Dermatology - ulcers, burns, hair and nails
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
irregular
Venous ulcers typically have ___ borders
3 multiple choice options
Venous insufficiency
M/C cause of venous ulcers?
eczematous changes
Often venous ulcers will be accompanied by ___ around the border
medial
Venous ulcers are more likely to be on the ___ side of the calf
- treat underlying contrition = swelling
- leg elevation
- unna boots
- topical steroid for underlying stasis dermatitis
- occlusive dressings (moist environment + mupirocin)
- skin grafts if necessary
Tx of venous ulcer?
Arterial
Which of the ulcers is most painful?
Arterial ulcer
What is the diagnosis?
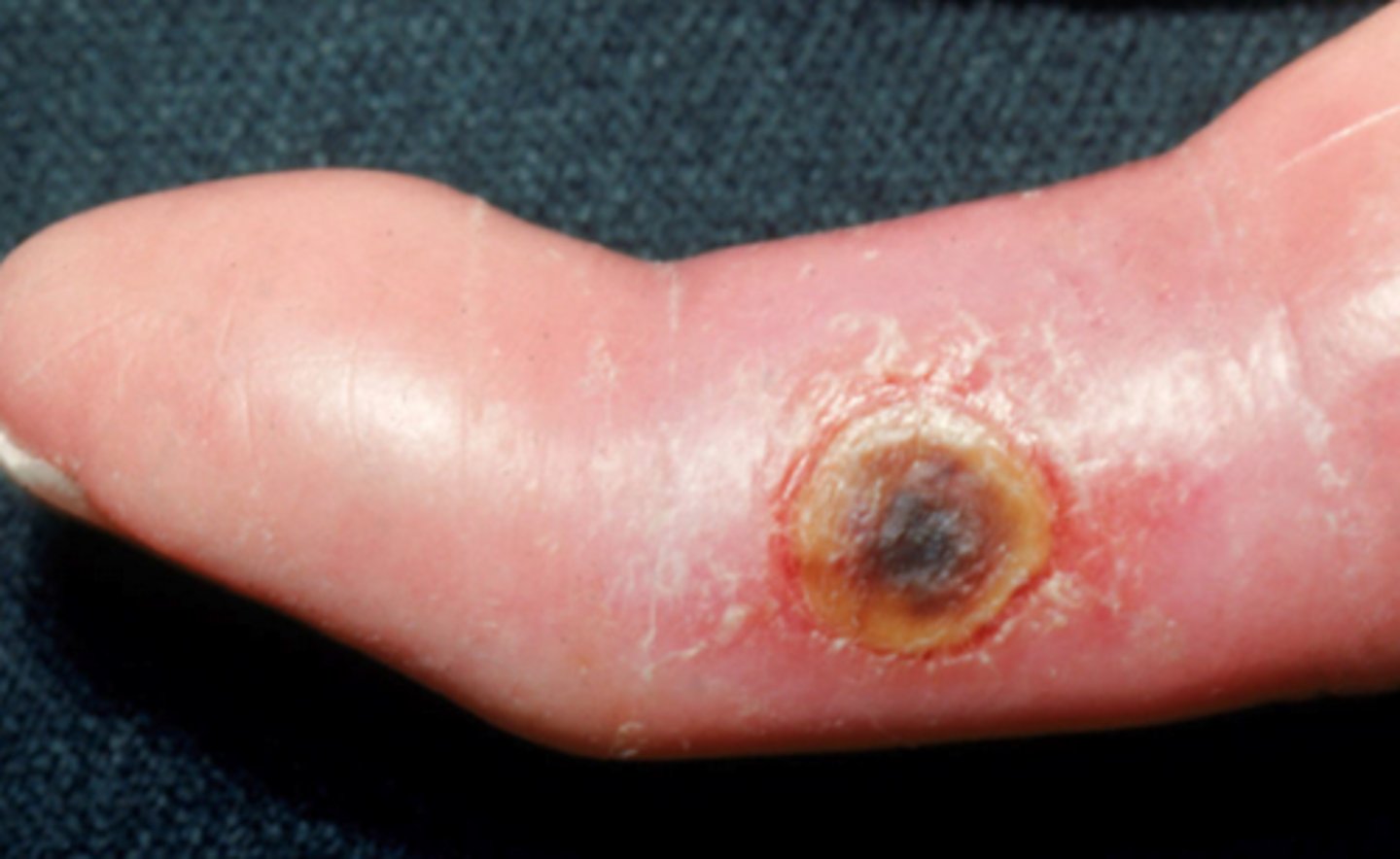
Venous ulcer
What is the diagnosis?
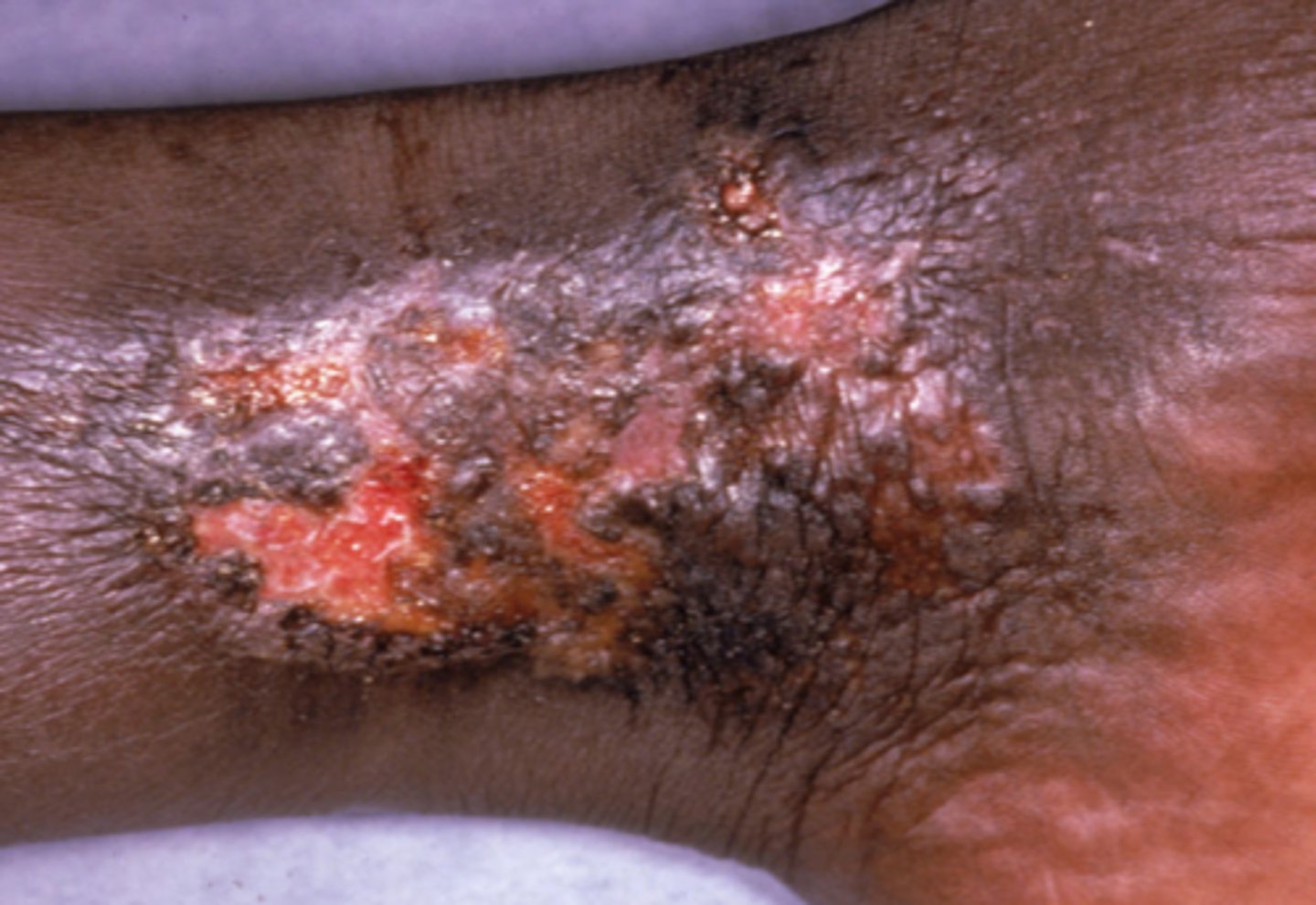
Venous ulcer
What is the diagnosis?
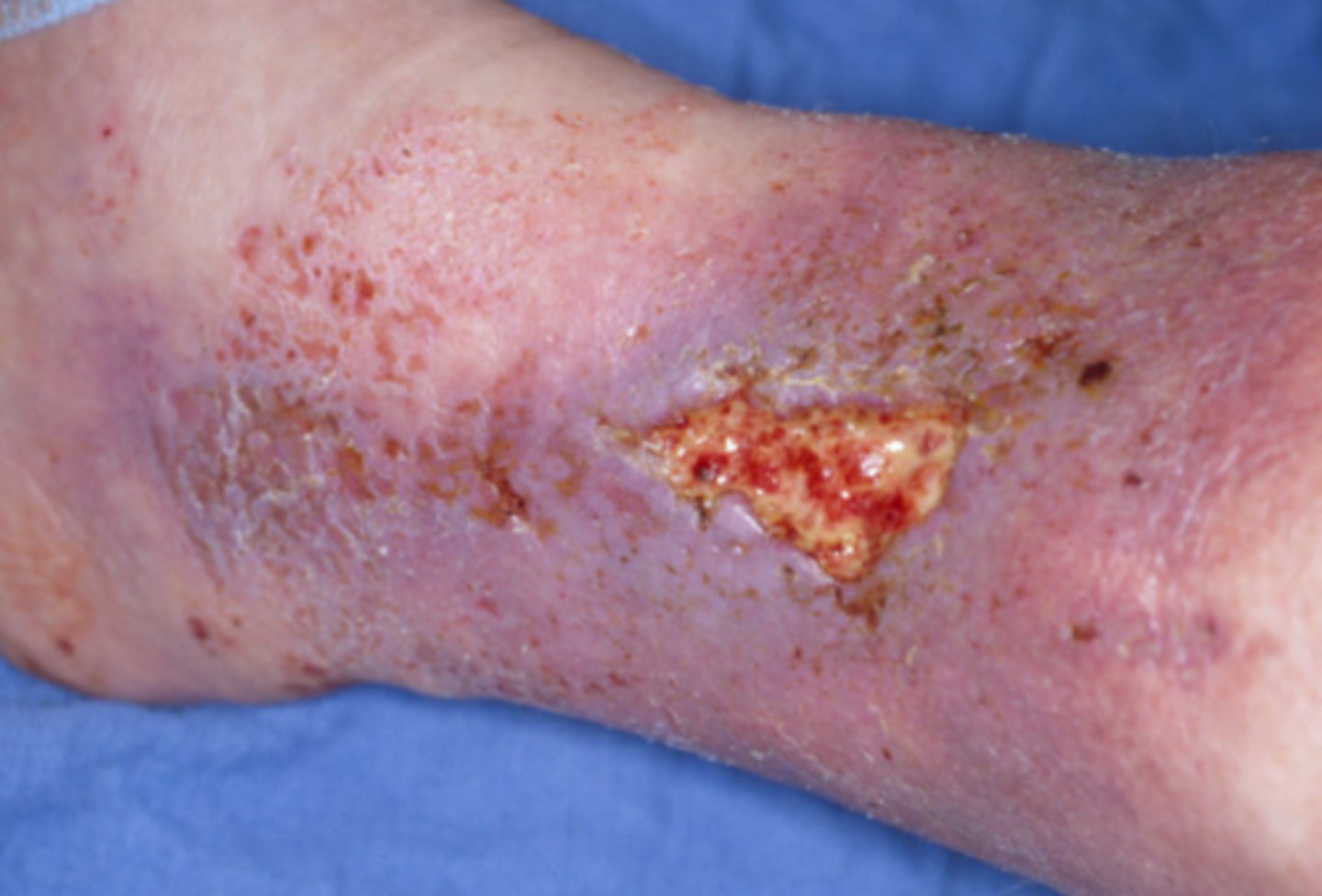
arterial ulcer
What is the diagnosis?
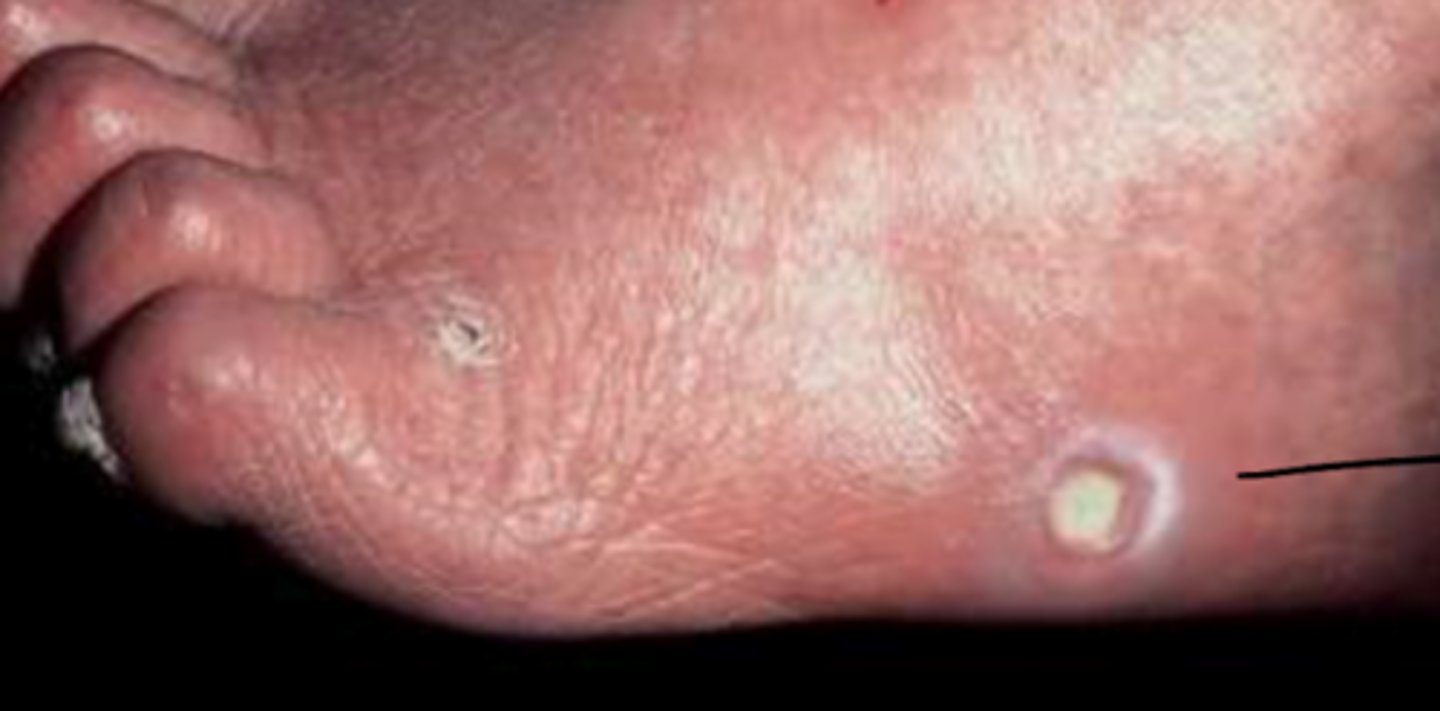
arterial ulcer
Symptoms of claudication are indicative of an ___
Arterial ulcer
Painful, sharply demarcated, and round ulcer
Venous ulcer
Which ulcer has granulation tissue?
- reperfusion
- vascular surgeon
- wound care similar to venous ulcer
Tx of arterial ulcer?
Neuropathic
___ ulcers favor the soles of the feet
Neuropathic
___ ulcers are surrounded by thick caluses
secondary infection
Neuropathic ulcers are prone to ___
- protect ulcer from pressure with brace
- moist environment in dressing
- order imaging if concern for osteomylitis
Tx of neuropathic ulcer?
Decubitus
Which type of ulcer is most common in non-ambulatory patients?
- frequent rotation
- keep clean and dry, barrier creams
- debride necrotic tissue
- negative pressure bandage
- skin graft if necessary
Tx for decubitus ulcers?
Neuropathic ulcer
What is the diagnosis?
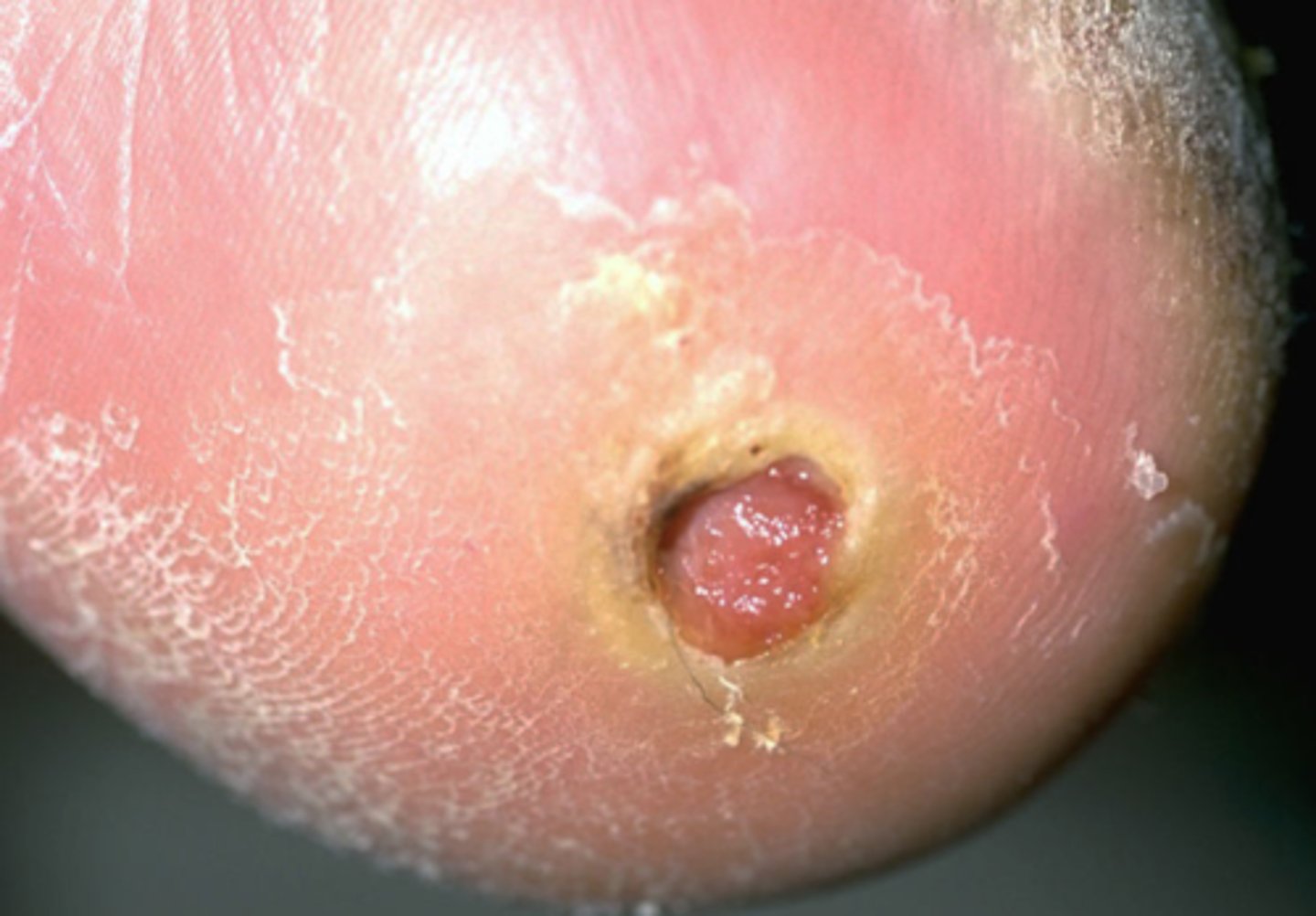
Decubitus ulcer
What is the diagnosis?
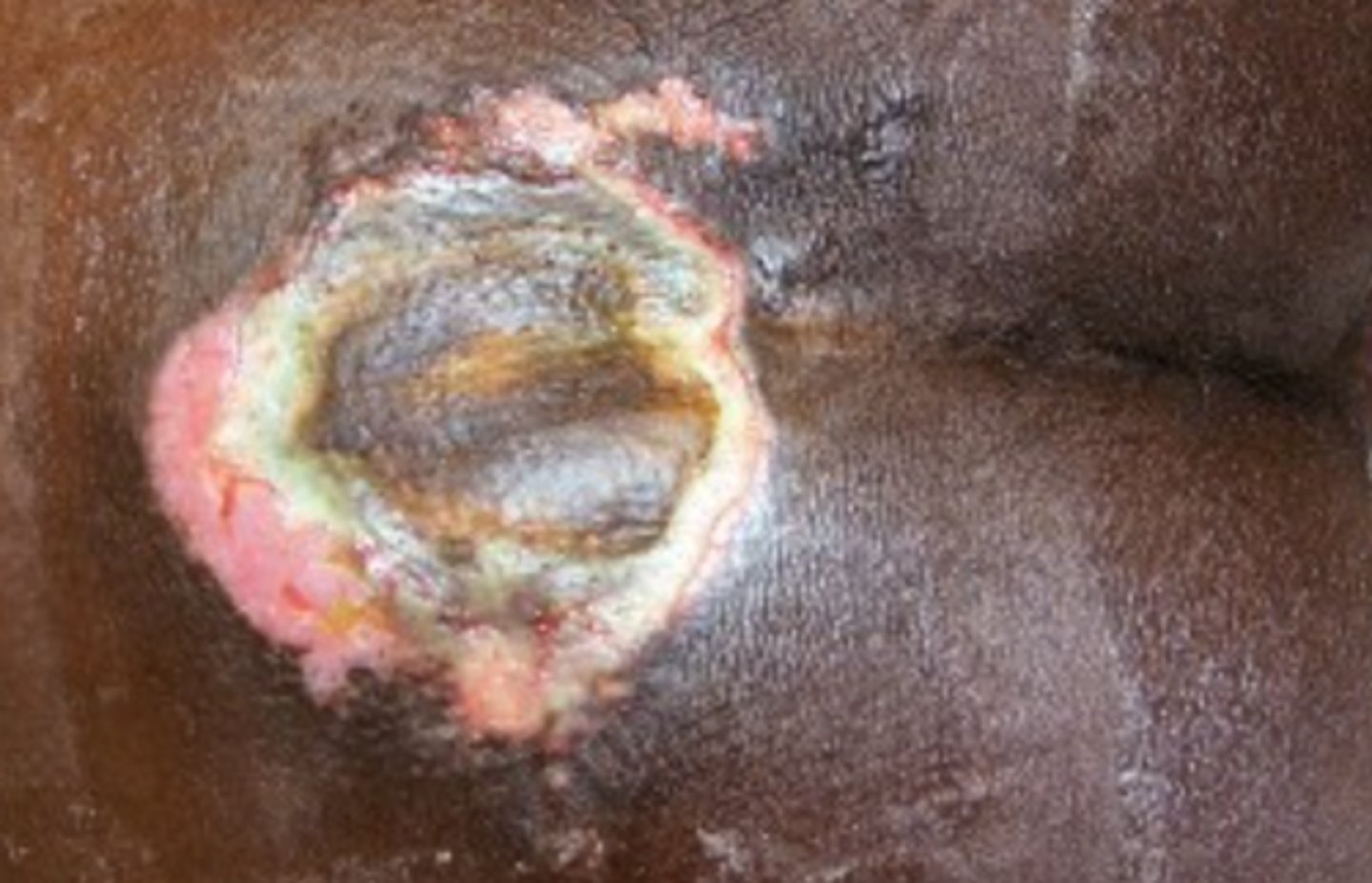
Decubitus ulcer
What is the diagnosis?
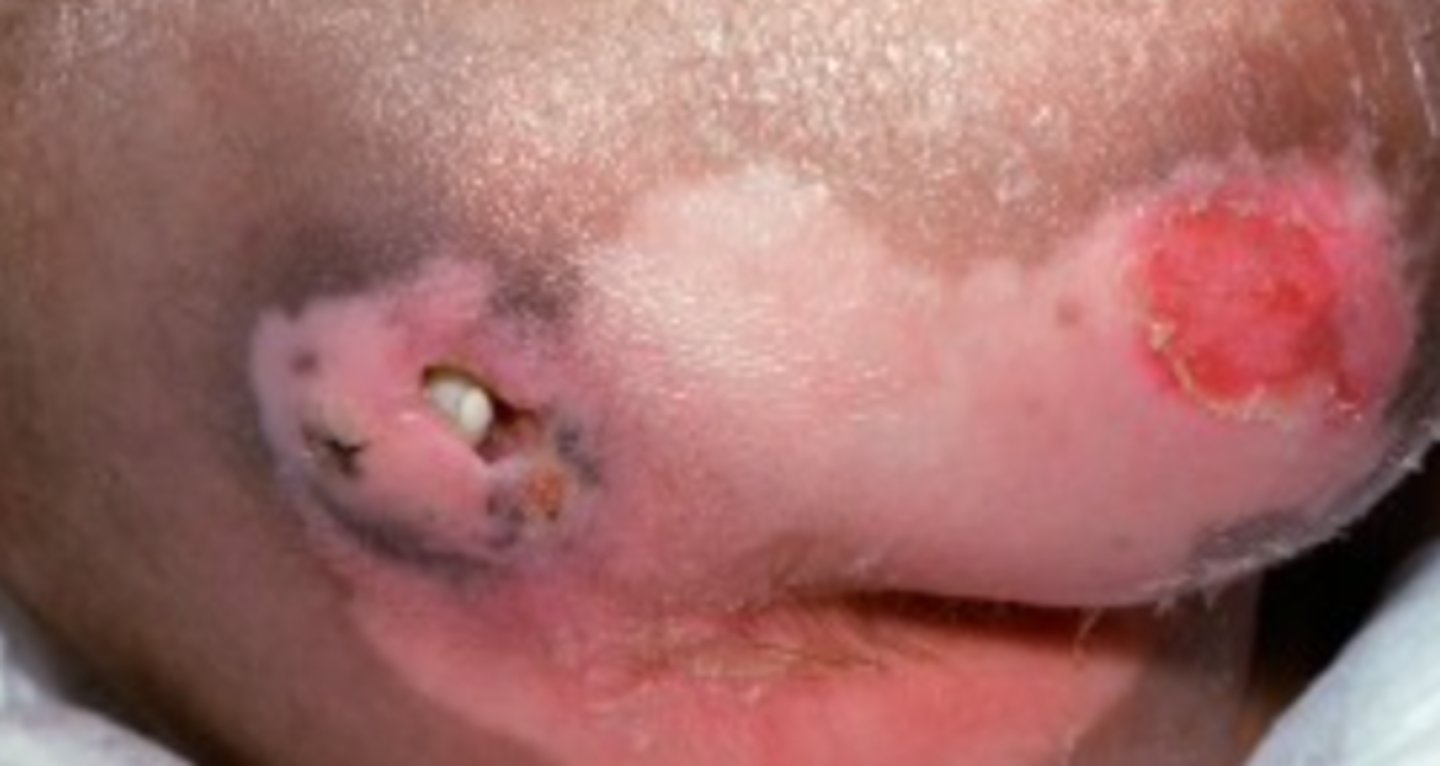
Neurogenic ulcer
What is the diagnosis?
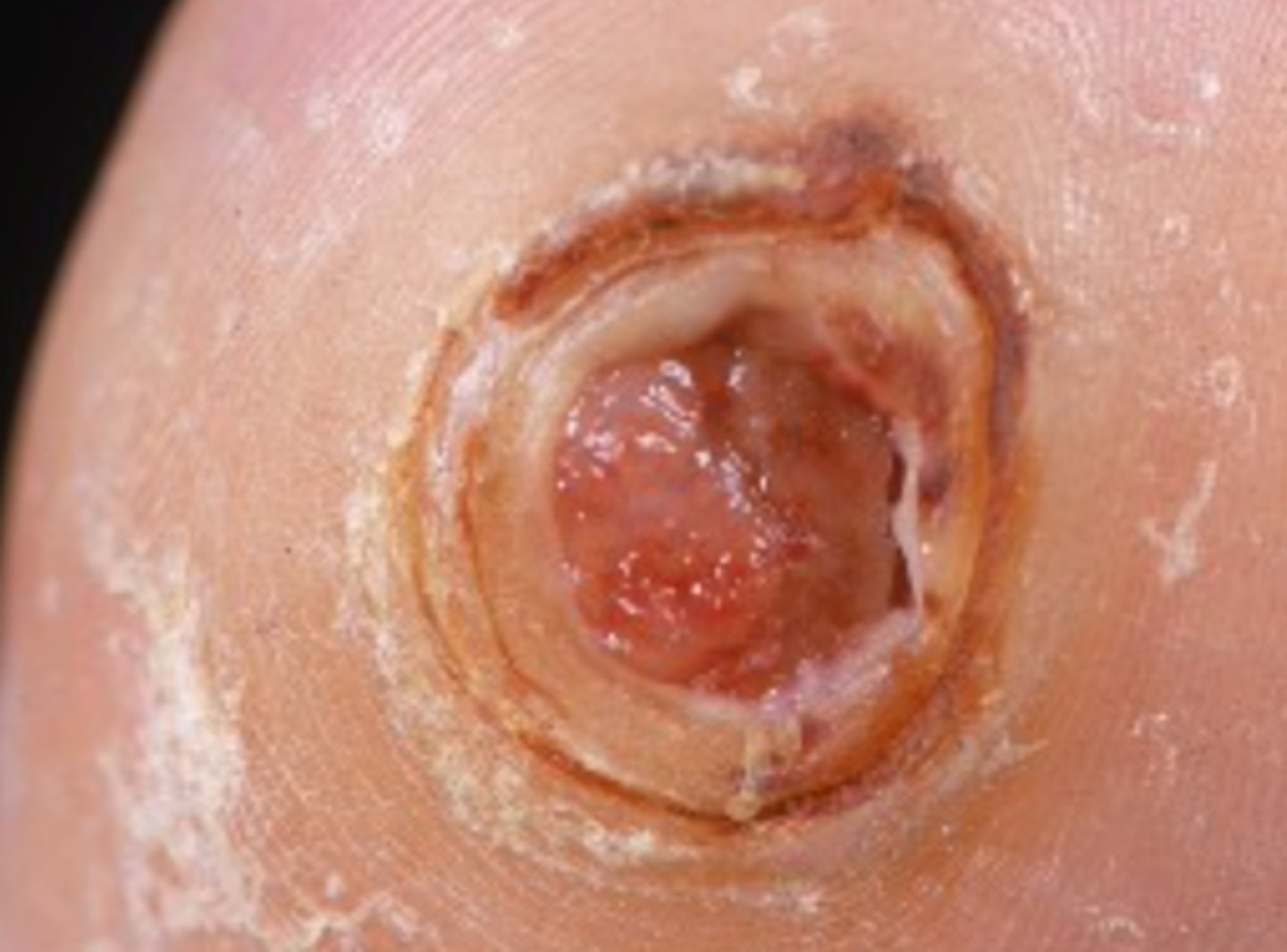
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Auto-inflammatory ulcerative process that begins as a small pustule/nodule and rapidly breaks down
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Which of the diagnoses is a neutrophilic dermatitis?
3 multiple choice options
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Which skin disease is associated with IBD, RA and malignancy?
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Which disease has characteristic violaceous undermined borders?
- topical/intralesional steroid injections
- oral steroids
- cyclosporine
- adalimumab, infliximab
Tx of pyoderma gangrenosum?
Partial thickness (2nd)
Which type of burn has blisters?
Presence of hair
Difference b/w superficial partial thickness and deep partial thickness?
Full
___ thickness burns are typically not painful due to loss of nerve endings
- ABC
- smoke inhalation
- fluid resuscitation
- high voltage burn = cardiac monitoring
- look out for compartment syndrome
- local wound care (antimicrobials)
- debridement, escharotomy, fasciotomy, skin grafts
Tx of burns?
anagen
Longest stage of hair growth?
- sudden vs gradual
- focal vs diffuse
- non-scarring vs scaring
Categories of hair loss to differentiate
Alopecia areata
What is the diagnosis?
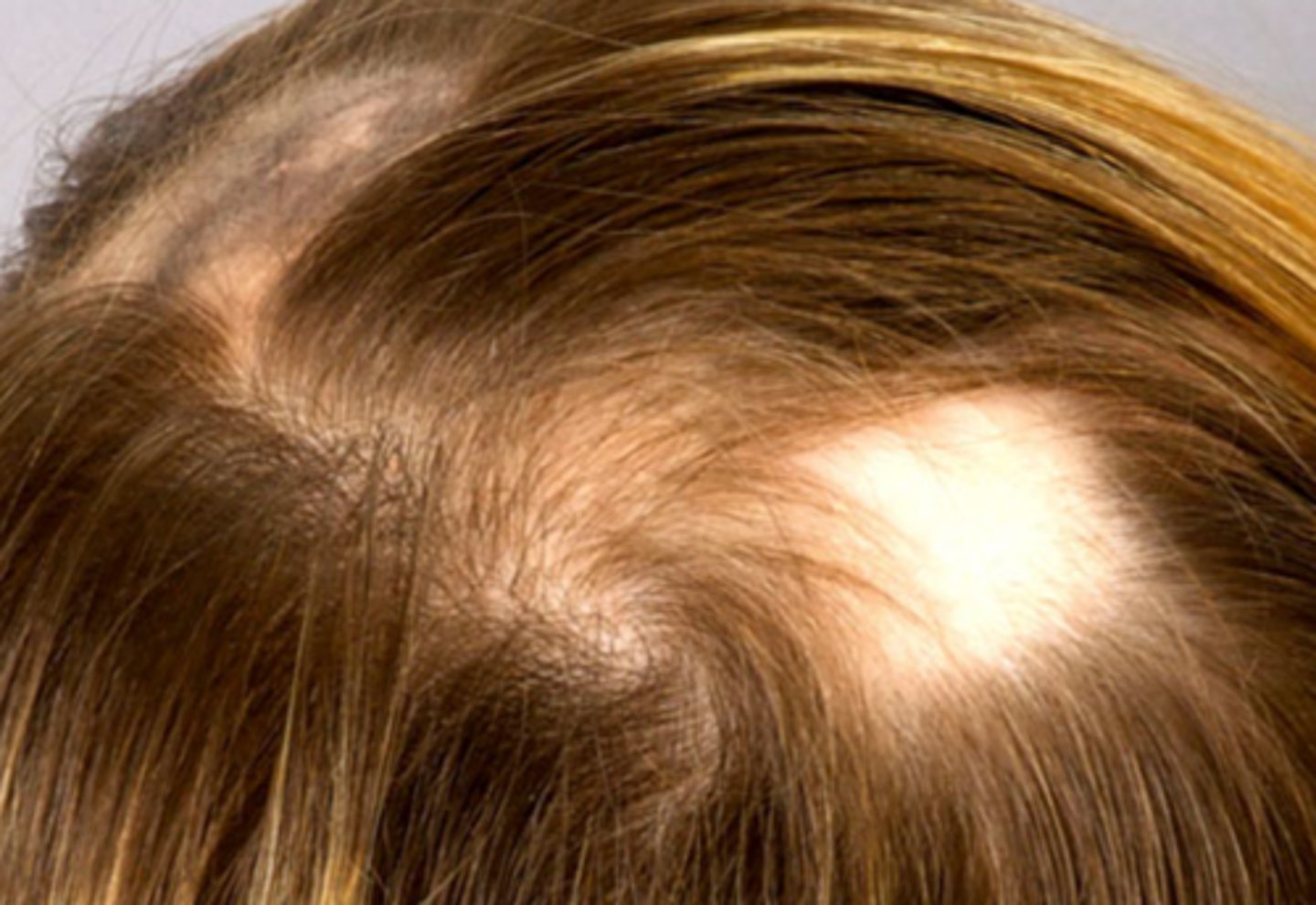
Alopecia areata
What is the diagnosis?
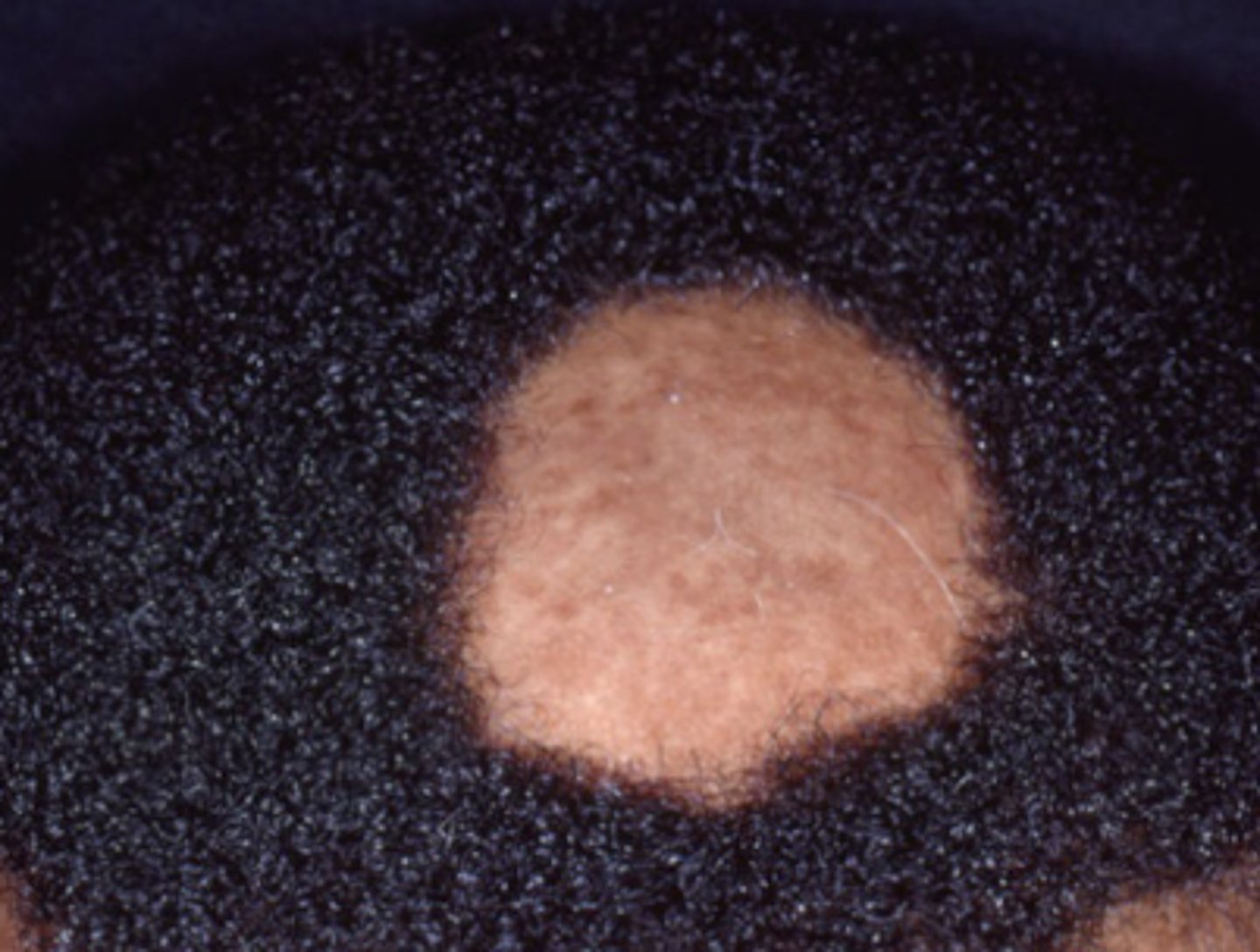
Ophiasis
What pattern of hair loss is this?
3 multiple choice options
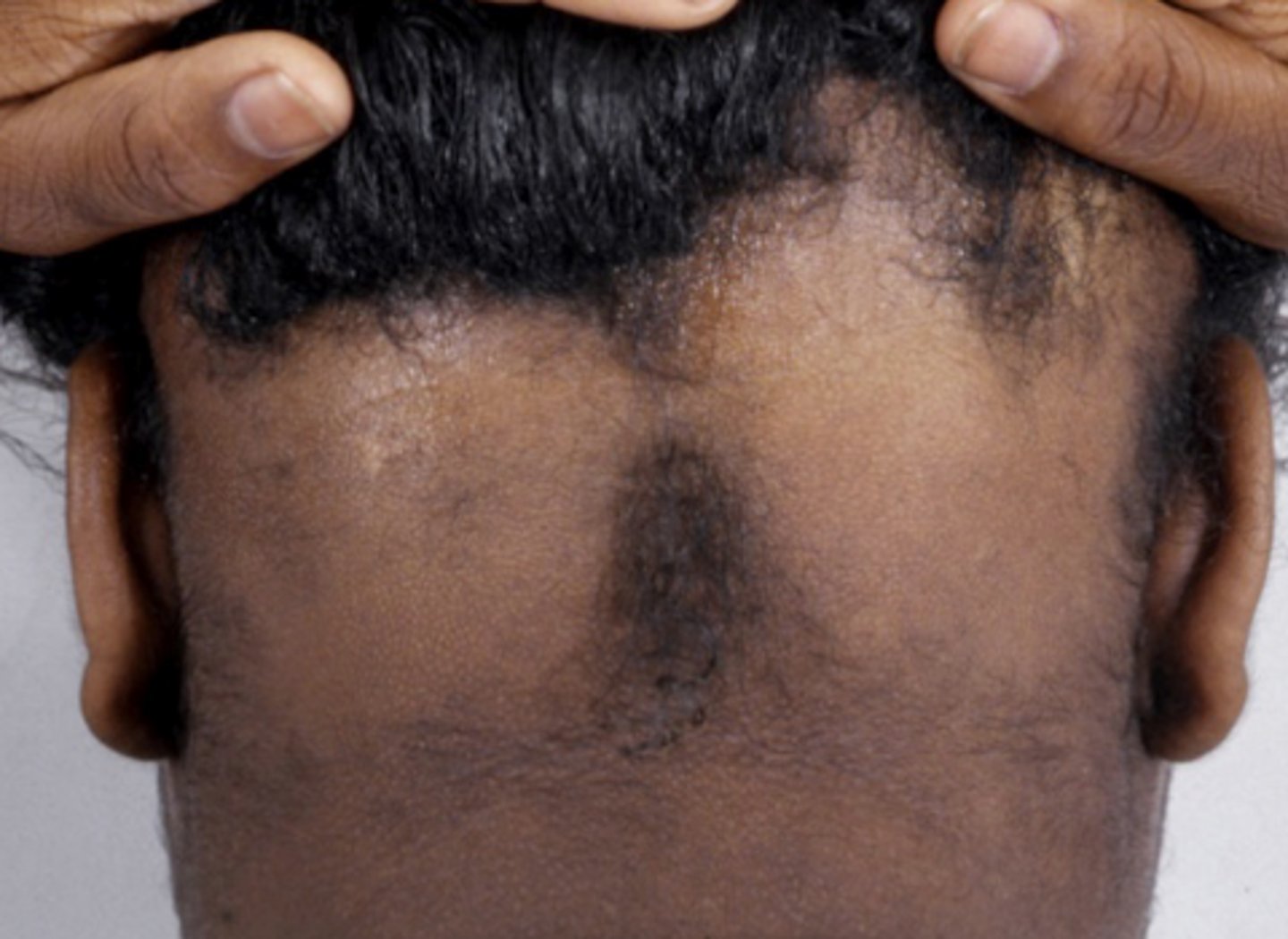
autoimmune - lymphocytes attack hair follicles
Etiology of alopecia areata?
Alopecia areata
Exclamation point hairs are indicative of
Thyroid
Which disorders are commonly associate with alopecia areata?
6 months
Alopecia areata usually resolves on its own in ___
- topical steroids +/- minoxidil
- intralesional kenalog (4-6 wks)
Tx for alopecia areata
totalis
Alopecia ___ is hair loss on entire scalp
3 multiple choice options
universalis
Alopecia ___ is hair loss on the entire body
- poor prognosis
- PUVA
- methotrexate
- prednisone
- topical steroids + minoxidil
- JAK inhibitors
Tx of alopecia totalis/universalis
Tinea capitis
fungal infection of the scalp
Tinea capitis
___ is associated with cervical and occipital lymphadenopathy
Black dot presentation of tinea capitis
What is the diagnosis?
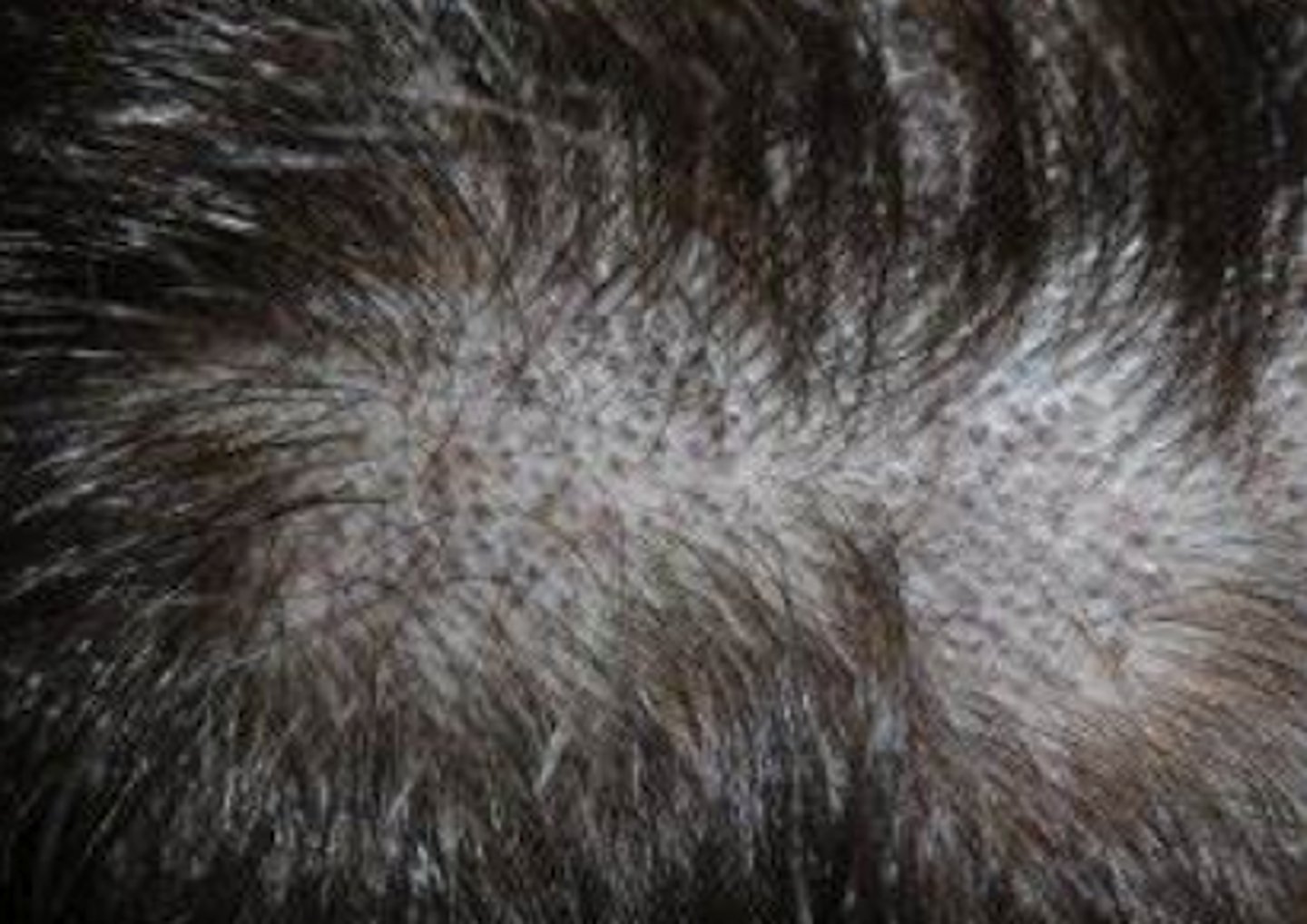
Gray patch presentation of tinea capitis
What is the diagnosis?
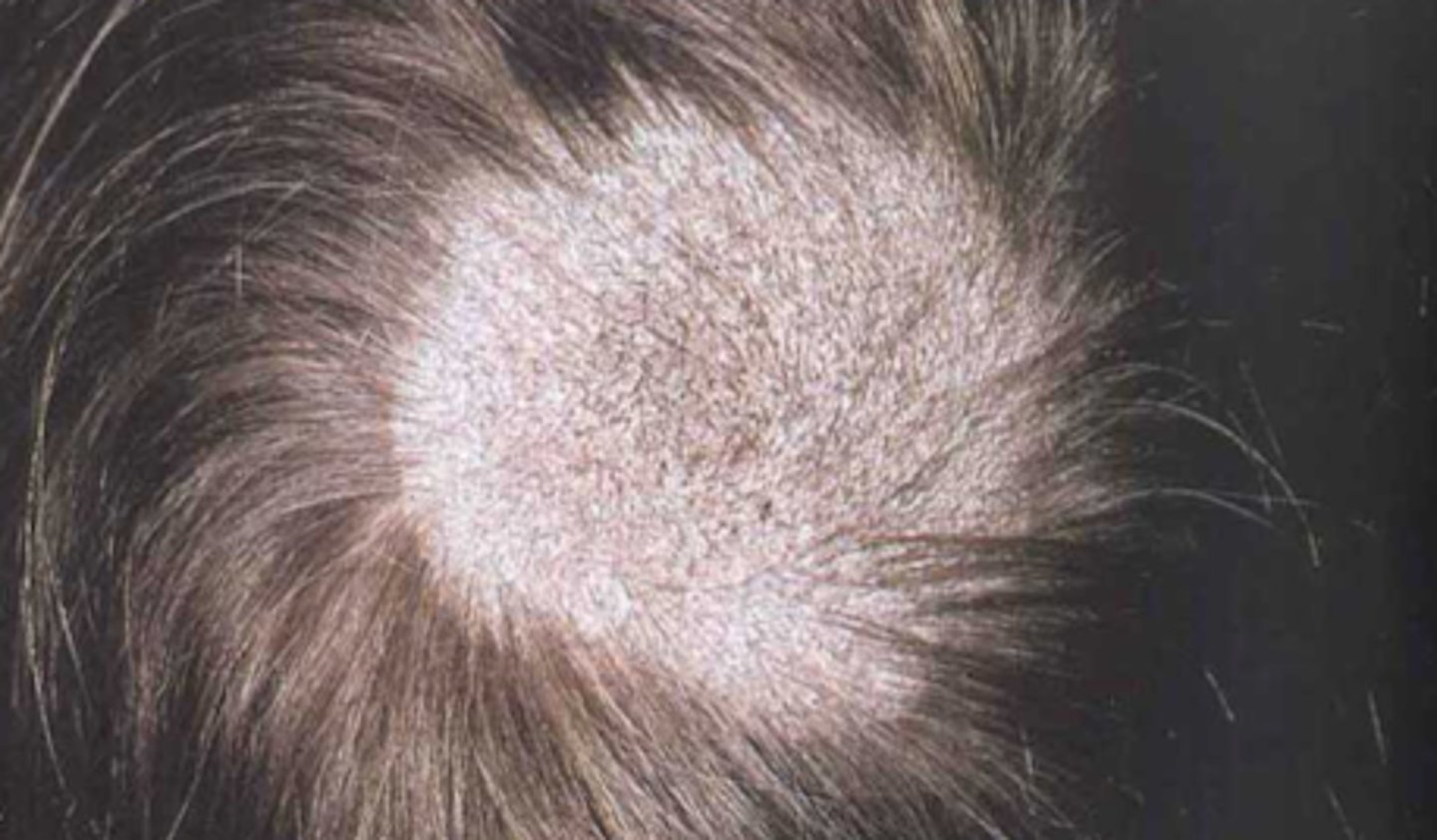
Tinea capitis
What is the diagnosis?
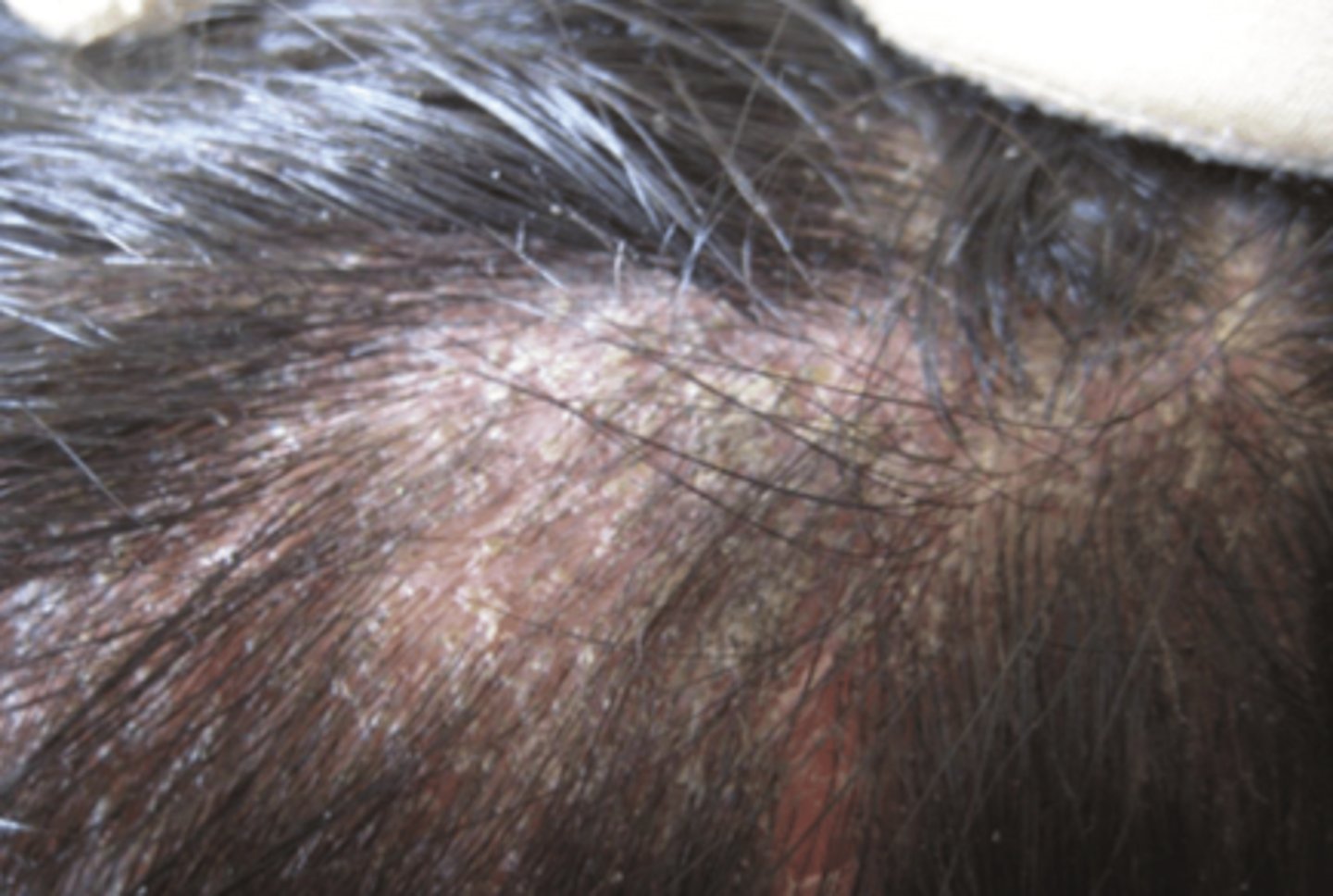
Kerion
A ___ is a form of inflammatory tinea capitis with a boggy mass and broken hair follicles
- ORAL
- griseofulvin
- terbinafine
- alt. fluconazole or itraconazole
Tx for tinea capitis?
faster cycling of the hair
Telogen effulvium is caused by a stressful event that leads to ___
Telogen effulvium
Widening part and a positive hair pull test indicates
iron deficiency
___ is the most common cause of treatable hair shedding
genetic predisposition and action of androgens
Which two factors cause androgenic alopecia?
weeks to months
DHT shortens the hair cycle from 2-6 years to ___
- topical minoxidil
- men = finasteride
- women = spironolactone or cyproterone acetate
- oral minoxidil (hair growth everywhere)
Androgenetic alopecia tx?
Androgenic alopecia
What is the diagnosis?
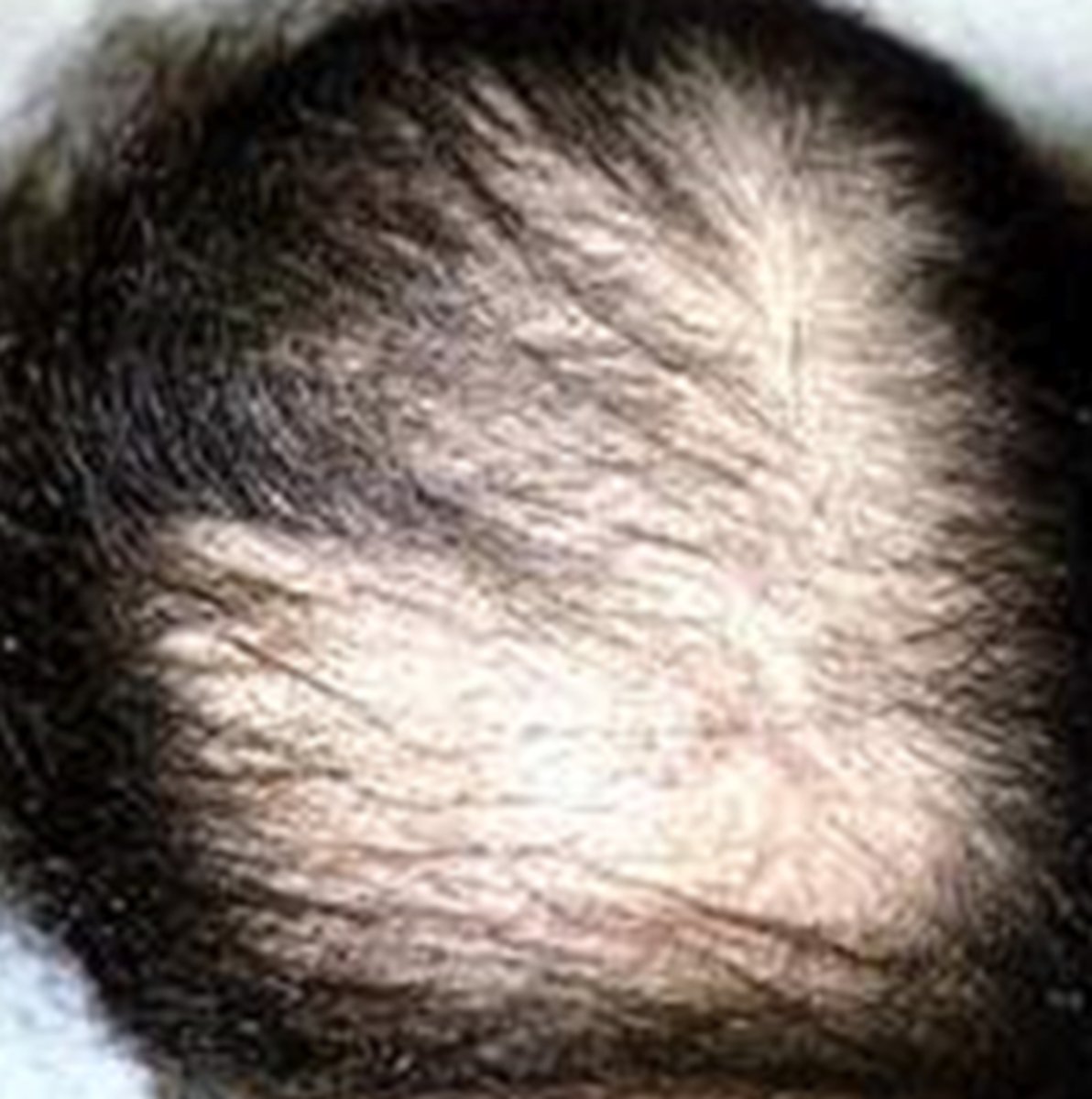
Traction
___ alopecia causes hair loss around the hair line and a (+) fringe sign
Traction alopecia
What is the diagnosis?
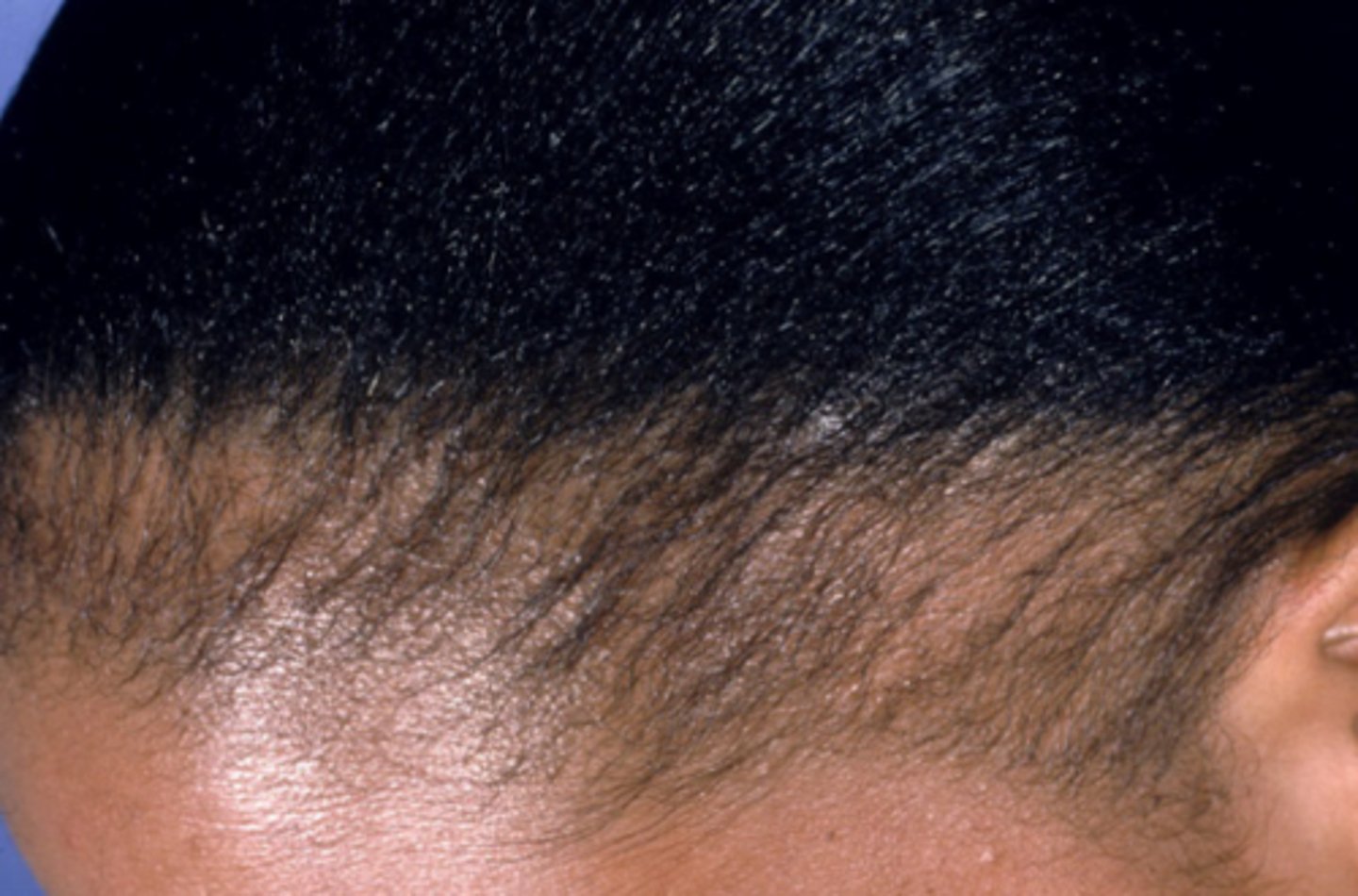
Tricotillomania
___ can be differentiated from alopecia based on differing hair lengths within a bald patch
Trichotillomania
What is the diagnosis?
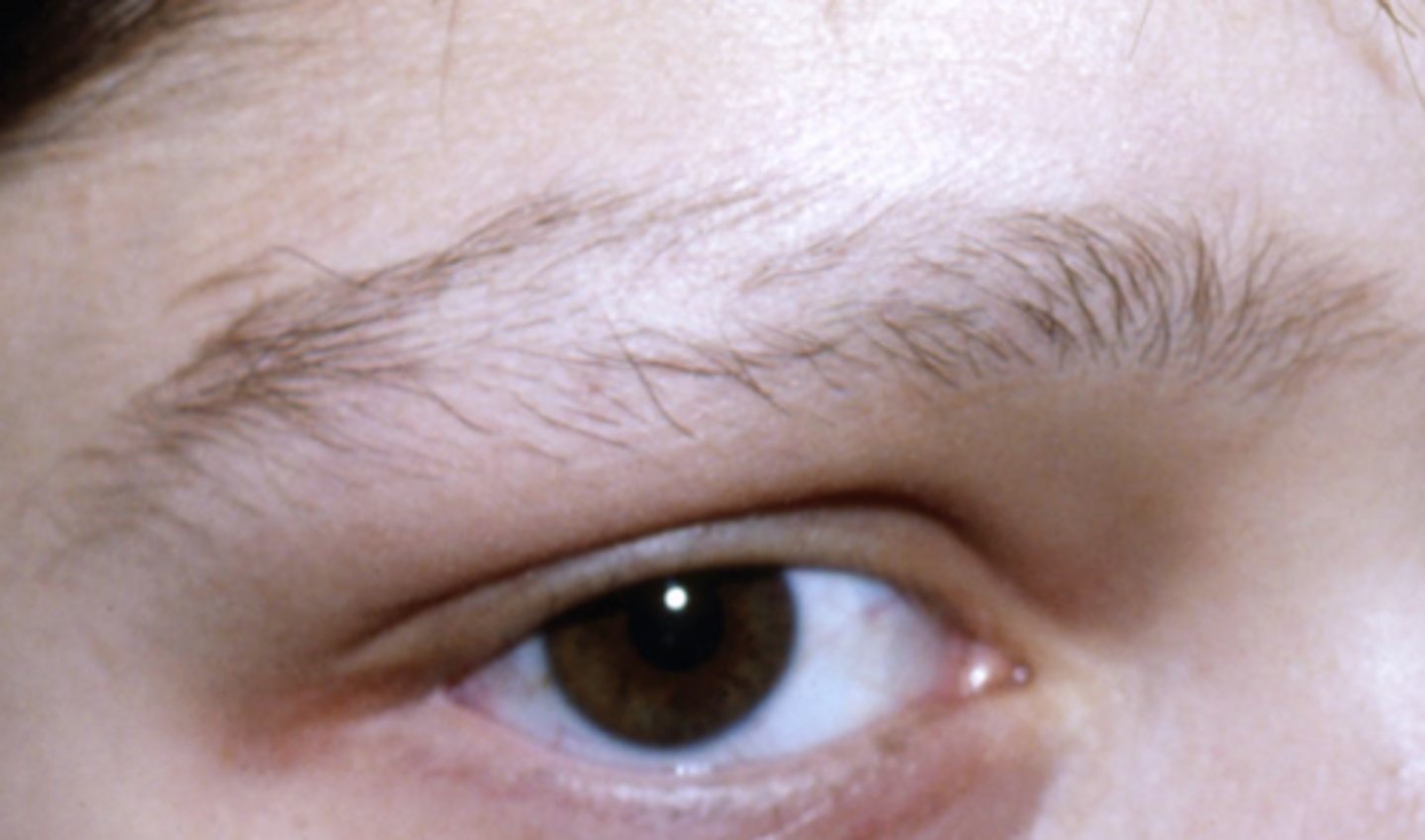
- psych eval
- clomipramine
- SSRI
- N-acetylcysteine
Tx of trichotillomania?
hair loss
Alopecia with inflammation and scarring causes permanent ___
scarring alopecia
A shiny scalp in a bald spot is indicative of ___
Discoid lupus
Oval areas of scarring alopecia with white atrophic center?
Discoid lupus
What is the diagnosis?
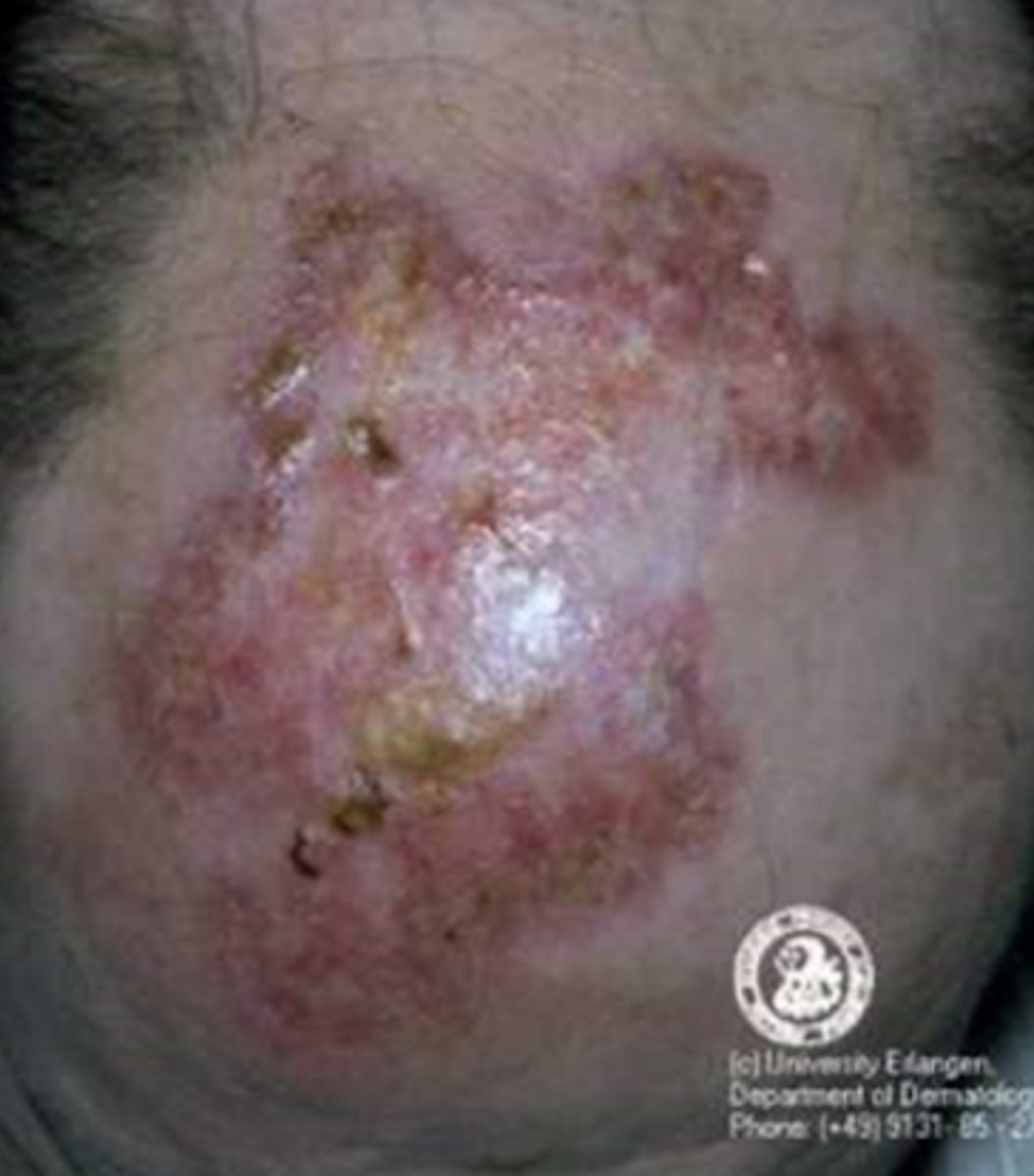
Discoid lupus
What is the diagnosis?
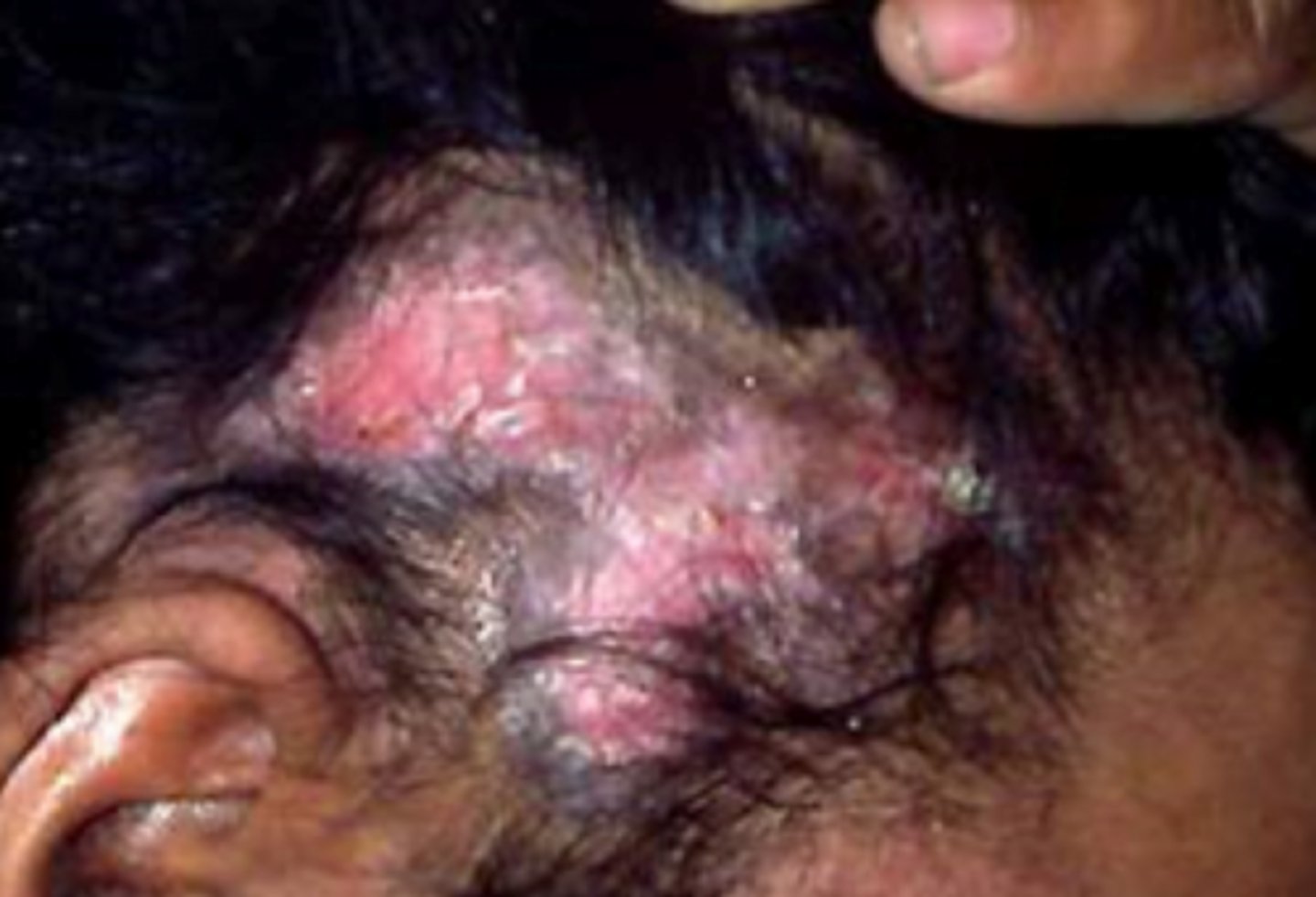
- biopsy
- CBC
- ANA
- Urinalysis
diagnosing discoid lupus requires:
- topical/intralesional steroids
- hydroxychloroquine
Tx of discoid lupus?
patients of color
Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia is more common in ___
Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia
Scalp symptoms including itching, burning, and tenderness
genetic predisposition
Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia is caused by ___
Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia
What is the diagnosis?
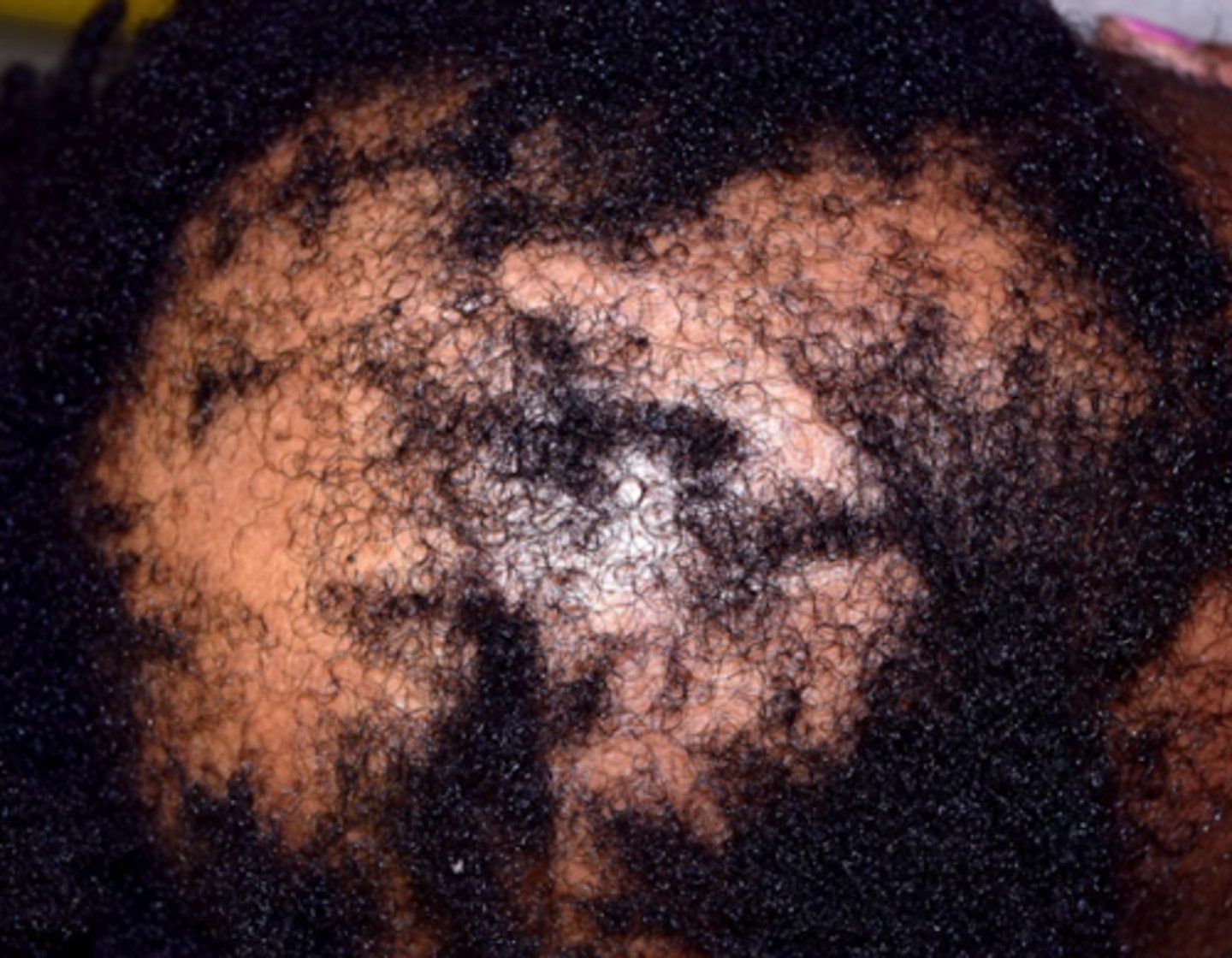
- prevention of further hair loss
- topical and intralesional steroid injections
- tetracyclines (anti-inflammatory properties)
- minoxidil
Tx of Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia?
Onychorrhexis and melanoychia striata
What are the normal changes associated with the nail?
Dry brittle nails
What is onychorrhexis?
multiple fingers
Melanonychia striata should be present on ___ or it could be melanoma
Fungal
Onychomycosis is a ___ infection of the tails (most commonly toe nails)
Mealnoychia striata
What is the diagnosis?
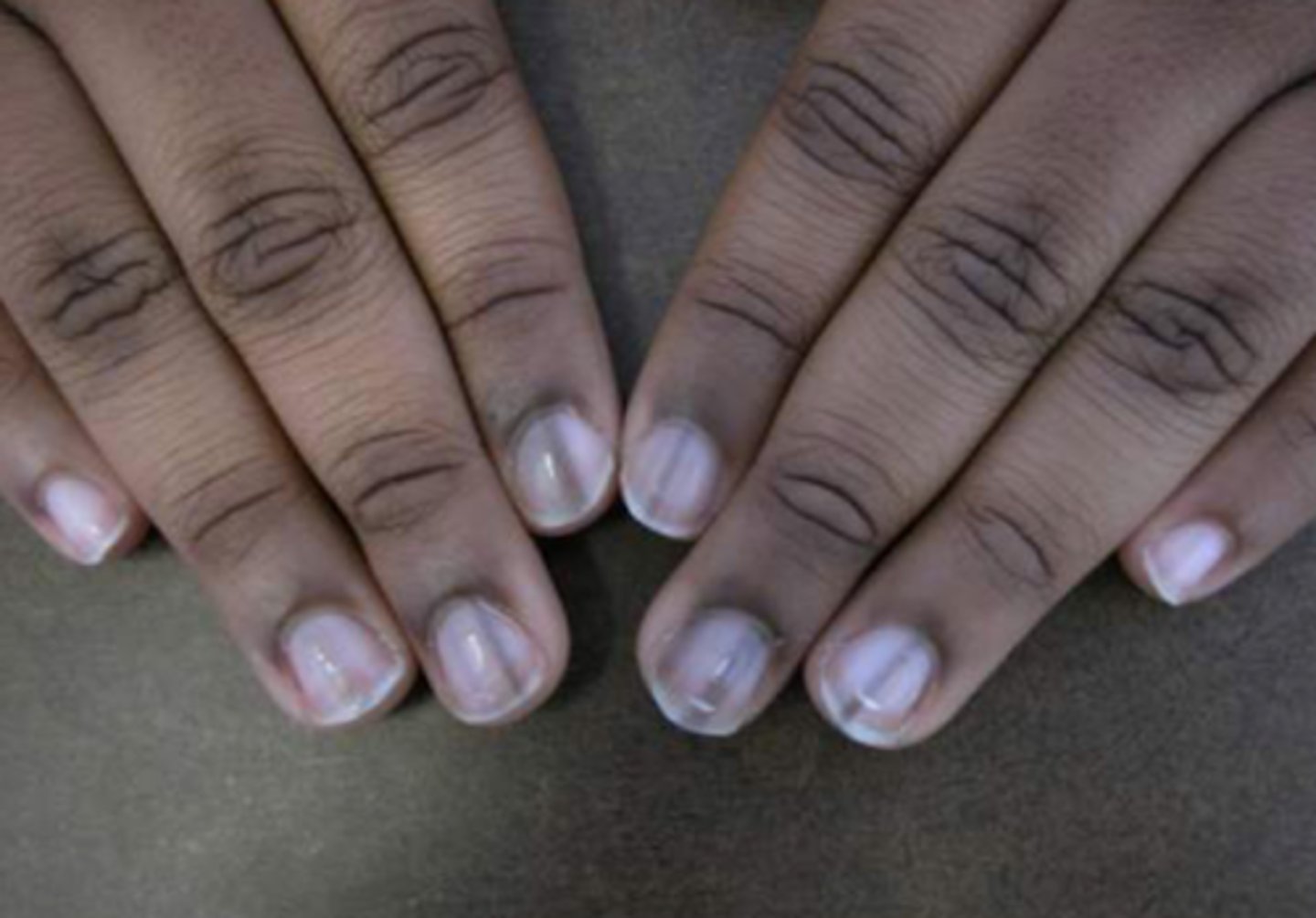

Onychorrhexis
What is the diagnosis?
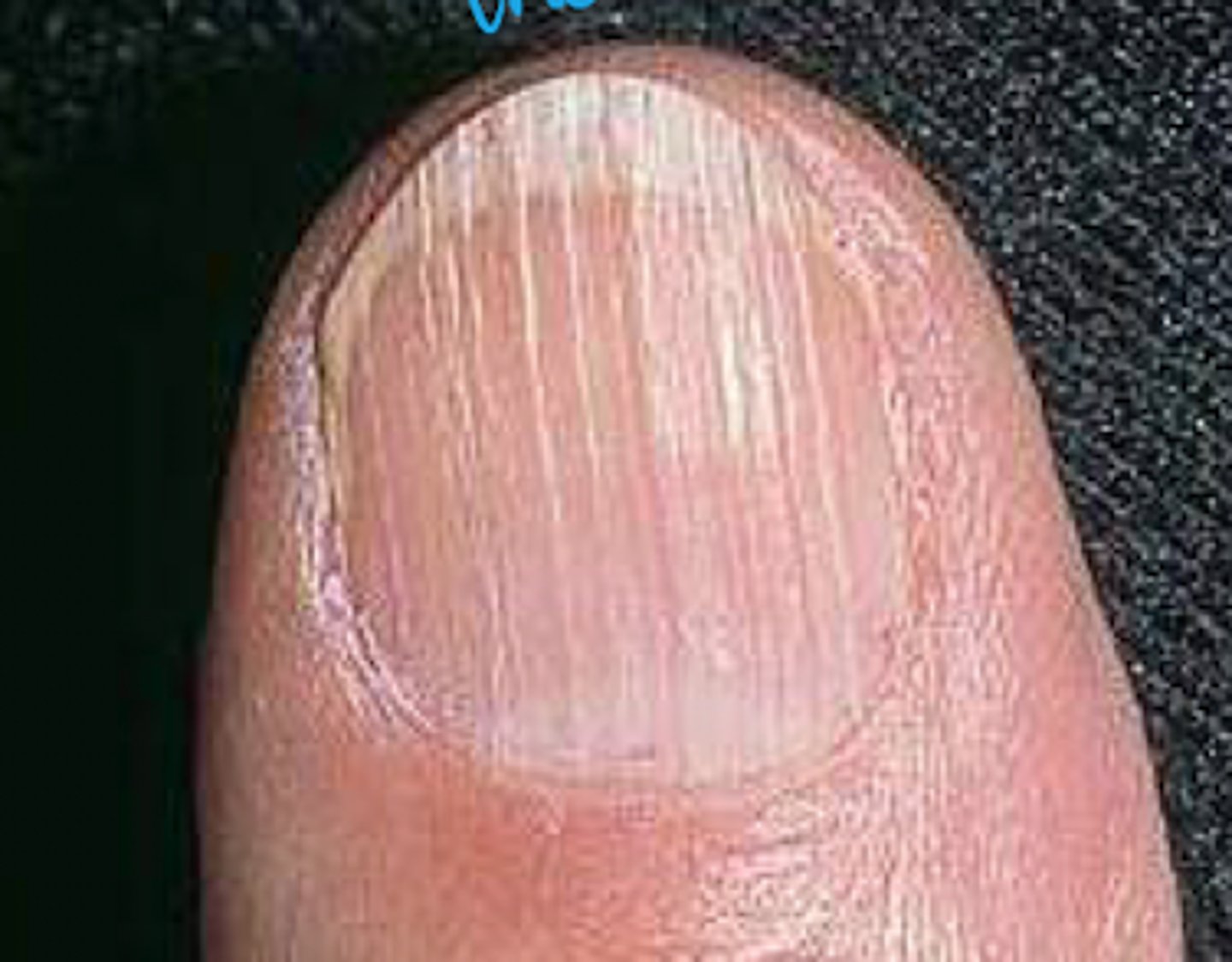
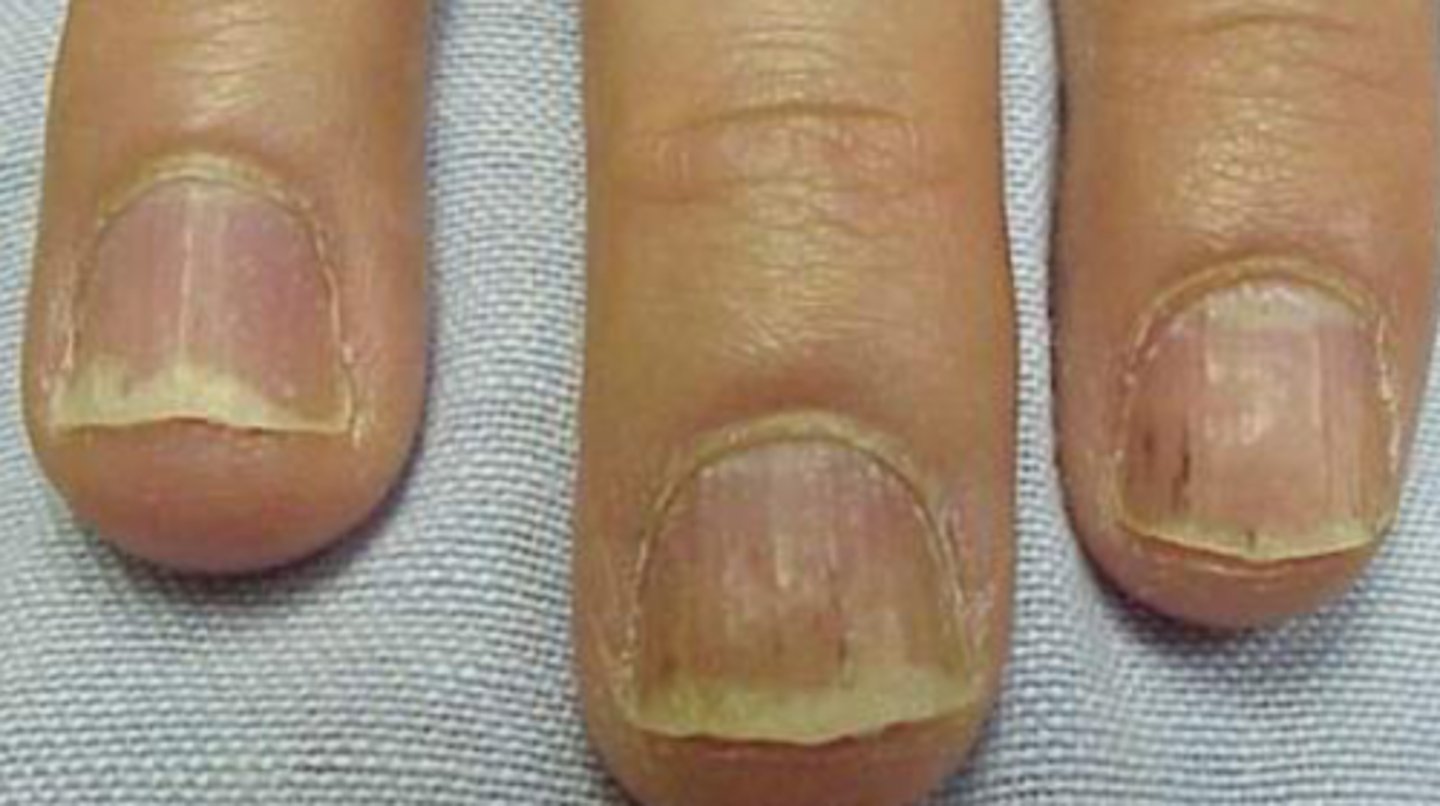
Onychomycosis
What is the diagnosis?
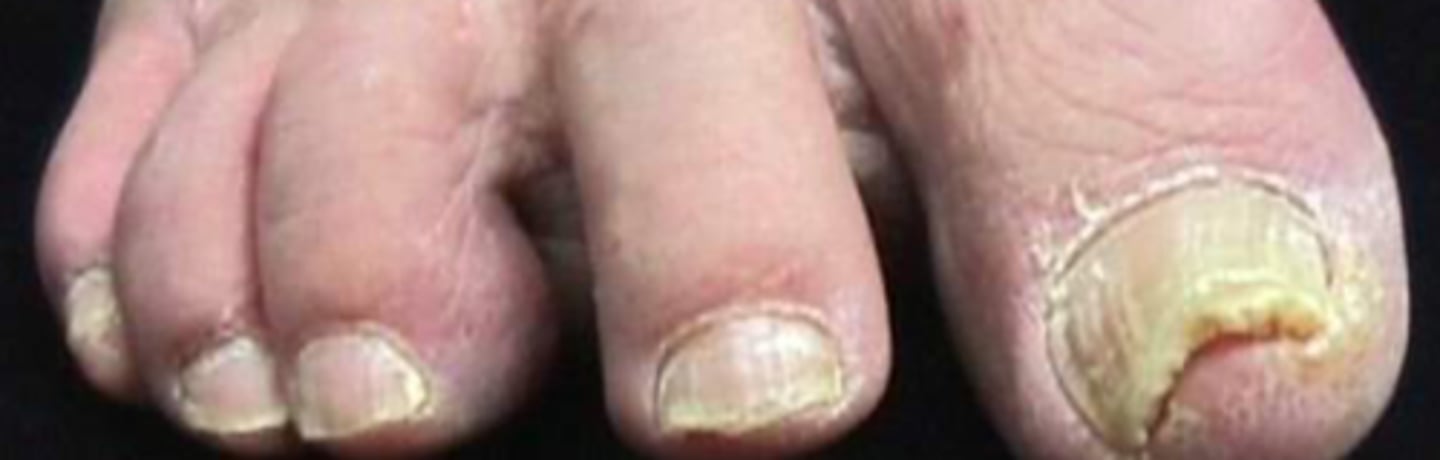
Onychomyosis
What is the diagnosis?
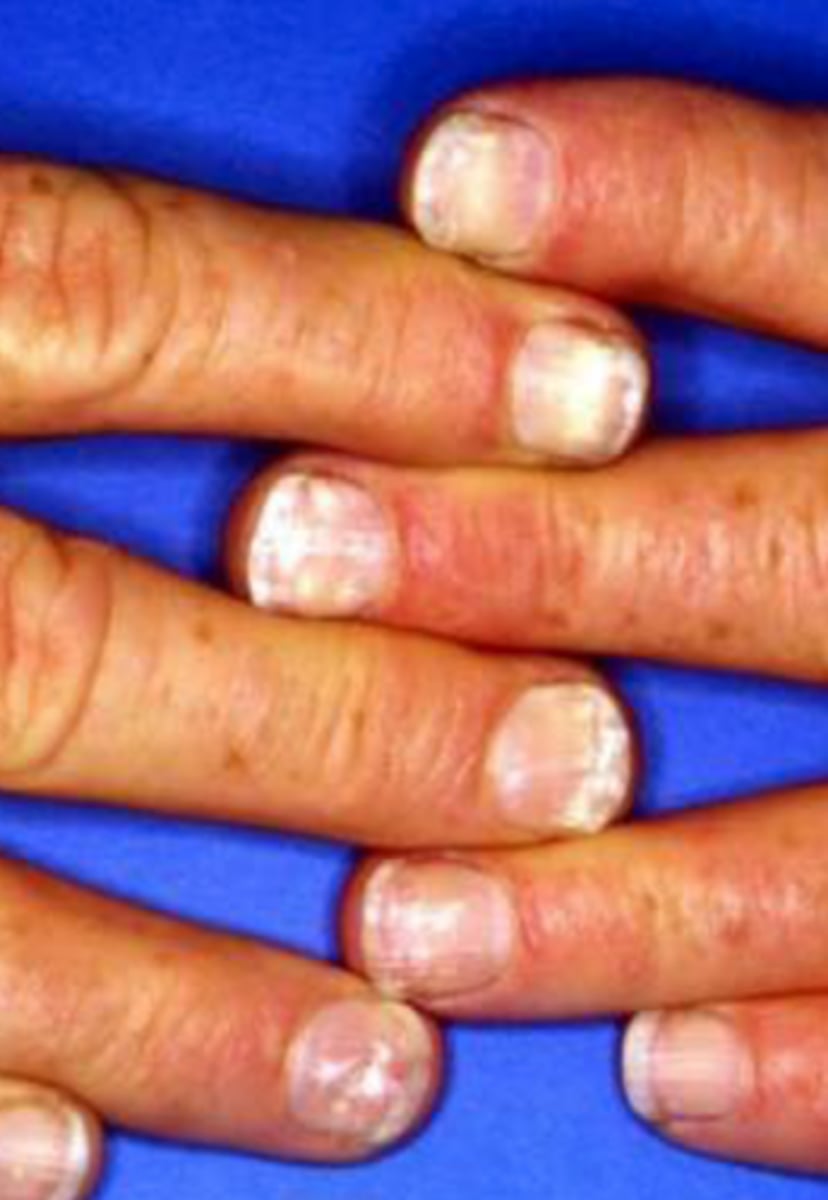
- KOH and PAS
- fungal culture for specific fungus
Dx of onychomycosis?
- oral terbinafine (6 wks fingers, 12 wks toes)
- oral itraconazole (pulsed doses)
- topical antifungals prophylactically
Tx of onychomycosis?
50
up to ___% of patients with psoriasis have nail involvement
pitting and oil stains
What are two characteristics of psoriatic nails?
Psoriatic nails
What is the diagnosis?
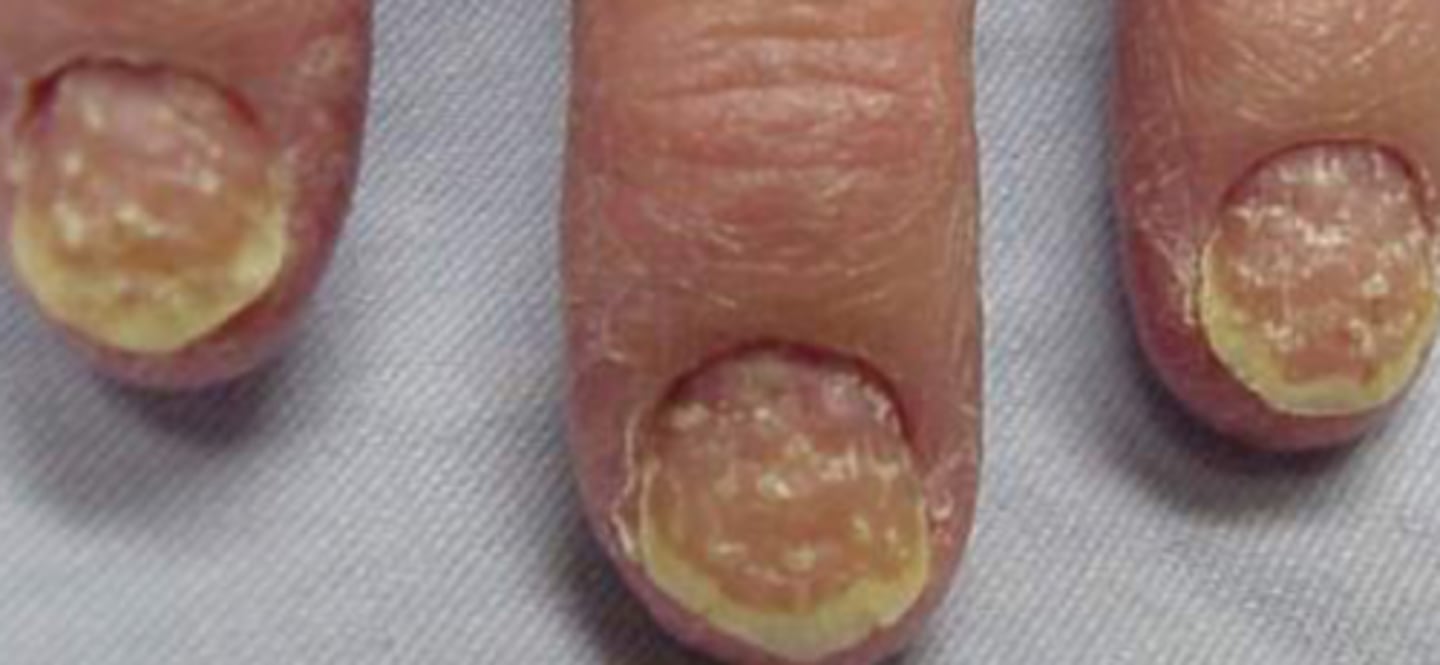
Psoriatic nails
What is the diagnosis?
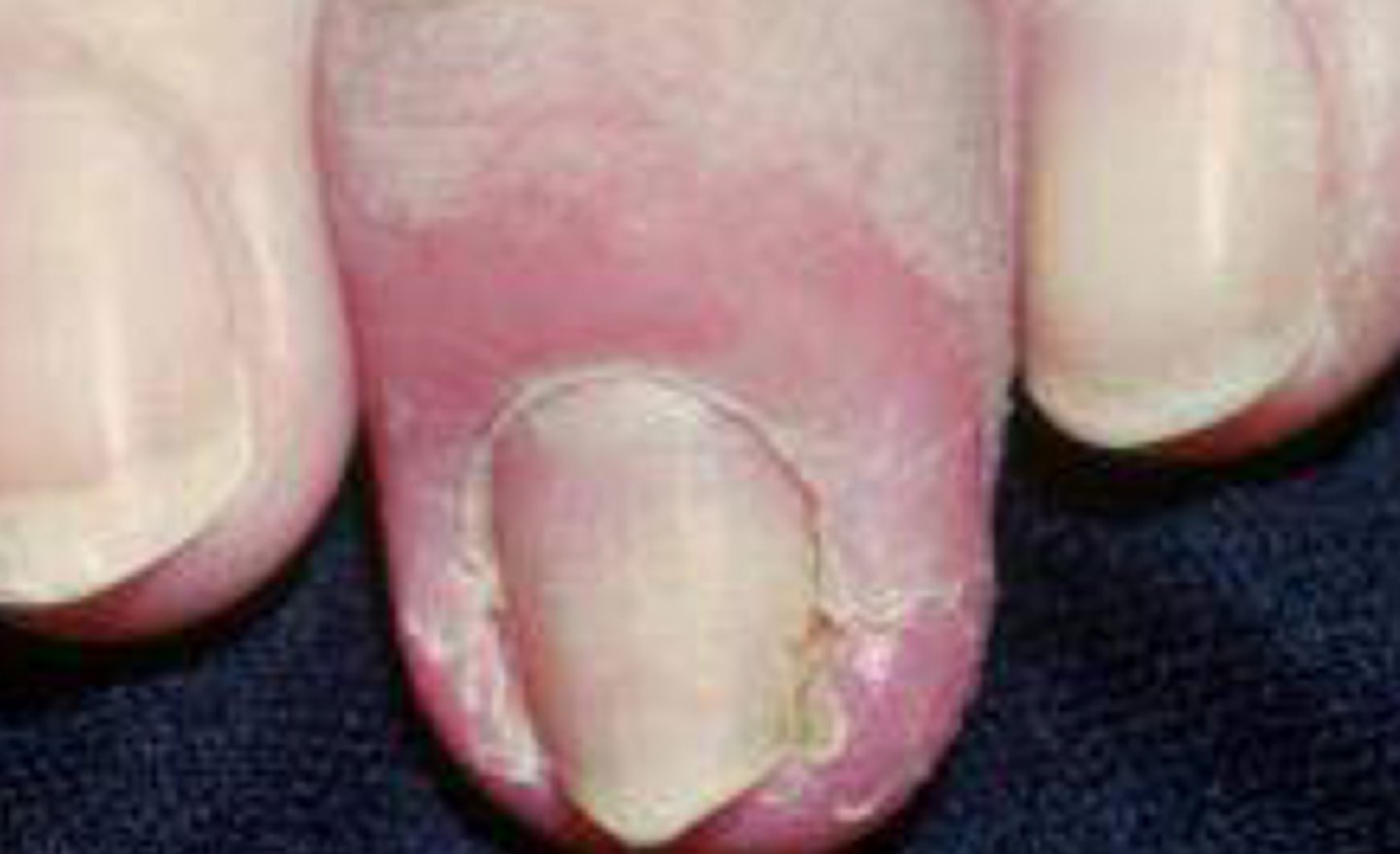
bacteria (usually staph)
Acute paronychia is caused by ___
fungal (candida)
Chronić paronychia is a ___ issue
Wet work, finger sucking, manicures
Risk factors for chronic paronychia?
Acute bacterial paronychia
What is the diagnosis?
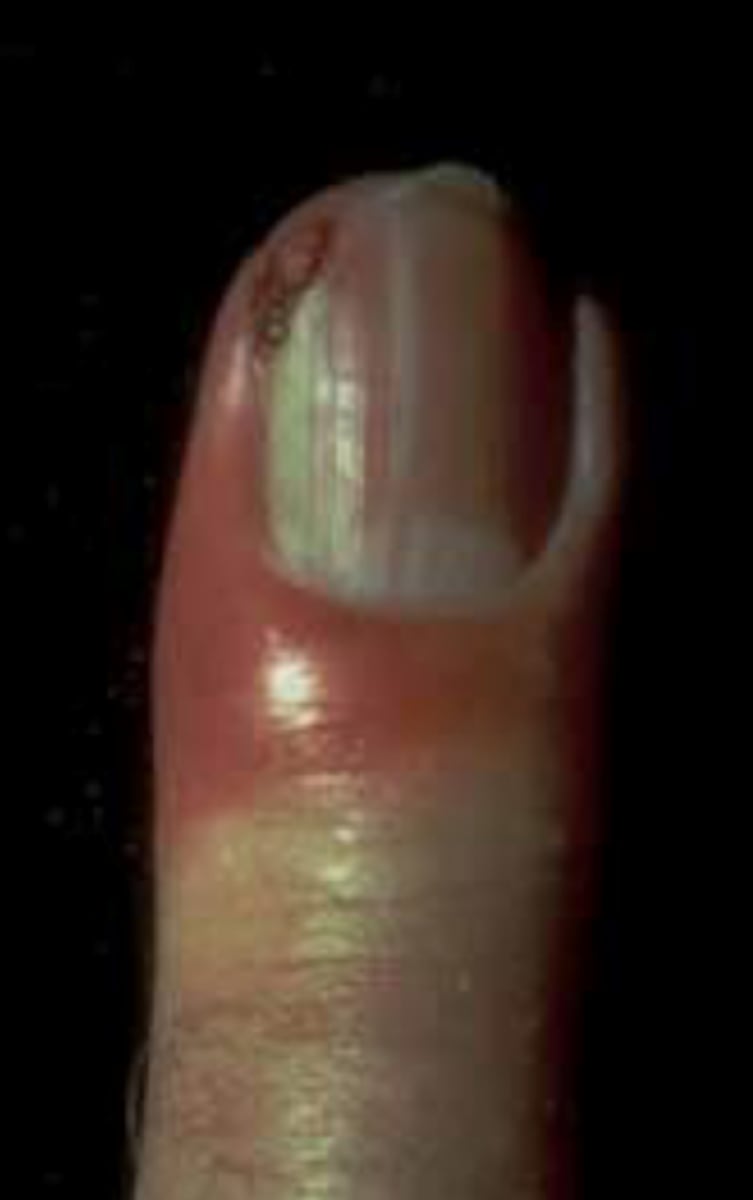
Chronic paronychia
What is the diagnosis?
- cephalexin
- erythromycin
- dicloxacillin
Acute paronychia tx?
- avoid trauma and water
- lotrisone
Chronic paronychia tx?
Ingrown toenail
Lateral portion of nail plate grows into the lateral nail fold causing inflammation
- nail trimming
- topical antiseptics
- severe cases: avulsion with matrix destruction
Tx for ingrown toenail?