BIO1320 LAB
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dr. Pass lab quiz prep materials
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Abbreviation
a shortened version of a word used to save time
Acronym
a combination of the first letters of a series of words making up a recognizable pattern to represent said phrase
Language of Origin for Biological Terminology
Greek and/or Latin
Prefix
at the beginning of a word
Root Word
the main focus of the word
Suffix
at the end of the word
Eponym
terms that generally include the name of the person who discovered the structure, pathway of event as a way of honouring their work
Descriptive Term
the ‘scientific’ or ‘technical’ name
Down’s Syndrome = Eponym
Trisomy 21 = Descriptive Term
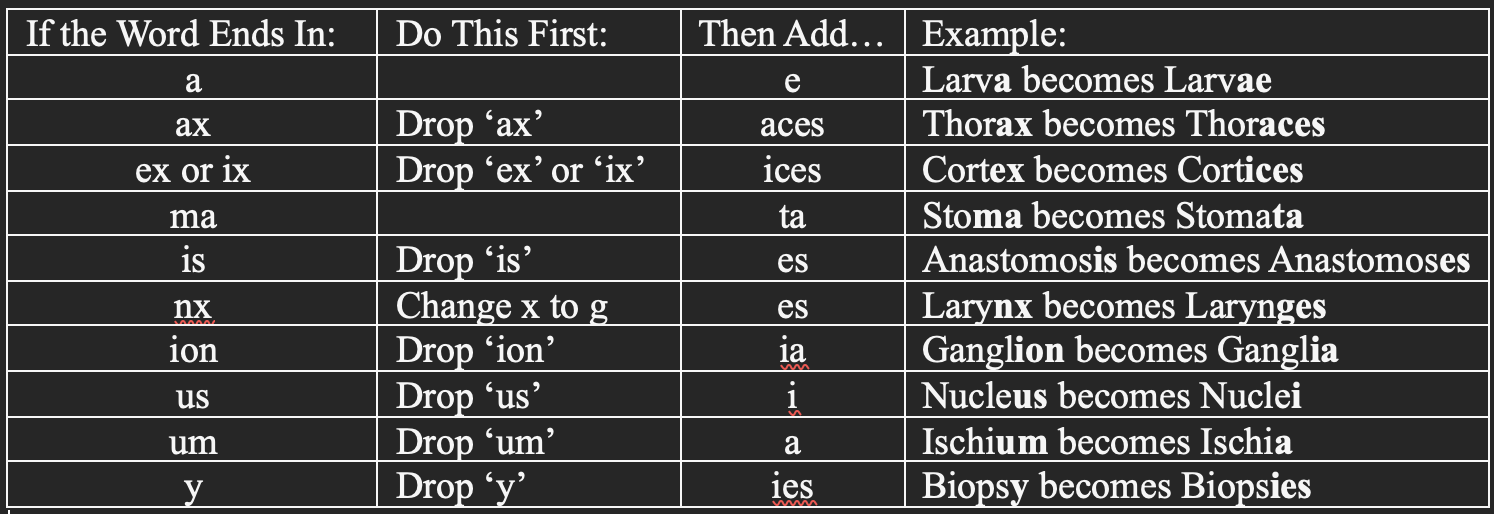
Pluralizing Terms
Classifications of Life
DOMAIN - Eukarya
KINGDOM - Animilia
PHYLUM - Chordata
CLASS - Mammalia
ORDER - Primates
FAMILY - Hominidae
GENUS - Homo
SPECIES - sapien
Mean Calculation
= sum of lengths/# of individuals in sample
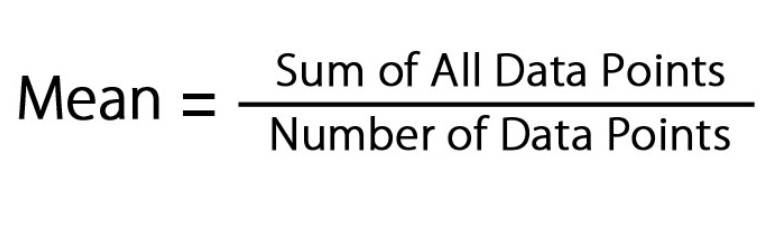
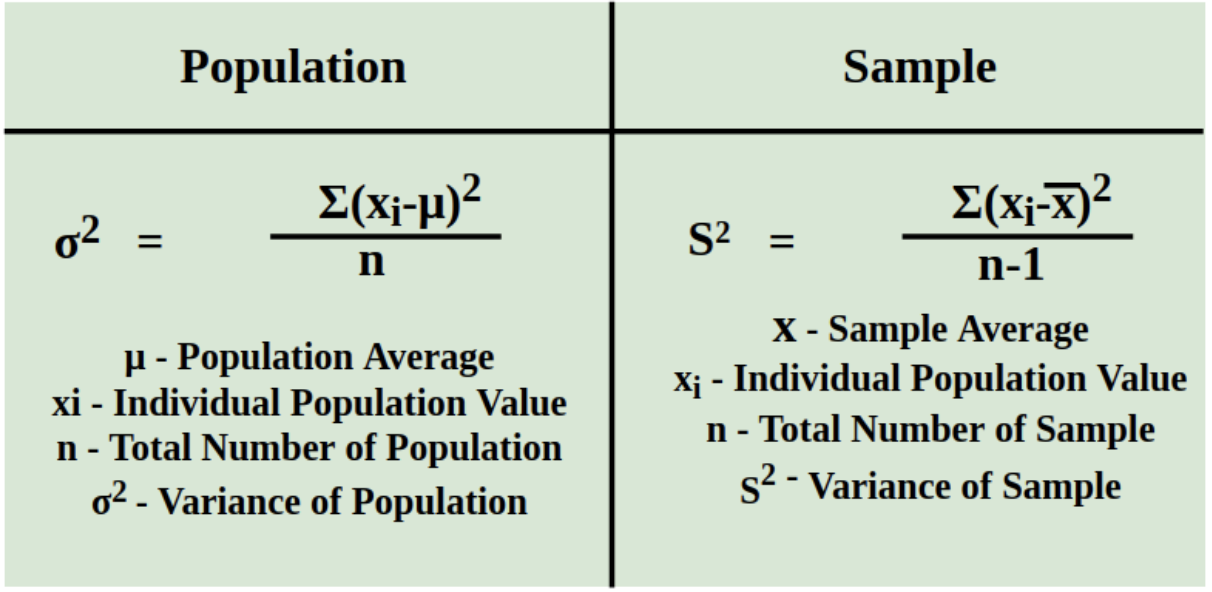
Variance Calculation
= sum of (differences between each length and mean)2 / #of individuals in sample - 1
Standard Deviation Calculation
= square root of Variance
Evolution
the process by which life has changed through time
Species
a group of similarly constructed organisms that share common genes
Population
all the members of a species living in a particular area
Adaptation
structures, physiology, and behaviour that make an organism suited to its environment
2 Types of Data to Support Evolution
Comparative Anatomy
Biochemical Comparison
Human Skull
consists of 22 bones including the lower jaw
8/22 bones are paired
bones fit together at immovable joints called SUTURES
Humans and Apes have
4 canine teeth
8 premolars
12 molars
8 incisors
Prognathism
is the extent to which the jaw and face protrude forward when viewed from the side
Brow Ridge
the mass of bone over the eye sockets, functions to support the upper facial skeleton against forces produced by chewing
Sagittal Crest
is a thin ridge of bone a top and down the middle of the braincase
associated with having a small braincase and powerful jaws
Foramen Magnum
is the large opening in the base of the skull through which the spinal cord passes
reflects the posture of the body
Canine Diastema
is the gap in the teeth corresponding to the canines opposite jaw
Homologous
if they exhibit similar basic structures and embryonic origins
Analogous
structures similar in function only
Molecular Clock Theory
states that the number of amino acid changes between organisms is proportional to the length of time since two organisms began evolving separately from a common ancestor
Cytochrome C
a sequence of amino acids
a carrier of electrons in the electron transport chain found in mitochondria and chloroplasts
found in a variety of organisms
Relatedness via Antibody-Antigen Tests
the more closely related these animals are to humans, the more precipitate forms during an antibody test with human serum
A Population Evolves IF:
it contains variation
the variation is at least partly heritable
some variants survive to reproduce at higher rates than others
Geological Time Scale
pertains to the history of Earth from its formation 4-4.5 billion years ago to the present
the ages of rocks can be measured in years by analyzing naturally occurring radioactive elements found in minute quantities in certain rocks and minerals
Eras of Time
Paleozoic (ancient life)
Mesozoic (middle life)
Cenozoic (recent life)
divided again into periods
Periods of Time
OLDER
Cambrian
Ordovician
Silurian
Devonian
Carboniferous
Permian
Triassic
Jurassic
Cretaceous
Tertiary
Quaternary
NEWER