Unit 3. Isomers
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Skeletal Isomers
are isomers with similar formula but different
arrangement of carbon atoms.
Constitutional Isomers
have the same molecular formulas, but they have different connectivities
Positional Isomers
isomers with similar formula and functional group but at a different position.
Functional Isomers
are isomers with similar formula but different functional group.
sulfide
thiol
alcohol
ether
aldehyde
ketone
alcohol ether
H = 2n + 2
aldehyde ketone
H = 2n
Stereoisomers
are any two or more molecules differing only at the spatial arrangement of their atoms
Conformation
Any spatial arrangement atoms may adopt and convert into thru rotation about individual single bonds, e.g. Sawhorse, Newman, and Ring conformations.
Configuration
It is a fixed 3D relationship of atoms in a compound as a results of the bonds between them, e.g. Optical and Geometric configurations.
Sawhorse conformation
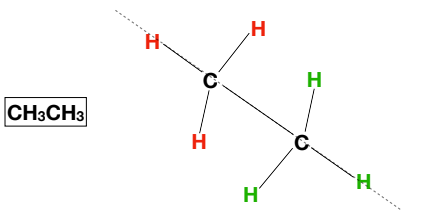
Newman Projection
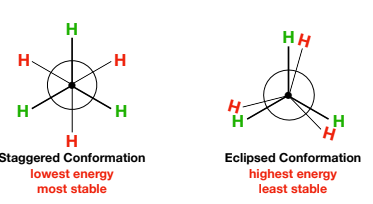
Staggered Conformation
lowest energy, most stable
Eclipsed Conformation
highest energy, least stable
Torsional Strain
is bending strain exhibit in the bond between the C’s at the point of rotation
Ring conformation
A ring conformation shows the arrangement of carbon molecules in a
cyclic / ring form.
Angle strain
results from the angular deviation of ring structures from
the normal 109.5°C angle of each carbon bond.
Cyclohexane D
has the most stable ring conformation, it does not
produce an angle strain.
Boat Conformation
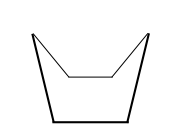
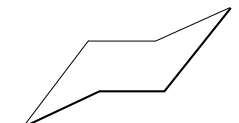
Chair Conformation
Optical Configuration
It is based on the surrounding bonds attached to a chiral carbon.
Enantiomers
are two compounds with same number and kind of atoms and bonds but differ at the spatial arrangement of the atoms and are non-superimposable mirror image of each other.
Diastereomers
are two or more compounds which have different configurations at two or more stereocenters and are not mirror images of each other.
Geometric Configuration
These are two or more compounds which differs from each other in the arrangement of groups in reference to a double bond, ring, or other rigid structure.
cis-trans isomers
are isomers with same connections but differ in the spatial orientation of the group of atoms
cis-trans isomers
It is used for disubstituted alkenes to illustrate the double-bond
geometry of the alkene.
cis
indicates that the groups are attached “on the same side”
trans
indicates that the groups are attached “across” each other
E-Z system
is used to illustrate double-bond geometry for alkenes which are trisubstituted or tetrasubstituted.
E-Z system
It makes use of the Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules to assign priorities to substituents to determine the geometry of the double-bond.
E
“entgegen” meaning “opposite”
Z
“zusammen” meaning “together”
R and S system
is used to illustrate specific configuration of substituents around a chiral center.
R
“rectus” = to the right = clockwise
S
“sinister” = to the left = counter=clockwise