Nuclear Cardiology Dynamic and PET
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
What are the two methods of dynamic cardiac imaging we can preform in nuclear medicine?
First Pass Study
Gated blood pool imaging (MUGA,RVG, ERNA or RNA)
What are indications for a First pass study
eval patients with
LV dysfunction
Interventricular shunts
Myocardial ischemia
MI
What are the advantages of first pass studies
tracer activity is limited to 1 chamber at a time
background is decreased
rapidly completed
What are the disadvantages of first pass studies
gamma cameras must be able to acquire data at 200,000 counts per second or greater
speical multi crystal cameras with high count rate capabilities are optimal but not widely available
increased count rate= increased sensitivity
What is the minimum dosage for a first pass study
10 mCi
What types of imaging would be preformed for a first pass study
gated images
What types of Tc tracers would be use for a first pass study
Sestamibi, tetrofosmine, pentetate and pertechnetate
What tracers should we NOT use for a fast pass study
MAA, SC (sulfur colloid), Tl-201
When preforming a fast pass exam, the volume should be greater than for a good bolus
1mL
How fast should a bolus be pushed when performing a LVEF fast pass study? What should follow it?
over 2-3 seconds
10ml flush
How fast should a bolus be pushed when performing a RVEF first pass study? what should follow it?
3-4 seconds
10 mL flush
When performing a first pass study what baseline test should be preformed before the injection of the tracer? why?
baseline ECG to assess rhythm
Through which veins are we injecting for first pass study
The right AC (median basilic vein) or jugular for direct path to superior vena cave
How can we tell it is a good bolus during a first pass study
time activity curve over superior vena cave, calculate FWHM
What is the rate of data acquisition for a first pass study
16-30 frames/sec or 1,200 frames in 60 sec
What matrix size would we use for a first pass study
64×64
What type of collimator would we use when preforming a first pass study.
high sensitivity
when imaging the patient under the camera a first pass study should be positioned at the top of the FOV, and the should be within the FOV
Sternal notch (at top of FOV)
xifoid (within the FOV)
How would the camera be oriented when assessing the LVEF during a first pass study
Supine or upright
LAO view
How would the camera be oriented with assessing the RVEF during a first pass study
supine or upright
RAO view
How would the camera be oriented when assessing both ventricles during a first pass study
anterior
During first pass study describe the sequential visualization a good bolus would give
Superior vena cava
RA
RV
Pulmonary artery to lungs
Pulmonary veins
LA
LV
Aorta
When interpretating a first pass study what are we looking for
EF
Left to right shunt
Right to left shunt
When interpreting a first pass study if a patient has a left to right shunt some of the oxygenated blood returning from the lungs will
will go through the shunt and circulate back to the lungs instead of the body
When interpretating a first pass study if a patient has a right to left shunt, some of the deoxygenated blood returning from the body will instead of
go through the shunt and be sent out to the body
On a time activity curve do the low points represent diastole or systole
systole
on a time activity curve do the high points represent diastole or systole
diastole
How would a right to left shunt be interpretate on a first pass study
appearance of bolus in left side of the heart and aorta before the appearance of lung activity
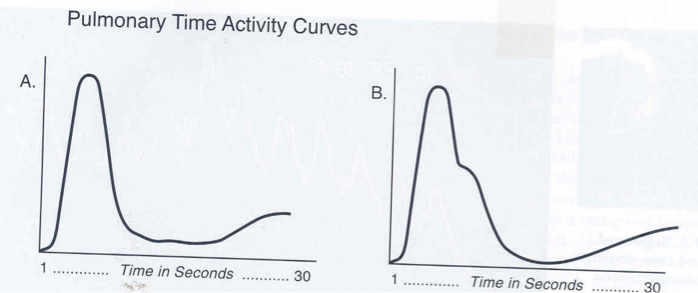
When interpreting a time activity curve for a left to right shunt A represents and B represents
Normal flow (1 peak)
left to right shunt (2 peaks)
In gated blood pool imaging how is data collected
over many cardiac cycles using ECG gating
Gated equilibrium is another name for
Gated blood pool imaging
gated cardiac blood pool study is another name for a procedure
Gated blood pool imaging
equilibrium radionuclide angiography (ERNA) is another name for a procedure
Gated blood pool imaging
Radionuclide ventriculography (RVG) is another name for a procedure
Gated blood pool imaging
Multiple gated acquisition study (MUGA) is another name for a procedure
gated blood pool imaging
What are the indications for gated blood pool imaging
Assessment of cardiac function in chemotherapy patients
Quantification of ejection fraction (LVEF, RVEF)
Estimation of wall motion abnormalities
detection of ventricular aneurysm
detection of ventricular regurgitation
eval of cardiotoxicity
Follow up of medical/surgical therapy
Why would we preform a gate blood pool image instead of a full stress test
its own exam because pt dont need stress test just EF
What is the patient prep for a gated blood pool imaging
none
What is the most commonly used radiopharmaceutical for a gated blood pool imaging
Tc-99m labeled RBCs
What are the 3 ways we can label RBCs
in vitro
modified
in vivo
When using the in vivo labeling method, blood is labeled
inside the body
When using the in vitro labeling method blood is labeled
outside of the body using an ultratag kit
The advantages of using an in vivo/vitro method of blood labeling
High efficiency (95%)
absence of blood manipulation
The in vivo method of blood labeling has a % labeling efficiency
60-90%
Describe the steps take when labeling blood using in vivo method
inject stannous ion
wait 20-30 min
inject 99m Tc-Pertechnetate
free 99m Tc is secreted through gastric musca and kidneys
not able to see bleed in stomach, small bowel and or the colon
what are the disadvantages of using the in vivo method
labeling constancies variable (60-90%)
Free 99m Tc is secreted through gastric mucosa and kidneys
not able to see bleed in stomach, small bowel and/or the colon
What is the advantage of using the in vivo method
convenient and easy
What blood labeling methods use stannous pyrophosphate
In vivo
modifies in vivo/in vitro
what is cold stannous pyrophosphate used for in blood labeling
to pretreat RBCs for labeling
What is the optimal dose of stannous pyrophosphate when labeling RBCs
0.5-1-0 mg
What if too little of stannous pyrophosphate is used when labeling RBCs
dose of Tc will not properly label RBCs
What will happen if too much of stannous pyrophosphate is used when labeling RBCs
some of tin will circulate freely and tag to Tc outside of RBCs
What will happen to image quality if too much or too little of the stannous pyrophosphate is administered when labeling RBCs
results in increased background as a result of free Tc
Describe the steps taken when labeling blood using the in vivo/vitro method
IV injection of stannous ion
blood sample is collected into a syringe containing Tc-pertechnetate and anticoagulant
re-injected
Describe the steps taken when labeling blood using the in vitro method
1-3ml of blood withdrawn into syringe containing anticoagulant
let sit for 5 min
add sodium hypochlorite and acid citrate dextrose (ACD)
add Tc-Pertechnetate
wait 20 mins (no longer then 60 min) and inject
T/F: when using the In vitro method to label blood, once the tracer has been added, we can use a sample that has been sitting for more than 60min
False
T/F: When using the In vitro method to label blood, we can inject immediately after adding the Tc-99m Pertechnetate
false
T/F: When using the In vitro method to label blood, we have to wait at least 60 minutes after the Tc-99m Pertechnetate has been added before injecting.
false
T/F: When using the In vitro method to label blood, once the Tc-99m Pertechnetate has been added, we have to wait at least 20 minutes, but no more than 60 min before injecting
true
What is the advantage of using in vitro method for labeling blood
High labeling efficiency, superior imaging quality
Describe the procedure for a gated equilibrium study
In Vivo, In Vitro, or modified In Vivo/In Vitro labeling of RBC’s w/ Tc-99m
3 gated planar images obtained
Anterior
LAO
Lft Lateraral
What views are obtained when performing a gated equilibrium study?
planars:
Anterior
LAO
Lft Lateraral
T/F: When performing a MUGA (multiple gated acquisition study), an ECG rhythm strip should be obtained and reviewed before injection
true
Why should a ECG rhythm strip be obtained and reviewed before injection during a MUGA procedure?
rapid atrial fibrillation or frequent PVCs (premature ventricular contractions) are contraindications to study
One cardiac cycle can be divided into intervals of ___
8 (16, 24. or 32) frames
What triggers gating in cardiac images?
R wave
During a gated study, 24 frames per cardiac cycle are obtained. If a patient’s heart rate is 65 bpm, the length of time per frame is:
a. 38 msec
b. 3.8 msec
c. 41 msec
d.4.1 msec
3.8 msec
In a gated study, if the patient’s heart rate is 65 bpm, and 24 frames per cardiac cycle was obtained, How do you calculate the length of time per frame in msec?
60 sec/min divided by 65 beats/min = 0.92 sec/beat
divide by 24 frames = 0.038 sec X 1,000 = 38 msec
Which view provides the best separation between the L. and R. ventricles during a gated study?
LAO
How should a technologist reposition the camera if trying to separate the atria from the ventricles in a gated study?
apply a 5-10 degree caudal tilt
From the best LAO view, the anterior and lateral views are obtained ± ____ degrees
45 degrees
how would the camera be positioned during a gated study if trying to visualize the Right ventricle?
20 degrees anterior (5 degrees of caudal tilt)
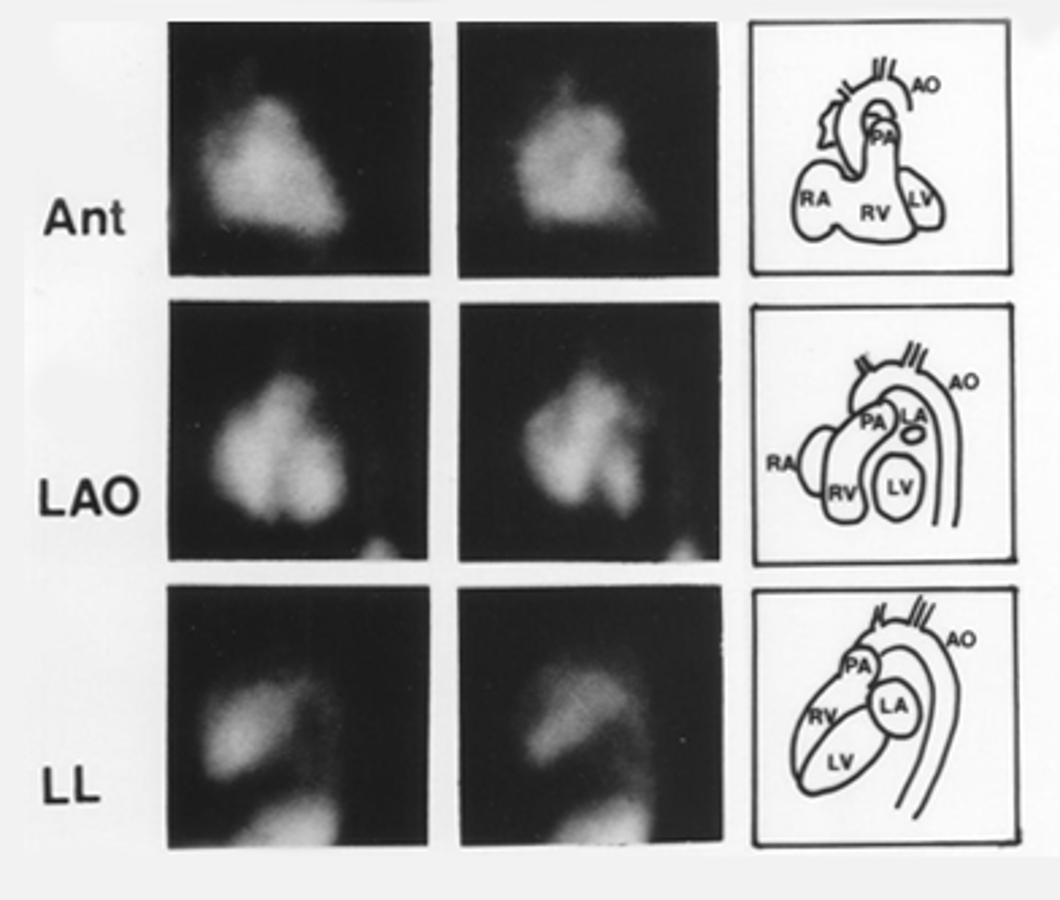
Based on this image, which is systole and which is diastole?
1st row diastole, 2nd row systole
During a gated study, in what views would we potentially apply a caudal tilt?
only for LAO or RAO
When performing a gated study, can we use a caudal tilt for anterior or lateral views
no
If we apply a caudal tilt to the camera, we are tilting the camera towards the _______
Pelvis (caudus)
How does a caudal tilt affect images?
used to elongate ventricles
When performing a gated blood pool imaging, are we acquiring rest or stress images?
rest
During a gated equilibrium study, what energy window are we using?
20% window centered at 140keV
What type of collimator are we using during a gated equilibrium study?
LEHR
What is the R-R acceptance window in a gated equilibrium study?
10-15%
What matrix size are we using for a gated equilibrium study?
64×64×16
When taking images for a gated equilibrium study, we have to acquire a minimum of ________ counts per frame, or about ___ to ___ minutes per view
250,000 counts
~5-10 min
T/F: If the heart rate is irregular, imaging during a gated equilibrium study will take longer
True
How is a gated equilibrium study data reconstruted?
added together to form a representative cardiac cycle
simulates the heart beating
Qualitative anaysis of a gated equilibrium study can be used to assess:
cardiac chamber size
overall biventricuar function
regional wall motion
extra cardiac abnormalities such as aneurysms
What does Akinesis mean?
absence of wall motion
What does hypokinesis mean
decreased wall motion
What is dyskinesia
outward bulge during systole
What is stroke volume
volume of blood ejected by either ventricle during systole
what is the cardiac output
volume of blood that heart pumps per minute
CO=SV at heart rate
what is the ejection fraction
% of blood ejected from ventricules during each contraction
What does qualitative analysis of a gated equilibrium study use to analyze
LVEF
How are images processed for quantitative analysis during a gated equilibrium study
ROI’s drawn on LV at diastole and systole
Background ROI selected about 3-6 o’clock from LV
ROI can be manually drawn or generated by computer
In images taken at end diastole, the ventricle is and counts obtained would be
relaxing
highest
in images taken at end systole the ventricle is and the counts obtained would be
contracted
lowest
How do you calculate ejection fraction
[(net diastolic counts - net systolic counts) / net diastolic counts] X 100
Calculate the Ejection fraction if ED (end diastolic counts) are 90,400 and ES (end systolic counts) are 40,000
(90,000 - 40,000) / 90,400 = 0.557
0.557 X 100 = 55.7%
What is a normal LVEF range
55-75%
What is a normal RVEF range
>40%