Terms List - Topic 3 (Appendicular)
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Skeleton
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
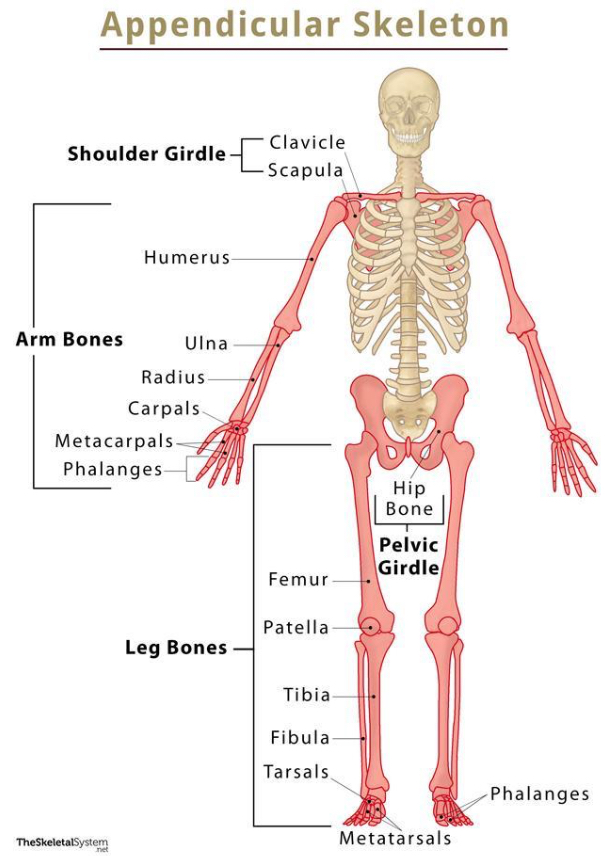
appendicular skeleton
consists of upper limbs, pectoral girdle, and lower limbs & provides movement/physical activity
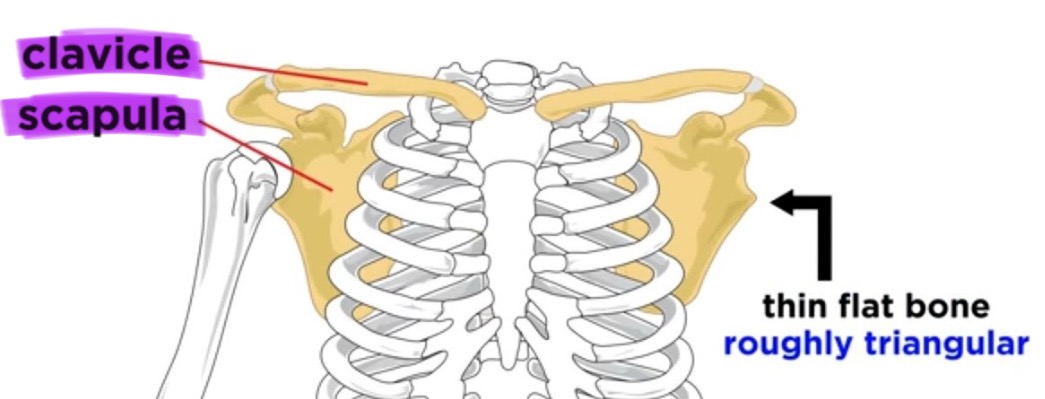
pectoral girdle
the set of bones (clavicle and scapula) that connects the arm to the body and allows shoulder movement
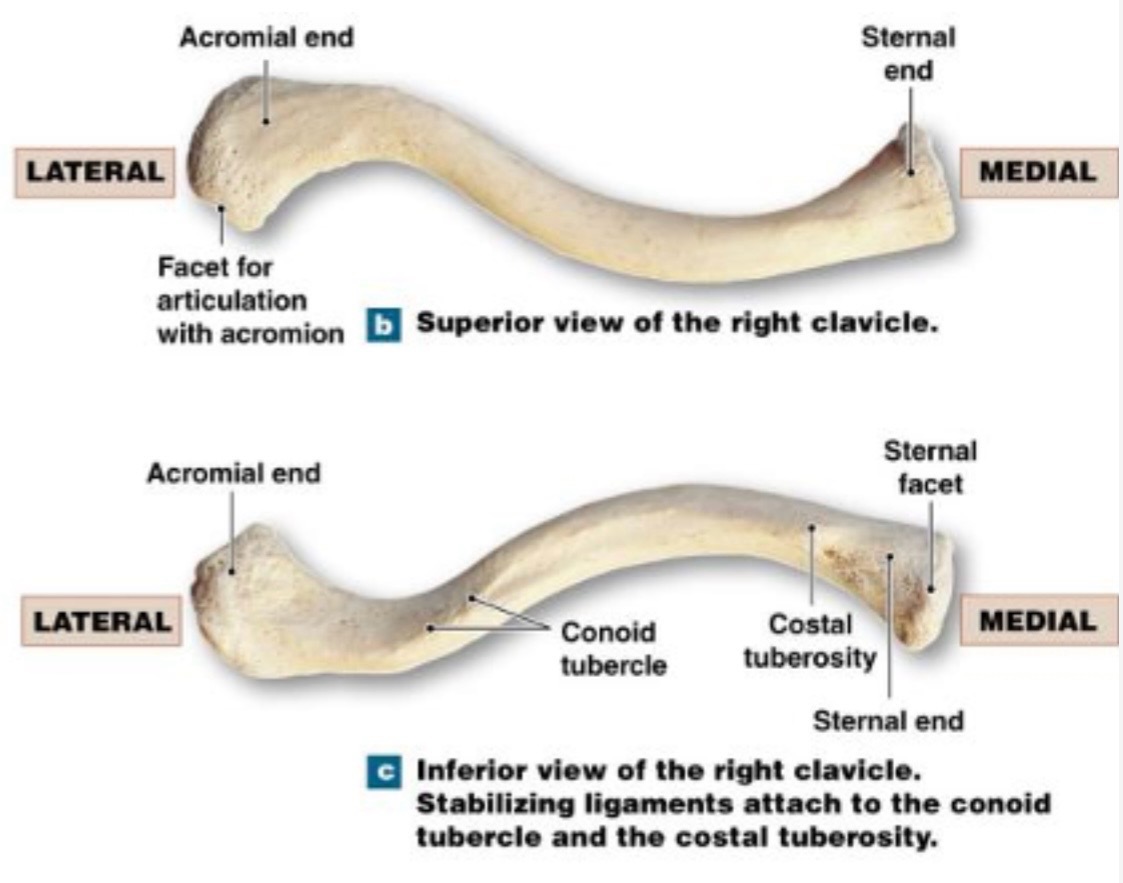
clavicle
collarbone, slightly S-shaped somewhat flattened from the upper to lower surface
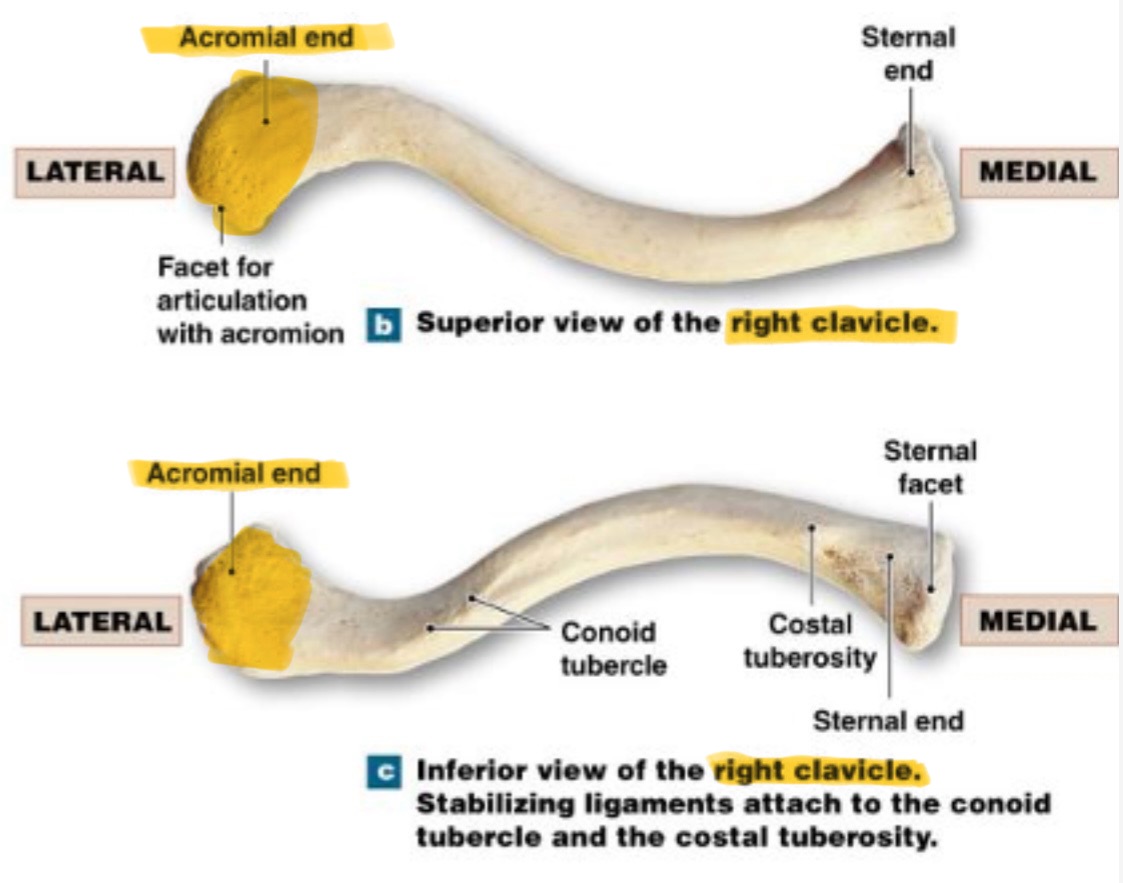
acromial end
lateral end, rounded/hammer like head
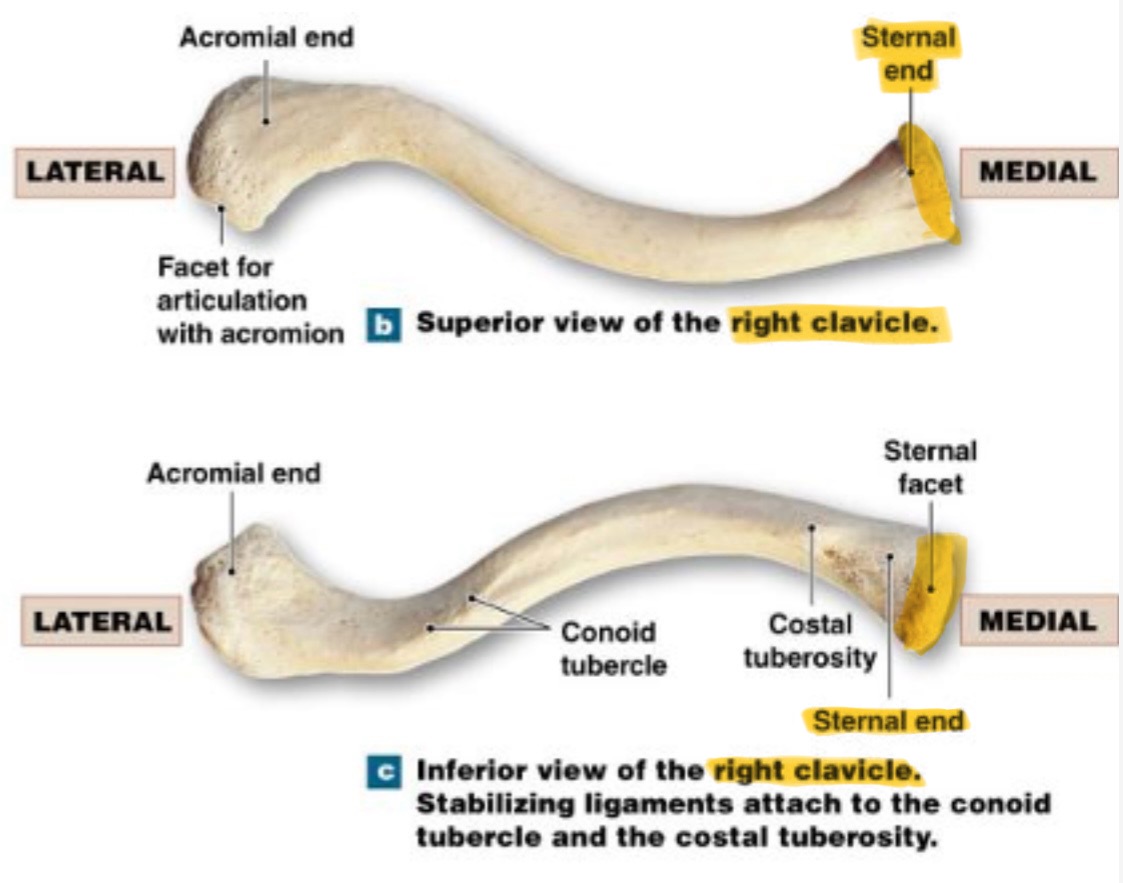
sternal end
medial end; markedly flattened
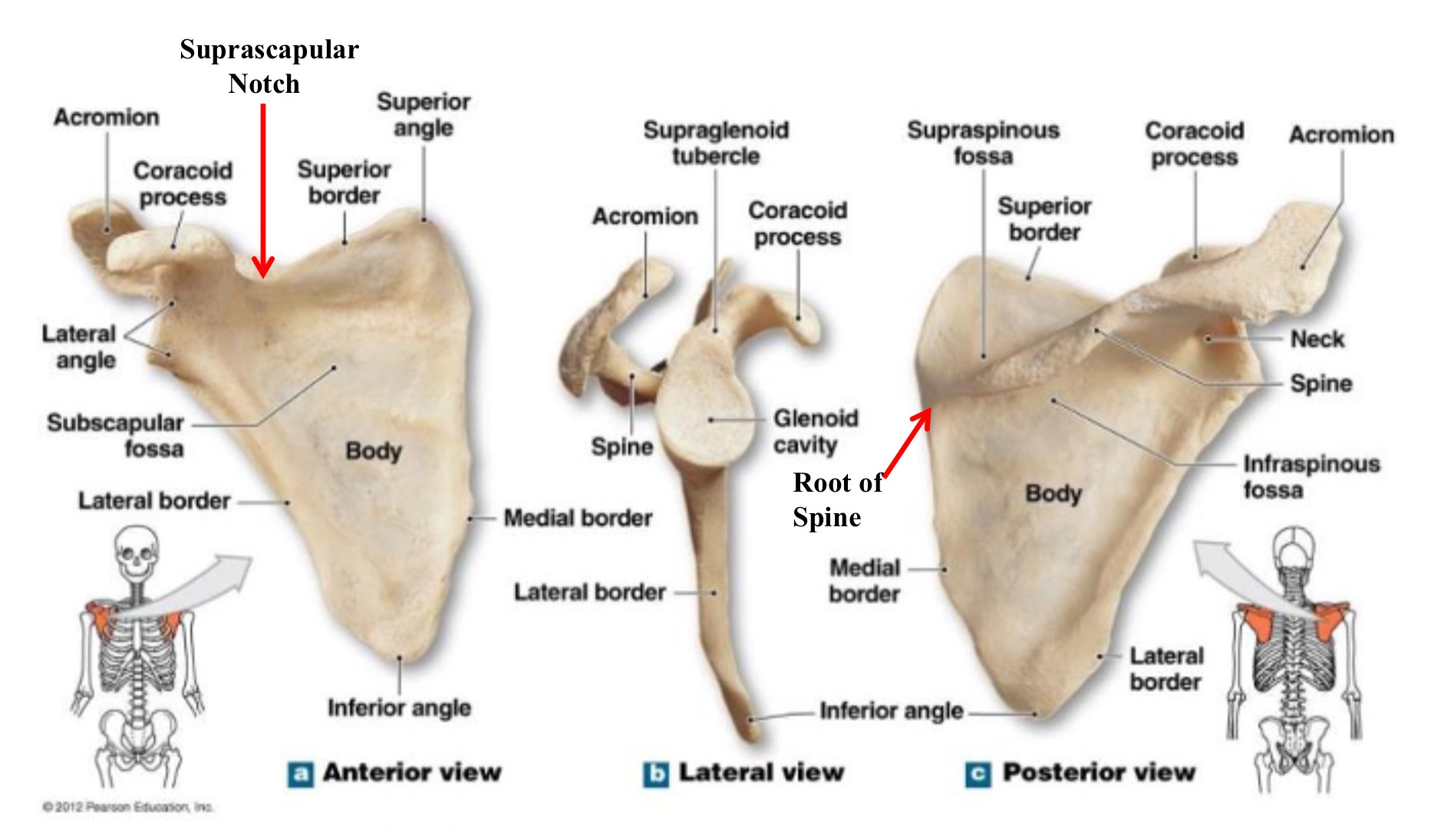
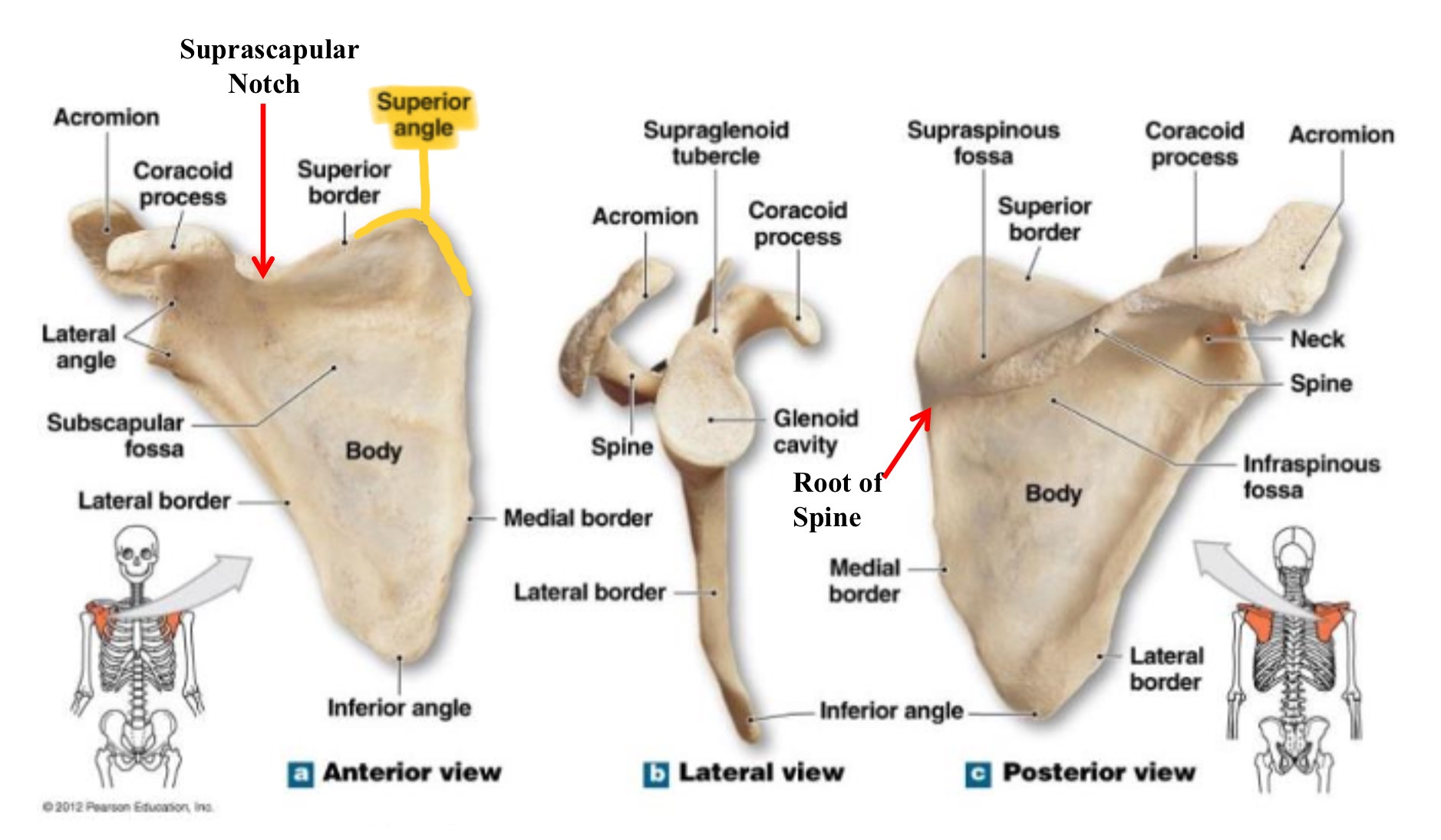
scapula
shoulder blade
superior angle of scapula
uppermost point of the scapula, where superior & medial borders meet
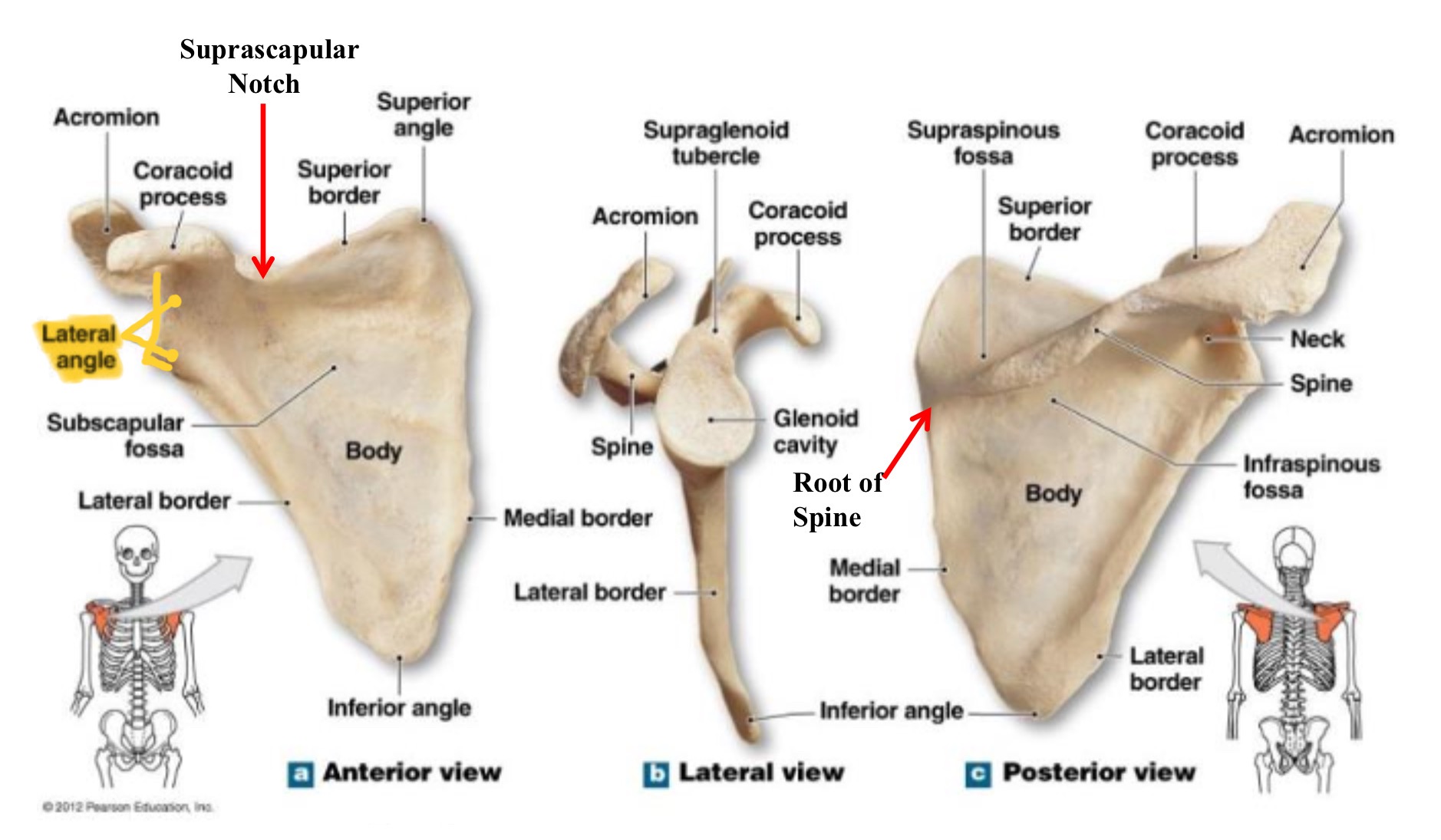
lateral angle of scapula
thickened end of the scapula where glenoid cavity articulates with the humerus
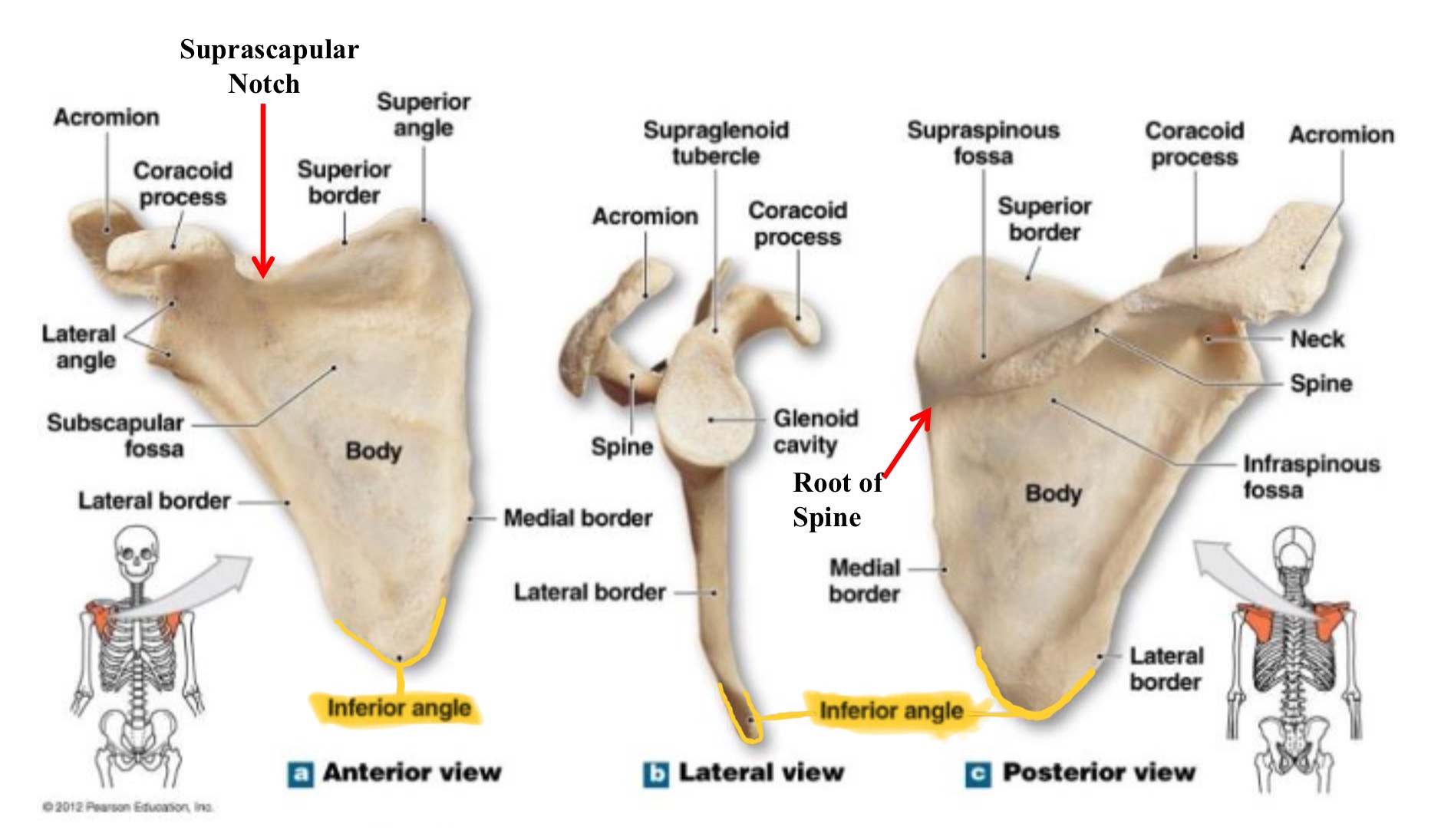
inferior angle of scapula
lowest part of scpaula where medial & lateral borders meet
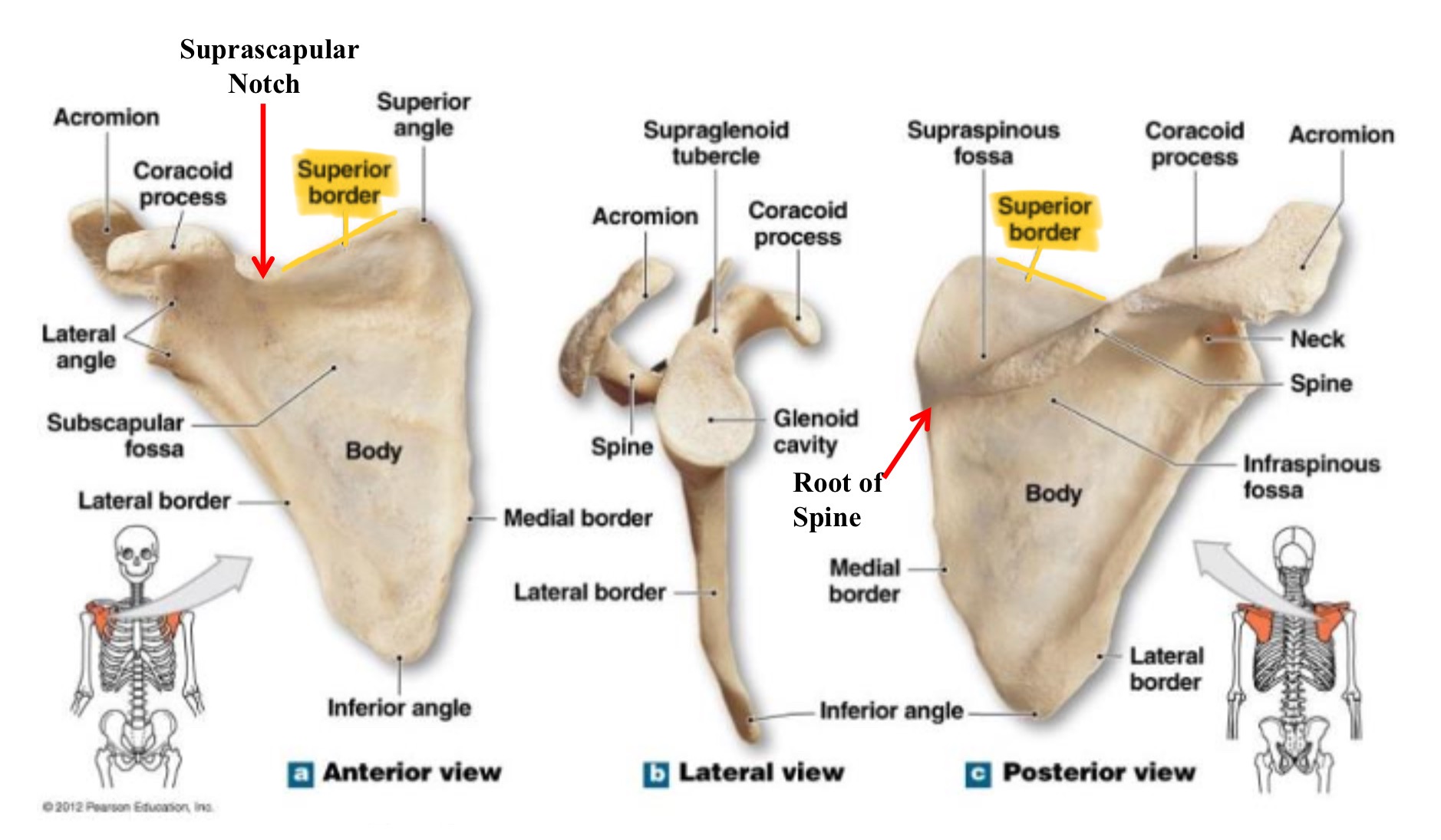
superior border of scapula
upper edge of the scapula running between the superior angle & the base of the coracoid process
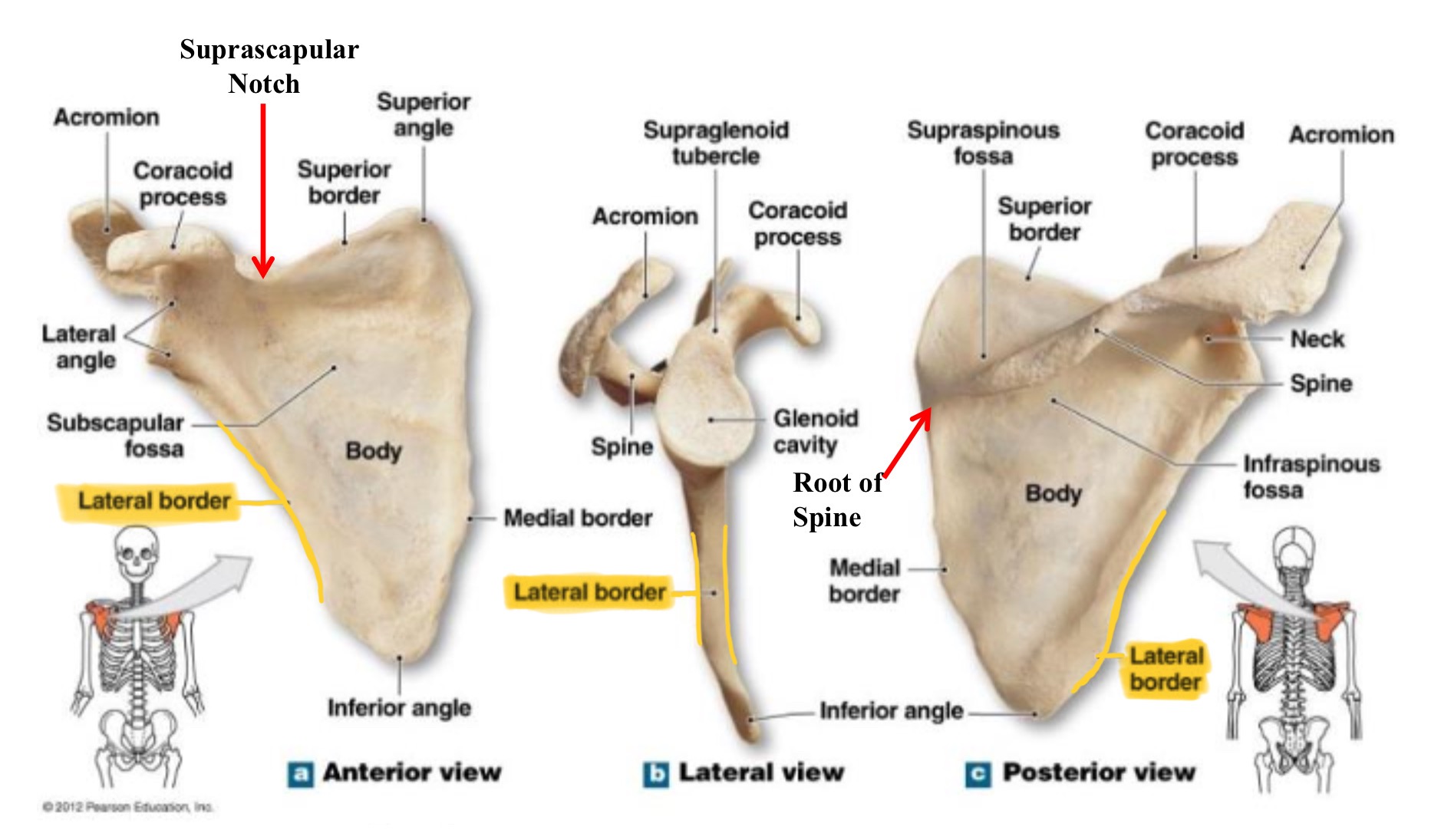
lateral border of scapula (axillary border)
edge of scapula closest to armpit, running from glenoid cavity to inferior angle
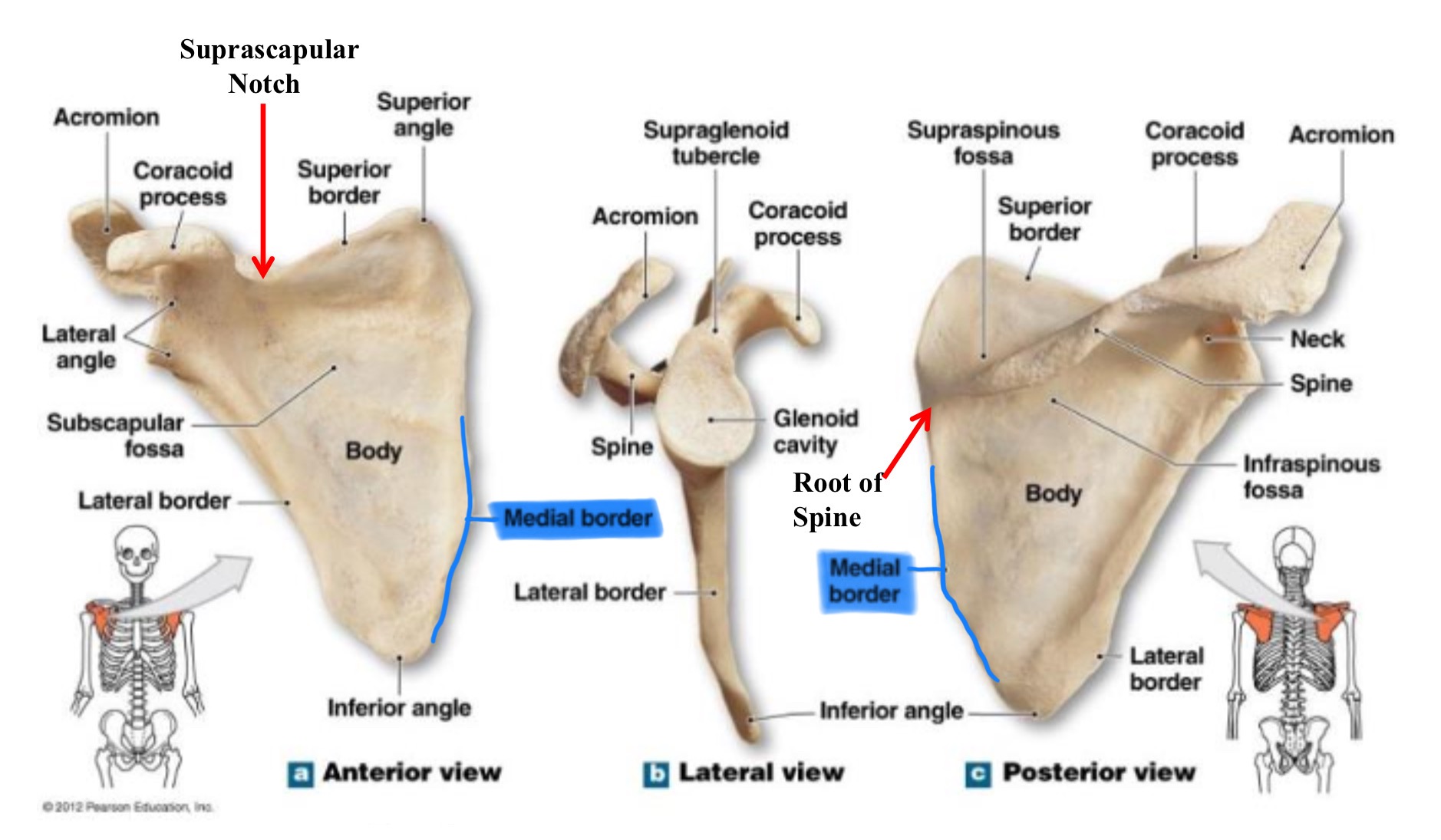
medial border of scapula (vertebral border)
edge closest to the vertebral column, running from the superior to the inferior angle
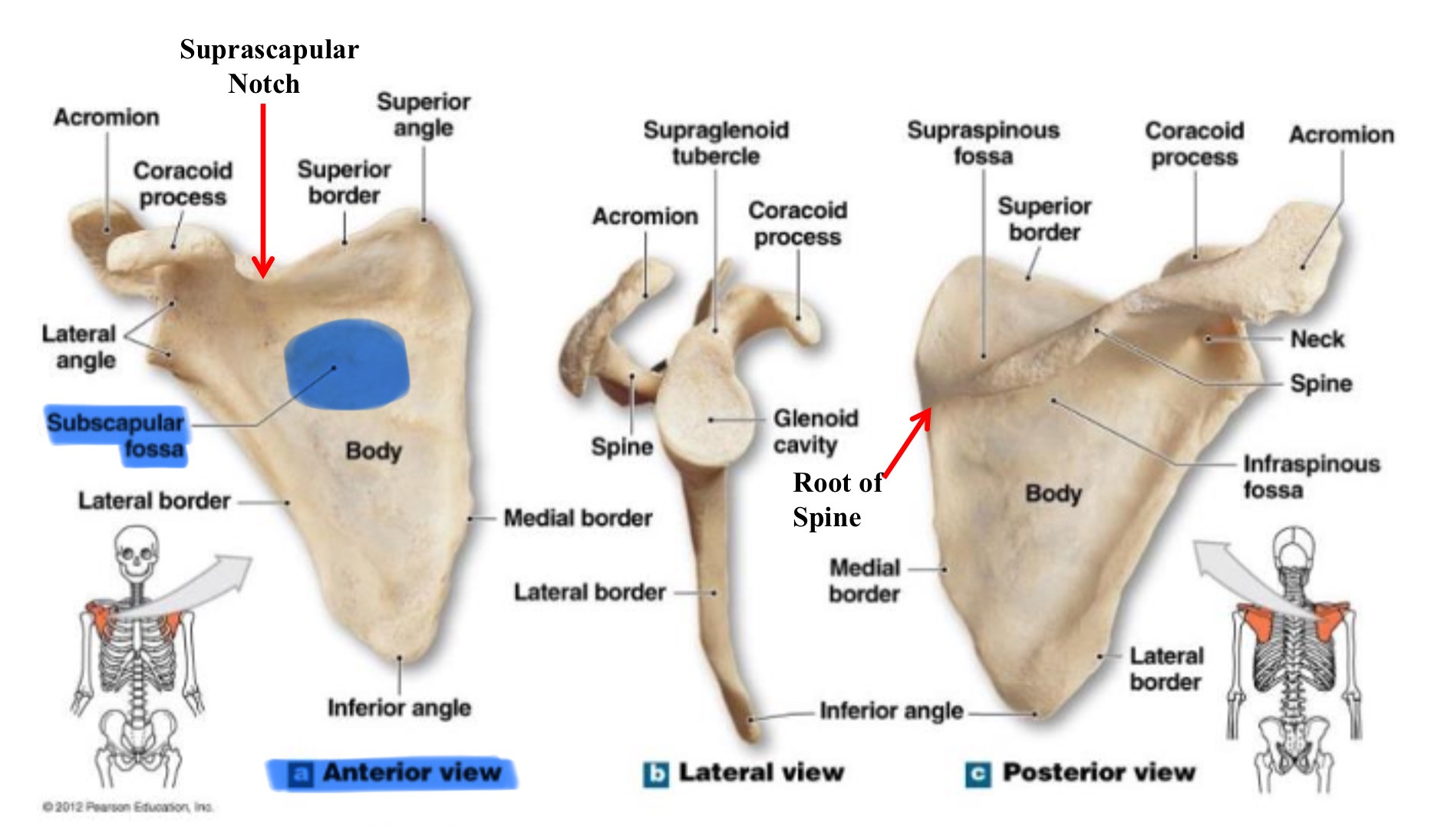
subscapular fossa
large, shallow depression on the anterior surface of the scapula that serves as the origin for the subscapularis muscle
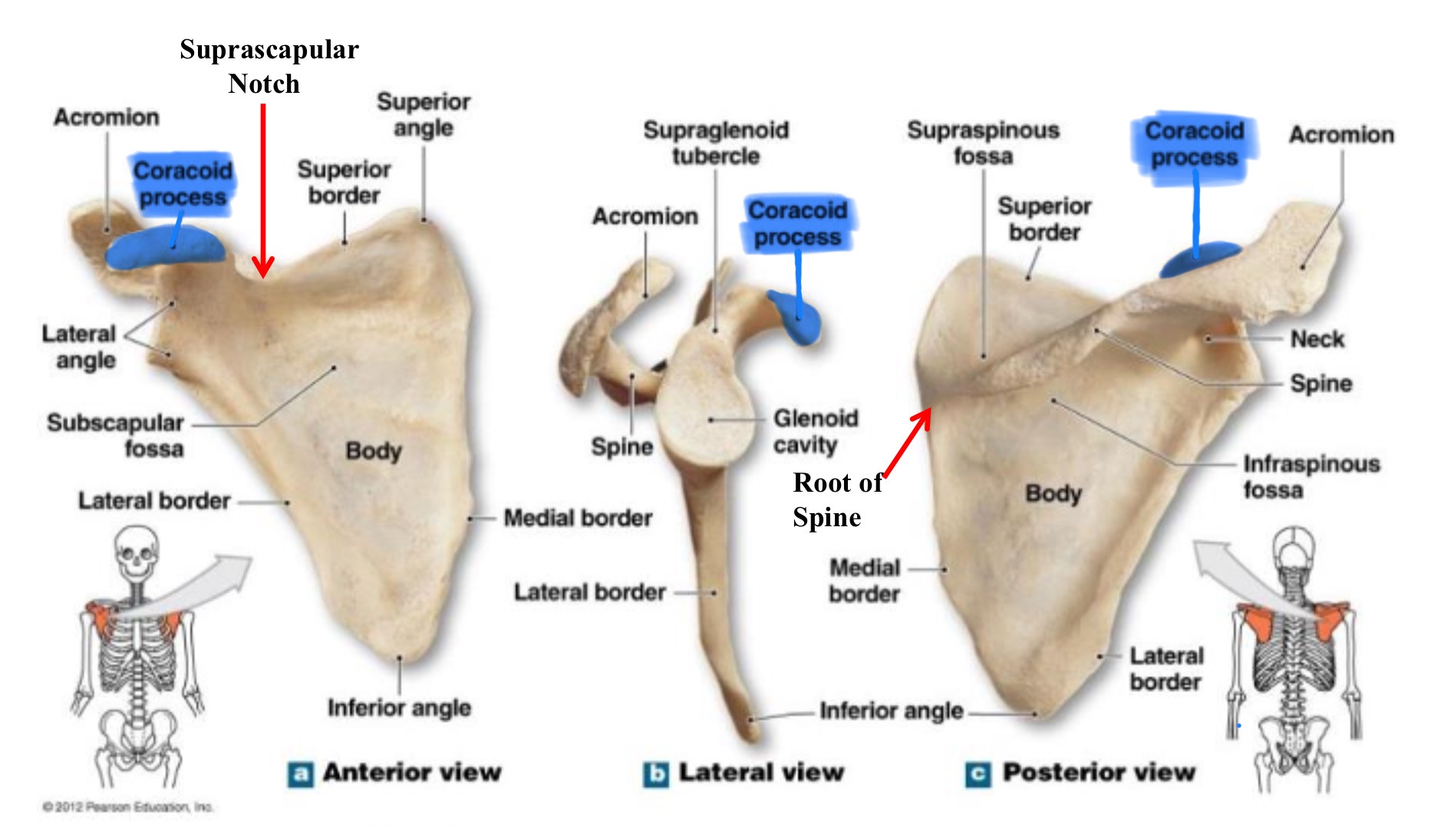
coracoid process of scapula
hook-like projections on the anterior surface, superior to the glenoid cavity; serves as attachment for muscles & ligaments
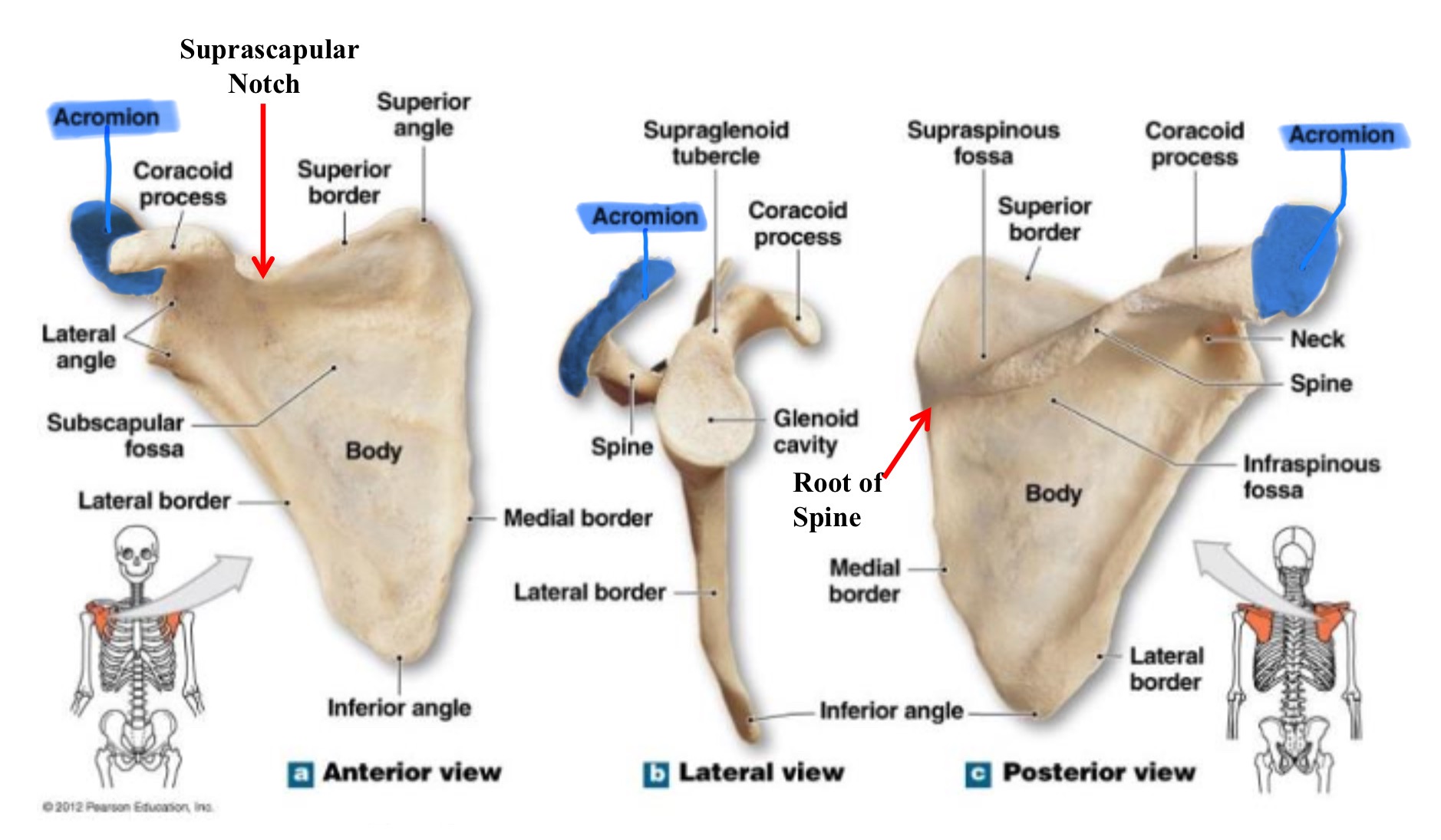
acromion of scapula
flat, expanded process ectnending from the spine of the scapula; forms the highest part of the shoulder & articulates w/ the clavicle
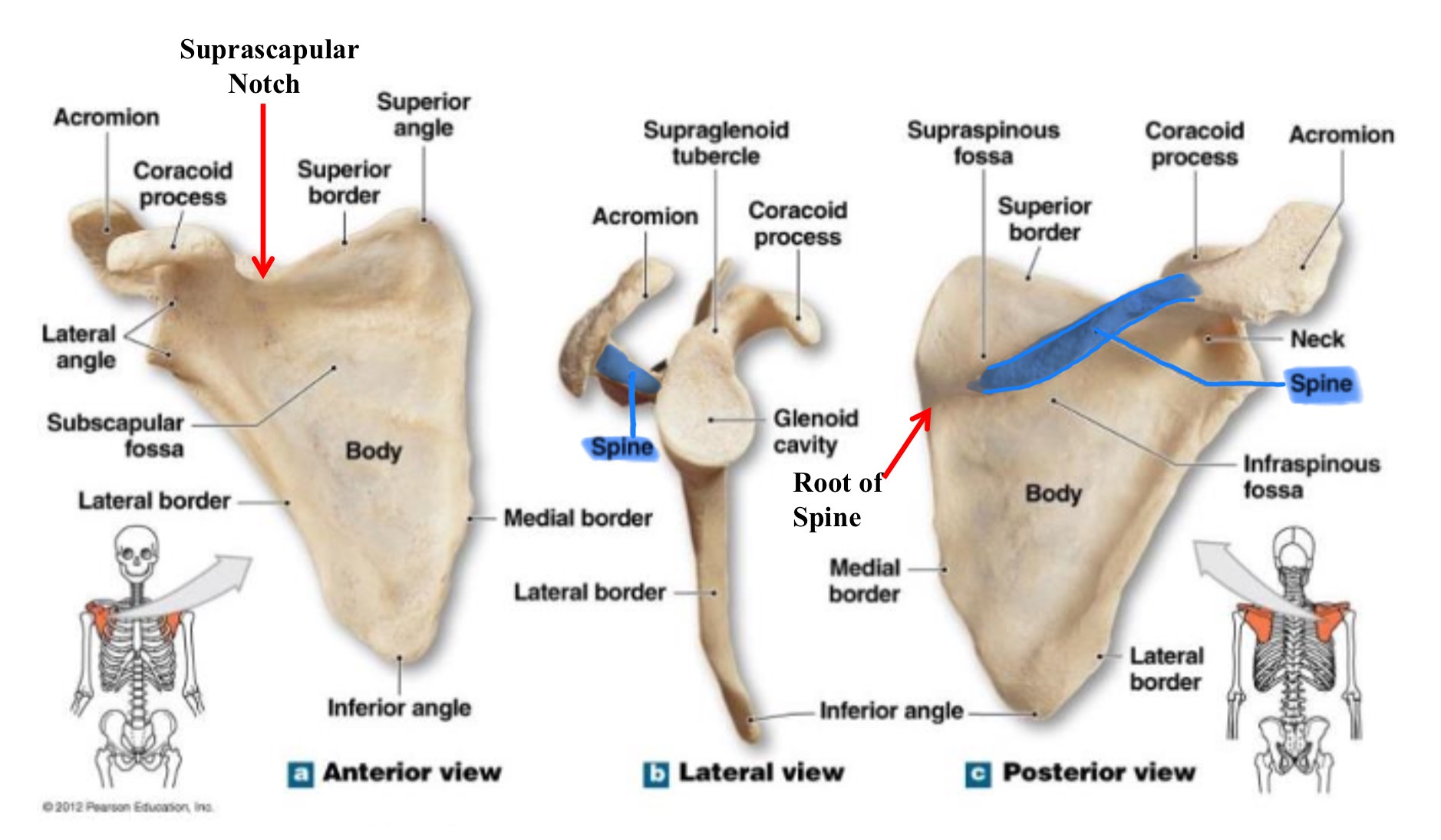
spine of scapula
promiment ridge running across the posterior surface of the scapula; divides it into the supraspinous and infraspinous fossae
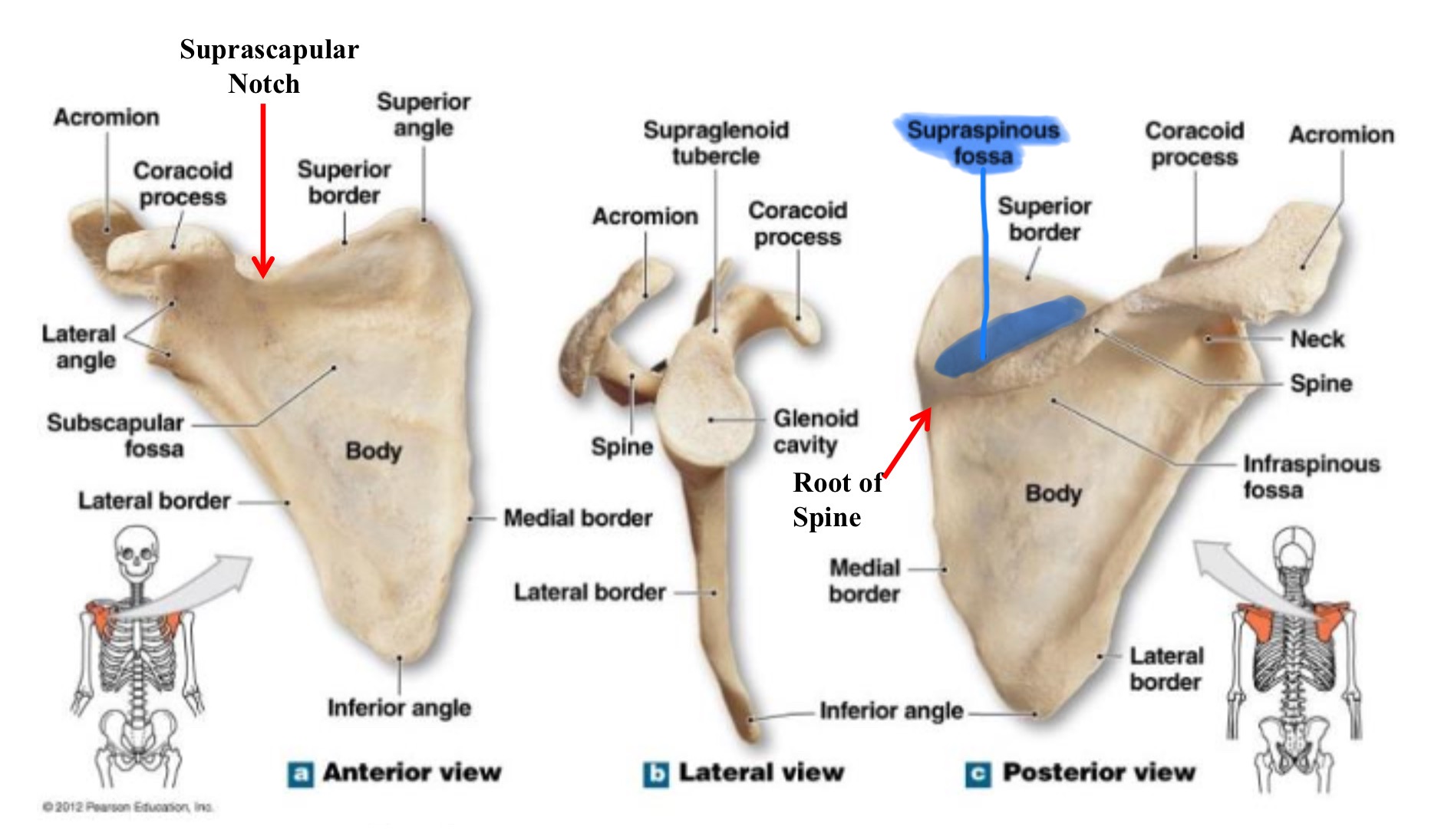
supraspinous fossa of scapula
shallow depression located above the spine; serves as the origin for the supraspinatus muscle
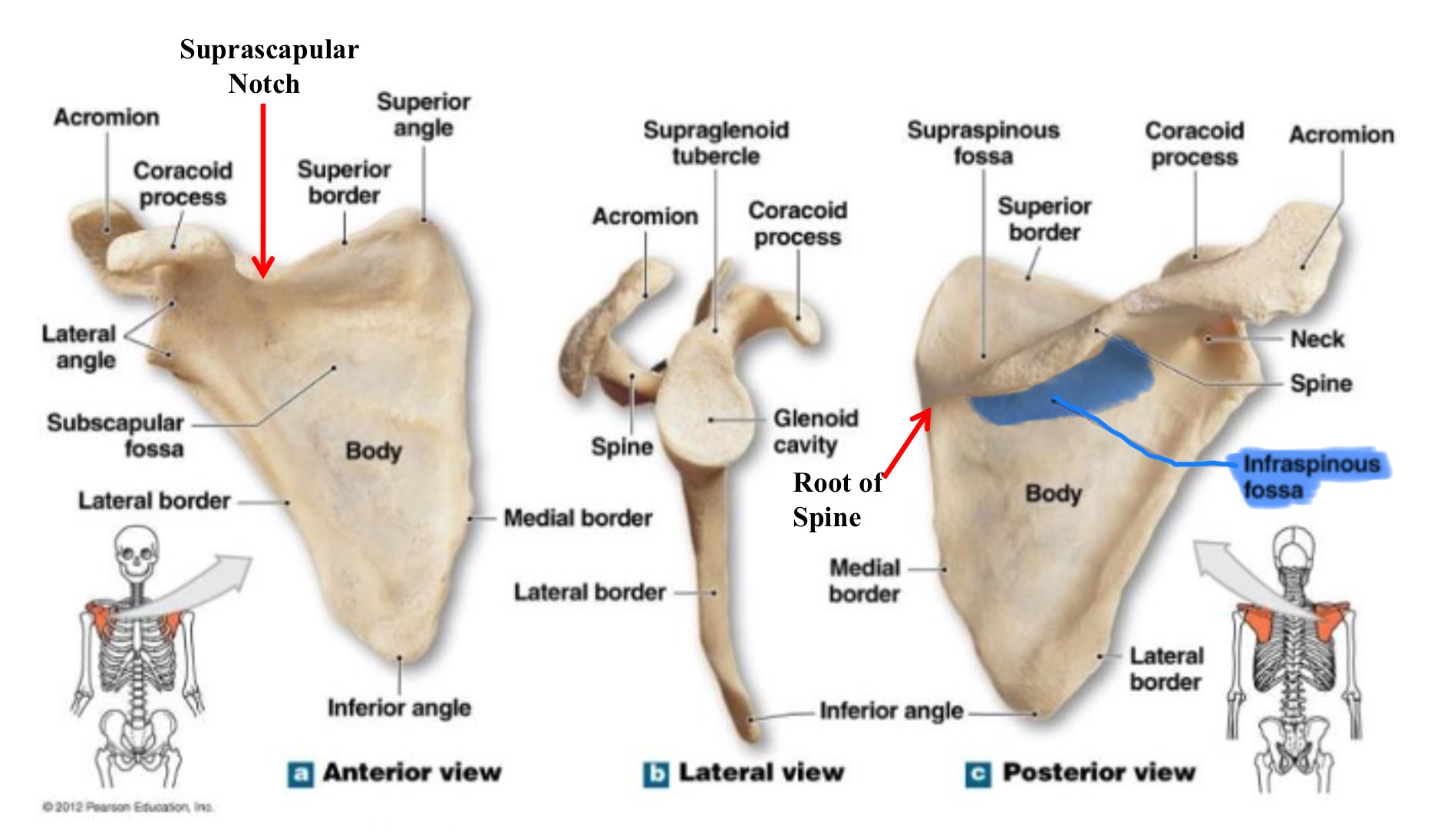
infraspinous fossa of scapula
large depression below spine, serves as orogin for infraspinatus muscle
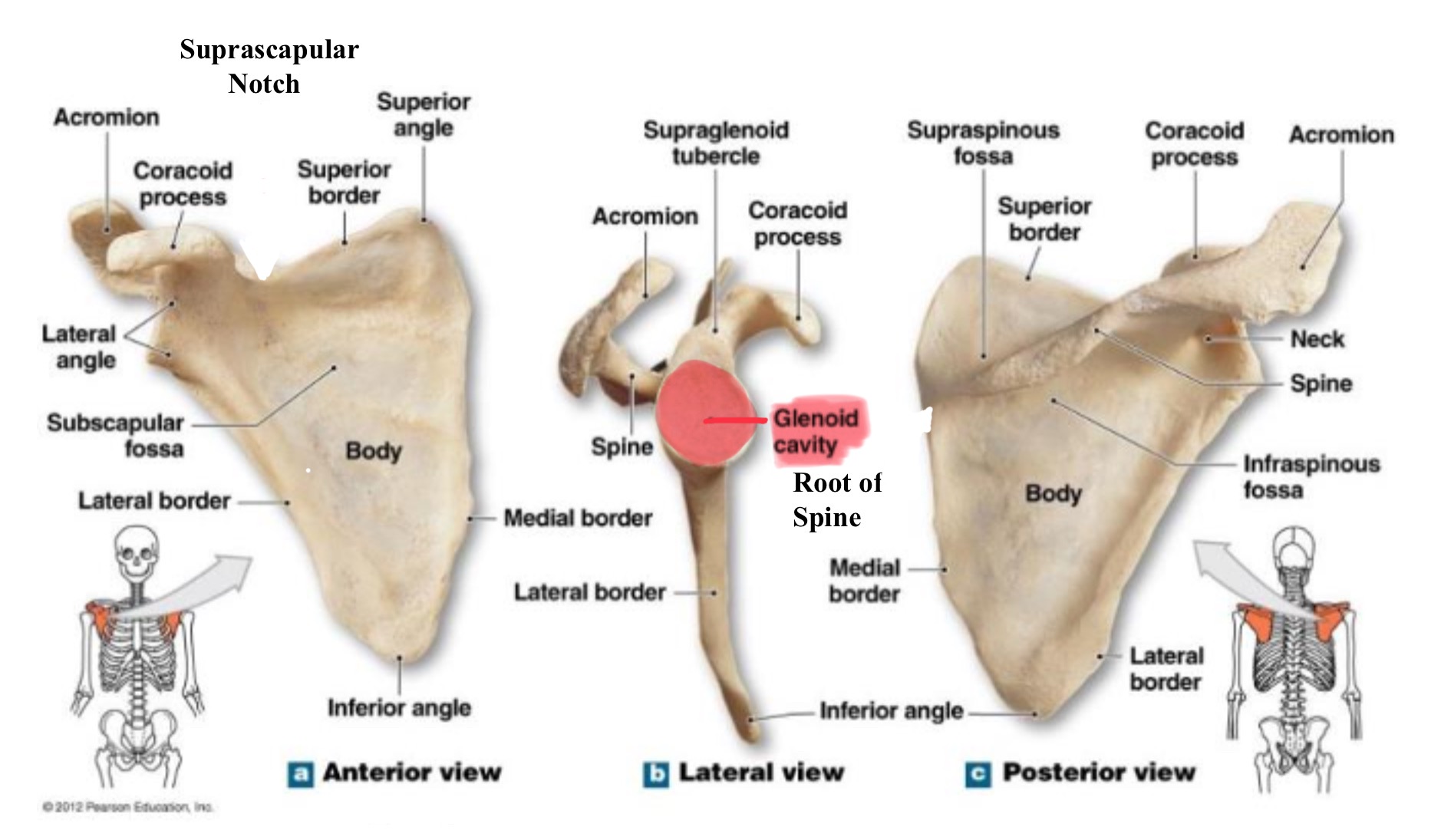
glenoid fossa (cavity)
shallow, oval depression the lateral angle of the scapula; articulates w/ head of humerus to form the shoulder (glenohumeral) joint
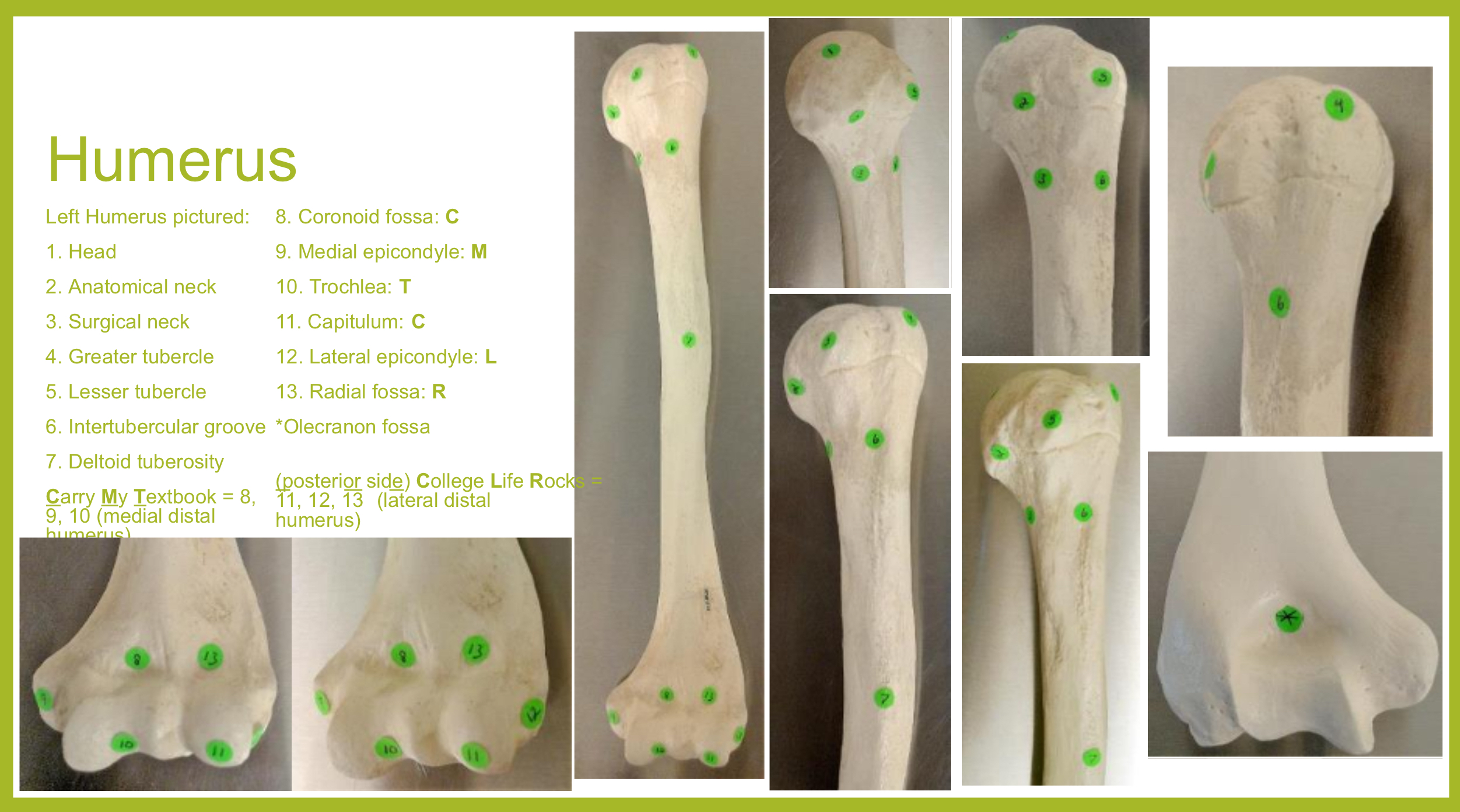
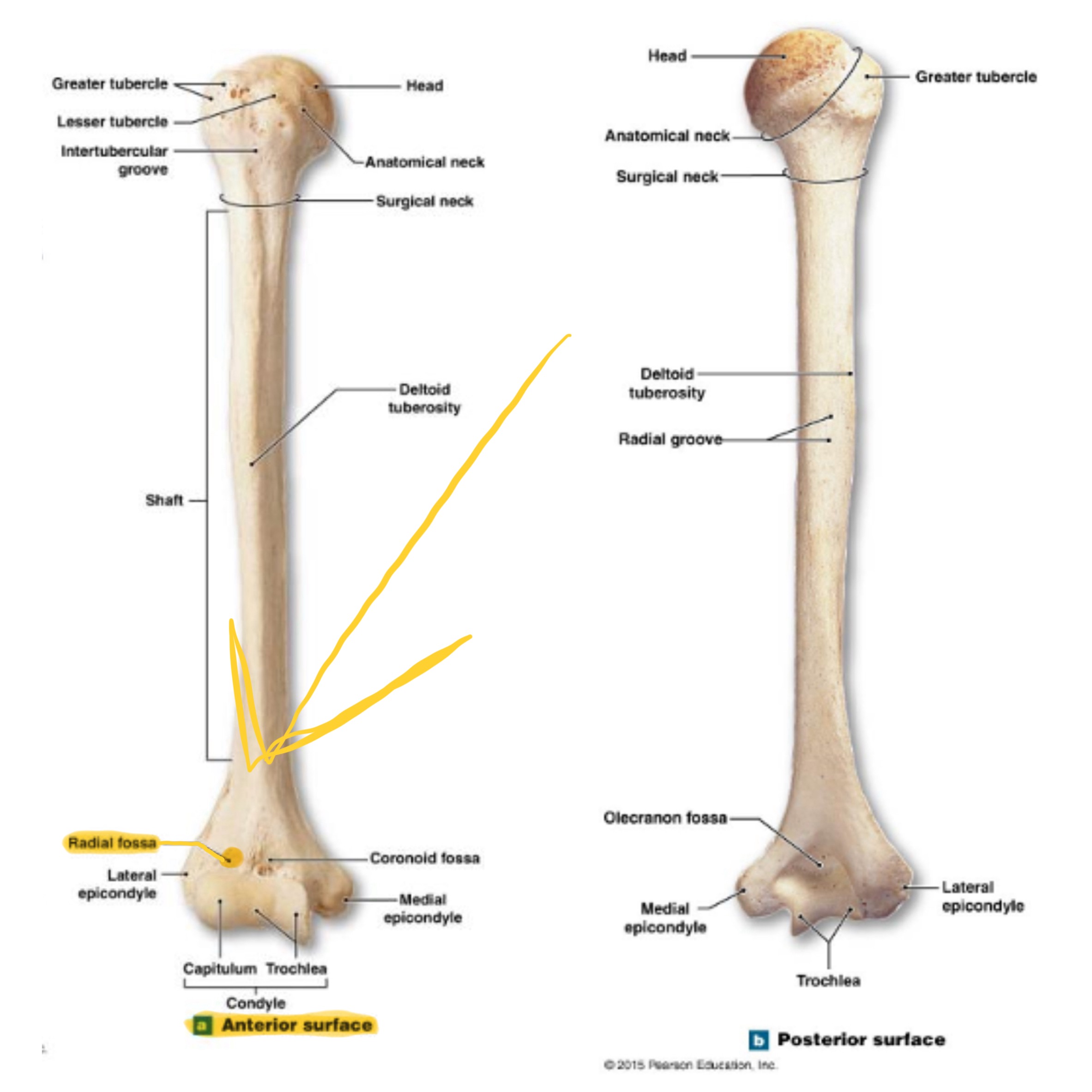
humerus
inside the brachium, extends from shoulder to elbow
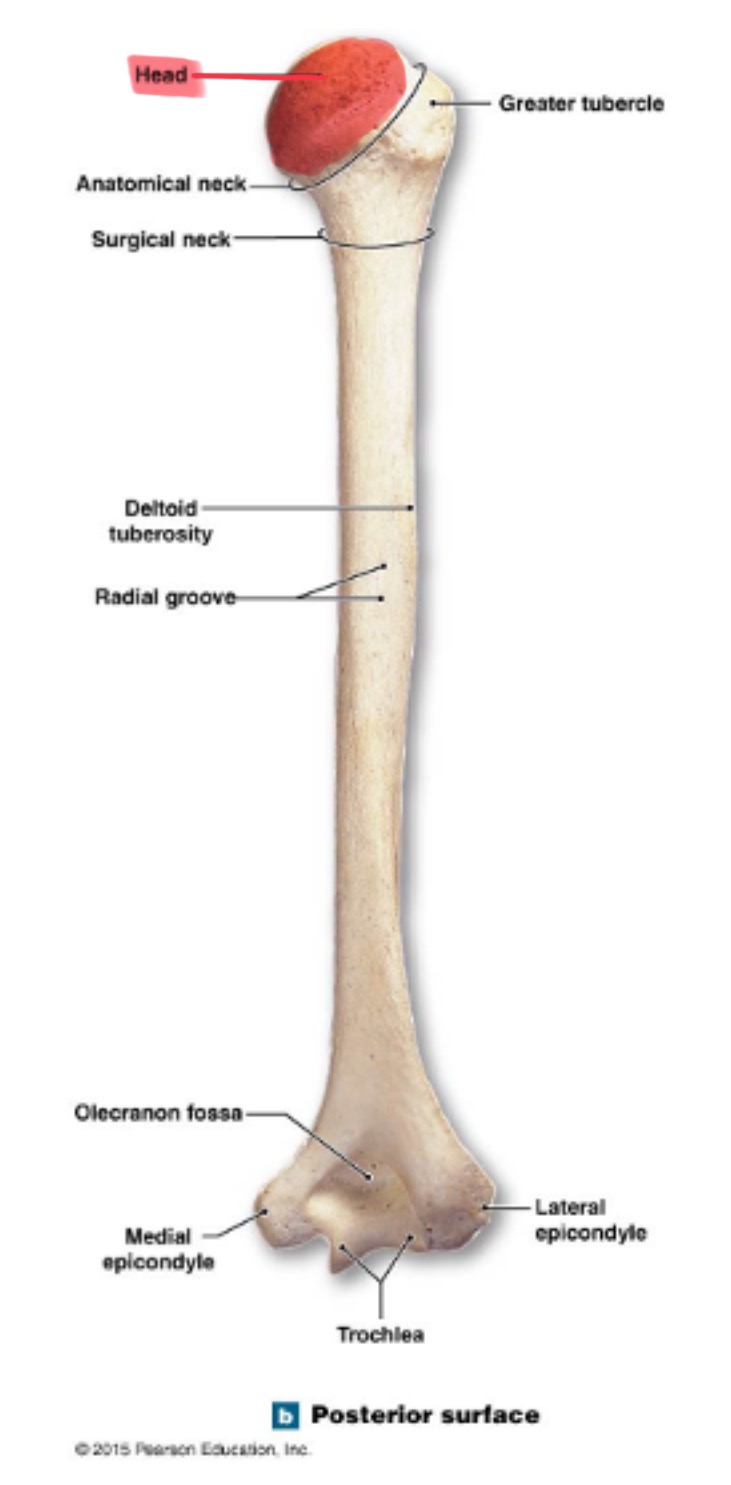
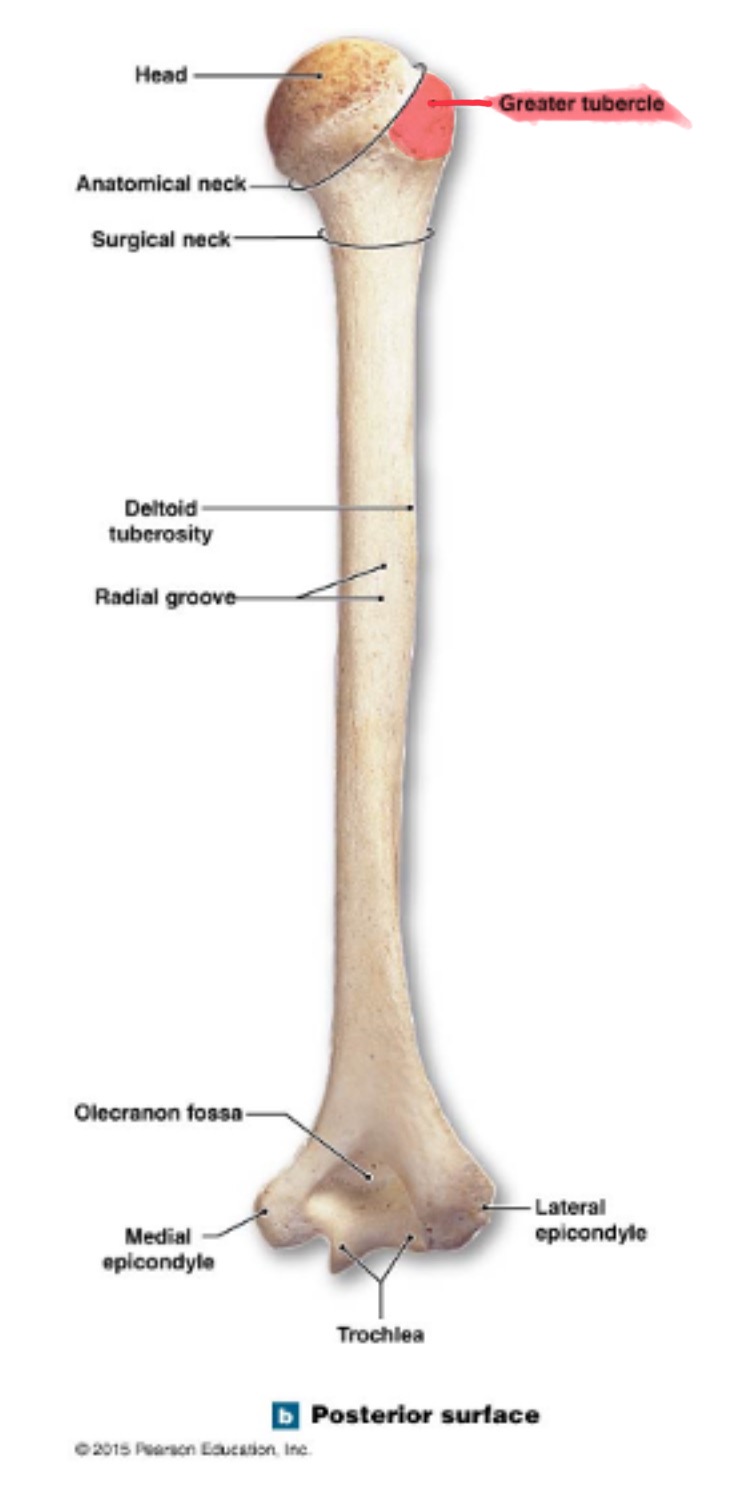
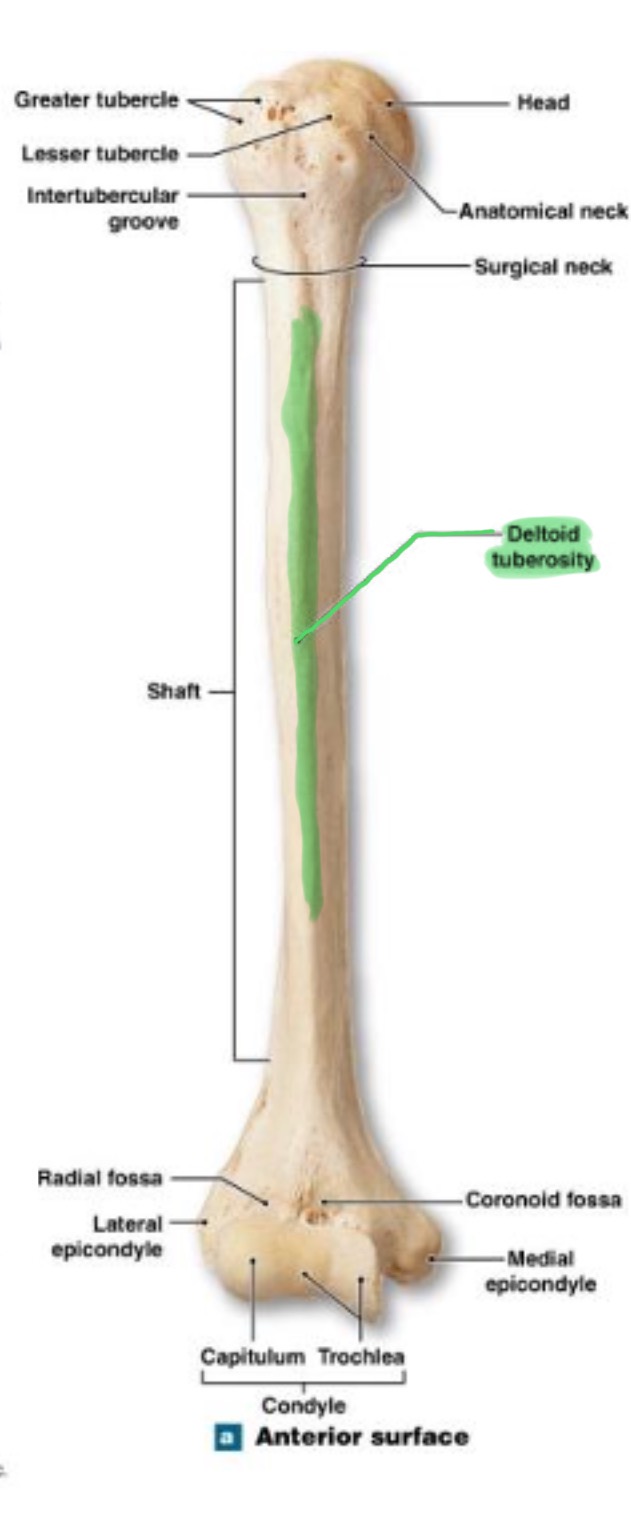
head of humerus
hemispherical, articulates w/ the glenoid cavity of the scapula
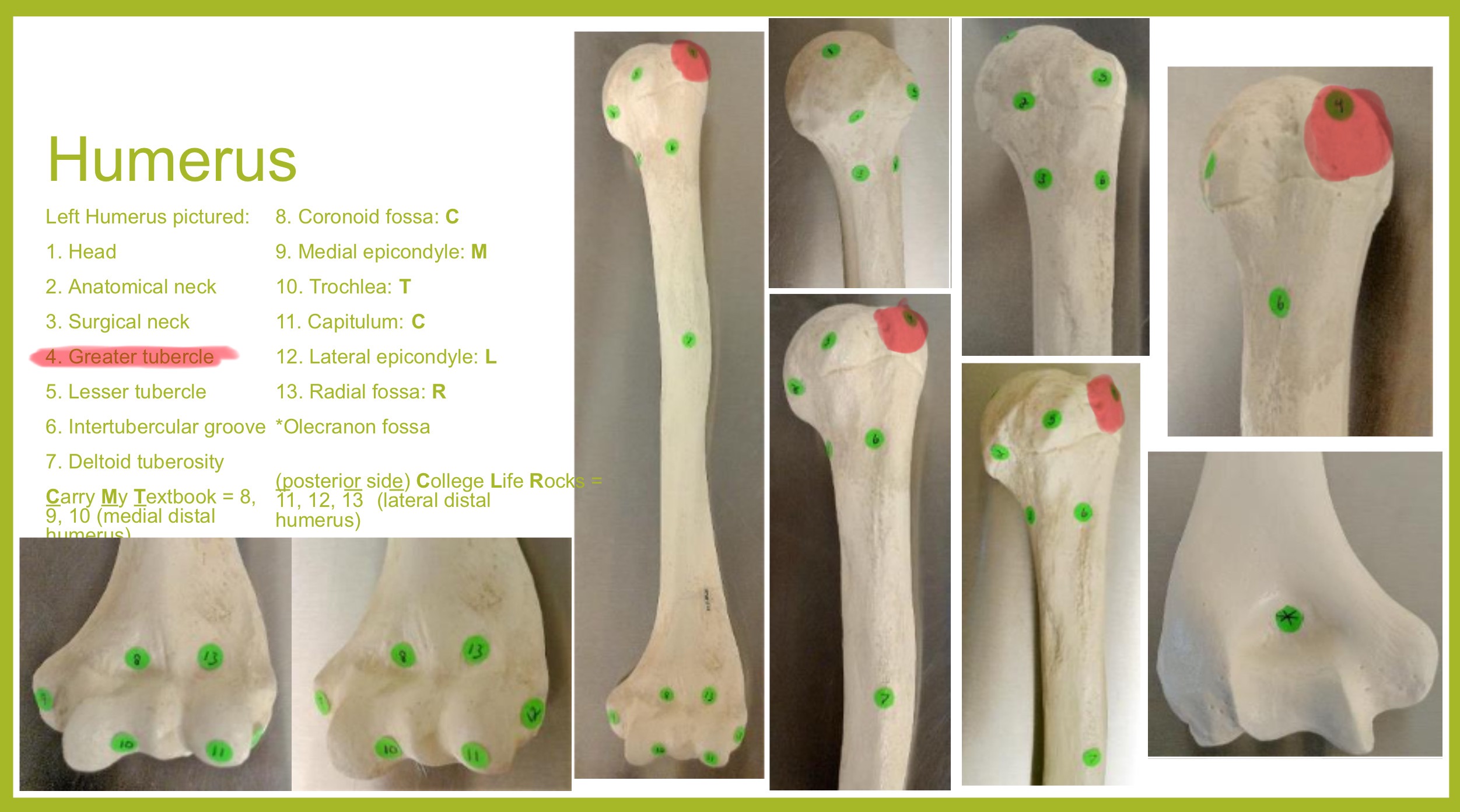
greater tubercle of humerus
prominent feature of the proximal end are muscle attachments
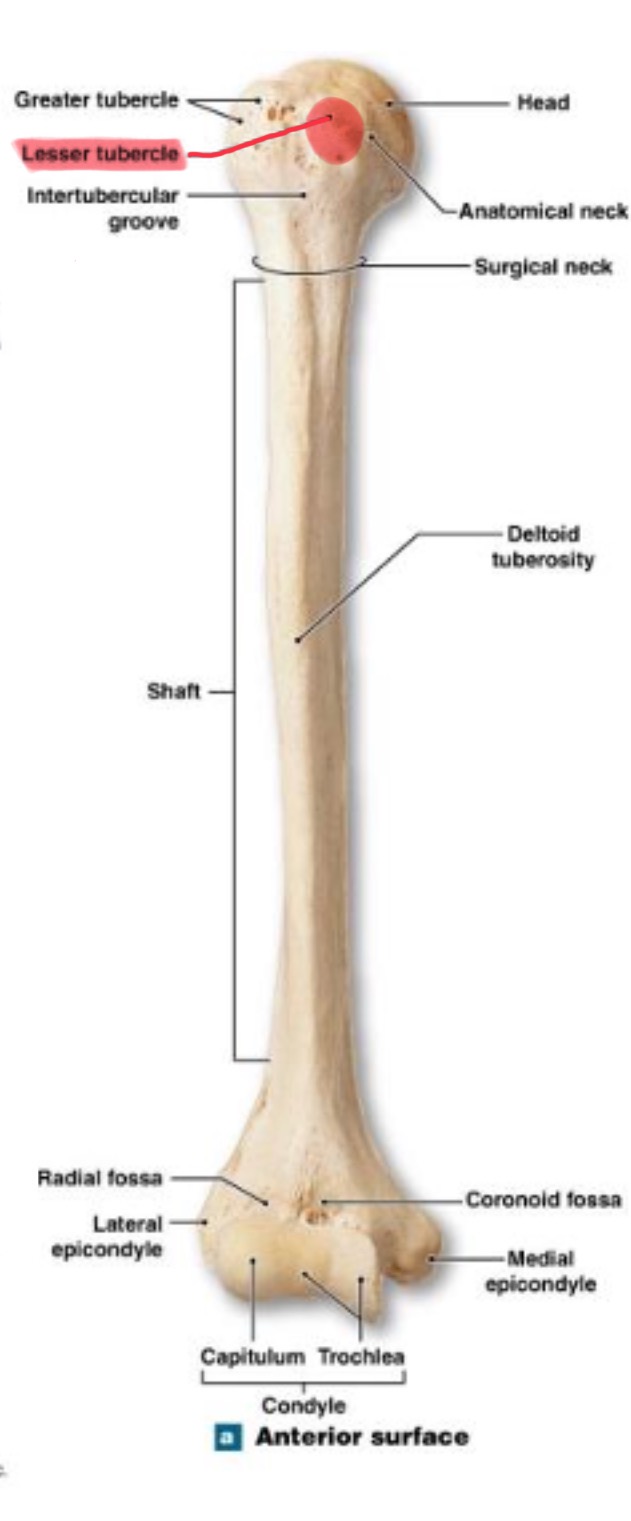
lesser tubercle of humerus
prominent feature of the proximal end are muscle attachments, inferior to the greater tubercle
located on same side as deltoid tuberosity
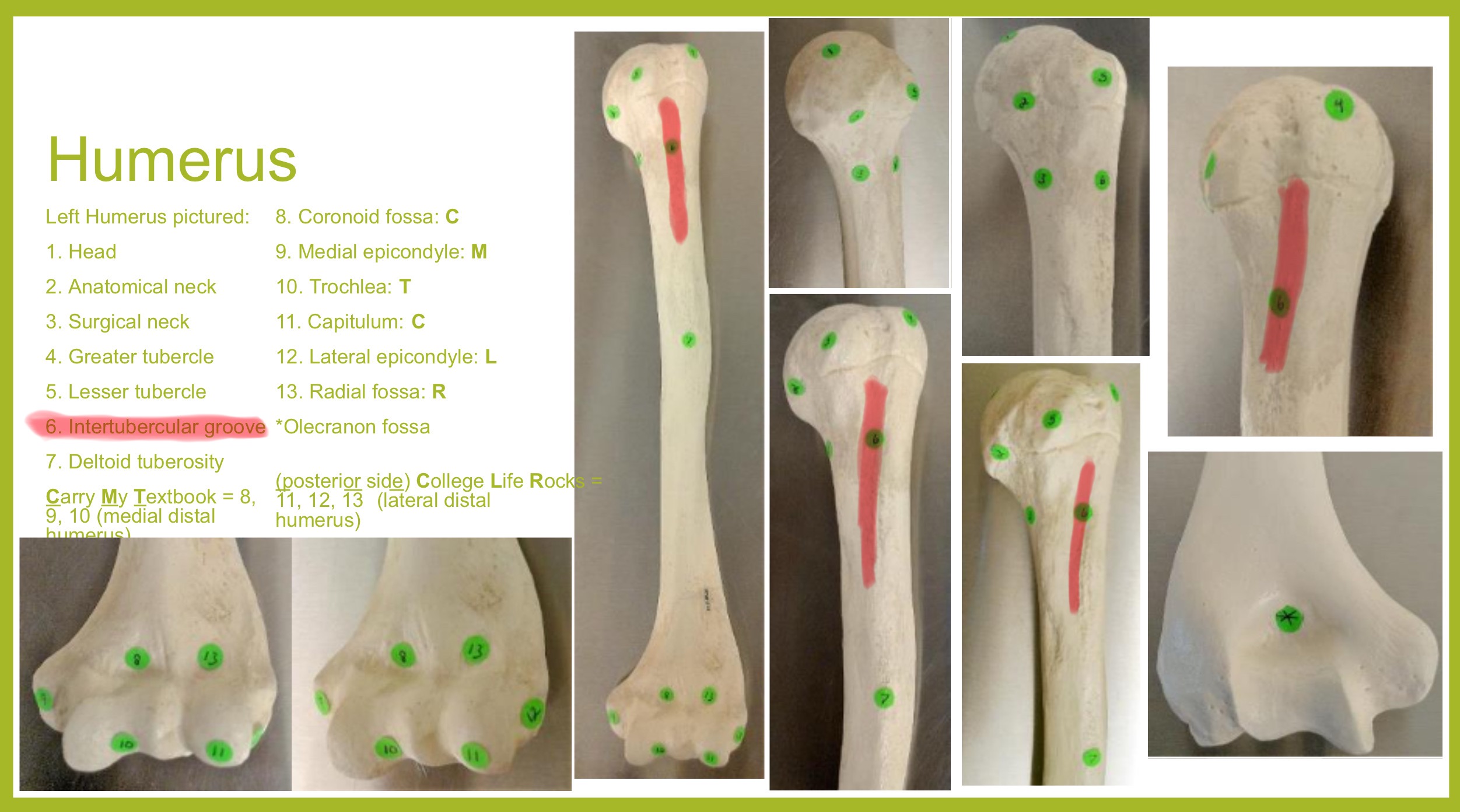
bicipital groove of humerus
(intertubercular sulcus) accomodates a tendon of the biceps muscle
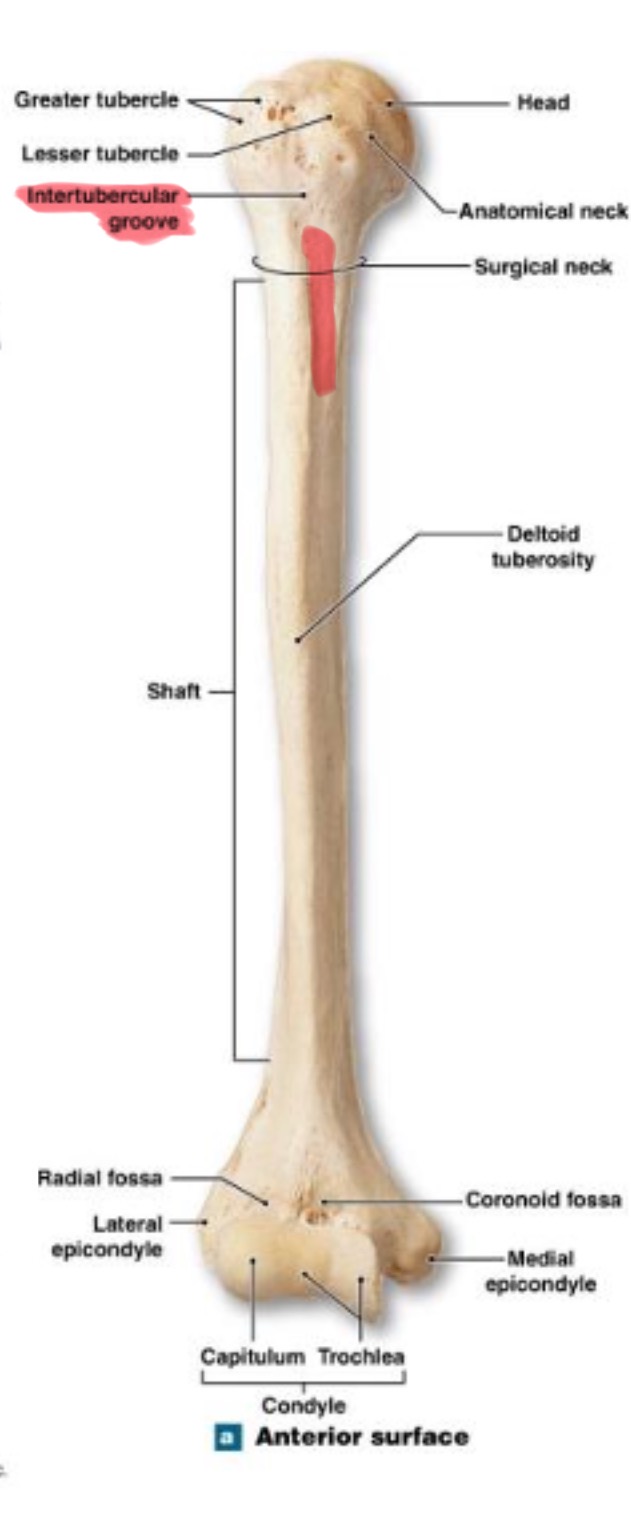
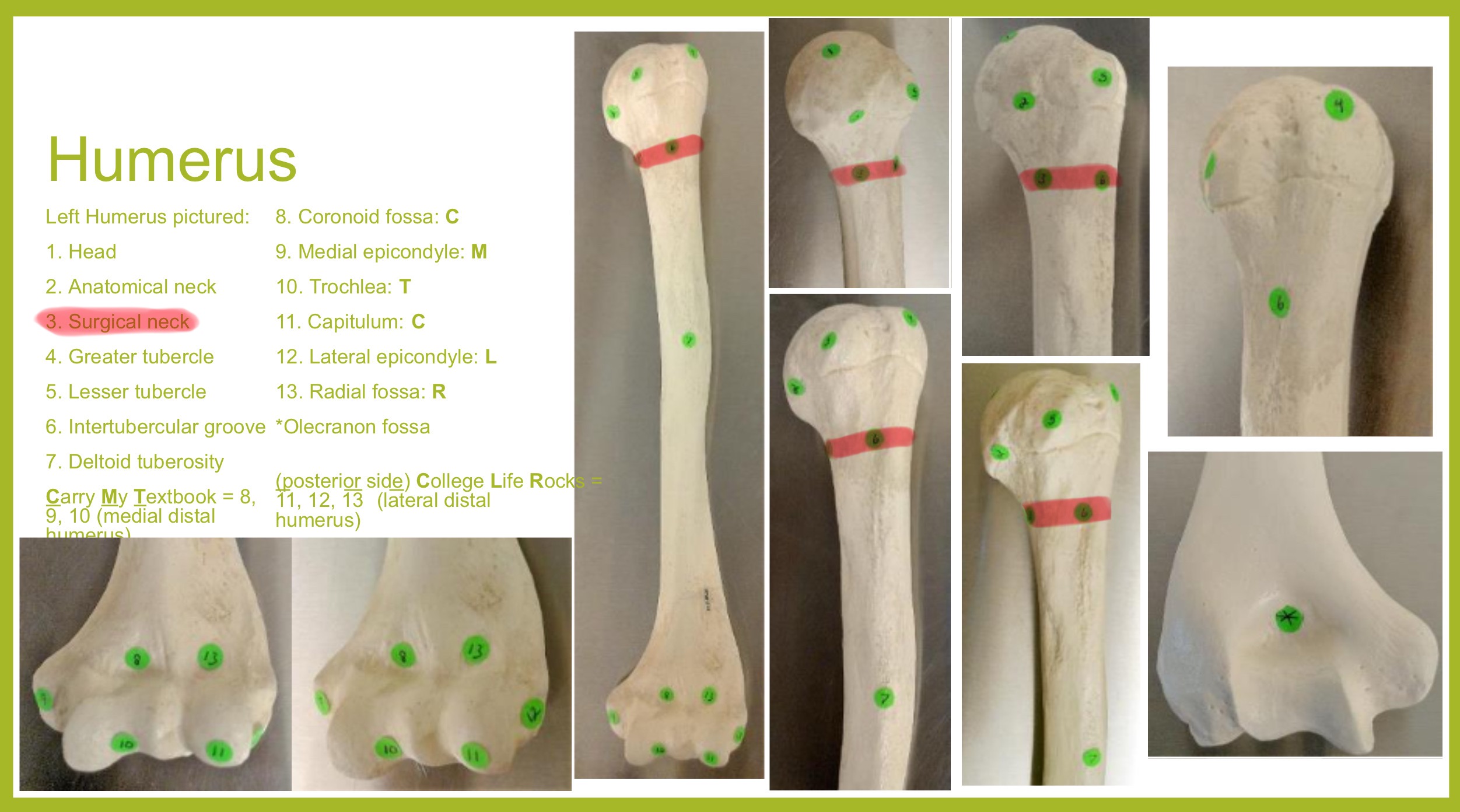
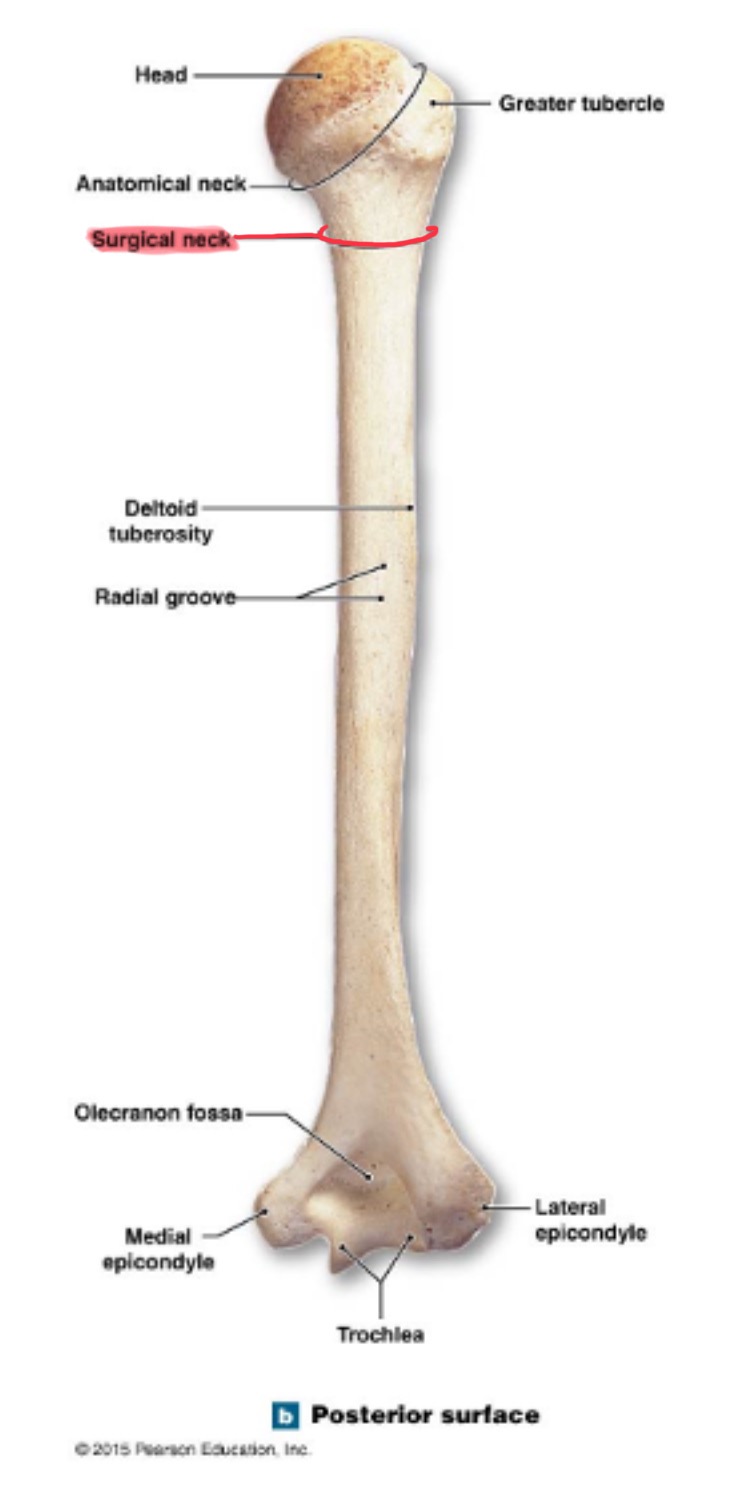
surgical neck of humerus
narrow region below tubercles and head; a common fracture site
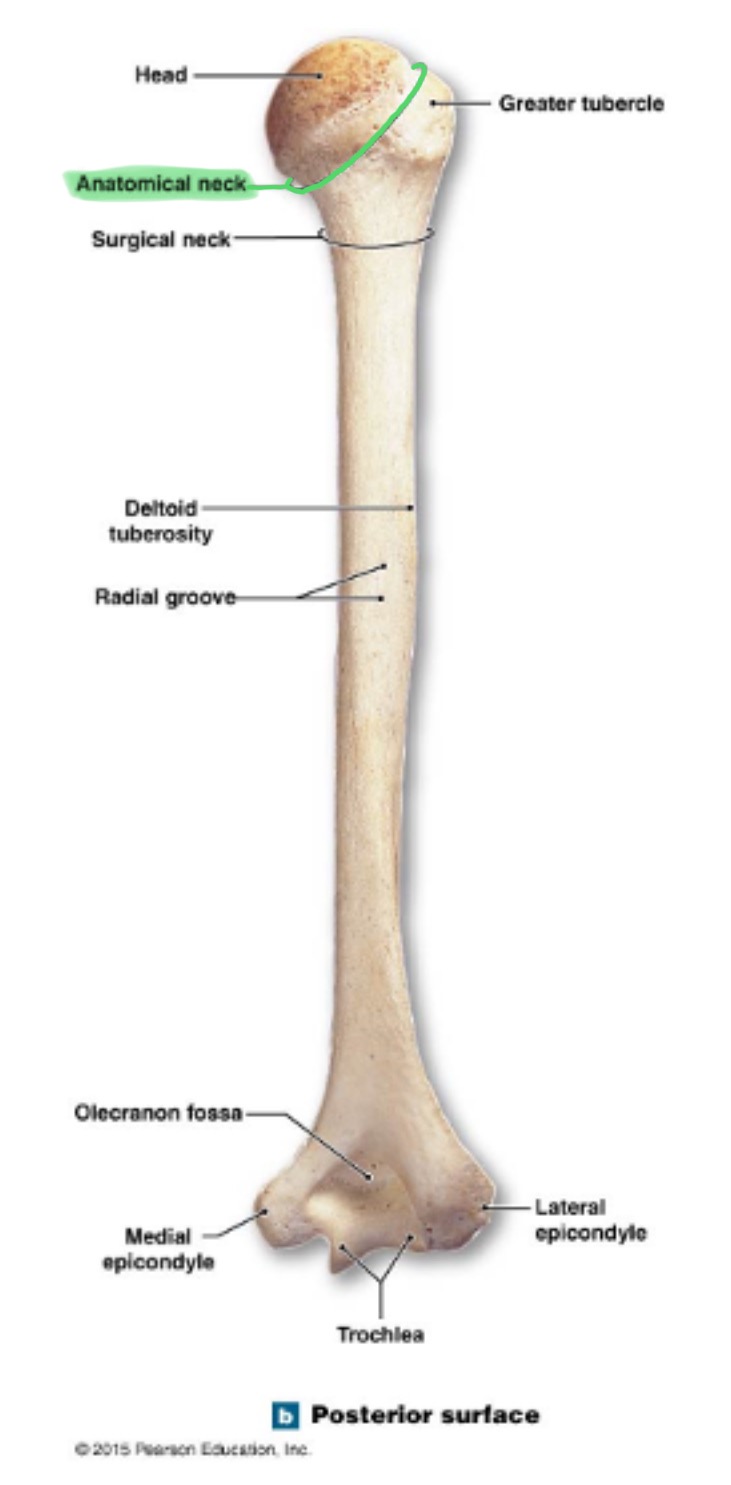
anatomical neck of humerus
around the head, boundary of articular surface
deltoid tuberosity of humerus
on lateral surface, insertion for the deltoid muscle
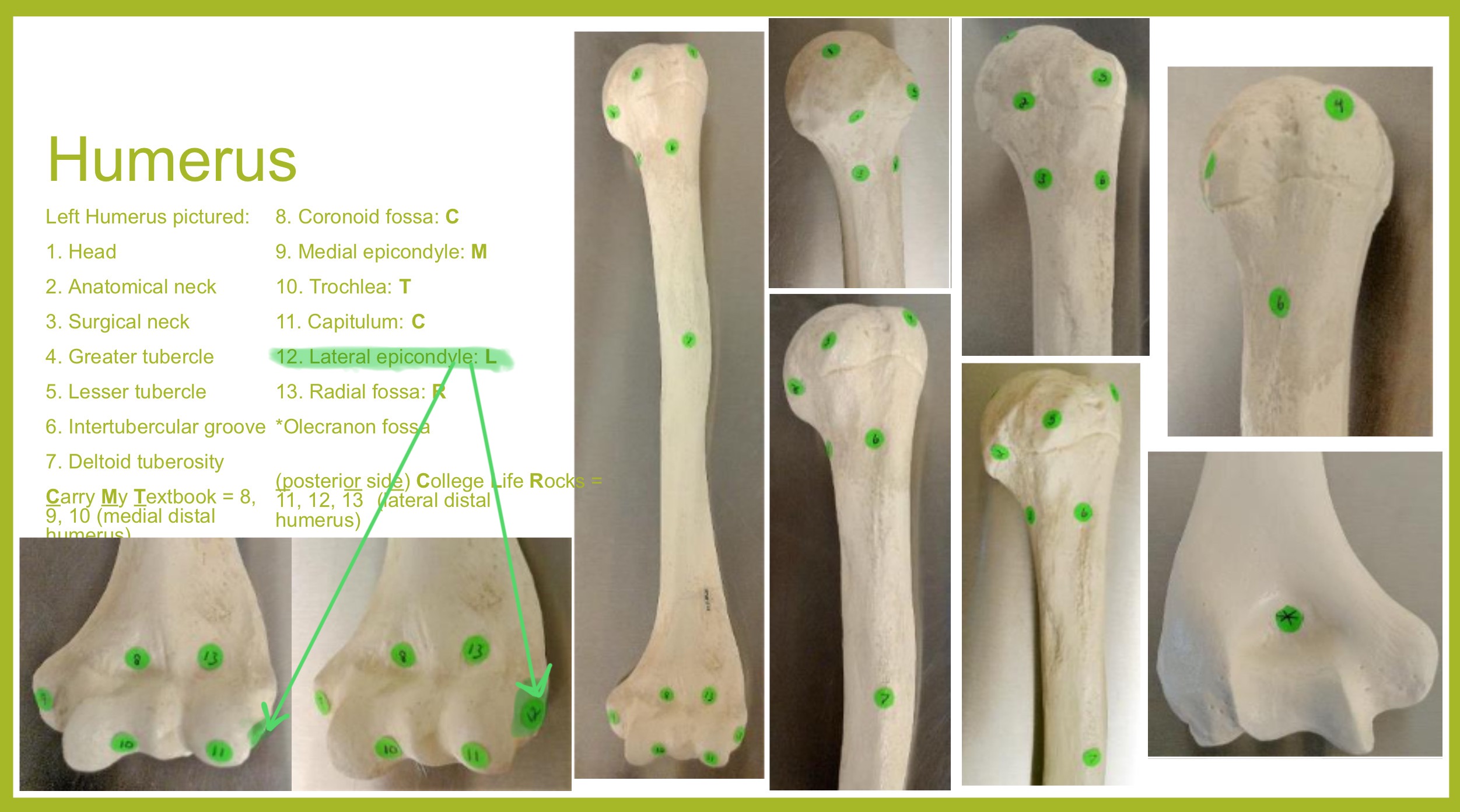
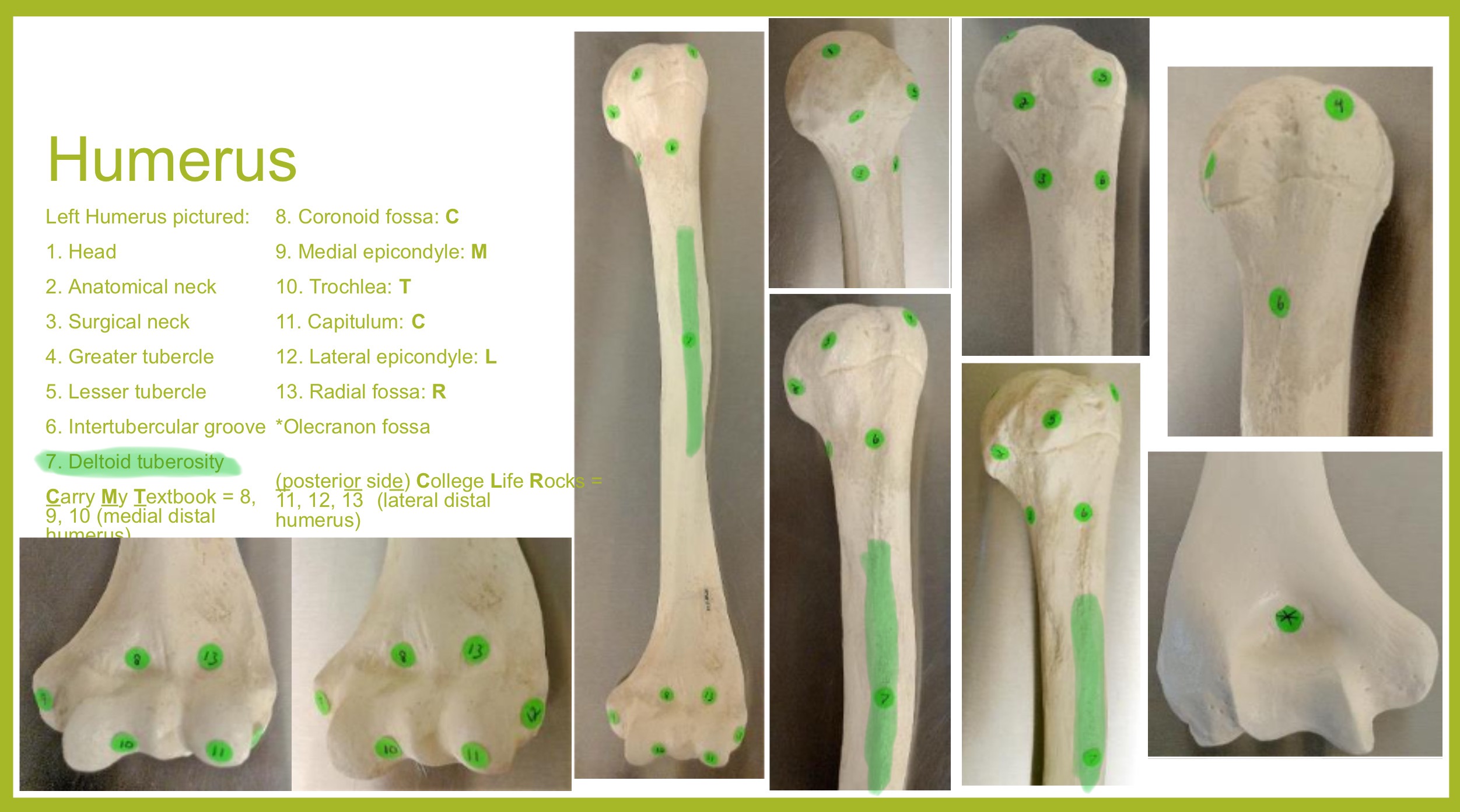
lateral epicondyle of humerus
small projection on distal, lateral side; attachment for muscles of forearms (extensors)
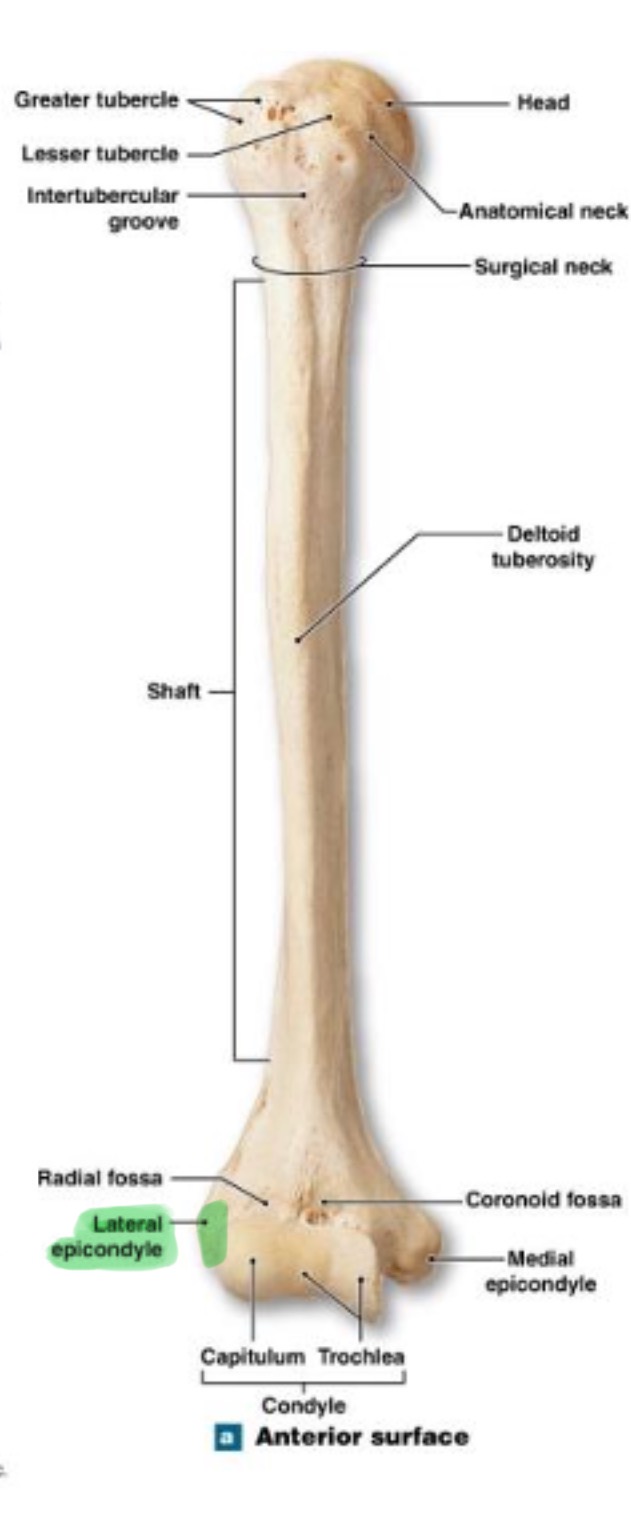
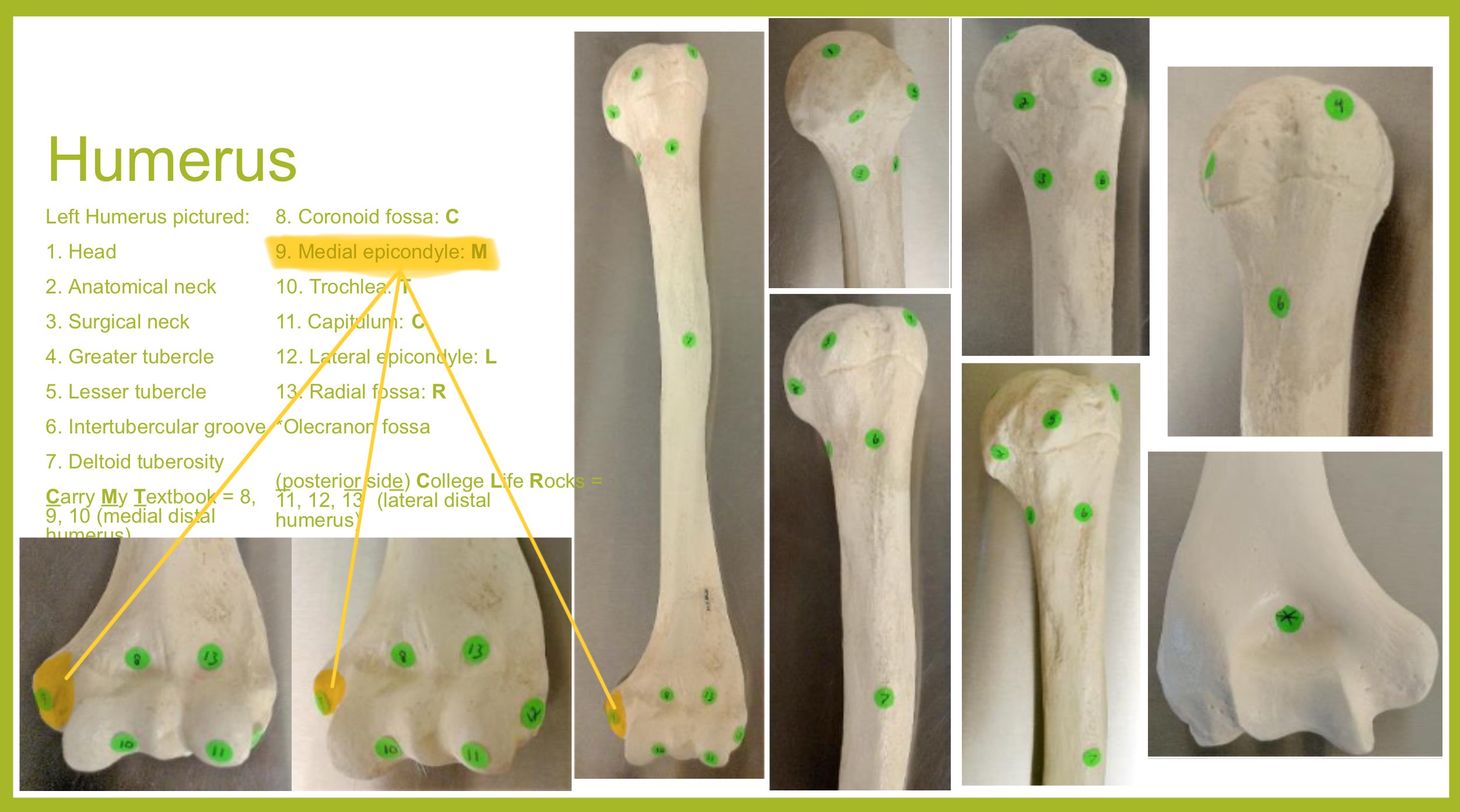
medial epicondyle of humerus
larger projection on the distal, medial side; attachment site for forearm flexor muscles & ulnar nerves passes behind it (“funny bone”)
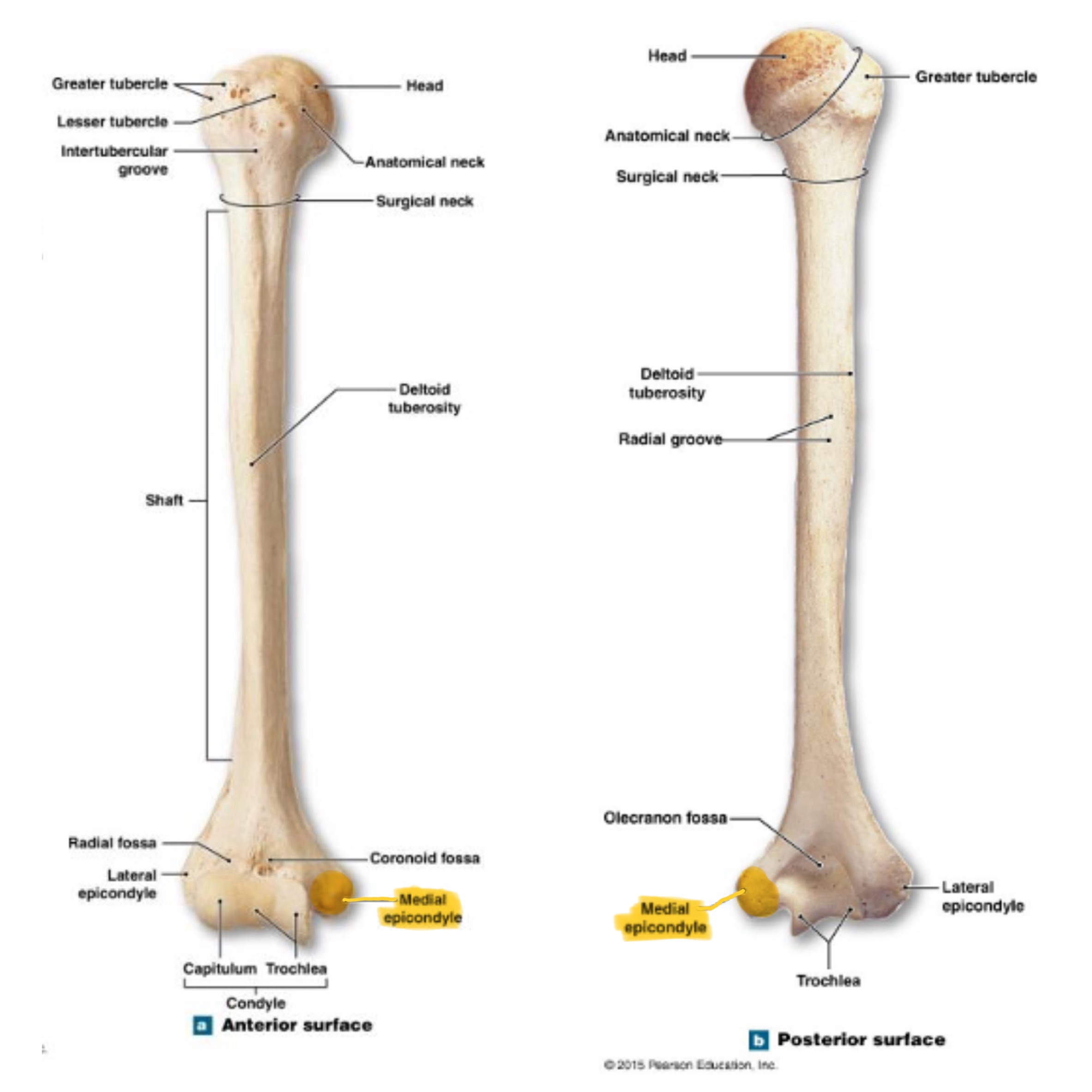
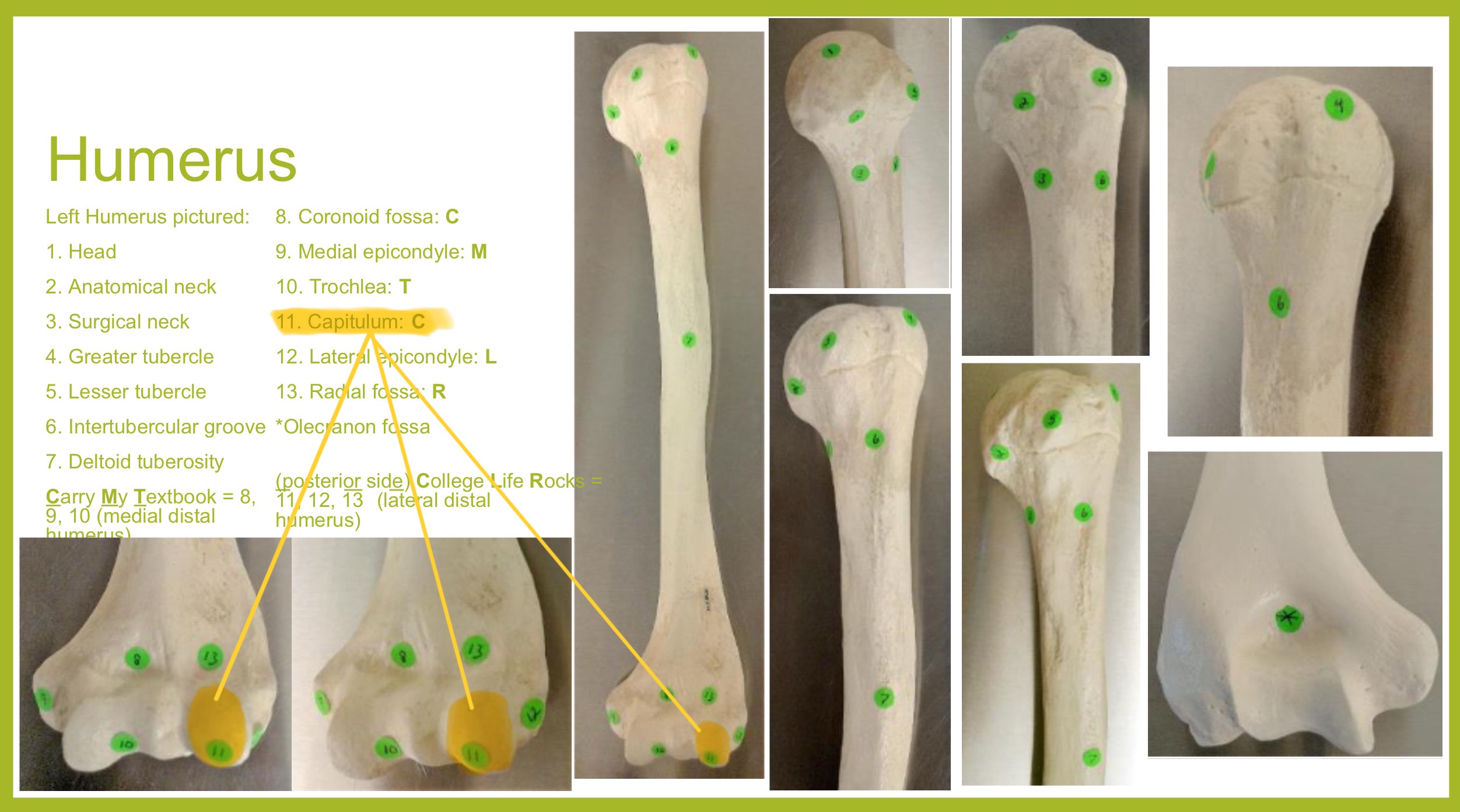
capitulum (condyle) of humerus
rounded knob on the distal, medial side; articulates with head of radius
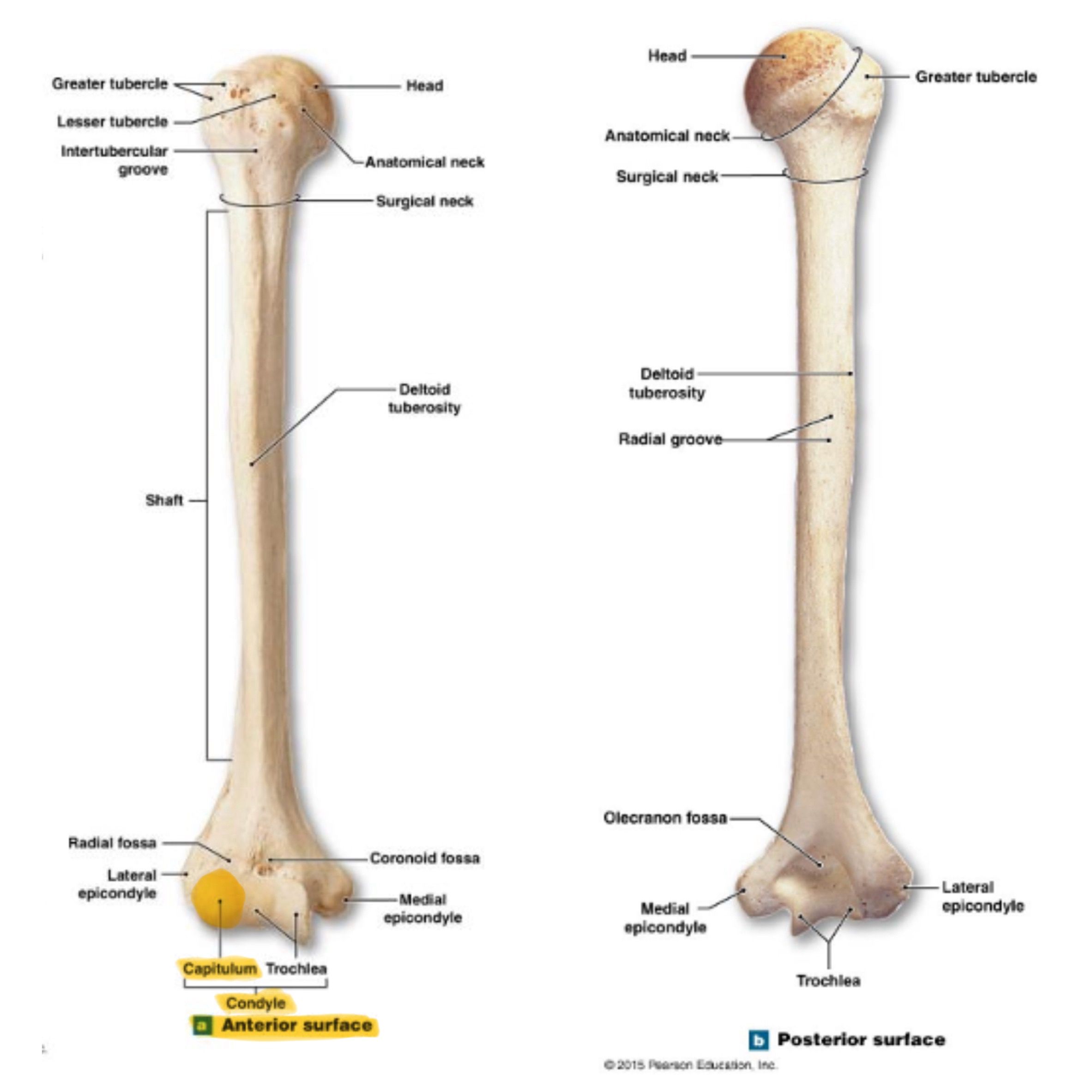
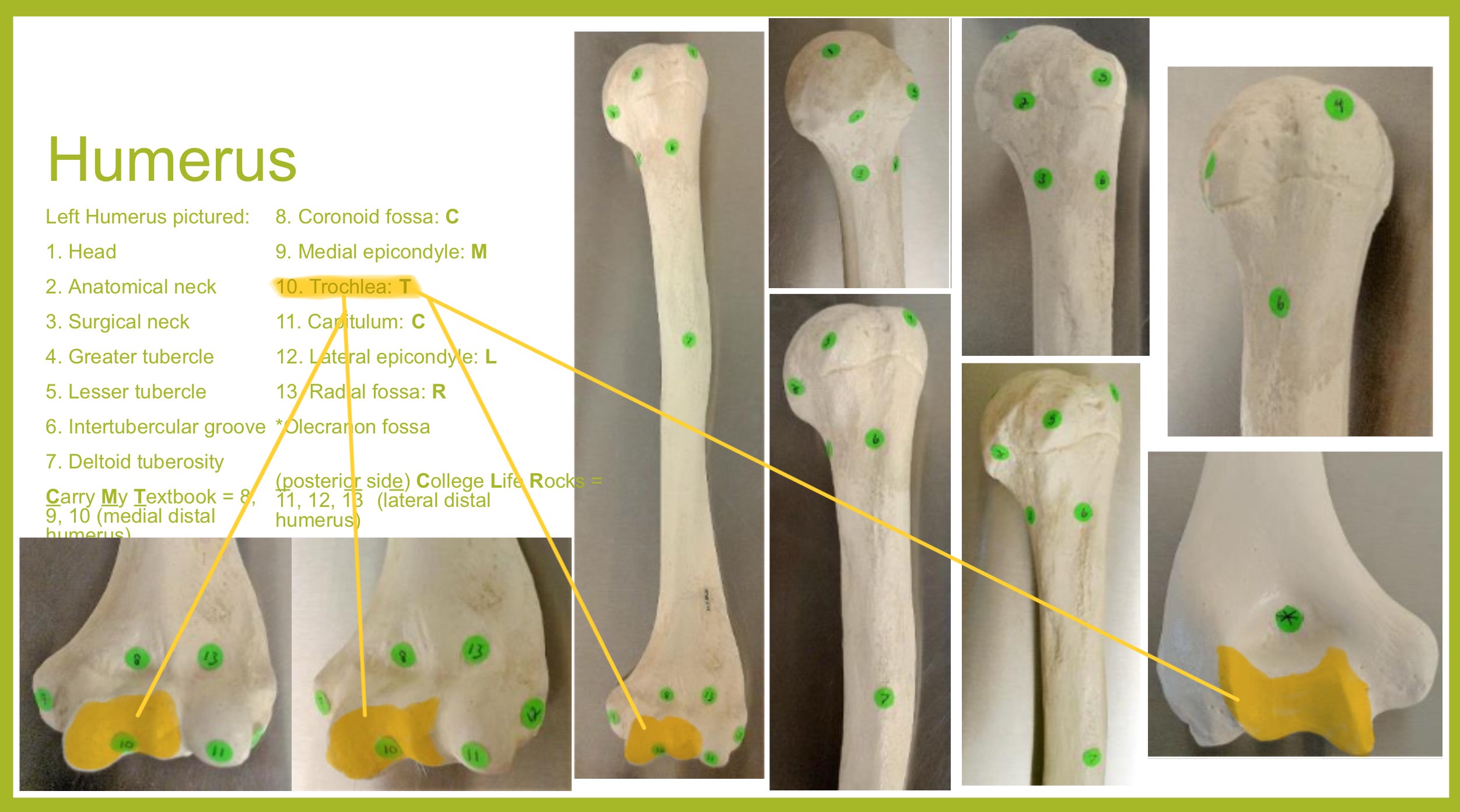
trochlea (condyle) of humerus
rounded knob on the distal, medial side; articulates with trochlear knotch; larger than the capitulum
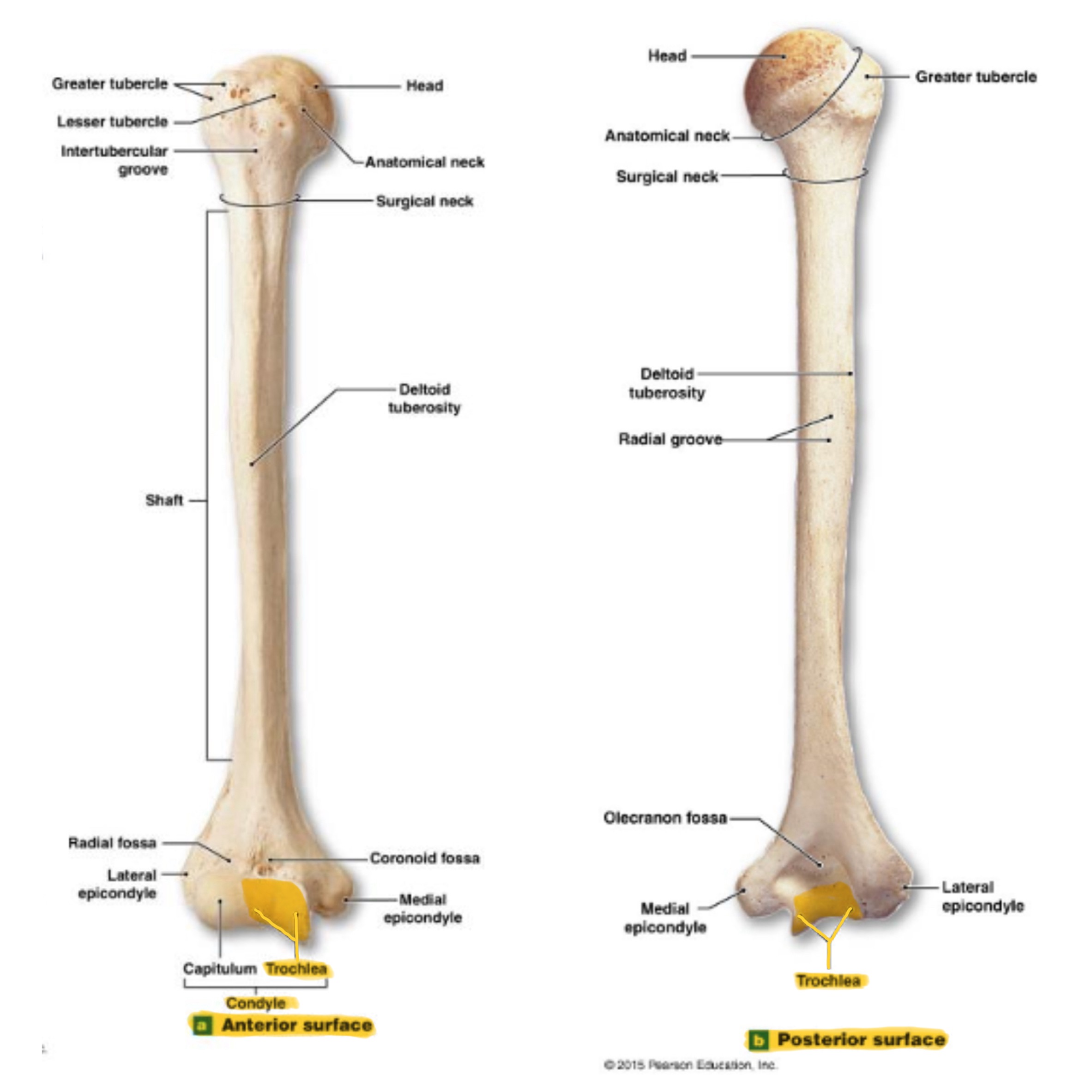
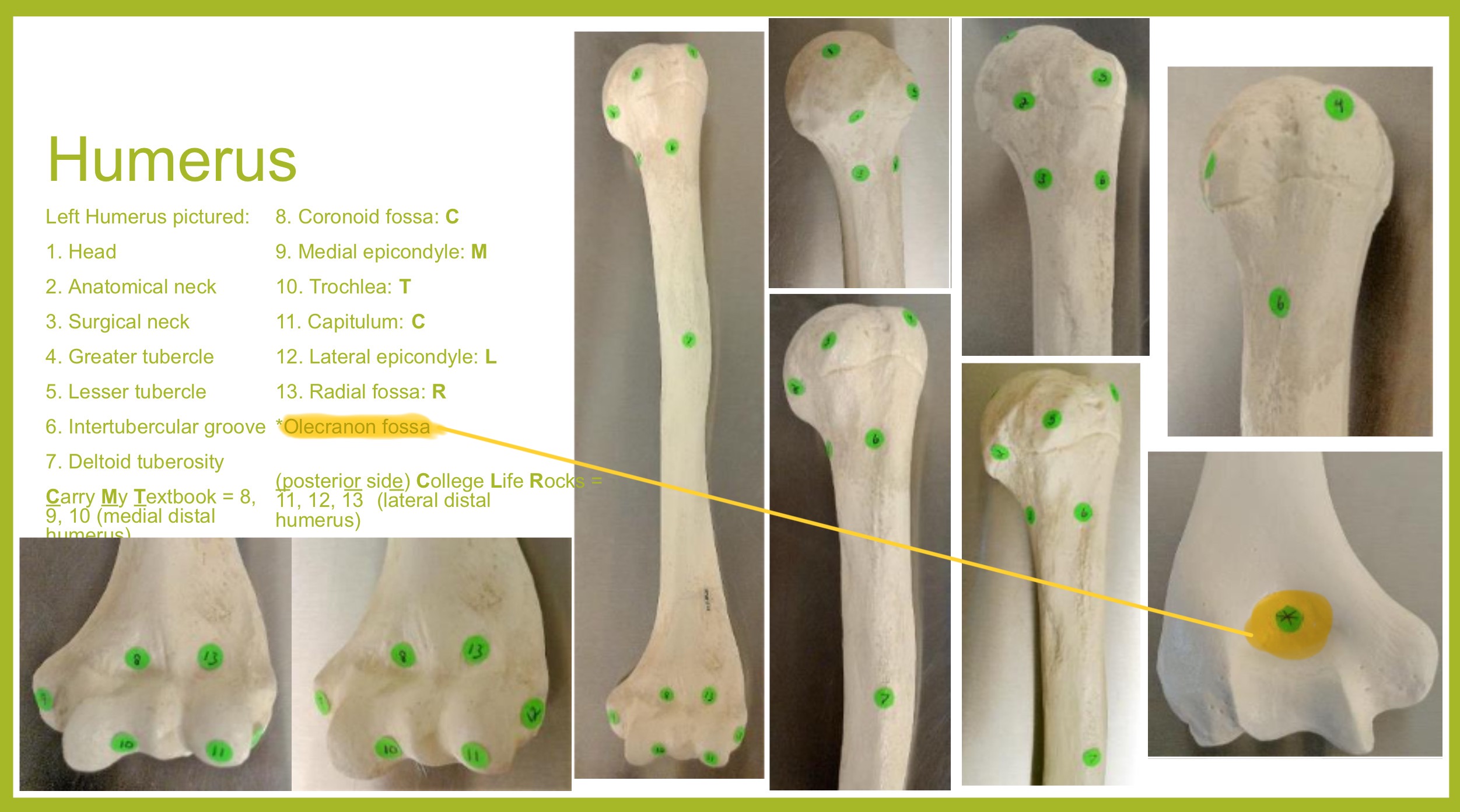
olecranon fossa of humerus
deep depression on posterior side above trochlea; receives olecranon process of ulna when the arm is extended
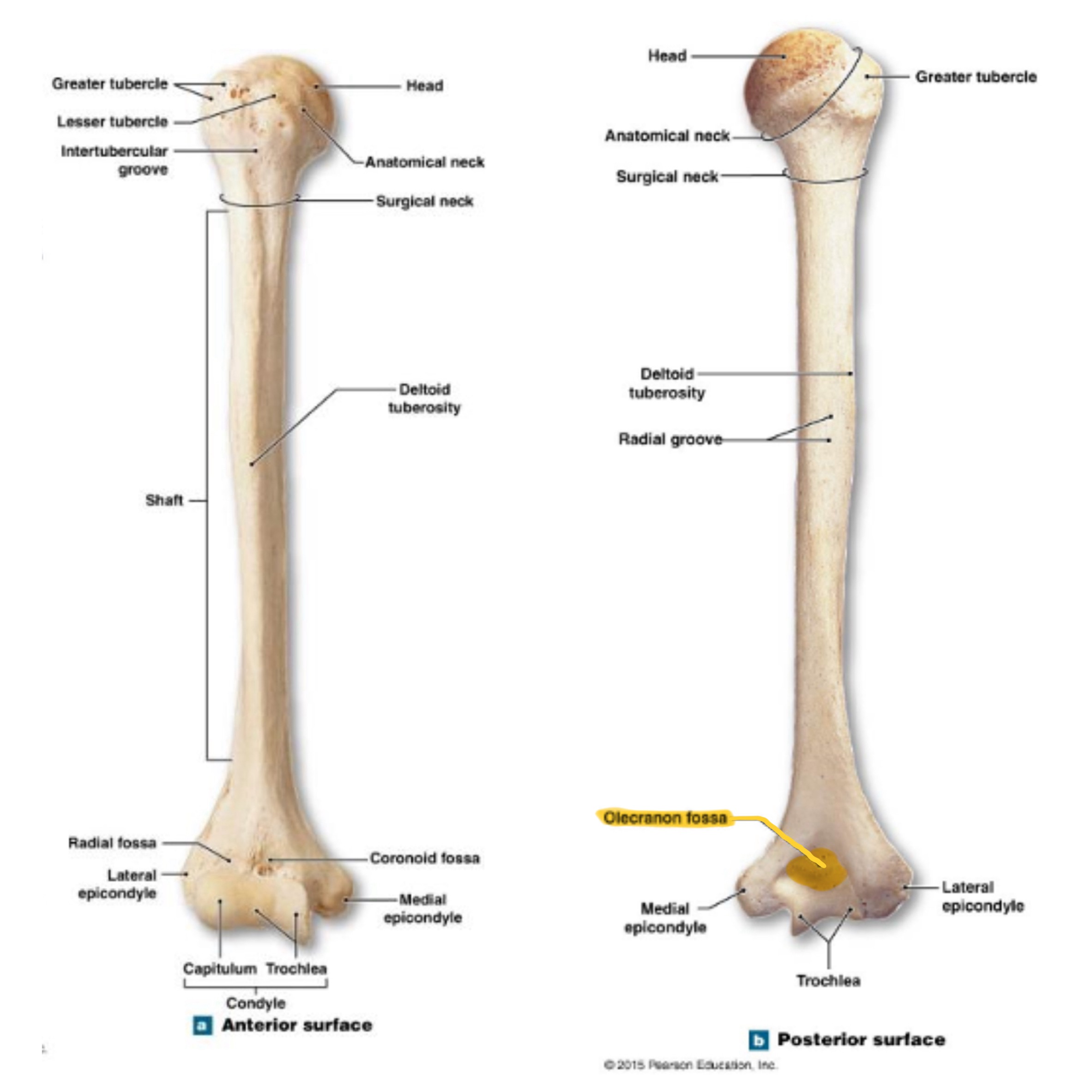
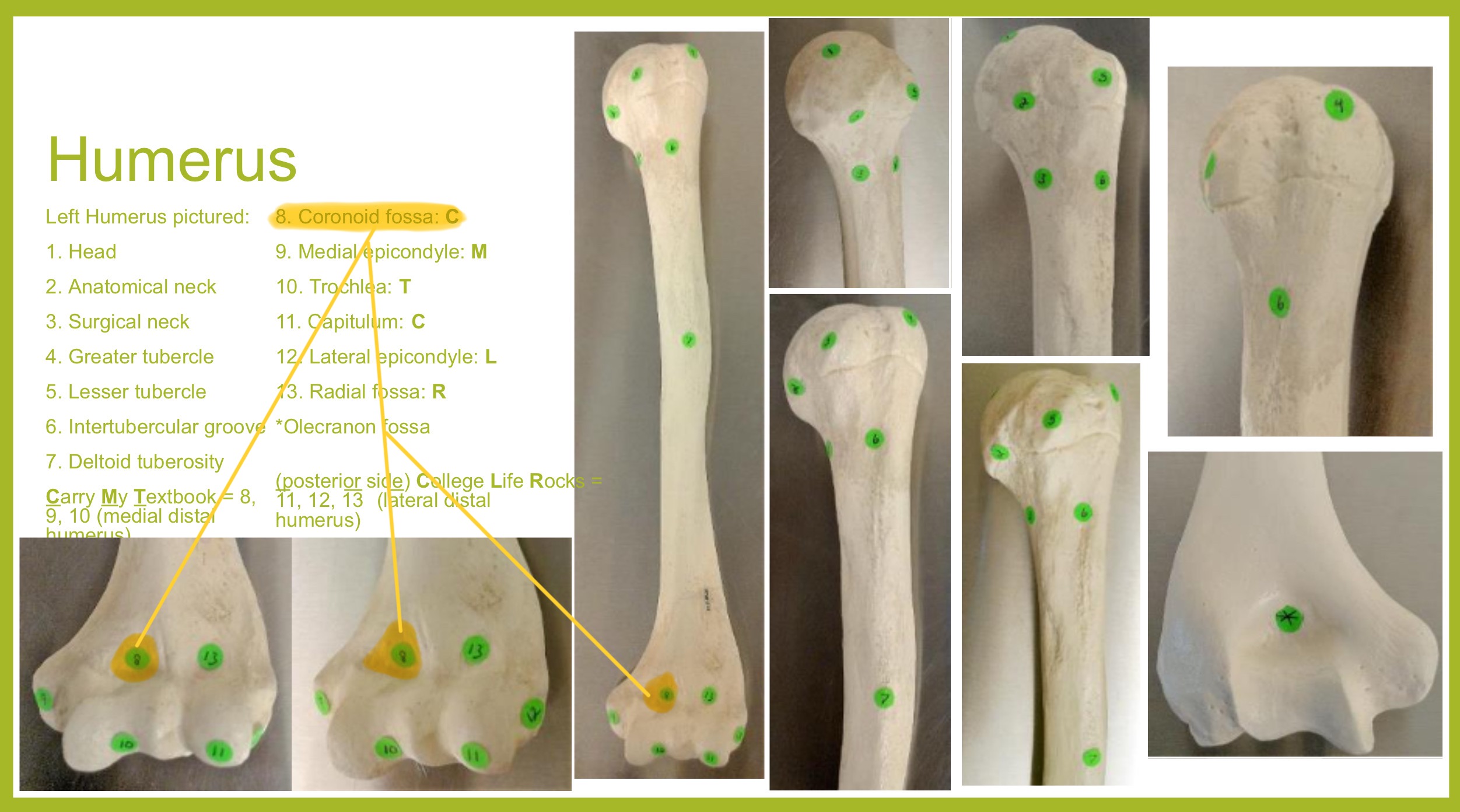
coronoid fossa of humerus
depression on anterior surface above trochlea; receives coronoid process of ulna during elbow flexion
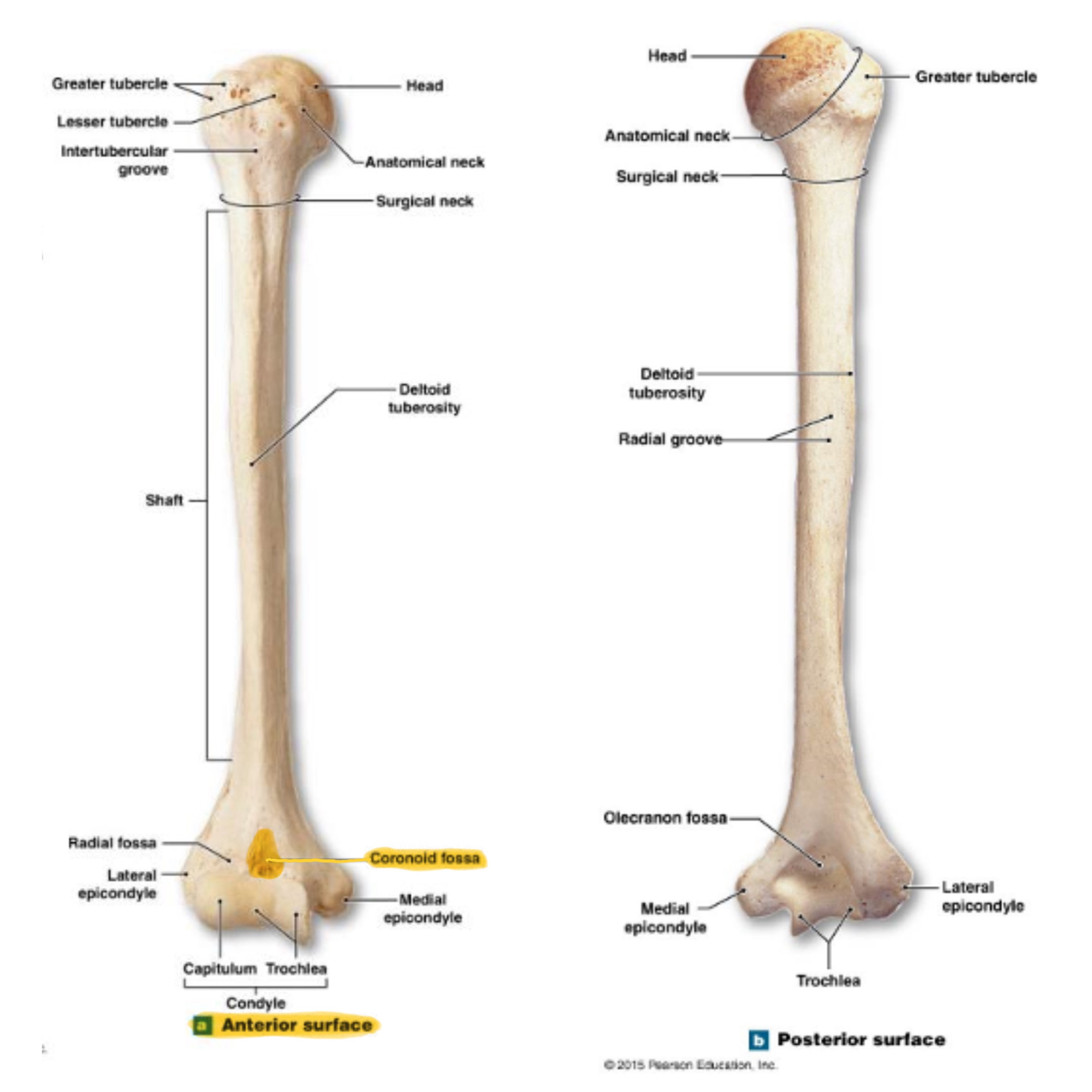
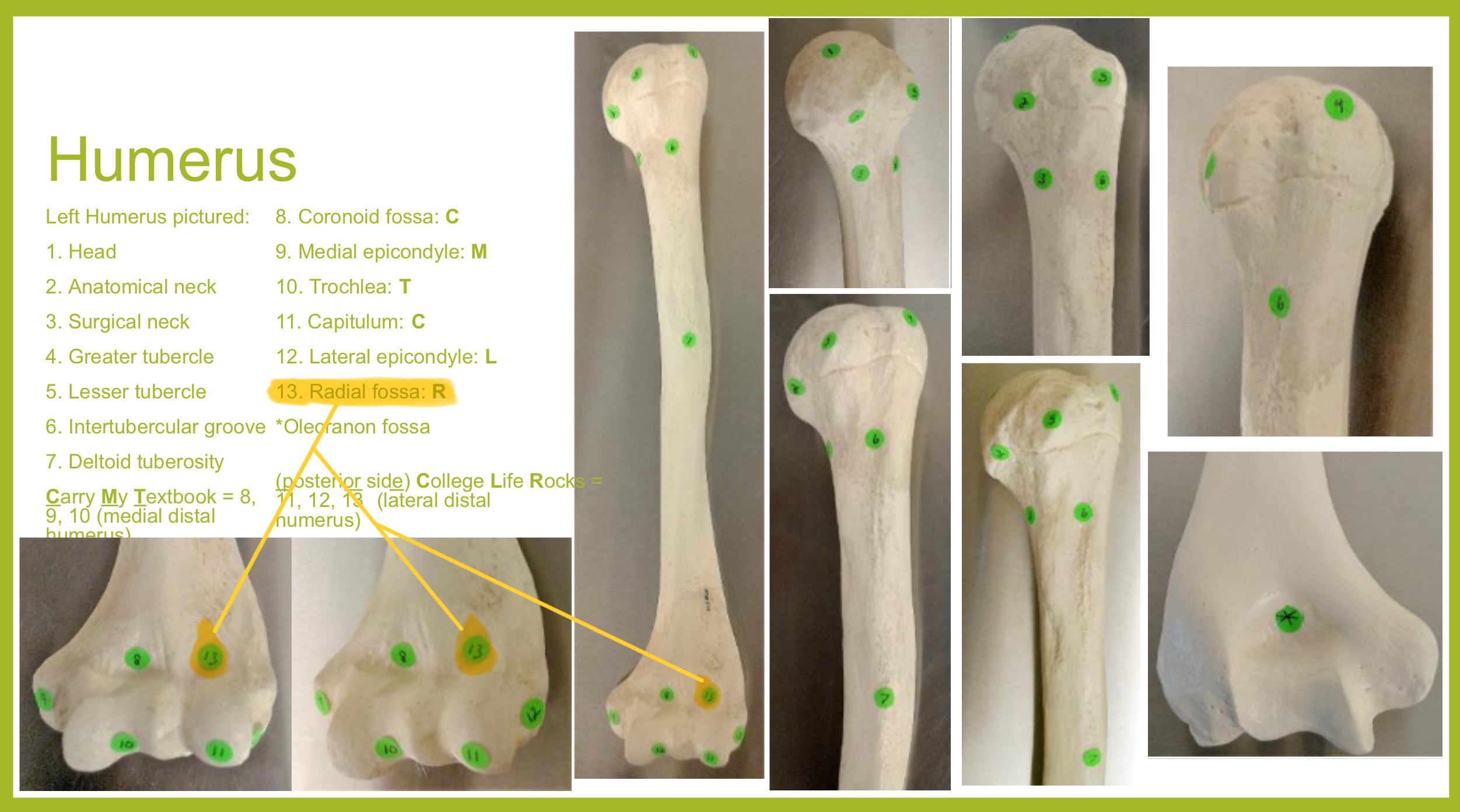
radial fossa of humerus
small depression above capitulum on anterior surface; receives head of radius when elbow is flexed
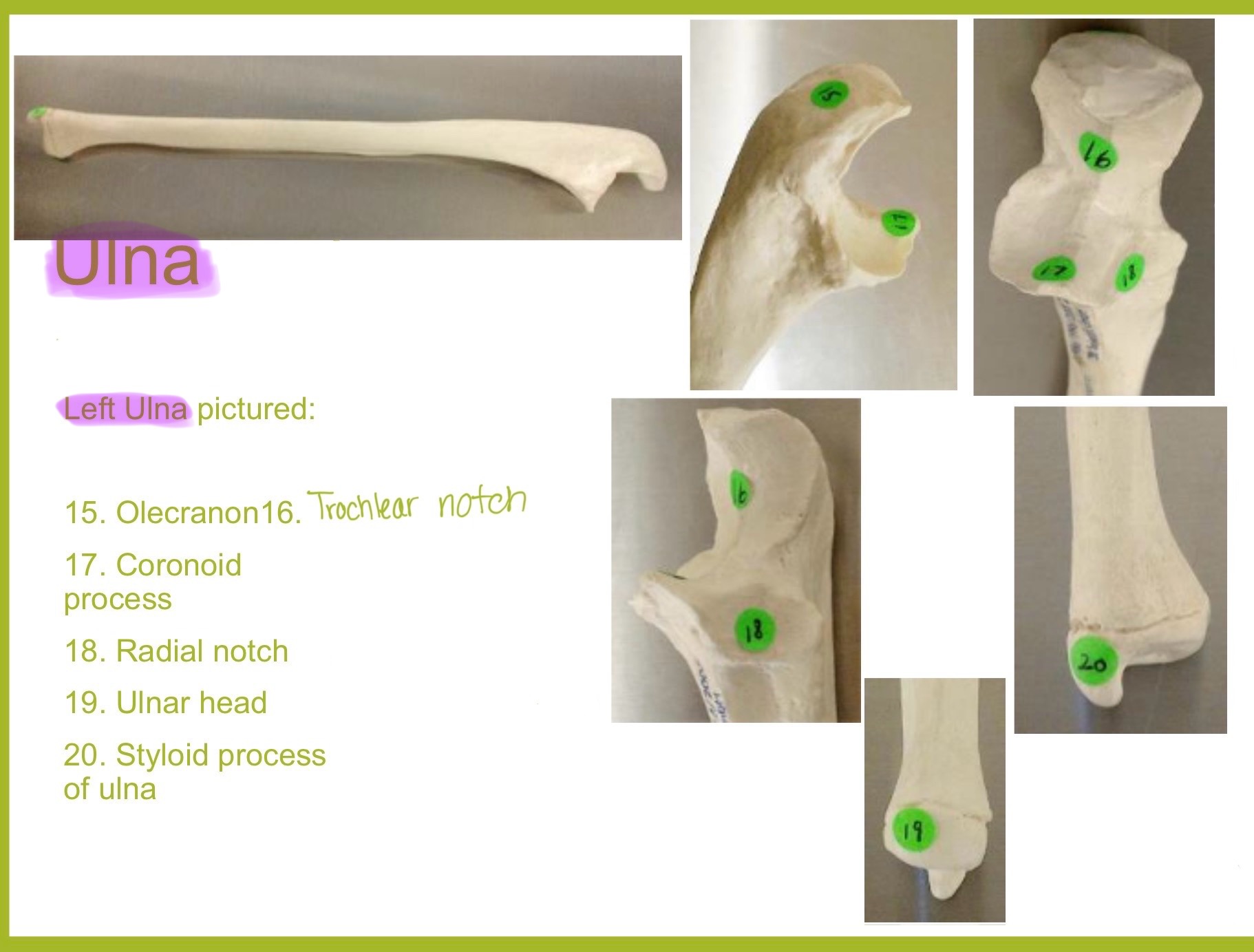
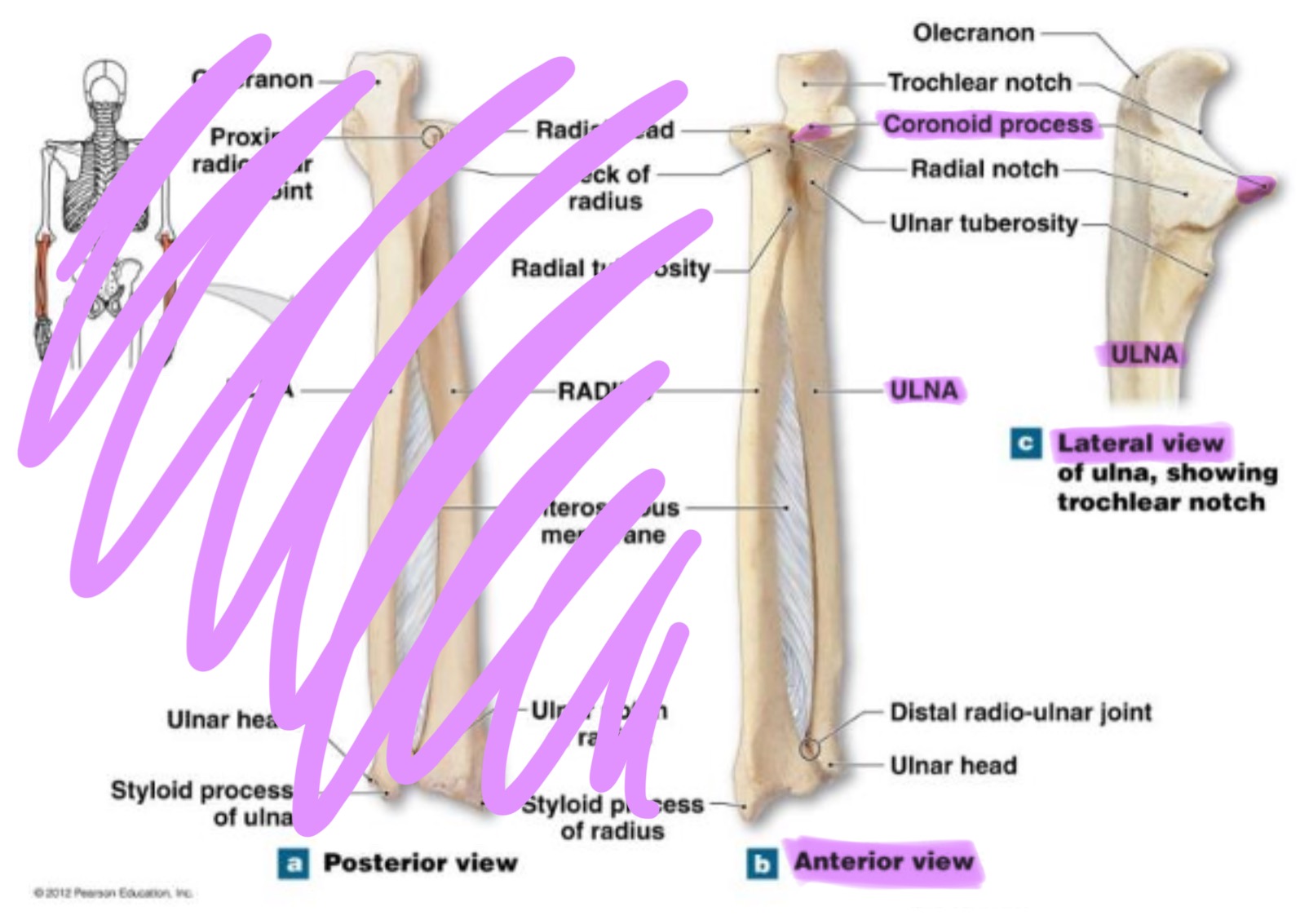
ulna
main bone of the forearm that forms the elbow joint w/ the humerus; allows pronation and supination; identified by large hook at the top of bone
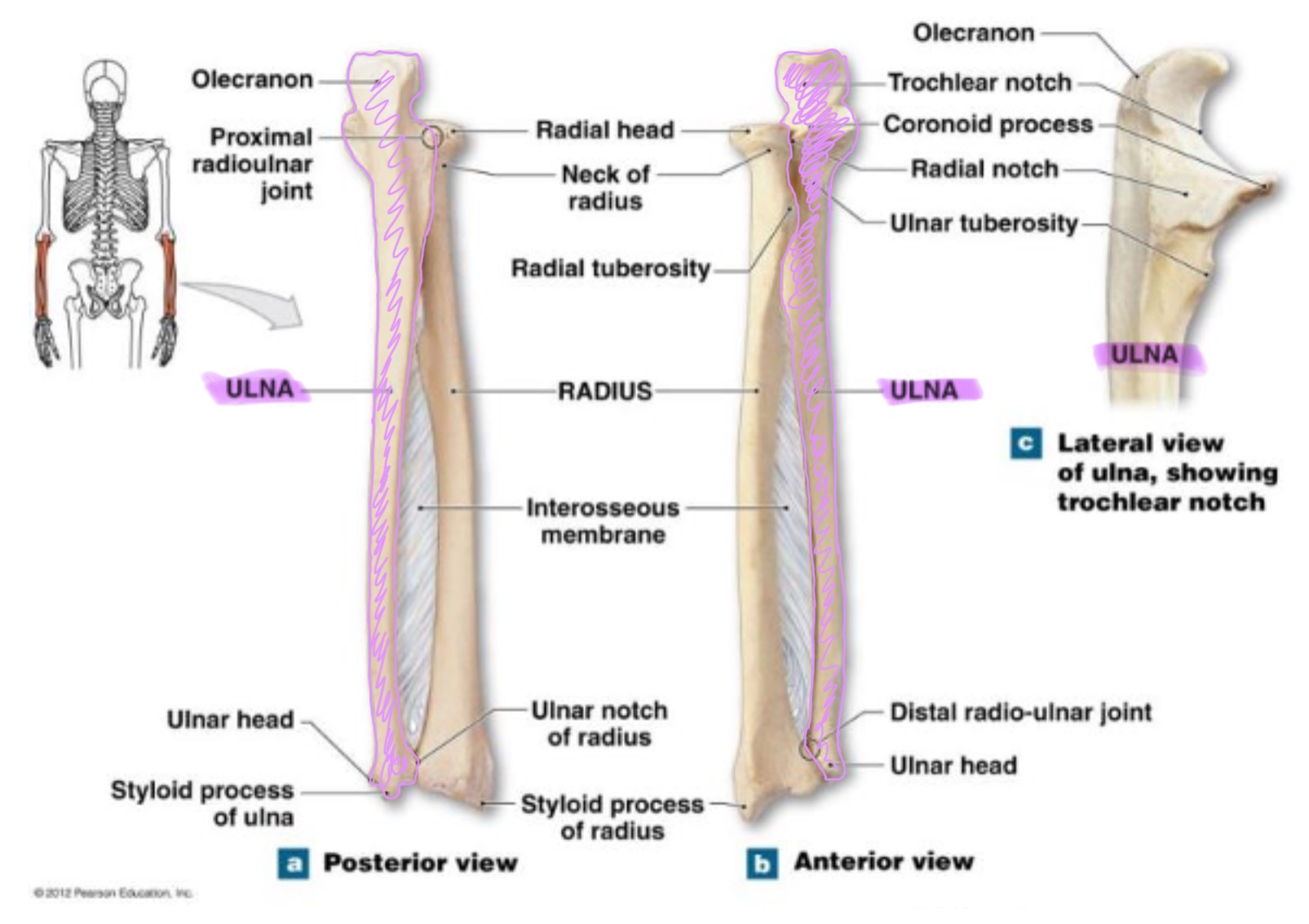
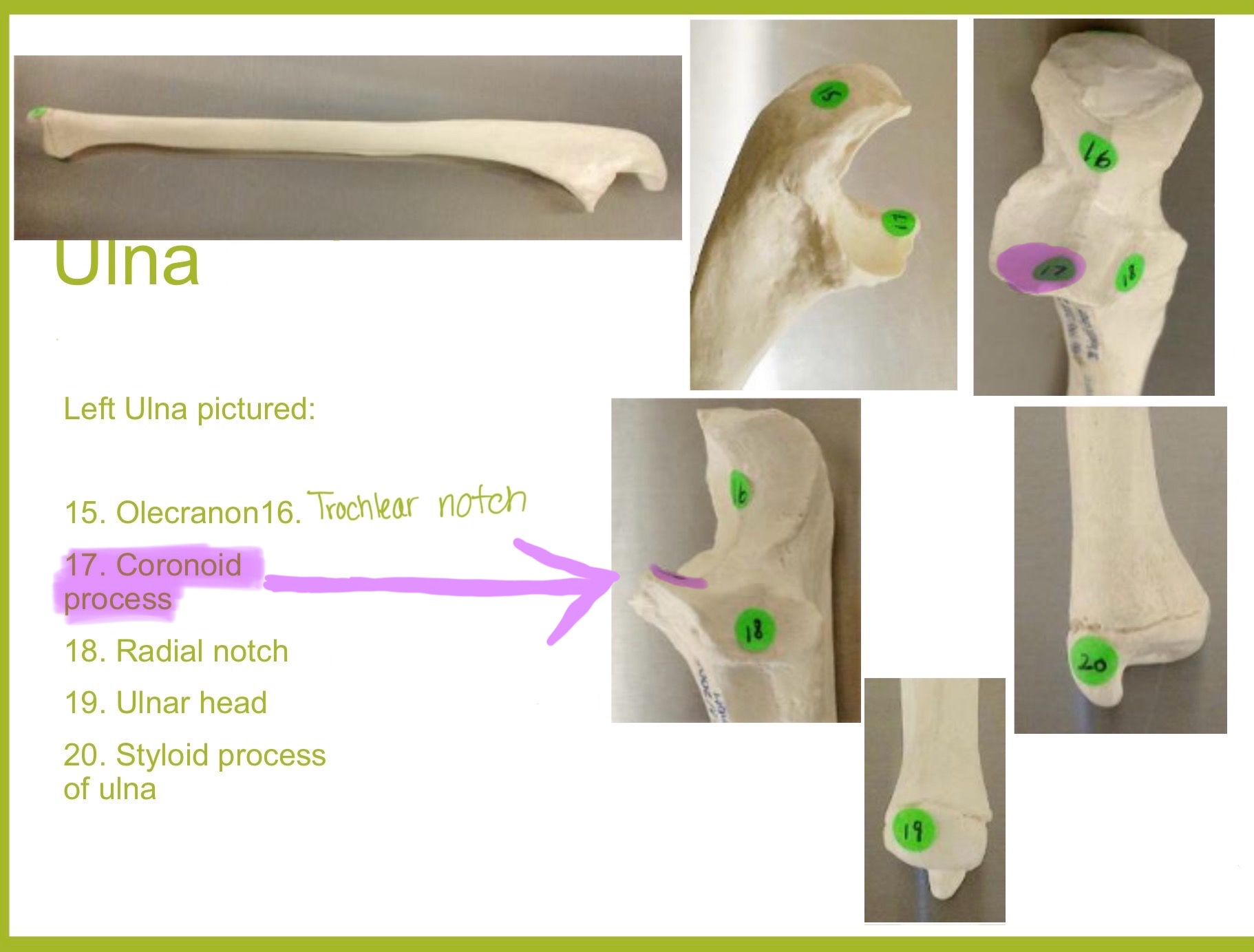
coronoid process of ulna
triangular projection on anterior side of proximal ulna; fits into coronoid fossa of humerus when elbow is flexed & provides attachment for brachalis muscle
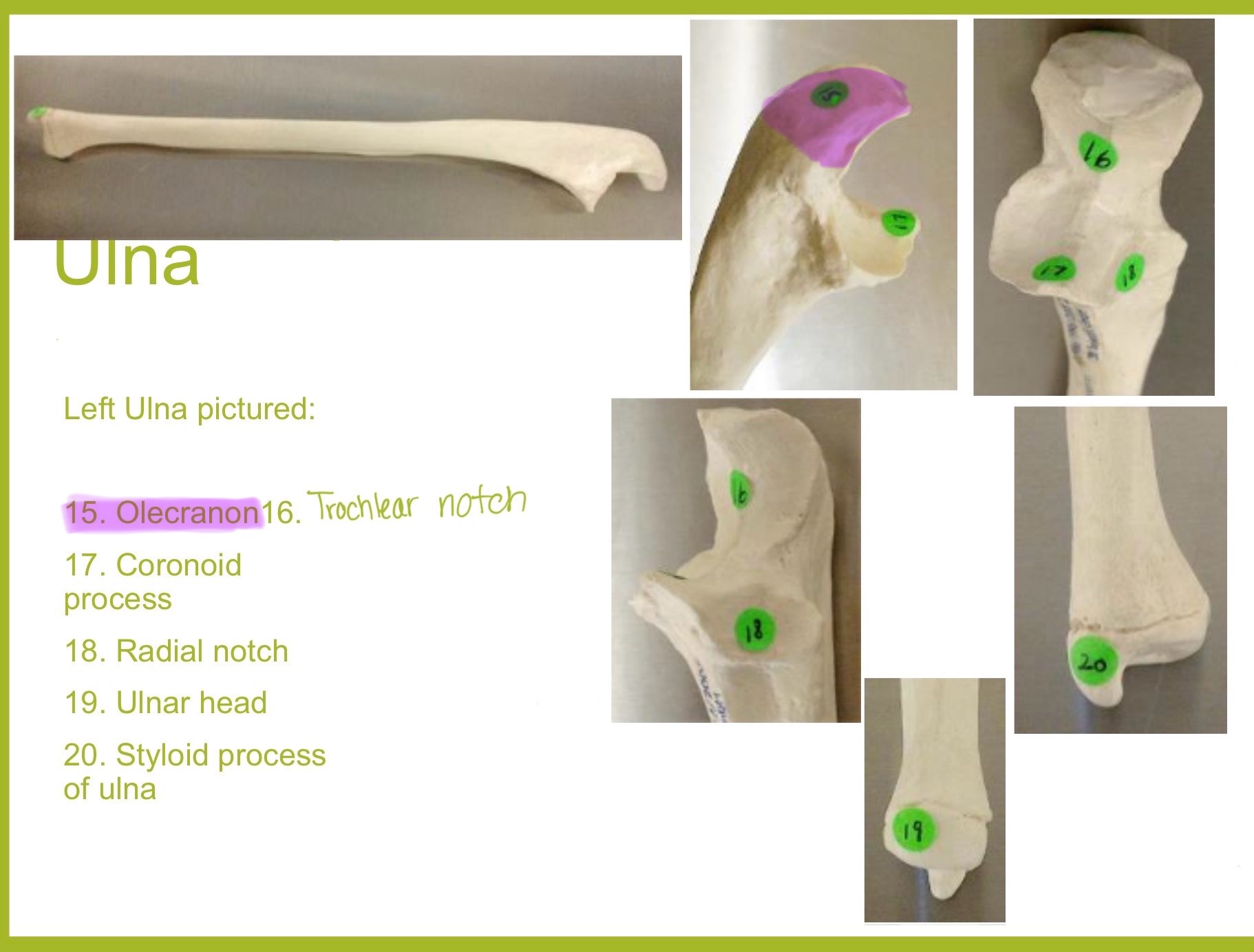
olecranon process of ulna
large, curved projection on posterior side of proximal ulna; forms tip of elbow & fits into the olecranon fossa of humerus wehn arm is extended. it serves as an attachment site for triceps brachialis muscle
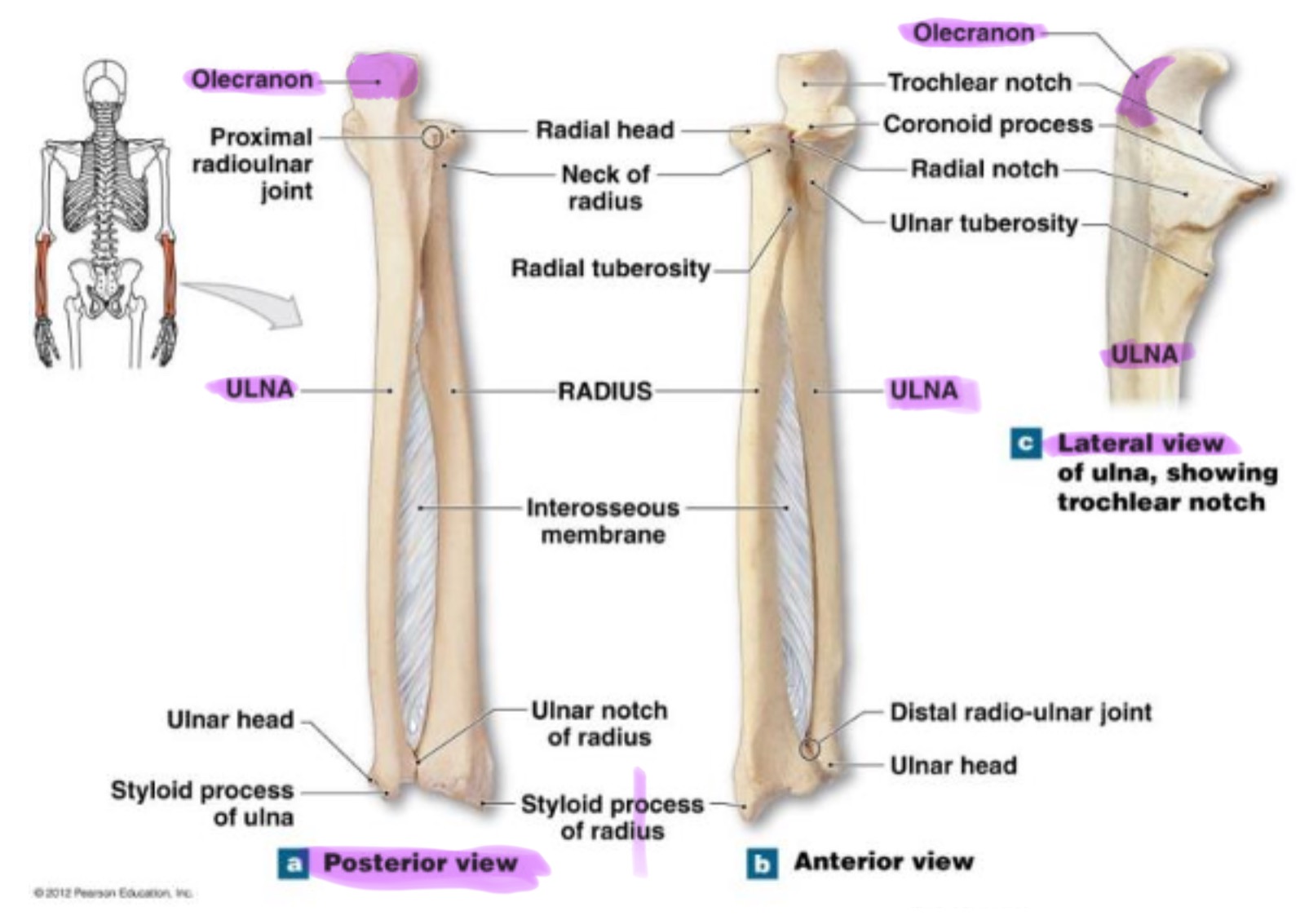
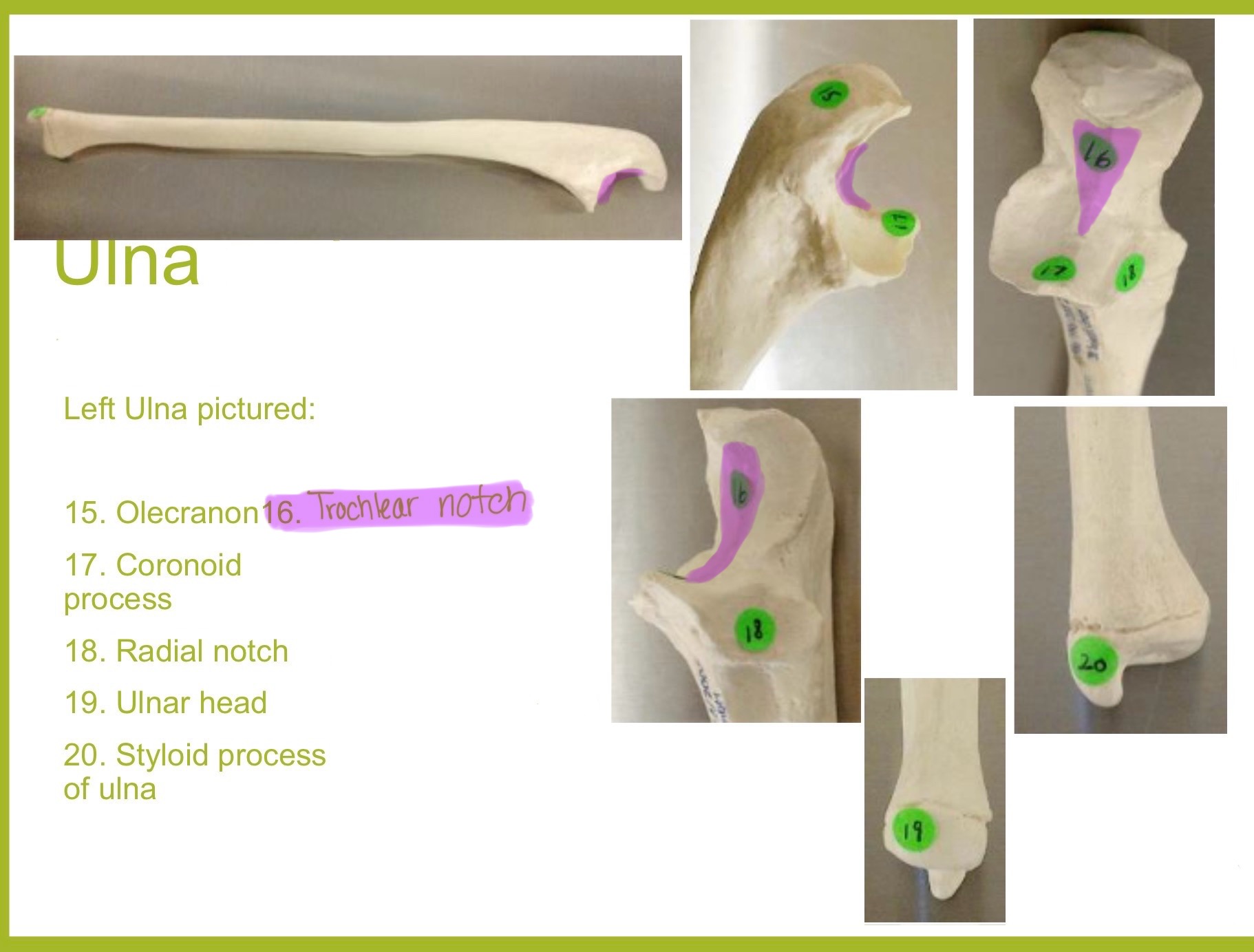
trochlear notch of ulna
deep, curved notch between the olecranon & coronoid processes; articulates w/ trochlea of humerus to form part of elbow joint
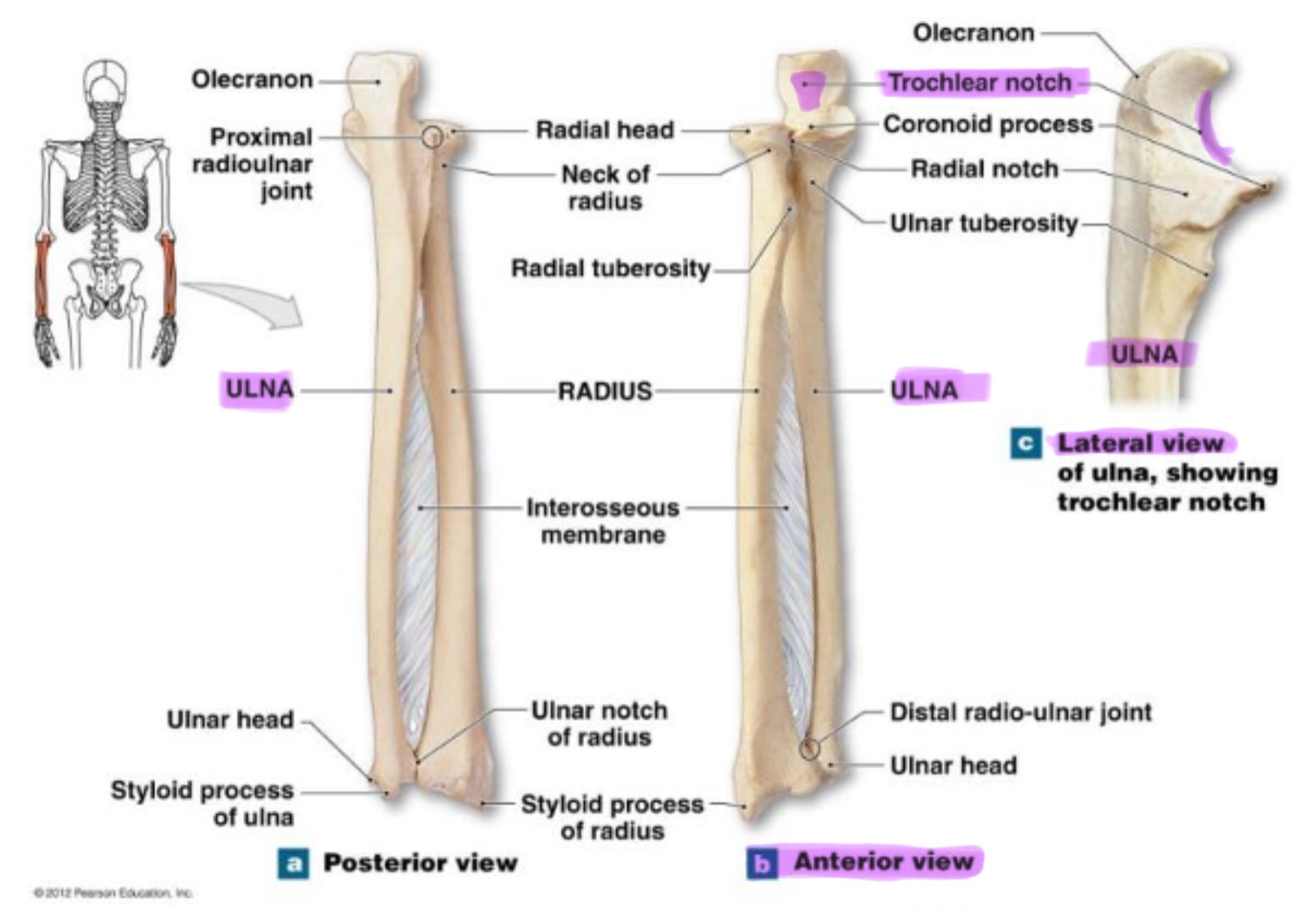
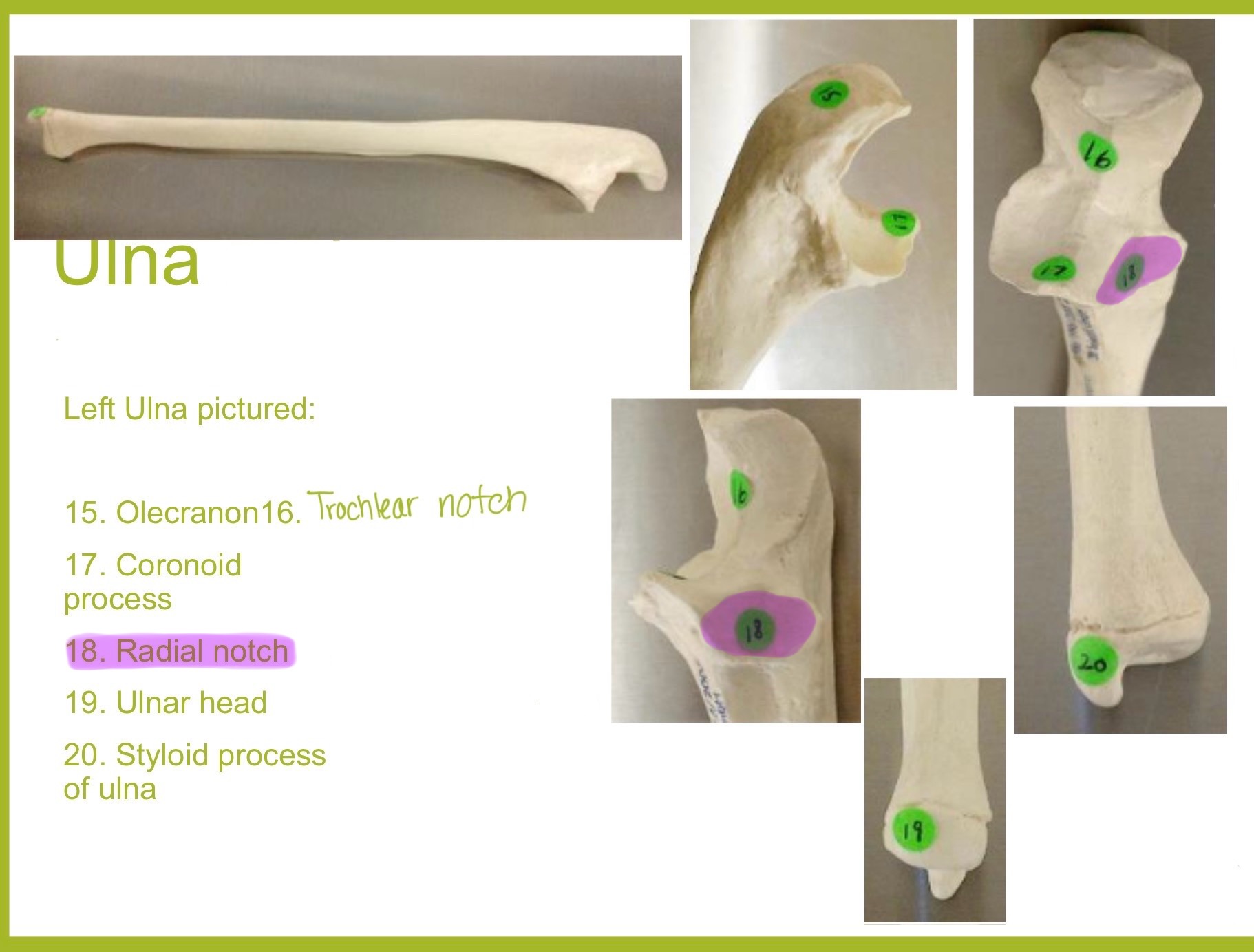
radial notch of ulna
small, smooth depression on the lateral side of proximal ulna; articulates w/ head of radius to form proximal radioulnar joint (rotation of forearm)
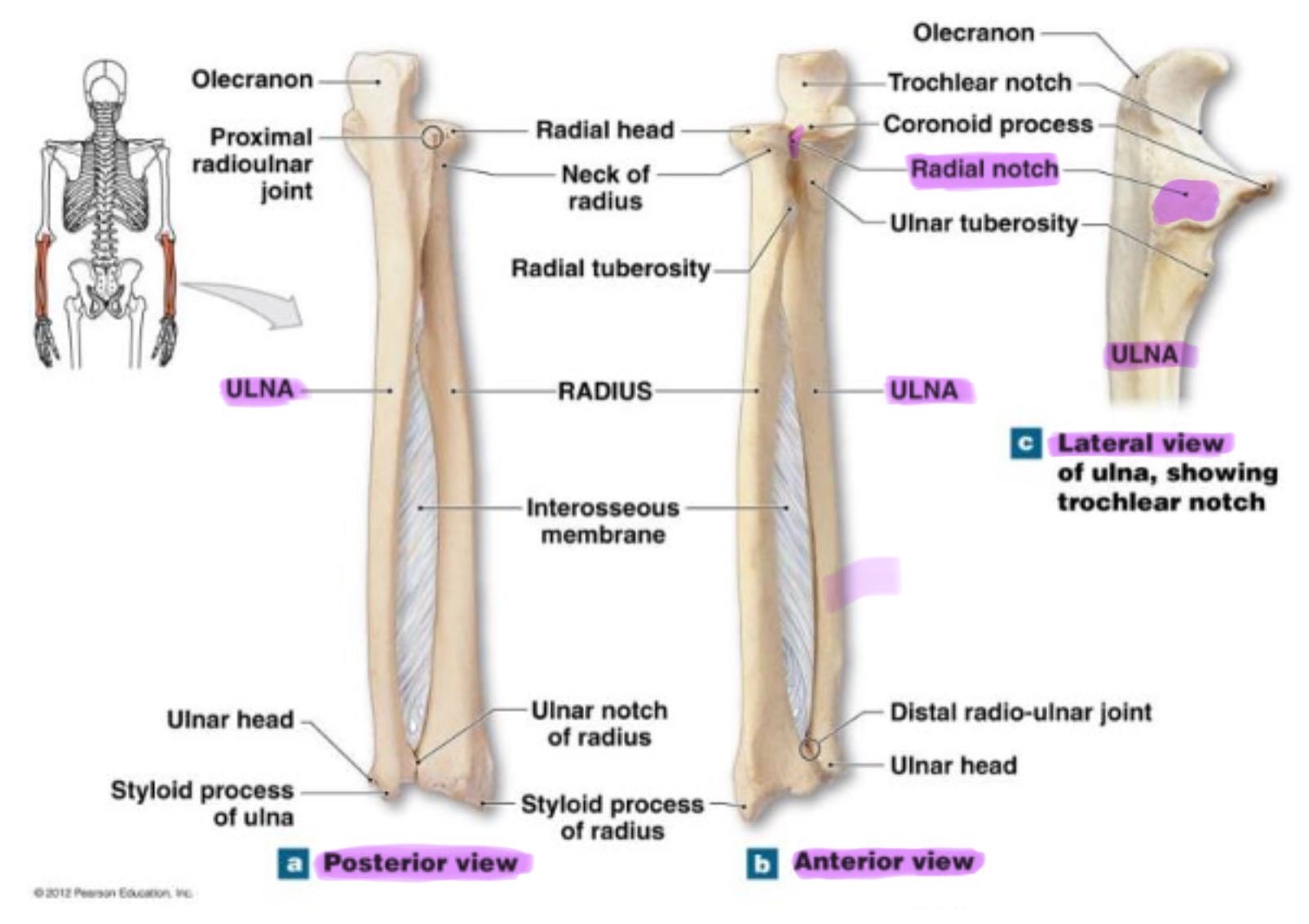
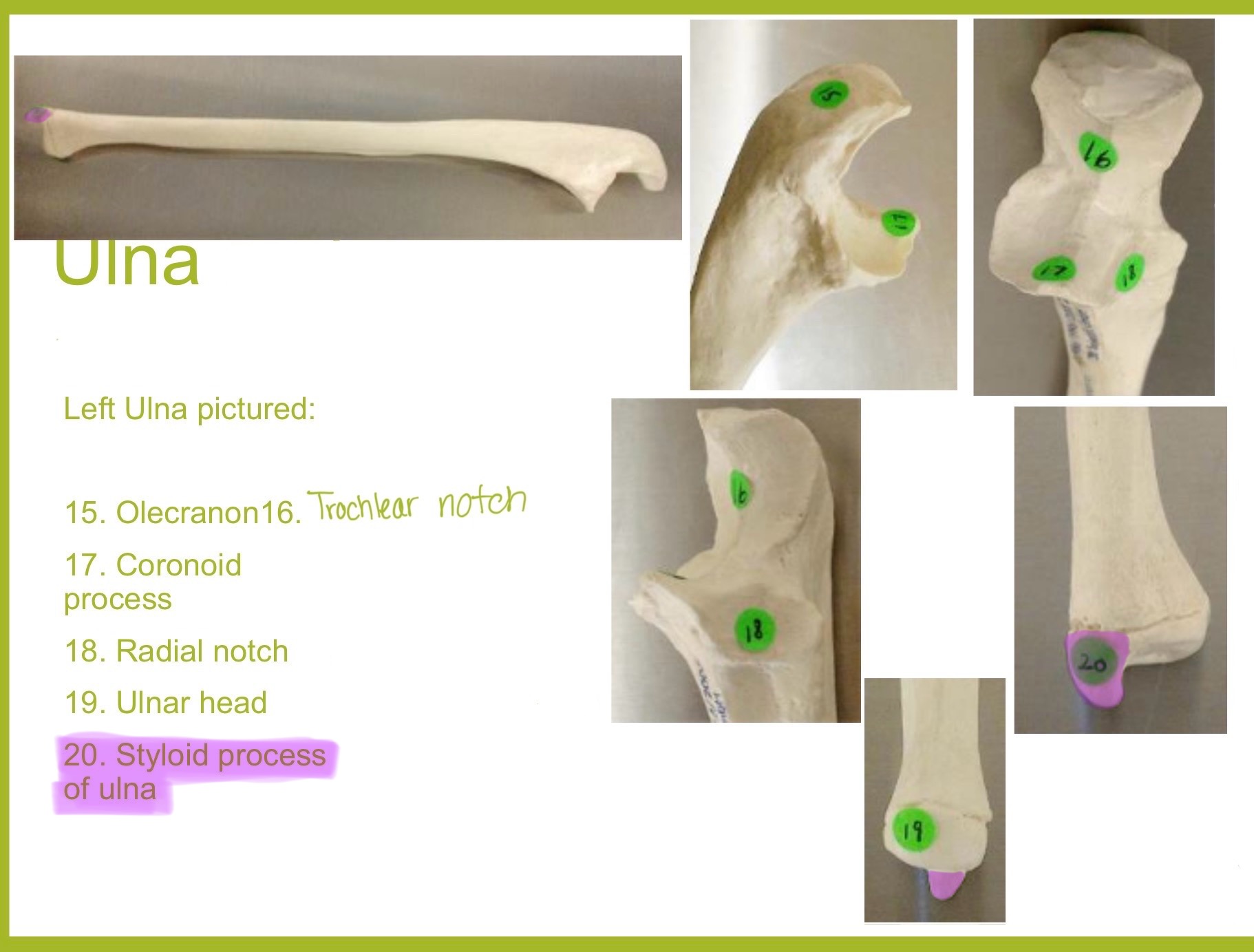
styloid process of ulna
pointed projection on the distal end of ulna; provides attachment for ligaments of wrist & helps stabilize ulnocarpal joint
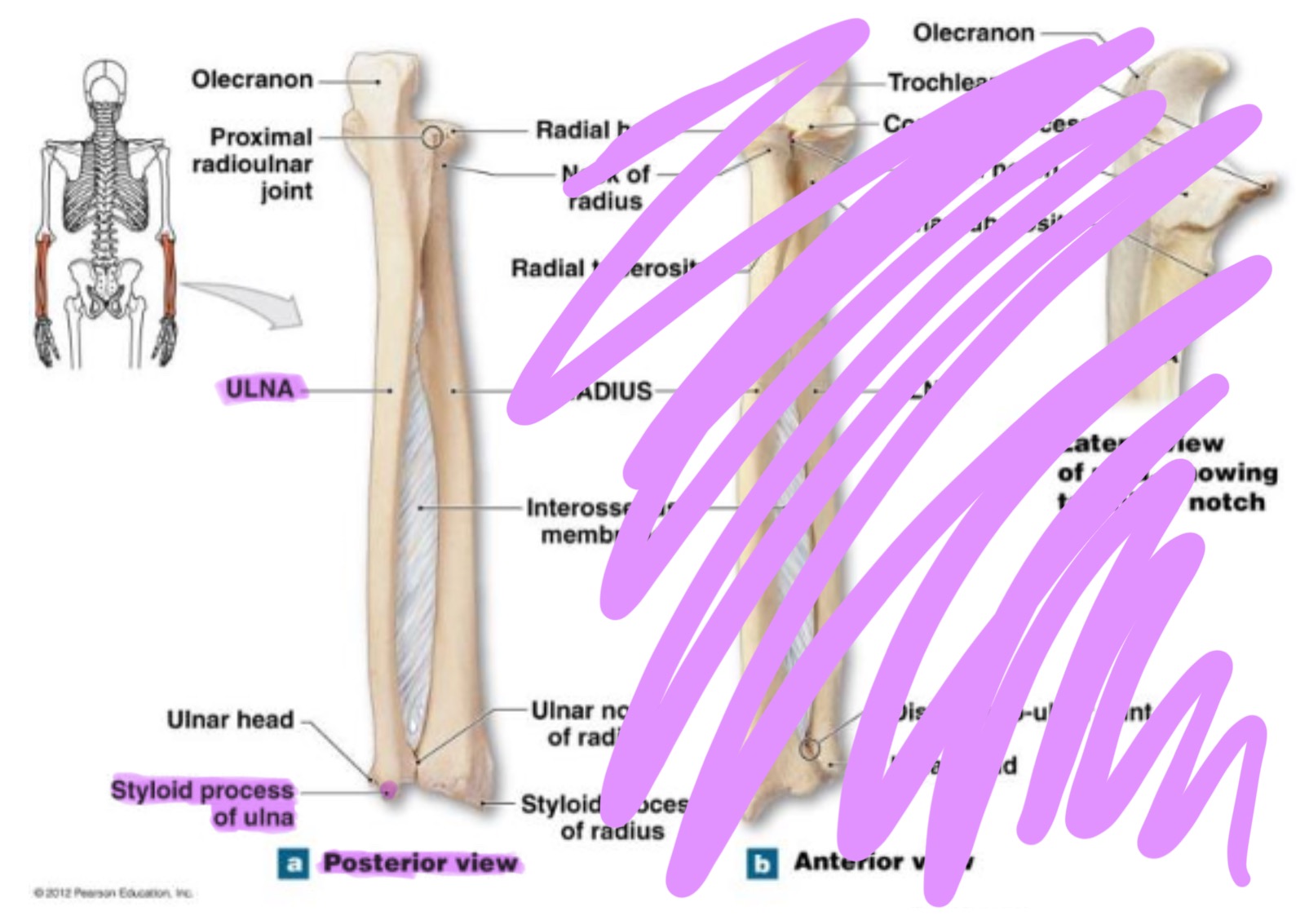
radius
works w/ ulna to allow rotation of forearm (supination/pronation)
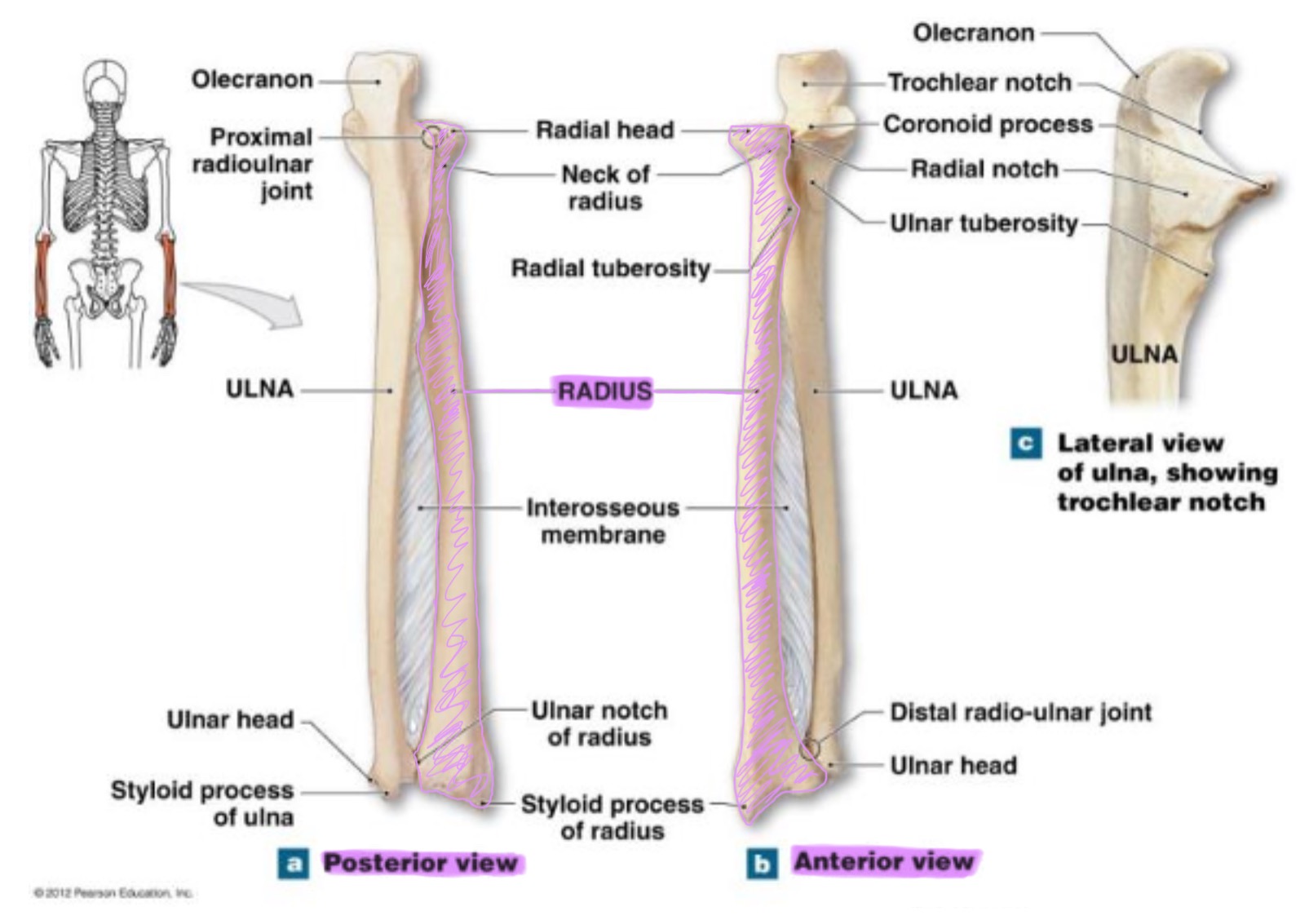
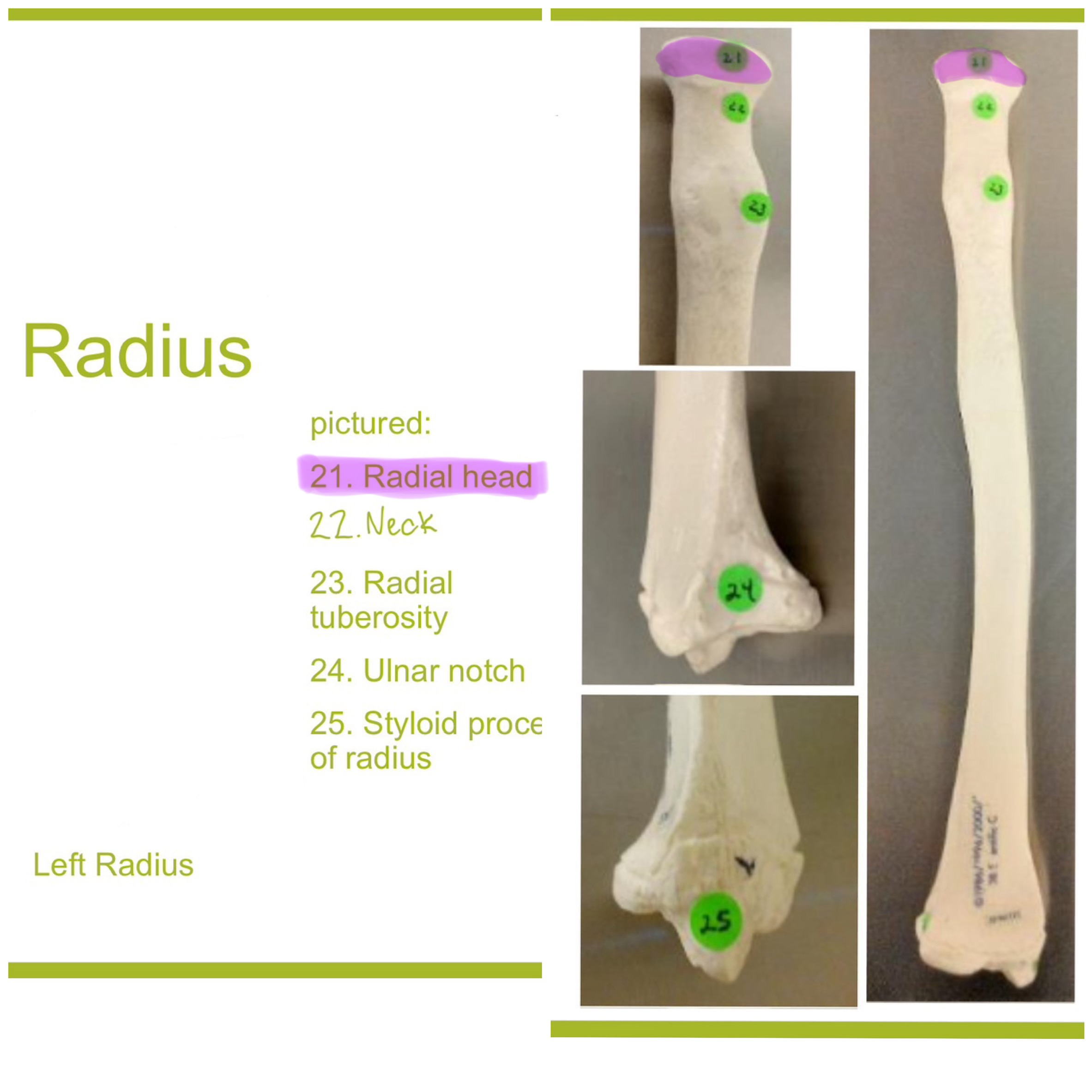
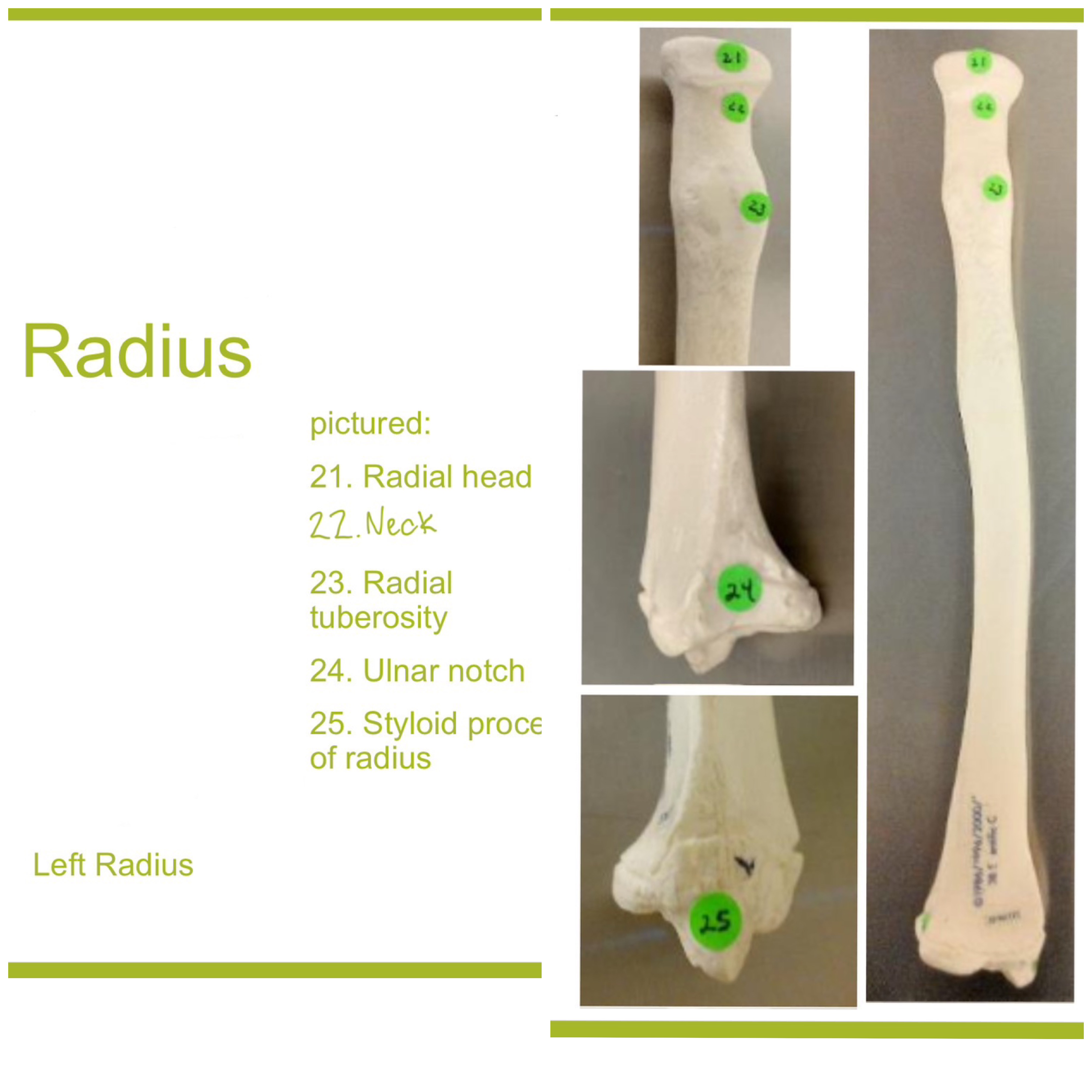
head of radius
disc-shaped proximal end that articulates w/ the capitulum of humerus & radial notch of ulna; allows radius to rotate around the ulna
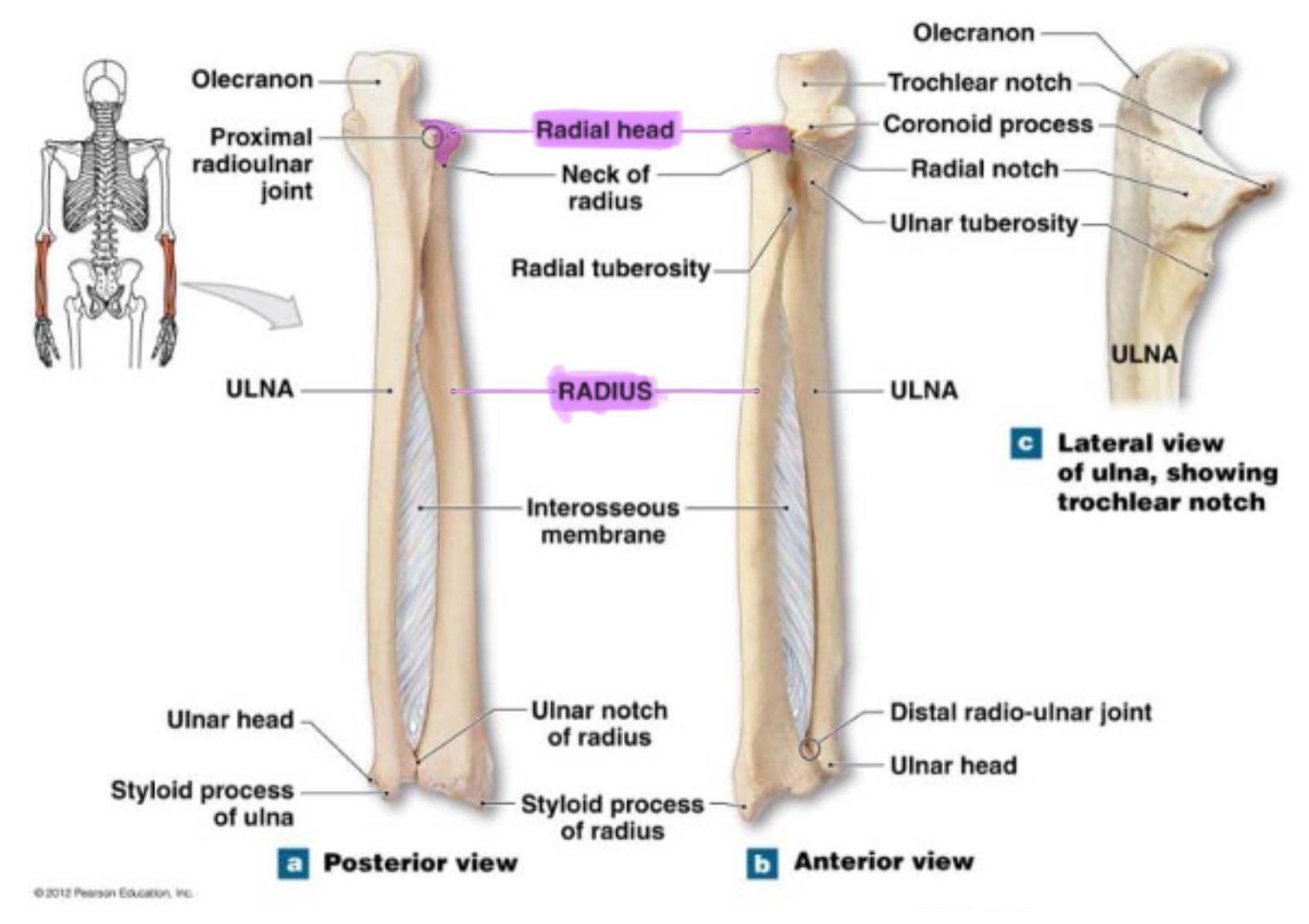
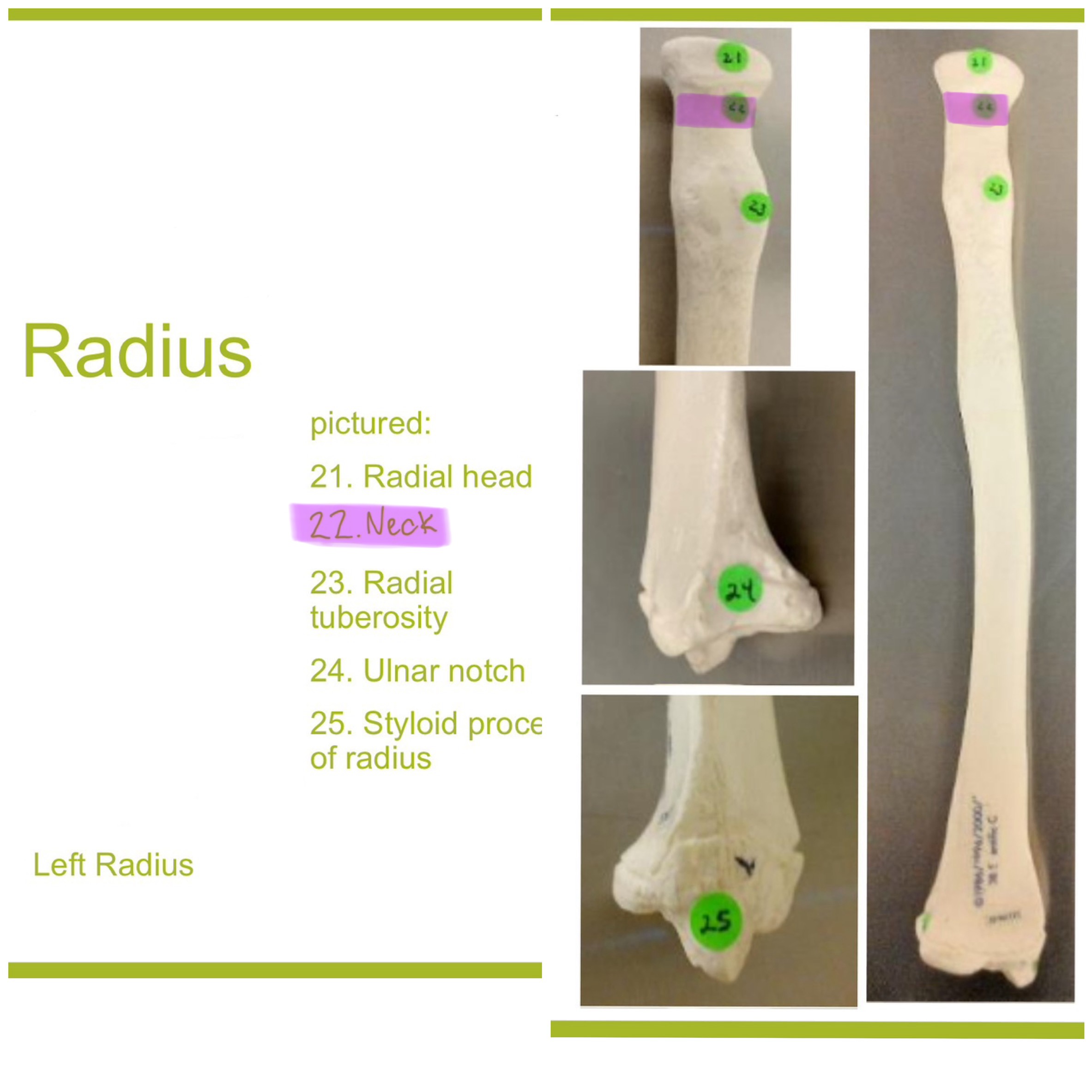
neck of radius
narrow region just below the head; supports the head & serves as a passage for ligaments & muscle attachments
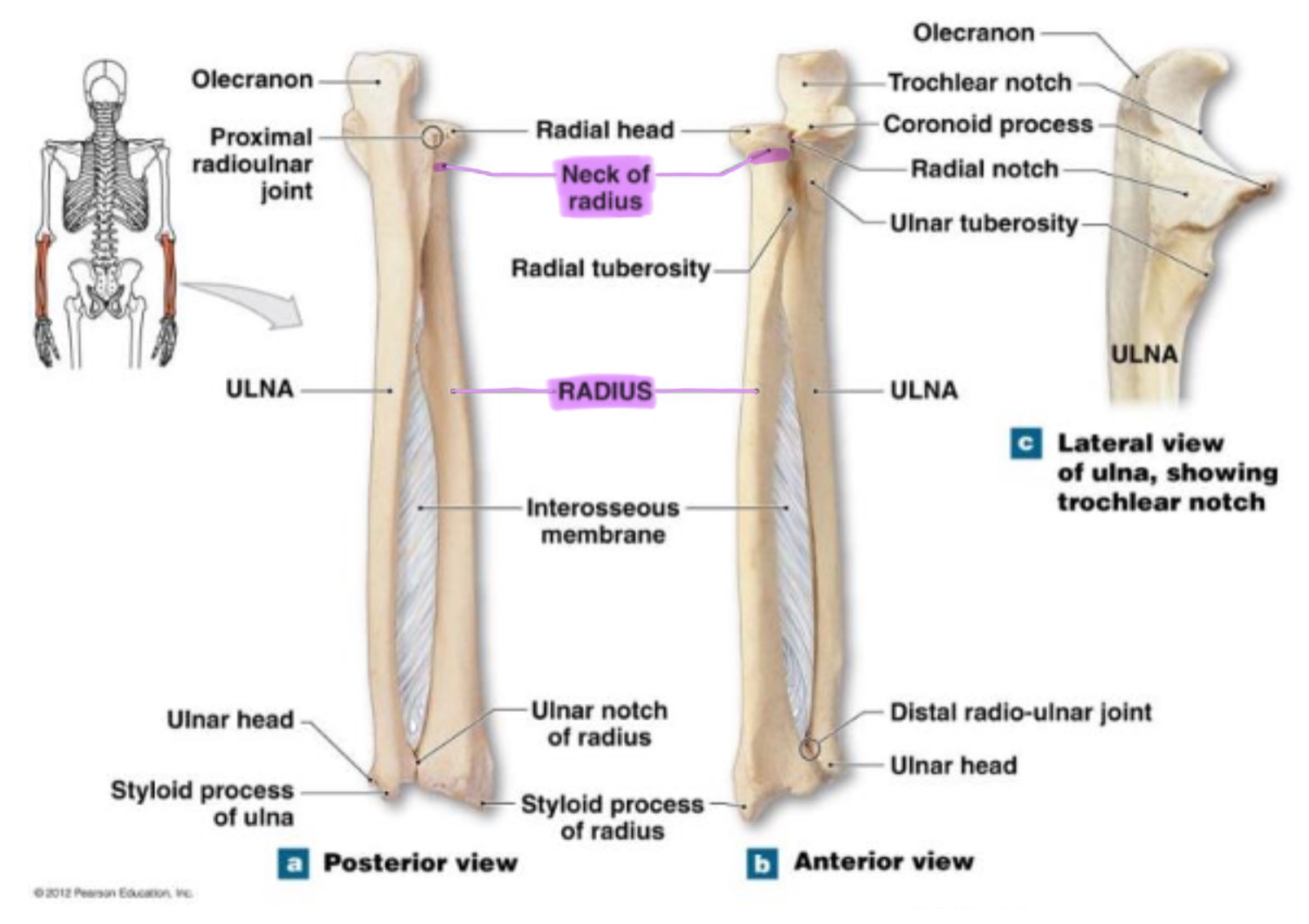
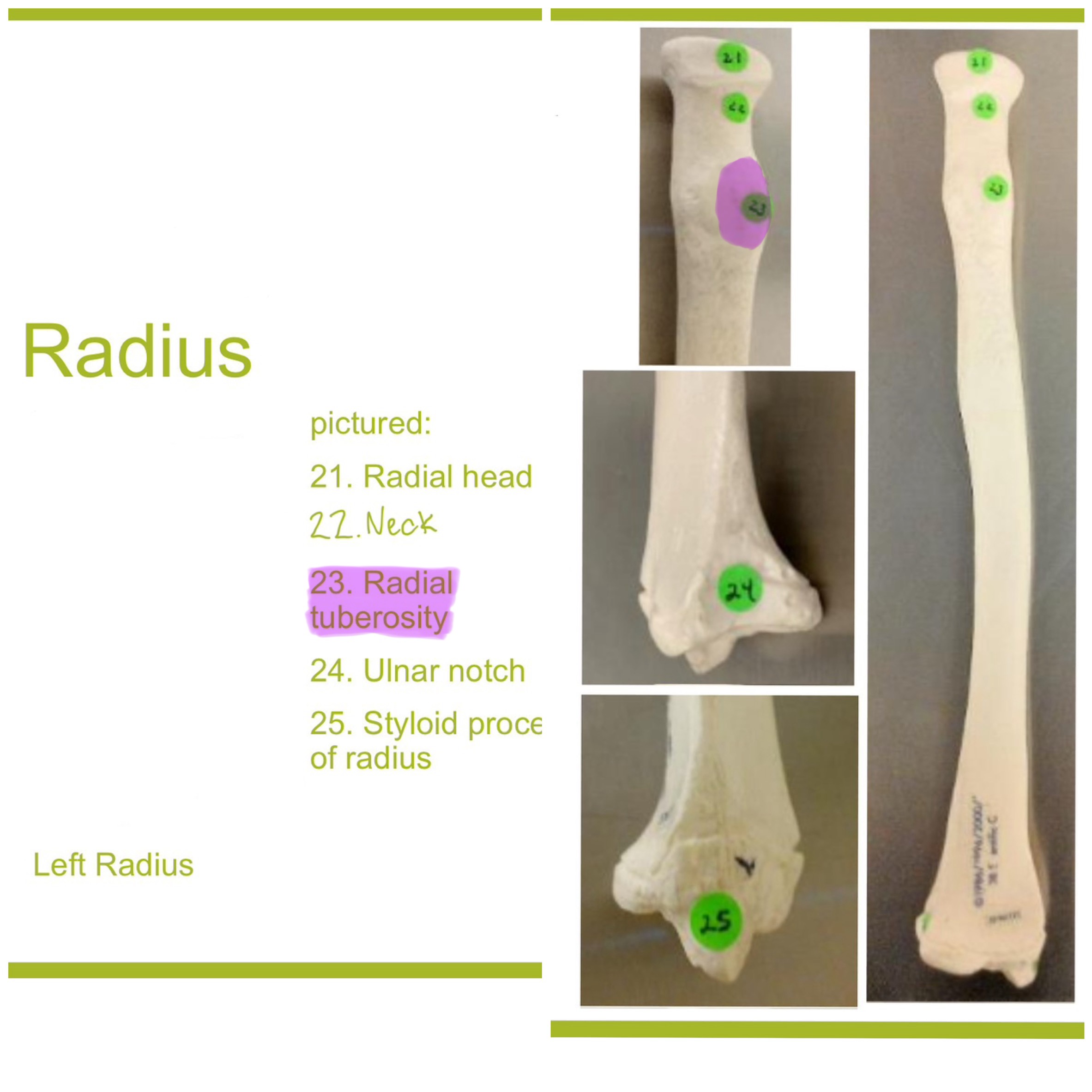
radial tuberosity of radius
rough projection just below the neck of the radius on the medial side; serves as attachment point for biceps brachii muscle
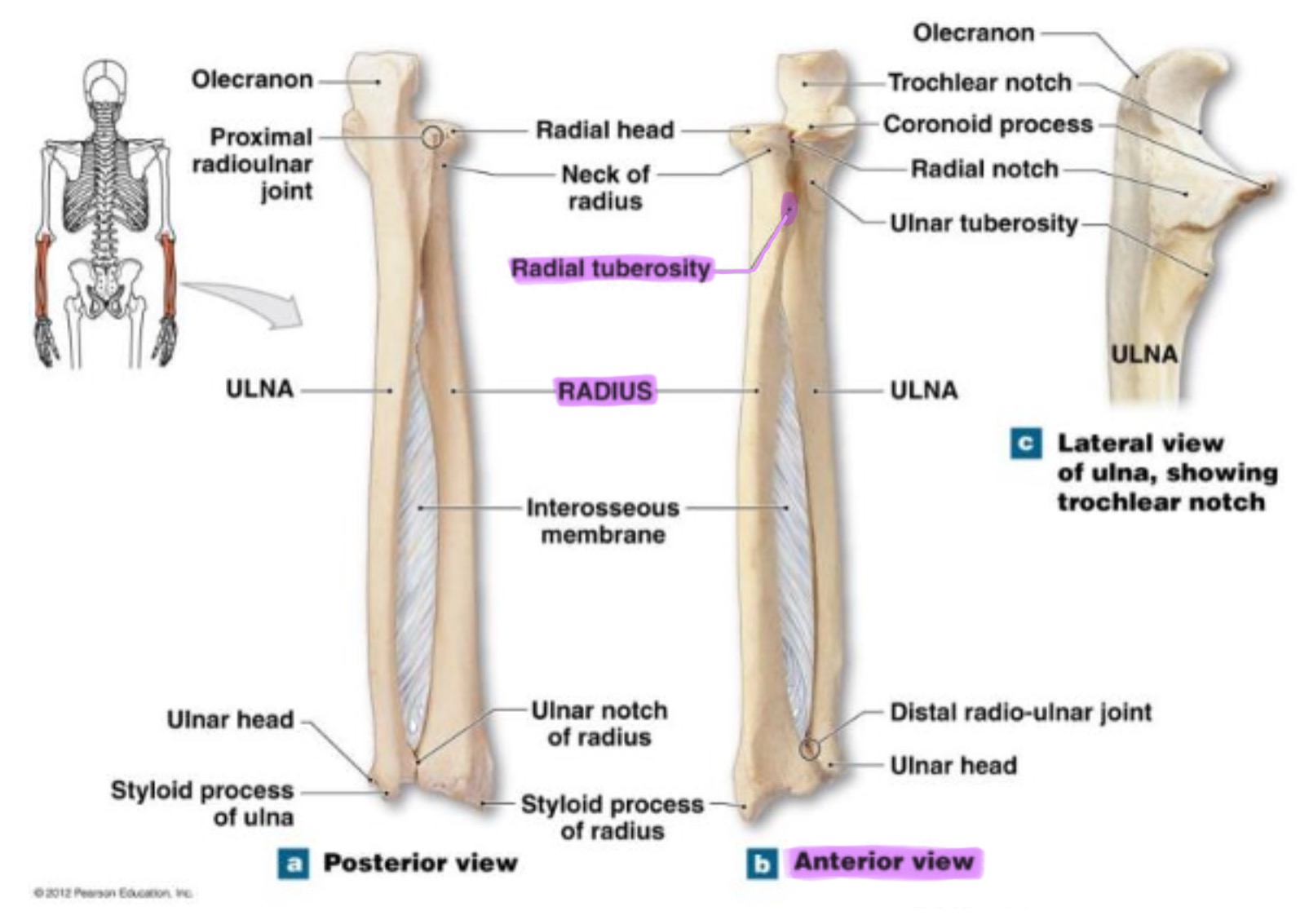
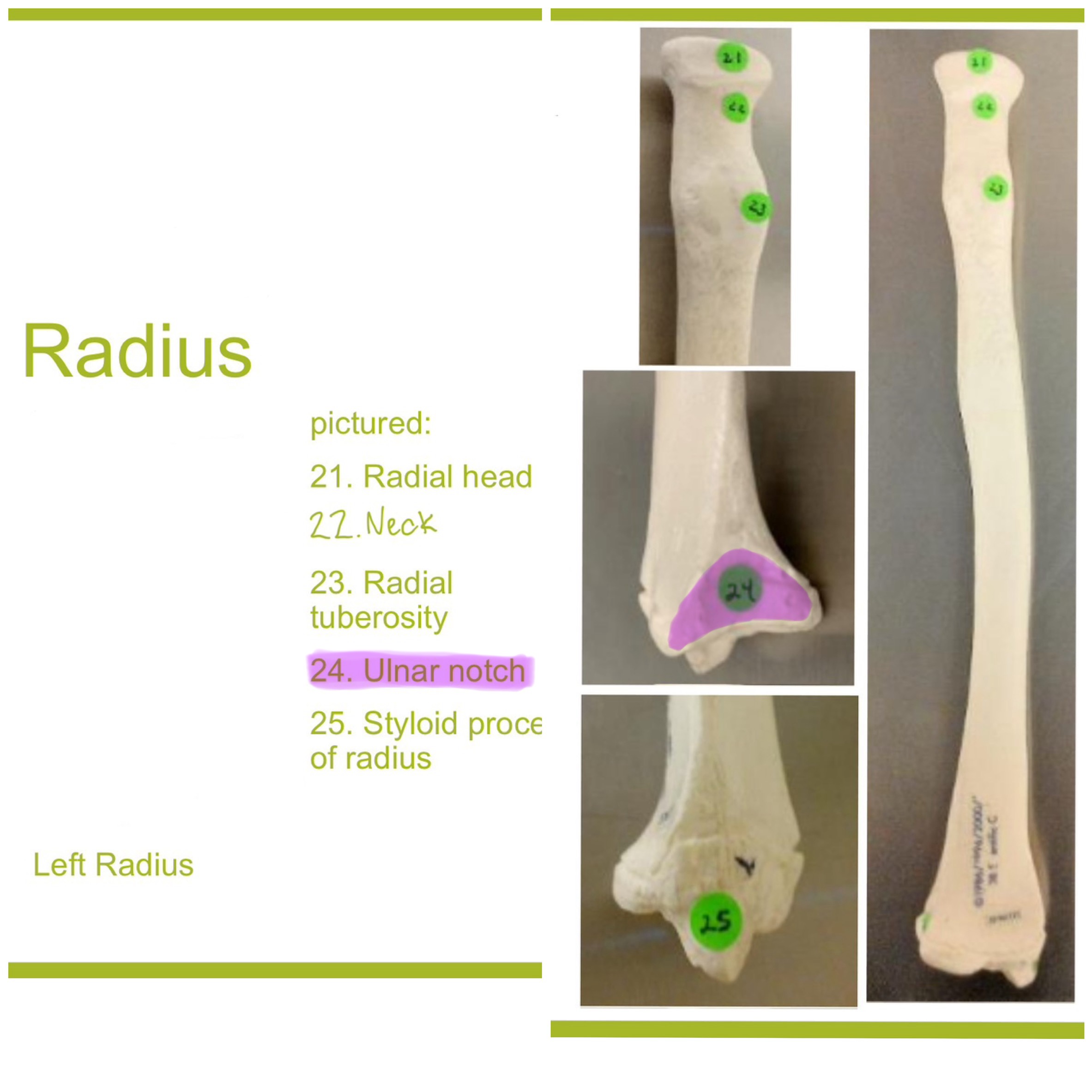
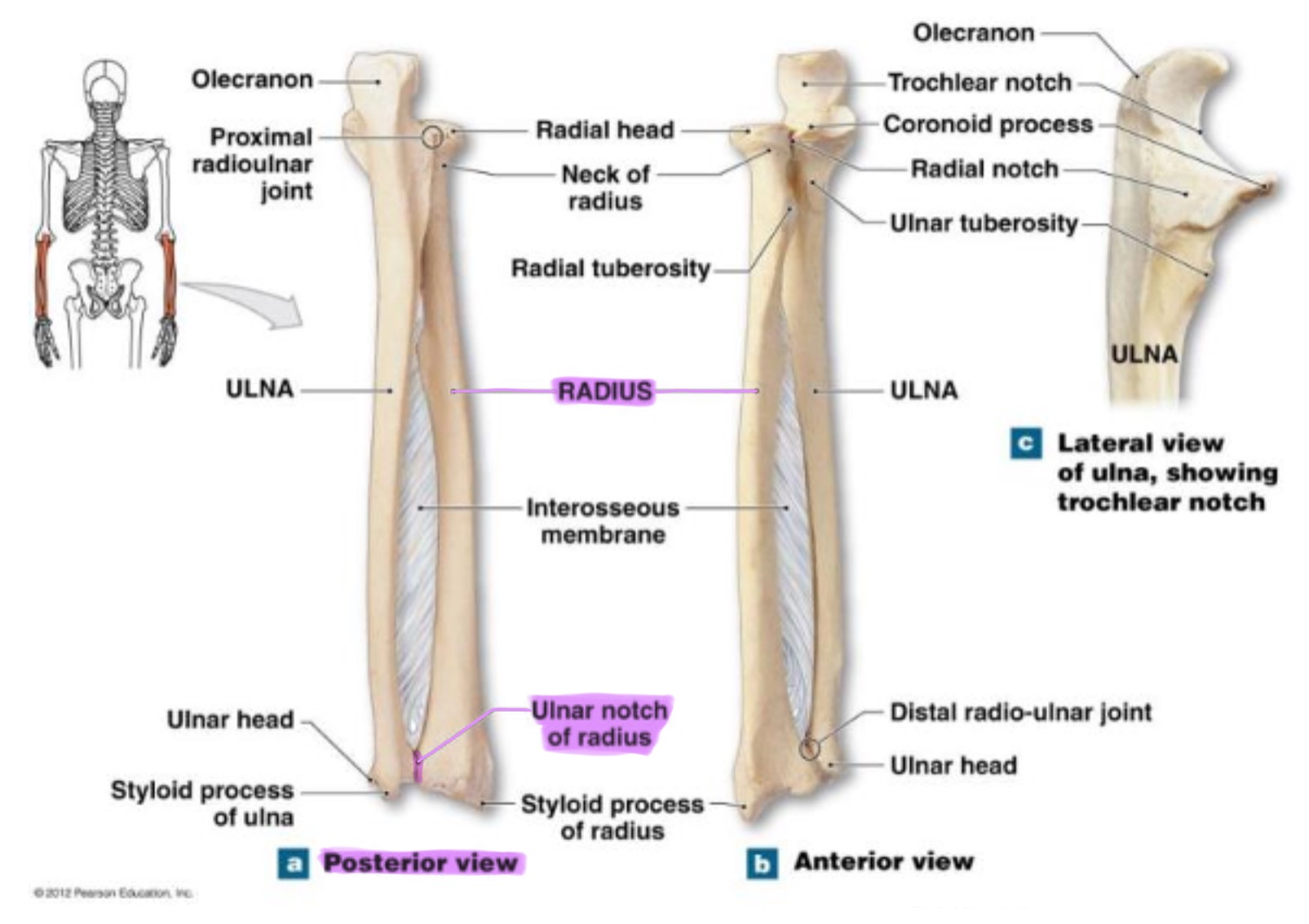
ulnar notch of radius
small depression on distal medial side; articulates w/ head of ulna to form the distal radioulnar joint
carpals
wrist bones, 2 rows of 4 bones each (proximal & distal)
proximal row of carpals
(lateral to medial) scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform
scaphoid
boat-shaped near thumb; articulates w/ radius (most commonly fractured)
lunate
moon-shaped; articulates w/ radius; helps form wrist joint
triquetrum
pyramidal-shaped: articulates w/ the pisiform & ulna (through cartilage)
pisiform
small, pea-shaped on top of triquetrum; serves a sesamoid bone for flexor, corpi ulnaris
distal row of carpals
(lateral to medial) trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate
trapeziUM
articulates w/ 1st metacarpal (thUMB); allows opposition
trapezoid
small bone between trapezium & capitate; articulates with 2nd metacarpal
capitate
largest carpal bone; centrally located;; articulates w/ 3rd metacarpal
hamate
has hook-like projection (hamulus); articulates w/ 4th and 5th metacarpals
Some Lovers Try Positions That They Can’t Handle
Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, Pisiform, Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, Hamate
metacarpals
framework of palm & connect wrist to fingers
metacarpal I
thumb
metacarpal II
index finger
metacarpal III
middle finger
metacarpal IV
ring finger
metacarpal V
little finger
base of metacarpals
proximal end; articulates with carpal bones
shaft (body) of metacarpals
elongated middle portion
head of metacarpals
distal, rounded; articulates w/ proximal phalanges (forms knuckles)
phalanges
finger or toe bones
proximal phalanx
closest to the hand or foot
middle phalanx
in between the proximal and distal phalanx
distal phalanx
finger or toe tip
how many phalanges does the pollex/hallux have?
the thumb/big toe only 2 phalanges
os coxa
fusion of 3 bones (ilium, ischium, & pubis)
ilium
largest, superior piece; supports abdominal organs & provides attachment for trunk and hip muscles
anterior superior iliac spine
anterior projection for muscle & ligament attachment for trunk & hip muscles
iliac crest
upper ridge of ilium; attachmnet for abdominal, back, & thigh muscles (anterior to posterior)
sacroiliac joint
where each os coxae is joined the vertebral column (sacrum)
auricular surface
rough area that articulates w/ sacrum, forming the sacroiliac joint
greater sciatic notch of ilium
large notch below the posterior inferior iliac spine; allows passage of the sciatic nerve
ischium
inferoposterior part of hip bone; supports body weight when sitting
ischial spine
projection for ligament attachment between greater and lesser sciatic notches
lesser sciatic notch of ischium
below ischial spine; allows passage for tendons, nerves, and vessels
ischial tuberosity
thick, rough surface that supports your body when you are sitting; attachment for hamstring muscles
ischial ramus
extends anteriorly to join the pubis; helpsn enclose the obturator foramen
pubis (pubic bone)
inferoanterior portion of the hip bone; nearly horizontal in anatomical position & supports the urinary bladder
inferior & superior pubic ramus
extends laterally to join ischium and contribute to obturator foramen
pubic symphysis
cartilaginous joint between the two pubic bones
pubic angle
angle formed below the pubic symphysis; wider in females for childbirth
acetabulum of os coxa
deep socket where the ilium, ischium, & pubis fuse; articulates w/ head of the fermur to form the hip joint
obturator foramen
large opening formed by the ischium & pubis; allows passage of blood vessels & nerves and mostly closed up by the obturator membrane
femur
longest & strongest bone, ¼ of a person’s height; sends body weight from hip to knee & enables walking, running, or jumping
head of femur
rounded proximal end that fits intop acetabulum to form the hip joint
fovea capitis of femur
a small hole/pit in the head where a ligament attaches femur to acetabulum
neck of femur
narrow region distal to the head, connecting it to the shaft; common fracture site in elderly
greater trochanter of femur
large projection on lateral side; attachment for gluteal muscles
lesser trochanter of femur
smaller projection on medial side; attach for iliopsoas muscle
linea aspera of femur
ridge on posterior shaft; attachment for thigh muscles
lateral and medial condyle of femur
distal surface that articulates w/ tibia at knee joint
intercondylar fossa of femur
deep groove between the condyles on posterior side for ligament attachment
lateral epicondyle of femur
widest points of the femur, easily palpated at the knee; muscle and ligament attachment
patella
roughly triangular sesamoid bone embedded in tendon of the knee; protects knee joints & improves leverage of quadriceps femoris muscle during leg extension