LECTURE: Chapter 4 Tissues
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
tissue
groups of cells similar in structure that perform common or related function
fixed, sectioned, stained
to be viewed under a microscope, tissues must be…?
transmission electron microscope (TEM)
electrons that are passing through the sample
scanning electron microscope (SEM)
creates an image by detecting reflected or knocked-off electrons
light microscope
microscopy that uses colored dyes
connective
Supports, protects, and gives structure to other tissues and organs in the body. Stores fat, helps move nutrients and other substances between tissues and organs, and helps repair damaged tissue.
What tissue type is described?
muscle
Pumping blood and supporting movement to lifting heavy weights or giving birth.
What tissue type is described?
nervous
Responsible for coordinating and controlling many body activities.
What tissue type is described?
nervous
tissue type found in brain, spinal cord, and nerves
muscle
tissue type found throughout the body, attached to bones via tendons, present in tongue, diaphragm, eye socket, and upper esophagus
connective
tissue type found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord
squamous, cuboidal, columnar, transitional glandular epithelial
what are the 5 types of epithelial tissues?
proper, cartilage, bone, blood
what are the 4 types of connective tissue?
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
what are the 3 types of muscle tissue?
neuron, neuroglia
what are the 2 cell types of nervous tissue?
epithelial
which cell type has polarity in the apical and basal surfaces?
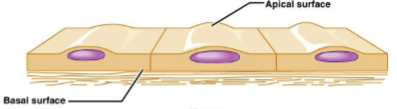
simple
what type of epithelia is shown?
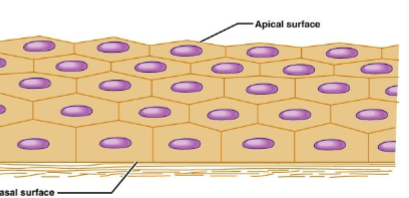
stratified
what type of epithelia is shown?
squamous, cuboidal, or columnar
what are the 3 classifications of epithelia?
simple squamous
Function: diffuse and filtration. Provides slick friction-reducing lining in lymphatic and cardiovascular systems
Location: kidney glomeruli, lining of heart, air sacs of lungs blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and lining of ventral cavity (serosae)
what is the epithelia?
simple squamous
Single layer of flattened cells with disc-shaped nuclei and sparse cytoplasm
what is the epithelia?
simple cuboidal
Function: secretion and absorption
Location: kidney tubules, ducts and secretory portions of small glands and ovary surface
what is the epithelia?
simple cuboidal
Single layer of cube like cells with large, spherical central nuclei
what is the epithelia?
simple columnar
single layer of tall cells with oval nuclei; contain many cilia. Goblet cells often found in this layer
what is the epithelia?
simple columnar
Function: absorption (microvilli) ; secretion of mucus enzymes and other substances
Location: Ciliated type line small bronchi, uterine tubes and some regions of uterus. Nonciliated in digestive tract and gallbladder
what is the epithelia?
pseudostratified columnar
single layer of cells with different heights; some do not reach the free surface. nuclei seen at different layers.
what is the epithelia?
pseudostratified columnar
Function: secretion and propulsion of mucus
Location: male sperm-carrying ducts (nonciliated). And trachea (ciliated)
what is the epithelia?
stratified squamous
thick membrane composed of several layers of cells
what is the epithelia?
stratified squamous
Function: protection of underlying areas subjected to abrasion
Location: forms external part of skin’s epidermis (keratinized cells) and linings of esophagus, mouth, and vagina (nonkeratinized cells)
what is the epithelia?
stratified cuboidal
RARE IN BODY
…typically 2 cell layers thick
Location: found in some sweat and mammary glands
what is the epithelia?
stratified columnar
RARE IN BODY
limited distribution in the body. occurs at transition areas between two other types of epithelia.
Location: found in pharynx, male urethra, lining some glandular ducts
what is the epithelia?
transitional
several cell layers, basal cells cuboidal, surface cells dome-shaped,
Function: stretches to permit distension of urinary bladder
Location: Lines urinary bladder, ureters, and part of urethra
what is the epithelia?
transitional
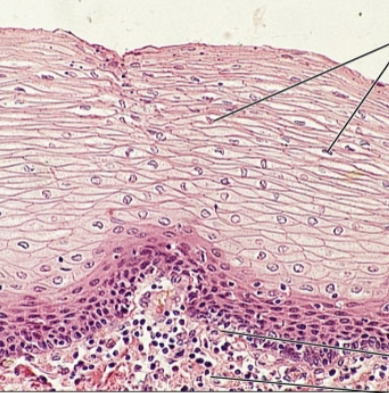
what is the epithelia?
stratified squamous
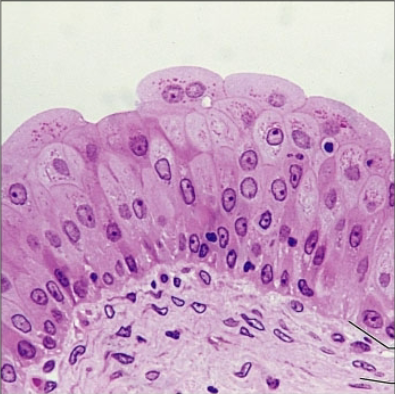
what is the epithelia?
pseudostratified columnar
what is the epithelia?
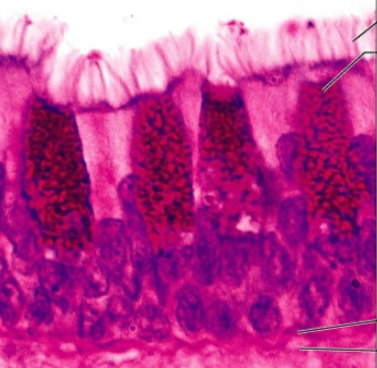
simple columnar
what is the epithelia?
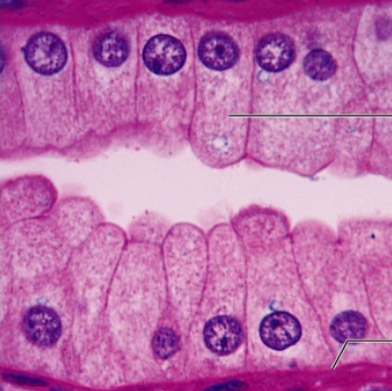
simple cuboidal
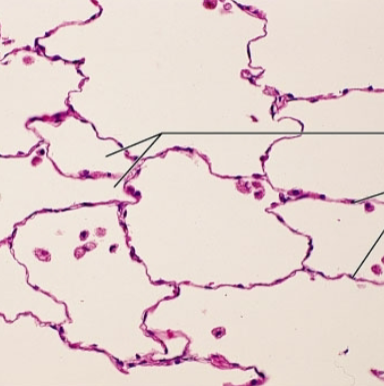
what is the epithelia?
simple squamous
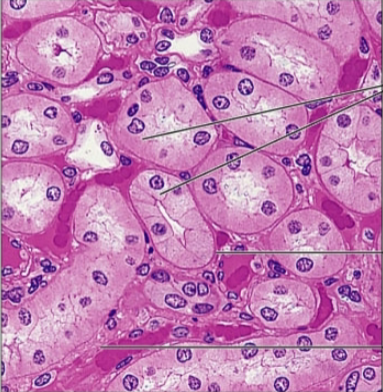
what is the epithelia?
glandular
gland is one or more cells that makes and secrete aqueous fluid
classified by: site of product release - endocrine, exocrine
relative number of cells forming gland- unicellular or multicellular
endocrine glands
ductless glands that produce hormones
secretions: amino acids, proteins, glycoproteins and steroids
exocrine glands
secrete products onto body surfaces (skin) or into body cavities
eg. mucous, sweat, oil, salivary glands
goblet cell
what is the only important unicellular gland?
merocrine
products secreted by exocytosis eg. pancreas, sweat, and salivary glands
what is the mode of secretion?
holocrine
products secreted by rupture (death) of gland cells, create oil eg. sebaceous glands
what is the mode of secretion?
function of connective tissue
binding + support, protection, insulation, transportation
mesenchyme
common tissue of origin for connective tissue
ground substance, fibers, cells
what is the 3 main structural elements of connective tissue?
ground substance
interstitial (tissue) fluid
FIBRONECTIN + LAMININ - adhesion proteins
GLYCOSAMINOGLYCAN (GAGs)
strong and porous
Functions as molecular sieve through which nutrients diffuse between blood capillaries and cells
what is the structural element of the connective tissue?
fibers
includes collagen (tough, high tensile strength), elastic (long thin fibers stretch), and reticular fibers (form delicate network + support elastisity)
what is the structural element of the connective tissue?
cells
fibroblasts- connective tissue proper
chondroblasts- cartilage
osteoblasts- bone
hematopoietic stem cells- cells in blood
what is the structural element of the connective tissue?
embryonic
gel-like ground substance with fibers and star-shaped mesenchymal cells
gives rise (ancestor) to all other connective tissue
found in embryo
what is the connective tissue?
embryonic
what is the connective tissue?
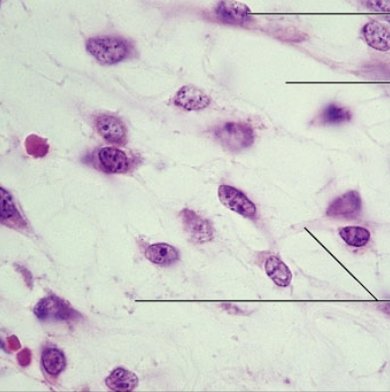
areolar connective tissue
loose connective tissue proper
-Gel-like matrix with all three connective tissue fibers
-Fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, and some white blood cells
Function: Wraps and cushions organs
Location: Widely distributed throughout the body
what is the connective tissue?
areolar connective tissue
what is the connective tissue?
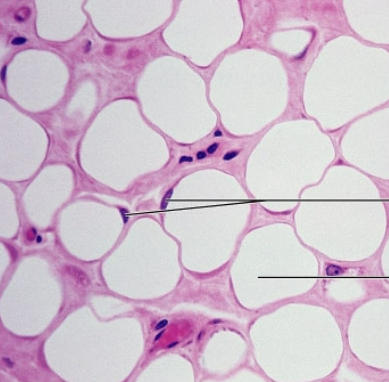
adipose connective tissue
loose connective tissue proper
Function: Reserves food stores, insulates against heat loss, and supports and protects
Location: under skin, around kidneys, within abdomen, and in breasts
-Local fat deposits serve nutrient needs of highly active organs
what is the connective tissue?
adipose connective tissue
what is the connective tissue?
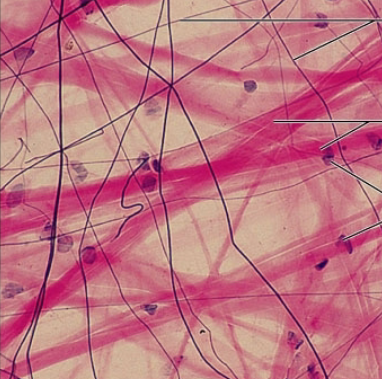
reticular connective tissue
loose connective tissue proper
-Loose ground substance with reticular fibers
-Reticular cells lie in a fiber network
Function: Forms a soft internal skeleton, or stroma, that supports other cell types
Location: lymph nodes, bone marrow, and the spleen
reticular connective tissue
what is the connective tissue?
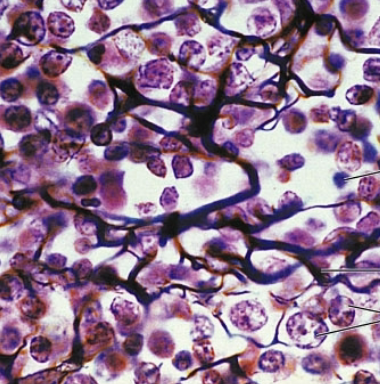
dense regular
dense connective tissue proper
Parallel collagen fibers with a few elastic fibers
-Major cell type is fibroblasts
Function: Attaches muscles to bone or to other muscles, and bone to bone
Location: tendons, ligaments, and aponeuroses
what is the connective tissue?
dense regular
what is the connective tissue?
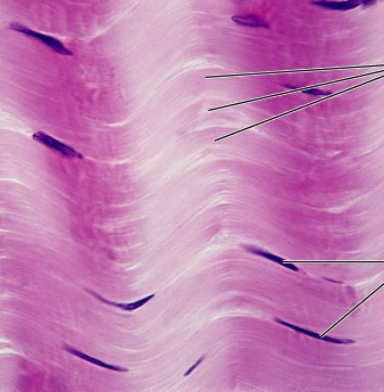
dense irregular
dense connective tissue proper
-irregularly arranged collagen fibers w/ some elastic fibers
-major cell type: fibroblasts
Function: withstands tension in many directions providing structural strength
Location: found in dermis, submucosa of digestive tract. fibrous organ capsules
what is the connective tissue?
dense irregular
what is the connective tissue?
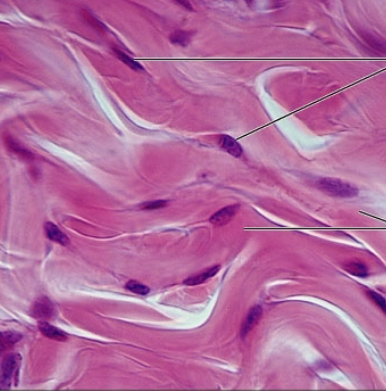
dense elastic
dense connective tissue proper
dense regular connective tissue containing high portion of elastic fibers
Function: allow tissues to recoil after stretching; maintains pulsatile flow of blood thru arteries; aids passive recoil of lungs
Location: walls of large arteries; walls of bronchial tubes
what is the connective tissue?
dense elastic
what is the connective tissue?
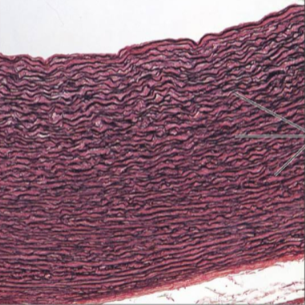
simple tubular
what is the exocrine gland?
simple alveolar
what is the exocrine gland?
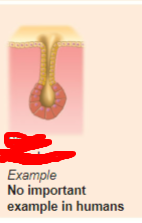
simple branched tubular
what is the exocrine gland?
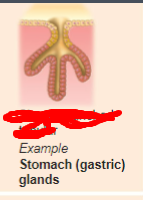
compound tubular
what is the exocrine gland?

simple branched alveolar
what is the exocrine gland?
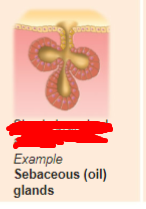
compound alveolar
what is the exocrine gland?
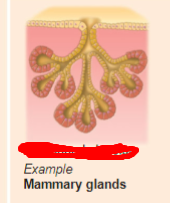
compound tubuloalevolar
what is the exocrine gland?

mucus
what do goblet cells make?
carcinoma
cancer cell originating epithelial tissue … 70% of all cancer b/c epithelial tissues damage first via physical/chemical assault
sarcoma
cancer cell originating in connective or muscle tissue
hyaline cartilage
inside the air pocket is lacunae and inside lacunae have chondrocytes
most abundant type of cartilage
Function: support and reinforces; has resilient cushioning properties; resists compressive stress
Location: form in embryonic skeleton, end of long bones, nose, trachea, and larynx
elastic cartilage
more elastic fibers
Function: maintain shape ad structure while allowing flexibility
Location: external ear (pinna) and epiglottis (when u swallow)
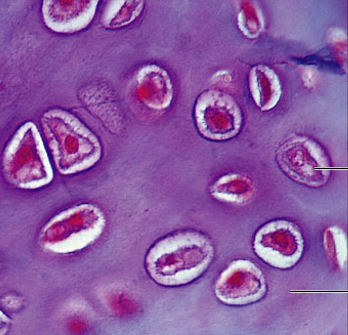
fibrocartilage cartilage
Matrix is similar to hyaline cartilage but less firm with thick collagen fibers
function: provide tensile strength and absorb compression shock
location: found in intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of knee joint
fibrocartilage cartilage
what is the connective tissue?
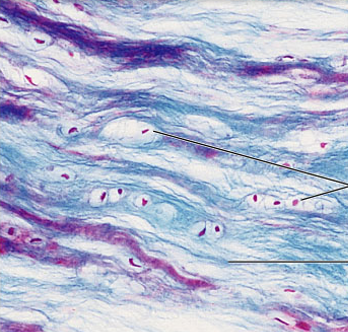
elastic cartilage
what is the connective tissue?
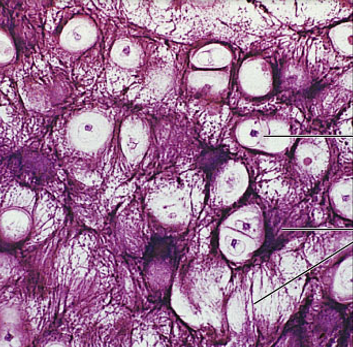
hyaline cartilage
what is the connective tissue?
spongy and compact
what are the two type of bone tissue?
osseous tissue
osteocytes found in *lacunae and well-vascularized
osteon- compact bone
Function: store calcium, minerals, and fat, marrow inside bones is the site for blood synthesis (hematopoiesis)
Location: bones
osseous tissue
what is the connective tissue?
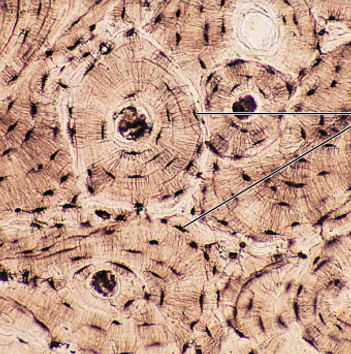
blood
red + white cells in fluid matrix (plasma)
Function: transportation of respiratory gases, and nutrients and wastes
Location: blood vessel
What is the connective tissue?
erythrocyte
scientific name for red cell
leukocyte
scientific name for white blood cell
thrombocyte
scientific name for platelets
blood
what is the connective tissue?
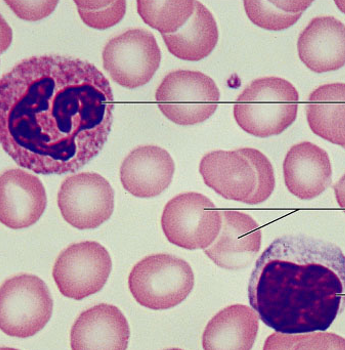
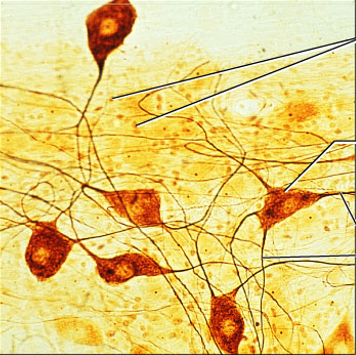
neuron and neuroglia
what are the two type of cell compromising nervous tissue?
nervous tissue
what is the tissue?
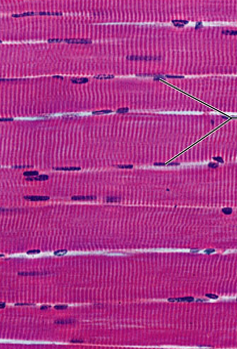
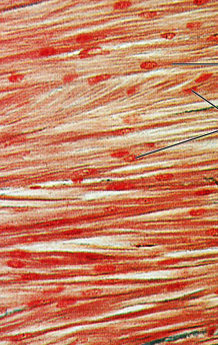
skeletal tissue
long, cylindrical, multinucleate cells with obvious striations
Function: initiate and control voluntary movement
Location: skeletal muscles that attach to bones or skin
what is the muscle tissue?
hypertrophy
when an organ increase in size but number of cell does not increase
hyperplasia
organ enlarge because a number of cells (cause cancer)
skeletal tissue
what is the muscle tissue?
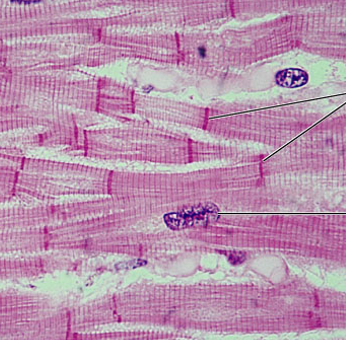
cardiac tissue
branching, striated, interdigitate at specialized junctions (intercalated discs)
Function: contractions propel blood into the circulation, involuntary control
Location: walls of the heart
cardiac tissue
what is the muscle tissue?
smooth tissue
spindle-shaped cells with central nuclei; no striation; cell arrange close to form sheet
Function: propels substances or objects along internal passageway; involuntary control
Location: walls of hollow organs (cavities)
smooth tissue
what is the muscle tissue?
redness (erythema), heat swelling (edema), pain (algesia)
what are the 3 signs/symptom in tissue trauma?
-itis
inflammation suffix