GE in plants and humans
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
describe and explain the process of inspiration in a mammal
Intercostal muscles contract and ribs move up and out
Diaphragm muscles contract and diaphragm flattens
Internal volume of thorax increases
Pressure in lungs/ thorax decreases
Higher/ difference in air pressure outside forces air into the lungs
Tracheoles are found on the outside of the muscle fibres suggest why the max diameter of a muscle fibre never exceeds 20 microm in diameter
Diffusion pathway would be too long, ensures a short diffusion pathway
Speed of diffusion would be too slow
To supply sufficient oxygen
9 marker 2024 a level
Describe the change in fluid level in the tracheoles during flight suggest how this change benefits gas exchange during flight
Less fluid, fluid moves into muscle fibres, fluid level decreases
More area for gas exchange and shorter diffusion pathway
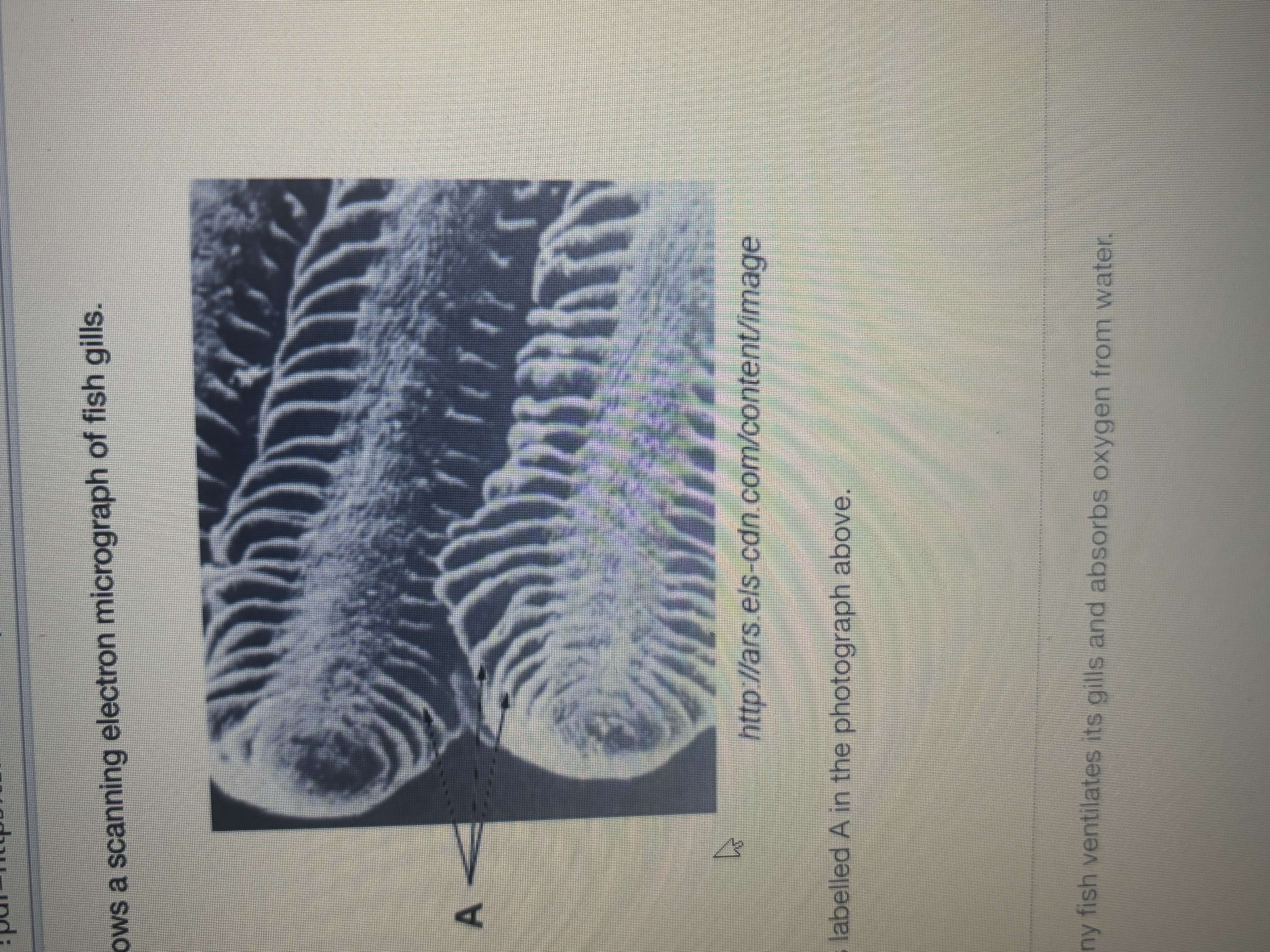
Name the structure labelled A in photograph thin strands coming out of fish gills
Gill lamellae/ gill plates
Explain how inspiration is brought about
Contraction of intercostal muscles and diaphragm or Ribcage cloves up and out and diaphragm flattens/ contracts
Increased volume and decreases pressure so air moved into the lungs
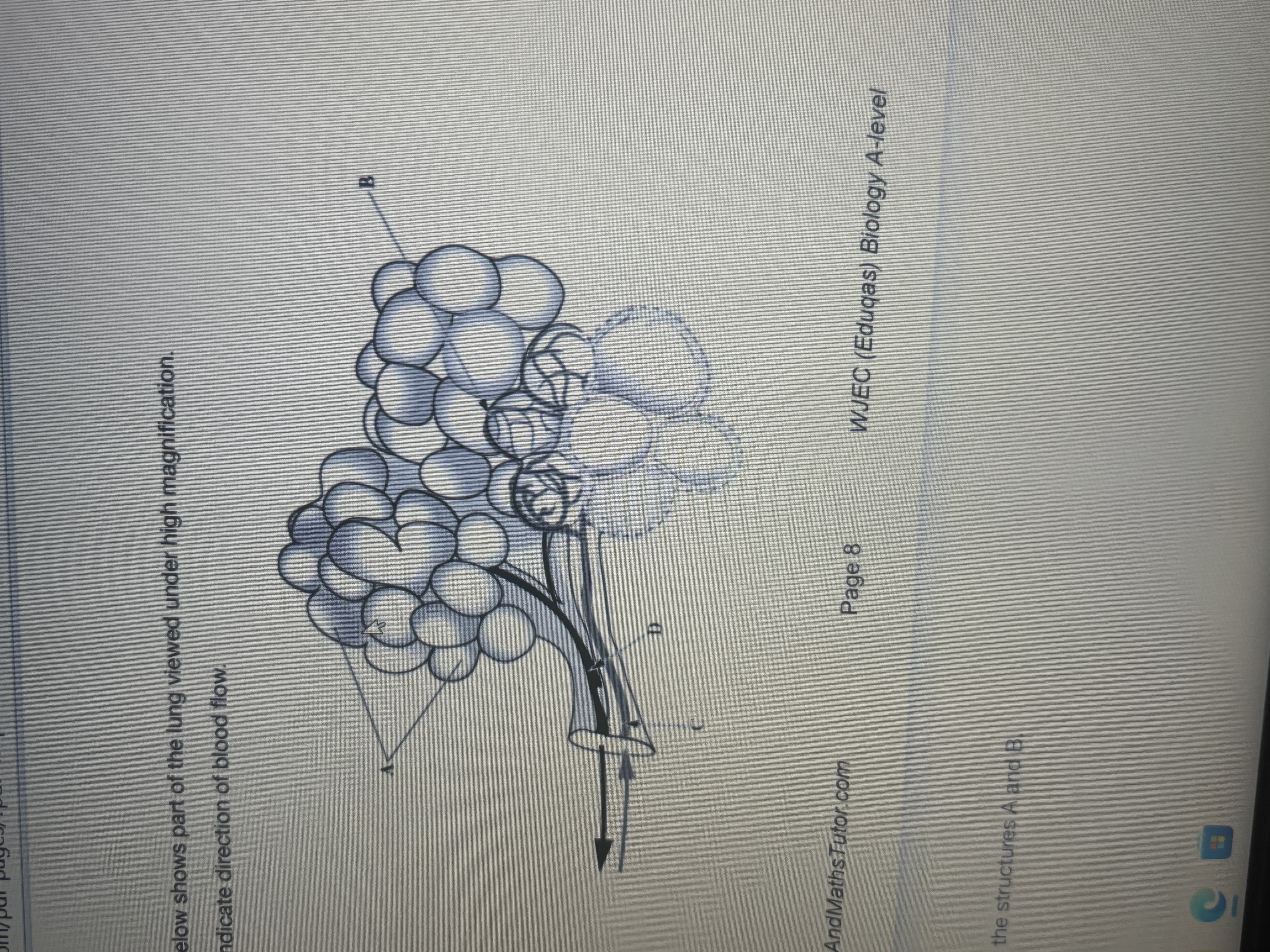
Part of lung labelled
A- alveoli
B- capillary network
Blood vessels that connect C and D to the heart respectively - pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein
Important structure features of alveoli
Large SA/ highly folded
large number of capillaries
Thin alveolus walls/ one cell thick
Describe and explain how the alveoli are adaptations for efficient gas exchange
They have many alveoli which increases or provides a large SA for gas exchange, alveoli walls are thin/ one cell thick providing a short diffusion pathway/ distance for oxygen to enter the blood
Describe how blood vessels are adaptations for efficient gas exchange
many blood capillaries/ vessels are good blood supply, capillary network to maintain stepp concentration gradient
Describe and explain the process of expiration in mammals
Intercostal muscles relax allowing Ribcage to move downwards and inwards
The diaphragm muscles relaxes and becomes dome shaped
This decreases the volume of the thorax
Which increases the pressure inside the lungs
Forcing/ pushing air out of the lungs/ moving air out of the lungs down a pressure gradient
Mammals have a high oxygen demand suggest why they need a complex ventilation mechanism
Have high metabolic rates
Ventilation maintains a steep concentration gradient at the alveoli/ sufficient/ enough/ more oxygen supplied to the alveoli/ GE surface
Give two adv of humans having internal gas exchange surfaces
Minimise/ reduce heat and water loss
State one medical use of artificial surfactant and explain why it would be needed
Lowers surface tension do the fluid in the alveoli to prevent alveoli from collapsing
Premature babies/ lung transplants/ respiratory distress syndrome
Explain how the outwards movement of the Ribcage causes the changes in pleural and alveolar pressures during breathing in
Intercostal muscles contract and expand the Ribcage
Outer pleural membranes pulled out by expanding the Ribcage
Pleural pressure reduced
Inner pleural membrane pulls on lungs and expands alveoli
Alveolar pressure lowers
Air moves in when alveolar pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure and increases alveolar pressure
Plant adaptation for efficient diffusion of gases
Stomata
Large air spaces, large SA in spongy mesohpyll
Thin leaf / short diffusion distance
Moisture on cell surface
Explain how stomata are opened
K+ or malate in guard cells/ cytoplasm/ vacuole
Reduces their water potential so water enters guard cells by osmosis and trig or pressure increases/ cell becomes turgid, ends of guard cell walls are thinner central wall is thicker, ends expand which opens stomata cells are forced apart
Main RS for fish, mammal, earthworm, insect
Fish- gills / lamellae
Mammal- alveoli NOT lungs
Earthworms- skin
Insect- tracheoles NOT trachea
Explain how in a mammal the Ribcage diaphragm and pleural membranes are involved in lowering the pressure in the alveoli to below atmospheric pressure during inhalation
Ribcage moves up/ expands
Diaphragm flattens/ contracts/ moves down
Pull pleural membranes out which expands volume of the lungs and reduces pressure
Two ways an O concent gradient is maintained between alveolar air and blood
Explain why the rate of GE between the air spaces of the leaf and the leaf tissues is lower than between alveoli and blood of a mammal 1b i
Describe how the muscles of the thorax together with the pleural membranes cause the change in alveolar pressure during inspiration
External intercostal muscles contract and rib cage lifts upwards and outwards
Diaphragm muscles contract and diaphragm flattens
Outer pleural membrane pulls inner pleural membrane
Outward/ reduced pressure
% of CO2 in exhaled air is lower than in alveolar air explain why
Some CO2 remains in the trachea/ bronchi/ alveoli
Exhaled air has a slightly higher % of nitrogen than inhaled air despite the gas being inert in mammals
The proportions/ quantities of other gases have changed (so N is a different proportion of the gas mixture)
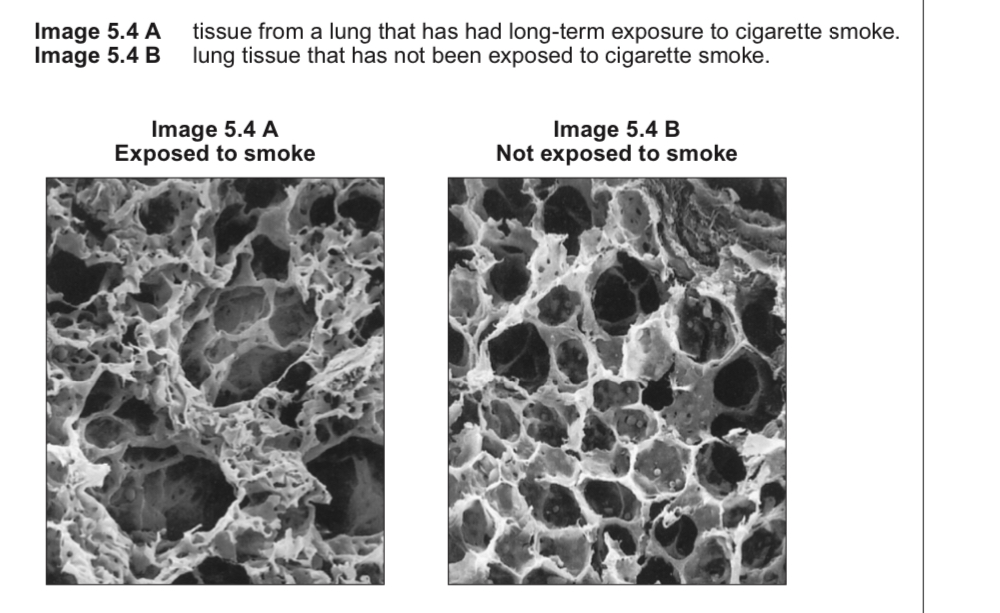
Describe a difference in appearance of the two lung samples and explain how this would decrease GE efficiency
Alveoli/ air spaces have become larger, air spaces have broken down
Reduced S.A. for gas gas exchange/ diffusion
Tissue between alveoli/ air spaces have become thickened
Increased diffusion distance for O/ CO2
Explain mechanism of stomatal opening which allows GE to take place
K+ pumped/ using AT into guard cells
Starch converted to malate ions
Lowering WP in guard cells
Water moves in by osmosis
Guard cells become turgid
Uneven beding of guard cells due to thickening of cell wall
Explain how the volume of the thorax is changed during inspiration
External intercostal muscles contract and Ribcage moves upwards and outwards
Diaphragm contracts and flattens
Role of pleural membranes
Explain change in alveolar pressure during inspiration
Pressure decreases in alveoli as thoracic volume increases
Pressure increases as air enters alveoli
During expiration there is a risk of the collapse of the alveoli due to positive pressure, suggest how alveoli are adapted to deal with this
Alveoli coated in surfactant
Reduces surface tension
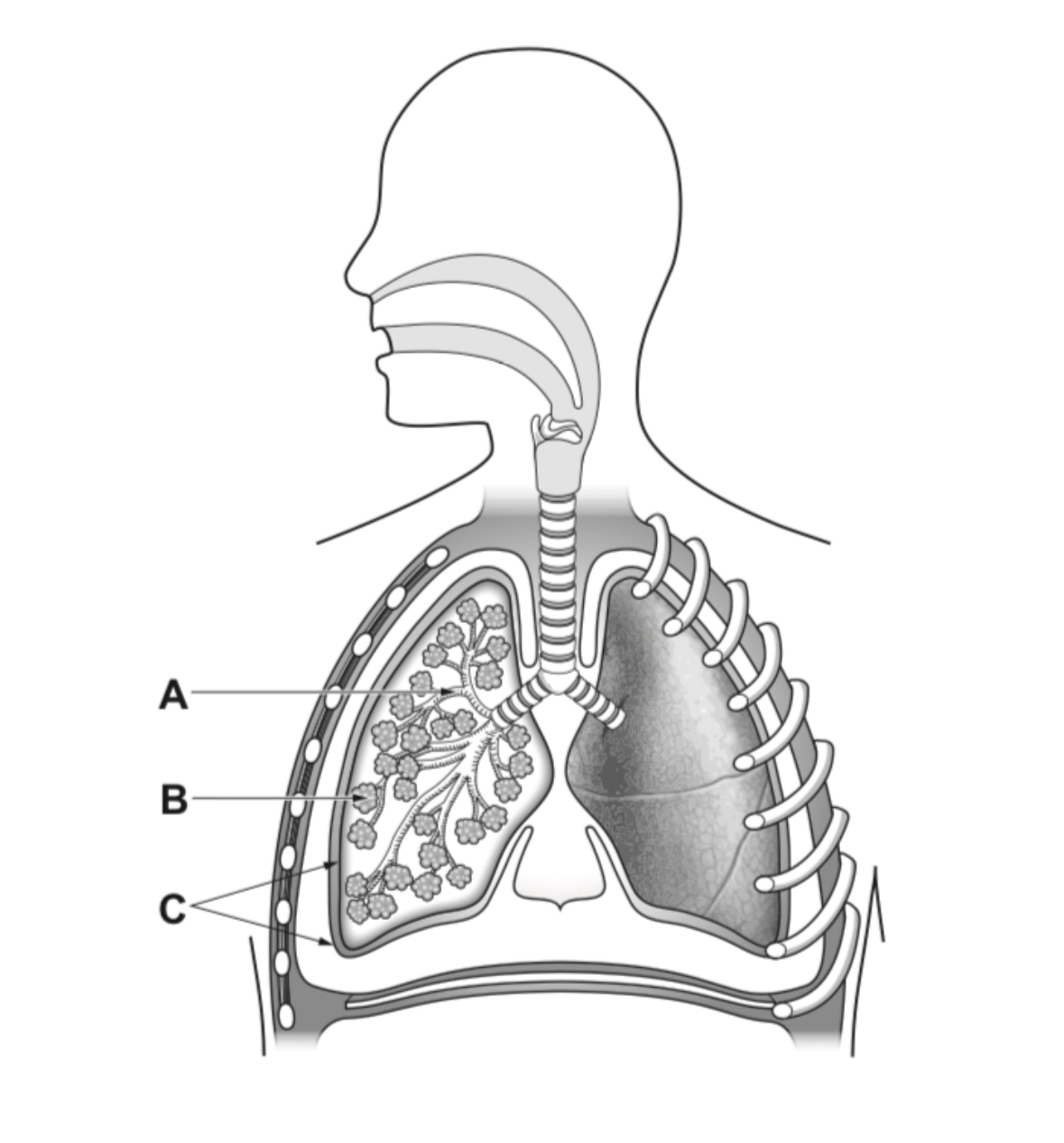
A- bronchiole
B- alveolus
C- pleural membranes
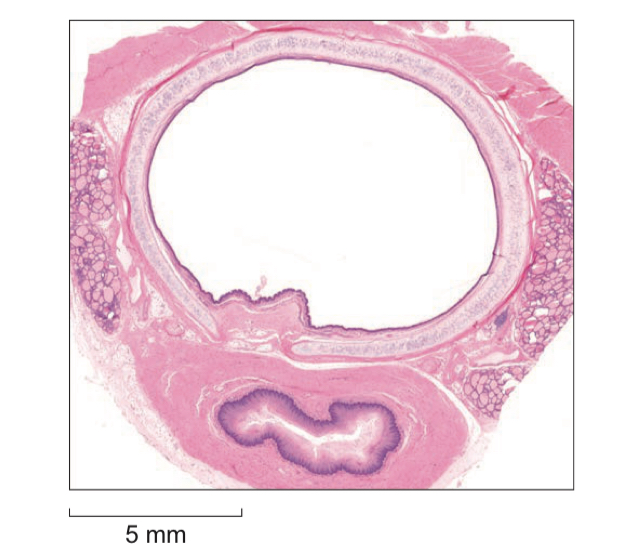
Explain how a feature visible in photograph ensures the trachea can function effectively during inspiration
Ring of cartilage
Prevents trachea from collapsing due to air pressure decrease during inspiration
Explain how muscles involved in the process of inspiration bring about changes in pressure
External intercostal muscles contract and ribs move upwards and outwards
Diaphragm contracts and flattens
Role of pleural membranes
Volume do thorax increases therefore pressure decreases
Air pressure in alveoli us falls below atmospheric pressure so air rushes in
Explain why ventilation rate increased as temp increased and why these fish gulp air during summer
Oxygen content of water decreases as temp increases
Increased ventilation rate/ operculum open more frequently, so more/ enough oxygen could be absorbed from the water;
Gulp air when ventilation rate reaches maximum, cannot breathe any faster, cannot absorb enough oxygen from the water , air has a higher O content, can absorb oxygen from the air when oxygen content of water is low/ gulp for more oxygen
Describe the mechanism that causes stomata to open
K+ actively transported into guard cell
Starch converted to malate
Lowers the WP of the cell
Water moves into the cell by osmosis
Due to increase in water cells well up, become turgid
stomata opens as inner cell wall is thicker than the outer cell walls, walls are unevenly thickened
Advantage of plant being able to close stomata
Reduce water loss
Mean number of stomata calculated for trees alter being placed in greenhouses with different CO2 concentrations , variables that should be controlled
Temp, light intensity, humidity, frequency of watering, volume of water, soil pH
Using knowledge of the functions of stomata explain why as the CO2 concentration increases the mean number of stomata decreases/ stomatal density decreases, there are fewer stomata
Stomata open to allow CD to diffuse for PR
At higher CD concent there is an increased rate/ more CD diffusion/ uptake
Sufficient CD can be absorbed with fewer stomata, therefore less water is lost from the plant
Explain how large insects ensure an efficient supply of oxygen to their tissues
Tracheal system, tracheoles
Oxygen is delivered directly to cells/ muscles
reason why both the insect and human systems are internal
To reduce water loss
Why the nasal cavity and the series o cavity have air
To filter air/ trap solid particles
Why walls of alveoli and tracheoles are one cell thick
Short diffusion pathway
Why alveoli and tracheoles are lined with surfactant
Reduce surface tension, prevent collapse of alveoli and tracheoles during expiration , prevent alveoli/ tracheoles sticking together
During inspiration external intercostal muscles contract which causes outer pleural memerbanes to move outwards explain causes of pressure and volume changes during inspiration
Pulling on outer puleural membrane lowers pressure in pleural cavity, inner pleural membrane pulls on the lungs, which increases volume of the lungs/ alveoli/ thorax, which decreases pressure in lungs, below atmospheric pressure so air moves in
Changes to the curve during strenuous exercise
Greater/ higher pressure , faster pressure changes
Greater volume , faster changes in volume
More rapid breathing, increased breathing rate
describe and explain the common adaptions found in fish and mammals
Thin- reduce diffusion distance
Moist for gases to dissolve
Extensive blood capillary network to maiantim diffusion/ concent gradient and
The body temp of cold blooded animals varies with temp according to temp of the environment suggest why warm blooded animals which have a constant body temp such as mammals have a higher metabolic rate
Body temp not dependent on that of the environment , energy needed to generate heat to maintain body temp , provide optimum temp for enzymes, so reaction rate is higher
Explain why spiracles close
To reduce water loss
Describe the relationship between body mass and metabolic rate
The greater the mass the greater the metabolic rate
Explain the advantages of insects have a ventilation system
maintain concentration gradient so that air has high CD concent is replaced with oxygen rich air
Suggest the role of air sacs in insects tracheal systems
To provide a store of oxygen when spiracles are closed
Outline a method which the stomatal density could be determined
Cost surface do leaf with clear nail varnish , examine using a light microscope, count the number of stomata in the field of view
Plant grown in temp and light controlled conditions state other control variables
Humidity, air movement , pH of soil, water availability, concent of CD/O
Explain why the GE between air spaces of the leaf and leaf tissues is lower than between alveoli and the blood of a mammal
Mammals have a ventilation system whilst plants rely on diffusion only
Higher concent gradient in mammals, lower in plants concent gradient is actively maintained in animals
Mammals have a higher rate of respiration, more active
Main tissue responsible for PT
Palisade mesophyll
Conclude whether th worst shown is from a hydrophyte or a xerophyte
hydrophyte, stomata in the upper epidermis/ surface , large air spaces in spongy mesophyll , thin cuticle on upper epidermis / surface
Explain why leaves and chloroplasts change their orientation during the day
To increase/ maximise absorption of light
So that greater S.A. of leaves face the sun
Explain why there is water loss when the stomatal diameter is 0
Water evaporates from leaf surface/ epidermis
What would happen to the rate of water loss form the plant when exposed to a high air speed
Decrease
Adv of plants closing stomata at high wind speeds
Less water loss
Suggest why increased CD concentration resulted in a reduction in stomatal density
CD is used for PT, increased CD causes increased rate of PT, higher CD concent causes faster/ more diffusion , higher concent gradient
Fewer stomata needed for the same CD intake
Give two function of stomata
Allow GE/ CD and O to enter and leave leave s
Control water loss
When guard cells are treated with cyanide the stomatal pores failed to open explain why cyanide is having this effect
Cyanide stops respiration, is a respiratory inhibitor , stops active transport of K+ ions into guard cells
Explain the distribution of the stomata
Lower surface of leaf is shaded therefore there is a higher density of stomata to reduce water loss
Use the photograph to explain why the less water vapour is lost from the stomata of one leaf then the stomata of another
Stomata are sunken, water vapours builds up in pits, reducing diffusion gradient, rate of transpiration is reduced
Other leaf has no sunken stomata, stomata are nearer to the surface
Which species are more likely to live in driest environment
Species that have the lowest stomatal density , higher % of stomata on the lower surface, lower rate of transpiration, , lower rate of water loss
Explain how investigating stomata density works
Obtain impression using clear nail varnish
Prepare a slide using impression, observe under microscope , count number of stomata in known area, repeat to obtain mean