Microbio lab quiz 5
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
How did we test for the production of antibiotics by our isolates?
zone of inhibition
Alexander Fleming
Father of antibiotics for the accidental discovery of Penicillin
Molecular Clock
the average rate at which a species' genome accumulates mutations, used to measure their evolutionary divergence
What is thermal cycler
Used to amplify DNA sequence by increasing and decreasing temperature
Extension (PCR)
DNA polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands by extending the primers. 72C for 90s
Polymerase Buffer
creates optimum activity of Taqpolymerase
Tris-HCl
maintains pH
Triton
stabilizes DNA
Loading and Tracking buffer
bromophenol blue (stain), glycerol
coliphage
bacteriophage that infects E. coli
Paul Ehrlich
-magic bullet hypothesis
-developed concept of selective toxicity
-identified dyes that effectively treated African sleeping sickness
magic bullet hypothesis
Chemicals can be designed to bind to and kill specific microbes or tumor cells without harming the host itself
Selman Waksman
coined the term "antibiotic", developed the antibiotic streptomycin
Streptomycin
cure for tuberculosis
Alma Whiffen
discovered the antifungal agent cycloheximide
Carolus Linnaeus
Father of taxonomy, Domains of life
Phylogenetic tree
is the evolutionary relationship between taxonomic groups
Molecular phylogeny
Comparison of genetic sequences used to deduce relationships.
Cycloheximide
inhibits the growth of fungi
Antagonism and how did you detect it
antagonism- inhibition of action of one organism by another (one organism benefits while the other is harmed)
detection- zones of inhibition
How and why is antibiotic resistance a concern?
resistance to antibiotics makes it harder to treat severe infections
How does antibiotic resistance arise?
spontaneous mutations, horizontal gene transfer
Targets of antibiotics
cell wall, ribosomes, folic acid, cell membrane, DNA & RNA
ideal antibiotic
readily available, inexpensive, chemically stable, easily administered, nontoxic & nonallergic, selectively toxic against wide range of pathogens
broad spectrum antibiotics
affect a broad range of gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria
Narrow spectrum antibiotics
Effective against specific bacteria
PCR
polymerase chain reaction
16S rRNA
- small subunit of the ribosome of Bacteria and Archaea
- evolutionary information can be obtained;
-These are conserved genes
16S rRNA size
A large polynucleotide (~1500 bases)
What are the steps of PCR?
denaturation, annealing, extension
What is the purpose of PCR?
A laboratory technique for rapidly amplifying millions to billions of copies of a specific segment of DNA
Thermus aquaticus
is the organism that is thermophile whose enzymes are stable at high temperature
Taq polymerase
DNA polymerase which is heat stable taken from Thermus aquaticus, polymerization of dNTP into a DNA strand
dNTP's
mix of nucleotides building blocks of new DNAstrand
Denaturation
In proteins, a process in which a protein unravels and loses its native conformation, 95C for 30s
Anealing (PCR)
The temperature is decreased so that the primers can anneal to the complementary sequences on the DNA templates. 56C for 30s
What are primers?
small nucleotide sequence - locate target DNAfragments
Which primers were used for the 16S rRNA?
27F and 1492R
Buffer composition
Tris-HCl, EDTA, MgCl2, KCl, Triton
EDTA
chelating agent, keep DNA intact
MgCl2
magnesium chloride, cofactor for Taq polymerase
KCl
neutralizes charges in DNA template
PCR applications
Bacterial identification, DNA fingerprinting, bioengineering
What is the principle and purpose of Gel electrophoresis?
procedure that separates molecules on the basis of their rate of movement through a gel under the influence of an electrical field, their charge, shape and size
DNA migration to opposite side from cathode to anode
DNA is negatively charged
What dictates how far a fragment will travel?
A porous agarose gel is used to slow the movement of DNA and separate by its size
What is agarose?
-first used in biology when Robert Koch*
-linear polymer extracted from seaweed
TBE buffer
(Tris/Borate/EDTA)
a liquid buffer that protects the DNA molecules and allows electricity to move through the chamber, driving the molecules across the gel
TAE buffer
tris-acetate w/ EDTA
good for DNA recovery
good for lg fragments
low buffering capacity
increases migration of DNA thru gel
Staining dye-Gel green stain
binds to DNA and fluoresces under UV light, allowing the visualization of DNA on a Gel
bromophenol blue (stain)
used to stain proteins and nucleic acids without UV
glycerol
loading buffer for weight
What is the DNA ladder?
a mixture of DNA fragments with known sizes.
How do we "read" the DNA migration?
Compare to known fragment sizes
plaques
zones of clearing from bacterial lysis, forming units (PFU)/ml
bacteriophage
A virus that infects bacteria
obligate intracellular parasites
cannot multiply unless they invade a specific host cell and instruct its genetic and metabolic machinery to make and release new viruses
titer
number of infectious units per volume of fluid
Coliphage and bacteria name used in lab
T4 and E.coli
lytic cycle
a viral reproductive cycle in which copies of a virus are made within a host cell, which then bursts open, releasing new viruses
lysogenic cycle
a viral reproductive cycle in which the viral DNA is added to the host cell's DNA and is copied along with the host cell's DNA
cloudy plaque
This means that there are some members of the bacterial population that are sensitive to this particular antibiotic, but others that are genetically immune to its effects. lysogenic
clear plaque
lytic
Calculation of titer
# of plaques x 1/dilution factor PFU/mL
PFU stands for what?
plaque foriming units
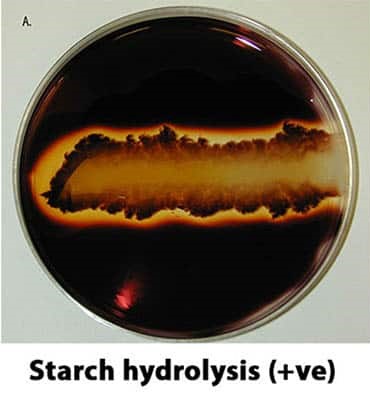
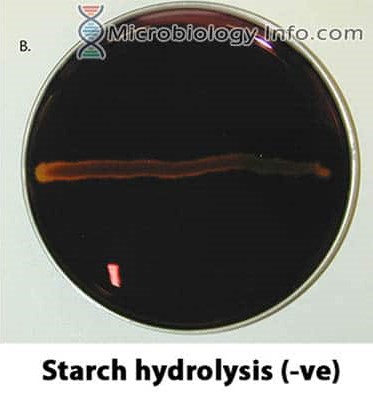
Starch test
Iodine solution turns blue-black
Which is the developer?
Iodine
Starch test negative
dark brown
Starch test positive
clearing zone