Monomers & Polymers: Carbohydrates
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Monomer
small soluble molecule from which larger molecules are formed
Polymer
Molecules made from many similar monomers joined together.
Monomer of carbohydrate
Monosaccharide
Polymer of carbohydrate
Polysaccharide
Monomer of proteins
Amino acid
Polymer of proteins
Polypeptide
Monomer of DNA
Nucleotide
Polymer of DNA
Polynucleotide
Lipids are not polymers. Why?
They are not made up of similar repeating subunits, this have both fatty acid and glycerol molecule
Elements that are in carbohydrates
Carbon hydrogen, oxygen.
Types of carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Disaccharides
Polysaccharides
Condensation reaction
Joins two molecules together by the formation of a chemical bond and it involves the elimination of a water molecule. Eg. monomers joining together
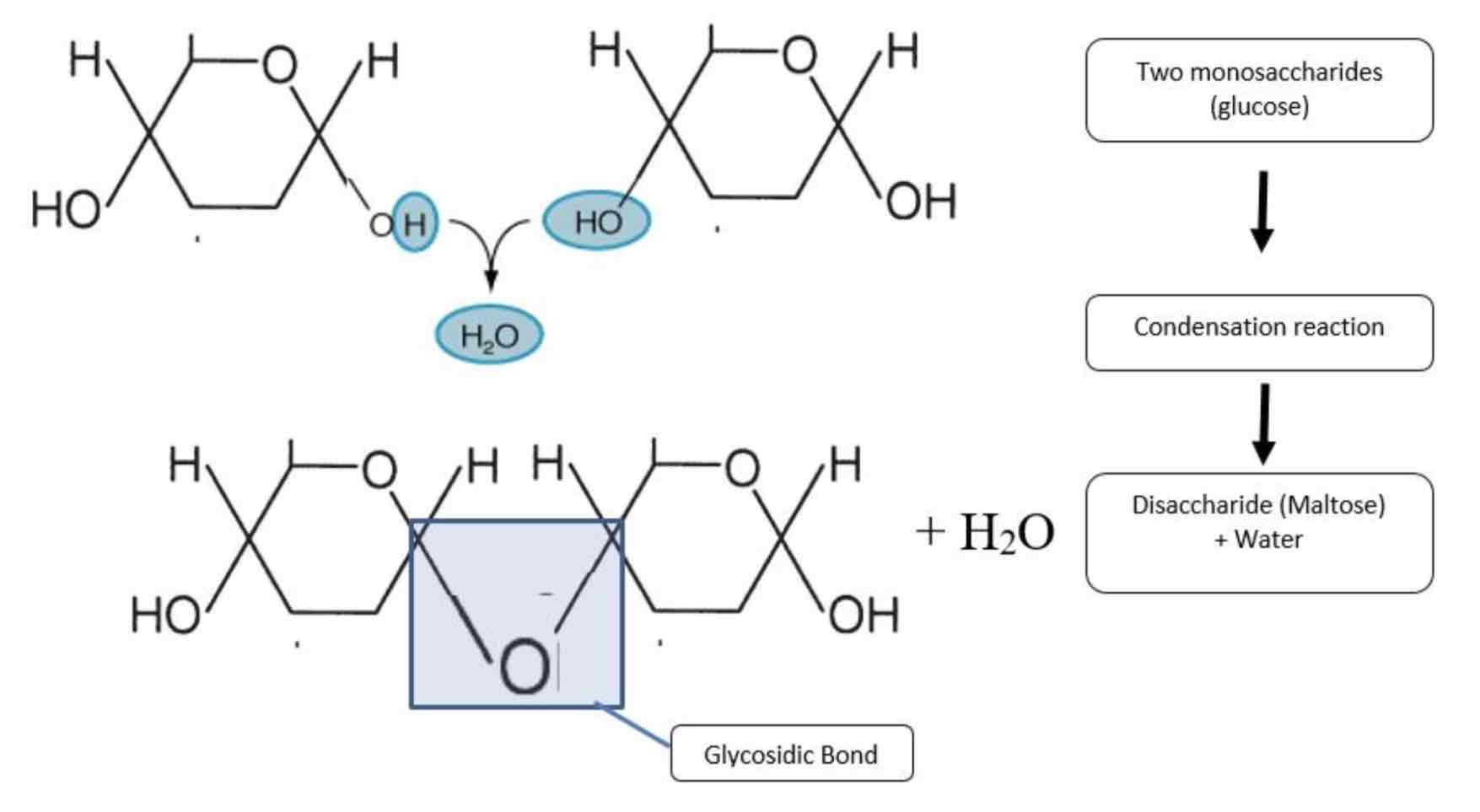
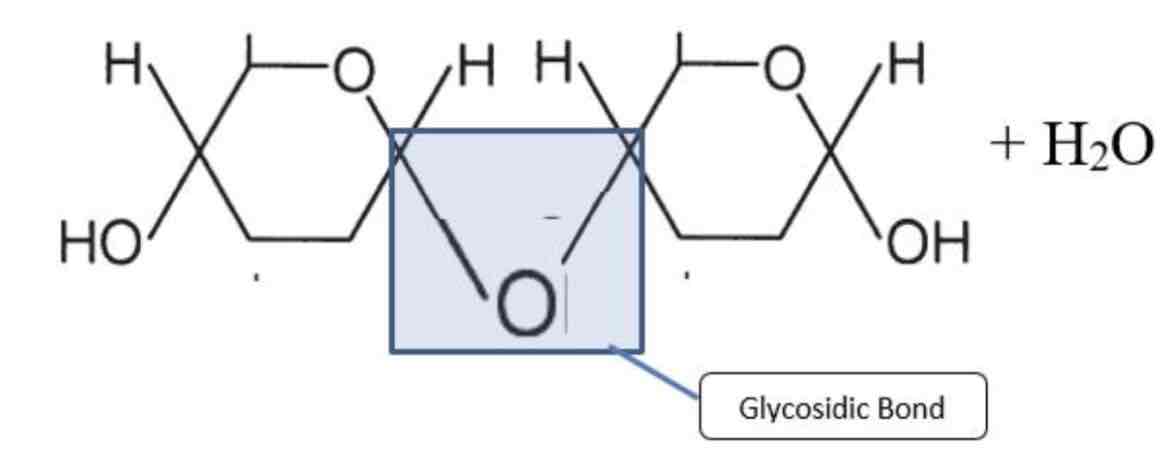
Glycosidic bond
Bond formed between monosaccharides and in condensation reaction
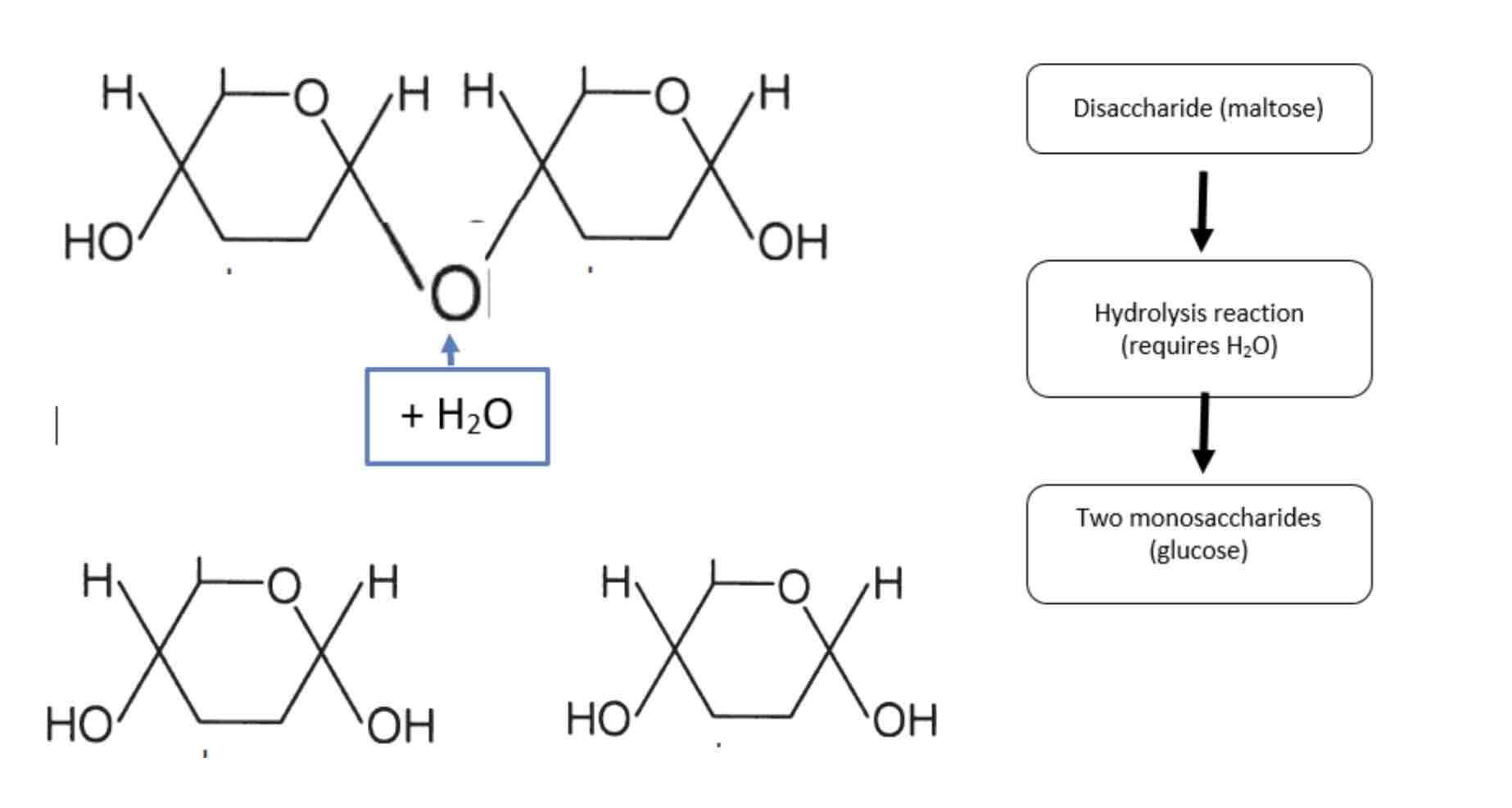
Hydrolysis reaction
Breaks a chemical bond between two molecules and it involves the use of a water molecule. Eg polymers breaking down
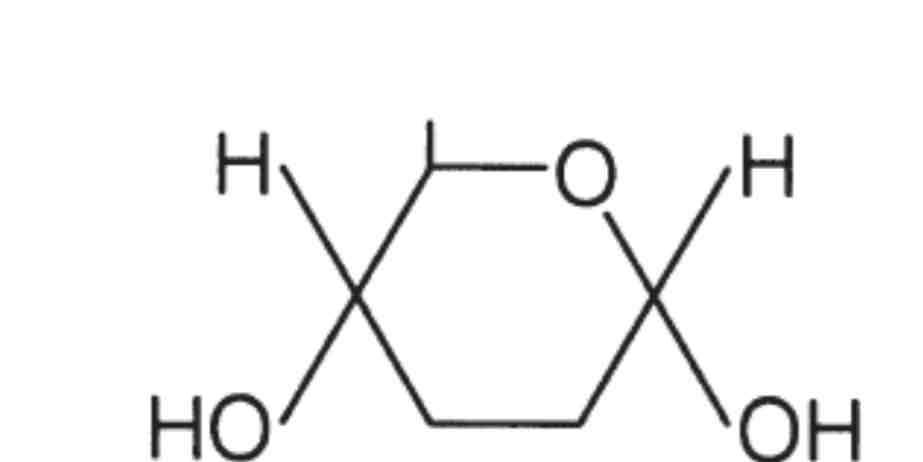
Monosaccharides
monomers from which larger carbohydrates are made
Monosaccharides
Glucose, fructose, galactose
General formula for monosaccharides
C6H12O6
Disaccharides
two monosaccharides joined together by a glycosidic bond which forms during a condensation reaction.
Disaccharides
Maltose, sucrose, lactose
General formula for disaccharides
C12H22O11 + H20
Formation of disaccharides
Maltose → glucose + glucose
Lactose → glucose + galactose
Sucrose → glucose + fructose
Isomers of glucose
Alpha- glucose and beta-glucose
Isomer
An isomer of a molecule has the same chemical formula, but a different structural formula
Alpha- glucose
Beta glucose
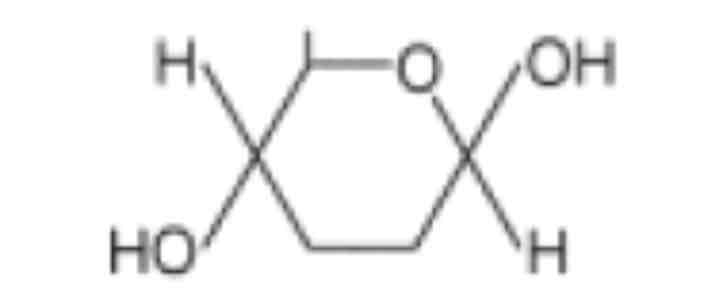
Difference between the two glucose isomers.
The position of the hydrogen (H) and hydroxyl (OH) groups on carbon 1 are INVERTED
Polysaccharides
formed by the condensation of many repeating monosaccharides.
Polysaccharides
Cellulose : beta-glucose
Starch: alpha-glucose
glycogen: alpha-glucose
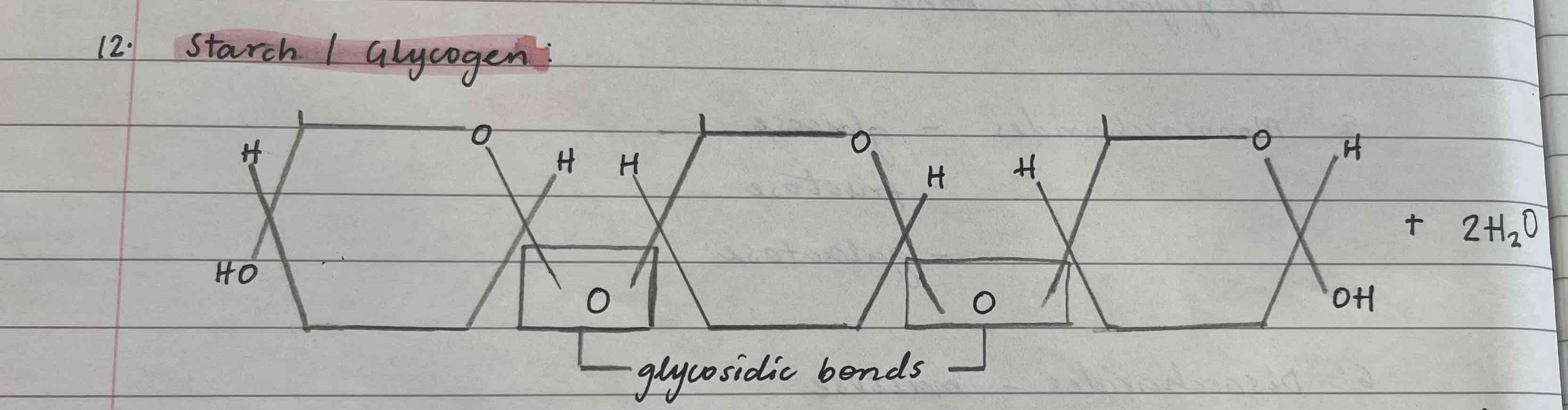
Starch + glycogen
Made from alpha-glucose
Found in plants
Insoluble
Has both 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bond
Cellulose
Made from beta-glucose
Found in plant’s cell wall
Insoluble
Has 1,4 glycosidic bond
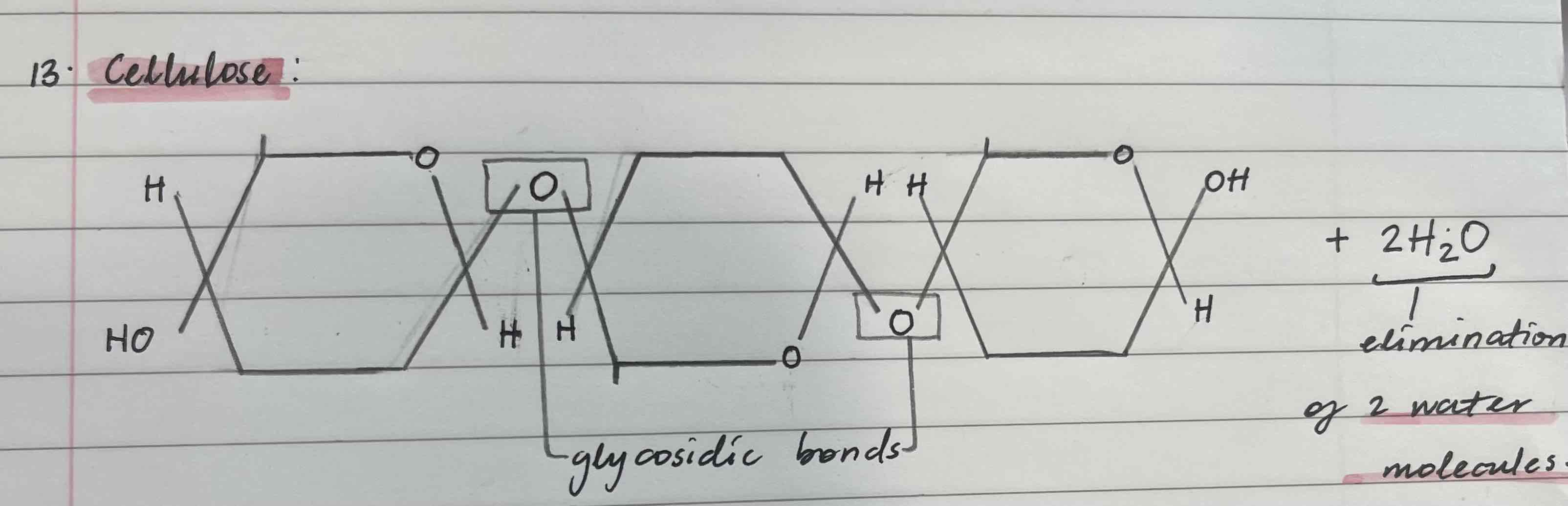
Difference between the appearance of a polymer of alpha-glucose ( glycogen or starch) and a polymer of beta- glucose (cellulose)
In cellulose, the monomers face in alternate directions rather them all in the same way like in starch or glycogen. This is because in beta-glucose, the position of the hydrogen and hydroxyl groups on carbon atom 1 are inverted
Structure of starch and it’s functions
Coiled into a helix so it is compact and can fit into a small space
Insoluble so it does not affect water potential OR so it does not affect osmosis and not easily lost from cell
Branches which gives a larger surface area so it is more rapidly hydrolysed and glucose can e released more rapidly for respiration for energy release
Large molecule so it does not diffuse out of cell membrane and out of cells
Structure of glycogen and its functions
Coiled into a helix so it is compact and can fit into a small space
Insoluble so it does not affect water potential OR so it does not affect osmosis and not easily lost from cell
Branches which gives a larger surface area so it is more rapidly hydrolysed and glucose can e released more rapidly for respiration for energy release
Polymer of alpha-glucose so it is rapidly hydrolysed
Structure of cellulose and it’s function
Long, straight and unbranched chains of beta glucose;
Linked together by many hydrogen bonds to for micro fibrils;
Provides strength and rigidity to plant cell wall
Biochemical test for starch
Add iodine solution (solid iodine + potassium iodide solution)
A colour change from orange to black indicates the presence of starch
Biochemical test for reducing sugars
Add Benedict’s solution to food sample
Heat to 95° C (don’t boil)
A colour change from blue to orange/red indicates the presence of reducing sugars
Benedict’s test
The difference in colours (blue - green - yellow - orange - red) means it is a semi-quantitative test as it can be used to estimate the concentration of reducing sugar in a sample.
To get a quantitative measure:
Filter the liquid and dry the precipitate in the sample
Find the mass
The higher the mass of the precipitate, the more reducing sauger is present.
Using a colorimeter:
A higher absorbance has a higher sugar concentration
Biochemical test for non-reducing sugar
Do Benedict’s test and the sample stays blue
Boil a fresh sample with acid to hydrolyse the glycosidic bond
Neutralise with alkali- sodium hydrogen carbonate
Add Benedict’s solution and heat to 95° C
A colour change from blue to orange/red indicates the presence of a non-reducing sugar.
Reducing sugars
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
Lactose
Maltose
Non-reducing sugars
Sucrose