Abdominal Pain
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
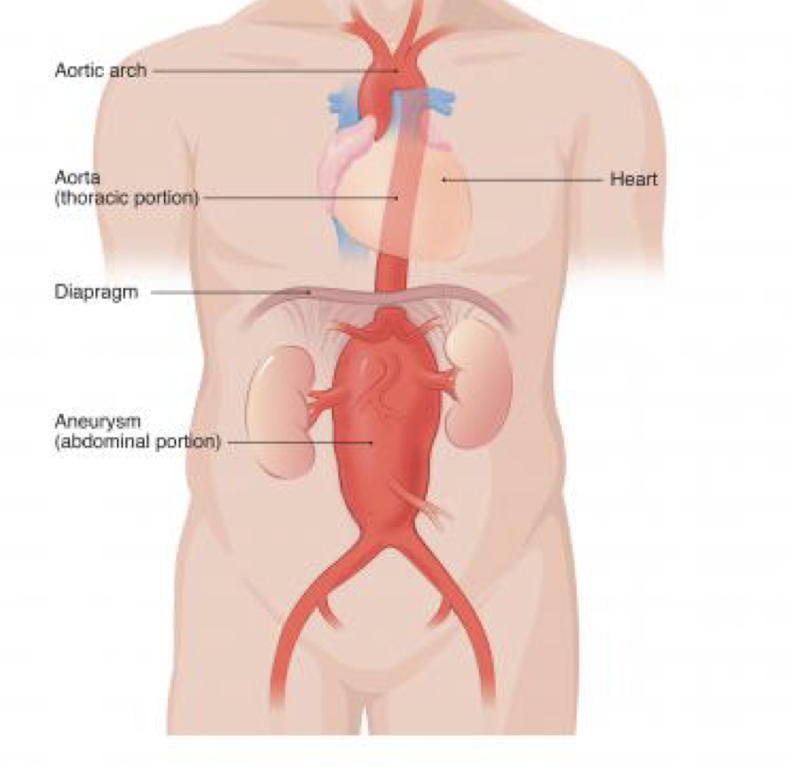
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)
focal dilation of all layers of aorta, most commonly below renal arteries
Risk Factors: AMAB, >65yo, family history, smoking, hypertension, CAD, DM, obesity, chronic alcohol use
S/S: back or abdominal pain, lower extremity weakness, radicular pain, GI hemorrhage, tachycardia if pain/hemorrhage, hypotension suggests rupture
PE: abdominal palpation, neurologic exam
Dx: CT or US, CBC, CMP, Coags, Urinalysis
Tx: Rupture: immediate surgical repair, pain control, blood pressure (permit hypotension, beta blockers for hypertension, rate control)
Symptomatic: repair recommended (esp. >5cm), admit to critical care/treat as ruptured if unstable
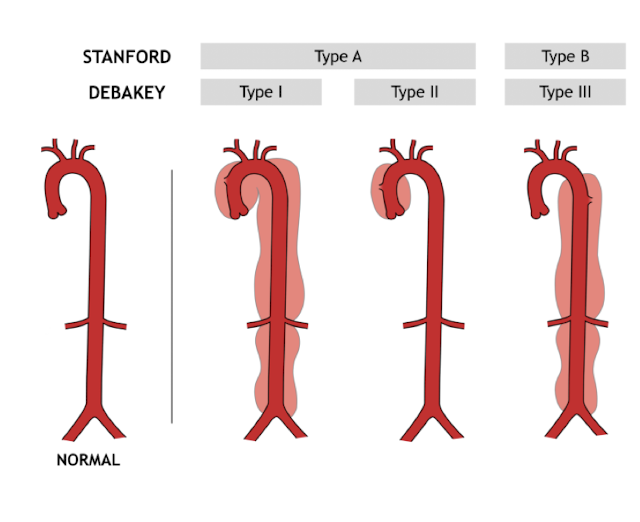
Aortic dissection
Failure of the aortic intima (90%)
risk factors: Coarctation of aorta, Cocaine, Connective tissue disease, Bicuspid aortic valve, Thoracic trauma, Recent instrumentation (cardiac cath, aortic valve replacement), Uncontrolled hypertension
S/S: sudden, severe, maximal intensity pain at onset of chest or midline abdominal pain
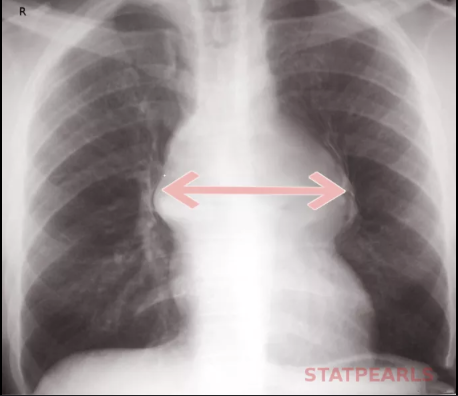
CXR: widening of mediastinum, Tropinin, D-Dimer, CT
Tx: IV and NPO, Analgesia, Heart rate and blood pressure control (IV beta blockers or calcium channel blocker)
Type A (ascending aorta) requires emergent repair
Aortic dissection
Which abdominal emergency presents with sudden, severe, maximal intensity pain at onset of chest or midline abdominal pain and may show widening of mediastinum on CXR?
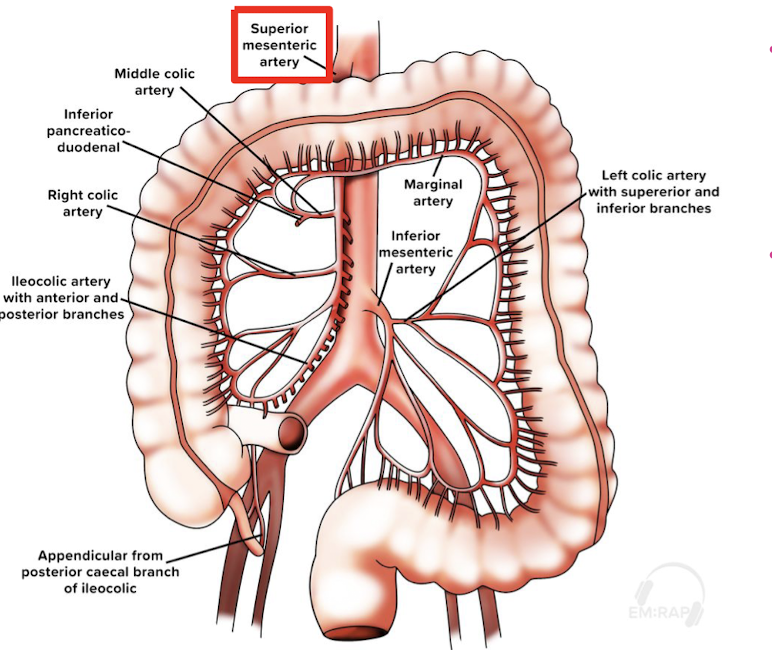
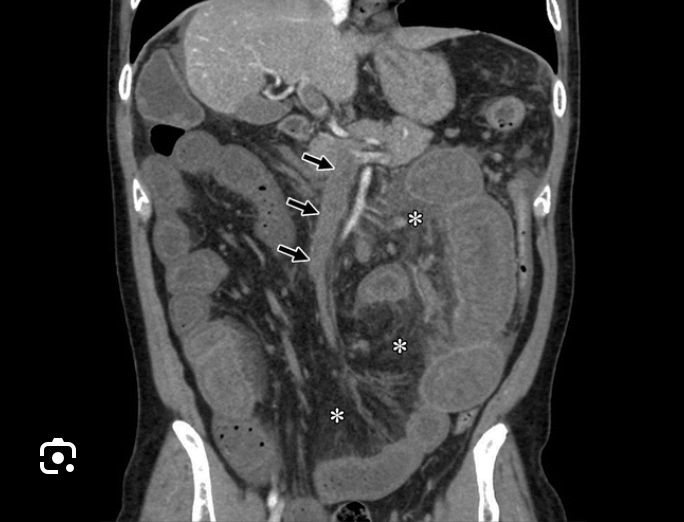
Mesenteric ischemia
occlusion of superior mesenteric artery by embolus (most common), venous thrombosis, nonocclusive
risk factors: atrial fibrillation, valvular disease, endocarditis, myocardial infarction, atherosclerosis, hypovolemia, sepsis, heart failure, diuretics, hypercoagulable state (pregnancy, malignancy)
S/S: abdominal pain “out of proportion” to examination, vomiting/diarrhea
Dx: CT angiography abdomen (diagnostic), CBC, CMP, Lactate
Tx: resuscitation, correct electrolytes, antibiotics
anticoagulation+ emergent surgical/interventional radiology consult
critically ill patient
Mesenteric ischemia
Which abdominal emergency is associated with atrial fibrillation causing abdominal pain ‘out of proportion to examination’ assessed by CT angiography of the abdomen and treated with anticoagulation and emergent surgery?
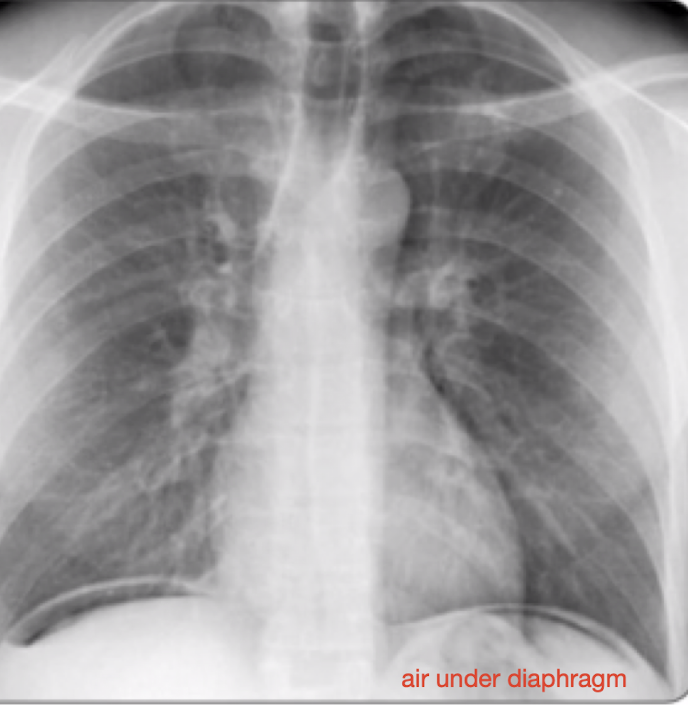
Perforated viscus
full thickness breach in organ, usually intestinal or gastric,
-often secondary to diverticulitis, appendicitis, peptic ulcer, trauma, bowel obstruction, mesenteric ischemia, foreign body
S/S: tachycardia, hypotension, abdominal pain, nausea/vomiting (looks like sepsis/peritoneal signs)
Dx: CBC, CMP, PT/INR, blood cultures if septic, CT or XRAY
Tx: NPO, IV resuscitate, broad spectrum antibiotic coverage for suspected GI pathogens, Surgical consultation
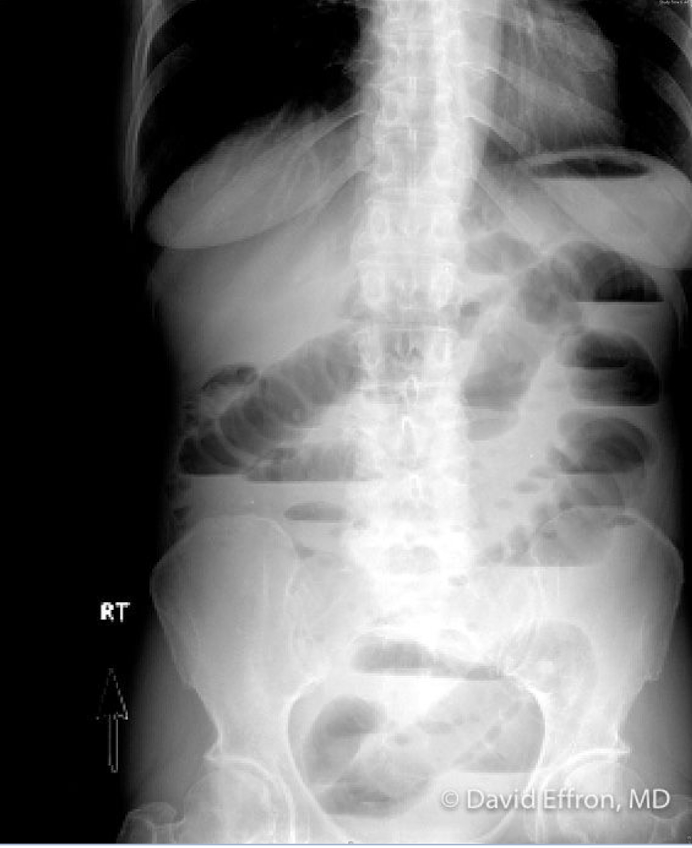
Bowel obstruction
blockage causing accumulated intraluminal contents resulting in distention, bowel wall edema, eventual bowel necrosis
risk factors:
small bowel: adhesions (MCC), hernia, foreign body, radiation, malignancy
large bowel: cancer, diverticulitis, volvulus, impaction, stricture
S/S: nausea, vomiting, pain associated with oral intake, stool changes
PE: abdominal auscultation (hyperactive, tinkling bowel sounds), DRE (impacted stool)
Dx: XRAY, CT imaging (air fluid levels)
Tx: NPO + Fluids, Antibiotics, Proximal decompression, Surgery consult
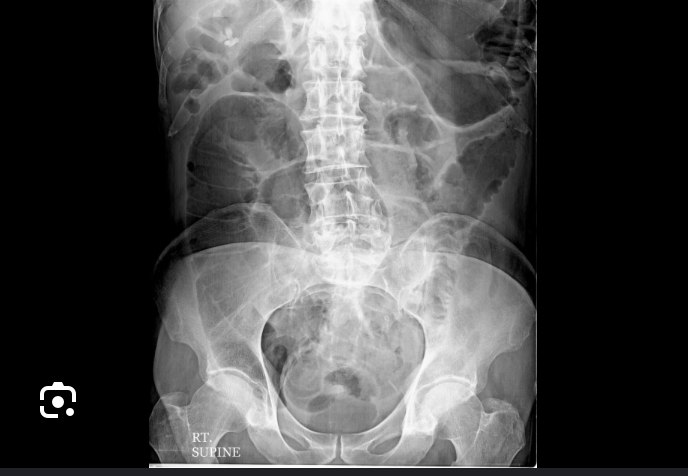
Bowel obstruction
Which abdominal emergency is associated with adhesions (small bowel) and malignancy, diverticulitis, volvulus, impaction (large bowel) causing hyperactive high-pitched, tinkling bowel sounds on auscultation treated with proximal decompression/surgery?
Biliary colic (Cholelithiasis)
paroxysms of pain due to biliary outflow obstruction causing increased intraluminal pressure and gallbladder spasm
risk factors: AFAB:AMAB 2:1, physical inactivity, obesity, insulin resistance, GLP-1, gallbladder hypomotility (fasting, rapid weight loss)
S/S: epigastric and RUQ pain (post-prandial, 1-2 hours after meal), nausea, vomiting, pain radiates to back/right infrascapular
PE: often normal, sometimes RUQ tenderness
Dx: RUQ ultrasound: gallstones or sludge in gallbladder;
Labs: ↑ALP, ↑bilirubin suggests ductal obstruction
Tx: analgesia, early or interval laparoscopic cholecystectomy
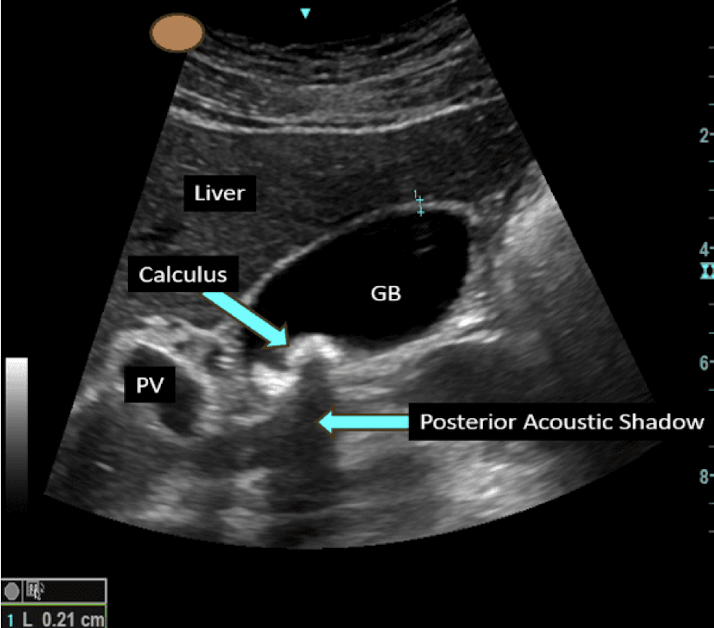
Choledocholithiasis
gallstone in common bile duct → obstruction of biliary flow → increased intraluminal pressure → inflammation of gallbladder and pancreas
risk factors; older adults and patients without gallbladder
S/S: RUQ pain, Jaundice, pale stools, persistently dark urine
Tx: analgesia: opioids, NSAIDs, Fluids and antiemetics if indicated
-stone extraction and cholecystectomy (definitive)
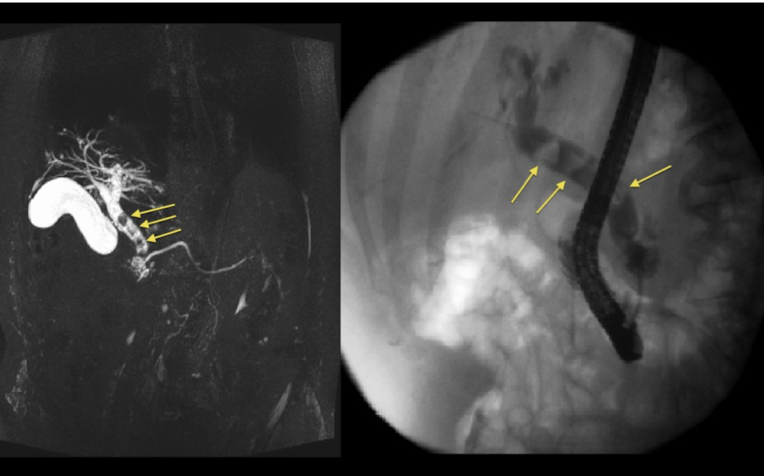
ERCP: minimally invasive stone extraction
MRCP: noninvasive imaging
gastroenterology and/or general surgery consult
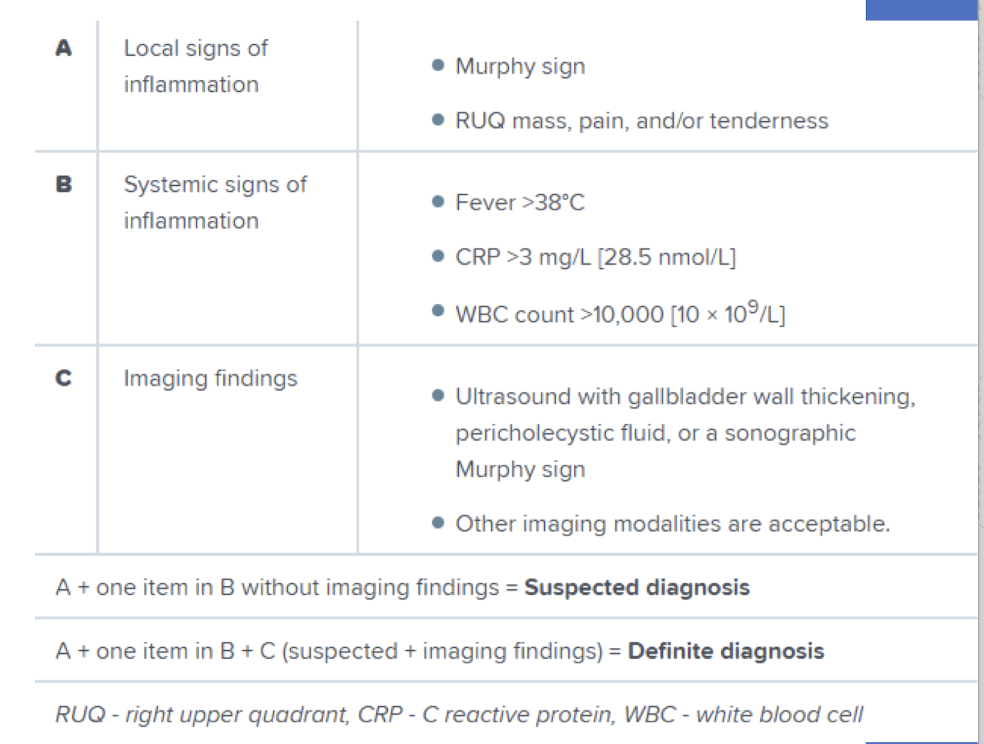
Cholecystitis
persistent outflow obstruction of gallbladder → distention + bile stasis → acute inflammation of gallbladder causing ischemia and necrosis
-most common complication of gallstone disease
S/S: RUQ pain, Nausea, vomiting, fever
PE: Positive Murphy sign (pain with palpation w/ inhalation at RUQ)
Dx: US (first line): stones/sludge + GB wall thickening >3mm
Labs: leukocytosis, LFT abnormalities
Tx: analgesia, antibiotics (IV Metronidazole + Ciprofloxacin), NPO
Admission + General surgery for cholecystectomy
Complications: empyema (pus in pleural space), perforation, pericholecystic abscess
Cholangitis
biliary obstruction causes increased bile duct pressure and inflammation leading to gallbladder infection (pathogens typically from duodenum)
risk factors: gallstones, stenosis, pancreatitis, prior biliary surgery, primary sclerosing cholangitis, malignancy
S/S:
-Fever + abdominal pain + jaundice/hyperbilirubinemia (Charcot triad)
-Charcot triad + altered mental status + shock (Reynold pentad)
Dx: US (first line), CT: source of obstruction, CBC/CMP, blood cultures
Tx: IV resuscitation, antibiotics, ERCP + surgical consult
Cholangitis
Which abdominal emergency associated with gallstones classically presents with:
-Fever + abdominal pain + jaundice/hyperbilirubinemia (Charcot triad)
-Charcot triad + altered mental status + shock (Reynold pentad)
treated with ERCP (stone extraction) + surgical consult?
Pancreatitis
inflammation of the pancreas (acute/chronic) due to gallstones (most common), chronic alcohol use, elevated triglycerides
Acute: pancreatic autodigestion
Chronic: progressive inflammation causing fibrosis
S/S: epigastric or upper abdominal pain (worse w/ oral intake), nausea/vomiting, upper abdominal or generalized abdominal pain, may have tachycardia, hypotension
Dx: RUQ ultrasound (initial), CT (diagnostic), elevated ↑ Lipase
Tx: IV fluids (if hypovolemic); opioid analgesics, antiemetics
ERCP if gallstones or cholecystectomy
Pancreatitis
Which acute or chronic abdominal disorder due to gallstones (most common), chronic alcohol use, elevated triglycerides causes epigastric or upper abdominal pain worse with oral intake?
Nephrolithiasis
obstruction of ureter (UVJ/UPJ) → upstream obstruction and increased intrarenal and intrauteral pressure → inflammation and pain due to spasm
-Calcium oxalate (most common), Struvite (staghorn calculi), Uric acid
S/S: colicky flank pain, hematuria, nausea, vomiting, unable to find position of comfort
PE: CVA tenderness (50%), lower stone radiates to groin, dysuria if near bladder
Dx: urinalysis: hematuria, evaluate for UTI (culture if positive)
imaging: US (initial); CT w/o contrast (diagnostic)
labs: CMP: assess renal function for risk of AKI (solitary kidney/transplant, bilateral staghorn calculus); CBC: leukocytosis may be stress response
Tx: analgesia: NSAIDs (Ketorolac, Ibuprofen), Opioids, Acetaminophen, expulsive therapy (Tamsulosin)
Emergent surgical decompression (ureteral stent) with infection, intractable pain, renal failure, solitary kidney, stones >10mm
Pyelonephritis
upper urinary tract infection, most commonly E. coli
risk factors: AMAB, urinary catheter, advanced age, immunocompromised instrumentation, renal stones, pregnancy
S/S: urinary urgency, frequency, dysuria, fever, flank pain
PE: +CVAT (costovertebral angle tenderness)
Dx: urinalysis + culture, CT or US to evaluate for stones or surgery
Tx: Analgesia, Antiemetics, Antibiotics (ie. Ceftriaxone, TMP-SMX)
-Well appearing and tolerating oral intake: Discharge
-Pregnant: consult for close follow up vs. admission
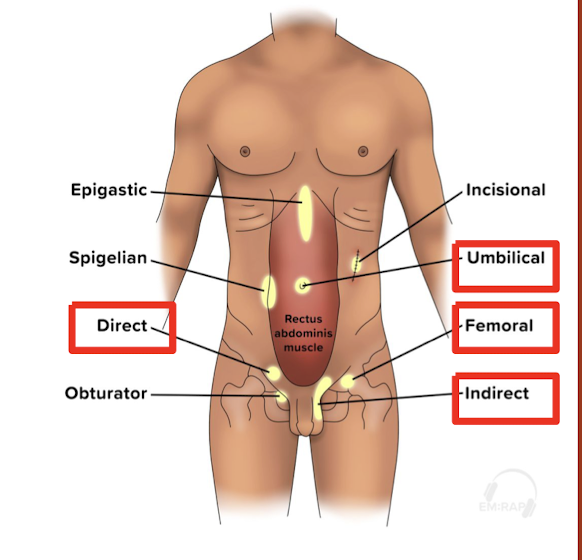
Strangulated hernia
protrusion of organ through normally intact wall
-Indirect inguinal (most common), Femoral (highest rate of incarceration/strangulation)
S/S: lump
PE: bulge, auscultation of bowel sounds, inspect the skin for changes (bruising/necrosis is indicator of strangulation)
Dx: clinical diagnosis, imaging if concern about complications (US/CT)
Tx: Reduction: contraindicated if strangulation
Admission: for observation if incarcerated and reduced/unsuccessful reduction attempts
Operative management for strangulated, closed loop obstruction w/ bowel
Diverticulitis
inflammation of colonic diverticula
risk factors: older adults, history of diverticulosis
Uncomplicated: localized to diverticula
Complicated: presence of abscess, obstruction, perforation, fistula
S/S: LLQ abdominal pain/tenderness to palpation, change in bowel habits, fever + tachycardia (complicated disease)
Dx: CT abdomen pelvis (diagnostic), CBC, CMP
Tx: Augmentin (first line) or ciprofloxacin + metronidazole (outpatient immunocompetent uncomplicated disease)
Admission if complicated or significant comorbidities, severely ill or perforated diverticulitis
Surgical intervention for abscess (can be drained percutaneously)
Diverticulitis
What abdominal disorder presents with LLQ abdominal pain/tenderness to palpation + change in bowel habits and fever + tachycardia (complicated disease) assessed with CT abdomen/pelvis and treated with Augmentin (outpatient uncomplicated)?
Appendicitis
inflammation of appendix through obstruction and increased intralumenal pressure
-most common abdominal surgical emergency worldwide, bimodal age distribution
S/S: periumbilical to RLQ abdominal pain, nausea ± vomiting, anorexia, fever
PE: tenderness at McBurney’s point, Rovsing sign, psoas sign
Dx: CT (diagnostic)
US: preferred in pregnancy/pediatrics, may be nondiagnostic, follow up with MRI
Tx: Appendectomy (first line), NPO, IV, analgesia, antiemetics, Antibiotics