Cellular respiration
1/40
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
How is ATP used in metabolic pathways?
As a link between energy releasing (catabolic) reactions and energy requiring (anabolic) reactions?
How is high energy ATP released and why?
Energy is released quickly for activities required in a cell
What does ATP stand for?
Adenosine TriPhosphate
What does ADP stand for?
Adenosine DiPhosphate
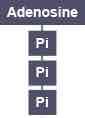
Diagram: ATP

Diagram: ADP
How is energy released from ATP to form ADP + Pi
The final (third) phosphate is broken off to pass energy onto other molecules when a phosphate is added to it
How is energy built-up from ADP + Pi to form ATP?
When chemical energy is released from the break down of food (glucose)
Phosphorylation
When molecules have a phosphate added to them they become energy rich and more reactive, cellular respiration provides the energy for this and ATP turning into ADP + Pi provides the additional phosphate
Example: phosphorylation
When ADP receives an inorganic phosphate from ATP synthase it has become phosphorylated
Cellular respiration
The process of making ATP (energy) which consists of many enzyme controlled steps to ensure energy is released in a controlled manner
Why is ATP built-up?
So supplies of ATP can provide the energy for other biochemical reactions
ATP
This is used to transfer energy to synthetic pathways and other cellular processes where energy is required
Concentration of ATP
ATP is constantly being used and produced in cells, thus the concentration of ATP is relatively balanced at all times
Glucose
An energy rich compound that is the starting substrate for the process of cellular respiration
Basic aerobic respiration equation
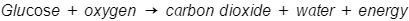
What are the three stages in cellular respiration?
Glycolysis
The citric acid cycle
The electron transport chain
Where does glycolysis occur?
In the cytoplasm
Where does the citric acid cycle occur?
In the (central) matrix of a mitochondria
Where does the electron transport chain occur?
In the inner membrane of a mitochondria
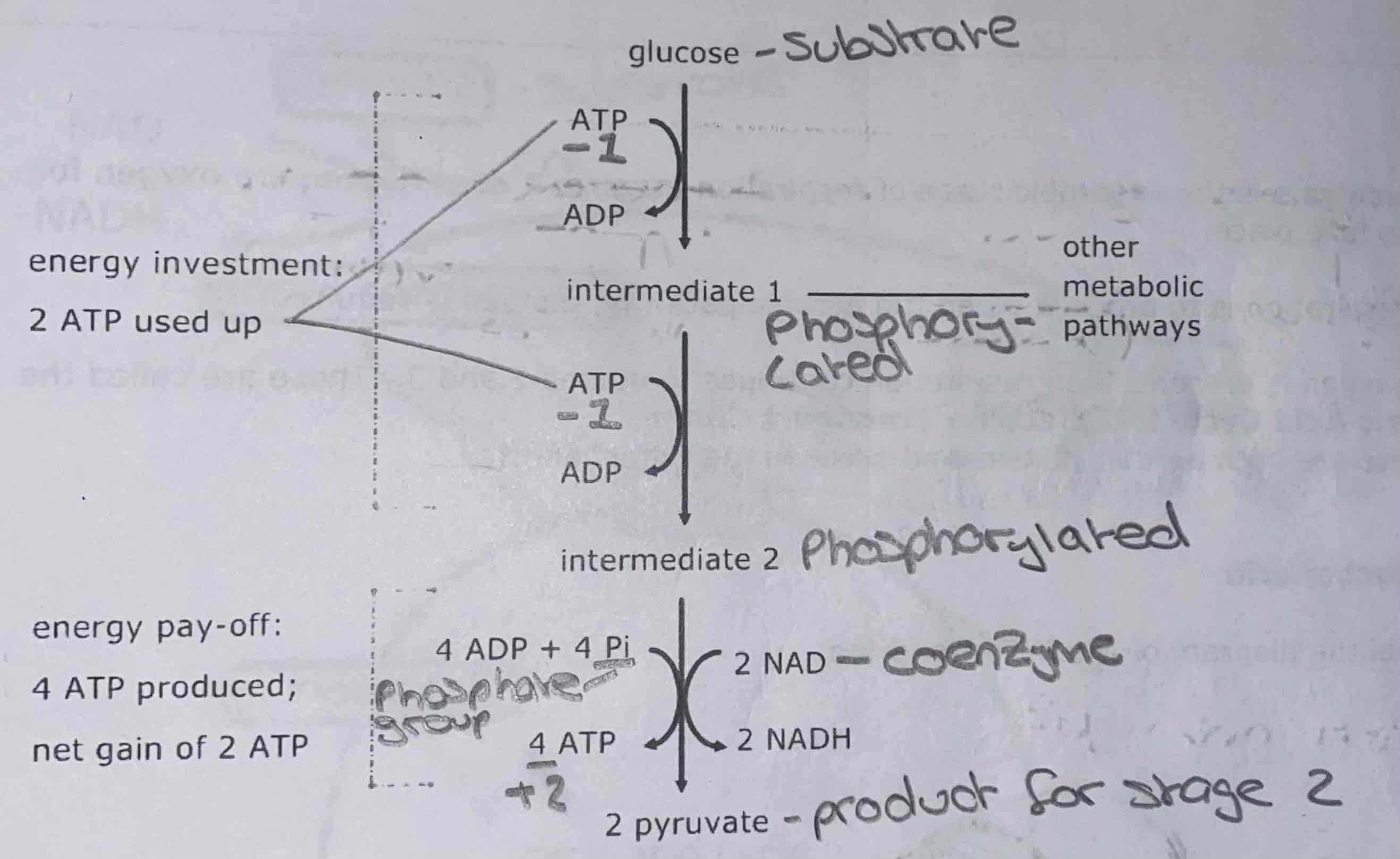
Diagram: glycolysis
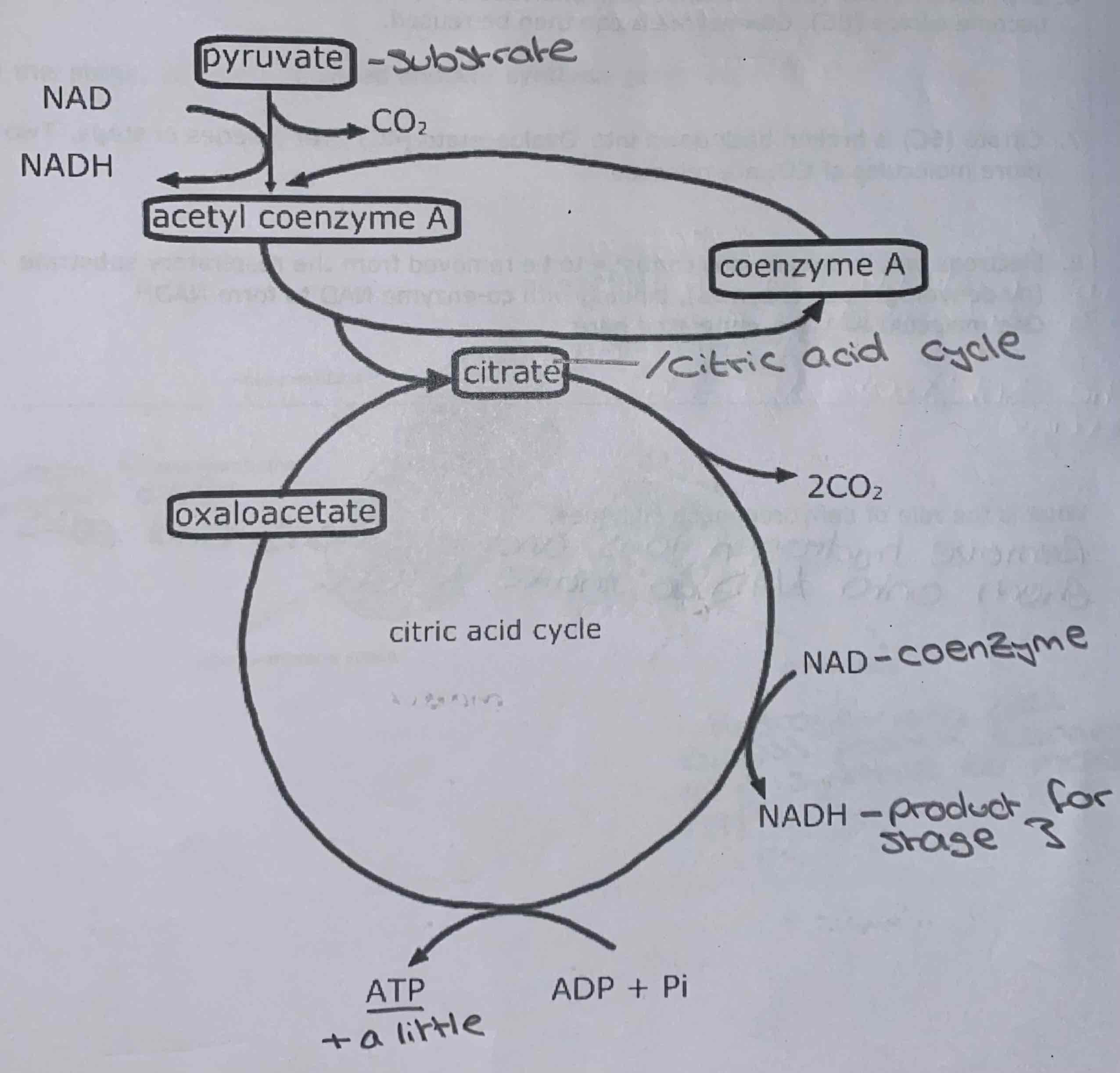
Diagram: the citric acid cycle
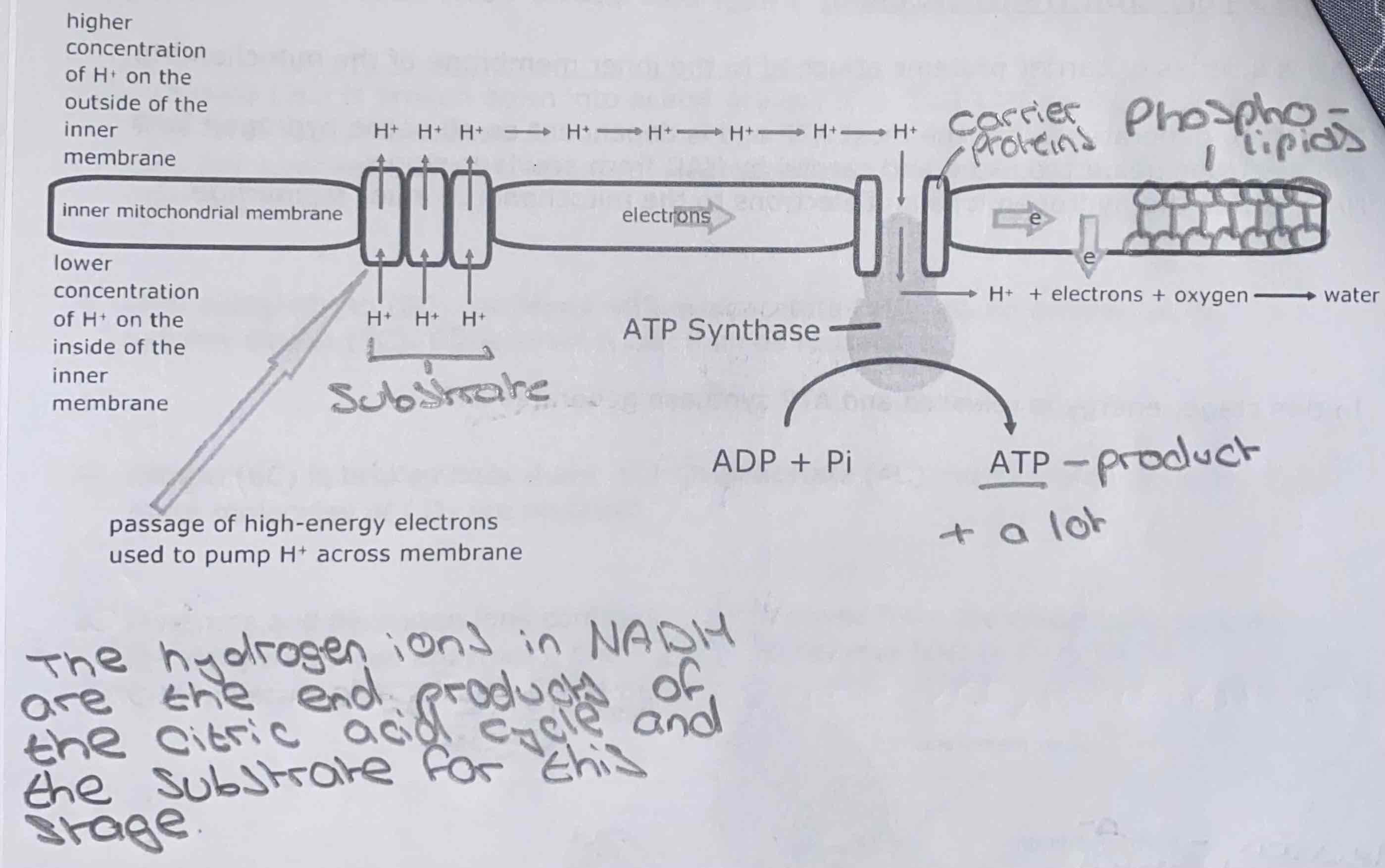
Diagram: the electron transport chain
What stage of cellular respiration is anaerobic?
Glycolysis
What are the two stages of cellular respiration that are aerobic?
The citric acid cycle and the electron transport chain
Aerobic respiration
With oxygen
Anaerobic respiration/fermentation
Without oxygen
What are the two phases of glycolysis?
The energy investment phase and the energy pay-off phase
What are the four stages of glycolysis?
Glucose becomes phosphorylated (gains phosphate from ATP) to form intermediate 1
Intermediate 1 is phosphorylated to form intermediate 2
Four molecules of ATP are generated as intermediate 2 forms two pyruvate molecules
Dehydrogenase (an enzyme) removes hydrogen ions and electrons which combine with the co-enzyme (hydrogen carrier) NAD to form NADH
What are the four stages of the citric acid cycle?
Pyruvate is broken down into acetyl group. This combines with coenzyme A to form acetyl coenzyme A
Each acetyl group combines with oxaloacetate, via co-enzyme A, to become citrate. Co-enzyme A can then be reused
Citrate is broken back down into oxaloacetate over a serious of steps. Two more molecules of carbon dioxide are released
Hydrogen ions and electrons continue to be removed from the respiratory substrate (by dehydrogenase enzymes), binding with co-enzyme NAD to form NADH. One molecule of ATP is generated here
What are the three stages of the electron transport chain?
Electrons are passed along the electron transport chain releasing energy that is used to pump hydrogen ions across the inner membrane of the mitochondria
The hydrogen ions then return (passively) to the matrix through the membrane protein - ATP synthase, causing it to rotate. It is the rotation of this protein that catalyses the synthesis of many molecules of ATP
The hydrogen ions and electrons are now in a low energy state and these combine with a molecule of oxygen. Oxygen is the ‘final hydrogen and electron acceptor’ in this chain - combining to form water
What is required for cellular respiration to proceed after glycolysis?
Oxygen
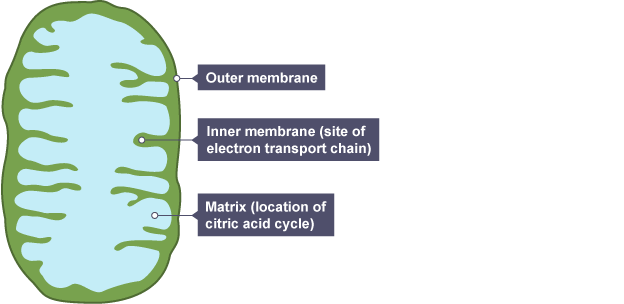
Diagram: structure of a mitochondria
Dehydrogenase enzymes
These remove hydrogen ions and electrons and pass them onto the coenzyme NAD
NAD
A coenzyme used to carry hydrogen ions and electrons to form NADH
NADH
A coenzyme used to carry hydrogen ions and electrons to the electron transport chain where they will be released at the beginning as a substrate
Basic anaerobic respiration (fermentation) equation in animals
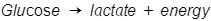
Basic anaerobic respiration (fermentation) equation in plants
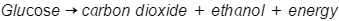
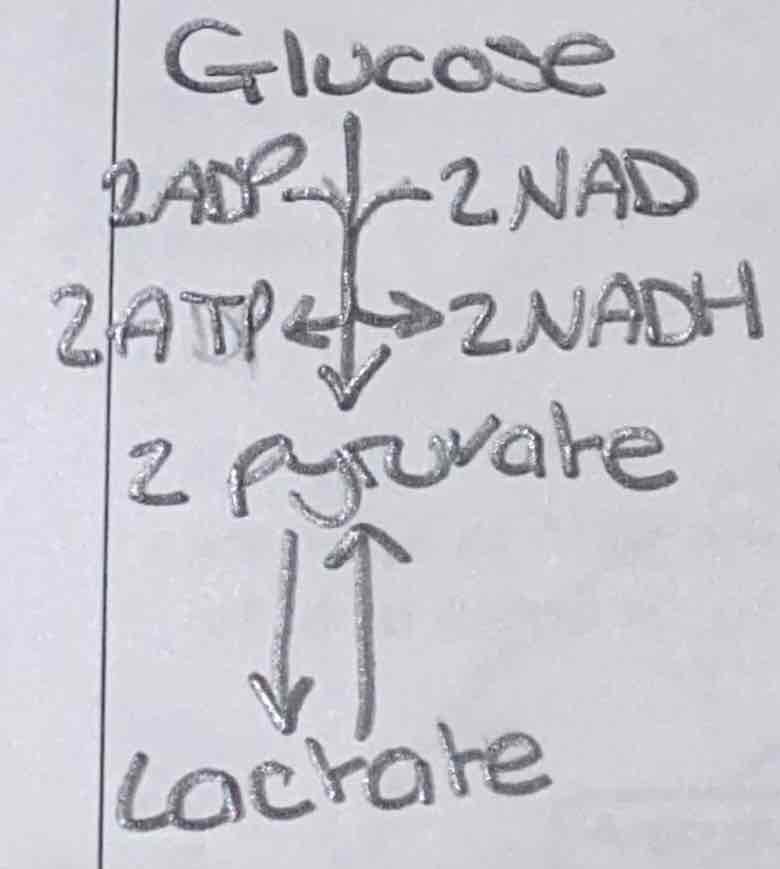
Diagram: anaerobic respiration (fermentation) in animals
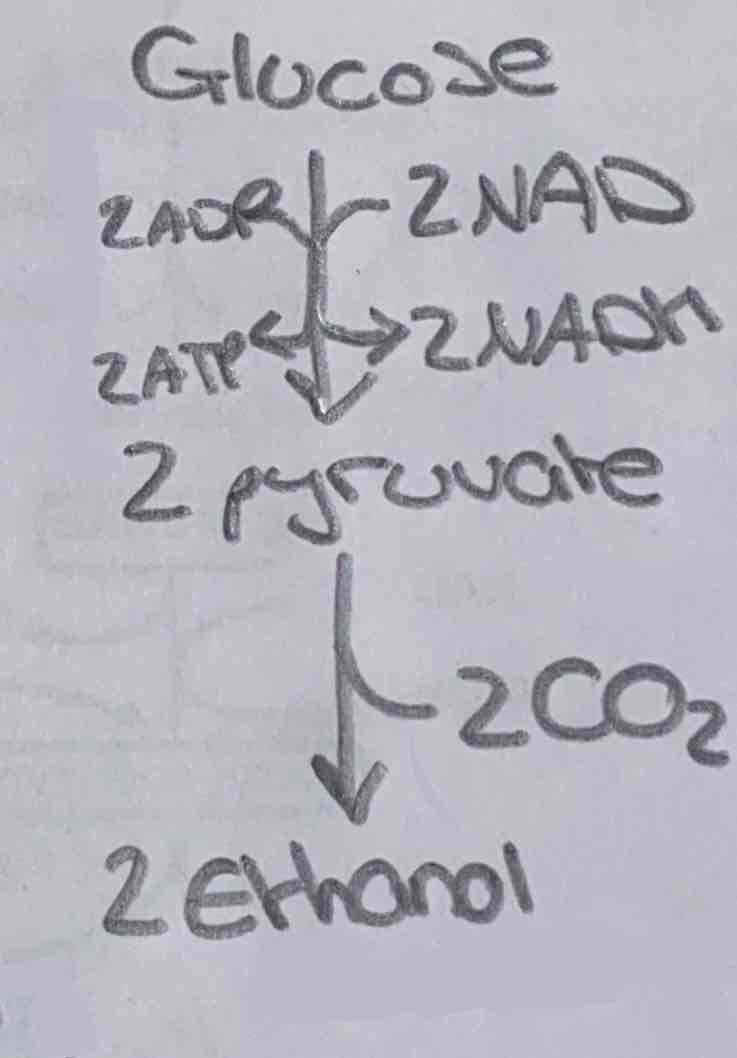
Diagram: anaerobic respiration (fermentation) in plants
Oxygen
The final hydrogen ion acceptor