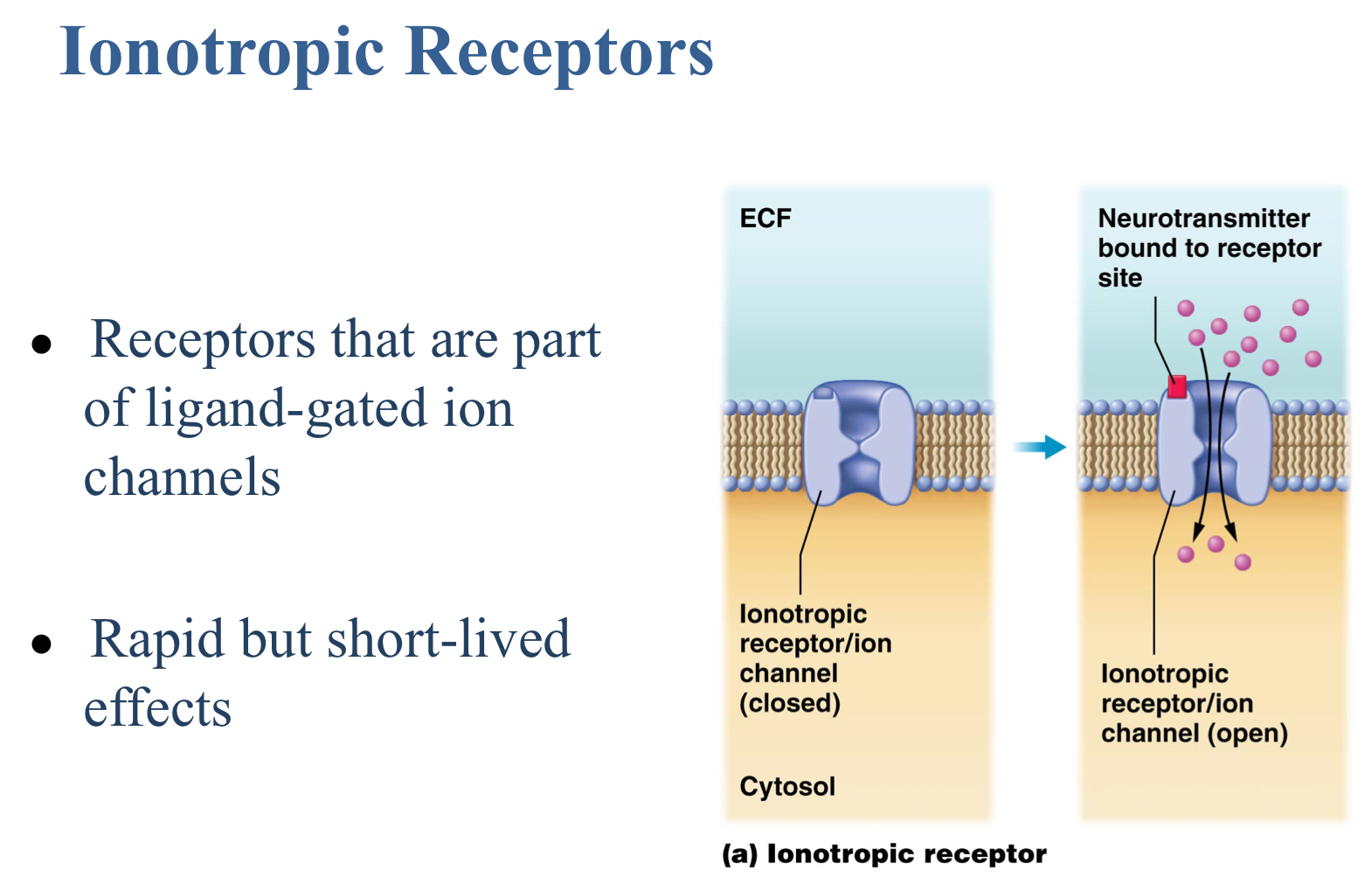
True or false: Most ionotropic receptors interact through intracellular enzymes called G-proteins that form a second messenger that opens or closes a channel.
False
Which is a neuropeptide?
A. Serotonin
B. Acetylcholine
C. Opioids
D. Glutamate
C. Opioids
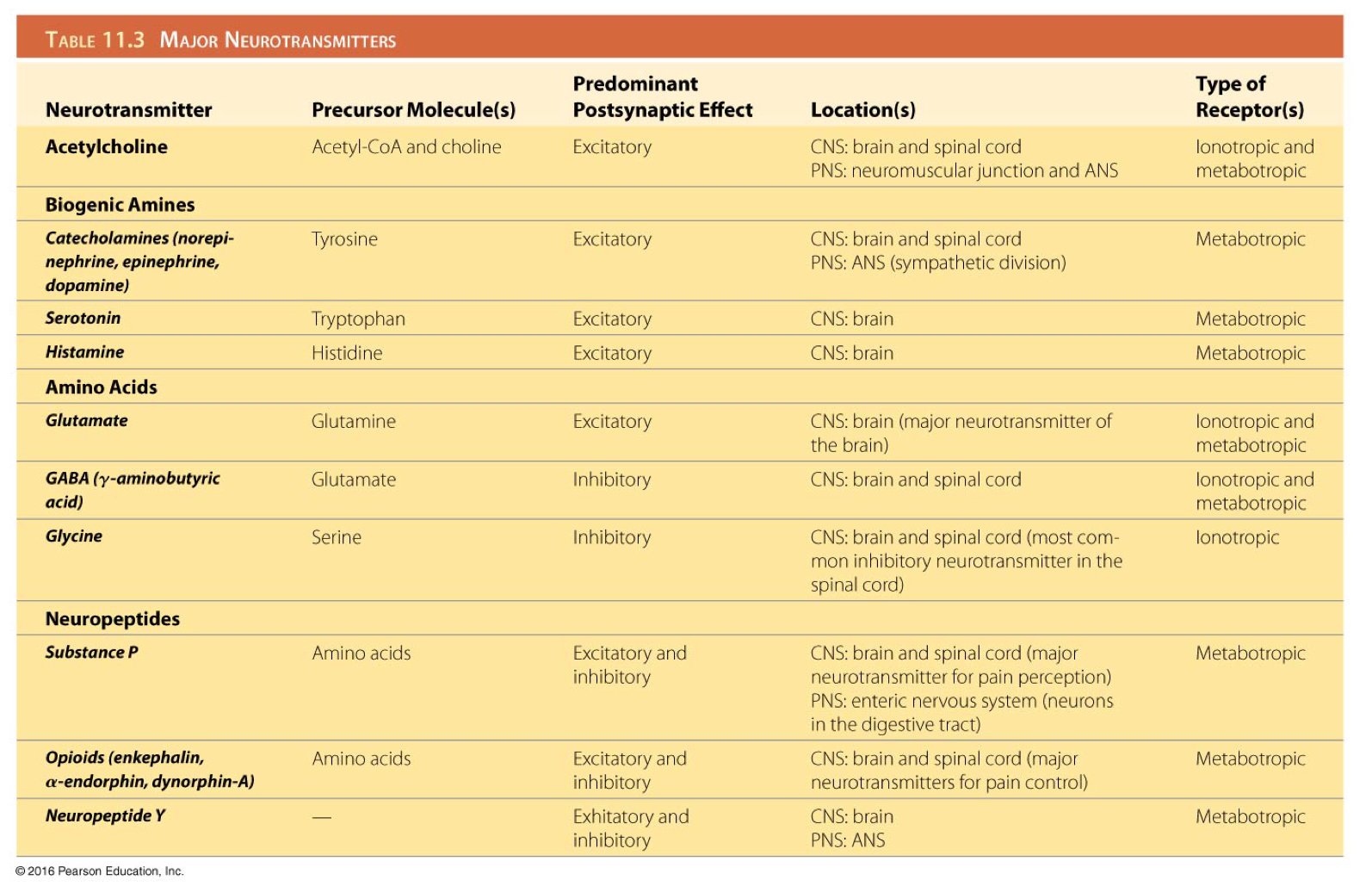
Which ions would produce an inhibitory post-synaptic potential?
Potassium and chloride
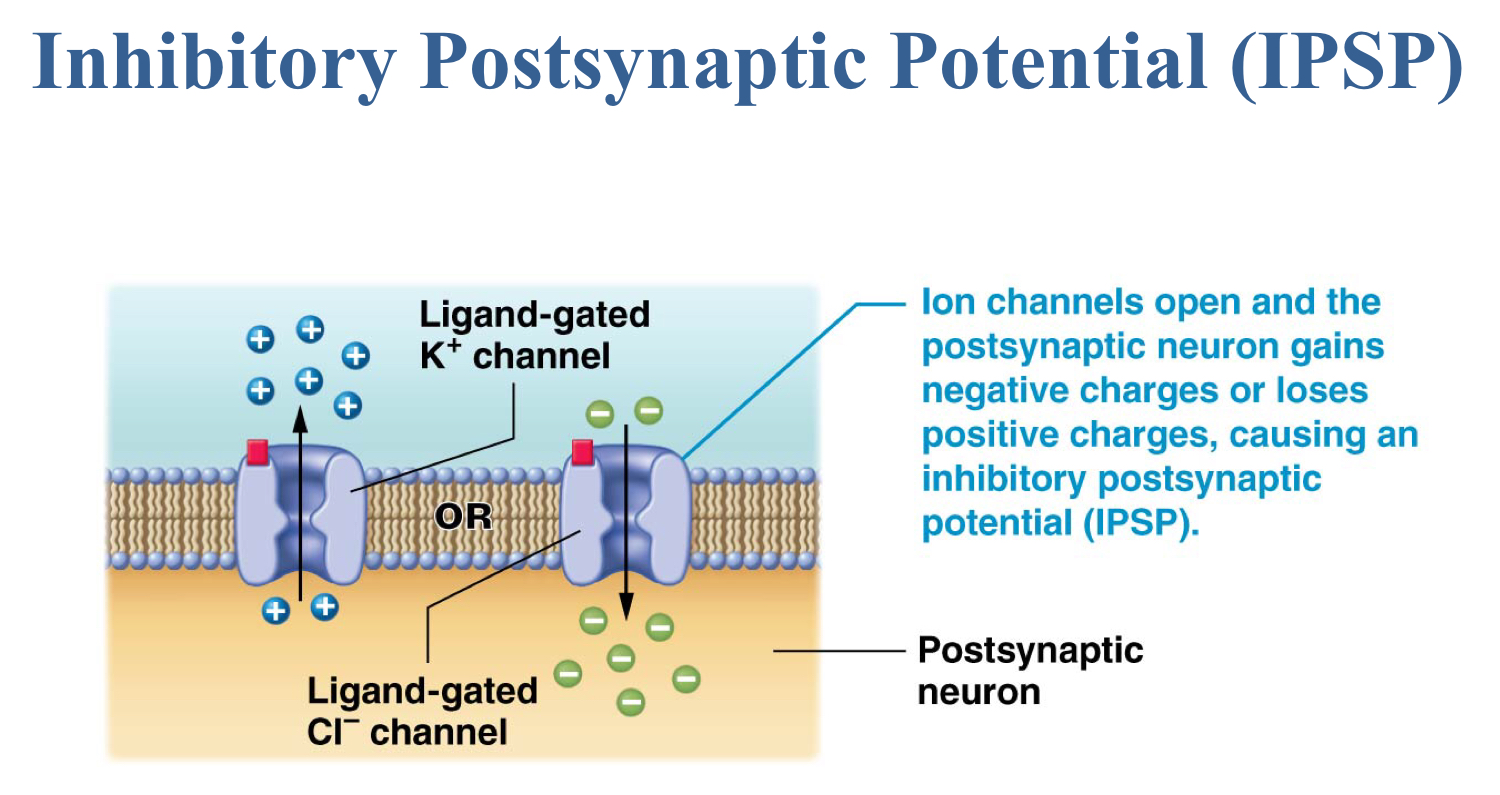
Place the events in the correct order:
Opening of voltage-gated calcium channels
IPSP or EPSP
Action potential along presynaptic axon
Exocytosis of neurotransmitters
Reuptake or degradation of neurotransmitter
3. Action potential along presynaptic axon
1. Opening of voltage-gated calcium channels
4. Exocytosis of neurotransmitters
2. IPSP or EPSP
5. Reuptake or degradation of neurotransmitters
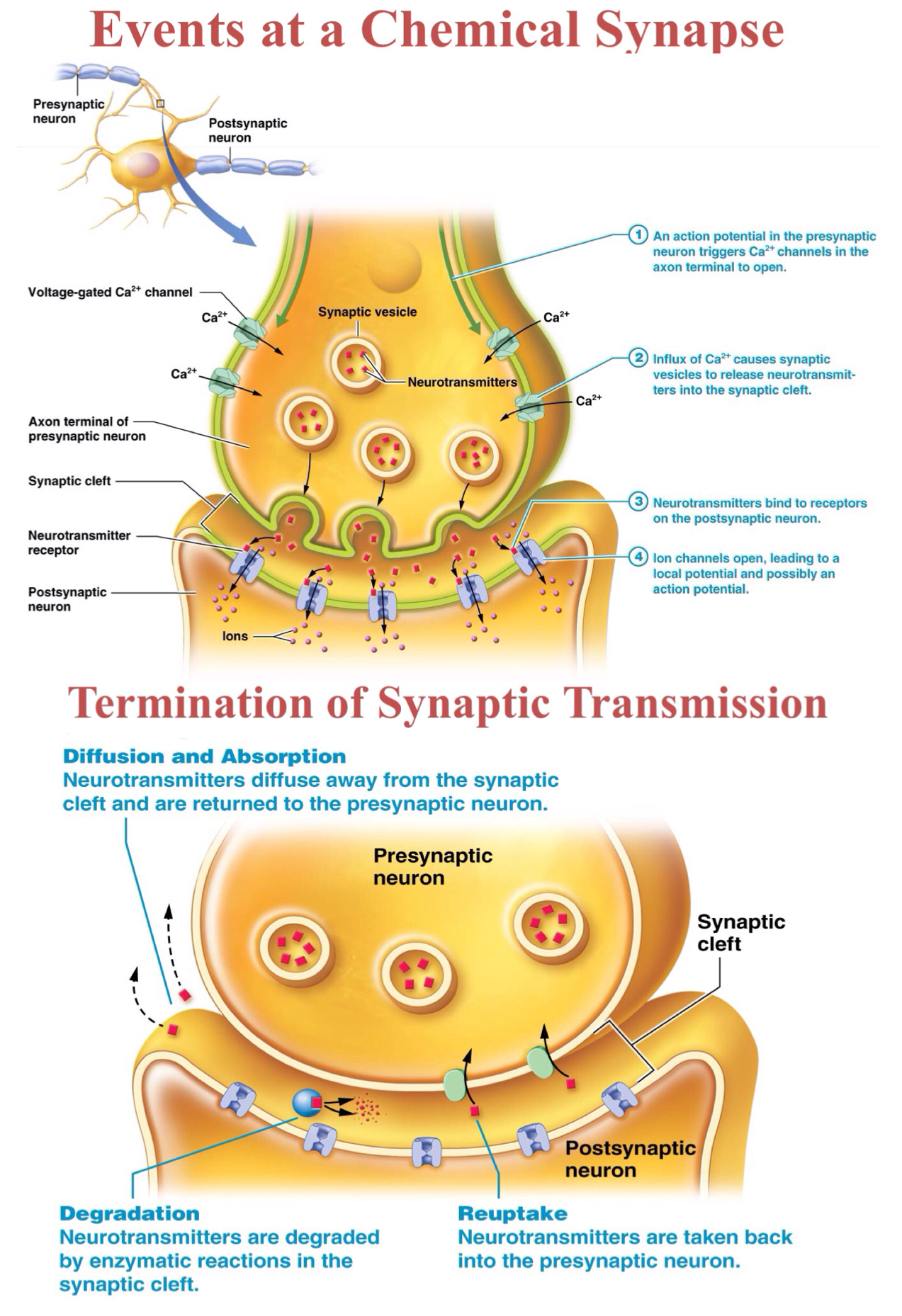
True or false: An EPSP is a small local hyperpolarization that moves the membrane potential of a postsynaptic neuron further away from threshold.
False
True or false: After image effects are produced from reverberating circuits.
True
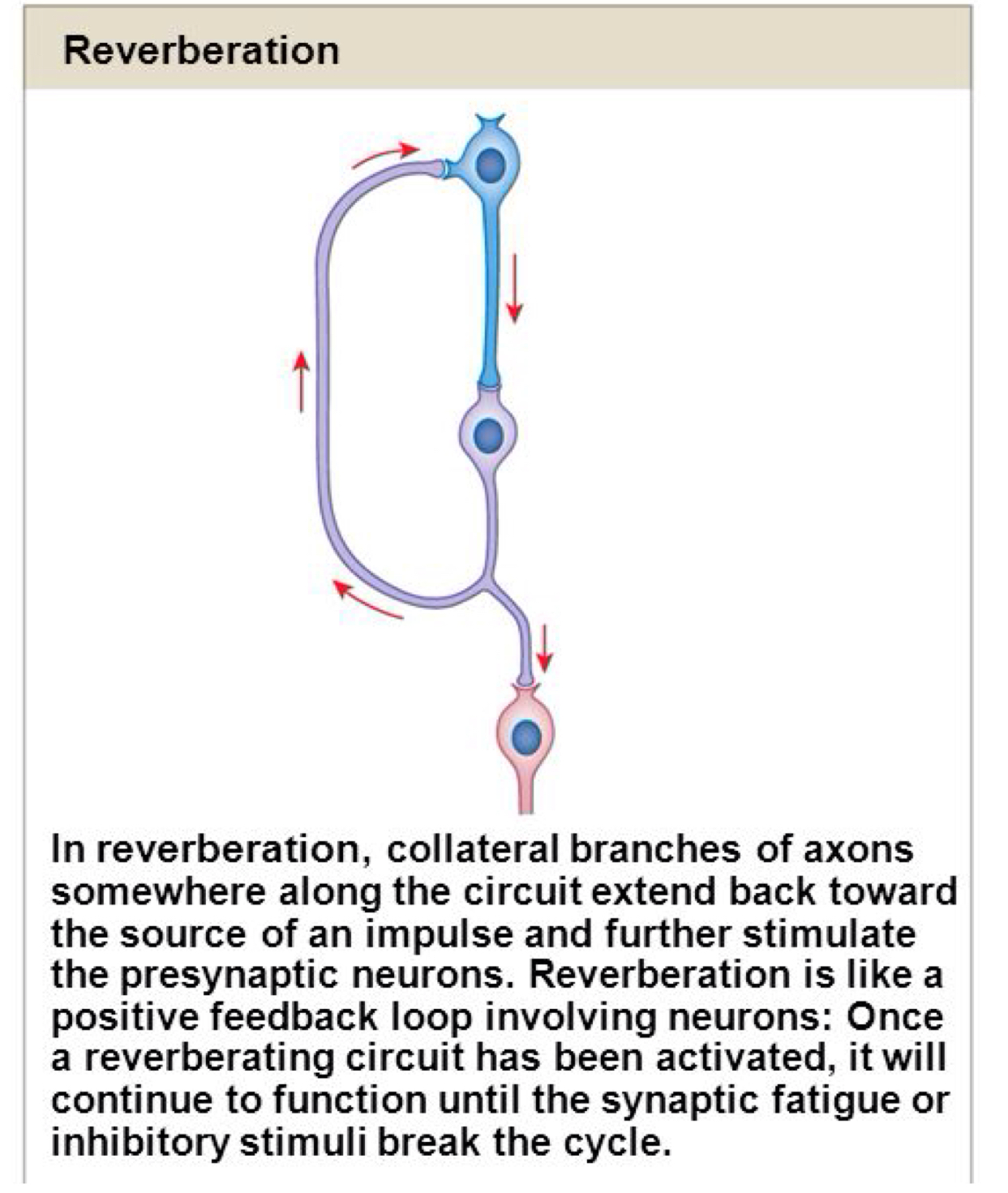
True or false: Neural integration is the process of comparing all stimuli that affect a neuron that either excite or inhibit the firing of an action potential.
True
Which is found in the spinal white matter?
Myelinated axons
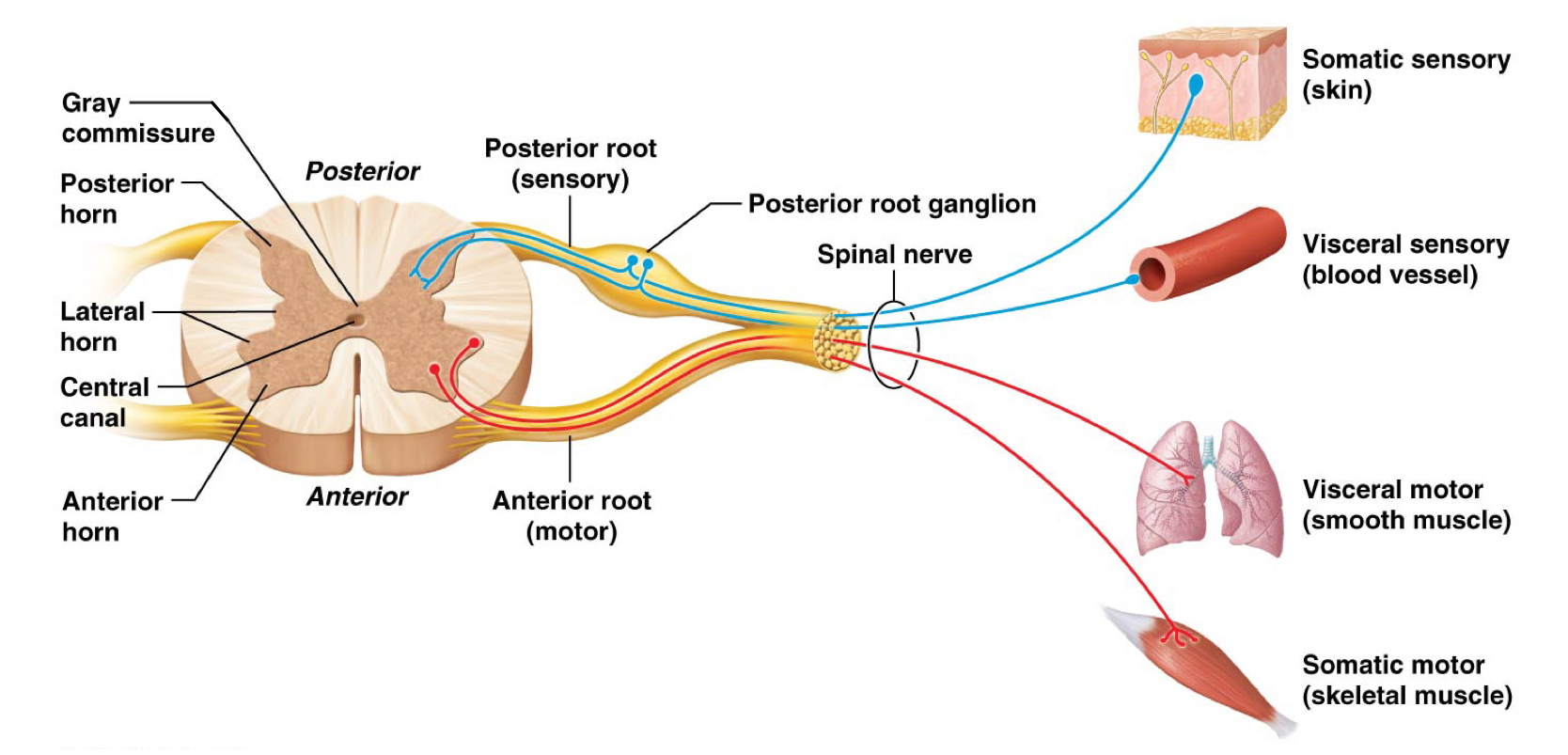
True or false: The anterior root is sensory in function while the posterior root is motor in function.
False
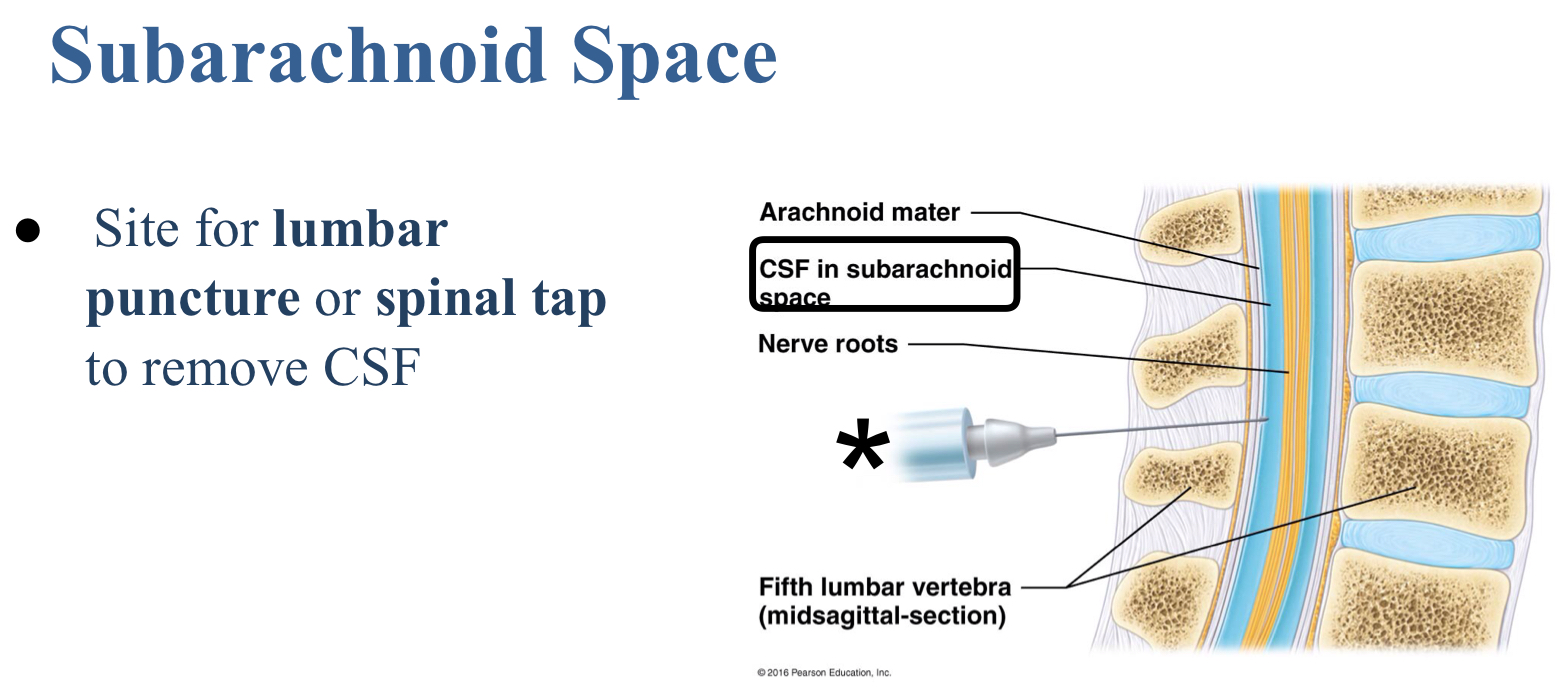
Which is the site for removal of cerebral spinal fluid in a spinal tap or lumbar puncture?
Subarachnoid space
Which functions for the control of the viscera through the autonomic nervous system?
Lateral gray horn

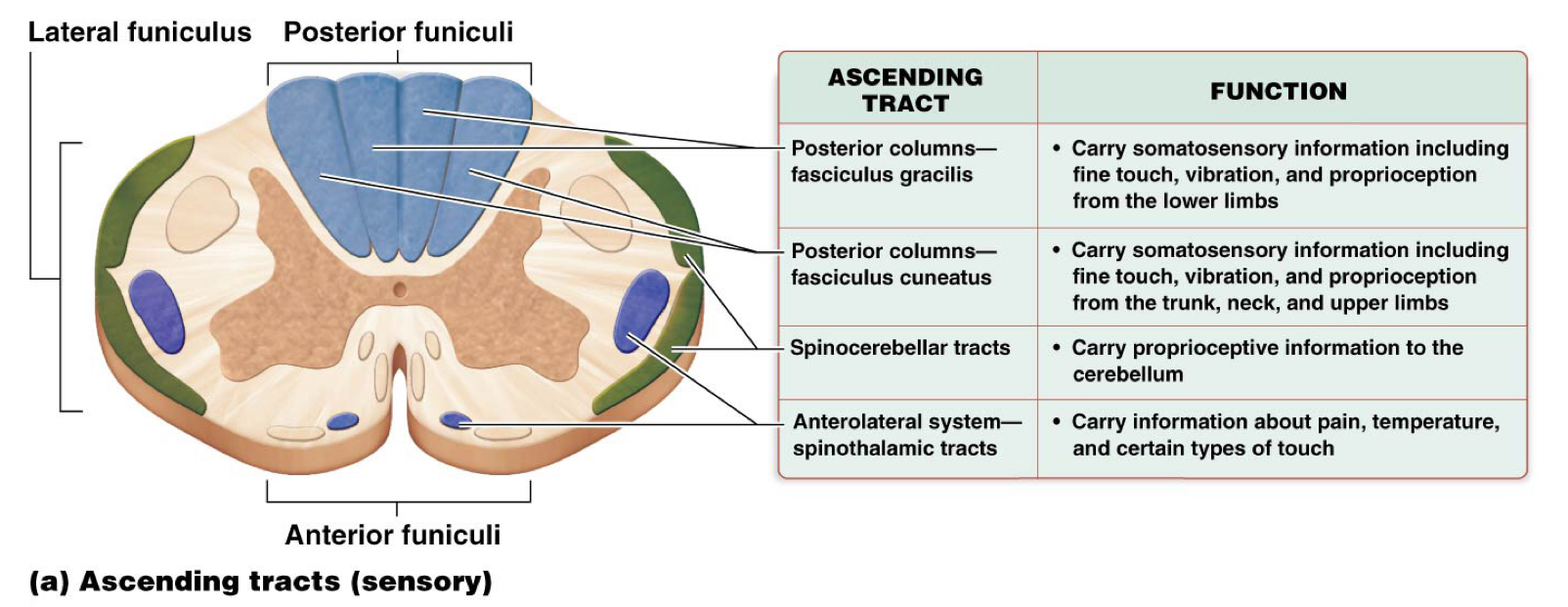
Which is an ascending tract of the spinal cord?
Spinocerebellar tract
All are characteristics of a reflex, EXCEPT?
A. Automatic
B. Programmed
C. Protective
D. Learned
D. Learned

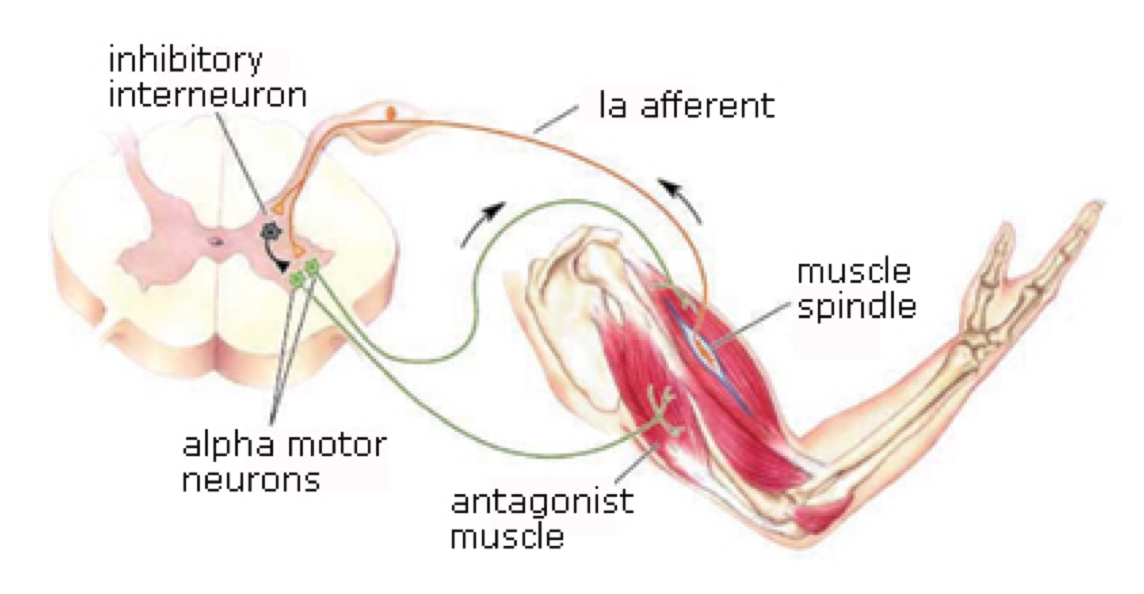
True or false: Reciprocal inhibition allows the antagonistic muscle to be inhibited at the same time when the muscle contracts.
True
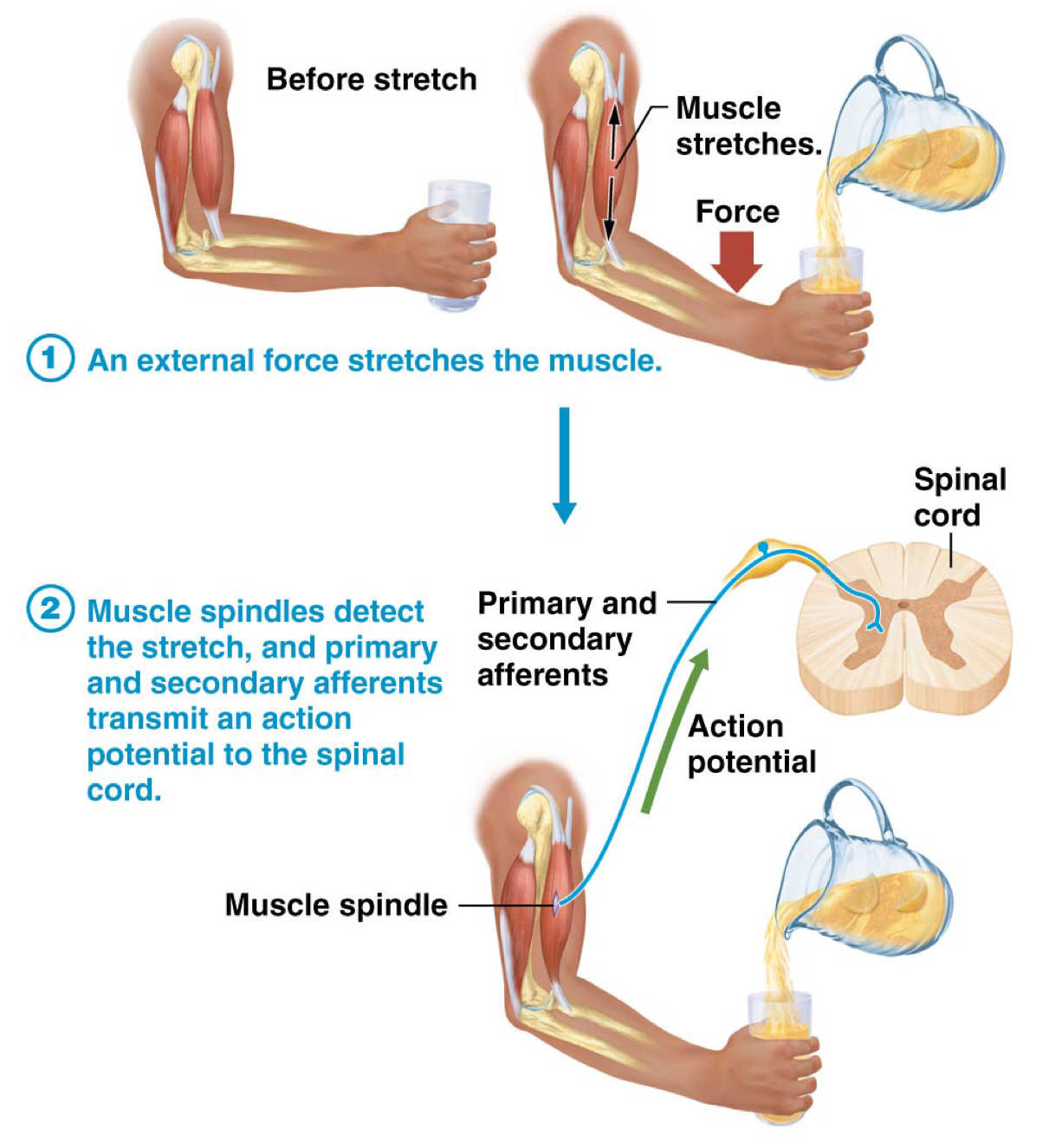
Which is the receptor in a simple stretch reflex?
Muscle spindle fibers
Which refers to a reflex that functions on the same side of the body?
Ipsilateral

True or false: The gag reflex is a type of cranial reflex.
True

Which brain regions are formed by the forebrain?
Cerebrum and diencephalon
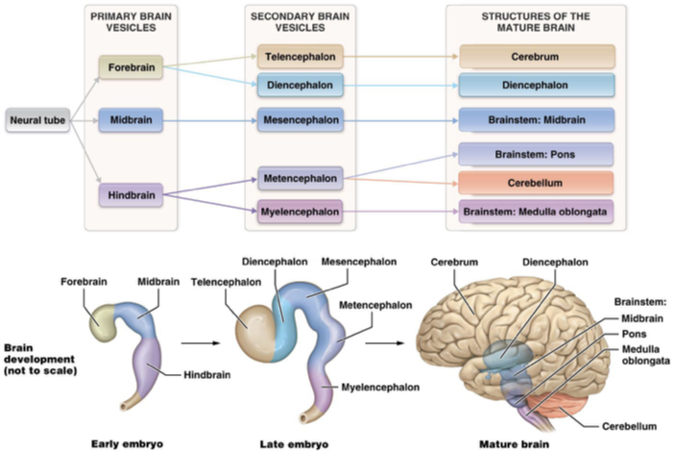
Which is the function of the choroid plexus?
It forms the cerebral spinal fluid
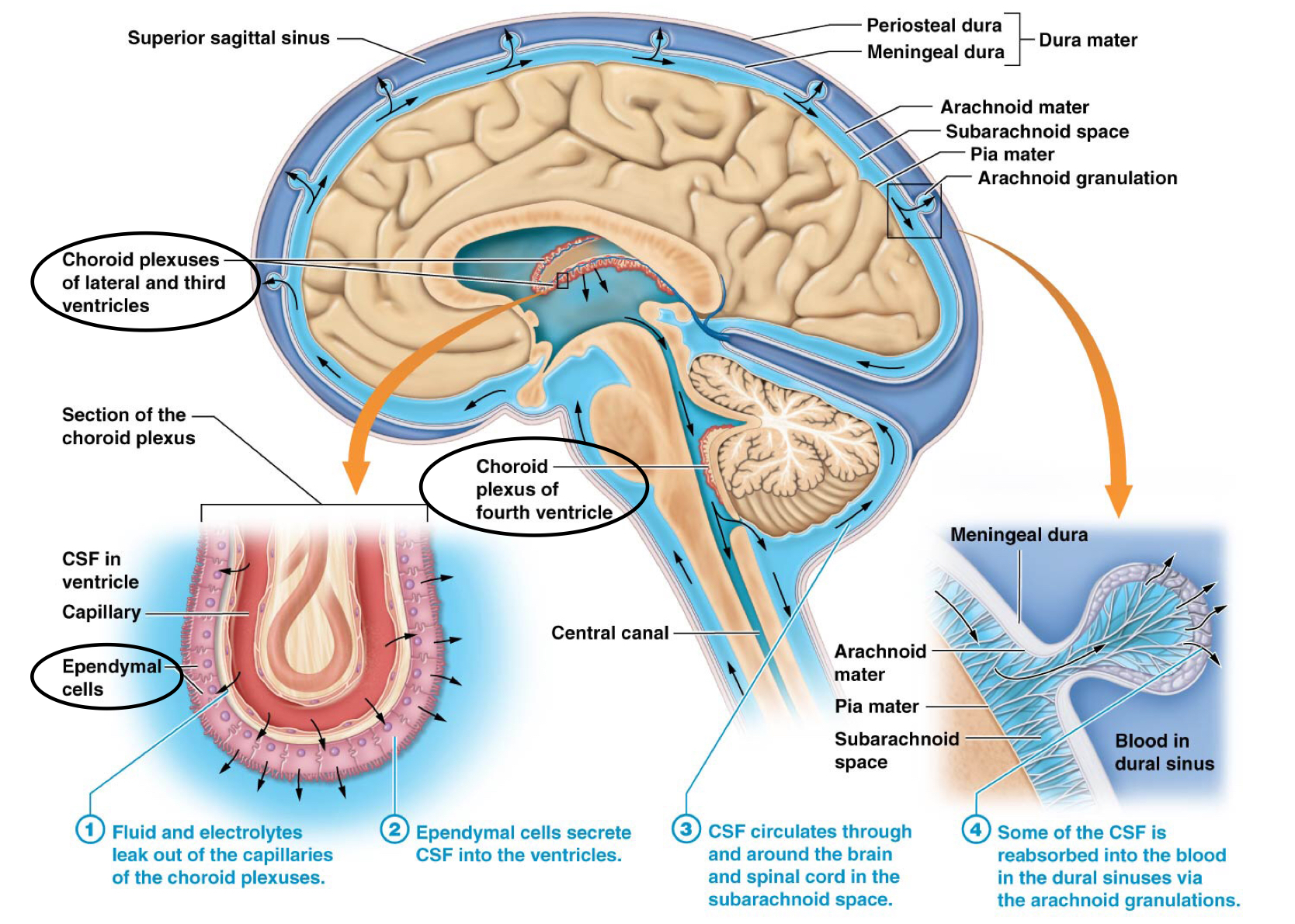
Which lobe of the brain functions for taste and visceral organs?
Insula

Which is the location of the primary motor cortex?
Pre-central gyrus
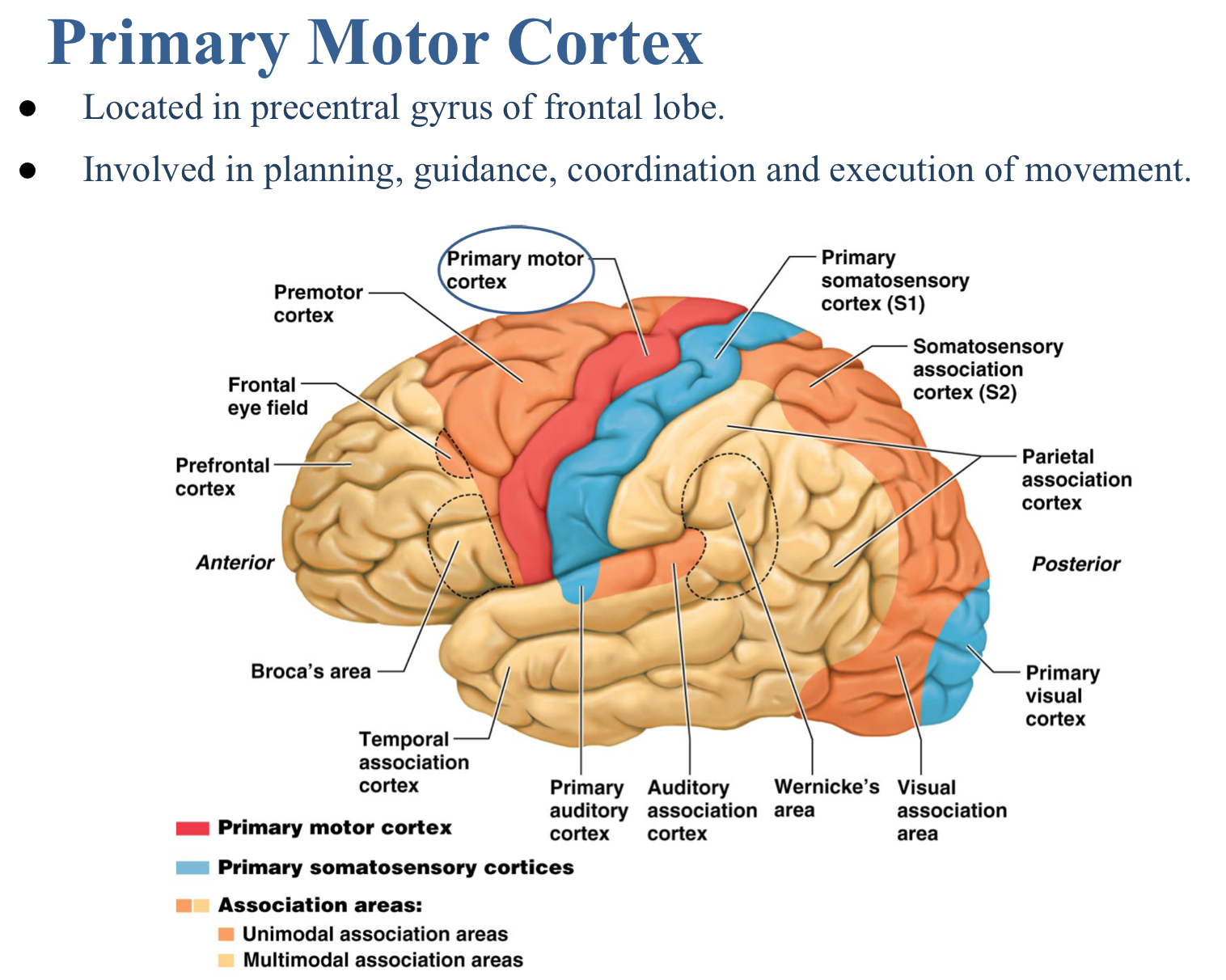
Which produces melatonin to regulate sleep/wake cycles?
Pineal gland
True or false: The basal nuclei functions in body movement but disorders also cause behavioral, cognitive and perception problems.
True

Which fiber connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres?
Commissural
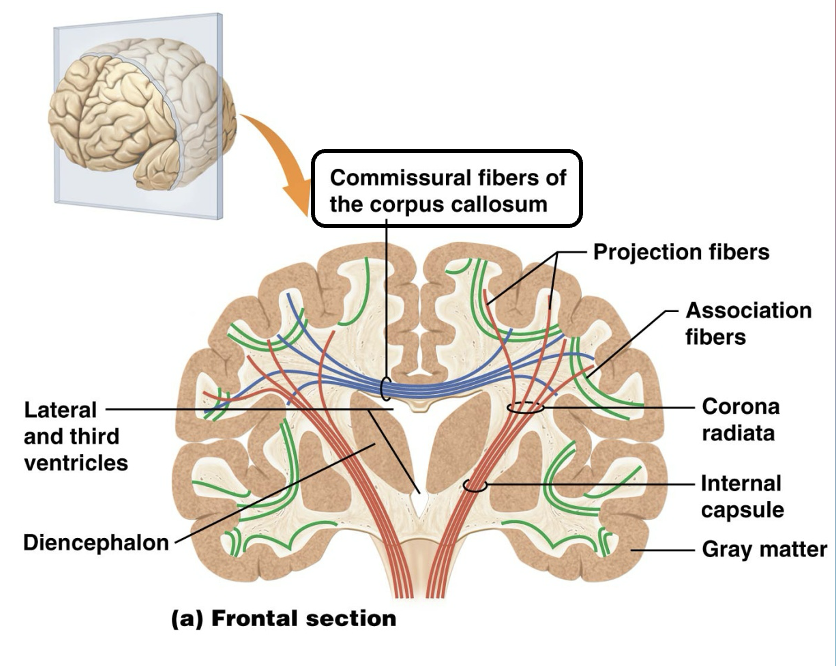
All are endocrine organs of the diencephalon EXCEPT?
A. Pineal gland
B. Mammillary body
C. Hypothalamus
D. Pituitary gland
B. Mammillary body
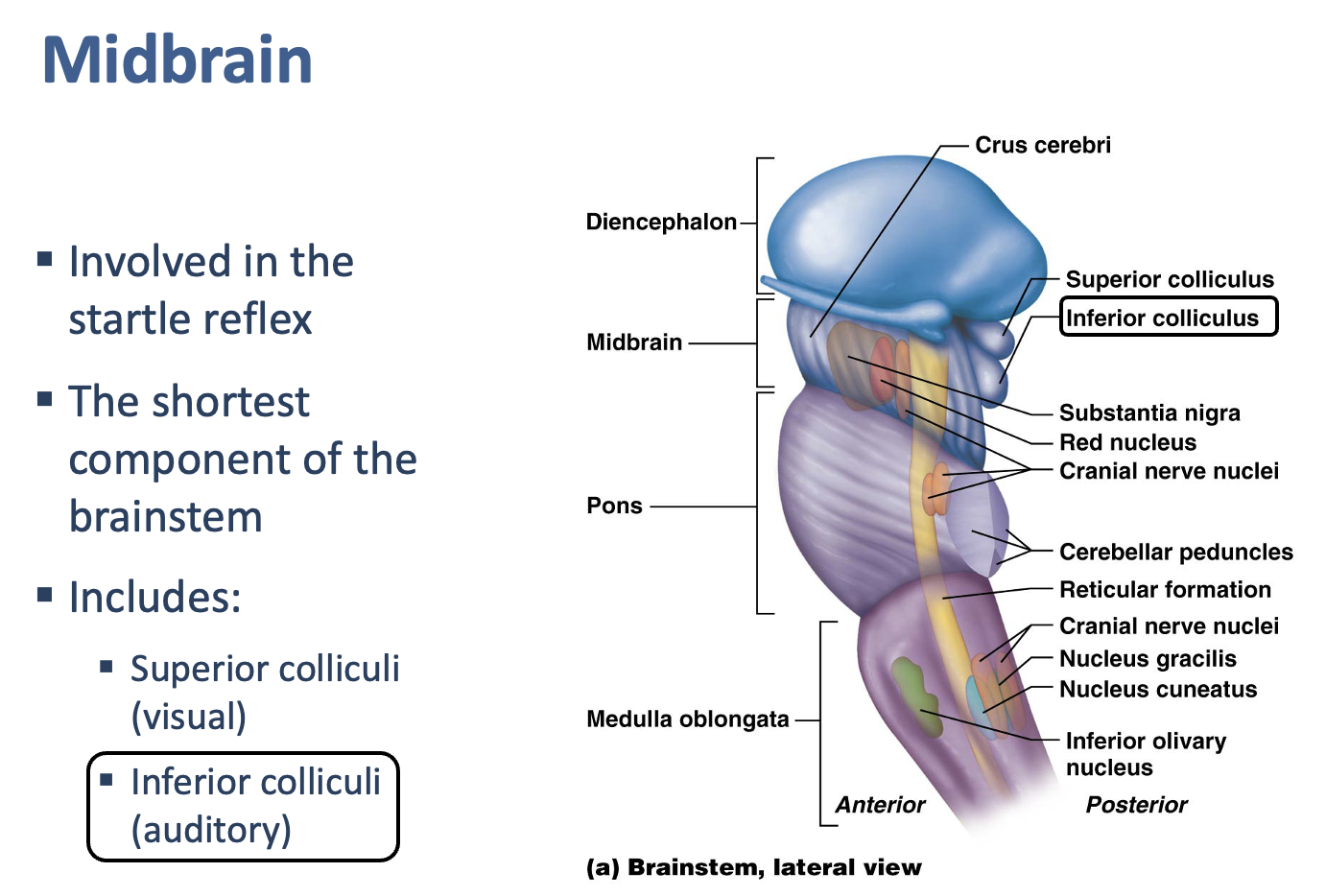
Which has a role in auditory function?
Inferior colliculus
Which statement has the correct cranial nerve number, name and function?
A. III, Oculomotor, sensory and motor.
B. V, Trigeminal, both sensory and motor.
C. VIl, Facial, motor only.
D. IX, Glossopharyngeal, motor only.
E. XI, Hypoglossal, sensory.
B. V, Trigeminal, both sensory and motor
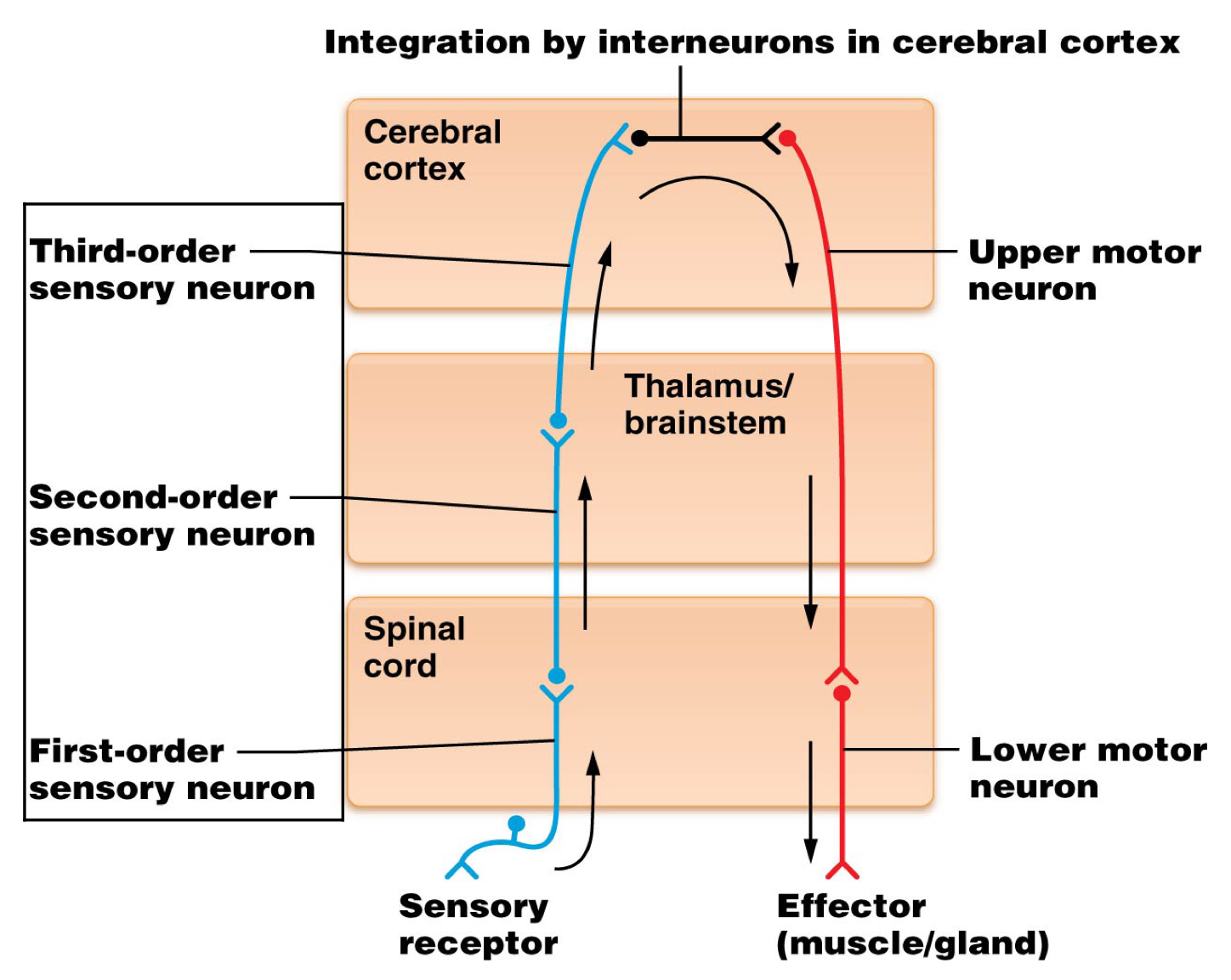
True or false: Motor pathways have upper and lower neurons.
True
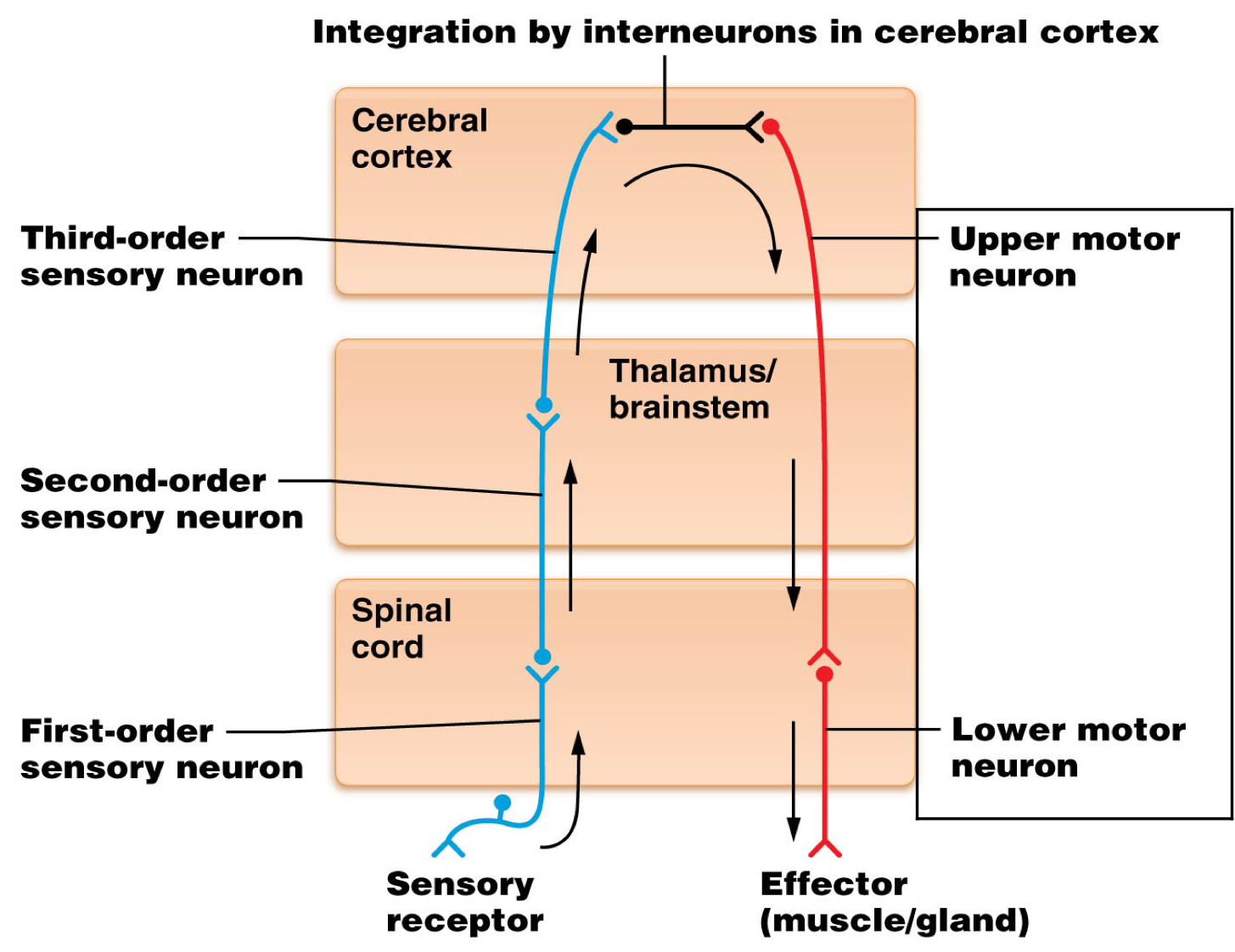
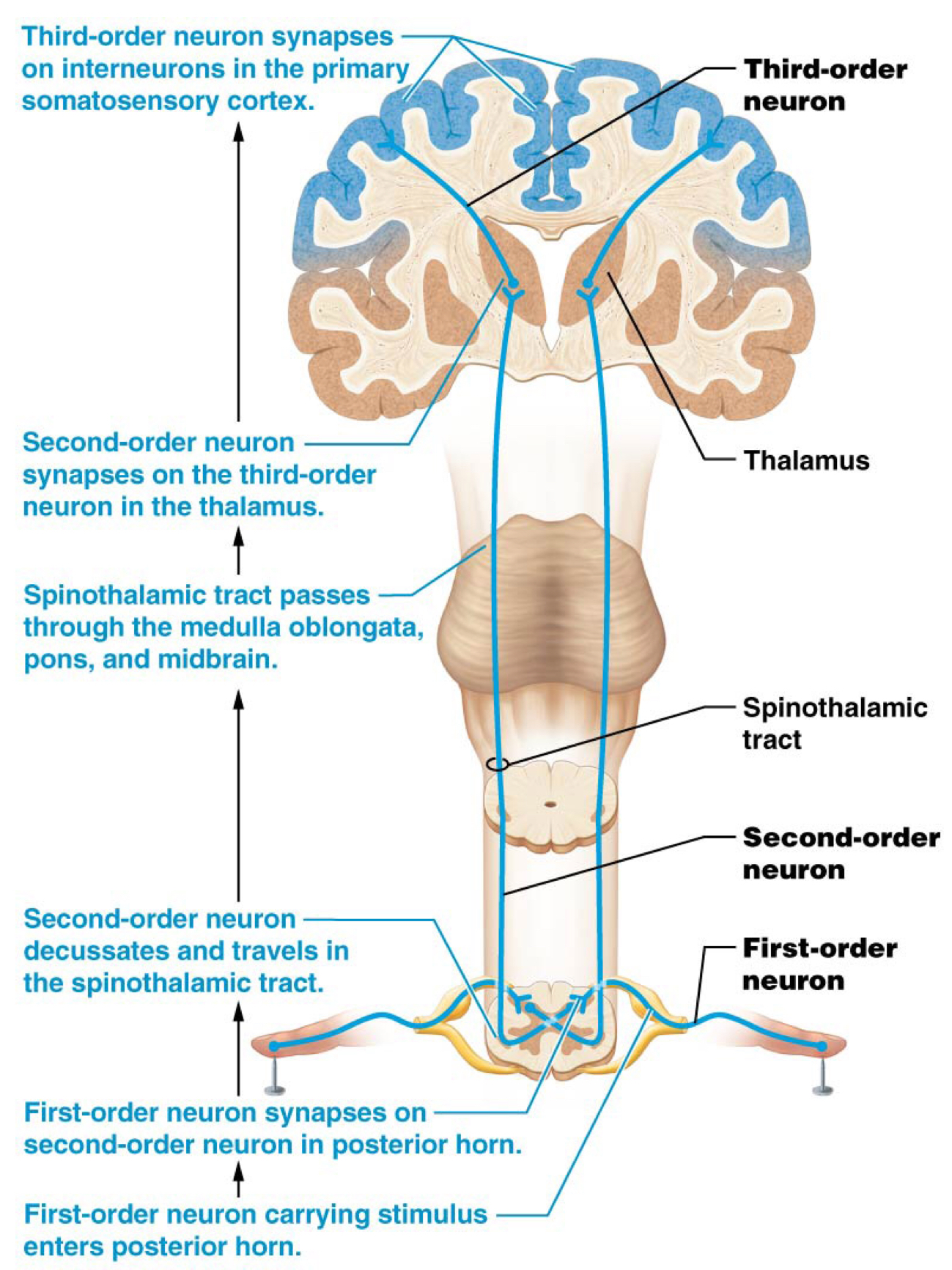
Which is the location of decussation for the spinothalamic pathway?
Spinal cord
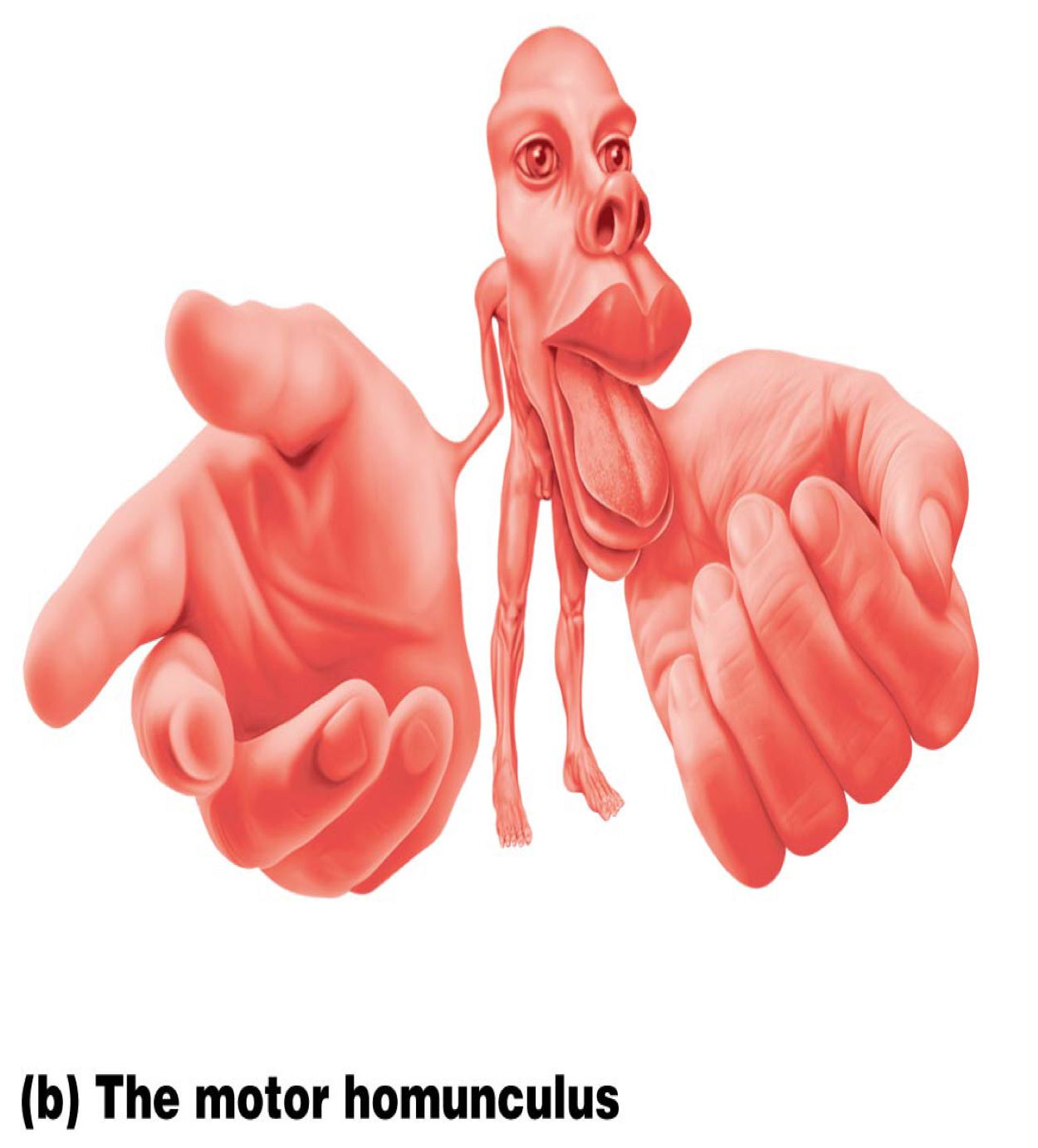
All are correct about the motor homunculus EXCEPT?
A. Big lips
B. Big ears
C. Big tongue
D. Big hands
E. Big fingers
B. Big ears
Which is the location of the cell body of most third order neurons?
Thalamus/brainstem
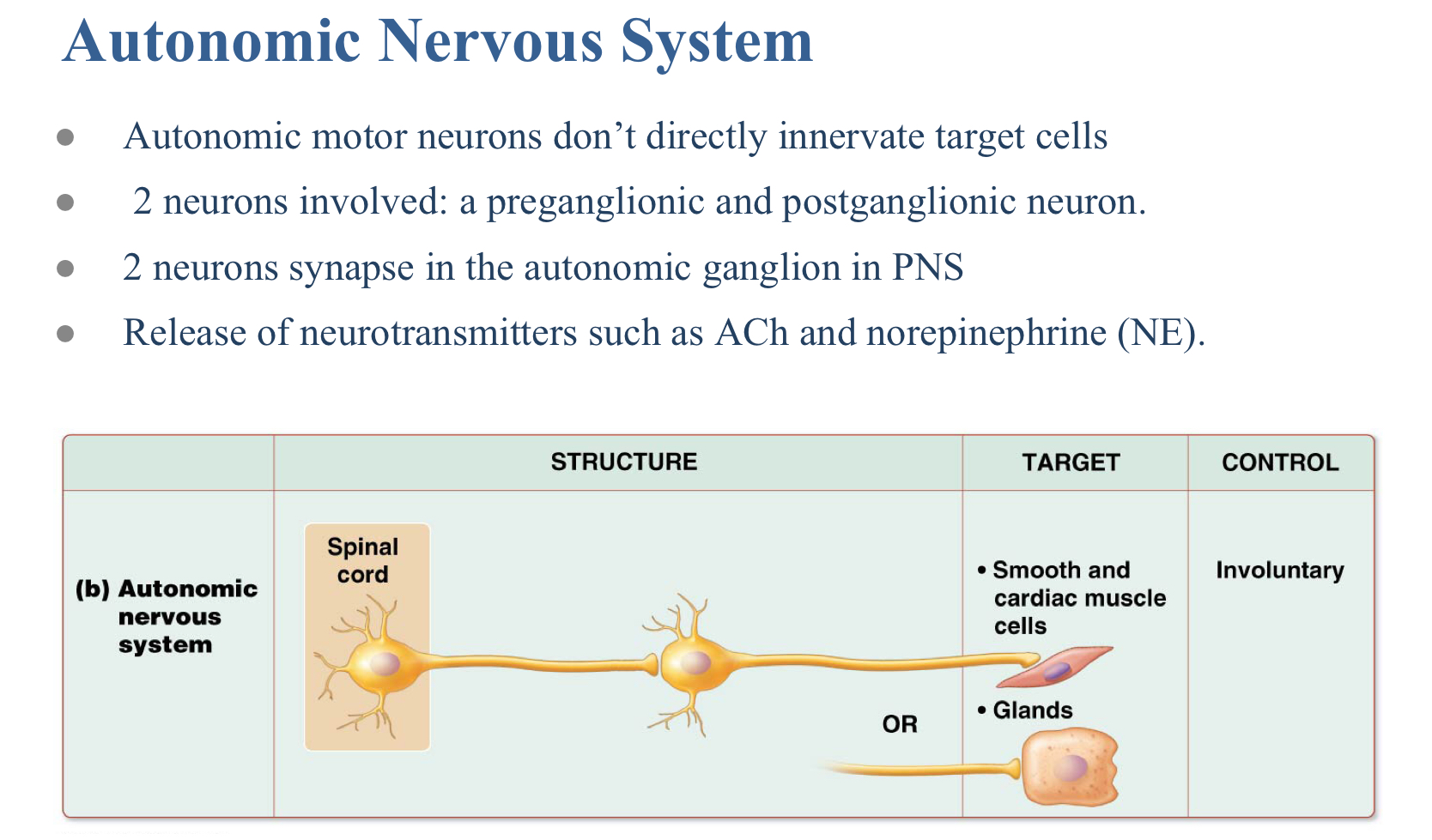
All are properties of the autonomic nervous system EXCEPT?
A. It is composed of two neurons
B. It has myelinated axons
C. It has targets that include smooth muscle
D. It is involuntary
B. It has myelinated axons
True or false: The sympathetic nervous system has cell bodies of preganglionic neurons that originate in the brain stem and sacral spinal cord.
False
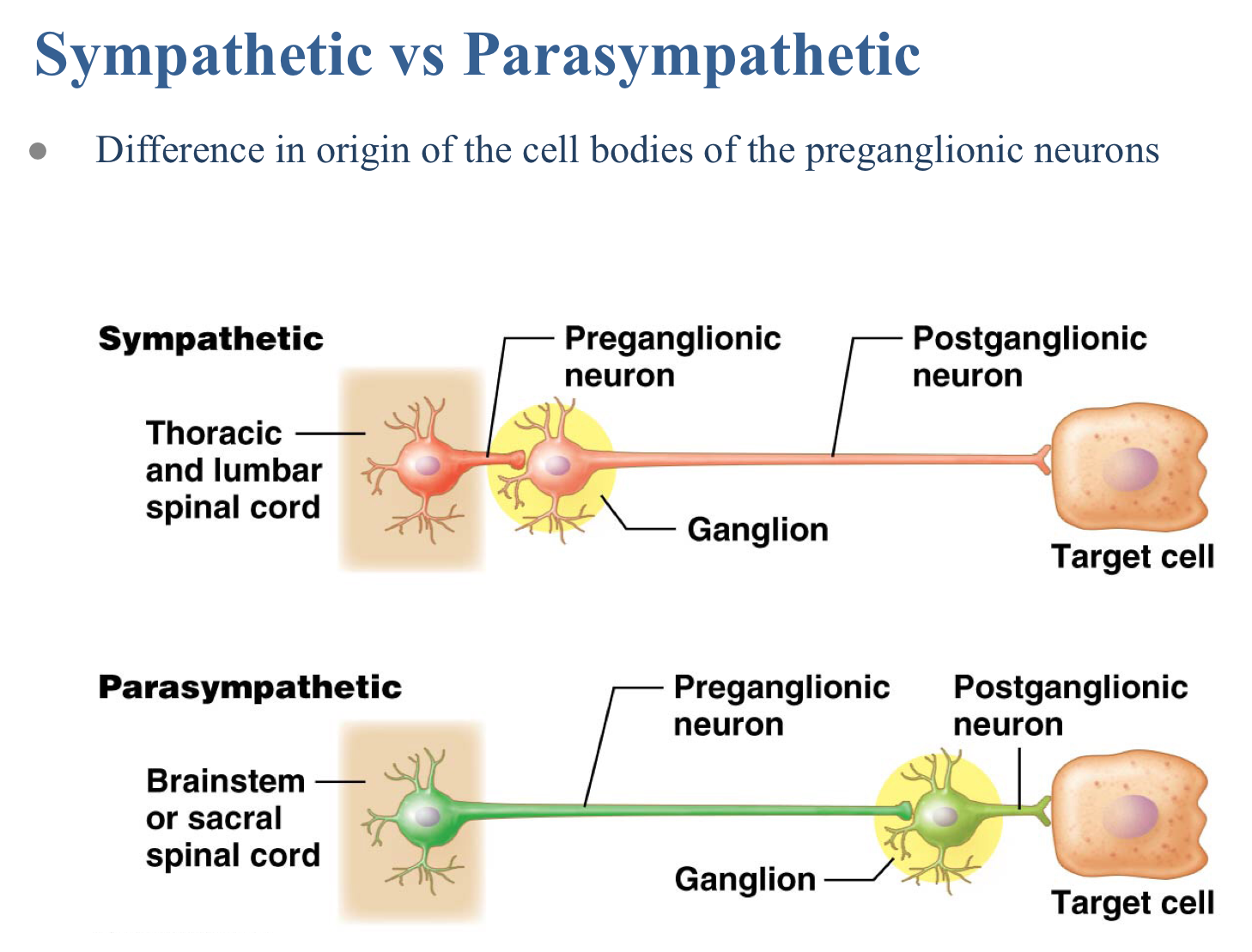
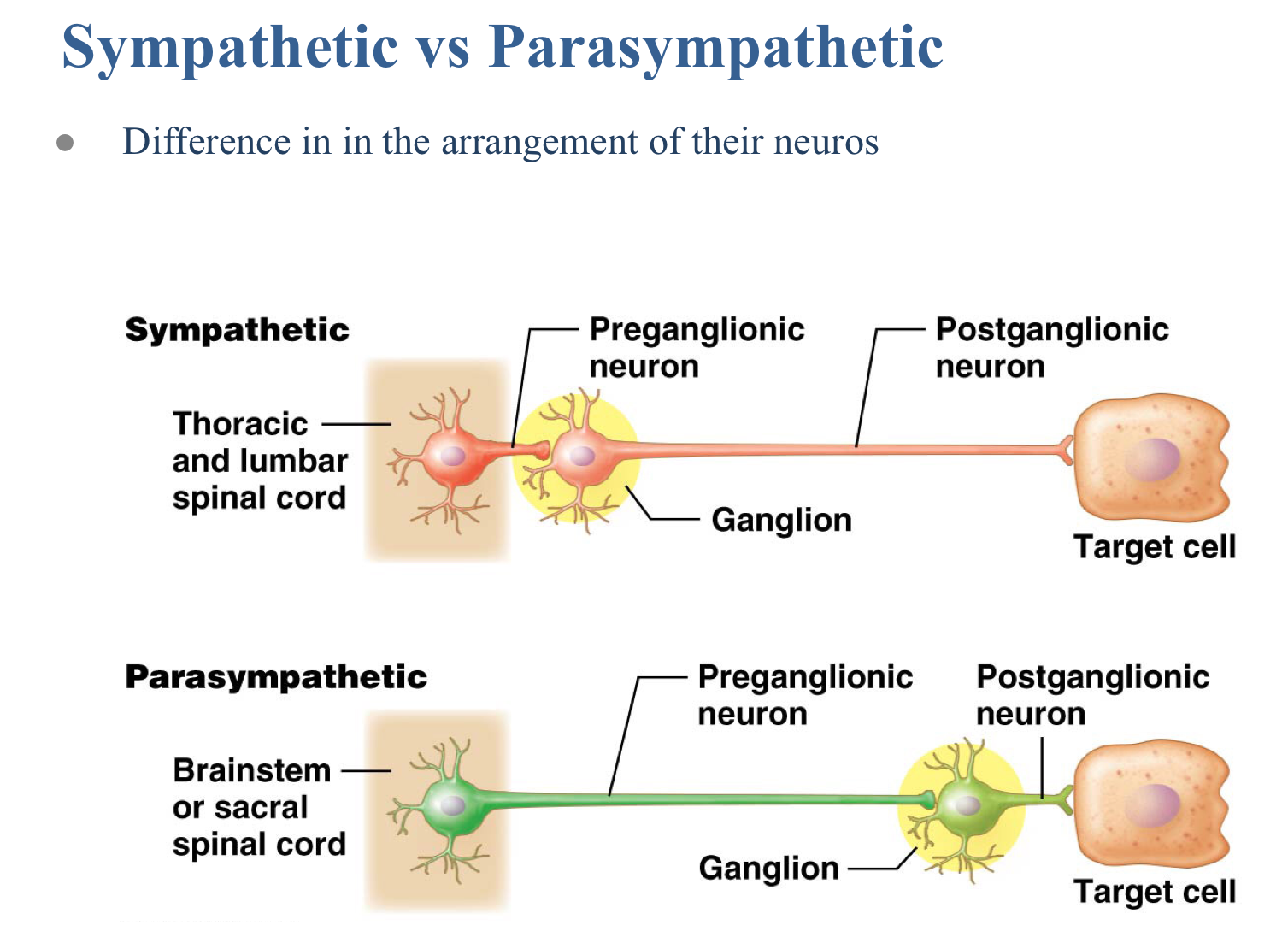
True or false: The sympathetic nervous system has shorter preganglionic axons and longer postganglionic axons than in the parasympathetic nervous system.
True
True or false: Acetylcholine is secreted from both the sympathetic and parasympathetic pre-ganglionic neurons.
True
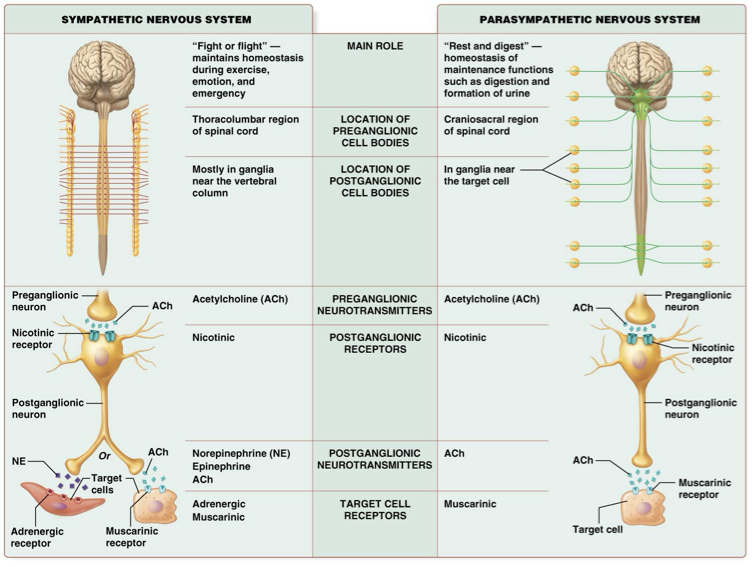
Which receptor is found on the target cells of the parasympathetic nervous system?
Muscarinic
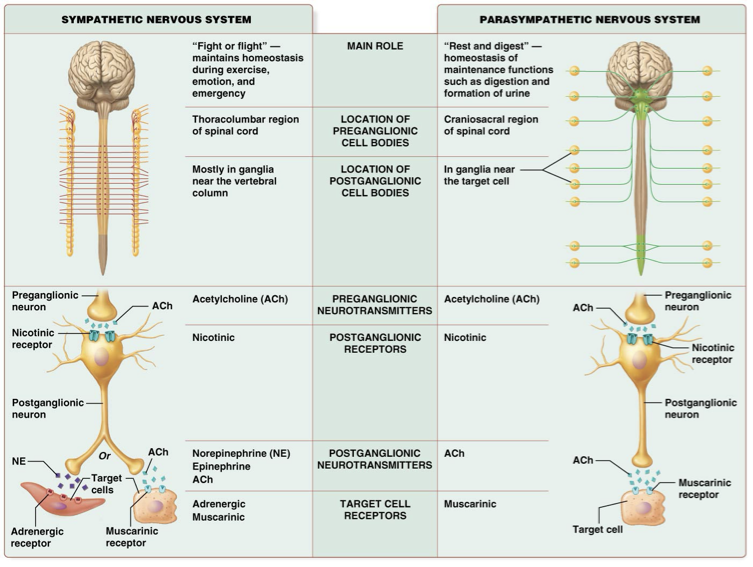
All are cranial nerves associated with the parasympathetic nervous system EXCEPT?
A. Oculomotor (III)
B. Glossopharyngeal (IX)
C. Facial (VII)
D. Accessory (XI)
E. Vagus (X)
D. Accessory (XI)
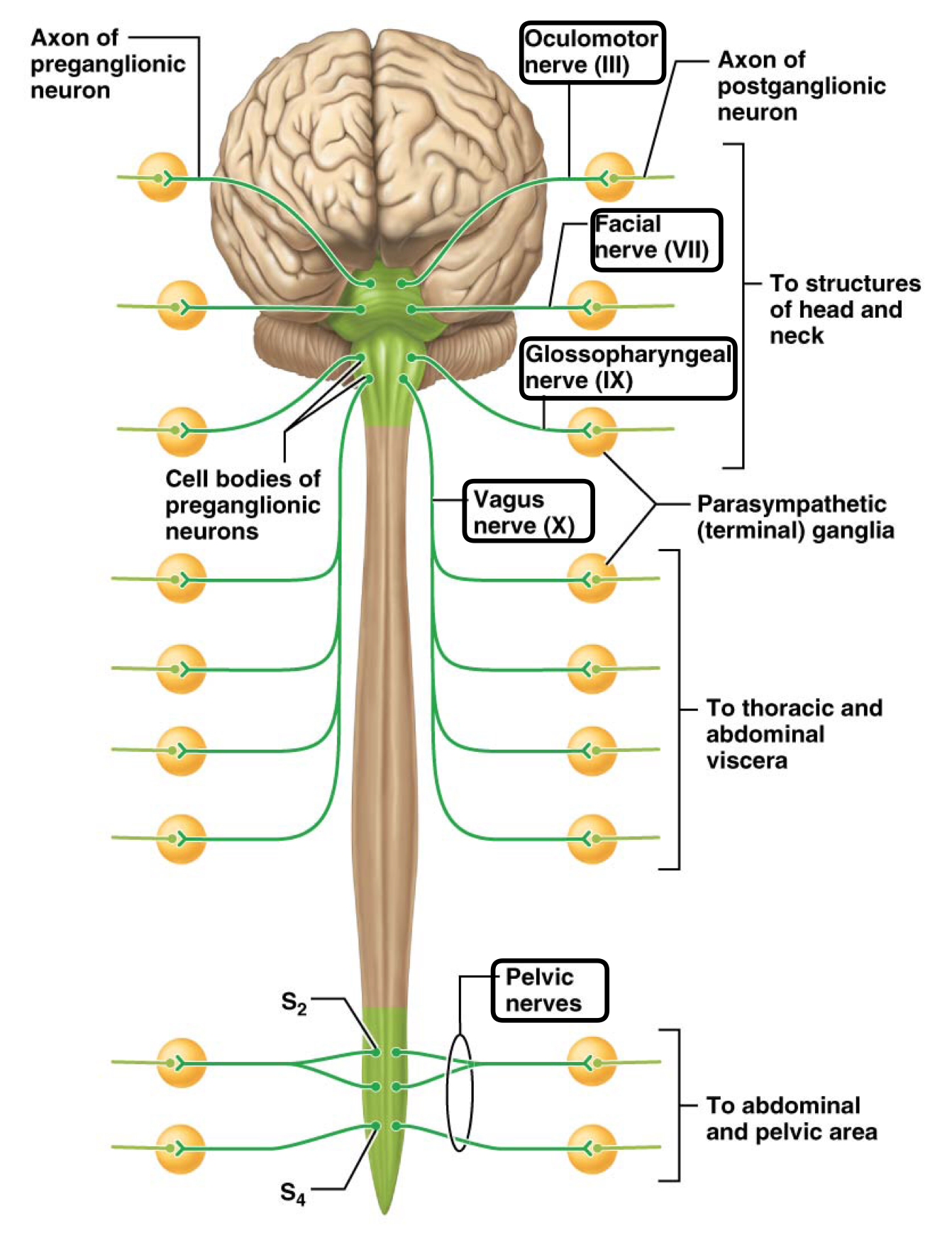
Which disorder is due to the degeneration of cell bodies of motor neurons in the anterior horn of the spinal cord and upper motor neurons of the cerebral cortex?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Which is an autoimmune disorder?
Multiple sclerosis

True or false: Sensory transduction is the process of converting a stimulus into an electrical signal.
True
Which are rapidly adapting receptors?
Meissner's corpuscles and Pacinian corpuscles
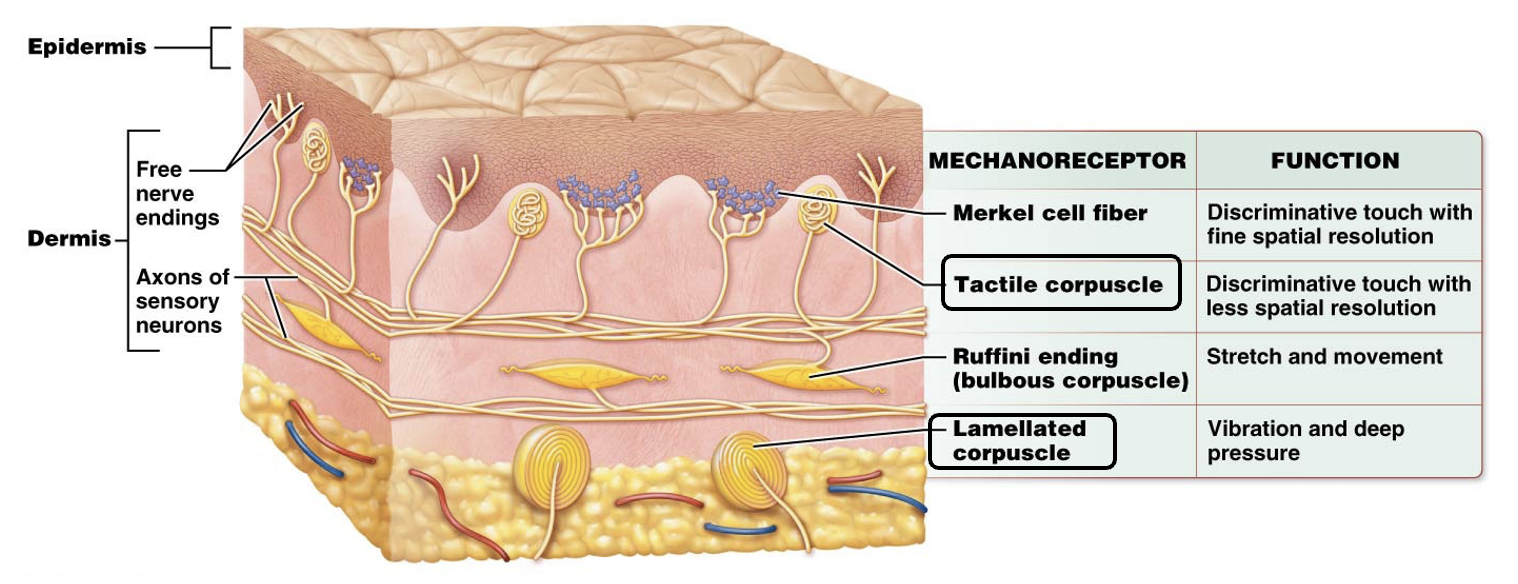
Which special sense does not have a specialized receptor cell?
Olfaction
Which is the age-related condition when close vision becomes difficult?
Presbyopia
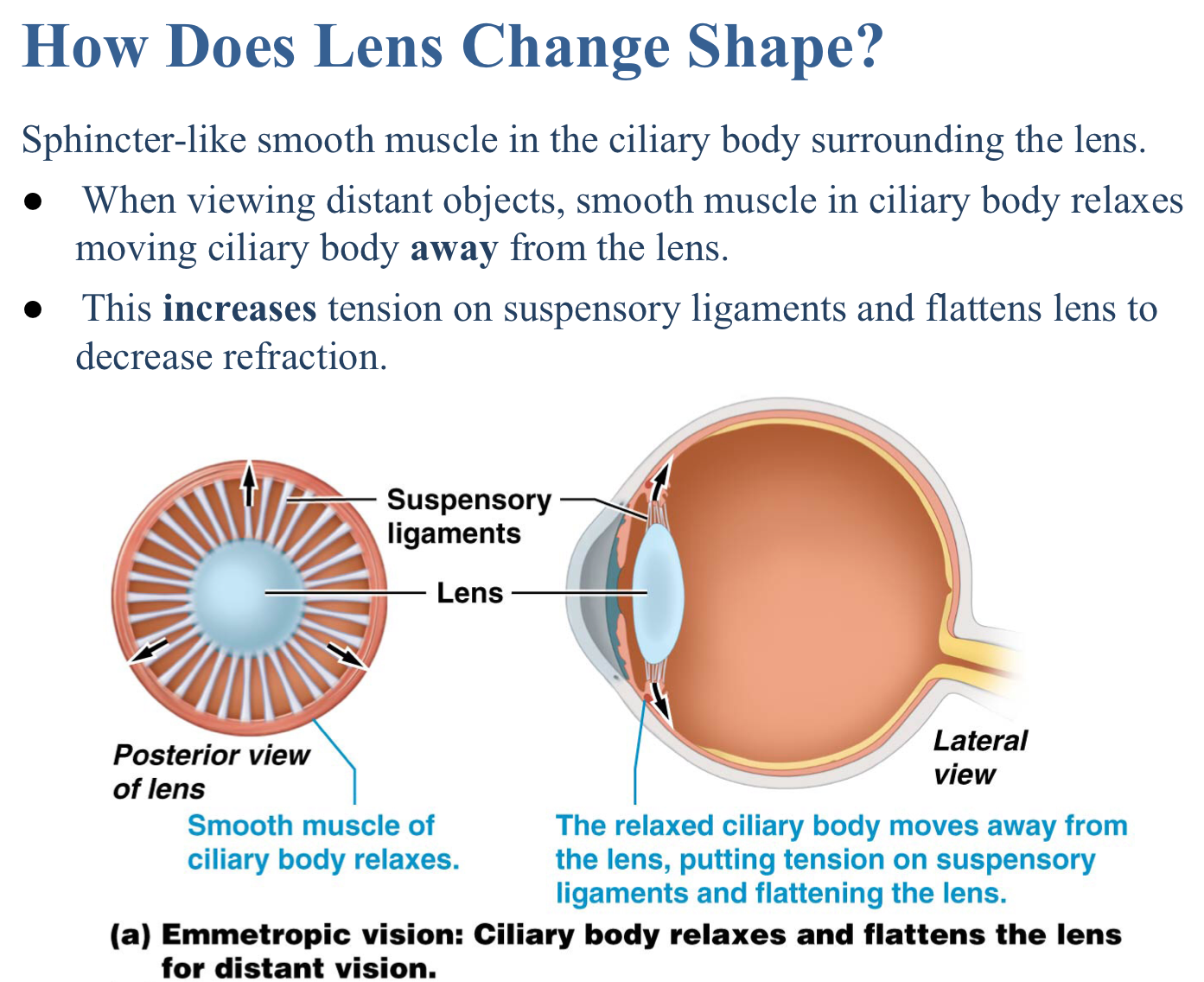
True or false: When viewing distant objects, the ciliary body contracts moving the ciliary body away from the lens to increase tension on the suspensory ligaments and the lens thickens.
False
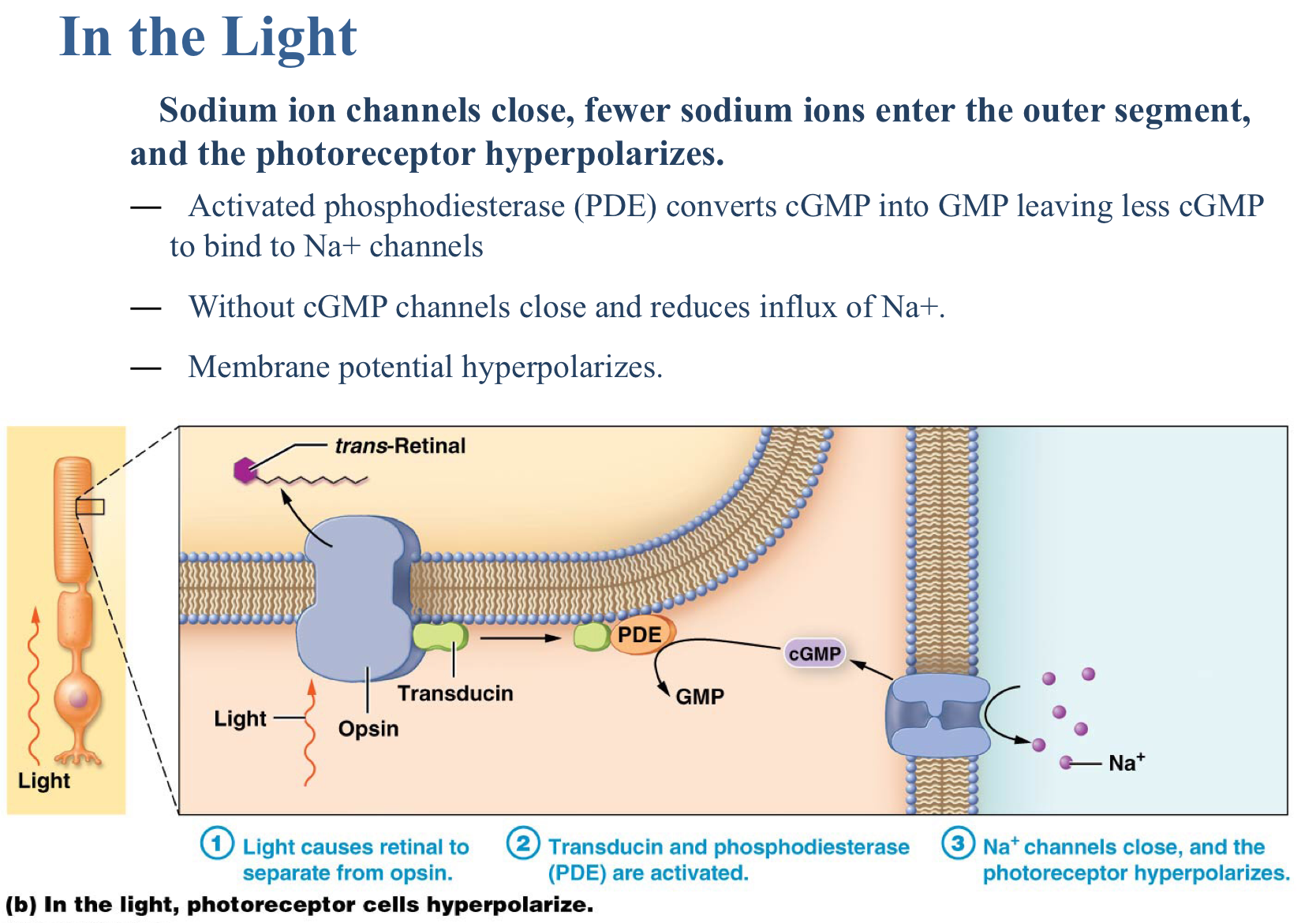
Which occurs in the light?
The outer segment is hyperpolarized
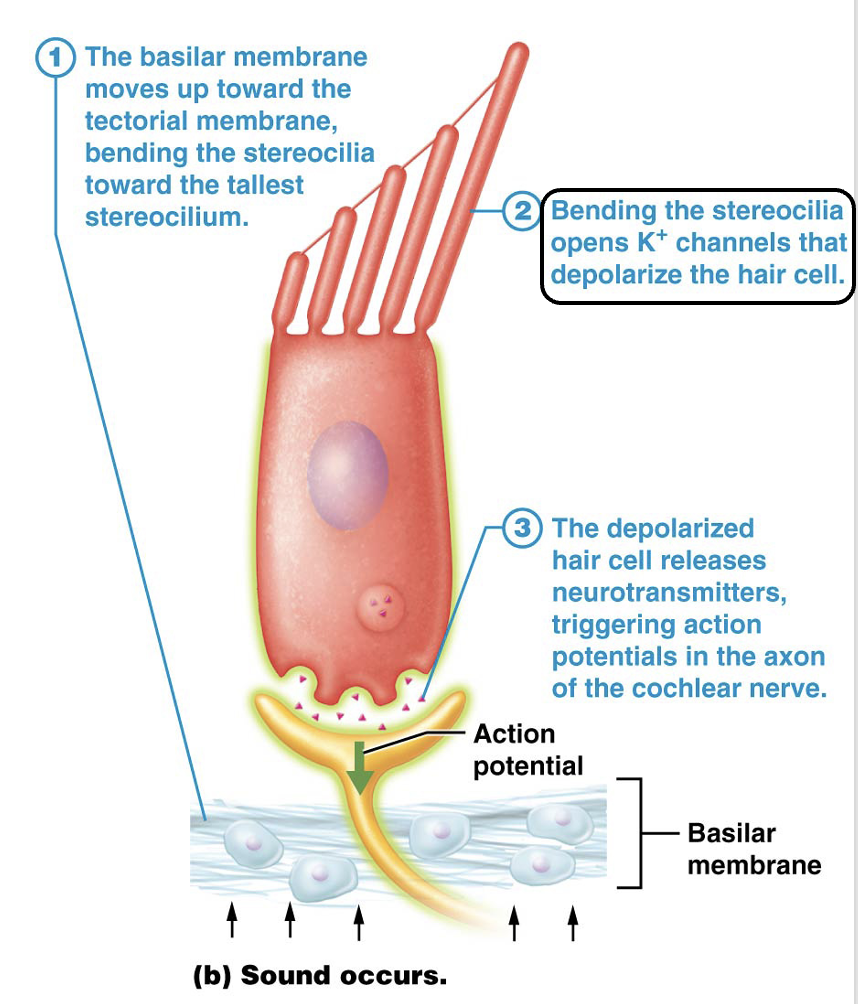
Which ion depolarizes the hair cells in the organ of corti?
Potassium
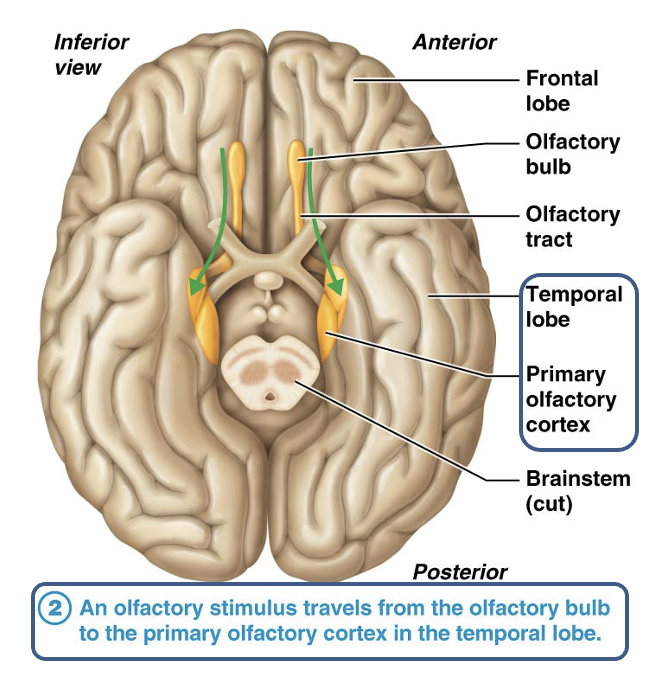
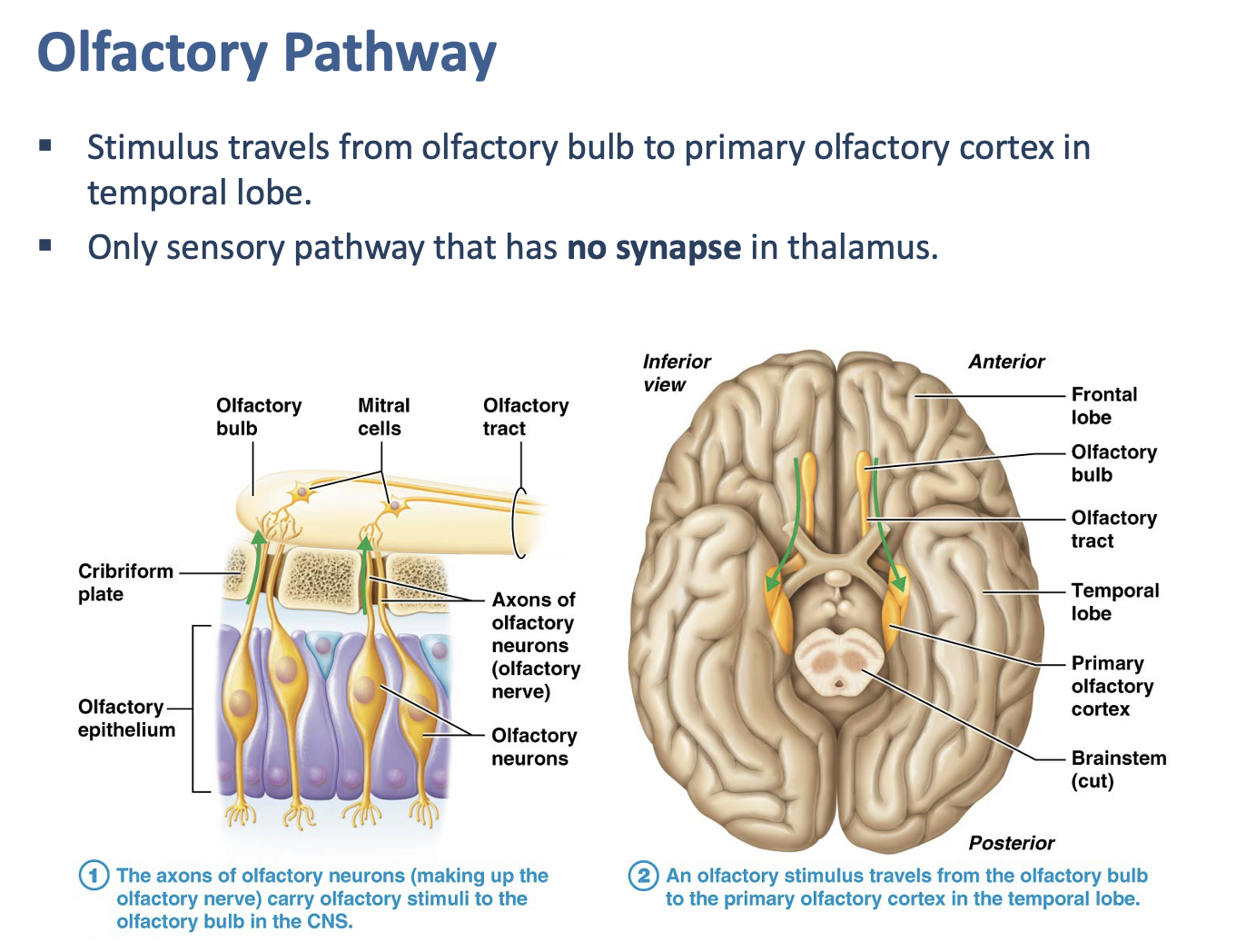
Which lobe contains the primary olfactory cortex?
Temporal
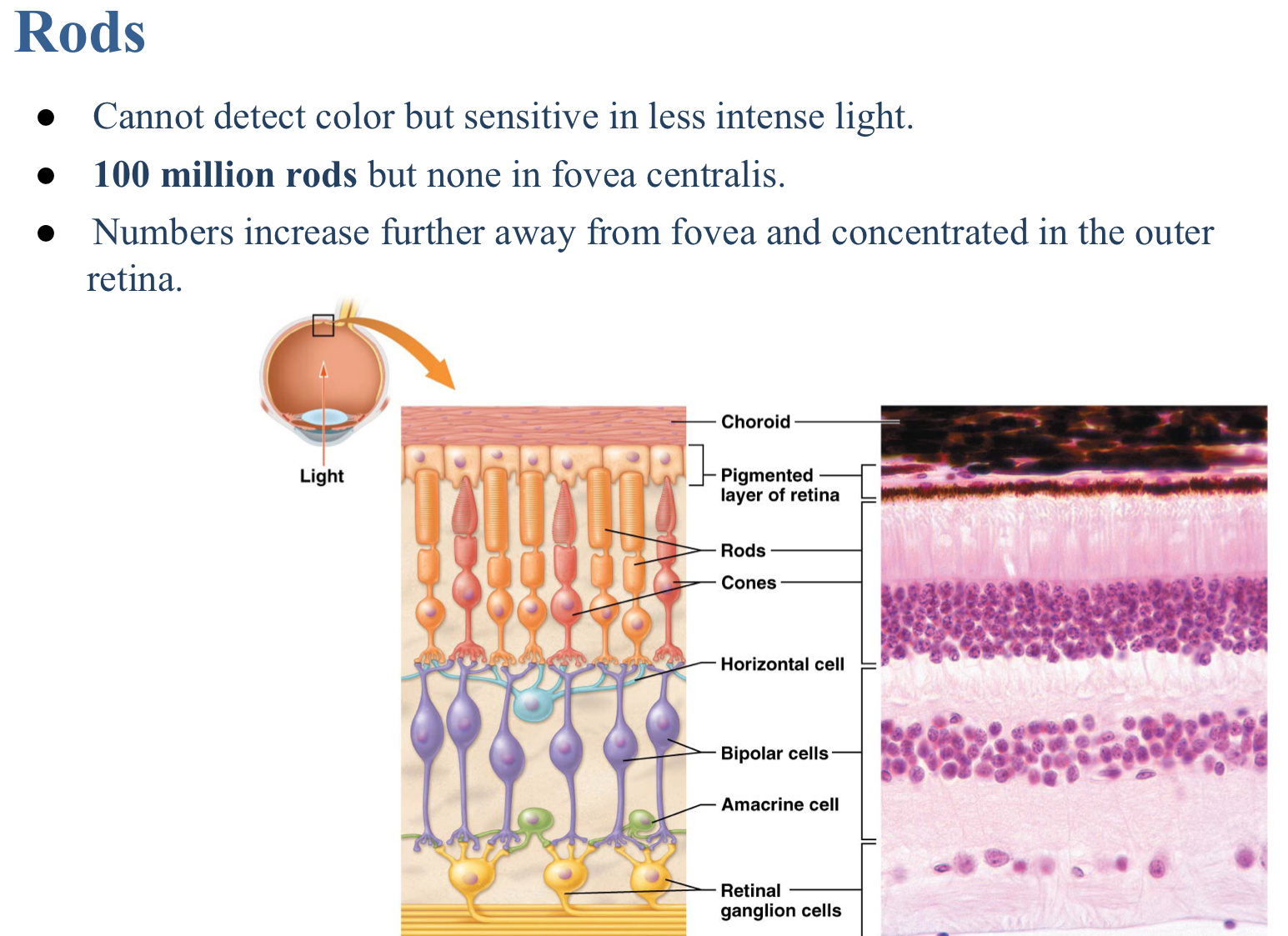
True or false: Rods are for color vision.
False
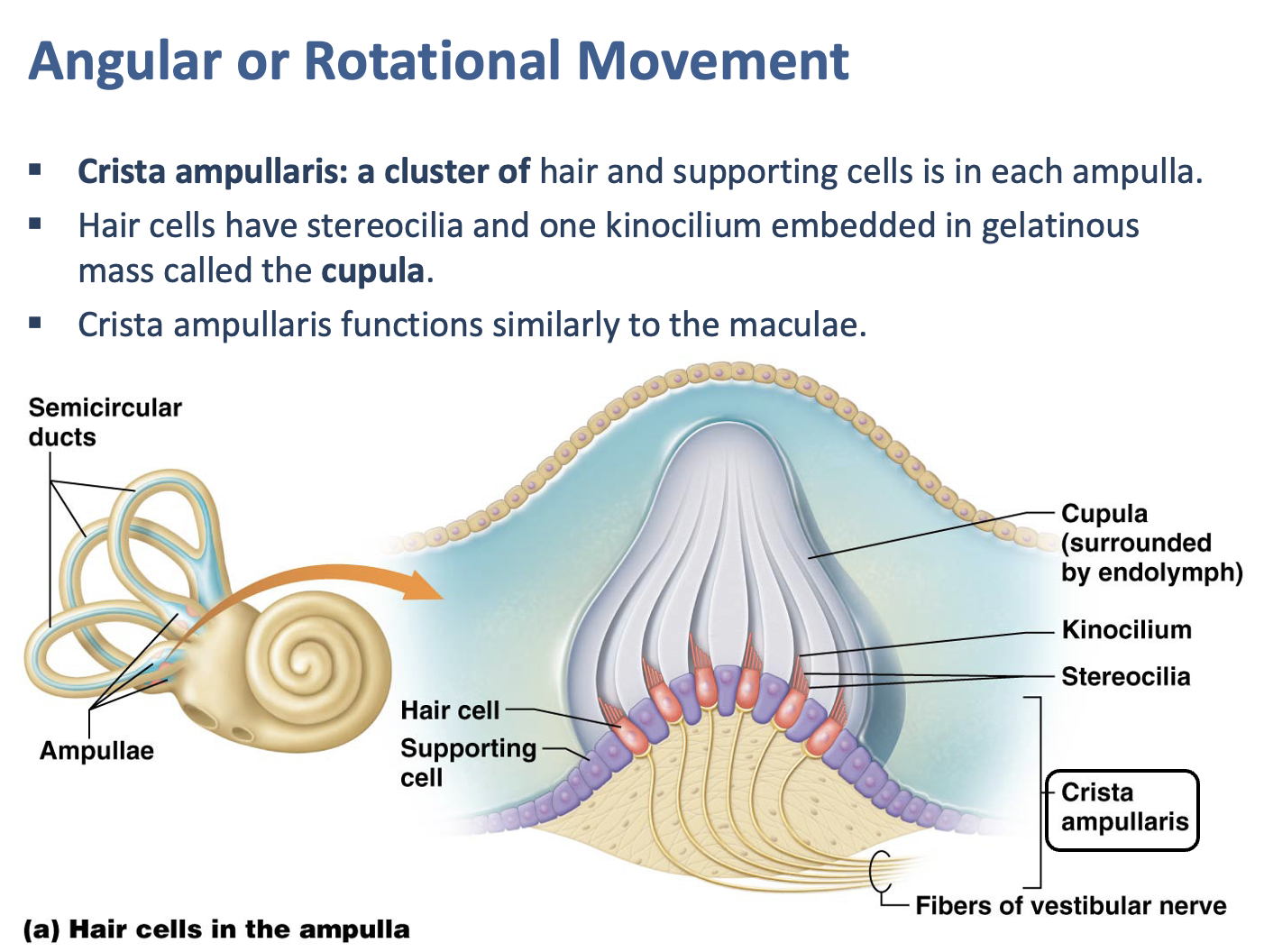
Which receptor is used for angular or rotational movement?
Crista ampullaris
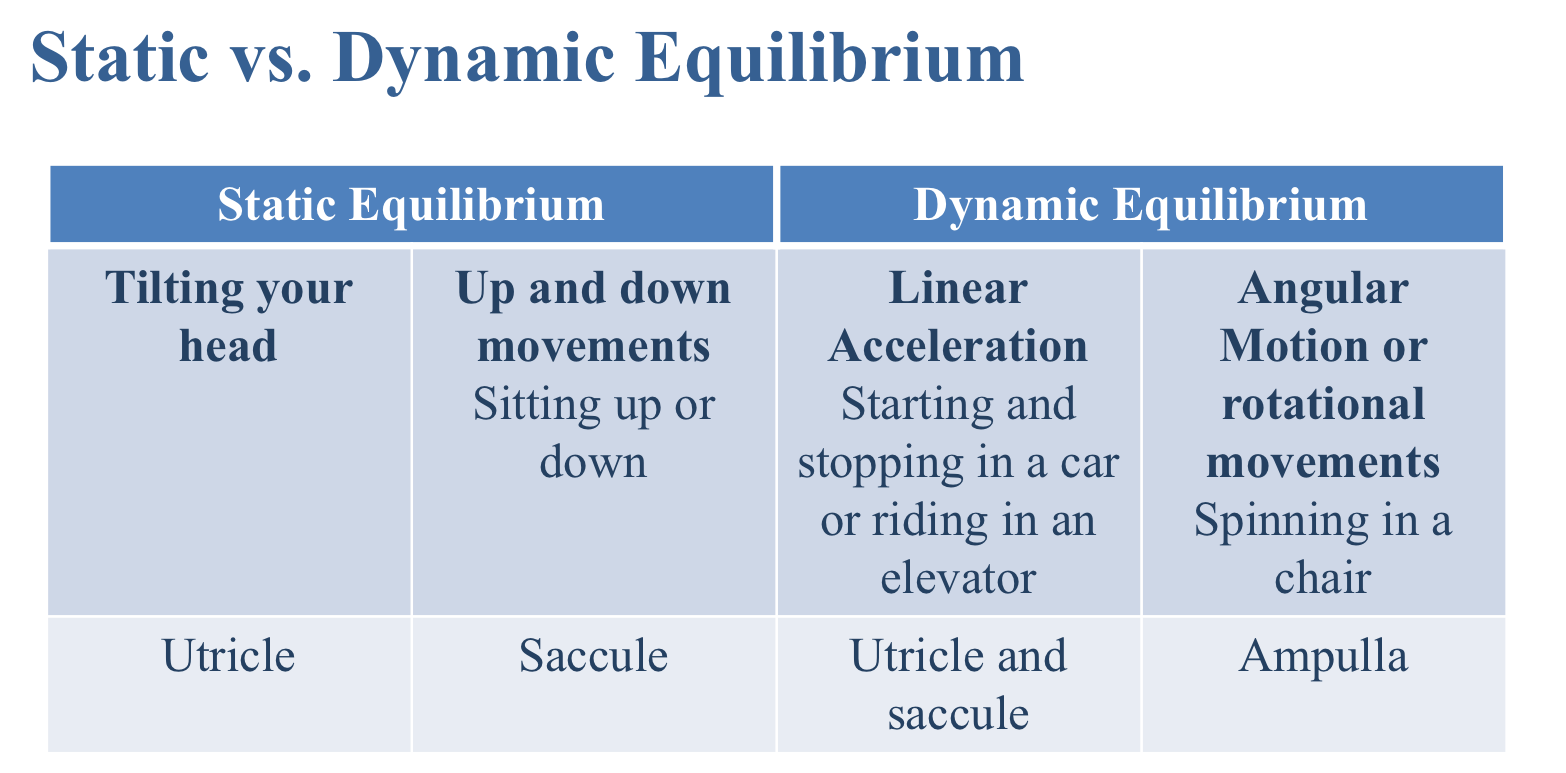
Which receptors are stimulated by up and down movements?
Saccule
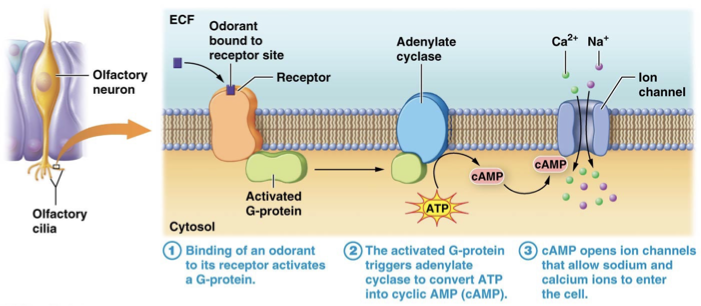
Which special sense involves a G protein, cAMP and the opening of a channel that allows sodium and calcium to enter the cell?
Olfaction
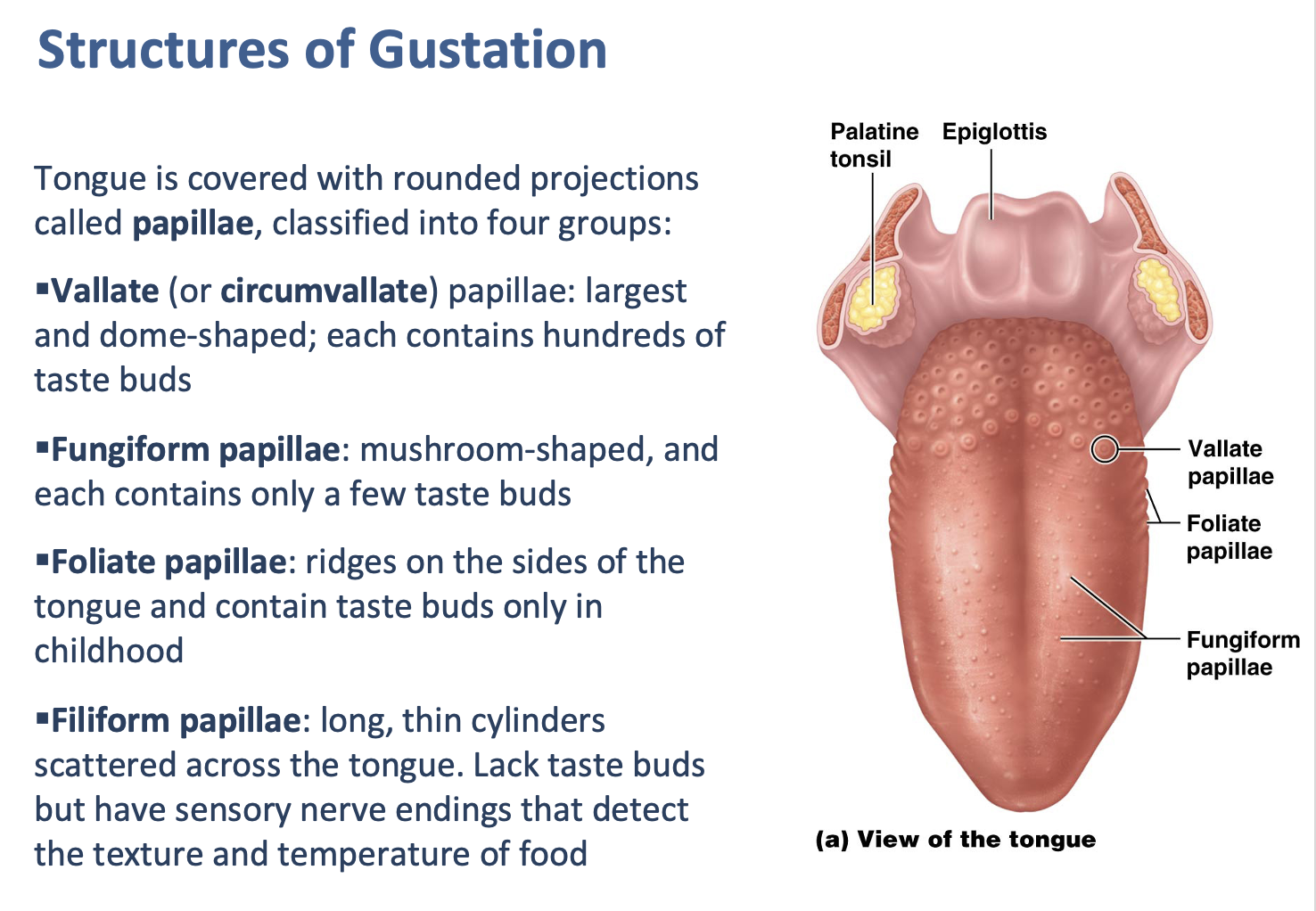
True or false: Which type of papillae only has taste buds in childhood?
Foliate
Which taste sensation is produced by glutamate or other amino acids?
Umami

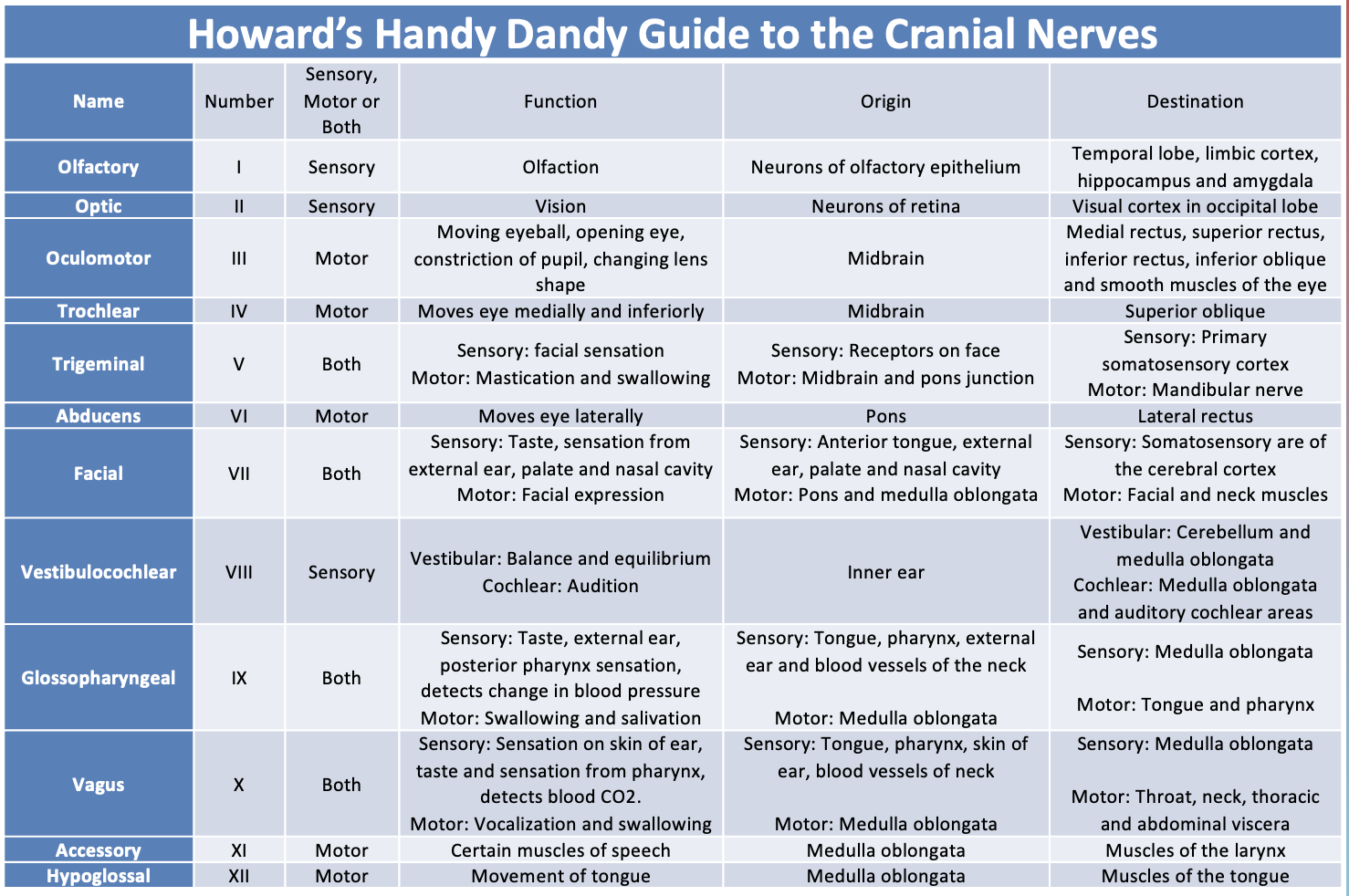
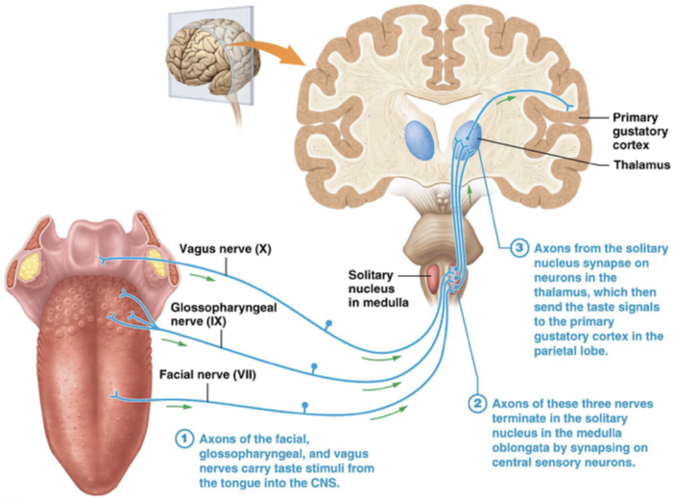
Which cranial nerves are involved in gustation?
Facial (VII), Glossopharyngeal (IX), Vagus (X)
All of the special senses synapse in the thalamus EXCEPT?
Olfaction
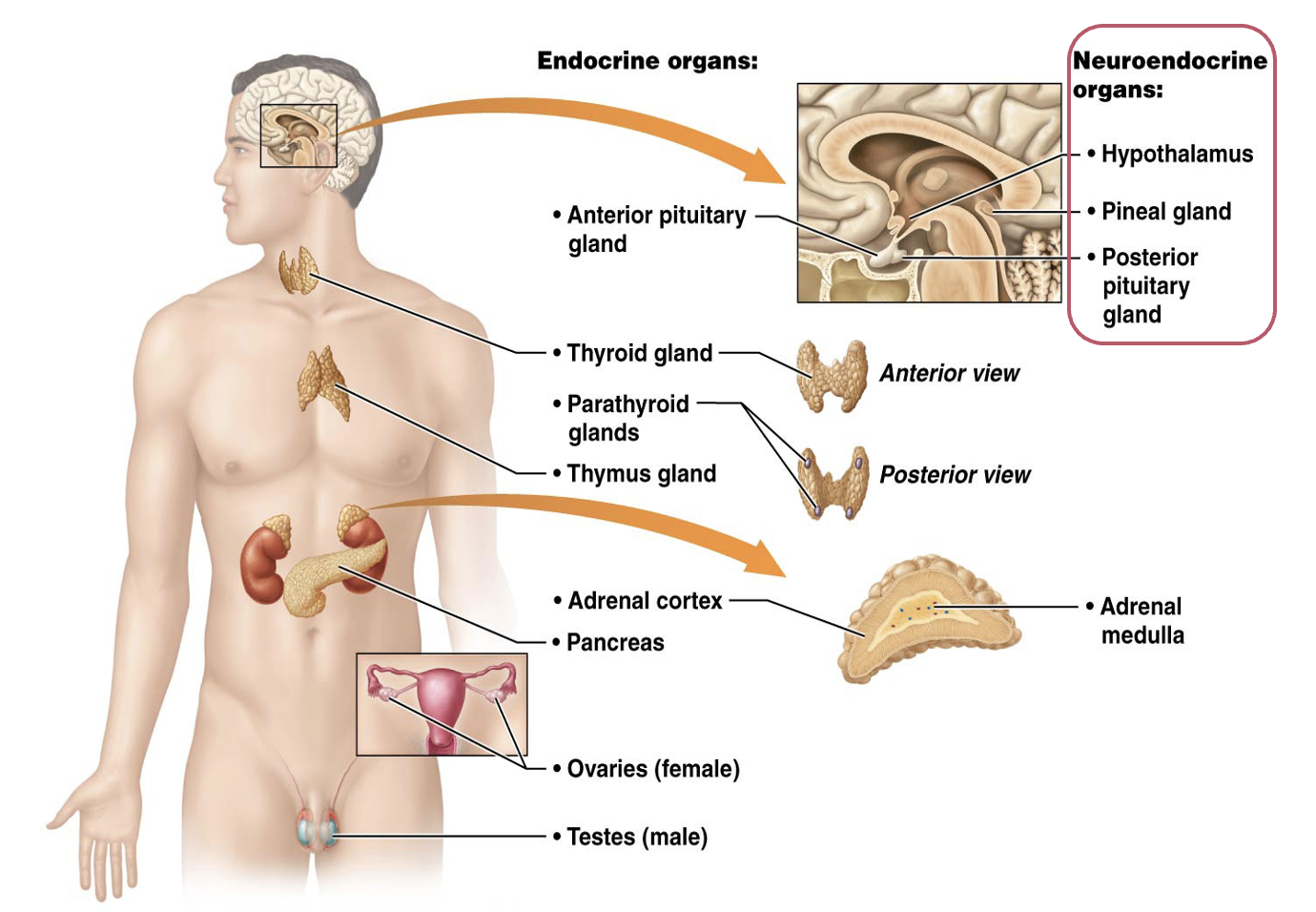
Which describes how the endocrine system is regulated?
Hormones secreted into the blood
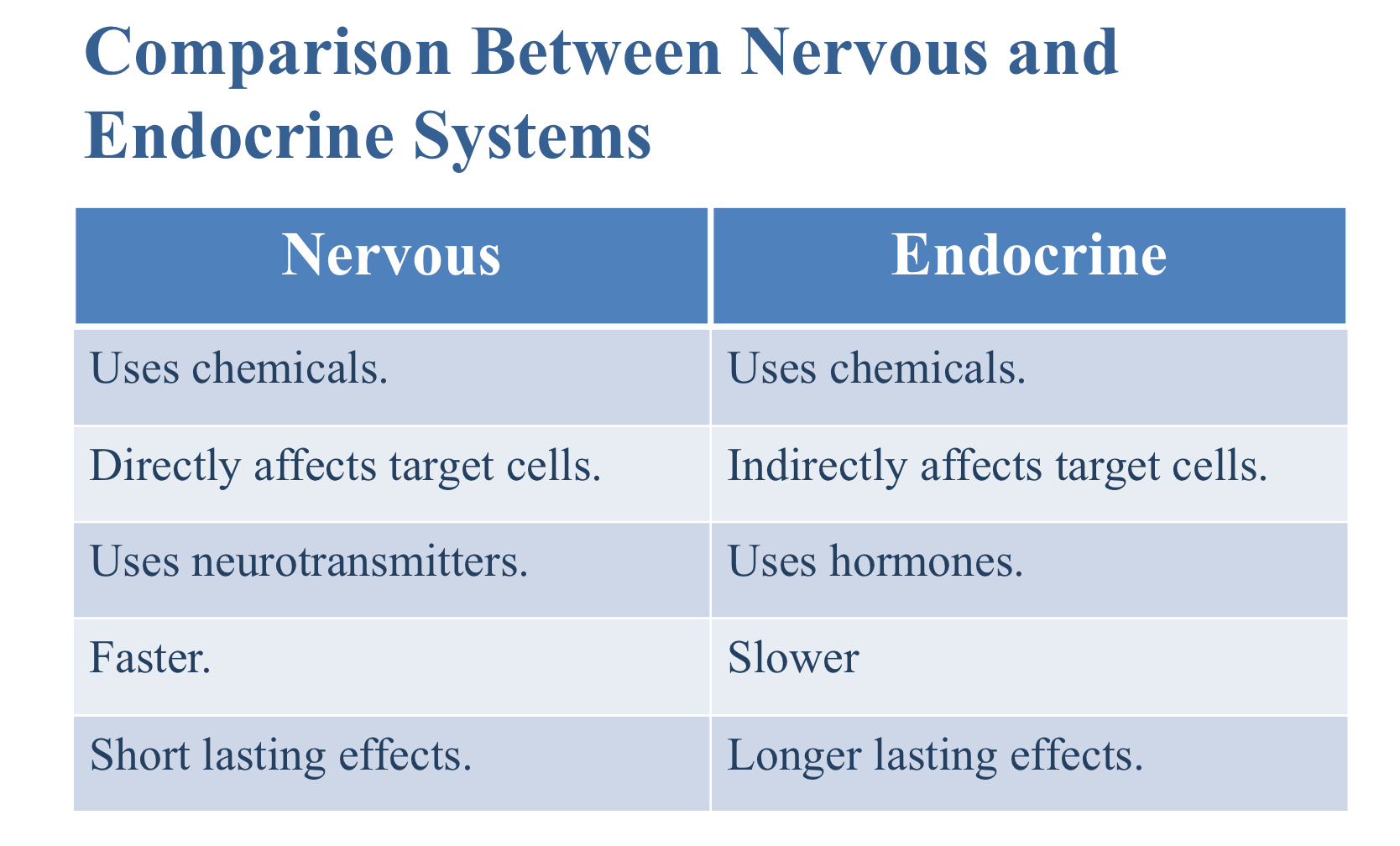
What are the characteristics of the endocrine system?
Uses chemicals
Indirectly affects target cells
Uses hormones
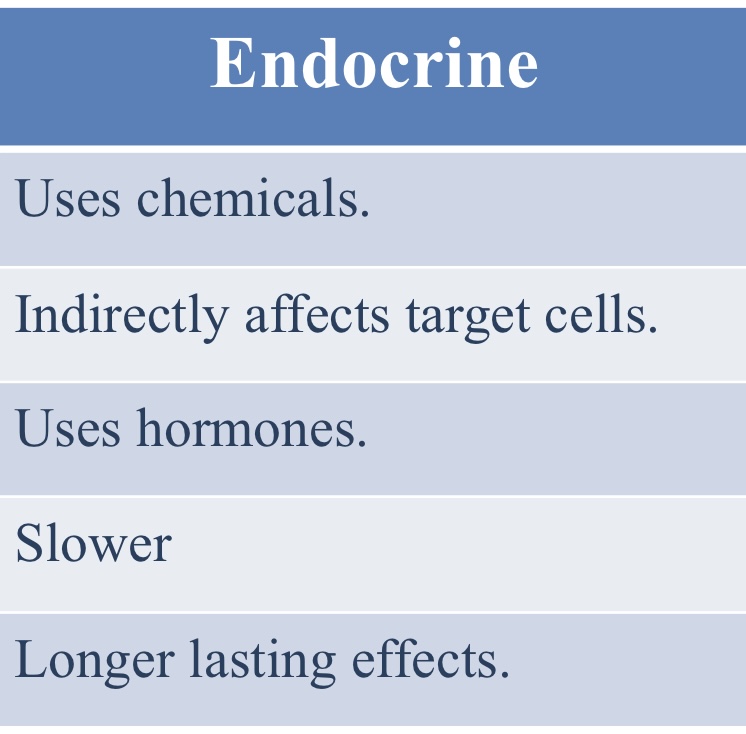
Which is faster: the nervous system or the endocrine system?
Nervous system
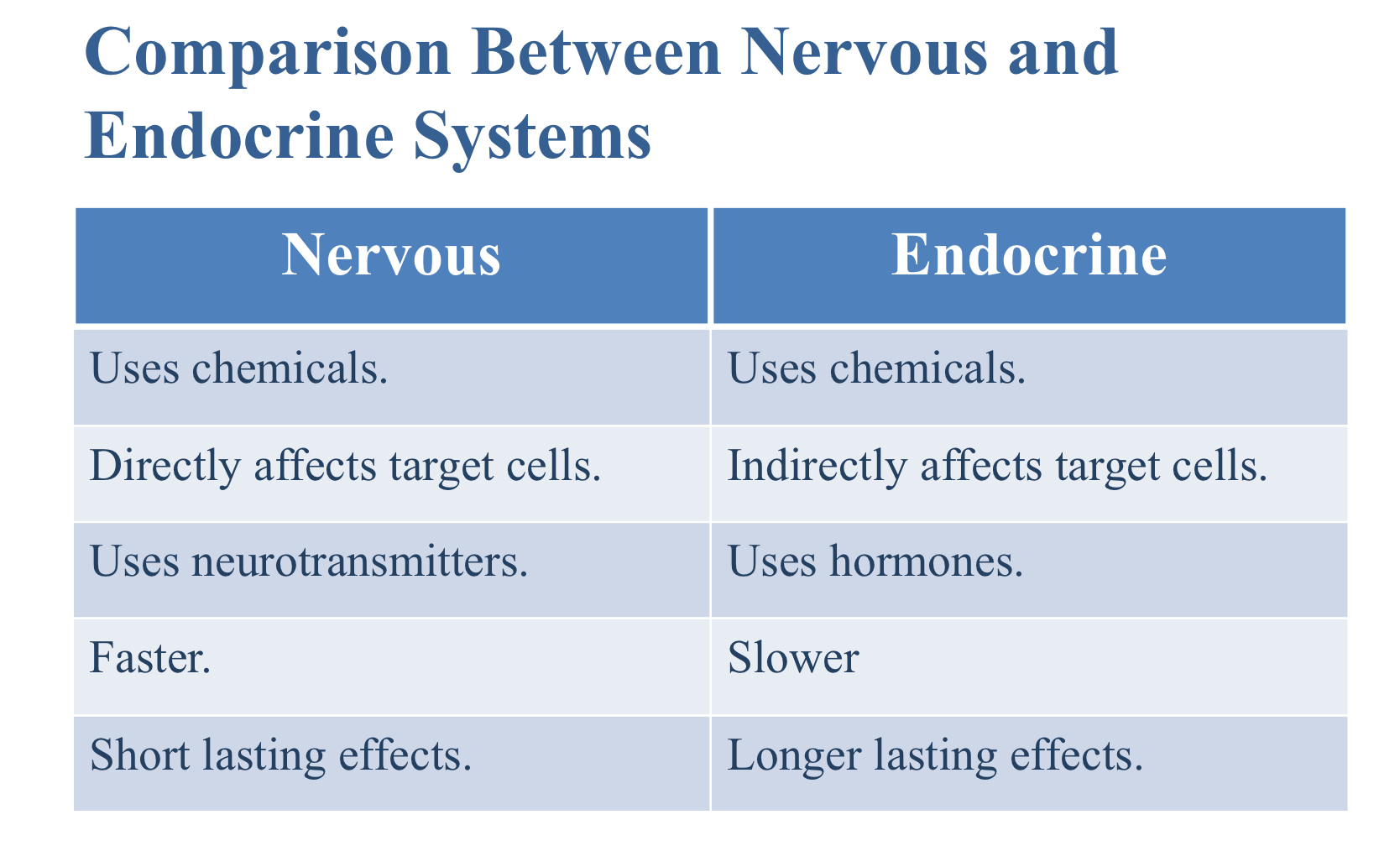
Which has longer lasting effects: the nervous system or the endocrine system?
Endocrine system
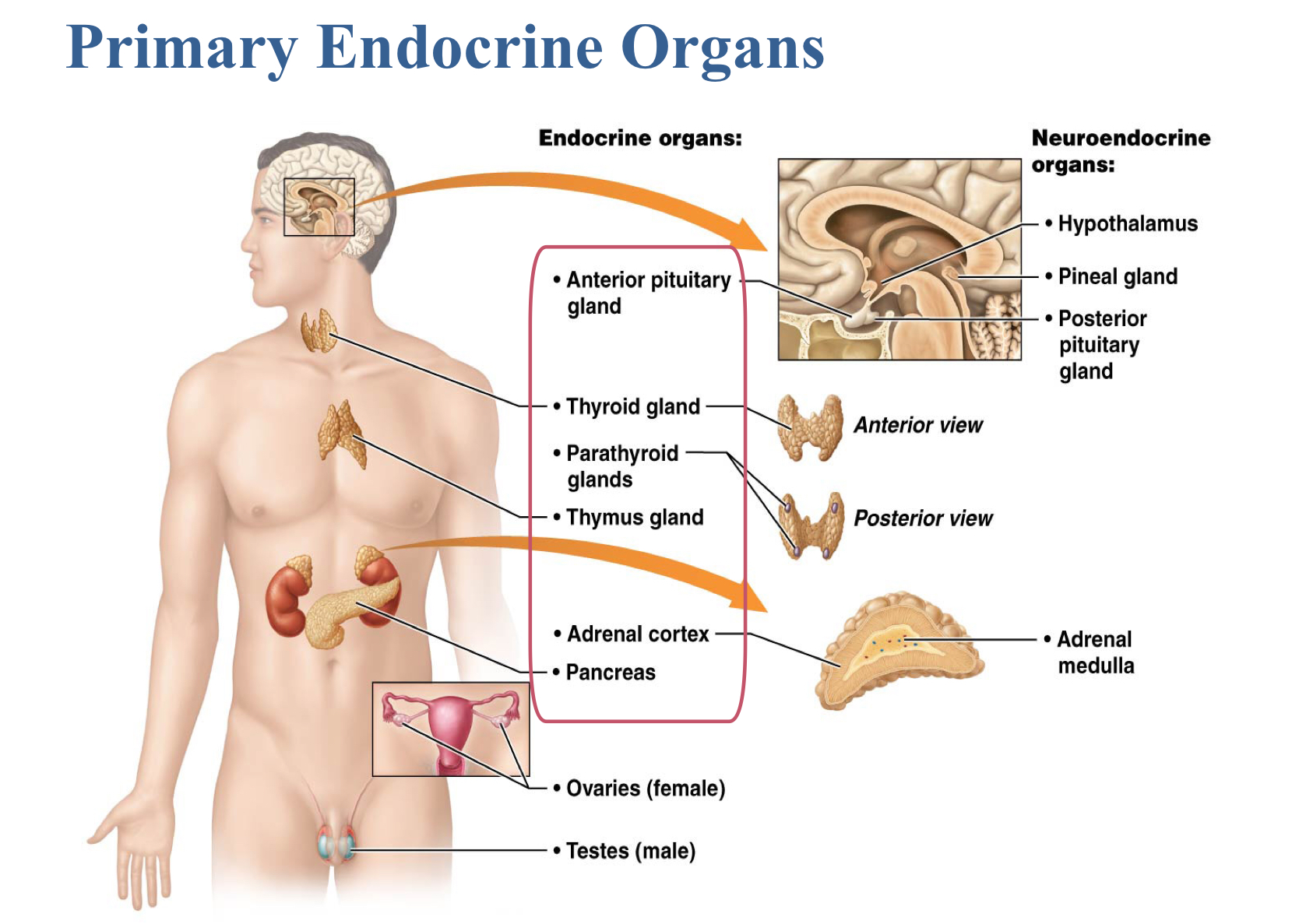
Which are the primary endocrine organs?
Anterior pituitary gland
Thyroid gland
Parathyroid gland
Adrenal cortex
Pancreas
Thymus
Which describes the transport of hydrophilic hormones?
Travel freely in blood
Which describes the transport of hydrophobic hormones?
Travel bound to plasma protein carriers
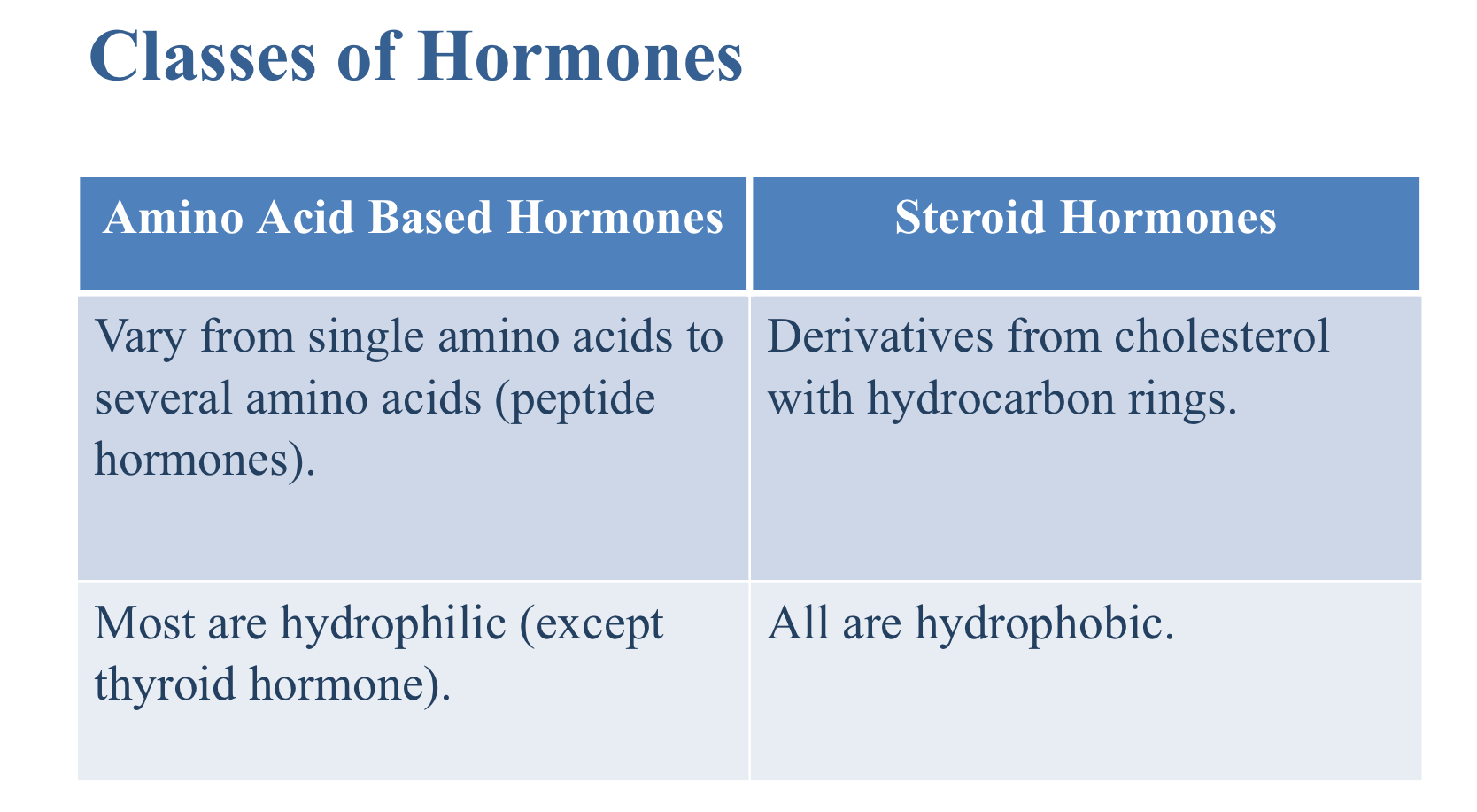
Which are characteristics of an amino acid based hormone?
Vary from single amino acids to several amino acids (peptide hormones)
Most are hydrophilic (except thyroid hormone)
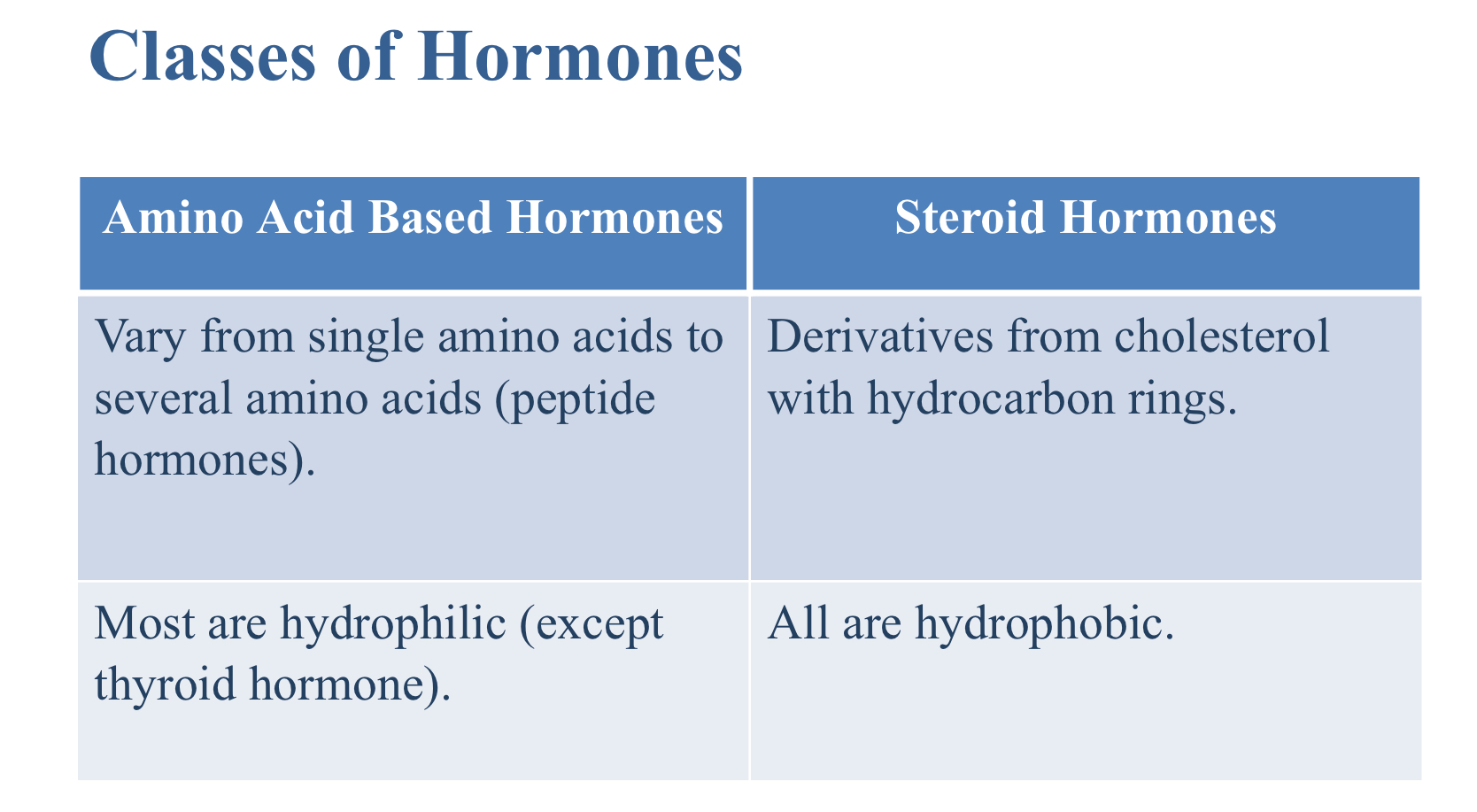
Which are characteristics of a steroid hormone?
Derived from cholesterol with hydrocarbon rings
All are hydrophobic
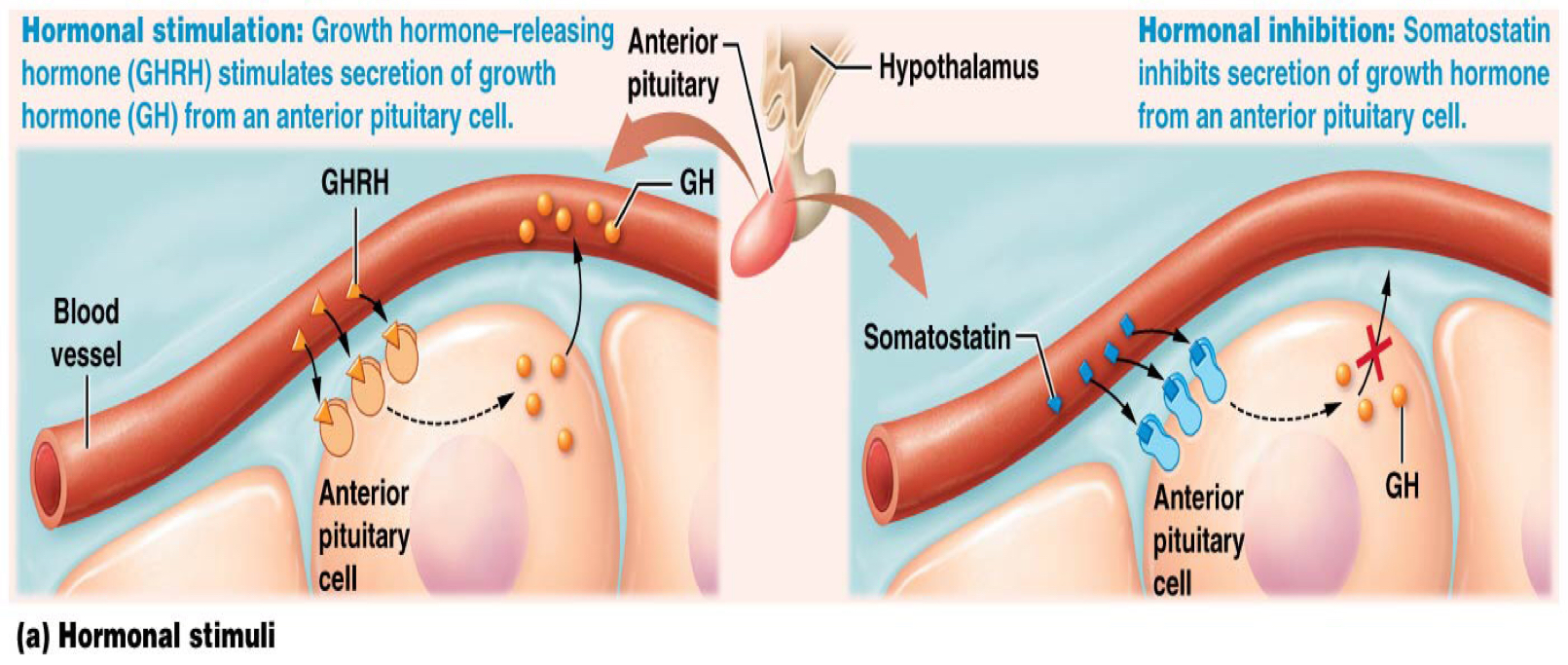
Which describes how hormonal stimuli initiate hormone secretion?
Endocrine cells alter secretion in response to other hormones
GHRH stimulates secretion of GH from an anterior pituitary gland
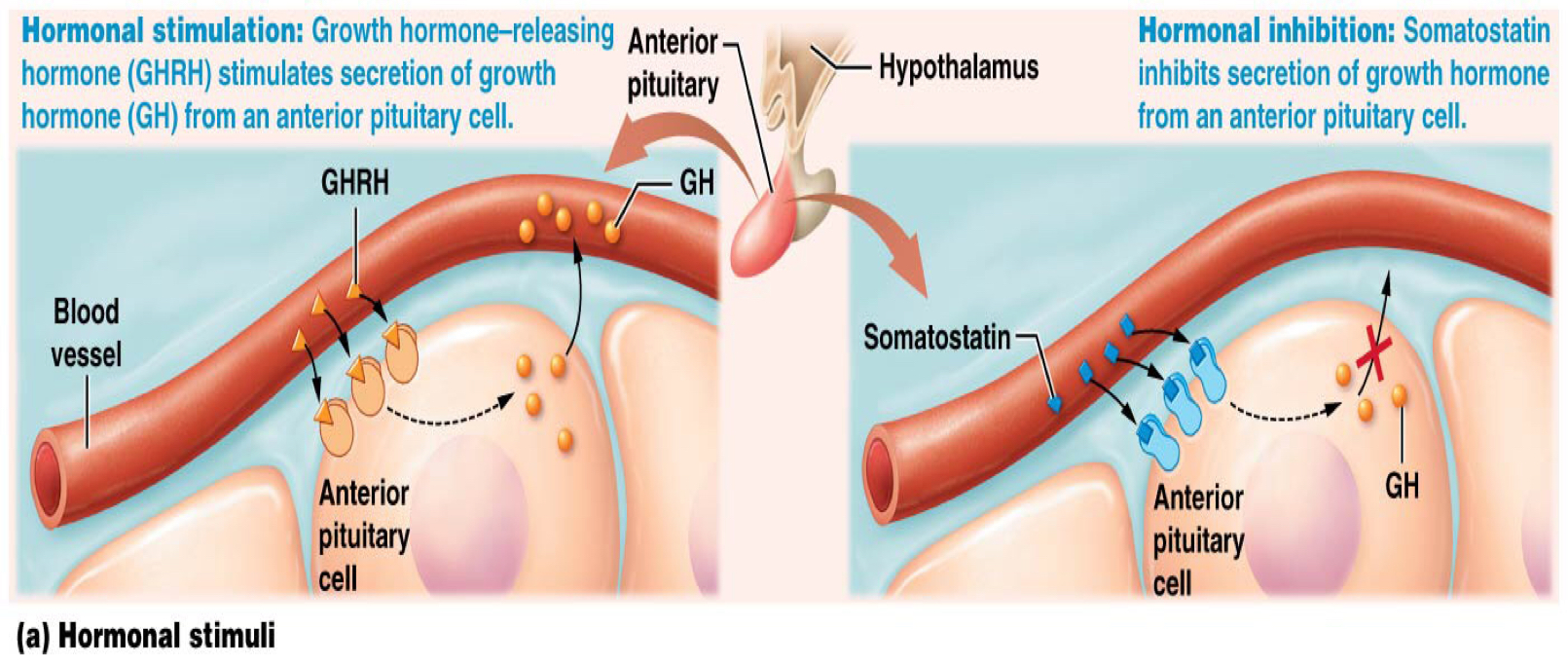
Which type of secretion-initiating stimuli is the hypothalamus an example of?
Hormonal stimuli: somatostatin inhibits the secretion of growth hormone from an anterior pituitary cell
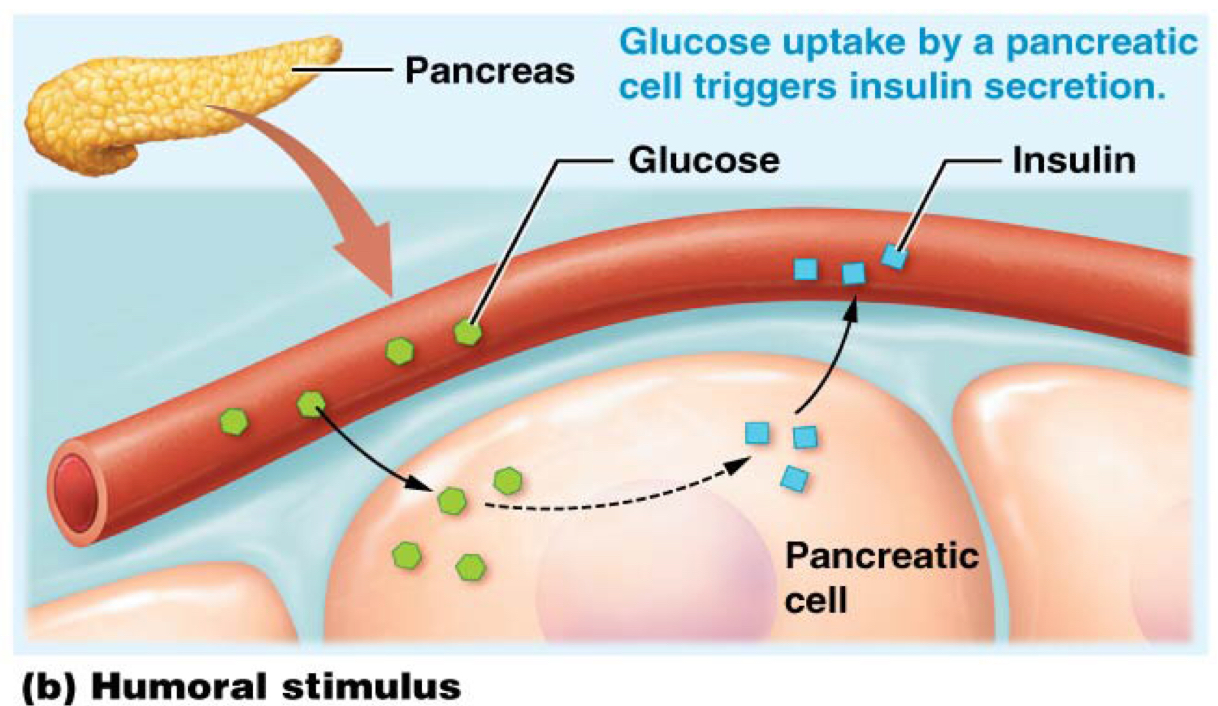
Which describes how humoral stimuli initiate hormone secretion?
Many endocrine cells respond to changes of certain ions or molecules in blood or extracellular fluid
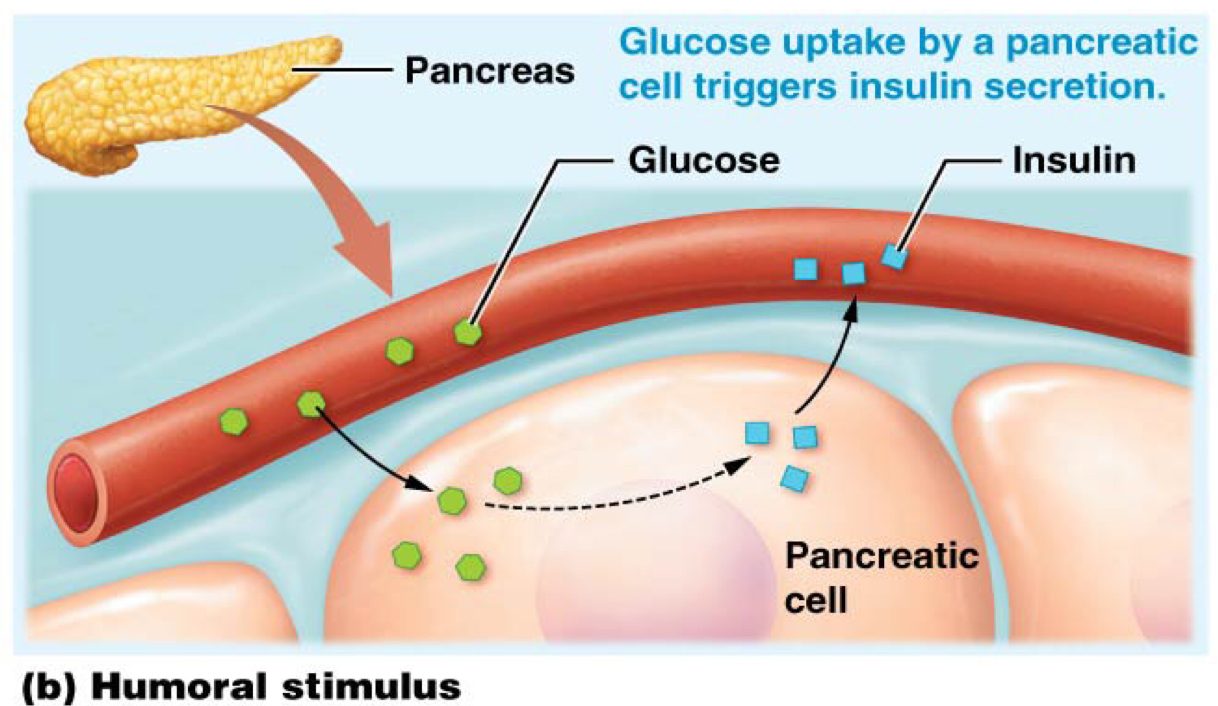
Which type of secretion-initiating stimuli is glucose an example of?
Humoral stimuli: glucose uptake by a pancreatic cell triggers insulin secretion
Which describes how neural stimuli initiate hormone secretion?
Some cells respond to signals from the nervous system
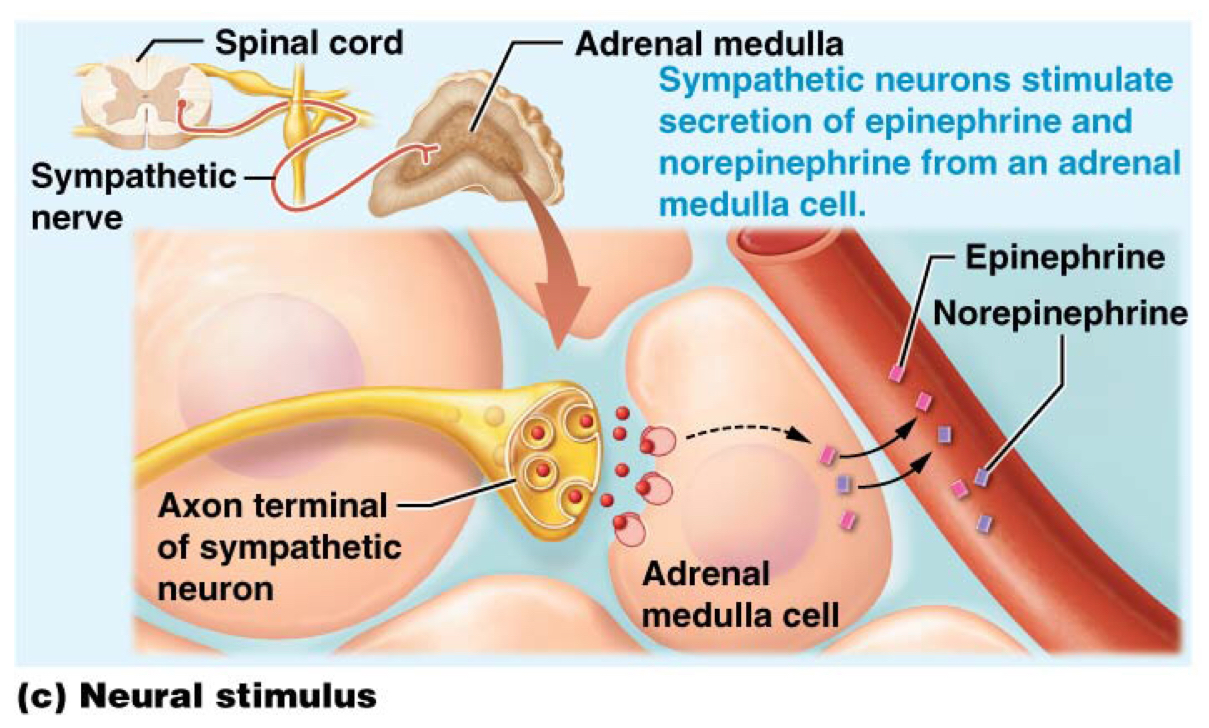
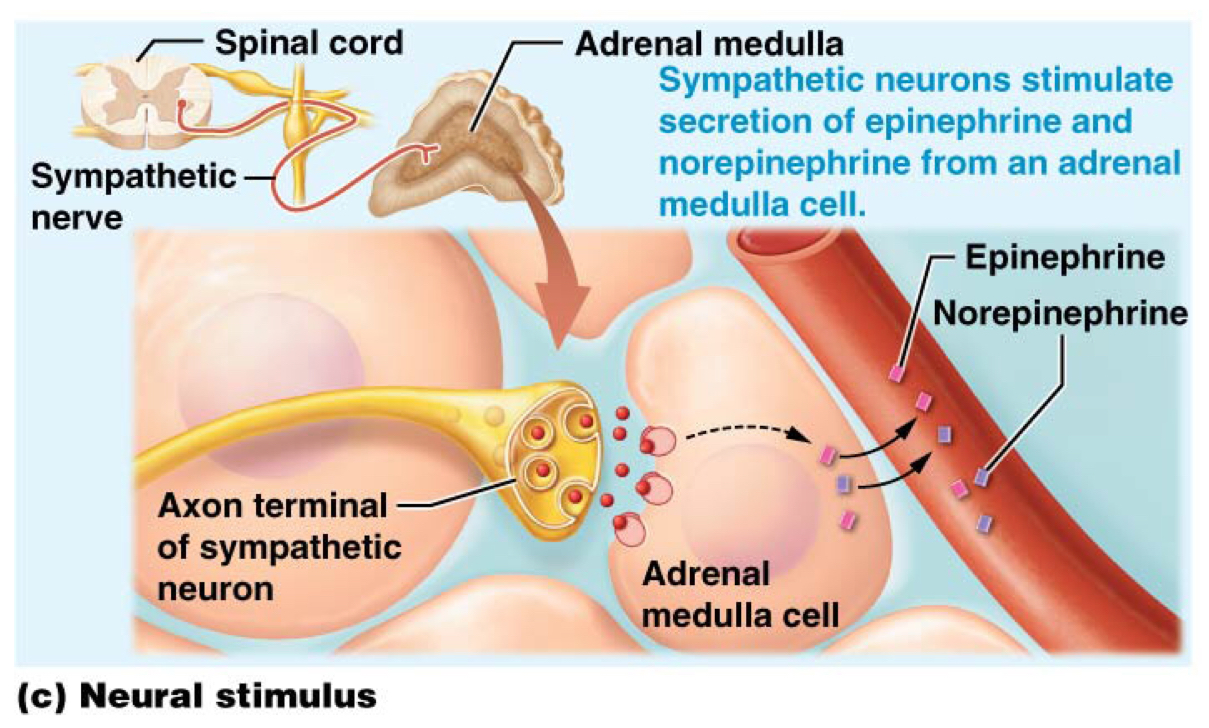
Which type of secretion-initiating stimuli is the adrenal medullas an example of?
Neural stimuli: sympathetic neurons stimulate secretion of EPI and NOREPI from an adrenal medulla cell
Which type of feedback loop generally regulates the secretion of anterior pituitary hormones?
Negative feedback loop via hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting of hormones
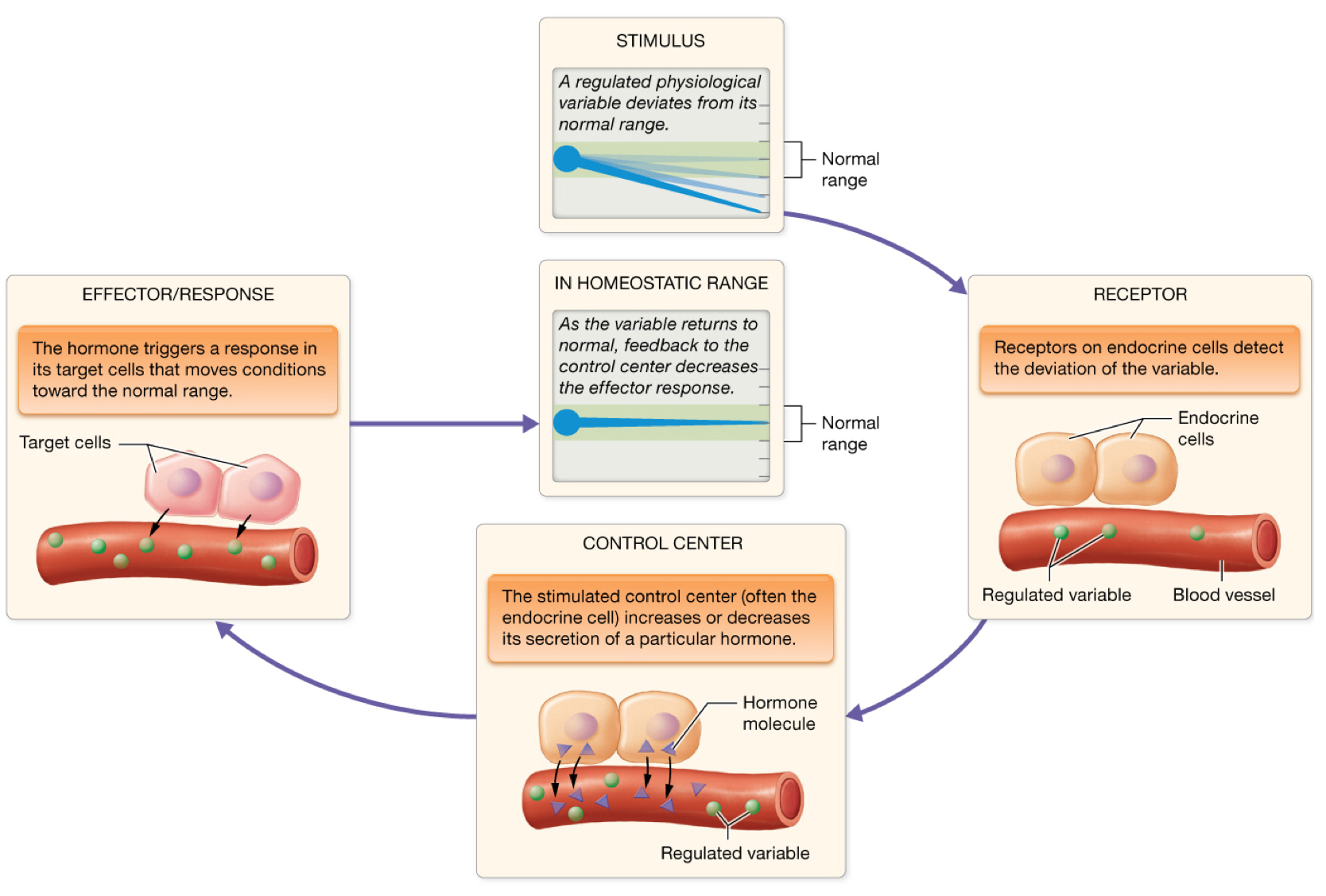
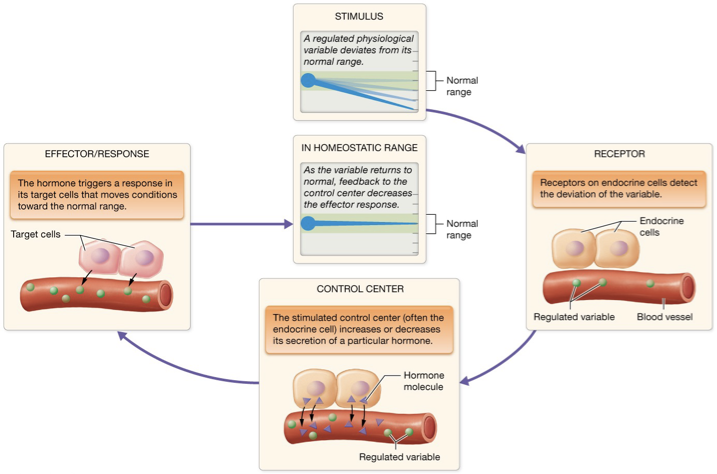
In negative feedback control of anterior pituitary hormones, what are the parts in each tier?
Stimulus
Receptor
Control center
Response/Effector
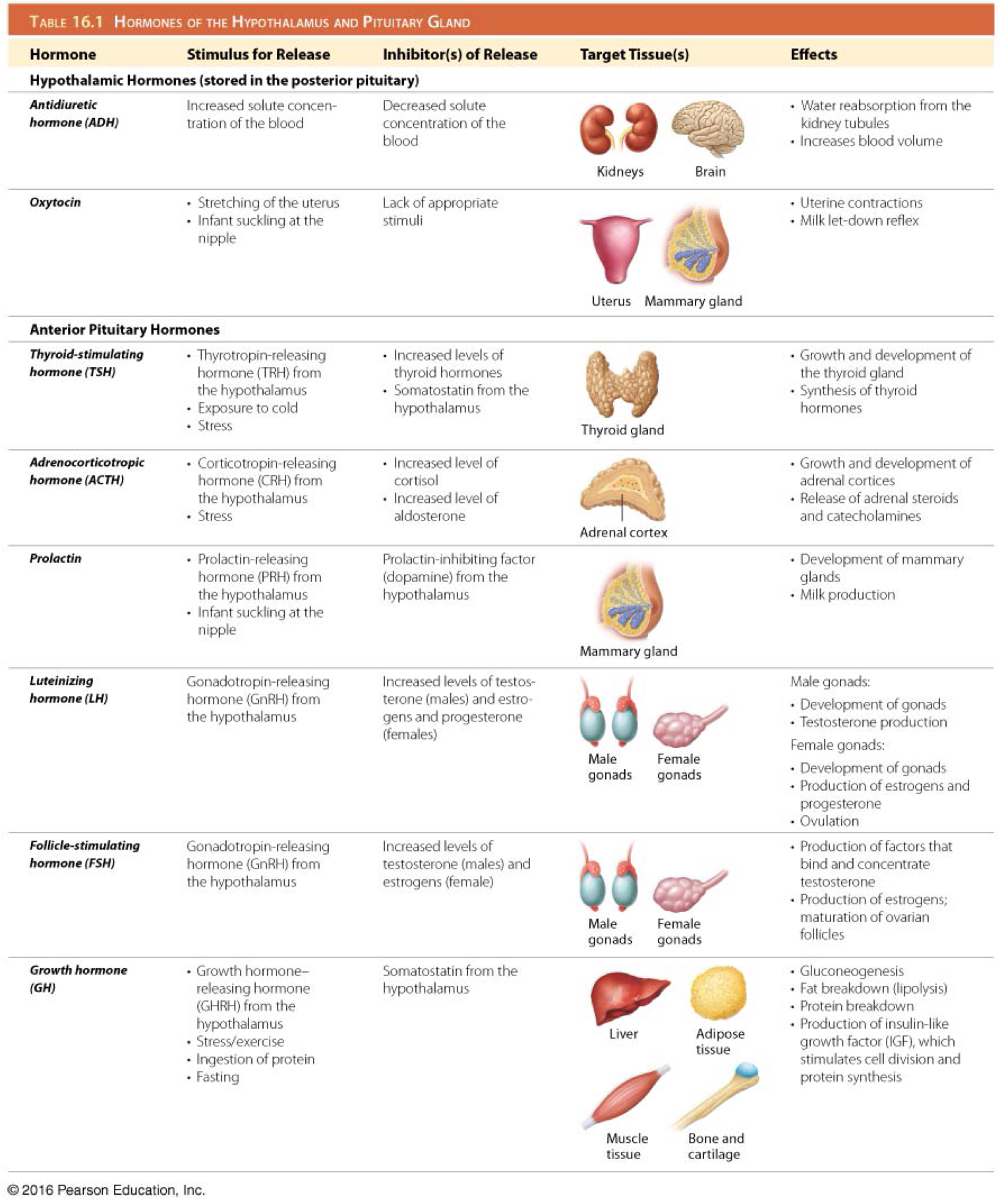
Which hormones are produced by the hypothalamus and stored by the posterior pituitary gland?
Oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Control the pituitary gland
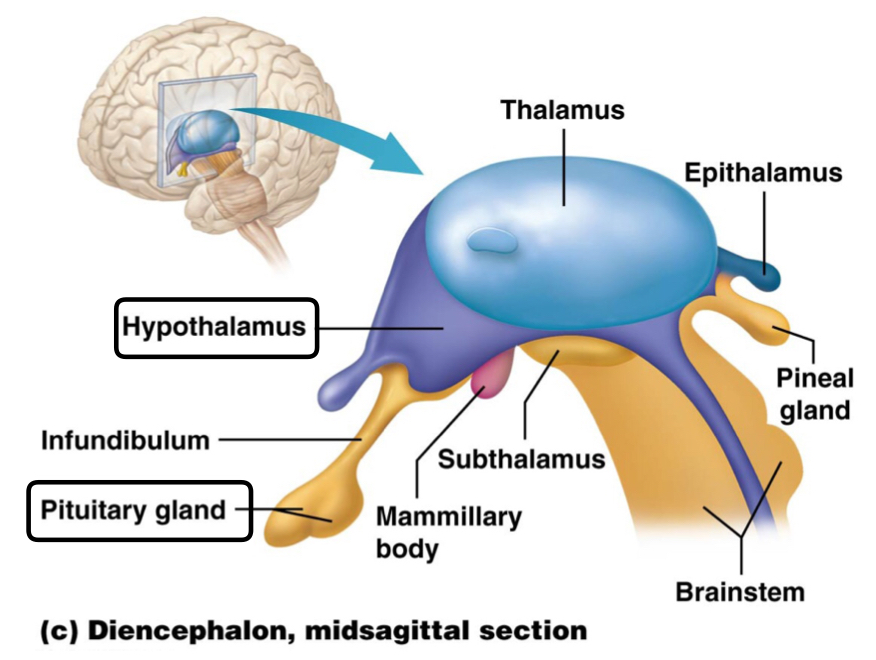
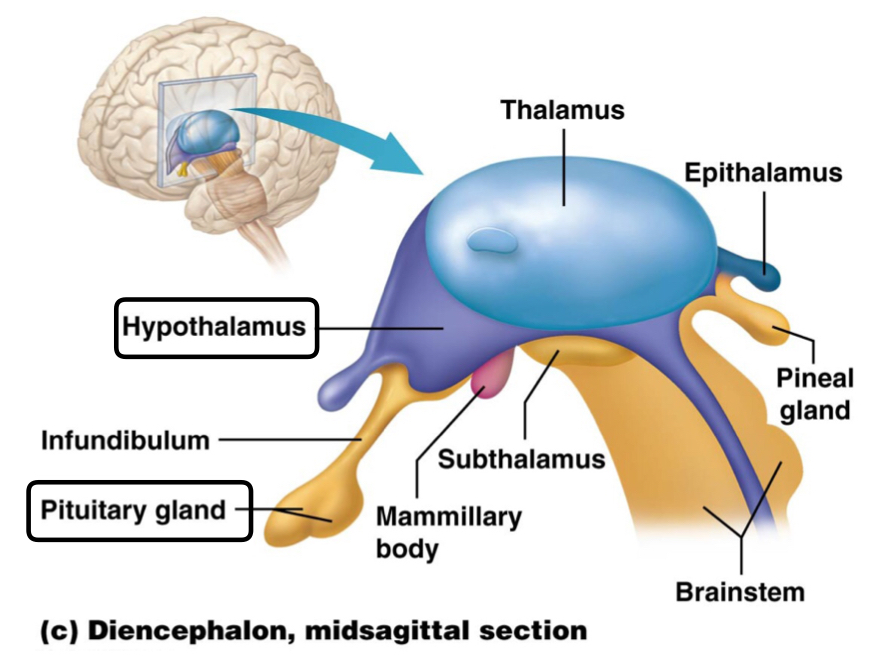
Which is the function of the mammillary bodies that receive input from the hippocampus?
To regulate memory and behavior
Which are tropic hormones of the anterior pituitary gland?
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PRL)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Growth hormone (GH)
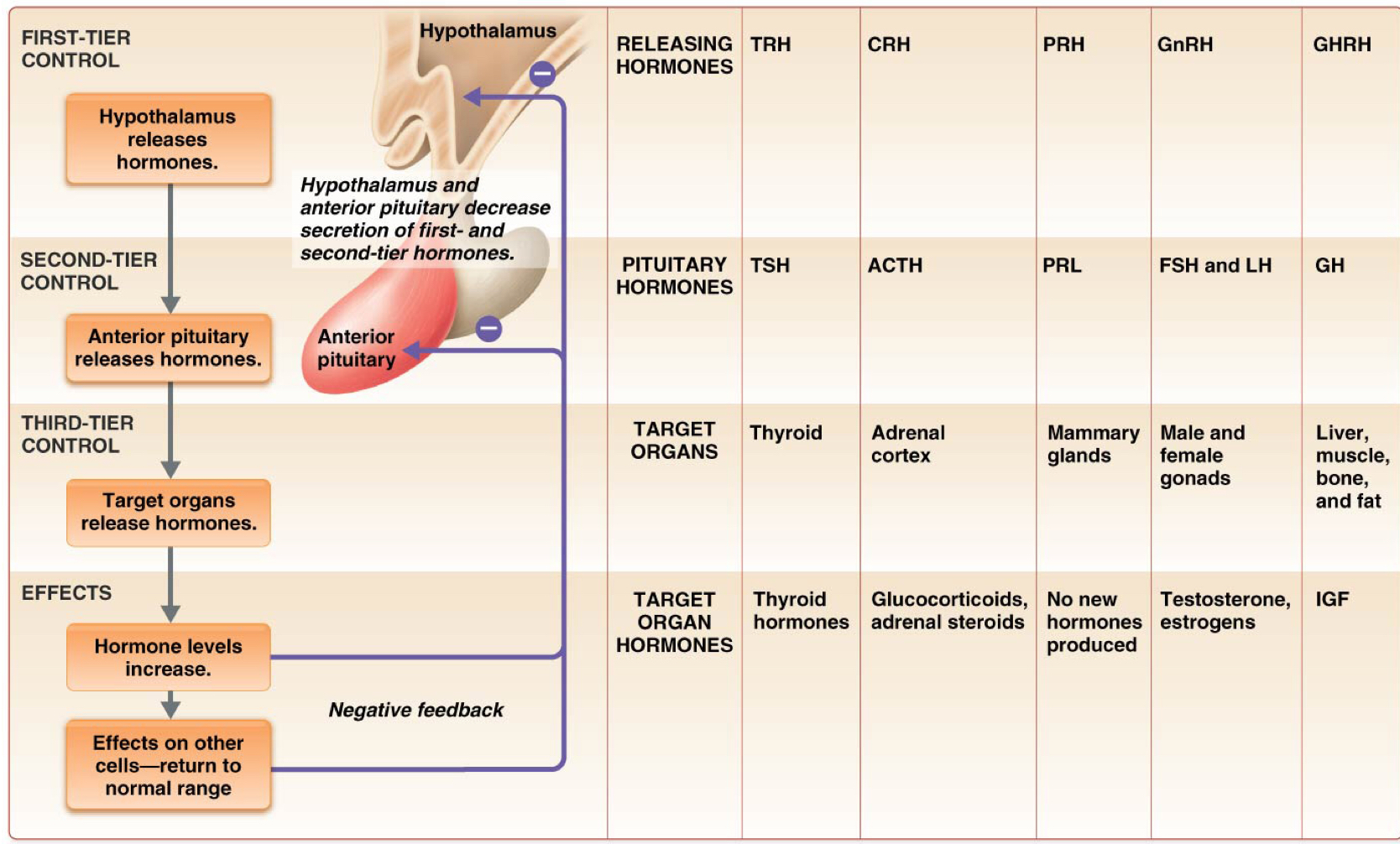
Which is the function of all tropic hormones?
Controlling secretion of other endocrine hormones
Which is the function of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)/thyrotropin?
Stimulates development of the thyroid gland and secretion of thyroid hormones
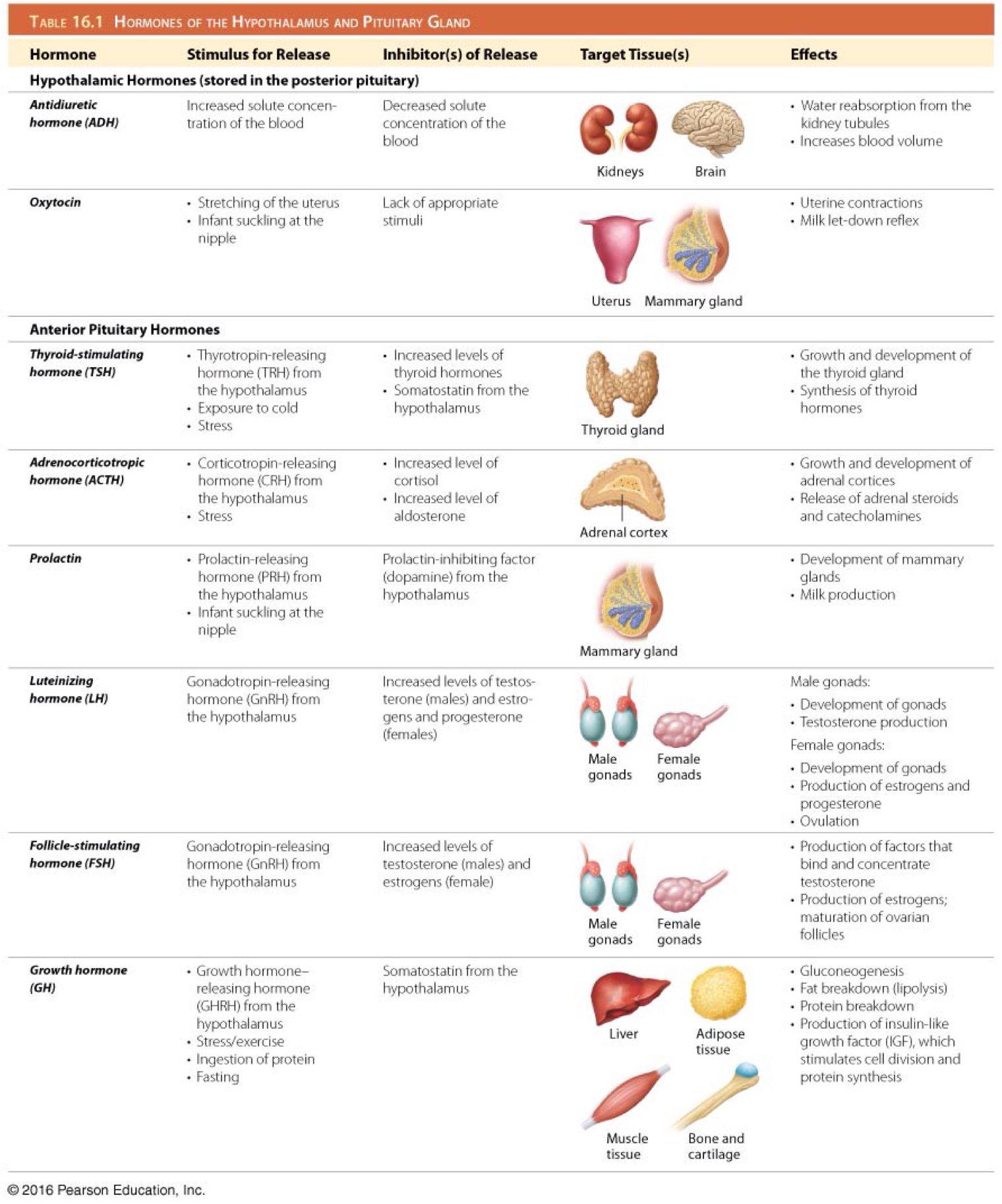
Which hormone stimulates the secretion of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)/thyrotropin?
Hypothalamic thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
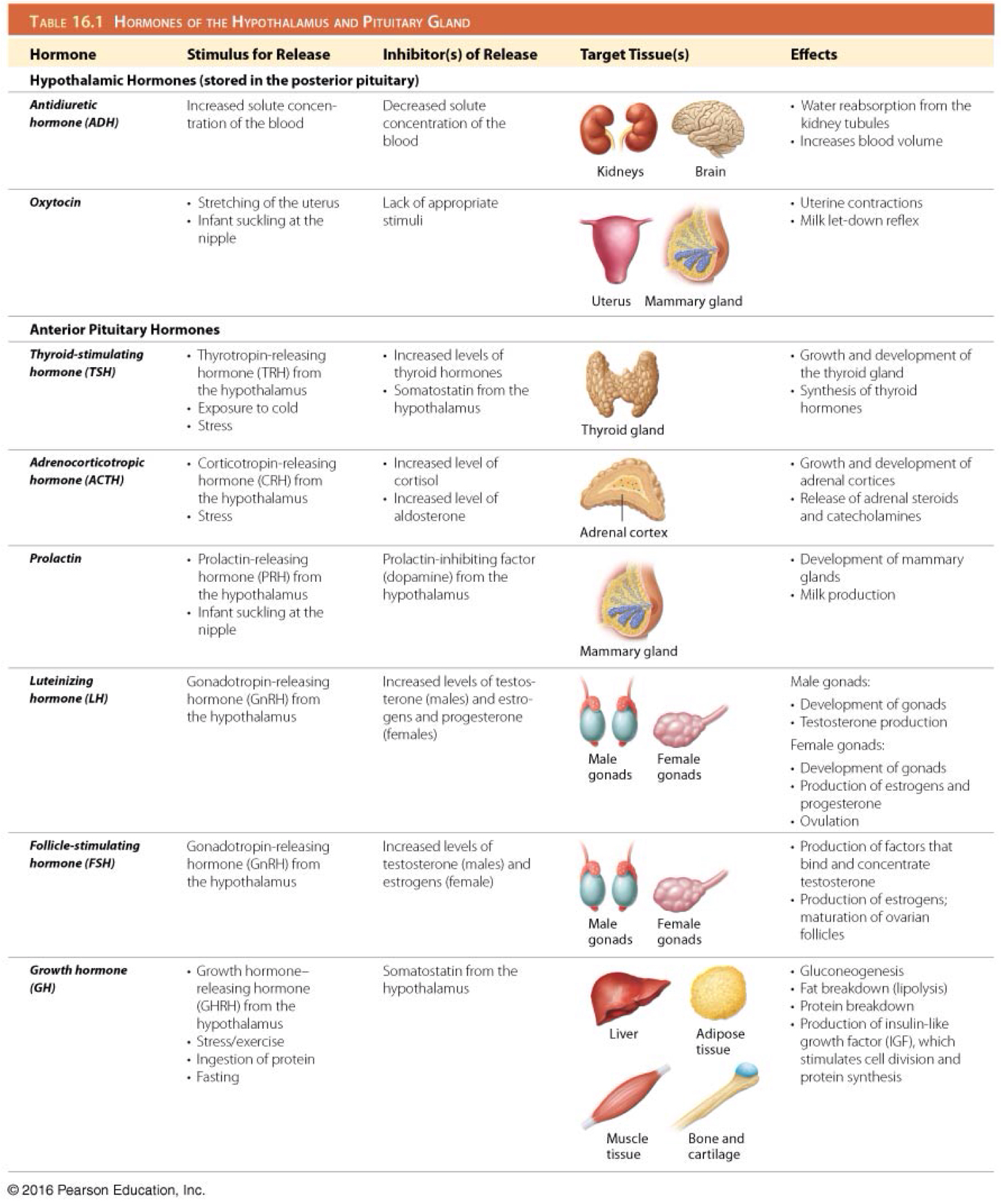
Which hormone inhibits the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)?
Somatostatin
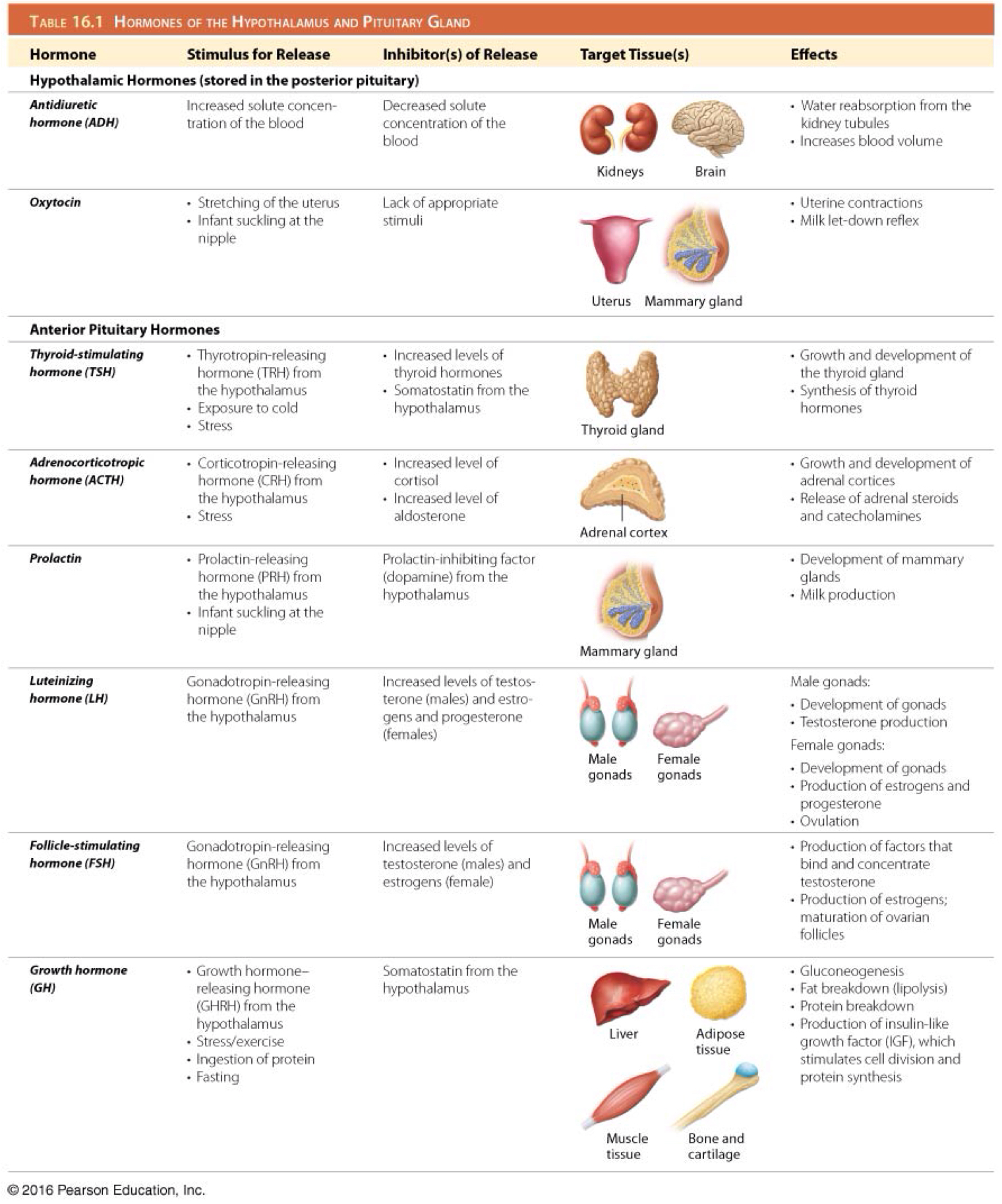
Which hormone inhibits the secretion of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)/thyrotropin?
Somatostatin
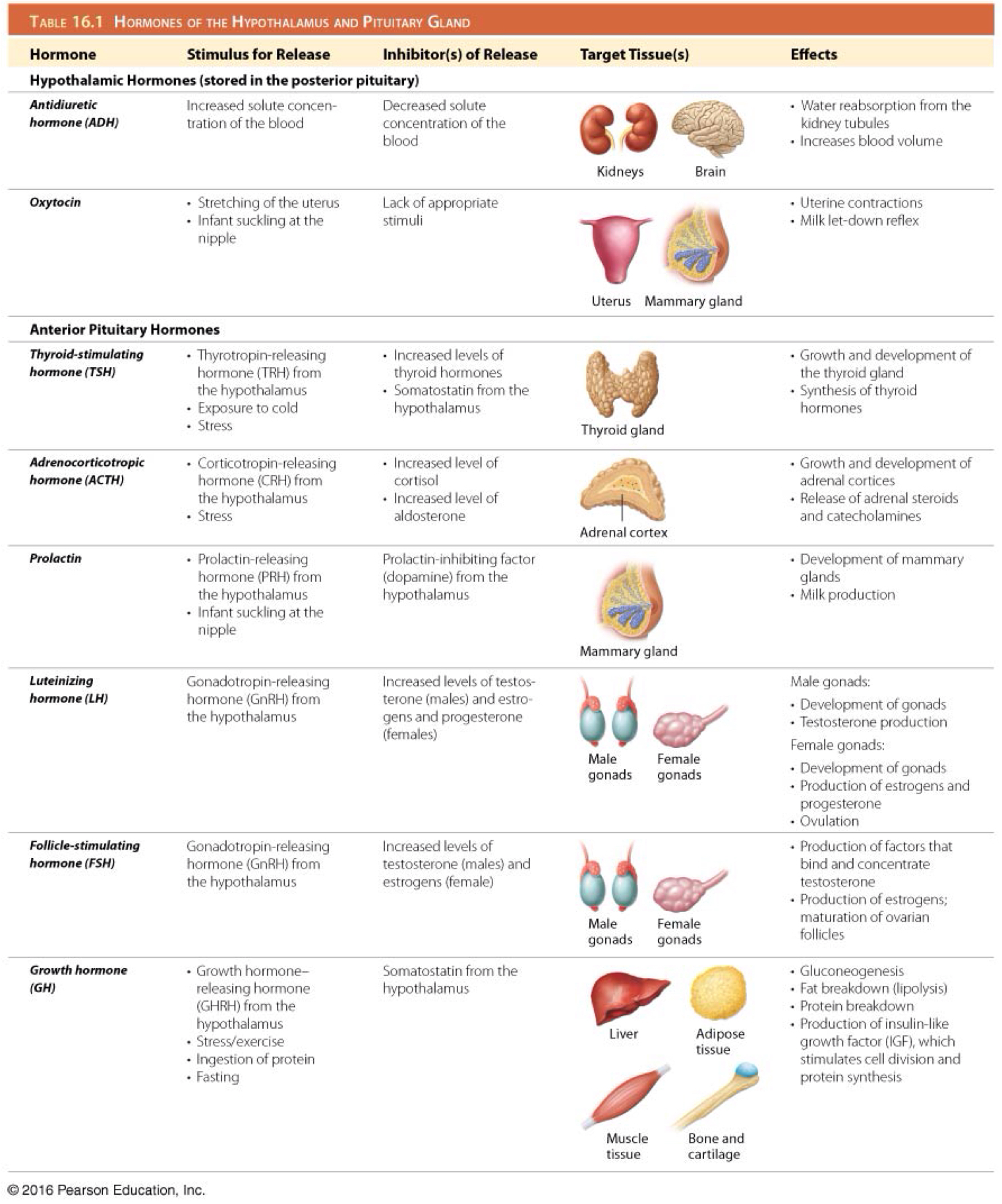
Which is the function of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)?
Stimulates development of the adrenal glands and their synthesis of steroid hormones
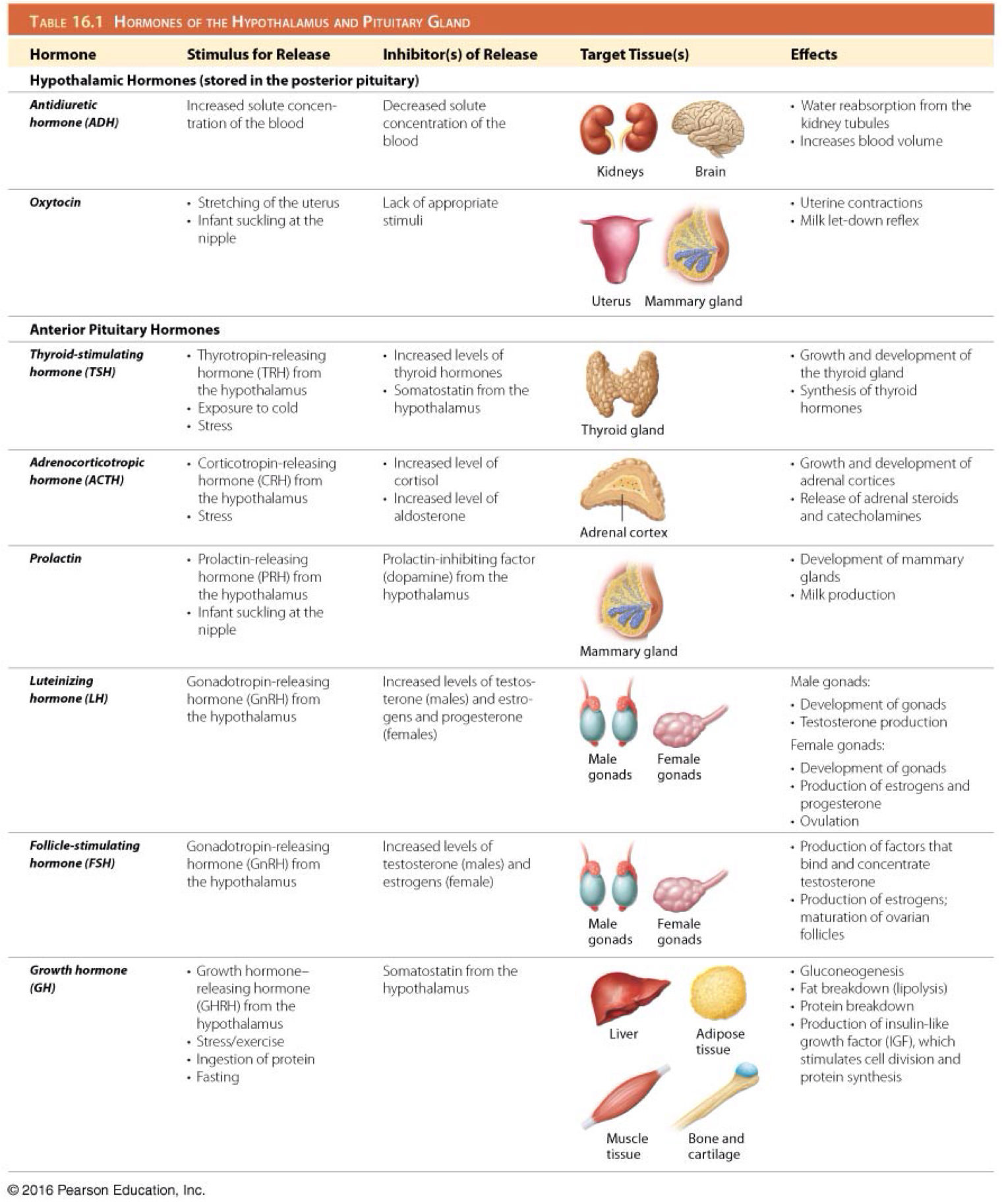
Which hormone stimulates the secretion of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)?
Hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
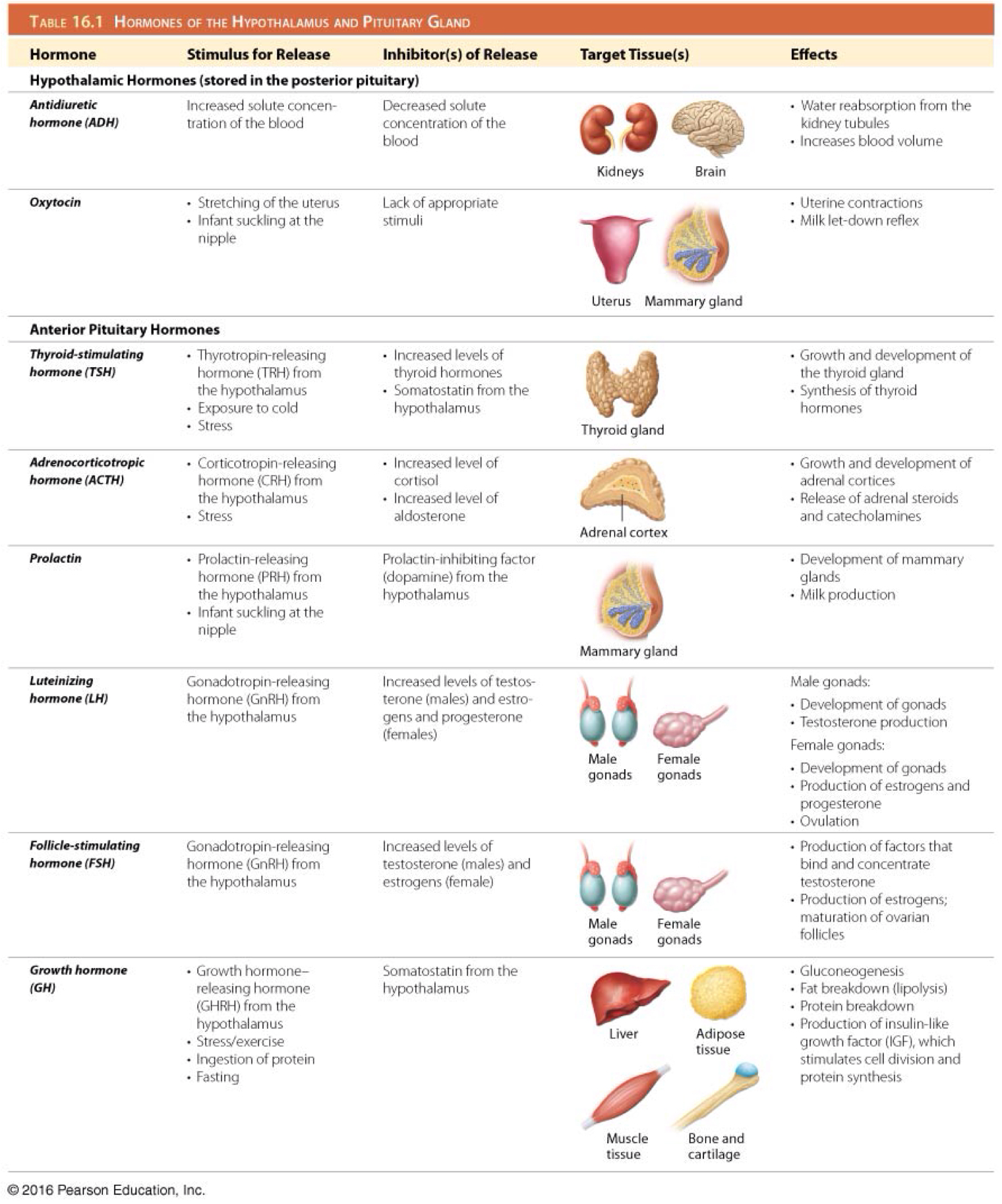
Which is the function of prolactin (PRL)?
Stimulates growth of mammary glands and initiation and maintenance of milk production
Secreted in females who have given birth
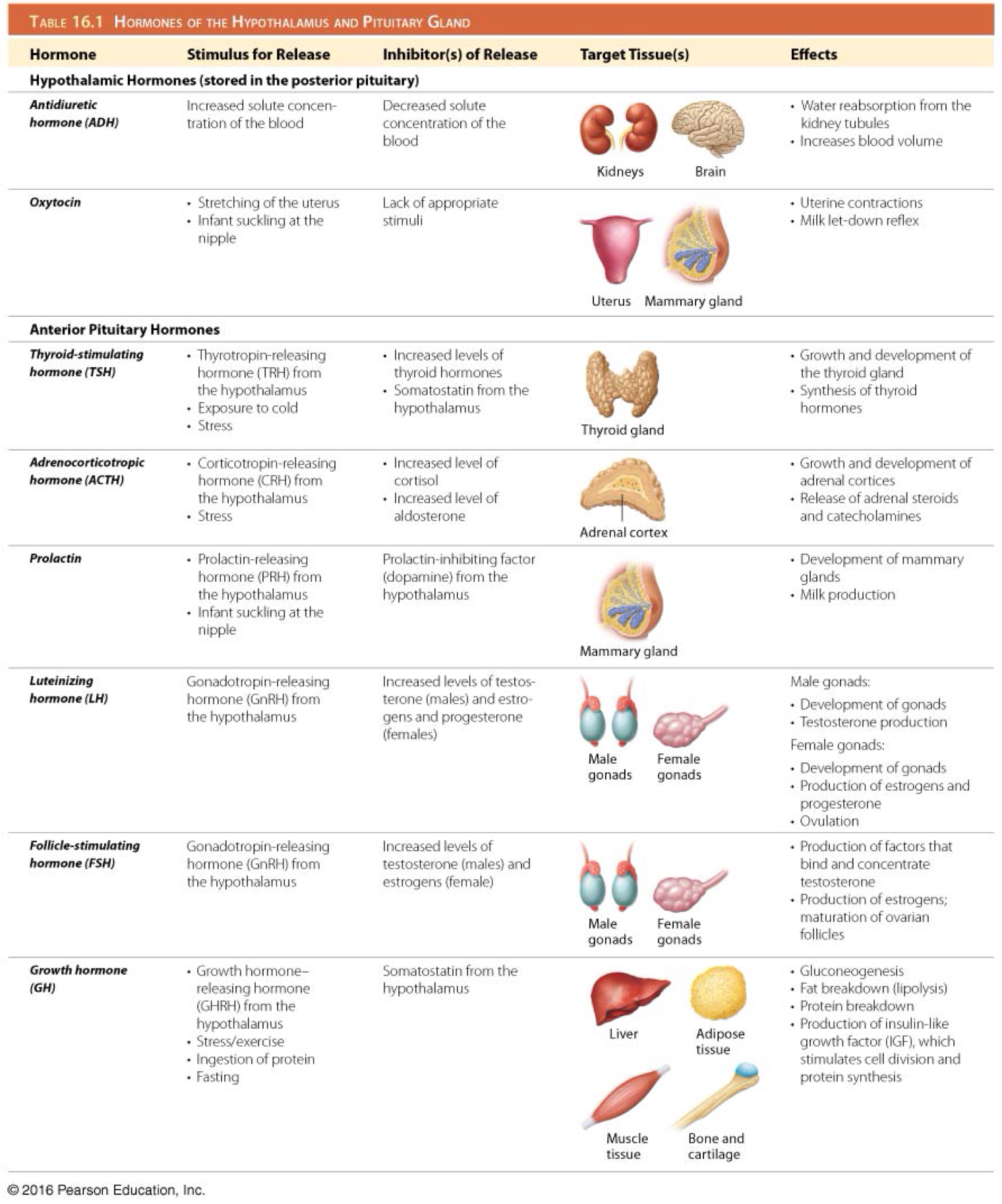
Which hormone inhibits the secretion of prolactin (PRL)?
Prolactin inhibiting factor (dopamine)