Charles Darwin and the Theory of Evolution
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Charles Darwin
Proposed natural selection as evolution mechanism.
Natural Selection
Process where organisms better adapted survive.
Microevolution
Small-scale evolutionary changes in gene pools.
On the Origin of Species
Darwin's 1859 book presenting evolution evidence.
Evolutionary Synthesis
1930s-1950s consensus on natural selection's role.
Common Ancestors
All species descended from shared predecessors.
Struggle for Existence
Competition among organisms for survival resources.
Fossil Record
Historical evidence of species changes over time.
Geometric Growth Rate
Population growth at exponential, unchecked rate.
Darwin's Elephant Problem
Hypothetical elephant population growth over centuries.
Inherited Variation
Genetic differences passed through generations.
Evolutionary Success
Contribution of genes to future generations' gene pool.
Fitness
Organism's reproductive success, not lifespan.
Beneficial Traits
Inherited characteristics improving survival chances.
Elephant Breeding Estimate
Projected 15 million elephants from one pair.
Survival Advantage
Traits enhancing an organism's ability to survive.
Desert vs. Mountain Hares
Adaptations for survival in different environments.
Variation Impact
Differences affecting reproductive success in species.
Static Environment
Concept that Earth's conditions are unchanging.
Species Change Over Time
Evolutionary modifications in traits across generations.
Peppered Moth
Biston betularia, native to England, exhibits color variation.
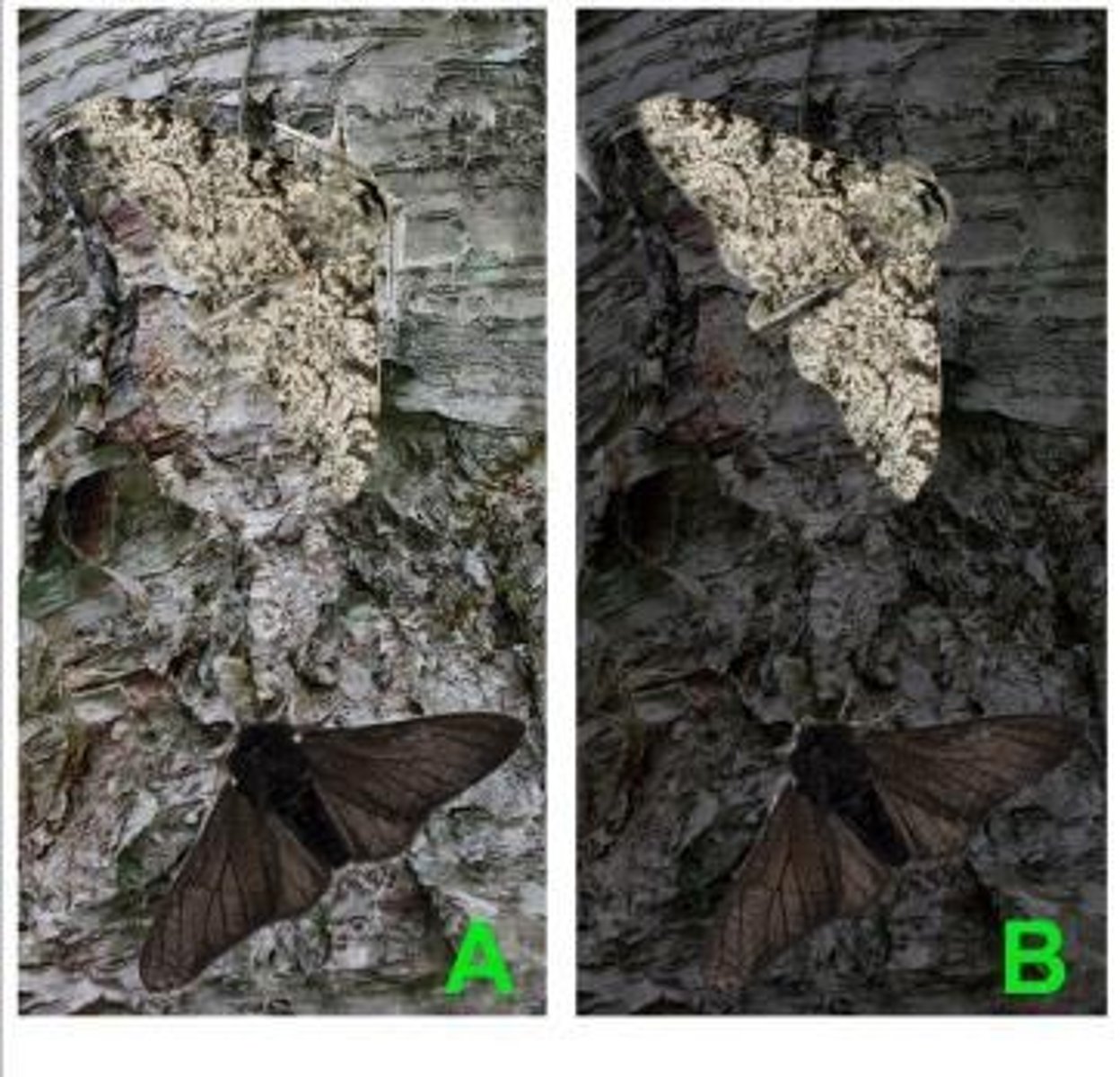

Industrial Revolution
Increased pollution altered moth coloration in England.
Macroevolution
Evolution resulting in new species from gene pool changes.
Gene
DNA sequence coding for a specific polypeptide.
Allele
Variant form of a gene influencing traits.
Gene Pool
Total genes present in a species.
Allelic Frequency
Percentage occurrence of a specific allele.
Mutation
Change in DNA sequence, source of genetic variation.
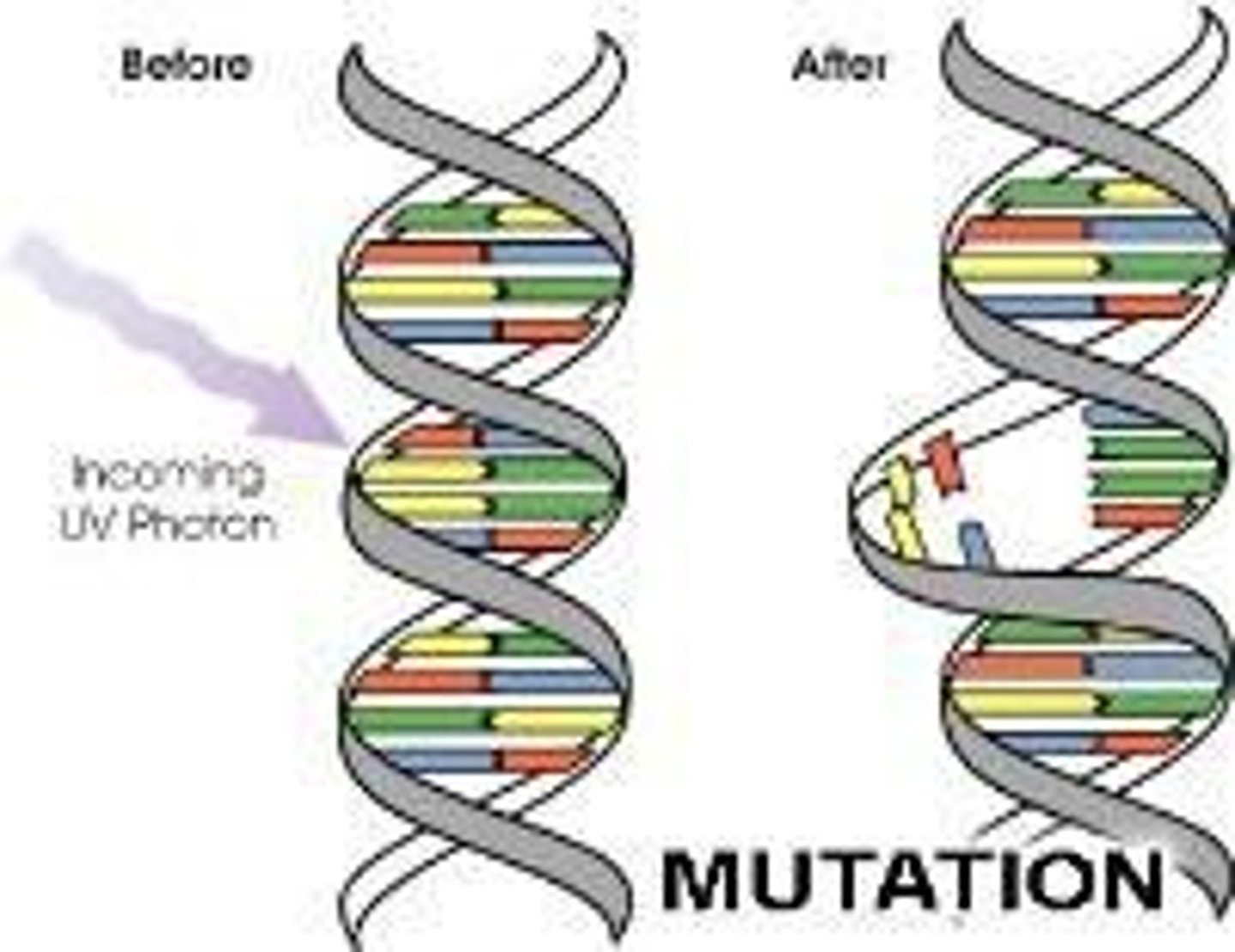
Point Mutation
Single nucleotide substitution in DNA sequence.
Synonymous Mutation
Mutation causing no change in amino acid.
Nonsynonymous Mutation
Mutation resulting in a different amino acid.
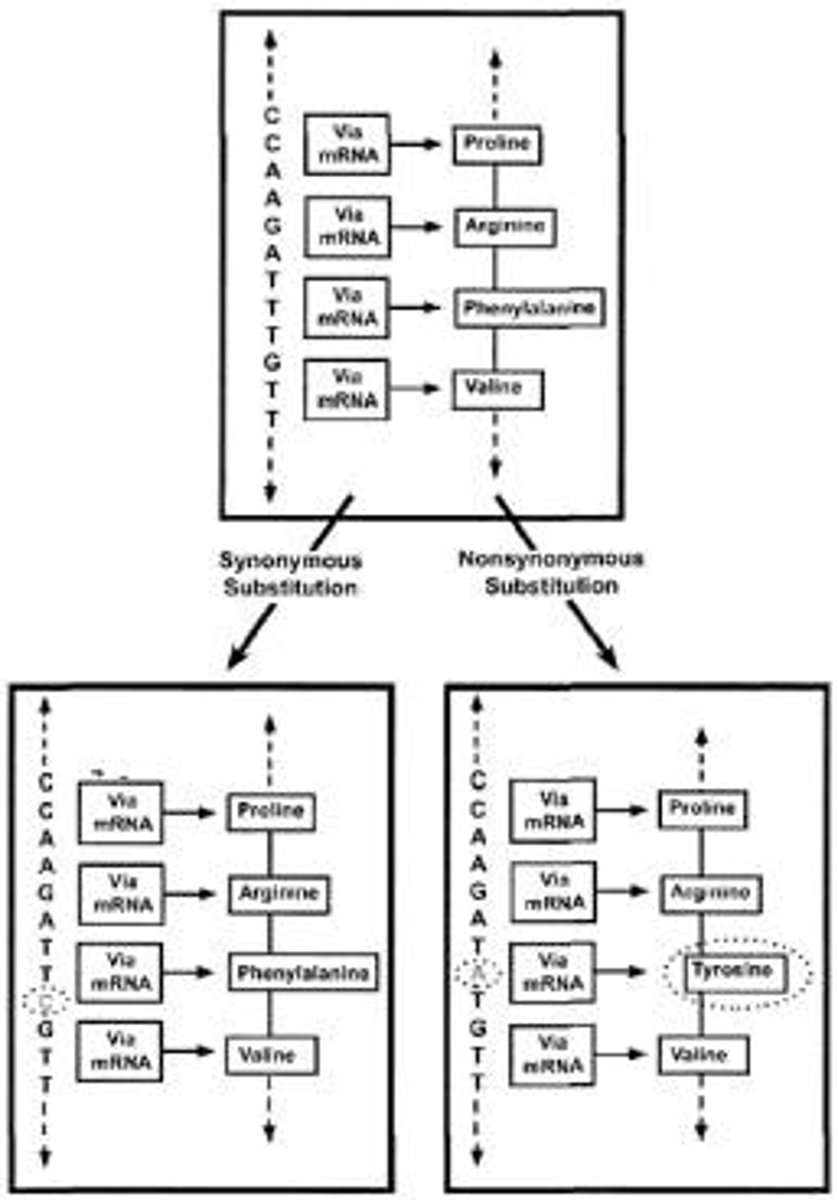
Speciation
Formation of new species through evolutionary processes.
Pesticide Resistance
Increased frequency of resistant genes in pests.
Gene Flow
Transfer of genes between populations.
Random Genetic Drift
Random changes in allele frequencies over generations.
Phenotype
Observable traits resulting from genotype expression.
Genotype
Genetic makeup of an organism.
Somatic Cell Mutation
Mutations not inherited by future generations.
Gamete Mutation
Mutations that can be passed to offspring.
Environmental Change
Alterations in habitat affecting species survival.
Sulfur Dioxide
Pollutant from coal burning impacting moth coloration.
Missense Mutation
Nonsynonymous mutation resulting in different amino acid.
Gene Duplication
Copying of a gene, potentially altering function.
Myoglobin
Oxygen-binding protein in muscle tissue.
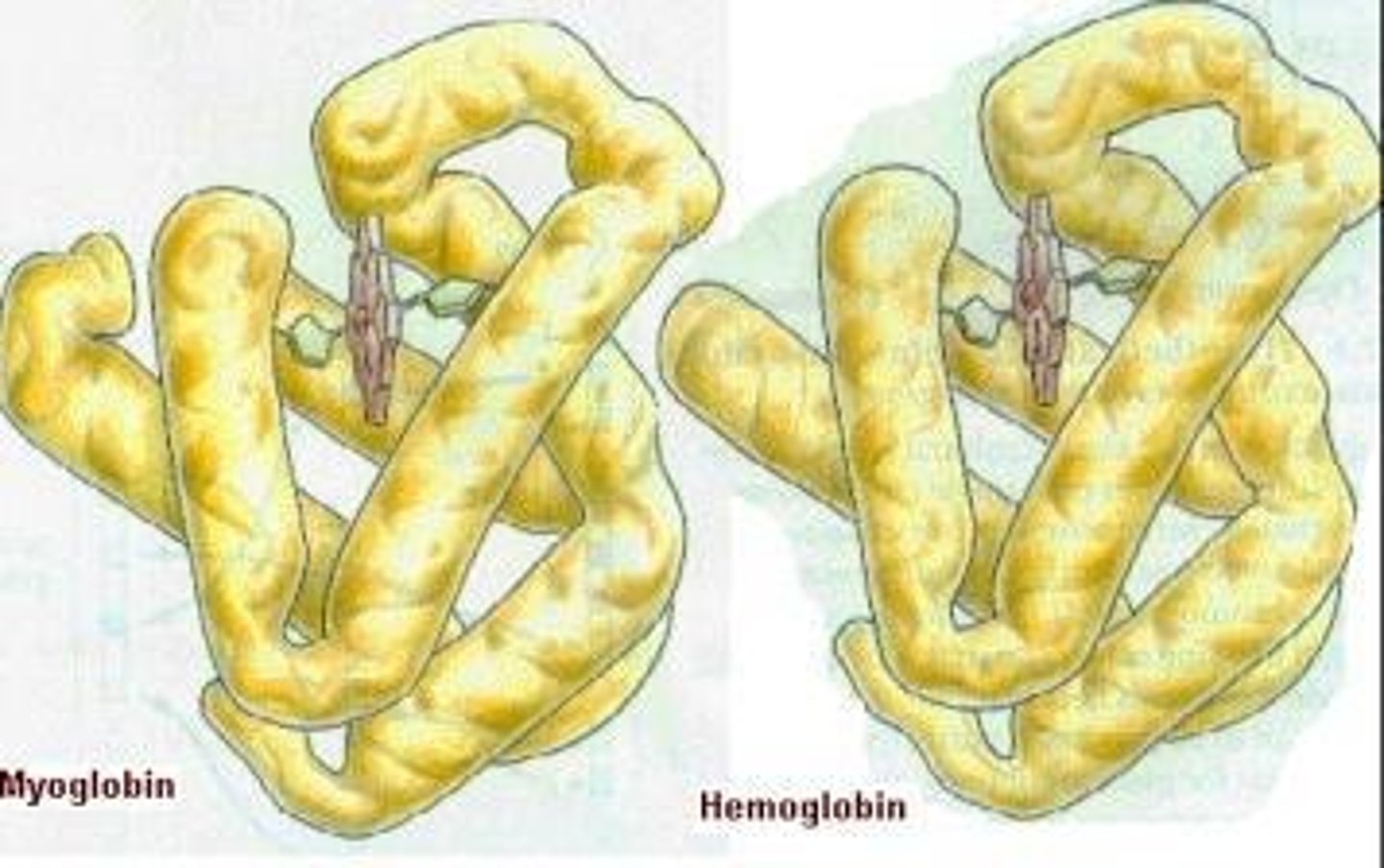
Hemoglobin
Oxygen-transport protein derived from myoglobin.

R Group
Variable side chain of amino acids affecting properties.
Neutral Mutation
Mutation with no significant effect on fitness.
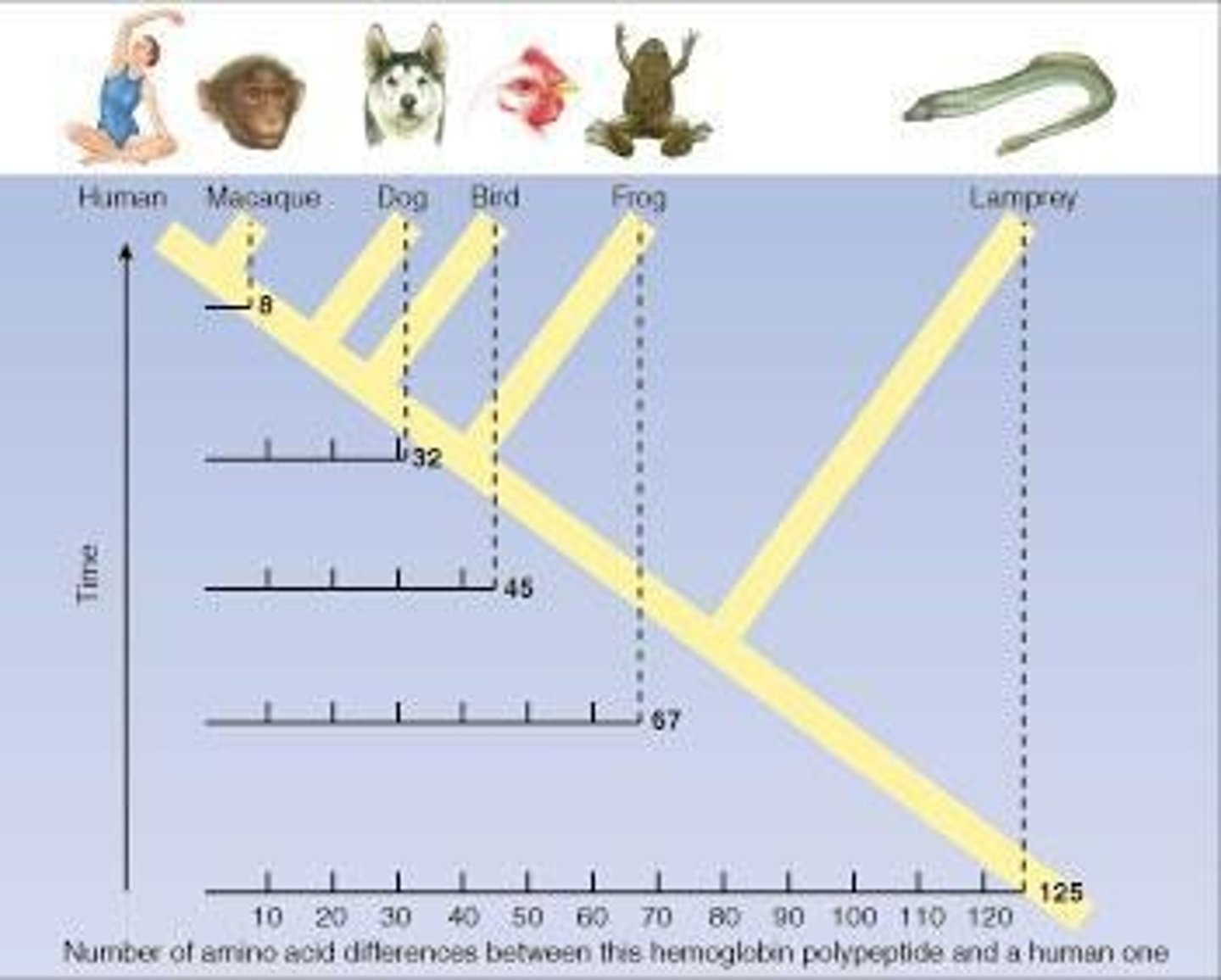
Molecular Clock
Rate of molecular evolution over time.
Cytochrome c
Protein involved in electron transport chain.
Amino Acid
Building blocks of proteins, encoded by genes.
Pseudogenes
Nonfunctional genes resulting from duplication and mutation.
Evolutionary Divergence
Separation of species leading to genetic differences.
Conserved Gene
Gene that remains relatively unchanged across species.
Functional Gene
Gene that produces a functional protein product.
Mitochondrial Membrane
Location of cytochrome c in cells.
Gene Modification
Alteration of gene structure or function.
Protein Functionality
Effectiveness of a protein in performing its role.
Amino Acid Sequence
Order of amino acids in a protein.
Inverse Relationship
Opposing correlation between two variables.
Species Comparison
Analysis of genetic differences among organisms.
Frameshift Mutation
Insertion or deletion alters amino acid sequence.
Deleterious Mutation
Most frameshift mutations negatively affect protein function.
Flavobacterium
Bacteria that digest nylon waste due to mutation.
Chromosomal Rearrangement
Changes in chromosome structure affecting species evolution.
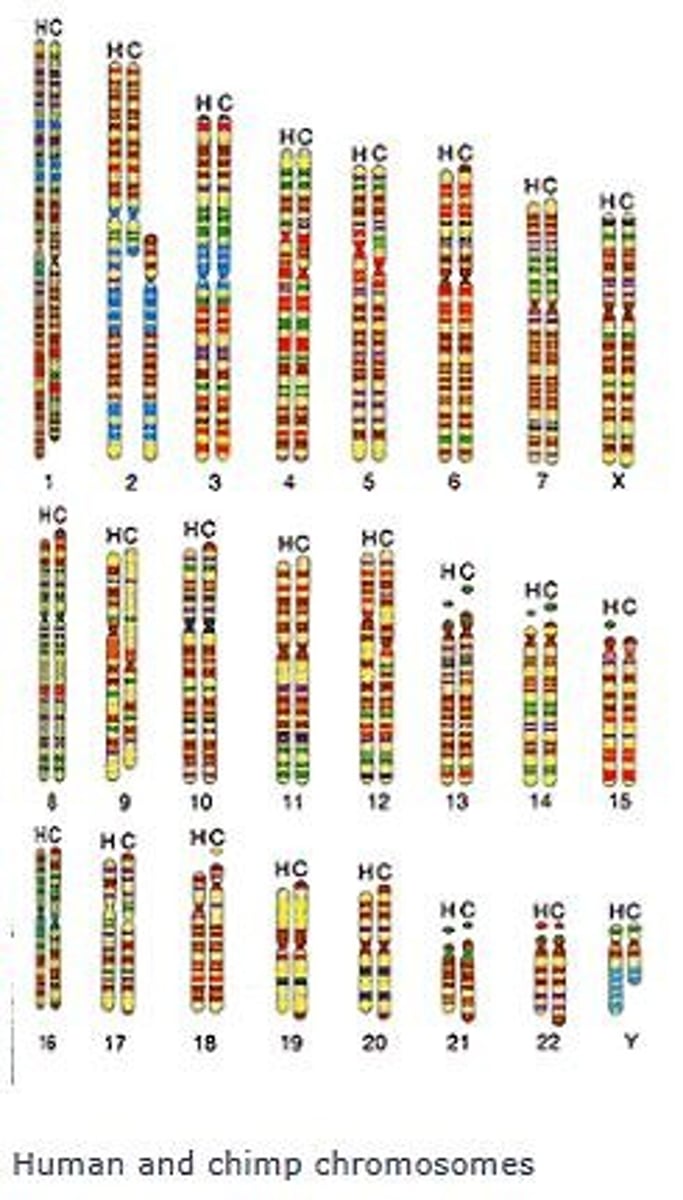
Karyotype
Chromosome number and structure comparison between species.
Inversions
Chromosomal segments flipped, altering gene order.
Deletions
Loss of chromosome segments, impacting genetic information.
Duplication
Copying of chromosome segments, increasing gene dosage.
Translocations
Segments of chromosomes exchanged between non-homologous chromosomes.
Fusions
Joining of two chromosomes into one.
Artificial Selection
Human manipulation of gene pools for desired traits.
Genetic Diversity Loss
Reduced variety due to selective breeding practices.
Super Bugs
Bacteria resistant to multiple antibiotics, posing treatment challenges.
MDR Bacteria
Multidrug-resistant bacteria, often found in hospitals.
Antibiotic Resistance
Natural immunity developed through random mutations.
Genetic Drift
Random changes in allele frequencies within populations.
Gene Flow
Movement of genes between populations, enhancing diversity.
Sexual Reproduction
Recombines genes, creating unique offspring.
Gametes
Reproductive cells producing genetic variation.
Unique Offspring Probability
Probability of genetically identical siblings is 1 in 446.
Evolution Driving Force
Sexual reproduction promotes genetic variation and evolution.
Managed Landscape Burns
Restores gene flow by reducing genetic drift.
Collared Lizards
Species affected by habitat disruption and genetic drift.