B244 Comprehensive Health Assessment Exam 3
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
what are the three main structures within the thorax/chest?
1. mediastinum
2. right pleural cavity
3. left pleural cavity
mediastinum
area between the lungs containing the heart, aorta, venae cavae, esophagus, and trachea
pleural cavities
contain the lungs
what are the two types of serous membranes that line the cavities?
1. parietal pleurae
2. visceral pleurae
how many lobes does the right lung have?
3 lobes
how many lobes does the left lung have?
2 lobes
what are the three parts of the sternum?
1. manubrium
2. sternum
3. xiphoid process
intercostal space
the space between two ribs
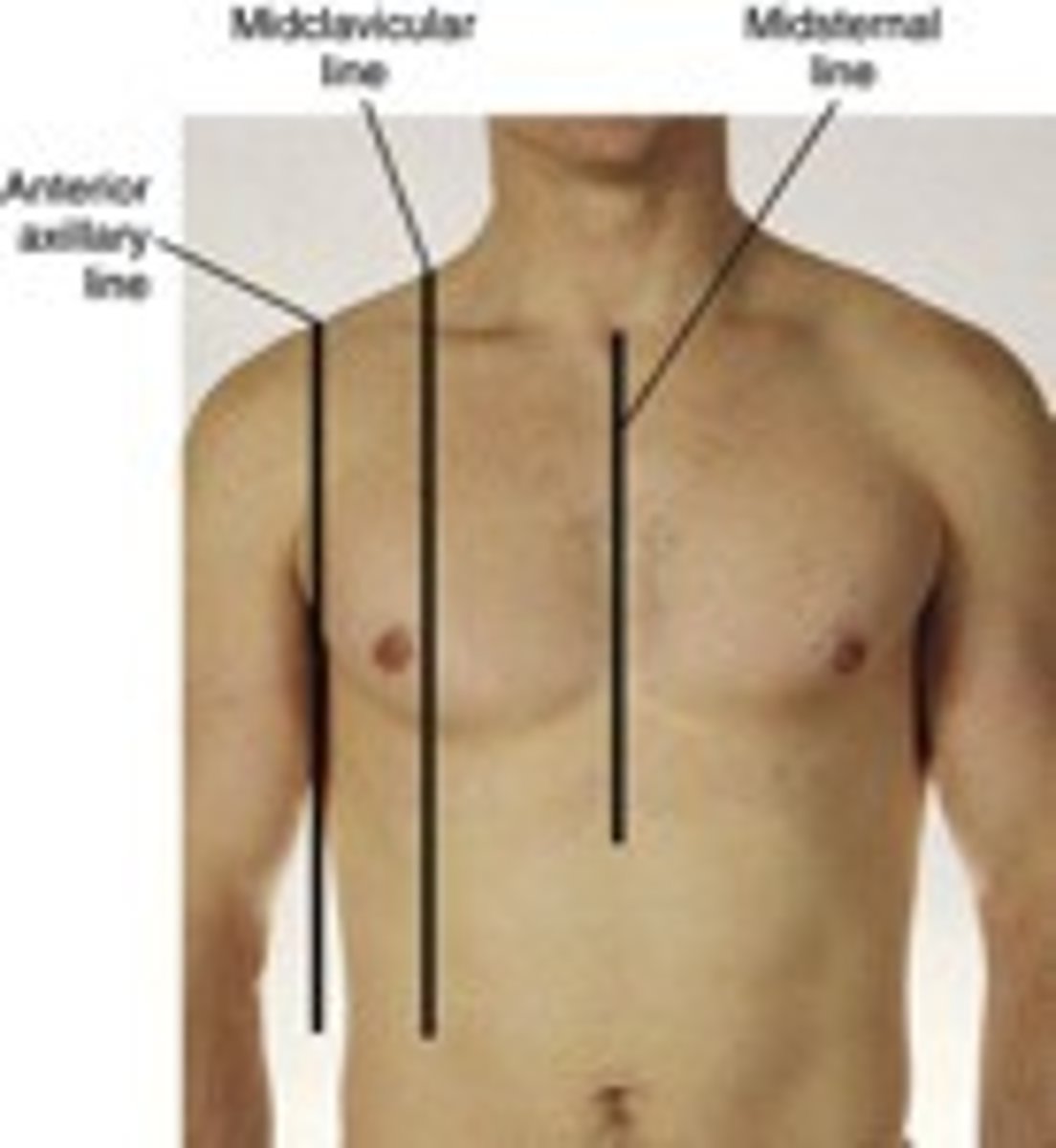
midsternal line
a vertical line down the middle of the sternum
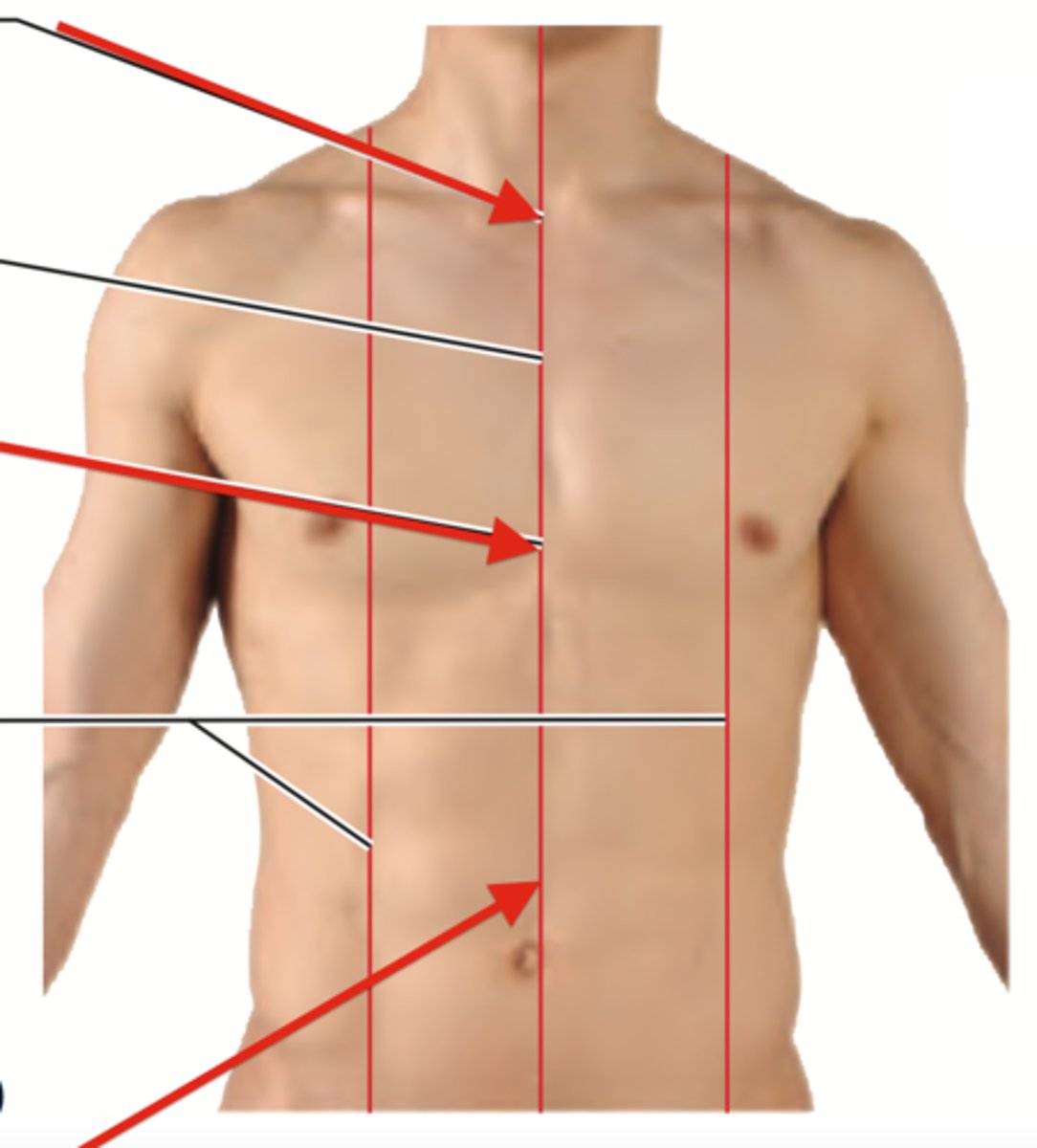
midclavicular line
imaginary vertical line bisecting the middle of the clavicle in each hemithorax
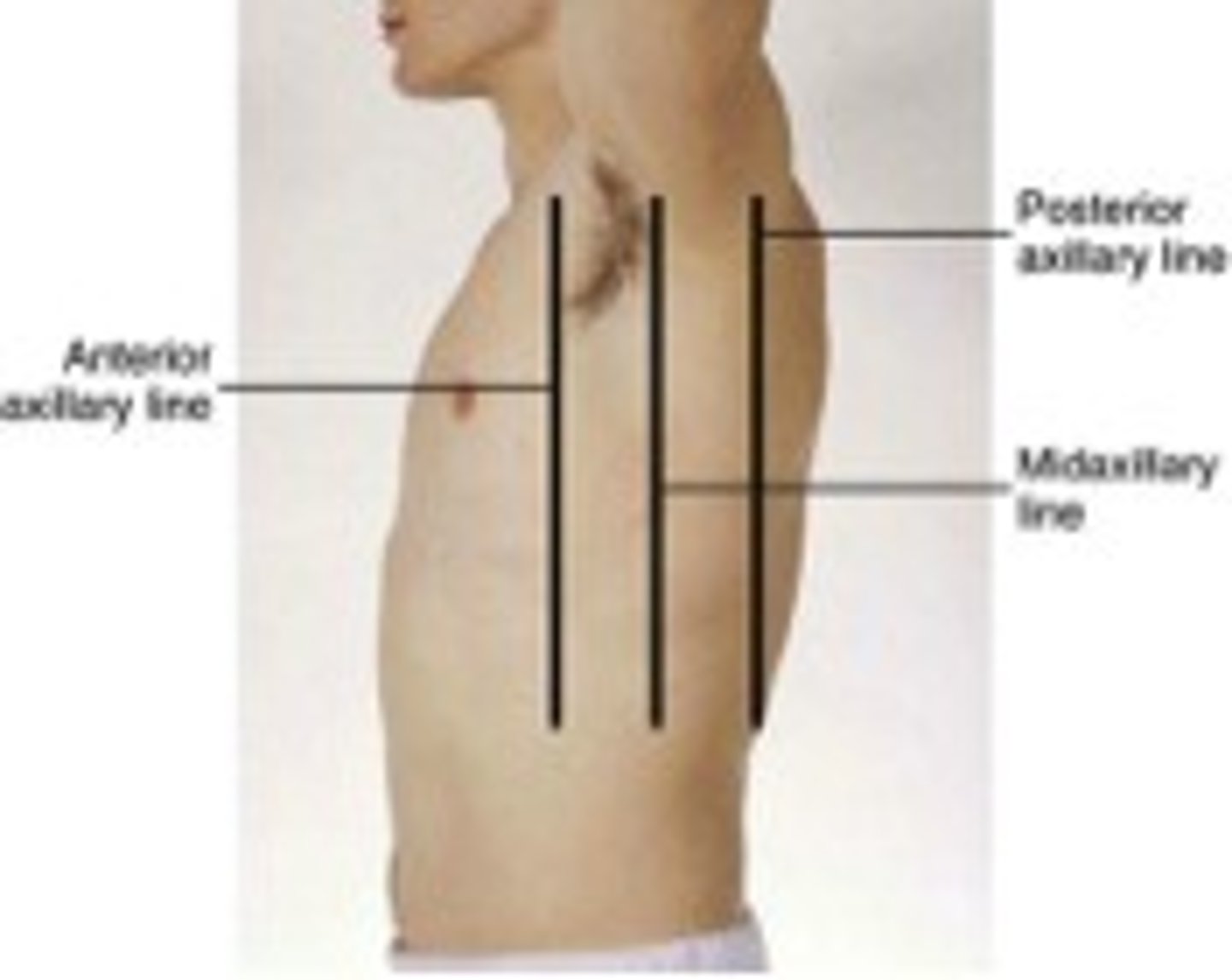
anterior axillary line
a line that is parallel to the mid-axillary line and passes through the anterior axillary skinfold
midaxillary line
An imaginary vertical line that starts at the middle of the axilla (armpit) and extends down the side of the chest.
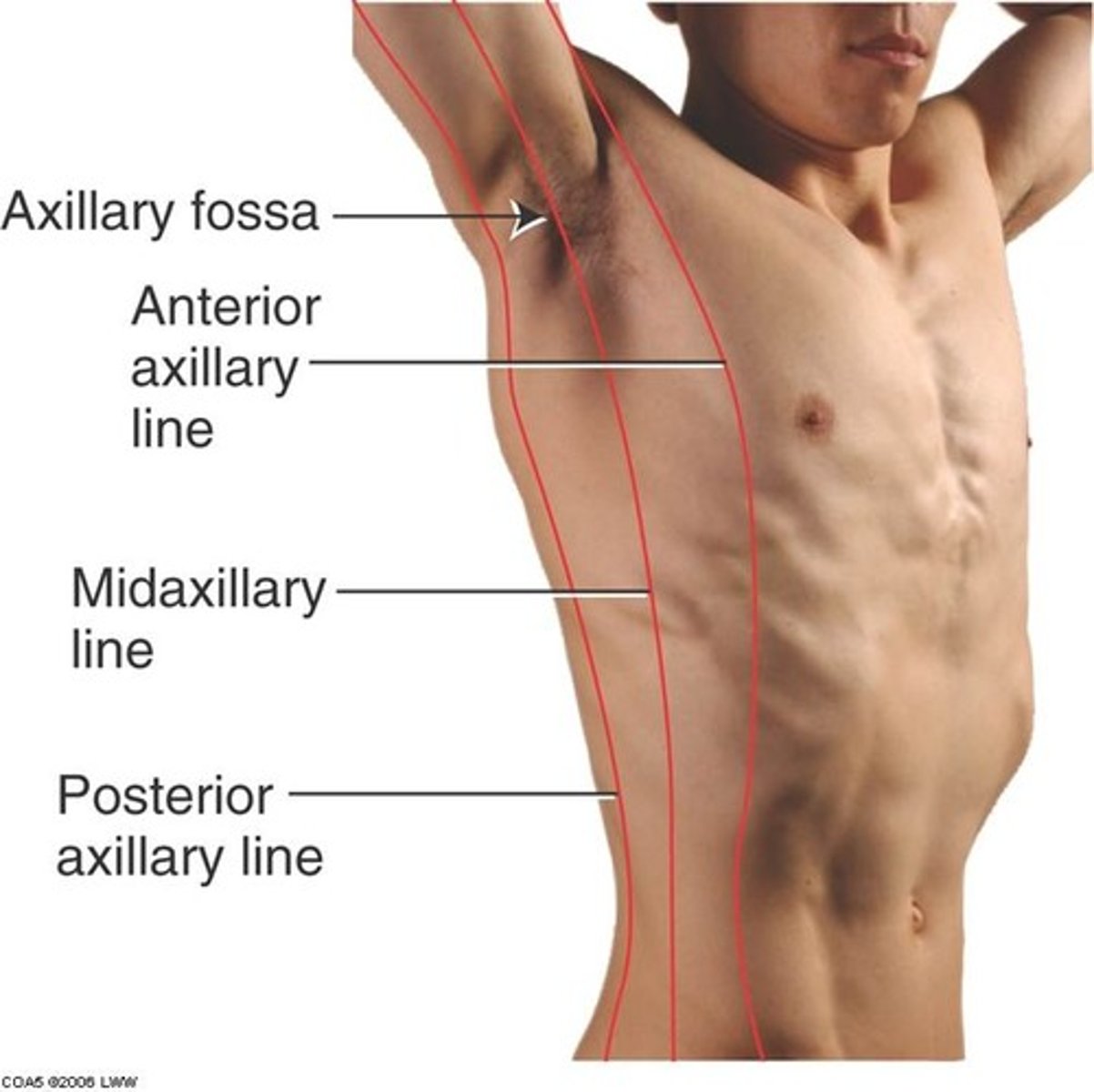
posterior axillary line
a line that is parallel to the mid-axillary line and passes through the posterior axillary skinfold
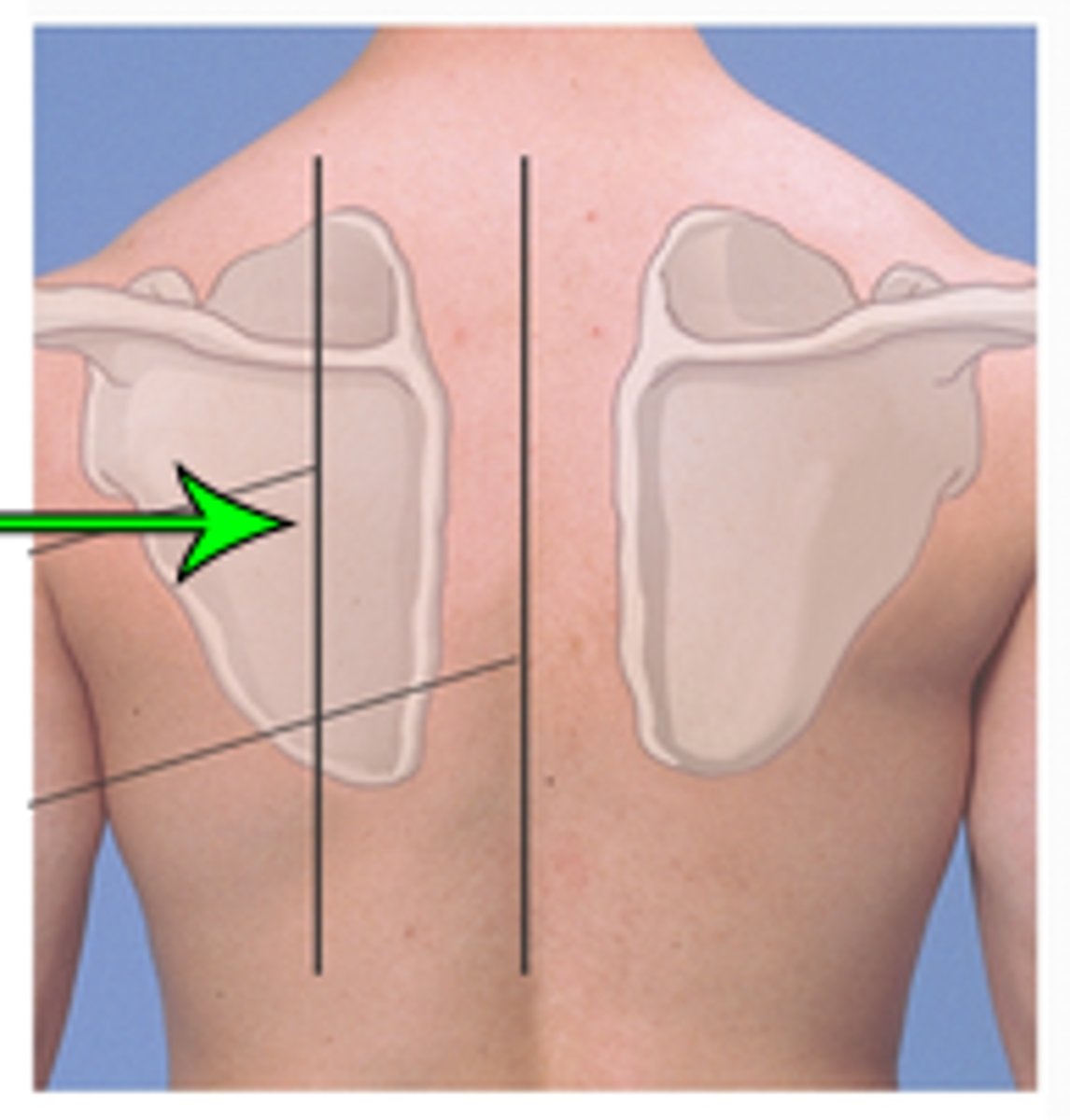
scapular line
extends through the inferior angle of the scapula when the arms are at the sides of the body
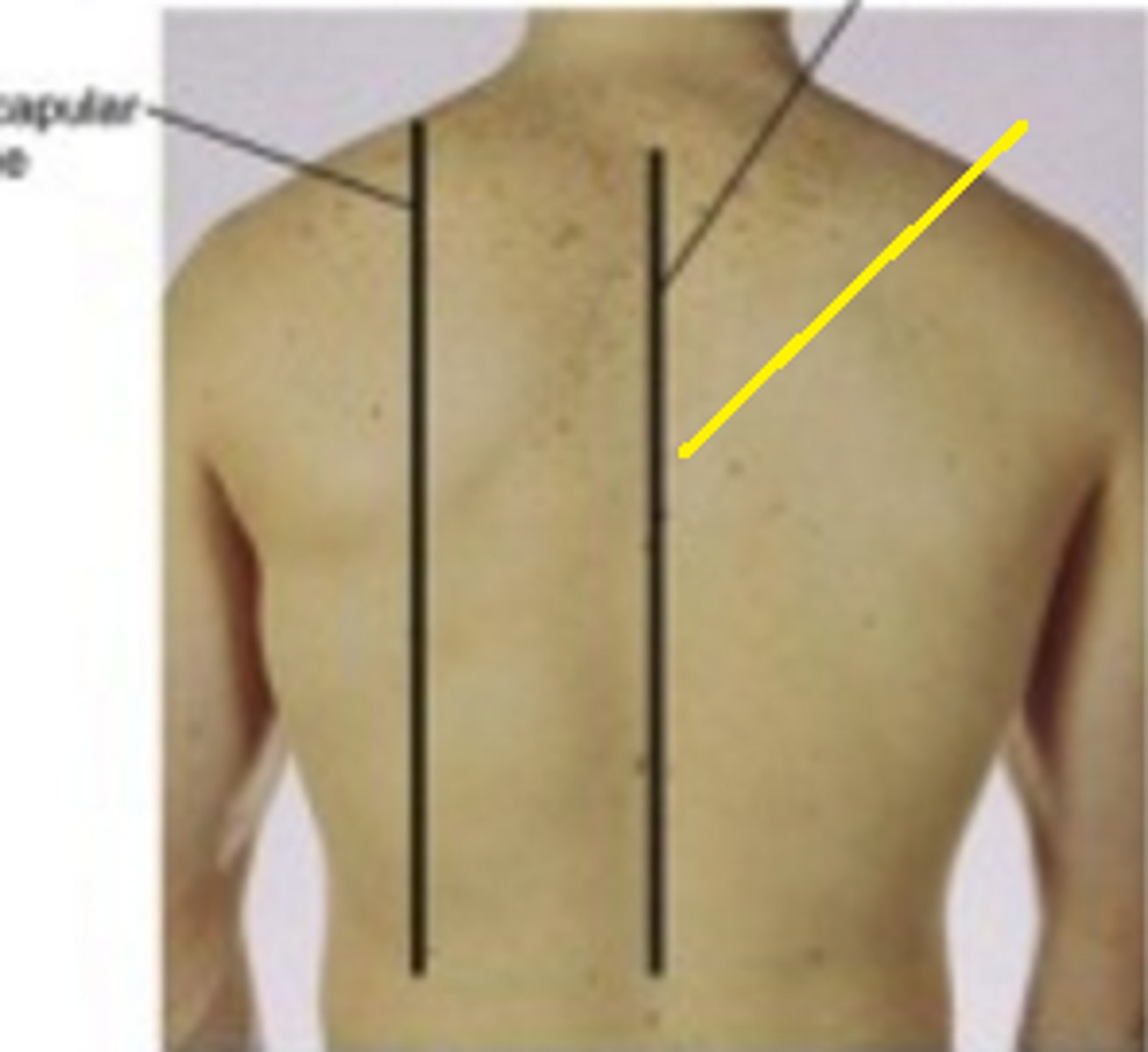
vertebral line
A line running vertically down through the spinous processes of the spine
diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
external intercostal muscles
A muscle that raises the rib cage, decreasing pressure inside the chest cavity
interior intercostal muscles
Decrease the transverse chest diameter during expiration
the use of what muscles indicate respiratory distress?
sternocleidomastoid and trapezius
the ____ is at the top of the lungs, whereas the _____ is at the bottom of the lungs.
apex; base
1 multiple choice option
what do the lobes of the lungs contain?
1. blood vessels
2. lymphatics
3. alveolar ducts connecting with alveoli
4. alveoli
how many alveoli are in an adult?
300 million
in the tracheobronchial tree, air is... (3)
filtered, humidified, and warmed
tracheobronchial tree
branching structures of the respiratory system that resemble an upside-down tree trunk and its branches; includes trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles.
right bronchus
larger and more vertical than the left, foreign bodies and pathogens can enter is more easily
what is the arterial supply of blood for the bronchi, lung, and pleura?
bronchial artery
the alveoli receive _________ blood from the branches of the pulmonary arteries
deoxygenated
1 multiple choice option
which of the following are INSPECTED during a lung examination?
1. appearance
2. posture
3. breathing effort
4. nails
5. skin
6. lips
7. posterior thorax
8. anterior thorax
which of the following are PALPATED during a lung examination?
1. thoracic muscles
2. thoracic wall
3. trachea
which of the following are AUSCULTATED during a lung examination?
1. posterior thorax
2. anterior thorax
3. lateral thorax
true or false: fetal lungs contain air
false
1 multiple choice option
what shape is an infant's chest?
round
diaphragmatic breathing
breathing with the use of the diaphragm to achieve maximum inhalation and slow respiratory rate.
what are common characteristics of infant breathing patterns?
1. diaphragmatic
2. abdominal
3. irregular
in infants, chest circumference is same as head circumference until about ____ years of age
2
3 multiple choice options
what are respiratory changes that occur during pregnancy?
1. lower rib flare
2. diaphragm rises above usual position
3. diaphragm movement increases
4. minute ventilation increases
5. respiratory rate remains unchanged
barrel chest
a condition characterized by increased anterior-posterior chest diameter caused by increased functional residual capacity due to air trapping from small airway collapse; common with COPD and in older adults
what respiratory changes occur in older adulthood?
1. barrel chest
2. dorsal curve in the thoracic spine
3. alveoli less elastic
4. decrease in vital capacity
5. increase in residual volume
6. mucous membranes drier
what factors should be questioned about during history of presenting illness?
1. coughing
2. shortness of breath
3. chest pain
what factors should be questioned about during past medical history?
1. thoracic trauma or surgery
2. use of oxygen and ventilation-assistive devices
3. COPD
sputum
mucous secretion from the lungs, bronchi, and trachea expelled through the mouth
average respiratory rate of infants
40-60
periodic breathing
Cessation of breathing lasting 5 to 10 seconds followed by 10 to 15 seconds of rapid respirations without changes in color or heart rate; common in infants
in infants, ______ is rare, but _______ is frequent
coughing; sneezing
1 multiple choice option
paradoxical breathing
the chest wall collapses as the abdomen distends on inspiration; common in infants especially during sleep
what are respiratory abnormalities in infants?
1. stridor
2. respiratory grunting
3. nasal flaring
children use the thoracic (intercostal) musculature for respiration by the age of ___ or ___ years
6; 7
3 multiple choice options
resonance
low-pitched, clear, hollow sound that predominates in healthy lung tissue in the adult
hyperresonance
lower-pitched, booming sound found when too much air is present such as in emphysema or pneumothorax
overall, the pregnant women increases her ventilation by breathing more ______, not more _________.
deeply; frequently
1 multiple choice option
kyphosis
hunchback
bronchophony
abnormal lung sound characterized by greater clarity and increased loudness of spoken words when increased lung consolidation; 99- 1-2-3 while auscultation
pectoriloquy
extreme bronchophony where even a whisper can be heard through stethoscope with consolidation or compression of lung
egophony
the voice sound of "eeeeee" heard through the stethoscope; intensity of spoken voice is increased and there is a nasal quality
asthma
small airways obstruction due to inflammation and hyperreactive airways; familial and allergen-induced
atelectasis
collapsed lung; incomplete expansion of alveoli
bronchitis
inflammation of the bronchi
pleurisy
inflammatory process involving the visceral and parietal pleura, which becomes edematous and fibrinous
pleural effusion
accumulation of serous fluid in the pleural space between the visceral and parietal pleurae
empyema
purulent exudative fluid in the pleural space
lung abscess
well-defined, circumscribed mass defined by inflammation, suppuration, and subsequent central necrosis
pneumonia
inflammatory response of the bronchioles and alveoli to an infective agent (bacterial, fungal, or viral)
tuberculosis
chronic infectious disease that most often begins in the lung but may then have widespread manifestations
pneumothorax
presence of air or gas in the pleural cavity
hemothorax
presence of blood in the pleural cavity
lung cancer
generally refers to bronchogenic cancer, a malignant tumor that evolves from bronchial epithelial structures
cor pulmonale
acute or chronic condition involving right-sided heart failure
pulmonary embolism
A blood clot that breaks off from a large vein and travels to the blood vessels of the lung, causing obstruction of blood flow.
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
permanent, destructive pulmonary disorder that is a combination of chronic bronchitis and emphysema
crackles
fine, high-pitched crackling and popping noises (discontinuous sounds) heard during inspiration and sometimes during expiration; not cleared by cough or altered by changes in body position.
rhonchi
Low-pitched, coarse, loud, low snoring or moaning tone; heard primarily during expiration but may also be heard during inspiration; coughing may clear
pleural friction rub
Superficial, low-pitched, coarse rubbing or grating sound; sounds like two surfaces rubbing together; heard throughout inspiration and expiration; loudest over the lower anterolateral surface; not cleared by cough
stridor
a harsh, high-pitched sound associated with breathing that is often caused by laryngeal or tracheal obstruction.
fremitus
vibration felt of the chest wall produced by vocalization.
wheezing
High-pitched, musical sound similar to a squeak; heard more commonly during expiration but may also be heard during inspiration; occurs in small airways
signs of poor oxygenation
Cyanosis (late stage)
Clubbing (chronic low O2)
if there is ever a question of adequate oxygenation, measure the patient's...
oxygen saturation
the anteroposterior diameter of the chest is approximately _____ the lateral diameter
one half
3 multiple choice options
costal angle
the right and left costal margins form an angle where they meet at the xiphoid process; should be less than 90 degrees
bell of the stethoscope
low pitched sounds
diaphragm of the stethoscope
high pitched sounds
bronchial breath sounds
those heard over the larynx and trachea are high-pitched, harsh "blowing" sounds, with sound on expiration being longer than inspiration
bronchovesicular breath sounds
normal breath sounds heard over the mainstem bronchus; they are moderate blowing sounds, with inspiration equal to expiration
vesicular breath sounds
normal sound of respirations heard on auscultation over peripheral lung areas; they are low in pitch and soft in intensity, with inspiration greater than expiration
lung consolidation
Firming of the lungs as a result of fluid accumulation.
what characteristics of sputum should be inquired about?
1. color
2. consistency
3. odor
4. how often it is coughed up
what abnormal breath sounds can be auscultated in a patient with pneumonia?
crackles or rhonchi
croup
an acute respiratory syndrome in children and infants characterized by obstruction of the larynx, hoarseness, and a barking cough
how should posterior chest movement be assessed?
With thumbs together on either side of patient's spinal process, extend fingers and ask patient to take deep breaths through the mouth
how should anterior chest movement be assessed?
hands placed on bare lower chest of a patient with thumbs placed on sternum and fingers extended on lateral side over the floating ribs.
how should fremitus feel?
bilaterally equal over posterior and anterior chest walls, although the quality of the vibrations may vary from person to person because of chest wall density and relative location of the bronchi to the chest wall.
hemoptysis
coughing up blood
how does a pleural friction rub differ from a cardiac friction rub?
asking the patient to hold his or her breath. If the rub is not heard, the source is lung pleura rubbing together. If the sound persists, it is caused by pericardial pleura rubbing together.6
thrombus
blood clot
pericardium
thin sac composed of a fibro serous material that surrounds the heart
what are the layers of the pericardium
fibrous and serous (parietal and visceral)
the _____ is at the top of the heart, and the ______ is at the bottom of the heart
base; apex
1 multiple choice option
where is the apical impulse located?
5th intercostal space, midclavicular line (point of maximum impulse)
what are the three layers of the heart wall?
epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
epicardium
visceral layer of serous pericardium; outer layer of the heart