ID E1 Study Guide
1/231
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
232 Terms
What are the prodromal sx associated w/ Measles?
fever, malaise, anorexia, conjunctivitis, coryza, cough
How does the rash that is associated w/ Measles present?
red, flat, blotchy, originates on the face/hairline and spreads cephalocaudally
What disease is associated with Koplik spots?
Rubeola (measles)
What are Koplik spots?
small, white spots on the inside of the cheek (occur prior to rash)
What are the S&S associated w/ Rubeola (measles)?
cervical LAD, high fever, pharyngitis, non-purulent conjunctivitis, Koplik spots
What are potential complications of a Rubeola (measles) infxn?
otitis media, blindness, pneumonia, croup, severe diarrhea, encephalitis
What is the tx for Rubeola (measles)?
supportive care: IV hydration, vit A, ± Ribavirin (immunosuppressed)
How does the rash associated with Rubella (German measles) present?
fine, pink, maculopapular, starts on the face and spreads down; spreads & fades quickly!
What S&S are associated in children w/ Rubella?
few to no constitutional sx
What S&S are associated w/ adults w/ Rubella?
low fever, coryza, HA, conjunctivitis, malaise, polyarthritis, LAD, Forscheimer spots
Which disease is associated with Forscheimer spots?
Rubella (German measles)
How do Forscheimer spots present?
discrete rose-colored spots on the soft palate
Which trimester is the fetus at greatest risk of developing Congenitial Rubella Syndrome (CRS)?
1st trimester
What congenital disabilities are associated with Congenital Rubella Syndrome?
deafness, cataracts, microcephaly, glaucoma, CV defects
What is the primary age of Roseola occurrence?
peak prevalence 7-13 months
What virus causes the majority of Roseola cases?
Herpesvirus 6
What S&S are associated with Roseola?
sudden high fever (3-5 days), rash originating on torso, TM inflammation, LAD, V/D, irritable
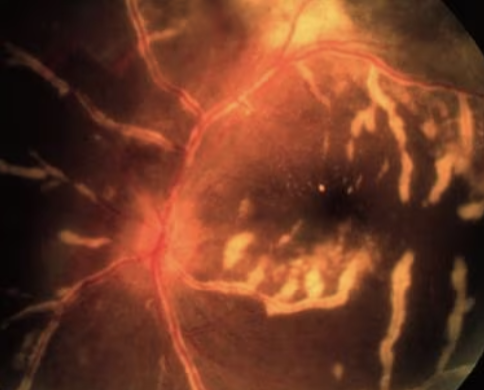
What would see on a funduscopic exam of a pt w/ CMV retinitis?
white granular retinitis w. intraretinal hemorrhage, retinitis that follows vessels; originates in one eye and progresses to the other
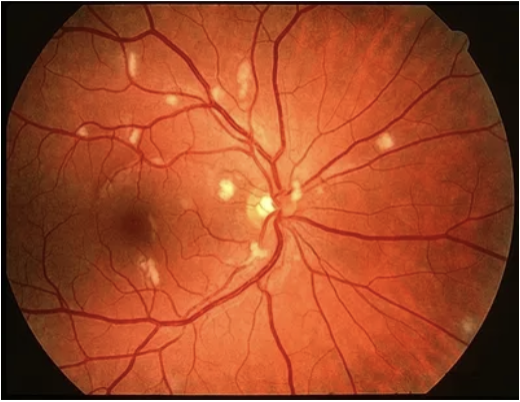
What would find you on a funduscopic exam of a pt w/ HIV retinopathy?
Asx, microvasculopathy, cotton wool spots, microaneurysms, intraretinal hemorrhages
Most newborns w/ congenital CMV infxn are Asx. What % have a symptomatic infxn?
10% of exposed
How does a congenital CMV infxn present in symptomatic newborns?
small for GA, microcephaly, ventriculomegaly, chorioretinitis, jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, petechiae, thrombocytopenia
Newborns w/ a congenital CMV infxn are at risk for what neurodevelopmental abnormalities?
hearing loss, motor disabilities, intellectual disability, chronic liver disease
Which virus is the primary cause of Mono infxns?
EBV
What S&S are associated with/ Mono?
fever, chills, malaise, myalgia, fatigue, sore throat, LAD, splenomegaly, rash
What neurological syndromes are associated with Mono?
GBS, nerve palsies, meningoencephalitis, meningitis, neuritis, myelitis
What tests are used to dx Mono?
Monospot, can also use ELISA
What is the tx for Mono?
supportive care, NSAIDS, corticosteroids
What pt education needs to be given when infected w/ Mono?
avoid contact sports for 6 weeks
What prodromal sx are associated with Mumps?
fever, HA, myalgia, fatigue, anorexia, salivary gland swelling, parotitis
What S&S are associated with the Mumps?
epididymo-orchitis, oophoritis, pancreatitis, arthritis
What complications can arise from the Mumps?
sterility, meningitis, encephalitis, deafness, death
How is Acute Poliomyelitis transmitted?
contact w/ stool or droplets from a sneeze/cough
What is the GOLD standard for dx Acute Poliomyelitis?
stool PCR or culture
What percentage Acute Poliomyelitis cases are Asx?
90-95%
What percentage of Acute Poliomyelitis cases are Abortive?
< 10%
What percentage of Acute Poliomyelitis cases are Paralytic?
< 0.1%
What is the classic presentation of Paralytic Poliomyelitis?
neck stiffness, back pain, flaccid paralysis, HA, fever, vomiting, weakness
What are the S&S associated w/ Varicella (chicken pox)?
low fever, malaise, loss of appetite, crops of pruritic erythematous vesicles that scab, “dewdrop on a rose petal” appearance
What are the possible complications of Chicken Pox?
pneumonia, skin infxns (Group A strep), septic sx (kids), encephalitis
How is Herpes Zoster (shingles) transmitted?
localized reactivation of varicella
How does Shingles present?
lesions appearing along dermatomes, unilateral -do not cross midline, closely aggregated, SEVERE pain, parasthesia
What are possible Herpes Zoster complications?
post-herpetic neuralgia, Zoster opthalmicus (emergency!)
What is Hutchinson’s sign?
vesicles on the tip/side of the nose preceding development of ophthalmic herpes zoster
What medications are used to tx Shingles?
Acyclovir, Valcyclovir, or Famicyclovir
When should tx for Shingles be started? How long should it last?
start early (<72 hrs); x 7 days
*14 if immunocompromised
How are Chickungunya, Dengue, and Zika virus transmitted?
Mosquitoes: Aedis aegypti & Aedis albopictus
What are the S&S of Chickungunya virus?
fever, malaise, joint pain, rash originating on limbs and trunk
What are the chronic sx associated w/ Chickungunya virus?
joint pain months after infxn; may relapse 2-3 yrs later as arthritis or tenosynovitis
What are the 3 phases of Dengue virus?
Febrile, Critical, Recovery
What are the S&S of Dengue virus?
rapid onset of fever, HA, N/V, retro-orbital pain, myalgia, rash, hemorrhagic manifestations
In addition to mosquitoes, how else can the Zika virus be transmitted?
sexual contact
What are the S&S of Zika virus?
low fever, fatigue, pruritic rash, HA, conjunctivitis, myalgia, retro-orbital pain, weakness
What congenital abnormality is associated with Zika?
microcephaly
How does Folliculitis present?
multiple, small, scattered, erythematous papules or pustules surrounding a hair, pruritic
What organism is most commonly involved with Folliculitis?
Staph
What is the tx for Folliculitis?
usually resolves on its own, warm compresses, avoid shaving, topical abx if needed
How does Hot tub Folliculitis present?
multiple, small, scatter, erythematous papules or pustules surrounding a hair, pruritic, more common in bathing suit areas
What organism is most commonly involved in Hot tub Folliculitis?
Pseudomonas
What is the tx for Hot tub Folliculitis?
usually resolves w/ good hygiene and avoidance of re-exposure
What is a circumscribed collection of pus appearing as an acute or chronic localized infxn w/ tissue destruction?
Abscess
What is an acute, deep-seated, red, hot, painful/tender nodule or abscess that evolves from staph folliculitis?
Furuncle
What is the most common location for an Abscess, Furuncle, or Carbuncle to occur?
nape of neck, back, butt, groin/thigh, axillae
What is the tx for a Furuncle?
warm moist compression; no abx if <2 cm; large → I&D
When should oral abx be prescribed in addition to an I&D?
multiple lesions, abscess >2cm, surrounding cellulitis, comorbidities/ immunocompromised, indwelling medical device
What is a deeper infxn composed of interconnecting abscesses usually arising in several contiguous hair follicles (coalescence of furuncles)?
Carbuncle
What is the tx for a Carbuncle?
swab for culture → I&D PLUS abx
How does Impetigo present?
pruritic, honey-colored crusts, lesions, bullae, LAD
What are the MC organisms associated with Impetigo?
S. aureus & Group A beta-hemolytic strep
What is the tx for Impetigo?
Mupirocin
*if Bullous add Doxy, Bactrim, or Clindamycin
How does Cellulitis present?
malaise, fever, chills, HA, warm/tender erythematous skin, bullous, poor margins
What organisms are most commonly involved in Cellulitis?
Staph (MRSA, MSSA) or group A strep
What is the tx for Cellulitis?
Oral: Bactrim or Doxycycline
IV: Vancomycin
What is SSSS also known as?
Ritter’s disease
What age group is most likely to get SSSS?
children < 6 yo
What are the S&S of SSSS?
fever, sore throat, malaise, warm tender skin, + Nikolsky, desquamation, rhinorrhea, conjunctivitis
What organism causes TSS?
S. Aureus (MSSA -mc, MRSA)
What are common sources of TSS?
tampons, nasal packing, wound packing
How does TSS present?
“flu like” sx, fever, confusion, chills, malaise, N/V/D, abd pain, rash, HA, hypotension, syncope, dizziness, involves at LEAST 3 organ systems
What is the tx regimen for TSS (ensure MRSA and MSSA coverage)?
agressive supportive tx; IV Abx- Clindamycin + Vancomycin + Zosyn or Maxipime (PCN + beta lactam inhibitors)
What age demographic is most susceptible to Erysipelas?
infants/ young kids & elderly 60+
How does Erysipelas present?
red w/ feeling of tightness and warmth, painful, sharply-demarcated, advancing edge, butterfly cheeks
What organisms most commonly cause Erysipelas?
Group A Beta-hemolytic strep (S. pyogenes -MC)
neonates: Group B strep
Where does Erysipelas commonly occur?
legs or face
What is the tx for Erysipelas?
Amoxicillin
Severe → ceftriaxone
How is Strep Pharyngitis transmitted?
direct person-person contact; inc in crowded settings
What organism causes Strep Pharyngitis?
Strep Pyogenes (GAS)
How does Strep Pharyngitis present?
sore throat, large red tonsils, ± exudate, odynophagia, cervical LAD, fever/chills, NO cough
What is the tx for Strep Pharyngitis?
1st line: PCN
Alt: Amoxicillin
PCN allergy: Azithromycin
What complications can arise from Strep Pharyngitis?
RF, glomerulonephritis, peritonsillar abscess, otitis media, pneumonia, meningitis
How does the rash associated with Scarlet Fever present?
fine, papular, sandpaper-like lesions originating on axillae, groin, neck → generalize; NO palms/soles; + pastia lines, flushed cheeks, strawberry tongue
What are the 5 major Jones Criteria for dx RF?
CCEPS- carditis, chorea, erythema marginatum, polyarthritis, subcutaneous nodules
What are the 4 minor Jones criteria for dx RF?
arthralgia, fever, elevated ESR or CRP, prolonged PR interval
What Jones Criteria must be met in order to dx RF?
2 major criteria OR 1 major + 2 minor
How does Erythema Infectiosum present?
“slapped cheek appearance”, lace-like body rash, circumoral pallor, fever, malaise, HA, arthritis
What virus causes Erythema Infectiosum?
Parvovirus B19
What is the historical name of Erythema Infectiosum?
Fifth disease
What is Pediculosis capitis?
head lice
What is Pediculosis corporis?
body lice
What is Pediculosis pubis?
pubic lice (“crabs”)
How does Pediculosis present?
pruritus over infected area (may be severe)