(b) elements, compounds and mixtures
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
element (1.8)
an element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into any other substances
compound (1.8)
a compound is a pure substance that is made from more than one element. these elements are very hard to separate since they are chemically bonded together e.g. H2O or CO2
mixture (1.8)
a mixture is when two or more elements or compounds are present without being chemically bonded together.
melting point (1.9)
a melting point is the temperature at which a substance goes from a solid to a liquid. pure substances have fixed melting points, but mixtures can melt over a range of temperatures
boiling point (1.9)
a boiling point is the temperature at which a substance goes from a liquid to a gas. pure substances have fixed boiling points, but mixtures can boil over a range of temperatures
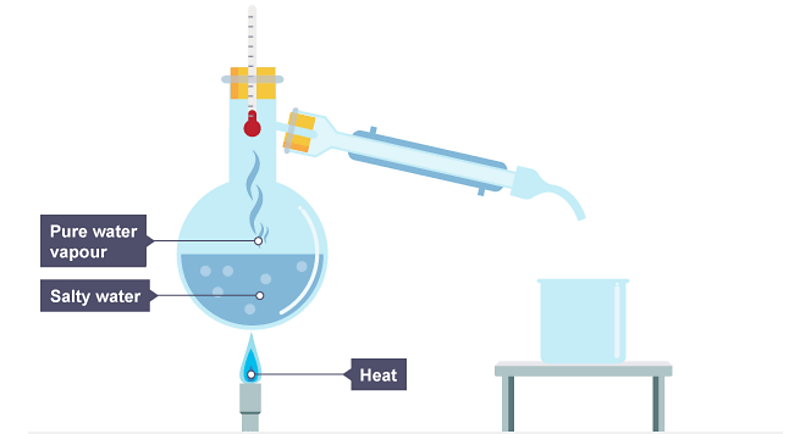
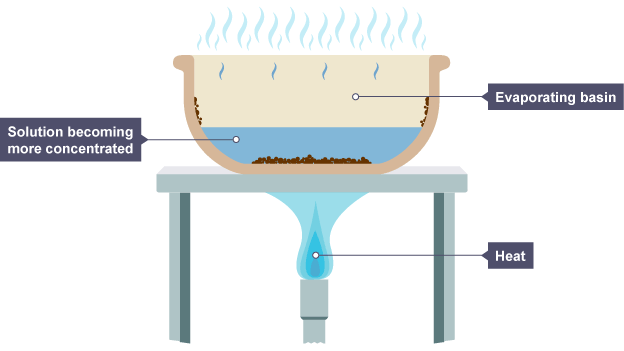
simple distillation (1.10)
the dissolved solute has a higher boiling point than the solvent
the solution is heated and the solvent evaporates
the solvent moves away and it cools and condenses
the remaining solution becomes more concentrated as there is less solvent
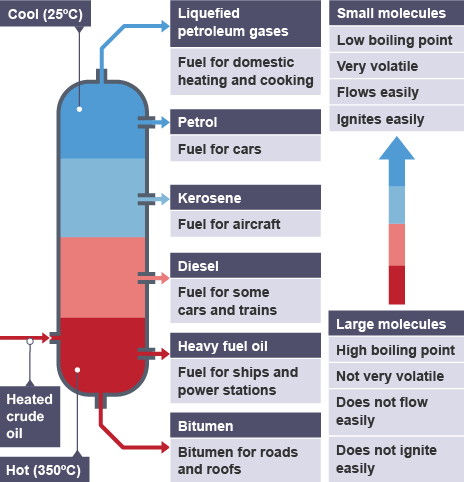
fractional distillation (1.10)
used to separate liquids from a mixture
e.g. crude oil
each liquid has a different boiling point
vapours rise and the column gets cooler at the top
liquids are led away / collected on trays
lower boiling point is at the top and vice versa
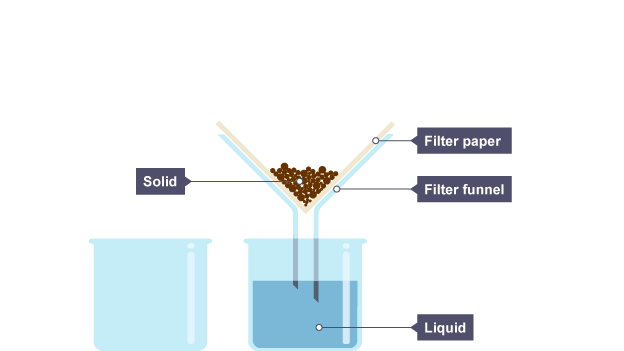
filtration (1.10)
used to separate insoluble solids from liquids
crystallisation (1.10)
produces solid crystals from a solution
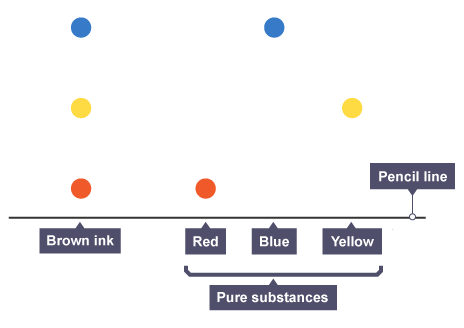
paper chromatography (1.10 / 1.11)
paper chromatography is used to separate mixtures of soluble substances. these are often coloured substances such as food colourings, inks, dyes or plant pigments.
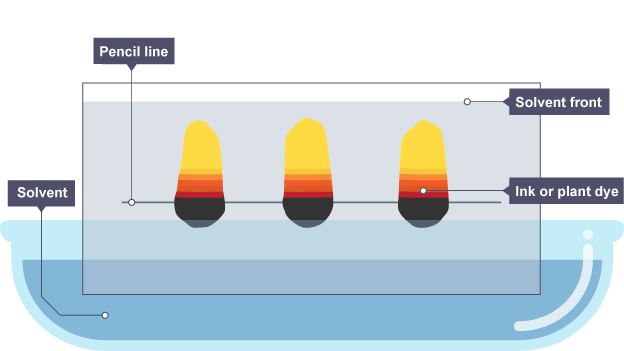
Rf value (1.12)
distance travelled by component / distance travelled by solvent
e.g. pigment moved by 3.4cm and solvent moved by 4.8 cm → Rf value = 3.4/4.8 = 0.71
investigate paper chromatography using inks / food colourings (1.13)
here, the brown ink is made of a mixture of the red, blue and yellow inks.