Chemistry (P2) - Structure and Formulae
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
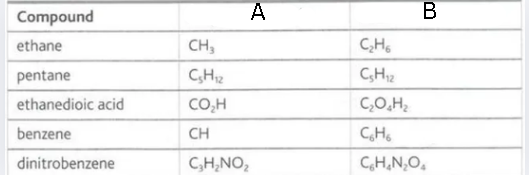
Label this diagram
A - empirical formula
B - molecular formula
How do we deduce the empirical formula of an organic compound?
We need the elements present in the compound and the mass of each element in the compound. We use the mass to find the number of moles of each element and create a mole ratio that, once simplified, would be equal to the proportions in the empirical formula
How do we deduce the molecular formula of an organic compound?
We need the empirical formula, molar mass of the compound and the mass of each element in the compound. We find the mass of the empirical formula and then we use it as a divisor with the molar mass of the compound and multiple the number of each atom in the empirical formula by the quotient

Label this diagram
A - displayed
B - condensed
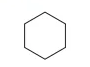
Identify this diagram
Cyclohexane
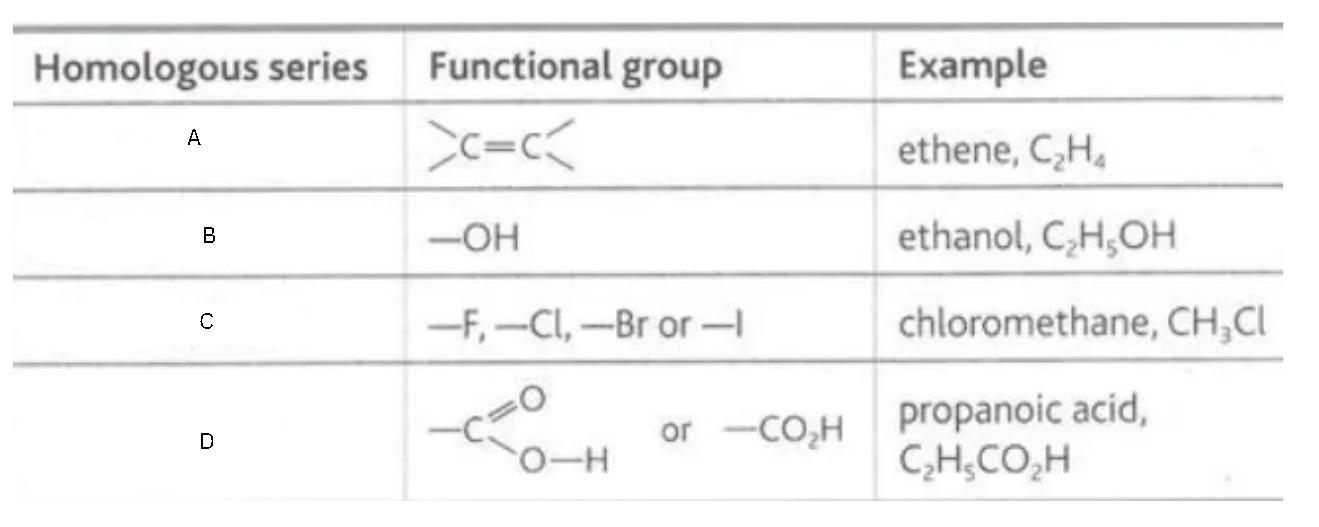
Label this diagram
A - alkene
B - alcohol
C - halogenoalkane
D - carboxylic acid
List the properties of a homologous series
There is a general formula which applies to all members in the series
Each successive member increases by the unit —CH2
The members have similar chemical properties due to having the same functional group
The physical properties gradually increase along with the amount of bonds present in the compound
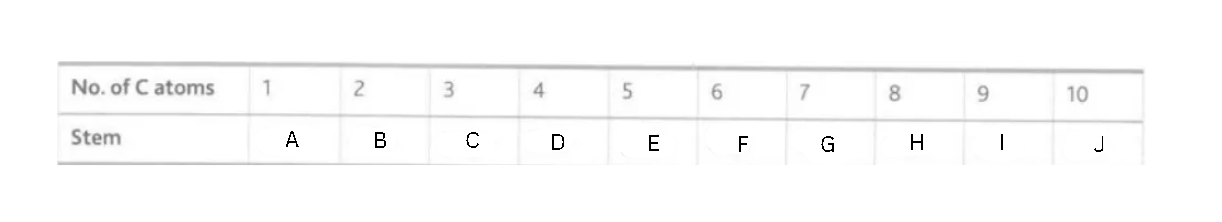
Label this diagram
A - meth
B - eth
C - prop
D - but
E - pent
F - hex
G - hept
H - oct
I - non
J - dec

Label this diagram
A - alkane
B - alkene
C - alcohol
D - carboxylic acid
E - ketone
List the rules of naming branched chains
The longest possible chain of atoms is always the main branch
The position of side branches are shown by numbering the carbon atoms
Carbon atoms are numbered starting at the end that gives the smallest number possible for the branch
A prefix is added to the stem to indicate the branch, which is named based on the amount of carbon atoms it contains
The position of the branch prefaces the prefix
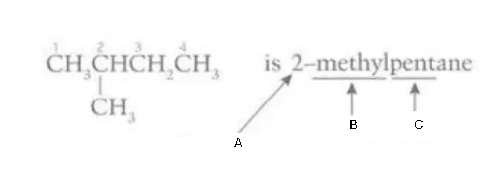
Label this diagram
A - position of side chain
B - prefix
C - stem
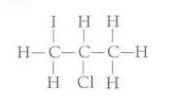
Identify this diagram
2-chloro-1-iodopropane
Which phenomenon allows organic compounds to have their chain structure?
Catenation
Which properties of carbon contribute to the structure of organic compounds?
The size of the carbon atom increases its effective nuclear charge, making the covalent bonds it breaks relatively hard to break, allowing the compound stability
The orbitals of carbon atoms hybridize allowing it to exhibit tetravalency which allows carbon atoms to form bonds in four directions, particularly contributing to the occurrence of branched and ring chains
How does resonance contribute to the stability of an organic compounds?
A delocalized system of electrons between atoms reduces the electron density concentrated around a singular atom and distributes it more easily which, decreasing the risk of an attack from an electrophilic species and also reducing repulsion between electrons, increasing the stability of the compound
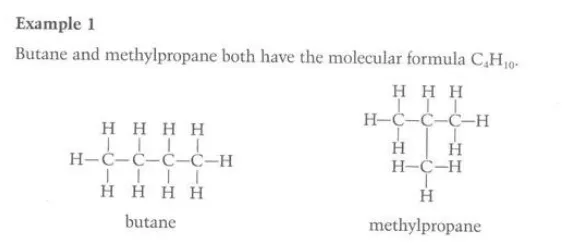
Identity the phenomenon in this diagram
chain isomerism
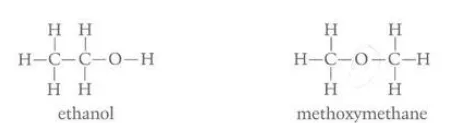
Identify the phenomenon in this diagram
functional isomerism
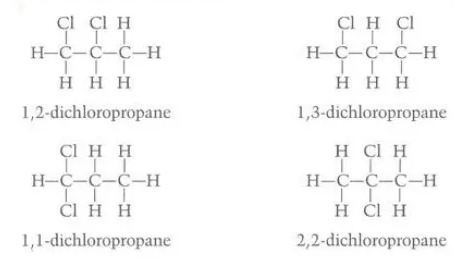
Identify the phenomenon in this diagram

Identify the phenomenon in this diagram
Geometrical isomerism
What causes geometric isomers and how do we differentiate between them?
Geometric isomers occur because there is no free rotation about a double bond, unlike with single bonds. If the two atoms are on the same side, the prefix cis- is attached to the compound otherwise the prefix trans- is attached
What causes optical isomers
Optical isomers rotate plane-polarised light in opposite directions by an equal amount as the electromagnetic field in plane polarised light only vibrates in one plane
State the steps for drawing all the isomers of a compound
