exam #1 - intro molecular lab (cls 607)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
preventing contamination in the lab
Surface decontamination—ethanol in, bleach out
Nucleases
Sterile technique
Reagent handling
Barrier tips for pipettors
Separation of pre- and post- amplification areas
basic ingredients in gels for electrophoresis (3)
Agarose
Buffer
Ethidium bromide
how much agarose (%age) should be put in a gel?
Percentage of agarose used in gel depends on what size of DNA fragments you are interested in
Small fragments = larger percentage
Large fragments = smaller percentage
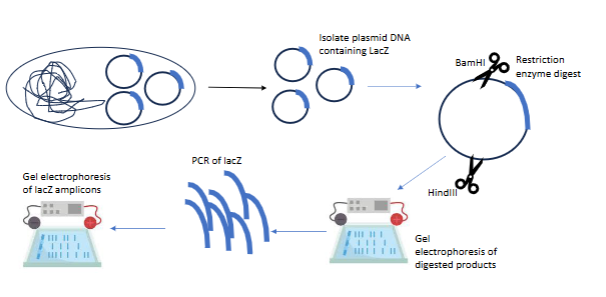
pCLS01/lacZ experiment steps
Isolate plasmid w lacZ gene
Restriction enzymes to cut specific section of plamid
Gel electrophoresis to see if the enzymes cut/worked
PCR of the actual lacZ gene/DNA
Gel electrophoresis of the lacZ amplicons to see if any DNA was amplified
how to use a nanodrop to find DNA yield and purity
Nanodrop: spectrophotometer used to find the concentration of DNA, RNA, or protein in a 2 ul drop of sample
Nucleic acids absorbance max at 260 nm
For DNA, a 260/280 ratio of 1.8 is considered pure
Low 260/280 ratios can indicate contamination with guanidine, phenol, or other reagents used in extraction
DNA quality and the nanodrop
must compare with DNA ladder to see if the DNA is the one we want
cannot tell if the product is digested or not (digested DNA absorbs at the same wavelength as undigested DNA)
only able to assess QUANTITY & PURITY
restriction enzymes
enzyme isolated from bacteria that cuts DNA at specific sequences
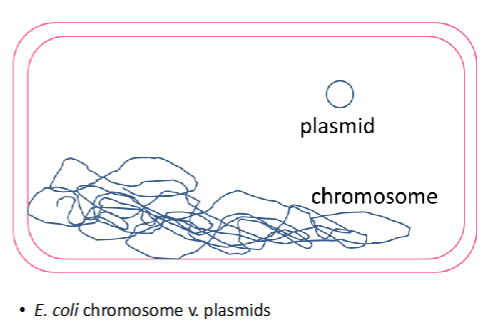
structure of plasmids vs bacterial chromosomes
plasmids are supercoiled ; denatured supercoiled plasmids are like interlocking rings
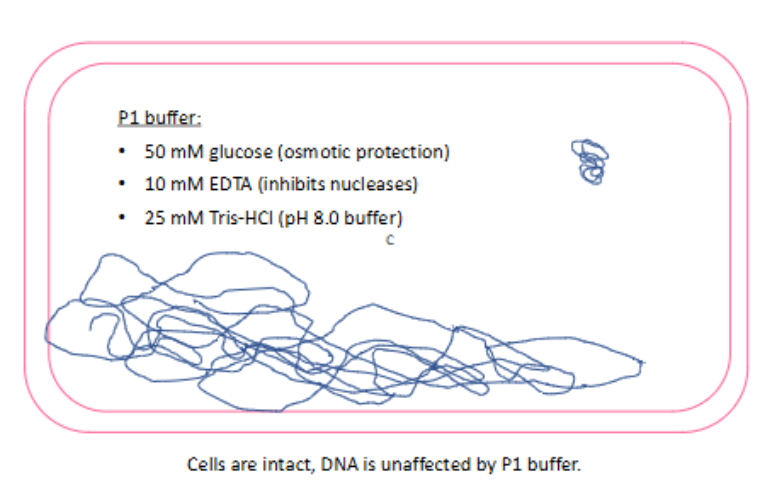
(plasmid DNA extraction by alkaline lysis) alkaline lysis w P1 buffer
cells are intact & DNA is unaffected by P1 buffer
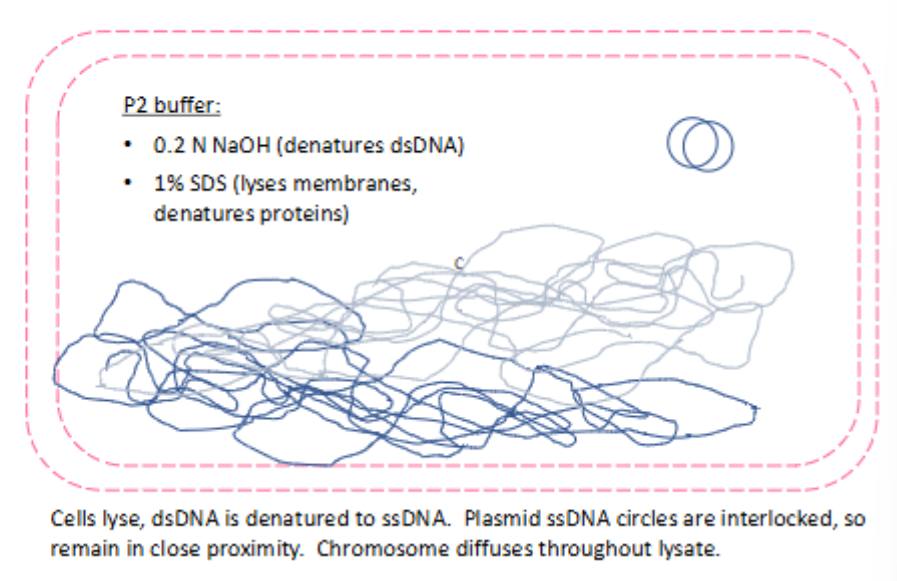
(plasmid DNA extraction by alkaline lysis) alkaline lysis w P2 buffer
cells lyse
dsDNA is denatured to ssDNA
plasmid ssDNA circles are interlocked, so they remain in close proximity
chromosome diffuses throughout lysate
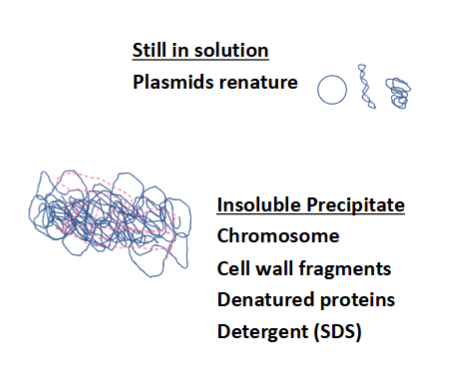
(plasmid DNA extraction by alkaline lysis) alkaline lysis w N3 buffer
5M K acetate
plasmids renature in the solution
insoluble precipitate includes: bacterial chromosome, cell wall fragments, denatured proteins, detergent (SDS)
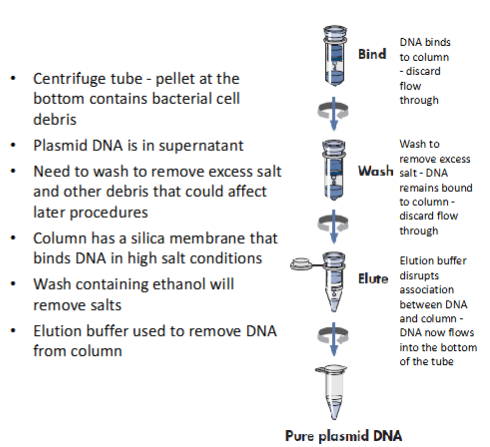
(plasmid DNA extraction by alkaline lysis) extraction step
centrifuge tube—bottom will now contain bacterial cell debris (discard); DNA is bound to the column
plasmid DNA is in the supernatant
wash to remove excess salt—DNA is still bound to the column
column has silica membrane that binds DNA in high salt conditions
wash again w ethanol to remove salts
elute w elution buffer—disrupts association between DNA and column
plasmid DNA now flows into bottom of the tube
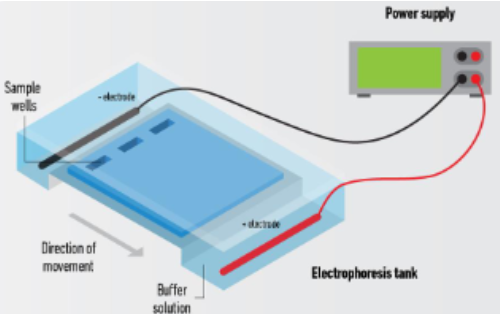
gel electrophoresis
A technique used to separate DNA fragments by size
DNA is negatively charged; therefore, it will move toward the positively charged anode (+) when an electric current is applied to the gel
Gel electrophoresis uses three main ingredients:
Agarose
Buffer (usually TBE or TAE)
Ethidium bromide
(gel electrophoresis) agarose
When dissolved in buffer and then cooled, it will form a gel with a network of pores
Small fragments of DNA can move more easily through the pores, so they will move through the gel faster than larger fragments
Percentage of agarose depends on size of fragments to be separated (usually ranges between 0.5% and 2%)
Large fragments = use SMALLER percentage
Small fragments = use LARGER percentage
(gel electrophoresis) buffer
Main purpose is to carry the charge and maintain the pH during the run
TBE = Tris-borate-EDTA
TAE = Tris-acetate-EDTA
Tris acid keeps DNA deprotonated & soluble
EDTA chelates magnesium ions which are often cofactors for nucleases
TAE lowers buffering capacity, TBE has borate which may inhibit downstream enzymes
(gel electrophoresis) ethidium bromide
Intercalates between base pairs and fluoresces upon exposure to UV light
Visualization of DNA product
(gel electrophoresis) components of loading the gel
DNA ladder: solution comprised of different fragments of DNA of known lengths, may already by mixed with a loading buffer
Loading buffer: has glycerol which helps DNA sink to bottom of well & has tracking dye which helps visualize progression of gel electrophoresis run

what is wrong with the image?
electrophoresis will run off the gel ; DNA migrates in direction of the anode (+)
(gel electrophoresis) voltage for running a gel
In general, 10 volts for every cm between cathode and anode
Voltage too high = overheat gel
Voltage too low = poor resolution
Run time = depends on size of gel and voltage; keep an eye on tracking dye location to ensure DNA does not run out the end of the gel

polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
laboratory technique used to make a huge number of copies of DNA from a small starting quantity
(PCR ingredients) template & nucleotide mix
Template DNA: DNA containing the sequence you are trying to amplify
Nucleotide mix: building blocks of DNA
(PCR ingredients) primers (2)
Forward primer (5’→3’): short DNA sequence complementary to MINUS strand (3'→5')
Reverse primer (3’→5’): short DNA sequence complementary to PLUS strand (5'→3')
(PCR ingredients) buffer & Taq polymerase
Buffer: provides optimal environment for Taq pol
Taq polymerase: heat stable enzyme that amplifies DNA
PCR steps
Pre-amplification step if using hot-start Taq
Amplification cycles:
Denature: time and temp depends on template--usually between 94-98 degrees for 0.5-2 mins
Anneal: temp dependent on primer pair (usually about 5 degrees below Tm) for 0.5-1 mins
Extension: temp depends on what polymerase you are using (usually about 72 degrees) & depends on template and polymerase (usually 1 min/kb)
Repeat above usually 30 times
what happens if you run too few PCR cycles? too many cycles?
Too few cycles = not enough product
Too many cycles = increased chances for nonspecific amplification and errors
considerations when setting up PCR reactions
Use thin walled 0.2 mL PCR tubes
Pipette water first
Dispense reagents into bottom of tube
Pipette up and down gently to mix, NO VORTEXING
Centrifuge briefly to ensure all reagents are in the bottom of the tube
preferred blood tubes for molecular testing
EDTA (lavender)
ACD (yellow)
human DNA extraction
Works based on binding of DNA to silica membrane
First step: lyse cells to release DNA
Protease K used to break down interfering proteins
Buffers used to generate correct conditions for optimal binding to column
Washes help remove additional contaminants
factor V leiden thrombophilia
inherited blood clotting disorder
Factor V is converted to Va which interacts with Factor X to convert prothrombin to thrombin
Activated Protein C inactivates Factor Va
Mutation of Factor V in codon 506 inhibits the ability of APC to inactivate Factor Va
Heterozygous individuals = 7x greater risk of clots
Homozygous individuals = 80x greater risk of clots
(FVL) PCR-RFLP
RFLP: differences in DNA sequences at sites recognized by restriction enzymes
Normal individuals: two MnII sites, when you cut their DNA you get three bands
FVL homozygotes: missing one MnII site, when you cut their DNA you get two bands
Heterozygotes: also three bands but of different sizes than the normal individual
master mix for PCR
mix all the ingredients for multiple PCR reactions (except for DNA) into a tube
Less pipetting = less chance for error
Because it is difficult to pipette exactly, typically want to take the amount you need for all your reactions and then add one
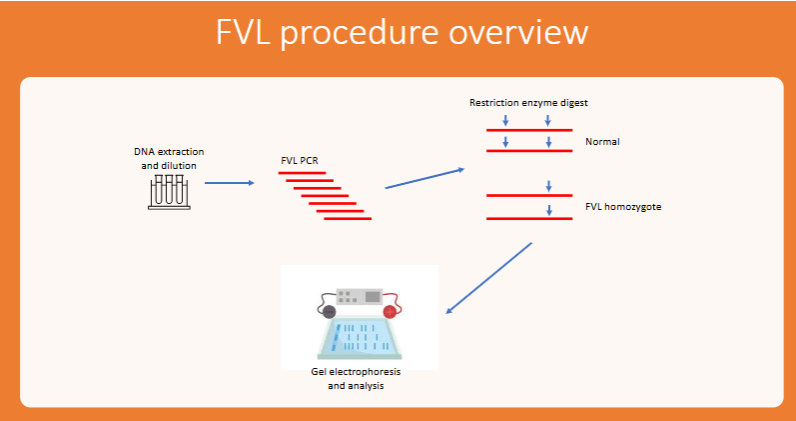
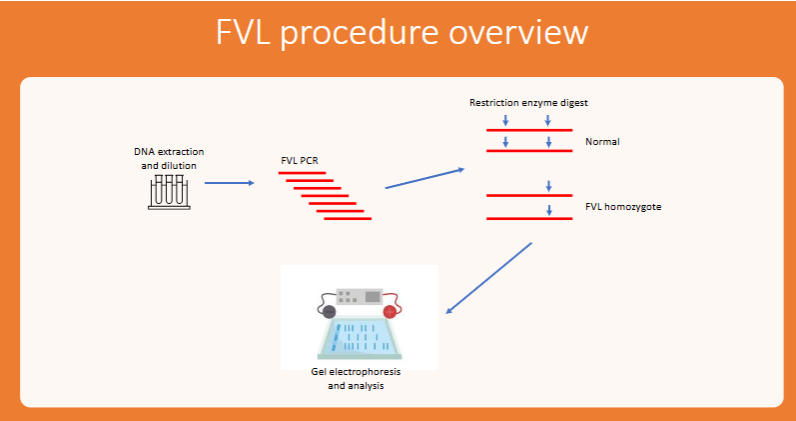
general procedure for FVL
DNA extraction
PCR of human DNA
Restriction enzyme digest of FVL PCR product
Run on gel electrophoresis
Analyze
normal FVL digest products
3 bands: 180 bp, 81 bp, & 35 bp
FVL homozygote gene products
2 bands: 143 bp & 81 bp
missing Mnl I restriction site
FVL heterozygote gene products
4 bands: 143 bp, 108 bp, 81 bp & 35 bp