Kidney related shit PEBC
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
CKD staging:
Name the eGFR ranges for each stage from G1-G5
name the albuminuria stage from A1-A3
G1 >90
G2 60-89
G3a 45-59
G3b 30-44
G4 15-29
G5 <15, on dialysis
A1 <3
A2 3-30
A3 >30
CKD changes to bloodwork
Decreased
Hgb, Hct, ferritin
Ca
Bicarb - more likely for metabolic acidosis
Increased
phosphate
potassium
Progressive Risk factors for development of CKD
unctrl DM
unctrl HTN
autoimmune disorder (glomerulonephritis, lupus nephritis, IgA nephropathy)
CVD (incl HF)
Smoking
obesity
Susceptibility risk factors for CKD
age >60
low SES
low birth weight
fam hx of CKD
drug induced nephrotoxicity
exposure to nephrotoxins
prior AKi
kidney fialure
hx of kidney stone
Polycystic kidney disease
systemic inflammation
dyslipidemia
tubular cell toxicity drugs - impair mitochondrial function and transport
Aminoglycoside
Amphotericin B
antiretrovirals
cisplatin
contrast dye
fascarnet
zolendronate
Drugs that cause glomerulonephritis - inflammation of flomerulus, leads to fibrosis or scarring (proteinuria >3.5g/day)
gold
hydralazine
interferon alfa
lithium
nsaid
PTU
pamidronate (high dose or prolonged course)
drugs that lead to Acute interstitial nephritis AIN - inflammation in renal tubules and intersititium = fibrosis and scarringDrugs that lead to Acute interstitial nephritis AIN - inflammation in renal tubules and intersititium = fibrosis and scarring
acyclocir
allopurinol
abx - beta lactam, rifampin, sulfonamide, vanco
diuretics - loop and thiazide
indinavir
nsaid
phenytoin
PPI
ranitidine
drugs that lead to chronic interstitial nephritis
acetaminophen (high doses chronically)
calcineurin inhibitors - cyclosporin, tacrolimus
chemotherapy
chenese herb with aristolochic acid
lithium
nsaid
drugs that cause rhabdomyolysis muscle injury, release more CK into blood and damage kidney, change GFR
AD: amitriptyline, doxepin, fluoxetine
diphenhydramine, doxylamine
Etoh, BZD, heroin, cocaine, ketamine, methadone, Methamphetamine
Li
statin
drugs that cause crystal nephropathy insoluble in urine = block urine flow
Abx ampicillin, cipro, sulfonamides
antiviral
chemo that cause tumour lysis syndrome (release uric acid and Ca)
indinavir
methotrexate
triamterene
when does someone have CKD
GFR<60 for over 3 months
ACR >3 over 3 months
and or some markers of kidney dmg for over 3 months with or without decreased GFR
When do people get symptoms in CKD
once at stage G3a - fatigue, poor appetite, itching
G4 signs of edema in lower extremities
G5 poor sleep, SOB, vomiting
Recommended therapy for CKD no DM
ACE/ARB
Statin
SGLT2i
optional
Antiplatelet (if hx of heart event)
Recommended therapy for CKD with DM
SGLT2i until dialysis or transplant
ACE/ARB
statin
optional
Antiplatelet (if hx of heart event)
GLP-1 if needed
nsMRA - finerenone!!
CCB, MRA if not at SBP target of 120
IBW in males
50kg + 2.3kg(inches over 5ft)
IBW in females
45.5kg + 2.3kg(inches over 5ft)
AdjBW calculation
IBW + 0.4(Actual BW- IBW)
when to use adjusted BW and IBW
IBW used UNLESS patient is obese (30% over IBW) OR if less than IBW
less than IBW = use actual body weight
if 30% over IBW use adjusted BW
nonpharm tx for CKD
smoking cessation
healthy diet <2g Na, SBP <120, avoid hyperkalemia
meats 0.8g/kg/day CKDG3-5
dietary phosphate CKD3-5
phys acitivity
weight BMI 18.5-24.9
prevent depression
A1c<7
amount of elemental iron in each
iron polysacc
ferrous fumarate
ferrous sulfate
ferros gluconate
FeraMax dose 150 / Fe 150mg
ferrous fumarate dose 300 / Fe 100mg
ferrous sulfate dose 300 / Fe 60mg
ferros gluconate dose 300 / 35mg
when to initiate erythropoiesis stim agents ESA
initate if Hbg 90-110
note that it does not improve mortality or CV outcomes in CKD and anemia but improves QoL (like furosemide in HF)
AE of ESA
Thromboembolism
Hypertension
allergic rxn
myalgia, flulike symptom
injection site pain
Complications of ESA
abx production
Al toxicity
pure red cell aplasia
Darbepoetin vs erythropoetin
Darbo has dosing of 1-2wk vs EPO of 1-3 times weekly, arget Hgb 115
IV Fe infusions considered
if oral failed.
target is hgb 115
monitor every 3 months
What is the definition of AKI
scr that increases over 26.5unol/L in 2 days
SCr that increases 1.5x baseline within last 7 days
urine volume <0.5mL/kg/hr for 6 hours
Risk factors for AKi
CVD, hx of cardiac sx
DM
multiple myeloma
hepatorenal syndrome
CKD
hypovolemia
sepsis
male
african american
advanced age
Pre renal AKI / functional (common 70%)
hypo perfusion of kidney - increases BUN and SCr
Intrinsic structural AKI 10%
Post renal AKI 20%
Severe AKI symptoms
confusion
fatigue
anorexia
flank pain
weight gain, edema
oliguiria <400mL/day or anuria <100mL/day
pre renal and intrinsic AKI treatment
fluid resus - isotonic crystalloid (NS or ringers lactate)
NaCO3 IV for metabolic acidosis and alkinizing urine
vasopressor if shock
diuretic for fluid overload
stop offending agents
post renal aki tx
removal of offending agent
renal replacement tx - dialysis to remove toxins
nonpharm tx for AKI
monitoring really
caloric intake 20-30kcal/kg/day
Allopurinol is also used in what?
prevention of AKI - cancer chemotherapy with risk of tumor lysis
prevents uric acid nepropathy - taken a few days prior to chemo
what is bad hyperkalemia? (ranges)
mild 5-5.9
mod 6-6.4
severe >6.5
What is used to shift K into cells?
sodium bicarbonate - used in acidosis
insulin
salbutamol
what is used to eliminate K from body?
furosemide
sodium polystyrene sulfonate
dialysis
When is metformin CI
CrCl <30
hepatic failure incl AUD
severe dehydration
hx lactic acidosis
When is acorbose CI
IBD
intestinal obstruction
intestinal diseases
ulceration
severe hepatic diesease
AE of acarbose
flatulence
diarrhea
abdominal pain
hepatitis
AE SU - gliclazide and glyburide and meglitide repaglinide
hypoglycemia (SU more, esp gliclazide)
weight gain (SU more)
HA
dizzy
GI
when are SU CI
T1DM
pregnancy
breastfeeding
ketoacidosis
severe liver or renal impairment
when is repaglinide CI
clopidogrel - clopidogrel inhibits repaglinide metabolism → higher change of hypoglycemia
gemfibrozil - same as above
same CI as SU.
MOA of SU and repaglinide
stimulate insulin release from beta cell
MOA Thiazolidindiones (TZD) - pioglitazone, rosiglitazone
increasing insulin sensitivity and decreasing liver glucose production
DPP4 inhibitors MOA
increase in incretin levels
Thiazolidinediones (TZD) AE
WORSEN HF → fluid retention and weight gain
fractures
URI
HA
Macular edema
TZD CI
HF
liver failure
bladder cancer - pioglitazone
Myocardial infarction - rosiglitazone
caution with DPP4 inhibitors
hx of pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer
GLP1RA CI
pregnancy
family hx of MTC or MENS2
causion in pancreatitis pancreatic cancer hx
GLP1RA AE
NVD
inj rxn
acute pancreatitis
gallbladder dx
weight loss
SGLT2i AE
UTI
yeast infx
hypotension
hyperkalemia
wt loss
DKA
fracture, amputation - canagliflozin
orlistat MOA
wt reduction - inhibit absorption of dietary fats
orlistat AE
NVD
more bowel mvt (not abs fat)
flatuence
steatorrhea (fat in poo)
ab pain
Rapid acting insulin is taken when because
right before eating (bolus)
short onset 4-15min
peak in 30-120min
lasts 3-5h
Fiasp is fastest.
SA insulin is taken when because
30 min prior to eating
onset 15-30min
peak 2-8h
duration 6.5-24h
RA insulin
Lispro
Aspart
Glulisine
SA insulin
Humulin R
Novolin ge Toronto
Entuzity
Longest acting insulin
Degludec - Tresiba
onset 90min
no peak
duration 42h
Second longest acting insulin
Glargine Lantus, Basaglar, Toujeo
onset 90 min
no peak
duration 24h (toujeo 30)
Intermediate acting insulin
NPH numullin N novolin ge NPH
onset 1-3h
peak 5-8h
duration 18h
ITS CLOUDY
TAKEN QHS or BID
Detemir/levemir
onset 90min
peak none
duration 6-24hr
has short duration - may need BID
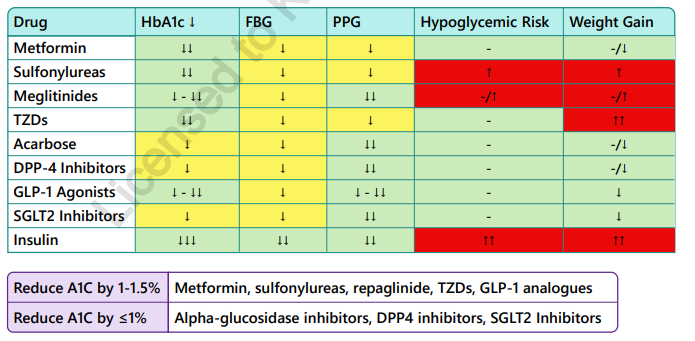
General summary of DM drugs
microvascular complications DM
eye, kidney, nerves
macrovascular complications
brain, heart, extremeties
diagnosis of DM - must be acle to repeat test to confirm diagnosis unless symptomatic hyperglycemia
FPG >7
Random PG >11.1 (anytime of day)
2hPG with 75g OGTT >11.1
A1c >6.5%
how to treat hypoglycemia
15 rule - 15g PO fast acting glucose - 4 glucose tabs, 3 tsp sugar, 1 tbsp honey, 150ml juice/soft drink → check BG in 15 min again → if <3.9, repeat, if >3.9 and next meal over one h away, take carb + protein
< 4, 40 minute rule for driving
Causes of T2DM - drugs
Glucocorticoids
atypical antipsychotics
FQ
Tiazides
protease and calcineurin inhibitors
HAART
Hyperglycemia inducing agent
Risk factors for T1DM
fam hx
genetics
finnish
younger age 5-14
risk factors for T2DM
non-modifiable
>40 yo
SEA, Latin american, FN
fam hx 1st degree relative
gestational DM, macrosomic infant
targets for A1c
<7 for most
<6.5 if low risk for hypoglycemia
7-8.5 if older, dementia, etc
non pharm DM recs
dietary
can effect A1c by 1-2%, less fat, more protein, less than 2 drinks a week or less
Exercise
150min /week mod aerobic exercise
resistance training 2 days a week
Weight loss
anything over 5% improve sugar ctrl and CVD risk
If pt has high CV risk and DM
GLP1RA, SGLT2i to decrease MACE
liraglutide
dulaglutide
semaglutide
empa
cana
If pt has HF and DM
SGLT2i decrease HF hosp and CV death
dapa
empa
If pt has CKD and DM
SGLT2i and GLP1RA, nsMRA
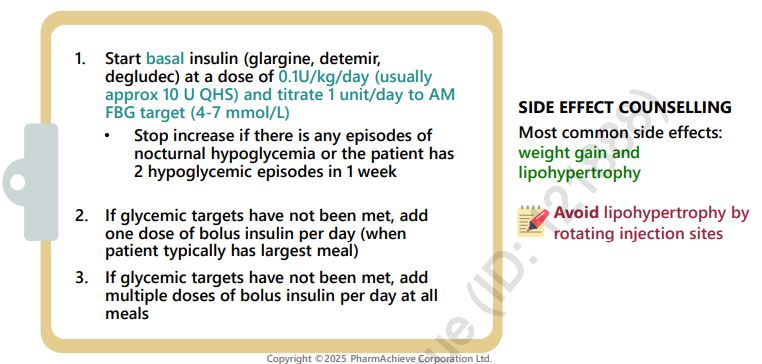
initiating insulin dosing
basal insulin first at 0.1-0.2u/kg/day, titrate by 1u to target (consider stopping Su, meglitinide, TSD bc hypoglycemia)
consider adding SGLT2i, GLP1RA/DPP4,
bolus insulin starting with 1 meal a day
Total insulin dose if using both basal and bolus is a 40% basal / 60% bolus (divided by how many meals)
how to change insulin doses
usualy adjust by 10% each time
target lows first then first elevated blood glucose of day
How to administer insulin

How to initiate insulin in T2DM
What is the somogyi effect

what is the dawn phenomenon

Medications that DM patient should be on
Statin - macrovasc dx, over 40, if less than 40 had DM over 15yr or microvasc complications
ACE/ARB for HTN if have CVD, CKD risk factors (if no risk factor can consider DHPCCB, Thiazide/like diuretic)
Aspirin if 2ndary prevention CVD (MI/STroke)
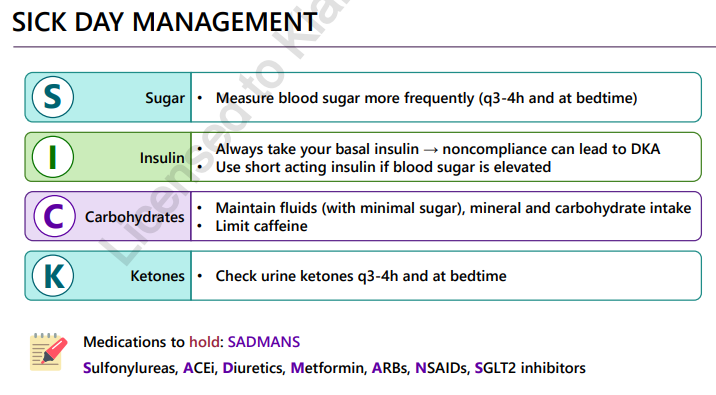
sick day management DM SICK and SADMANS
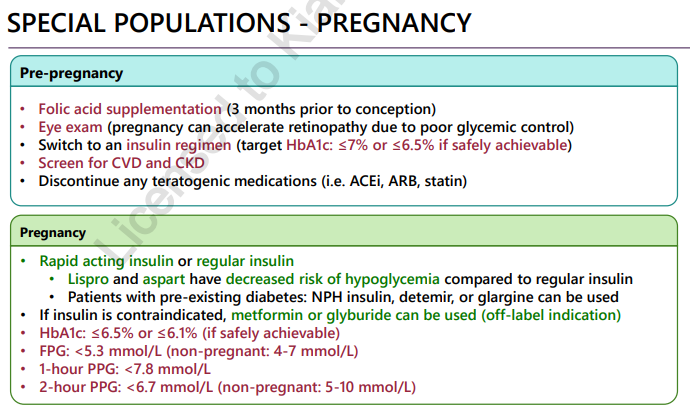
Pregnancy and DM
insulin and breastfeeding
breastfeeding increases risk of hypoglycemia and insulin is secreted in breastmilk - not risk to infant
how to monitor blood glucose in DM
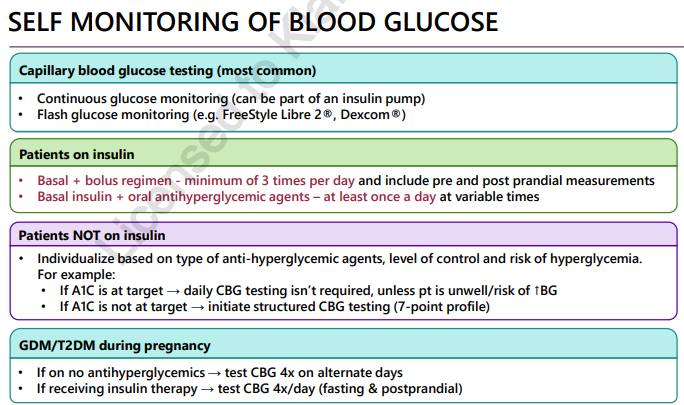
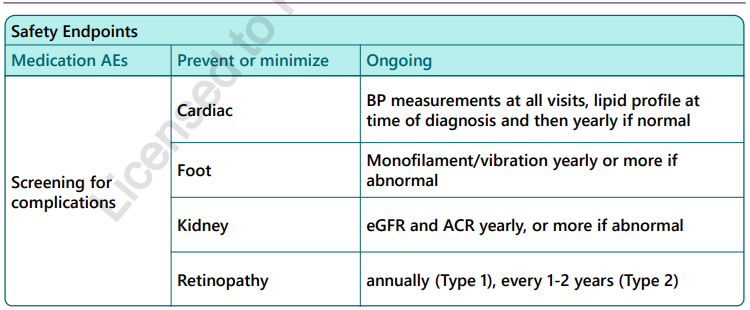
Monitoring complications in diabetes
Agents for neuropathy DM
pregabalin, gabapentin, 1st line
duloxetine, valproate, amitriptyline, venlafaxine
topical nitrate spray and casaicin
If patient’s A1c is >1.5% then start…
If patient’s A1c is <1.5% then start…
lifestyle plus metformin
lifestyle only