semester 1: biology exam revision
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
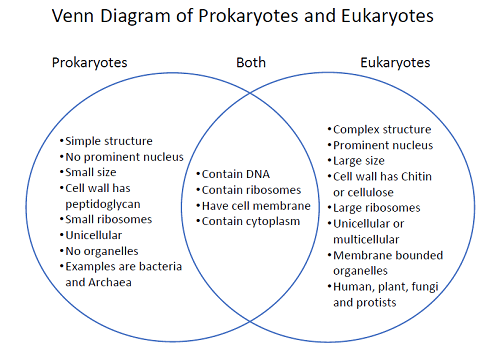
prokaryotes
lack membrane bound organelles: ribosomes
only membrane is plasma membrane
uni cellular
bacteria and archeans
villi
villi found in the small intestine has a large SA:V to maximise absorption of nutrients
damaged villi = malnutrition
eukaryotes
membrane bound organelle
nucleus
mini compartments
animals, plants, fungi
plasma membrane: controls what enters and exits (DNA, ribosomes)
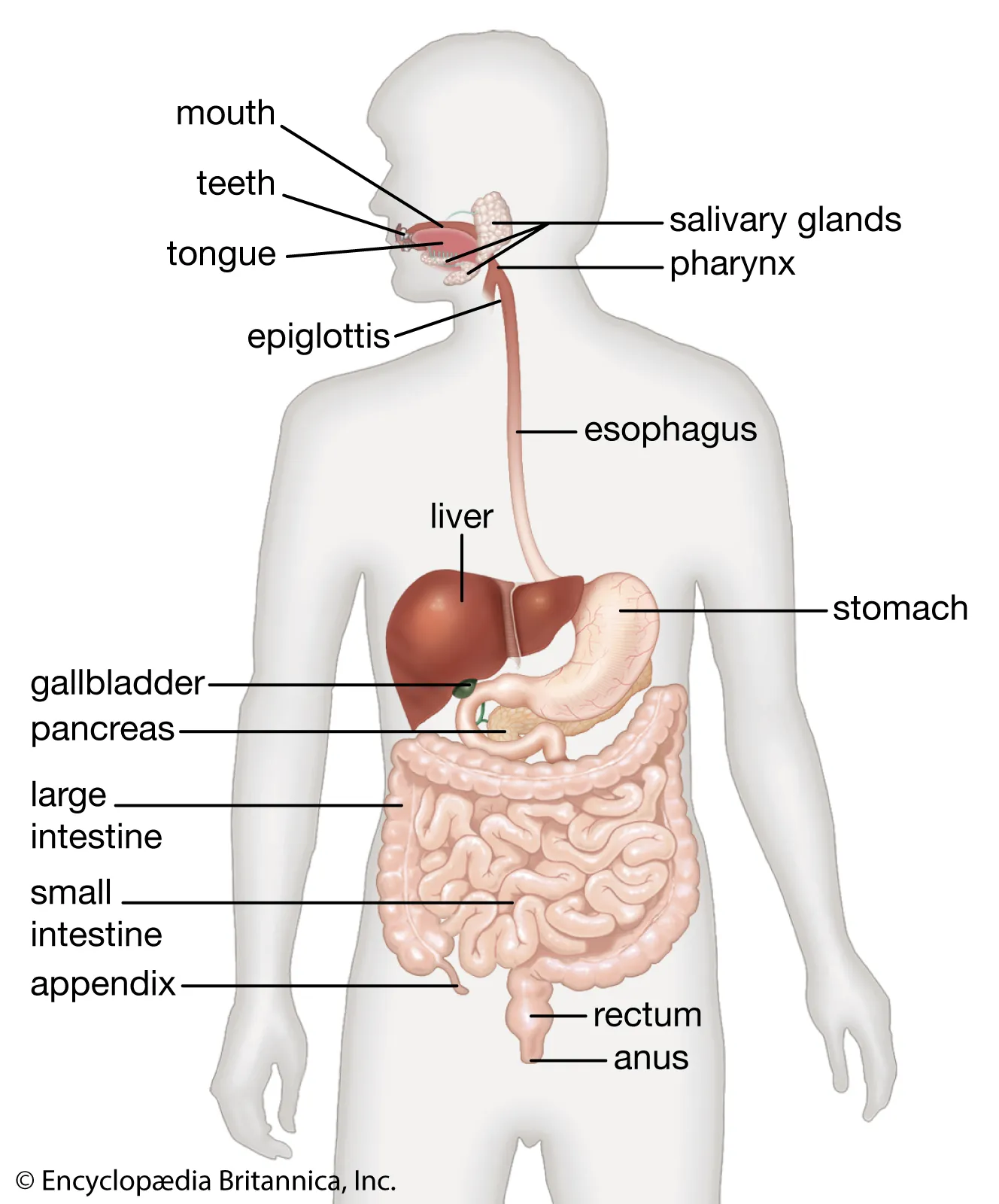
label digestive system
similarities + differences in eukaryotes and prokaryotes
SA:V ratio
big = decrease SA:V - slower rate of exchange for nutrients and waste
small = increase SA:V - faster rate of nutrients and waste
golgi complex + process
membranes sacs that package proteins out of the cells via vesicles - has a high SA: V for faster exchange
proteins are made at the rough ER (pepsin) that moves to the goldi complex where proteins are modified and packaged for secretory
secretory vesicle moves to the membrane, binds and is released via exocytosis
exports substances out of the cell - no Golgi = no modification of packaging for removal
chloroplasts
only found in plants
photosynthesis is the conversion of sunlight energy to chemical energy
has 2 jobs: catch the sunlight, green colouration
has more than 1 membrane: each membrane has an outer membrane, inner membrane stacks called grana with large SA: V —> more sunlight absorbed —> more glucose stacks = more photosynthesis
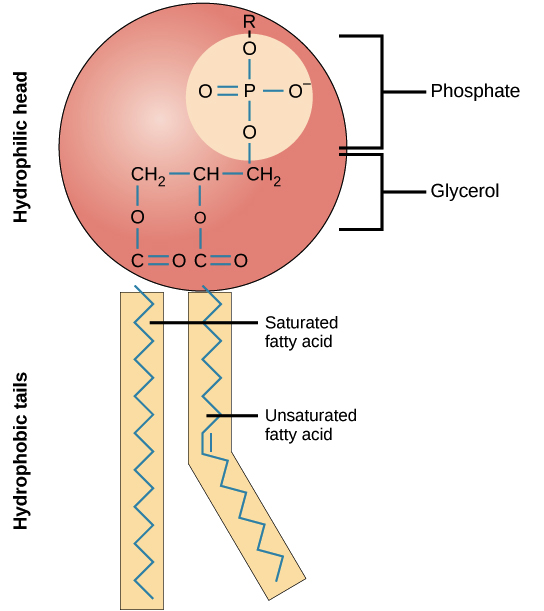
plasma membrane
entry and exit of dissolved substances in and out of the cell
partially permeable = only allows certain dissolved materials to pass through
phospholipid
hydrophobic = scared of water (fats, lipids and steroids) and goes straight through the membrane
hydrophilic = likes water (glucose and amino acids) and uses a protein channel to repel them
draw a phospholipid
simple diffusion
net movement of particles from a high solute concentration to a low solute concentration
does not require energy
facilitated diffusion
movement of some substances aided by a carrier protein
no energy required
low solute concentration —> high solute concentration with assisted protein channel
carrier proteins
open on only one side
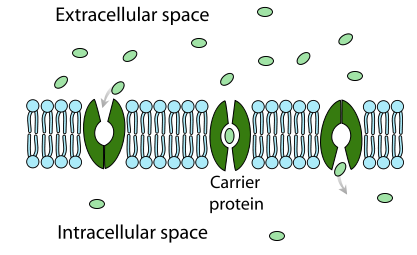
protein channels
open to both sides
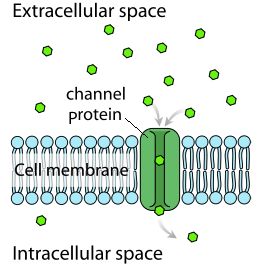
osmosis
movement of water across a partially permeable membrane without an input of energy
low solute concentration —> high solute concentration
osmosis in plant cells
hypertonic solution: water leaves —> high solute outside —> cell decreases in size (plasmolyzed)
isotonic solution: balance
hypotonic: water enters —> high solute inside —> turgid and chonk
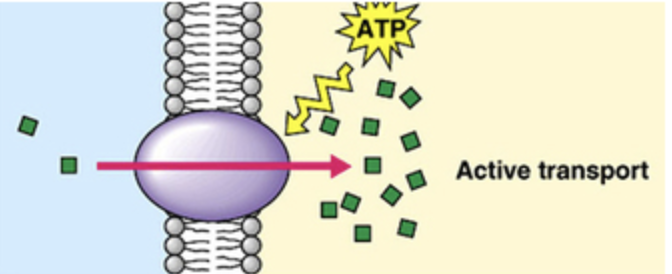
active transport
net movement of substances in/out of cell against concentration gradient
needs energy (ATP)
draw diagram
binary fission
sexual reproduction where one parent organism produces offspring genetically identical to it
daughter cell = identical
no gametes (sex cells) involved
in prokaryotes and protists meaning no mitosis = no stages
faster than eukaryote process as simpler
mitosis
the longest process where the division of a cell produces 2 daughter cells that are identical to the parent cell
in eukaryotes
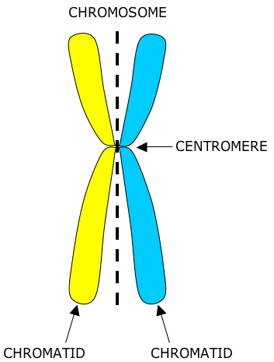
chromosomes are single-stranded but when mitosis occurs it becomes double-stranded
centromere - spindle fibres attach and split chromosomes
interphase
chromosomes are not visible but are duplicated
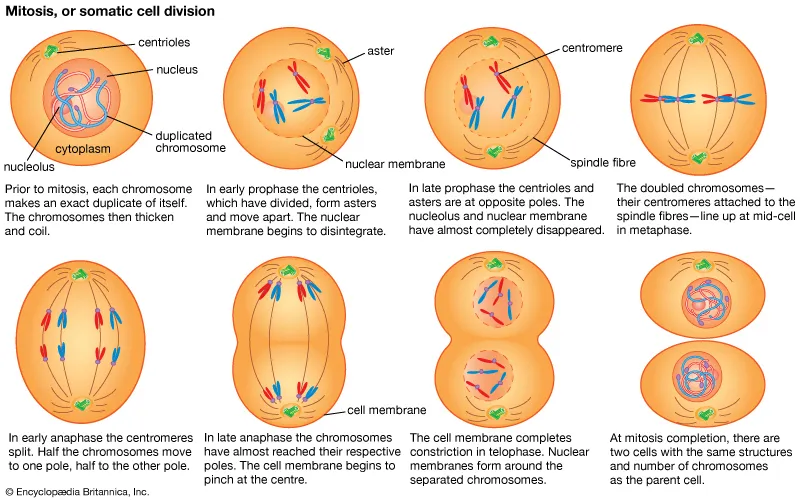
prophase
nuclear disappears, chromosomes become visible and thicken + double-stranded and centrosome visible
metaphase
chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell with spindle fibres attached to either side of the cell
anaphase
spindle fibres contract and pull chromosomes to either side to divide and separate with duplicated chromosomes on each side
telophase
spindle fibres disappear and chromosomes are less visible + new nuclear membranes form around each group of membranes
cell plate and firm cell wall in plant cell, cleavage furrow in animal cell
cytokinesis (not included)
cytoplasm divides and new membrane forms, enclosing and forming 2 separate cells
mitosis - cell cycle
time taken for a new cell to mature and give rise to 2 new cells
ensured DNA is passed from parent to daughter cells with no errors
2 checkpoints:
G2: check to see if there is an error in DNA or damage
metaphase (checkpoint 2 before chromosomes splt): where chromosomes line up and attached to spindles to make sure it can split evenly
if anything goes wrong, apoptosis occurs
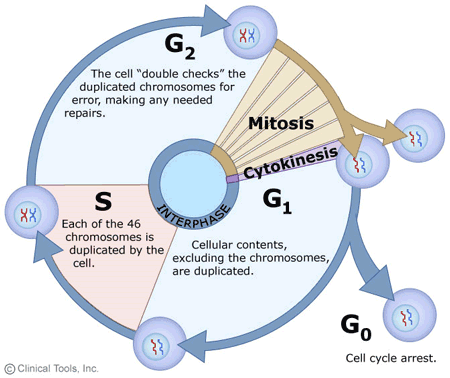
G1 phase
where cell contents duplicate
S phase
46 chromosomes in the cell are duplicated by replication
G2 phase
checks to see if there are any mistakes and corrects any damages or repairs
label cell cycle
apoptosis
natural programmed death
remove damage or non-functioning cells
more cells than needed: energy wasted to maintain
necrosis: unplanned cell death
apoptosis stages
cell responds to death signal and internal contents start to be digested
cell shrinks as cell volume decreases
plasma membrane starts to bleb due to plasma membrane detaching from cytoskeleton because of enzymes
nucleus and cell contents condense, fragments and cell brakes to form apoptotic bodies
apoptotic cells are engulfed by phagocytes via phagocytosis (draw)
stem cells
undifferentiated cells that have the ability to differentiate into organ or tissue specific cells with specialised functions
totipotent: any cell type e.g. zygotes
pluripotent: many cell types and form inner layer of blastocyst e.g. embryonic stem cells
multipotent: any family related group of cells
multipotent blood marrow stem cells can develop into a rbs, wbc or platelet
mechanical digestion
large pieces broken down into smaller pieces through chewing via teeth and muscular movements: mouth and stomach
if stomach is cut in half there is less room meaning less food can be eaten
chemical digestion
digestive enzymes speeding up breaking complex polymers (big) into simple monomers (small)
enzymes are involved to speed up the rate of reaction
intestines
small intestine is where most digestive enzymes and absorption of nutrients from food takes place: villi involved in only absorption
liver is involved to make bile that breaks down fat = bile is stored in gallbladder
no gall bladder = recommended less fatty foods as it cannot be broken down
osmoregulation
process of controlling water and solute (urea) concentration in the body
if dehydrated:
osmoreceptors in hypothalamus detect and ADH is released which increases permeability of tubule to absorb more water
produces a small volume of dark yellow (high conc. urea) urine
osmotic pressure falls
hypotonic
a solution with a higher solute concentration inside the cell than the outside of the cell. therefore water moves in (lysed ot turgid)
hypertonic
a solution with a lower solute concentration inside the cell than the outside of the cell so water moves out (shrivelled in animal, plasmolyzed in plant)
isotonic
where there is no gain/loss by the cell as there is the same concentration
negative feedback
reverses a stimuli —> back to normal
positive feedback
enhances stimuli —> keeps ongoing
glucose
source of energy in organisms
insulin
controls the uptake by cells of glucose from blood
decrease BGL via beta cells
glucagon
acts on the liver to release more glucose into the blood
increases BGL via alpha cells
thyroid hormone
released from the thyroid and affect cellular differentiation growth and metabolism
if thyroid is damaged or removed =reduction in thyroxine
hypothyroidism (underactive) = hormone replacement tablets
hyperthyroidism (overactive) = anti-thyroid drug, surgery
exercise and heat loss
evaporation: conversion of liquid water to vapour using heat
evaporation of water via sweat from moist skin cools the flow near the surface
reduce metabolic rate = reduce heat production (digestion)
vascular plants
xylem:
transports water and dissolved minerals/ions upwards
phloem:
transports sucrose are thin walled living cells
transpiration
transpiration is water loss from the stomata
stops at night or when it is too hot because no light for stomata to open and to not lose water
bad because it can lose too much water
good because it causes h2o to evaporate which causes water to pull up (moves from root up)
cohesion of water molecules allows movement up the xylem
valid
you get the results you’re supposed to get
precision
how close measurements of the same item are to each other
repeat or average
non-maleficience
encourages people to minimise harm which needs to be considered if dealing with living org.
homeostasis
maintaining a relatively stable internal environment within narrow ranges despite changes in external environment
loop of henle
The ascending limb secretes ions into the surrounding tissue to create a hypertonic environment
Water moves from the ascending limb into the tissue via osmosis
Less filtrate produced as more water is reabsorbed into tissue
how are thyroxine levels regulated by negative feedback when too high and too low
the anterior pituitary will not produce TSH which will stop the production of thyroxine and decrease levels
The hypothalamus will not release TRH to stimulate the anterior pituitary, resulting in no further TSH to stimulate the thyroid gland, stopping the production of thyroxine.
why there is a constant production in thyroxine even when the production of TRH and TSH is regulated
The thyroid gland does not need TSH to produce thyroxine
Even when TSH reduces because of an increase of thyroxine, the thyroid gland will still be stimulated
advantage of eukaryotes
can specialise in its own conditions
carry out complex tasks
advantage of small prokaryote
increase in SA: V for faster transport