Unit 1- Biology- B2- [Cell specialisation]
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is the B2 of the applied science foundation diploma series of Pearson edexcel
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Why do cells specialise?
So that they are tasked with different functions and roles
Where are palisade mesophyll cells found?
In plant leaves
What do palisade mesophyll cells contain?
Chloroplast
What is the chloroplast able to do?
Absorb a large amount of light for photosynthesis
What do the chloroplasts do in order to maximise the amount of light absorbed?
They move around in the cytoplasm
What are palisade cells surrounded by?
A plasma membrane and a cell wall made of cellulose
What does the cell wall and cell membrane do to the cell?
Helps protect the cell and keep it rigid
What feature does the pmc (palisade mesophyll cell) have to maintain turgor pressure?
It has a large centre vacuole
What is the meaning of Turgor?
The rigidity of plant cells due to pressure of cell contents on the cell wall
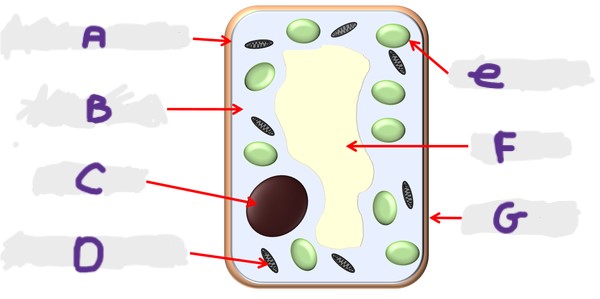
What is the structure A?
Cell membrane
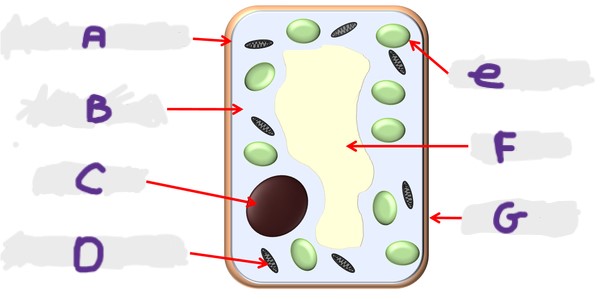
What is the structure G?
Cell wall
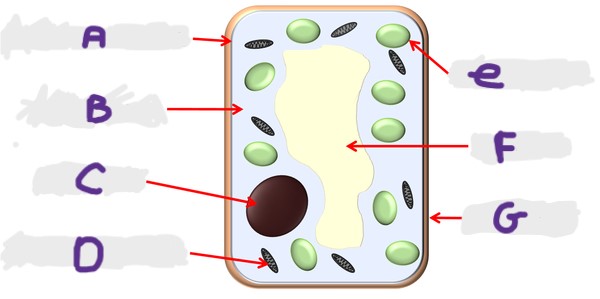
What is the structure D?
Mitochondria
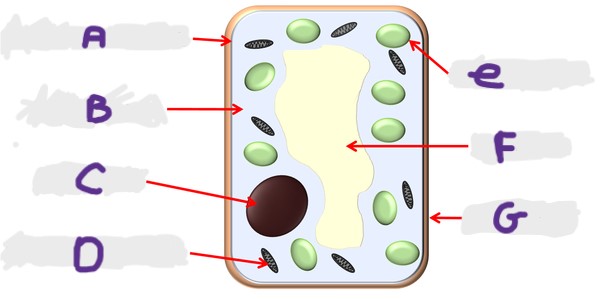
What is the structure F?
Vacuole
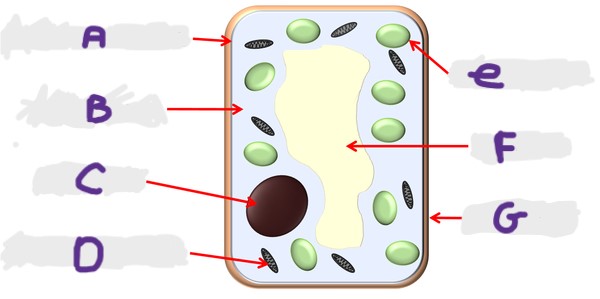
What is the structure B?
Cytoplasm
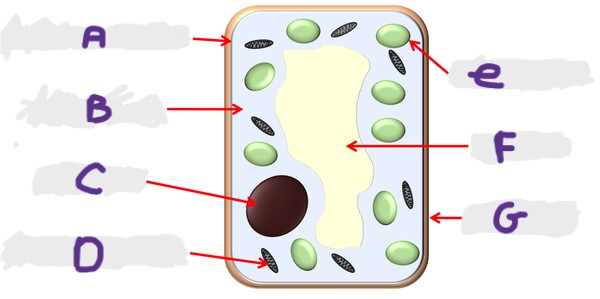
What is the structure E?
Chloroplast
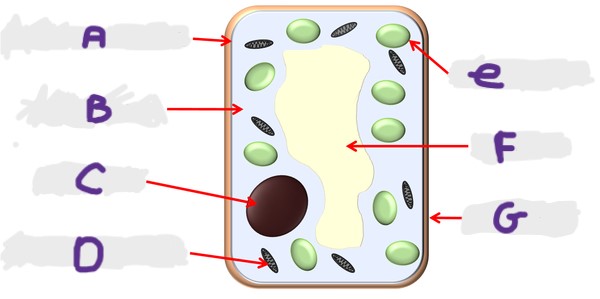
What is the structure C?
Nucleus
Where are root hair cells found?
They are found at the plants root, near the growing tip
What structure does the root hair cell have?
Long hair-like extensions called root hairs.
What does the root hairs enable the cell to do?
Increase surface area of the cell to maximise the movement of water and minerals from the soil into the plant root
What type of walls does the root hair cell have?
Thin cellulose walls
What else does the root hair cell have?
A vacuole which contains cell sap with low water potential
What is the meaning of water potential?
A measure of ability of water molecules to move in a solution
What does the low water potential in the vacuole encourage?
The movement of water into the cell
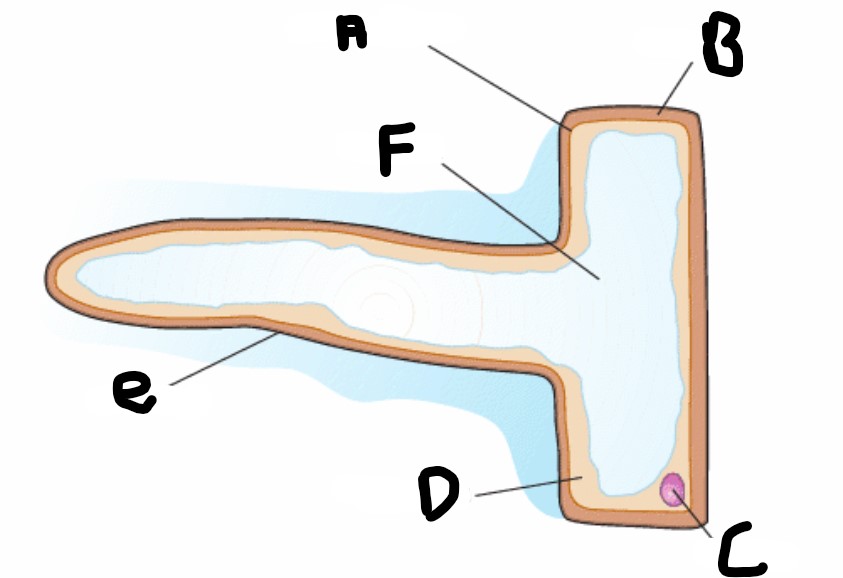
What is the structure A?
Cell membrane
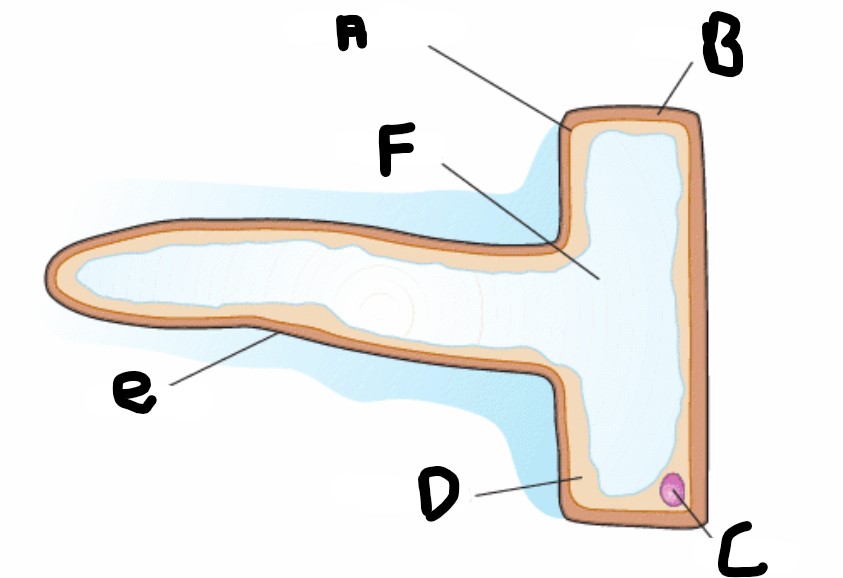
What is structure F?
Vacuole
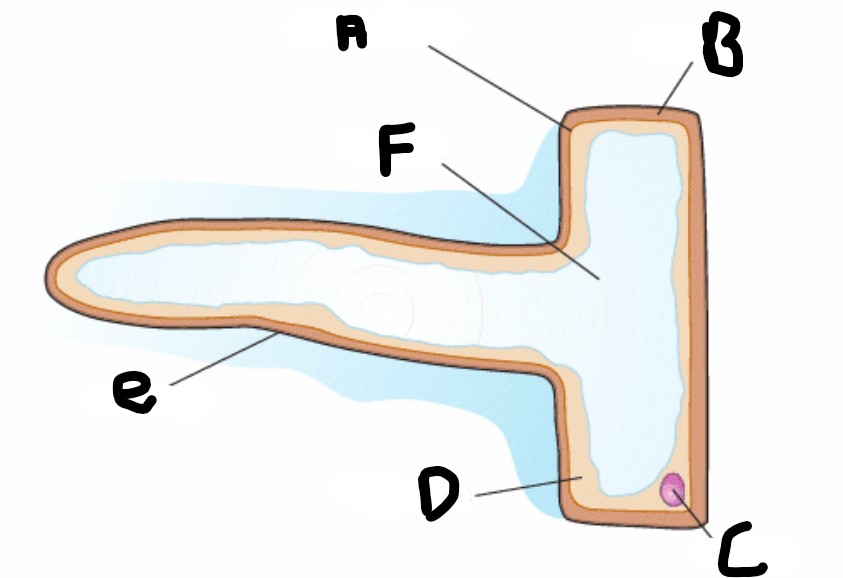
What is structure D?
Cytoplasm
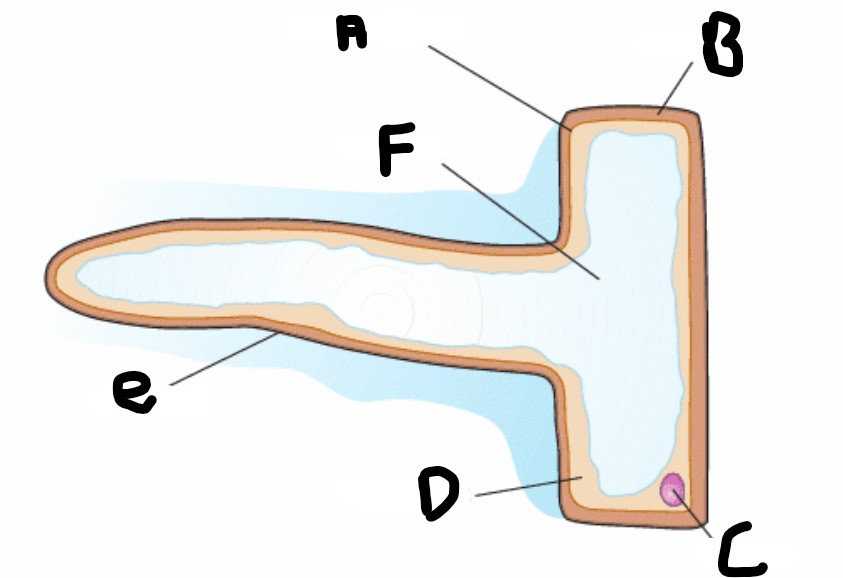
What is structure B?
Cell wall
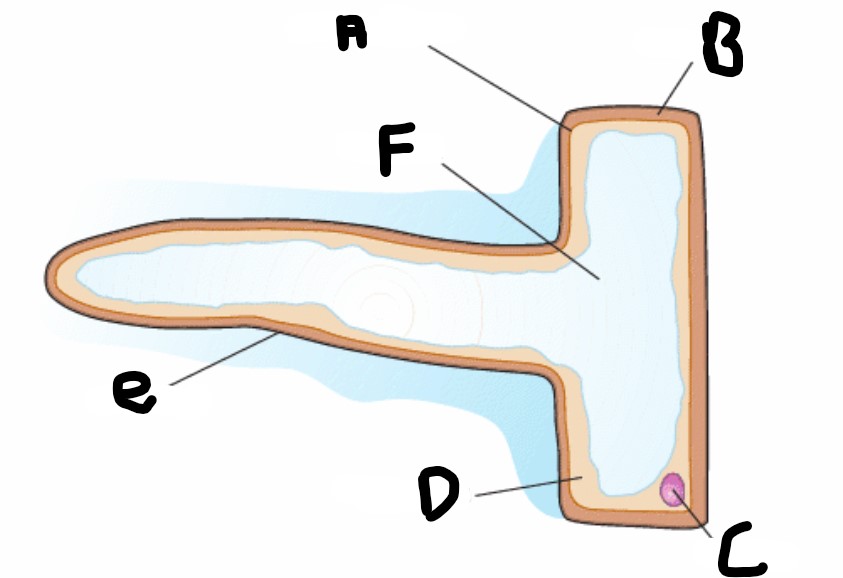
What is structure C
Nucleus
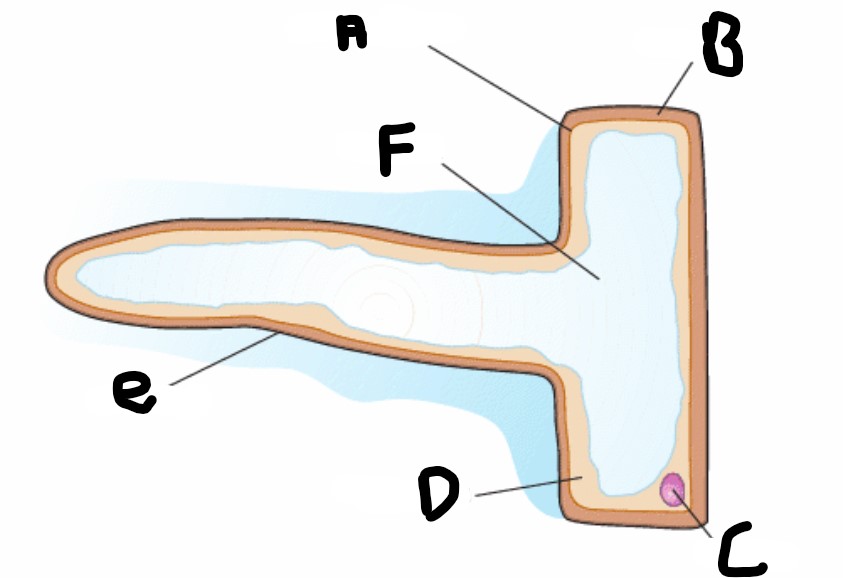
What is structure E?
Root hair
Whare sperm cells found?
In the testes
What are sperm cells?
Male gametes
What is the meaning of gametes?
One set of chromosomes compared to two sets in the parent cells
What is the name of the structure that enables to sperm to move?
Undulipodium or flagellum
Why do sperm need a lot of mitochondria?
To supply the energy needed for the locomotion
What is the head of the sperm made of ?
Acrosome
What is acrosome?
A digestive enzyme which is released when the sperm meets the egg, to digest the protective layer and allow the sperm to penetrate
What is the function of the sperm?
To deliver genetic information to the egg cell or ovum
When the egg and sperm join together, what is the process called?
Fertilisation
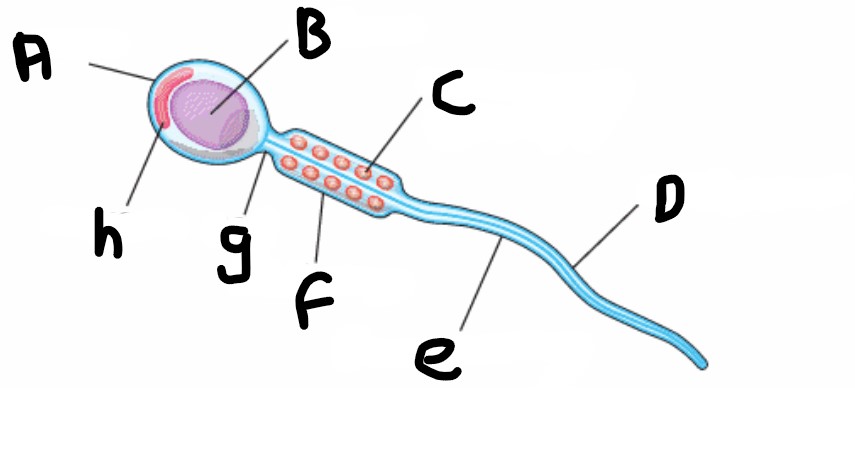
What is structure A?
Head
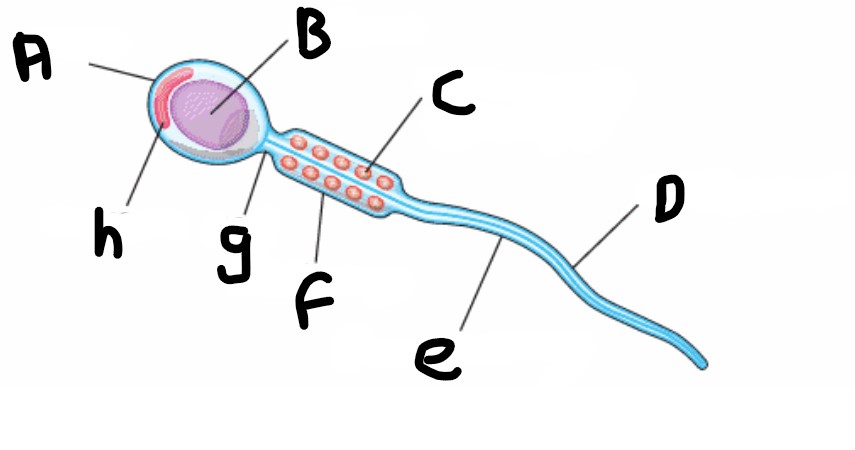
What is structure H?
Acrosome
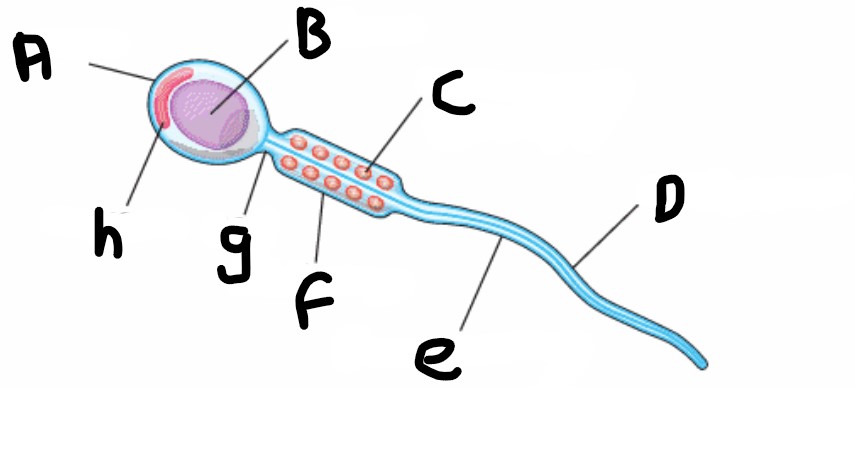
What is structure B?
Nucleus
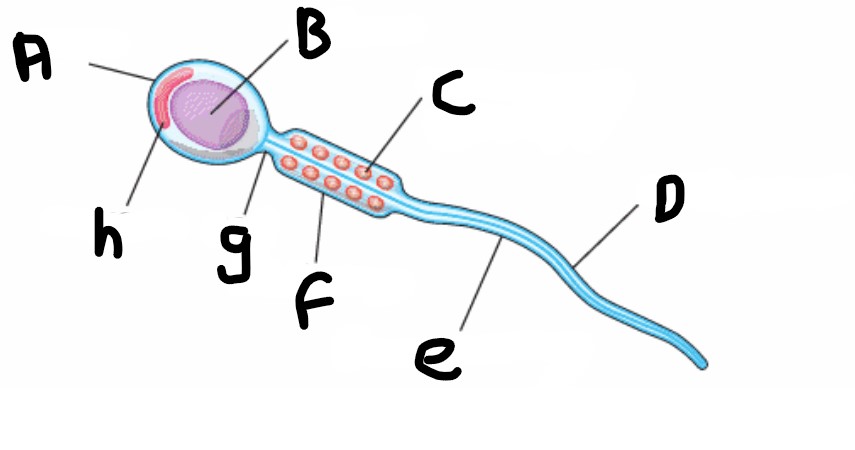
What is structure G?
Neck
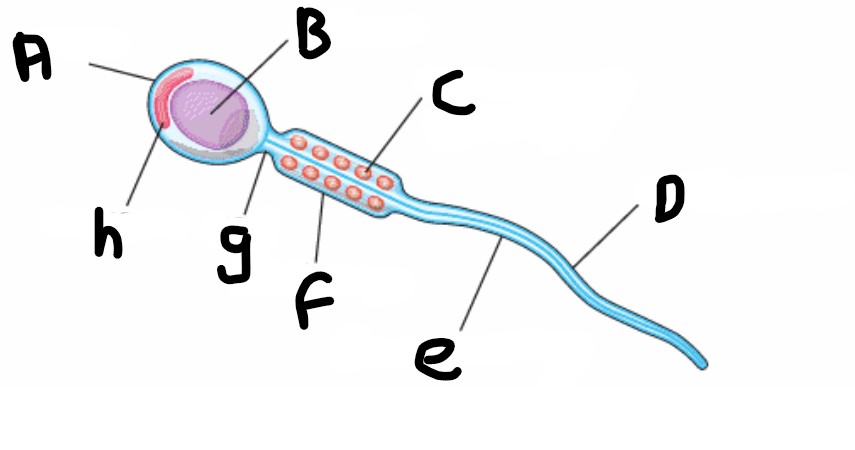
What is structure C?
Mitochondrion (spiral shape)
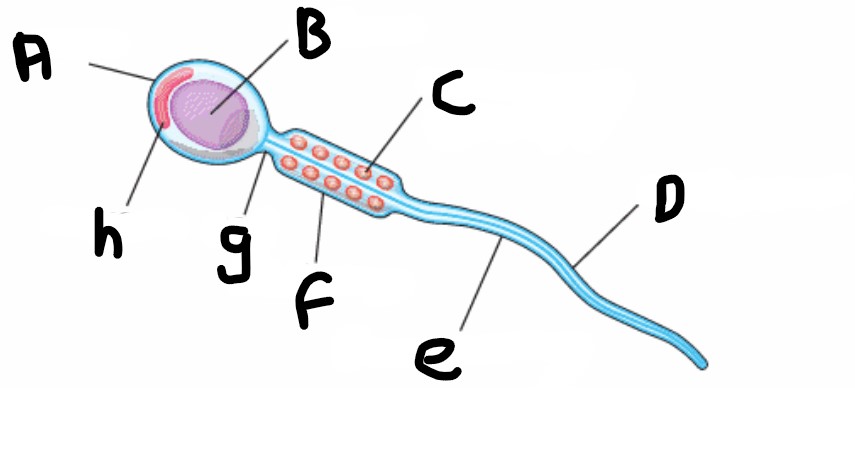
What is structure F?
Middle piece
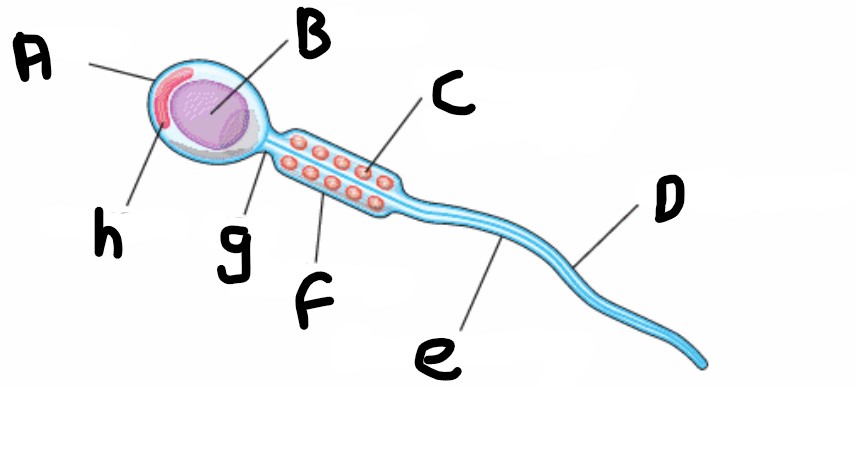
What is structure D?
Undulipodium
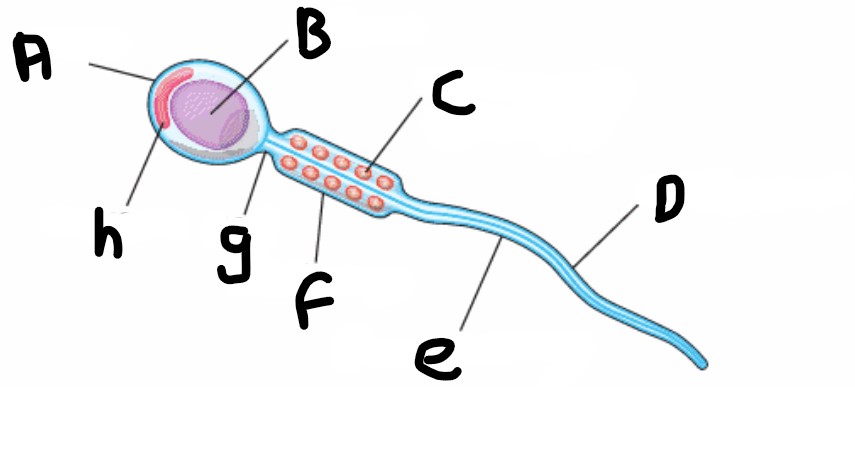
What is structure E?
Plasma membrane
Where is the egg cell found?
Ovaries
What are egg cells?
Female gametes
What is the zona pellucida?
The outer protective membrane of the egg
What is attached to the the zona pellucida?
The corona radiata
What is the function of the corona radiata?
To supply proteins needed by the fertilised egg cell
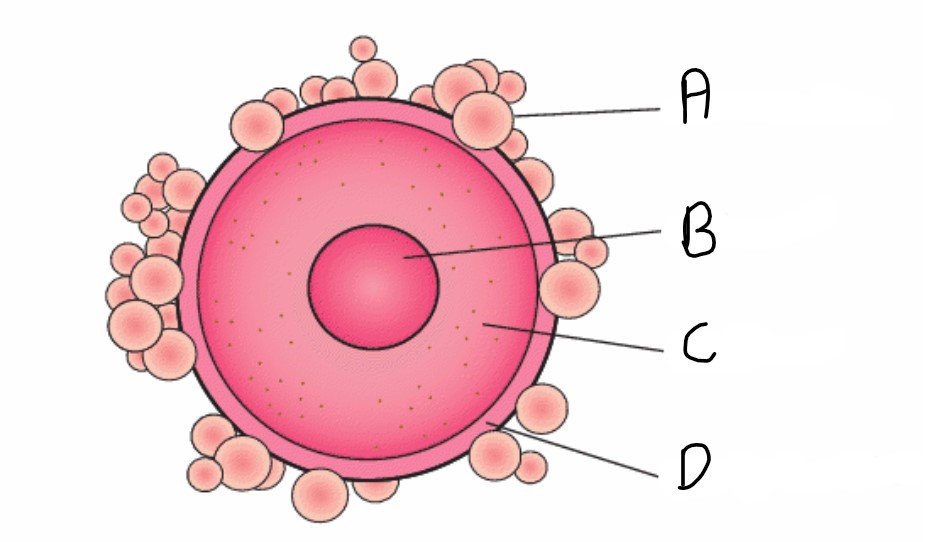
What is the name of structure A?
Corona radiata
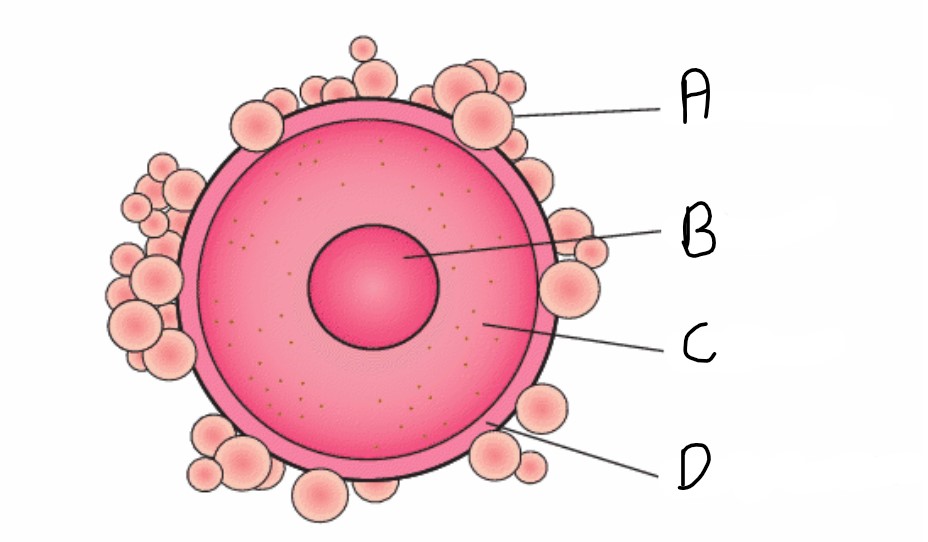
What is the name for structure D?
Zona pelluccida
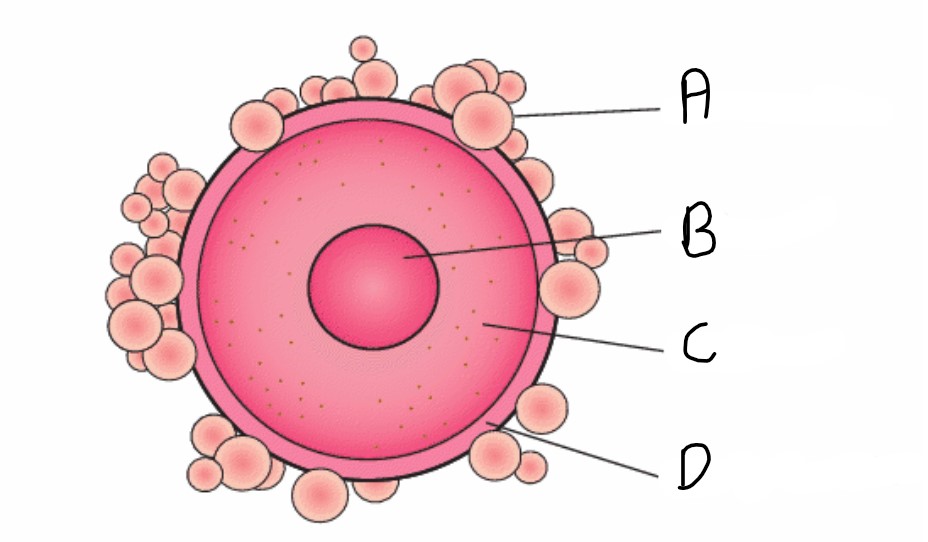
What is the name of structure B?
Nucleus
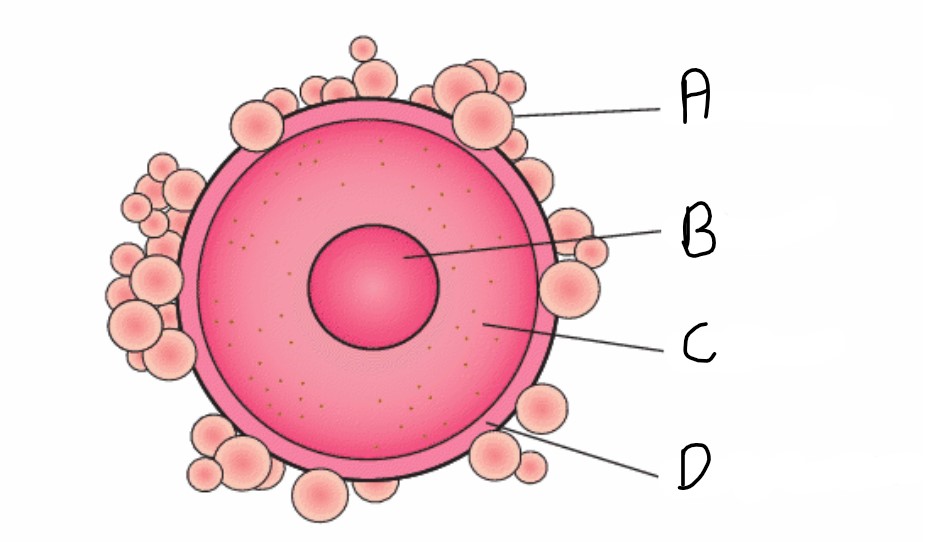
What is the name of structure C?
Cytoplasm
Where are red blood cells found?
In the blood stream
What is another name for red blood cells?
Erythrocytes
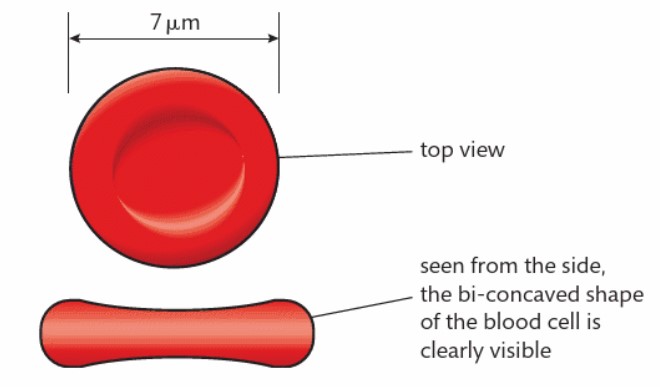
What type of shape is the red blood cell?
Biconcave shape
What does this shape do for the red blood cell?
Increases the surface area to volume ratio
Why are red blood cells flexible?
So that they can squeeze through narrow blood capillaries
What is the function of a red blood cell?
To transport oxygen around the body
What feature does the red blood cell NOT have that other cell have?
It has no nucleus
Why does the red blood cell not have a nucleus?
To increase the space for haemoglobin molecules inside the cell that carry oxygen
What is haemoglobin?
A protein molecule in red blood cells. It carries oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body and carbon dioxide back to the lungs
What is a Neutrophil?
A type of white blood cell
What feature does a neutrophil have that enables it to squeeze through gaps when travelling to a site of infection?
Multi-lobed nuclei
What does the cytoplasm contain?
Lysosomes
What do lysosomes contain?
Enzymes that are used to digest pathogens
What is a pathogen?
A microorganism that can cause disease
What role do neutrophils have?
They have an important role in the immune system
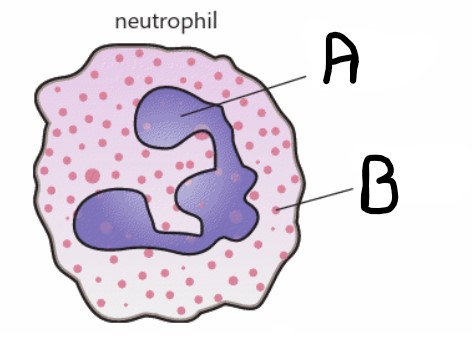
What is structure A?
Multi-lobed nucleus
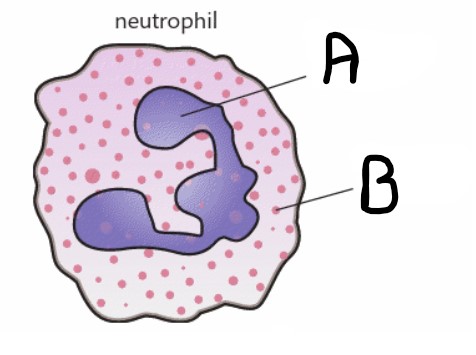
What is structure B?
Granulated cytoplasm