Nuclear Reactions
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
alpha-decay particle
on products side
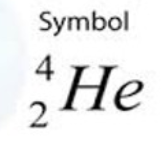
What type of nuclear decay would an atom with a large nucleus likely undergo?
Alpha decay
What is the result of alpha decay?
a reduction in mass
B decay (B emission) particle
on products side
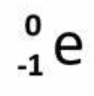
What is the result of B emission?
neutron transformed into proton
An atom has too high of a neutron to proton ratio, what type of decay is it likely to undergo?
Beta decay (B emission)
B+ decay (positron emission) particle
on products side
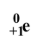
Positron emission result
conversion of a proton into a neutron
An atom has too low of a neutron to proton ratio, which type(s) of decay is it likely to undergo?
Electron capture or B+ decay (positron emission)
Electron capture particle
on reactant side
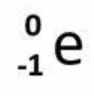
What order of kinetics is radioactive decay?
always first order, half-life is constant
Nuclear half-life equation
t1/2 = 0.693/k
t1/2 = half-life
k = decay constant
An element is stable against nuclear decomposition, what must be true of this element?
Its nuclear binding energy must be high