genetics
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
f2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
raw material of evolutionary change
problem of darwin’s mechanism of natural selection
mechanisms of natural selection needed a heredity model that preserves variation rather than diluting it
scientific paradigms
a theory (natural selection) becomes powerful when paired with a compatible mechanism (genes that segregate and assort) that makes quantitative prediction possible
darwin’s postulates
Individuals vary
some of the variations are passed to offspring
variants differ in survival/reproduction
natural selection
individuals who survive and go on to reproduce are those with the most favorable variations
transmission genetics (eukaryotes)
population can be explained by how alleles are packaged into gametes and passed to offspring
blending inheritance
law of segregation
each parent only passes on one allele
law of independent assortment
locus
information stored by DNA
depends on copying mechanism that has high fidelity and occasional mutation
raw material of evolutionary change
alleles
heritable variation + differential reproductive success —>
predictable change in allele frequencies over generations
mutation vs substitution
single mutation changes gene frequencies, substitution is when mutation rises to 100% frequency in the population
transitions and transversions
transition: purine ←> purine
transversion: purine ←> pyrimidine
synonymous
changes codon without changing amino acid
non-synonymous
changes amino acid
nonsense mutation
introduces premature stops
SNPs
single nucleotide polymorphism
single-base differences
hapmap project
measure SNP frequencies
chose sites and gene mapped people from there
looks at geographic/ancestral distributions and correlations with nearby SNPs
allows us to make inferences from patterns
insertions
adding bases in multiples of 3
deletions
removes bases in multiples of 3
frameshift
adding/deleting bases in not groups of 3
microsatellites
short tandem repeat whose length can change by slippage
more likely than SNPs
copy number variants
chromosomal segments are duplicated or deleted
unequal crossing over (missing or added some info)
whole genome duplication
meiosis doenst happen properly
somatic vs germline mutations
somatic rates can be higher than germline rates
germline mutations contribute directly to evolutionary change across generations
population thinking
mutations are rare on an individual level but are numerous on the population scale
intra vs inter-specific variation
intraspecific: differences within a single species, necessary for evolutionary change
interspecific: differences between 2+ species, outcome of evolutionary change
why continuous variation?
multiple polymorphic loci in a population
many loci with allelic variation produces continuous variation
environmental variation in the population
variance partitioning
partitioning variance into different sources
can find phenotypic variance
phenotypic variance (Vz)
genetic variance (Vg) + environmental variance (Ve)
what influences a phenotype
Genetics
alleles and their independent/additive effects (Va)
combination of alleles at a locus (dominance, Vd)
combination of alleles between loci (epistasis, Vi)
Environment
diff environments can cause diff phenotypes to develop (Ve)
Vz=[Va+Vd+Vi]+Ve
*assumption: parents pass alleles, not whole multilocus genotypes
additive genetic variance
component of genetic variance that “shows up” next generation
selection acts on phenotypic variance (response to selection depends on how much is due to additive genetic effects)
heritability
h²=Va/Vz
proportion of phenotypic variance that is attributed to additive genetic effects
proportion of variance that “shows up” next generation
if h² = 0, evolution won’t occur (requires heritable variation)
h²
heritability ranges between 0 and 1 (proportion)
measured with parent-offspring regression
sleeper slopes imply more additive variance relative to total variance
breeder’s equation
R=h²S
change in z = h²S
even strong selection (large S) produces little change if h² (heritable variation) is small, because most variance is not transmitted
will traits that have been evolving under a history of strong natural selection show high heritability or low heritability
low heritability because selection reduces genetic variation
evolution
change in allele frequencies
hardy weinberg
p² + q² + 2pq = 1
idea population assumptions
No natural selection of the gene
No genetic drift or random allele frequency changes
No gene flow (no new alleles added or lost through immigration/emigration; all alleles from original gene pool)
No mutations
Random mating with respect to gene in question
→ allele frequency won’t change under ideal conditions
allele frequency dynamics
p value will move to the right (0.4)
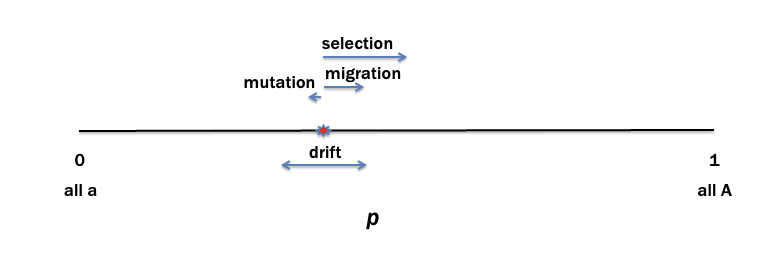
does crossing over change allele frequency?
won’t do anything to a single locus (if A is independent to B)
probability: AND
multiply the probabilities
probability of rolling 1 and a 2
(1/6)(1/6) + (1/6)(1/6) = 2/36
can tell mating is random from allele frequency because…
p², 2pq, q² all correspond