Exam #2
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
contralateral
located on the opposite side of the body
contralateral example
nerves on the left side of the brain send axons to a structure located on the opposite side of the brain
cross section
a slice taken at right angles to the neuraxis
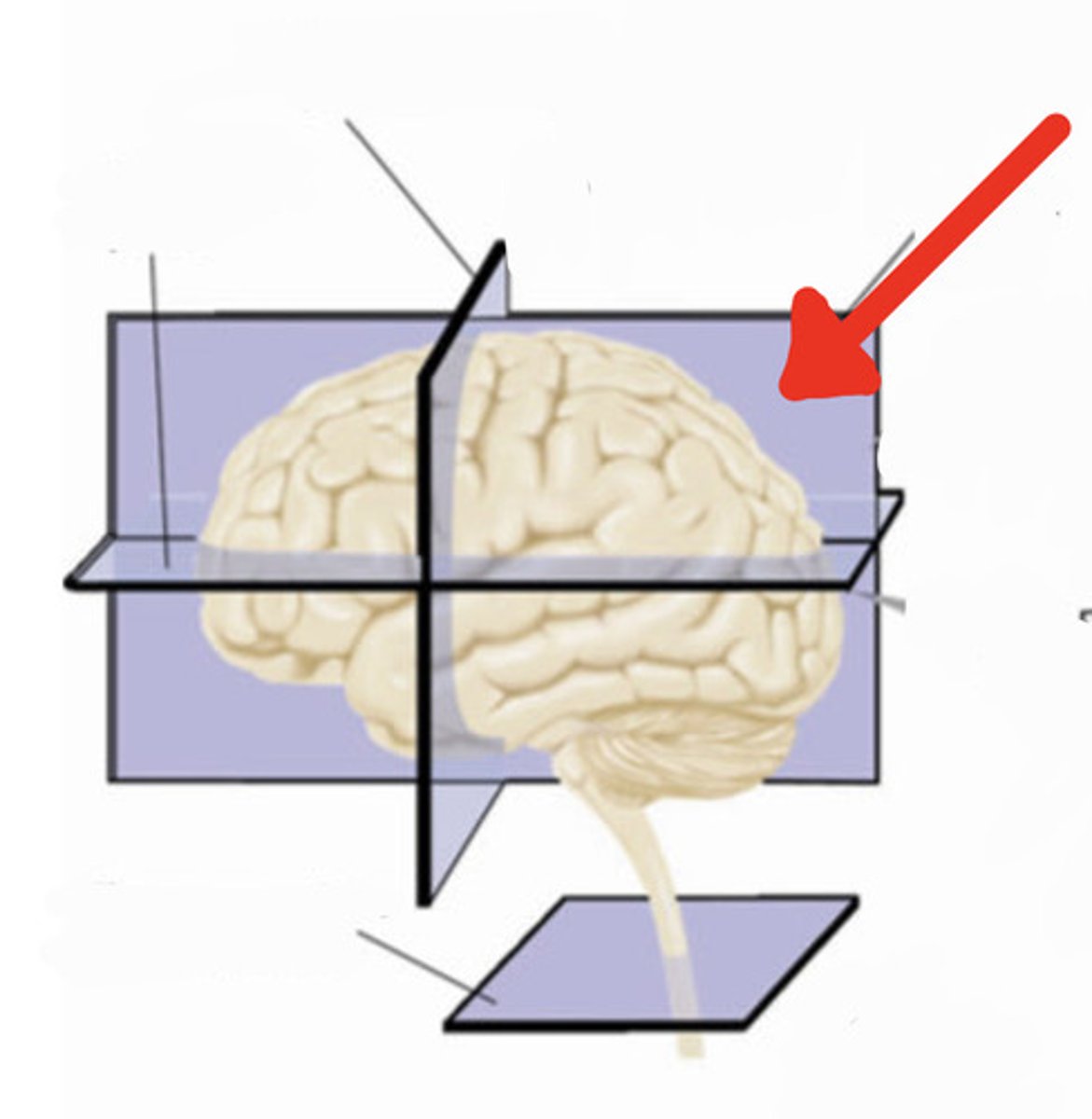
frontal section
a slice through the brain parallel to the forehead
horizontal plane
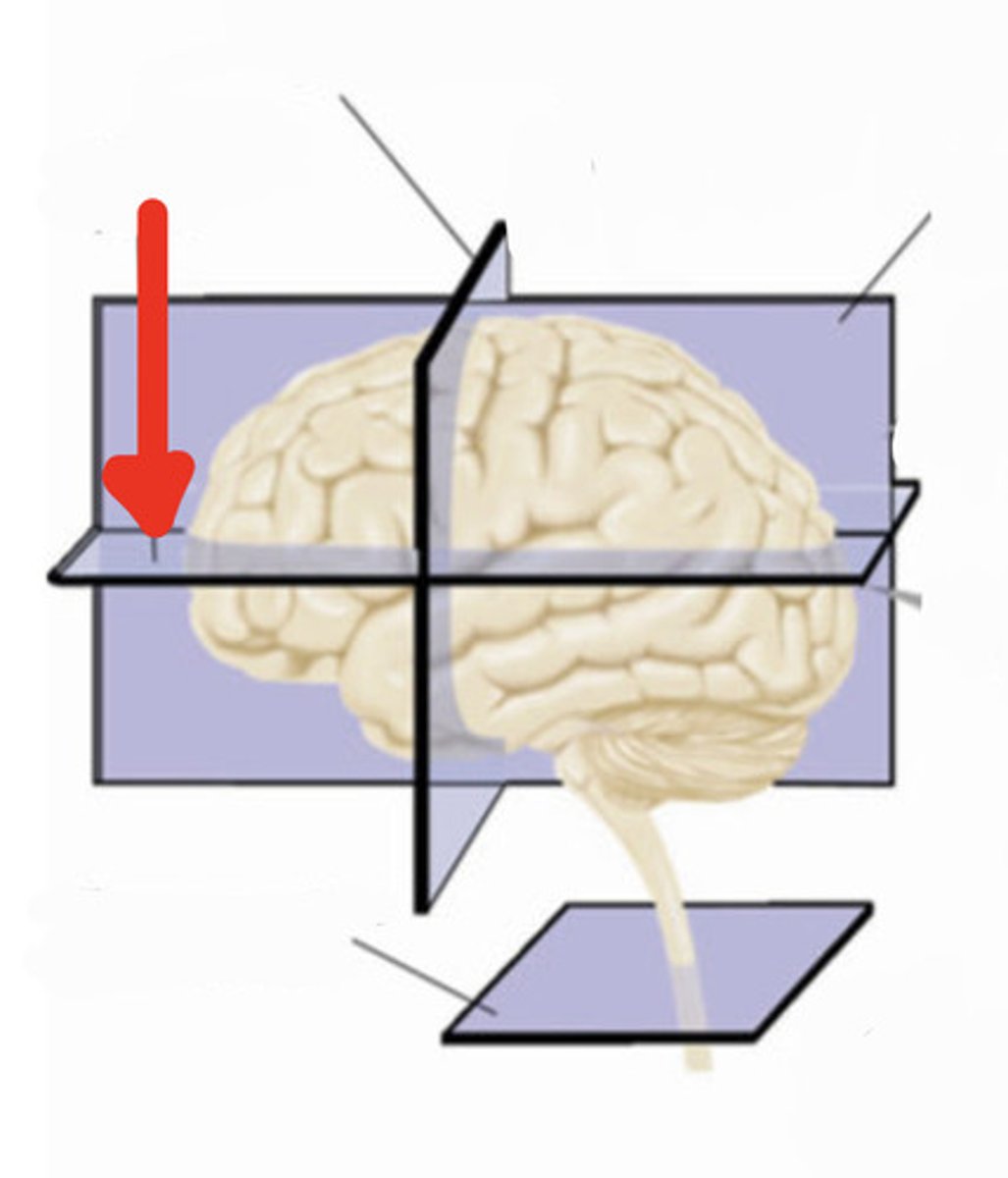
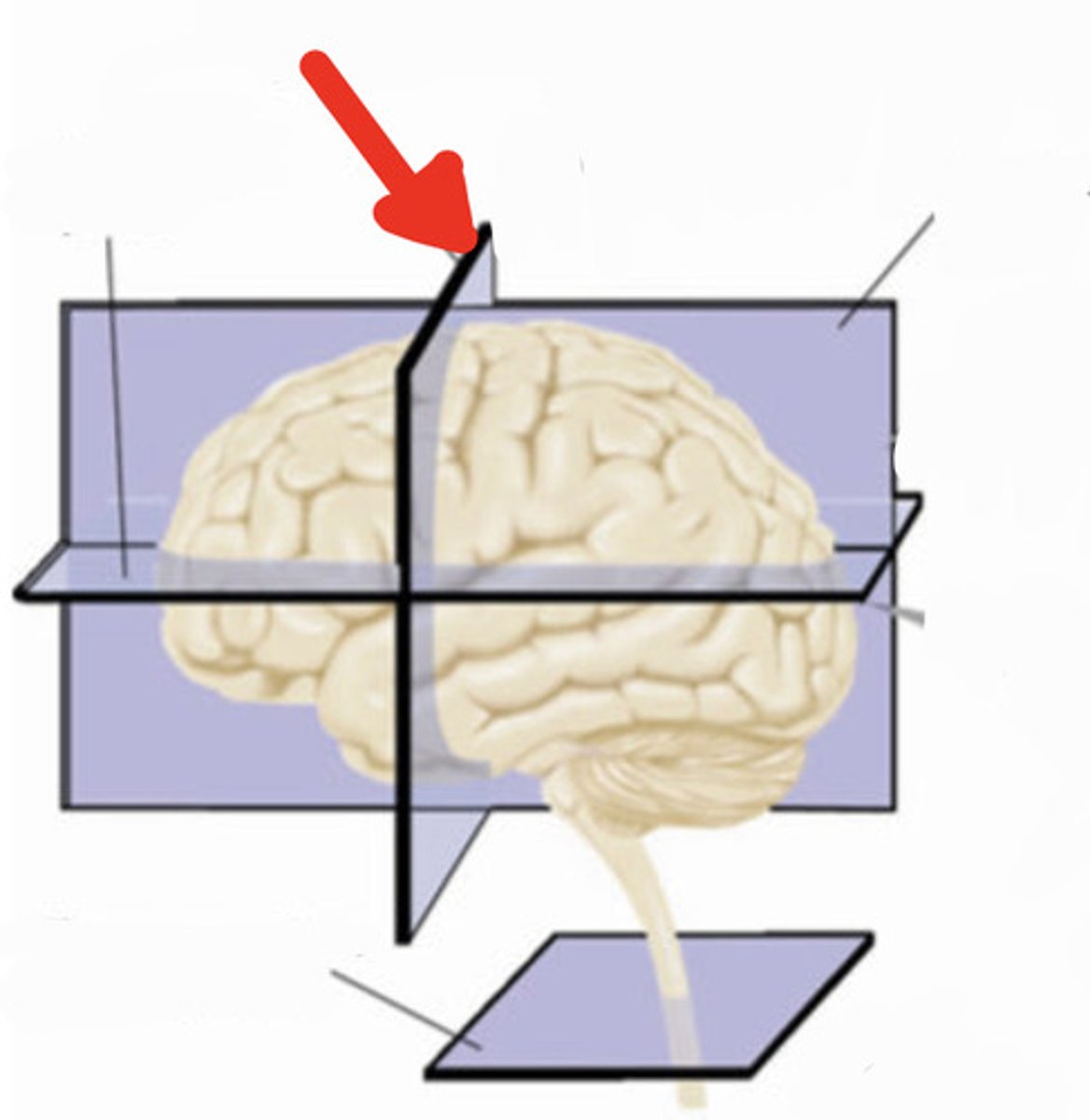
saggital plane
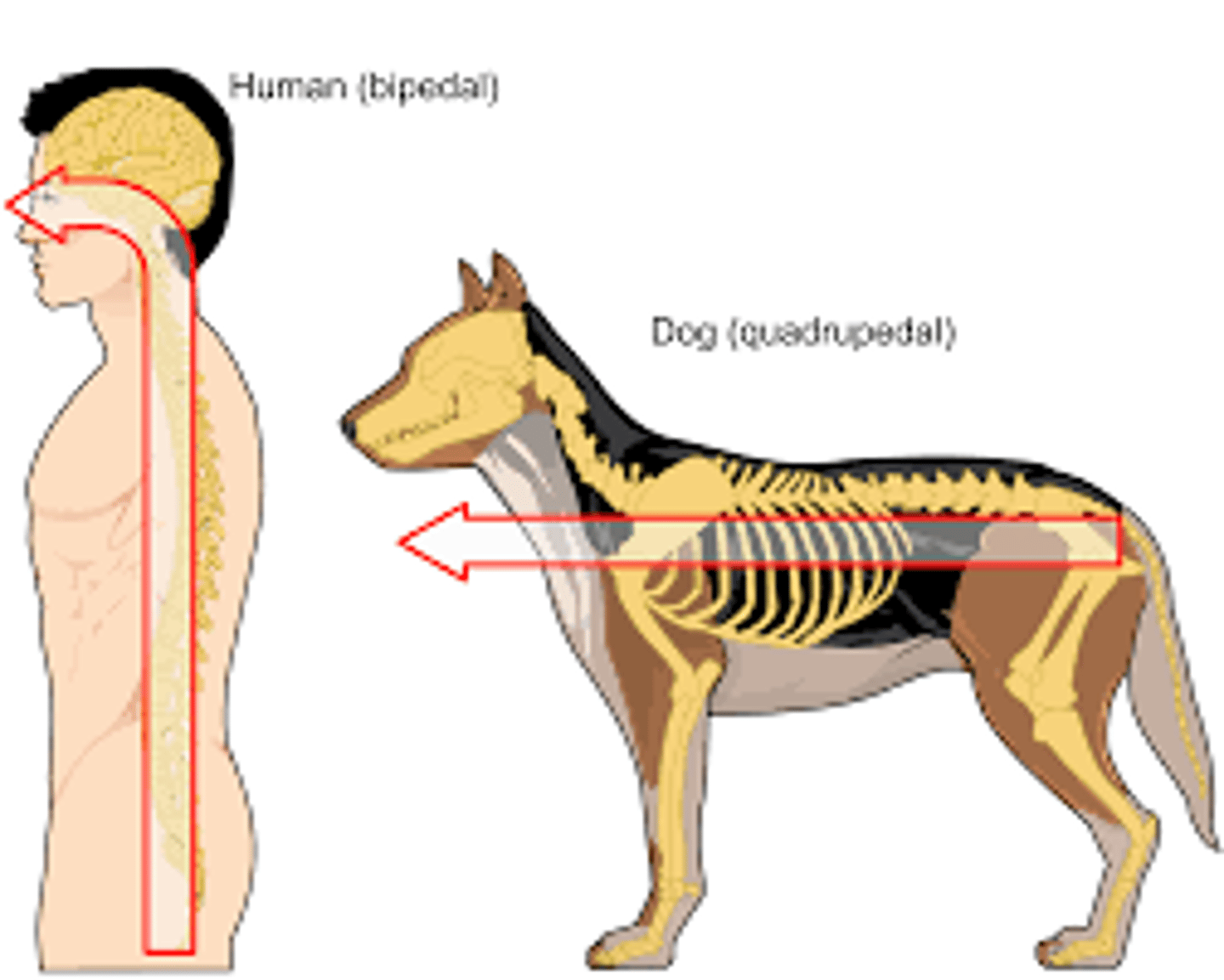
Neuraxis
an imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the CNS, from the bottom of the spinal cord to the front of the forebrain
neuraxis
ipsilateral
located on the same side of the body
ipsilateral example
nerves on the left side of the brain send axons to a structure located on the same side of the brain
transverse plane (frontal section)
horizontal section
a slice through the brain parallel to the ground
saggital section
a slice through the brain parallel to the neuraxis and perpendicular to the ground
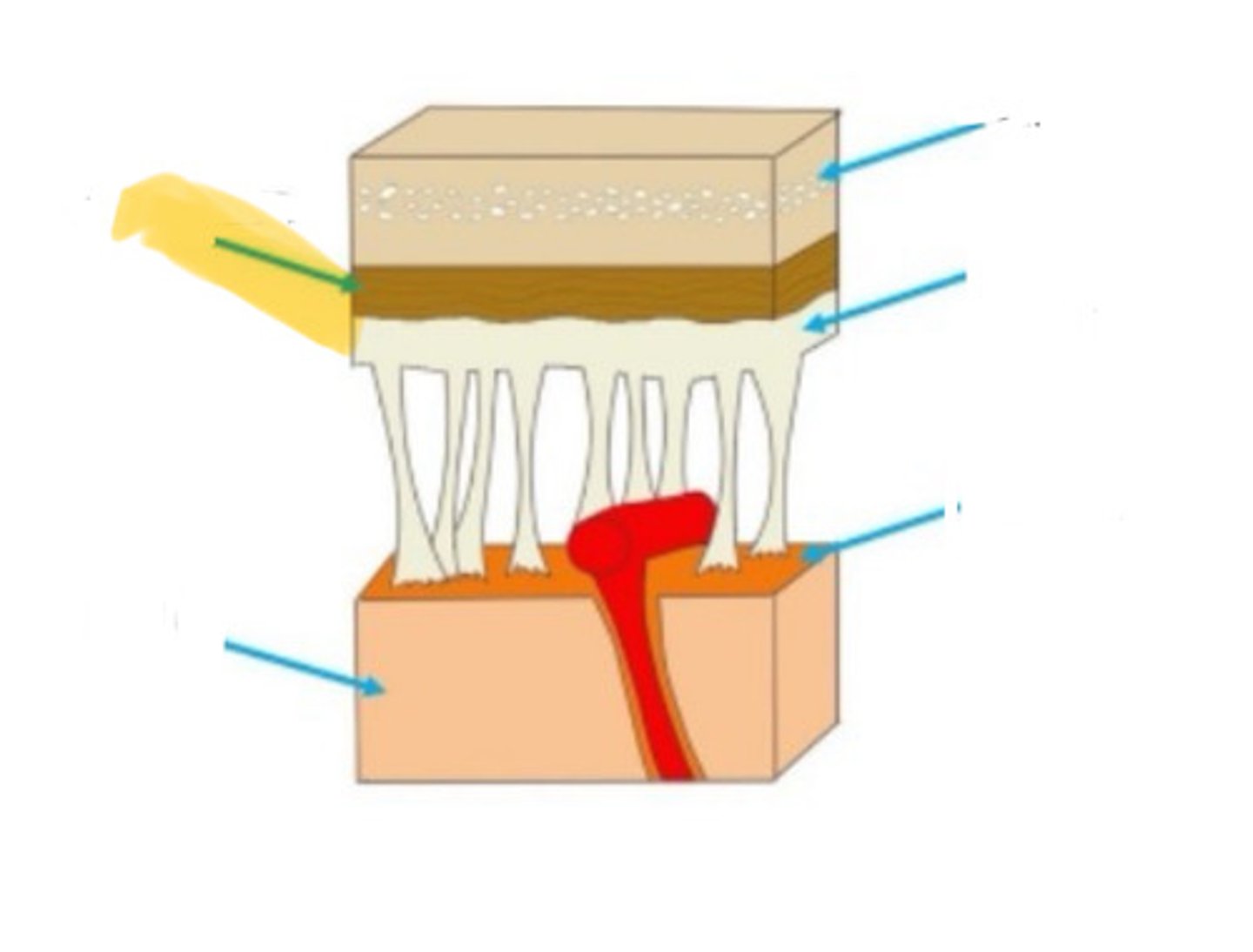
meninges
the three layers of tissue that encase the nervous system
dura mater
the outermost of the meninges: tough and flexible
arachnoid membrane
the middle layer of the meninges, located between the outer dura mater and the inner pia mater
pia mater
the layer of the meninges that clings to the surface of the brain; thin and delicate
subarachnoid space
the fluid-filled space that cushions the brain
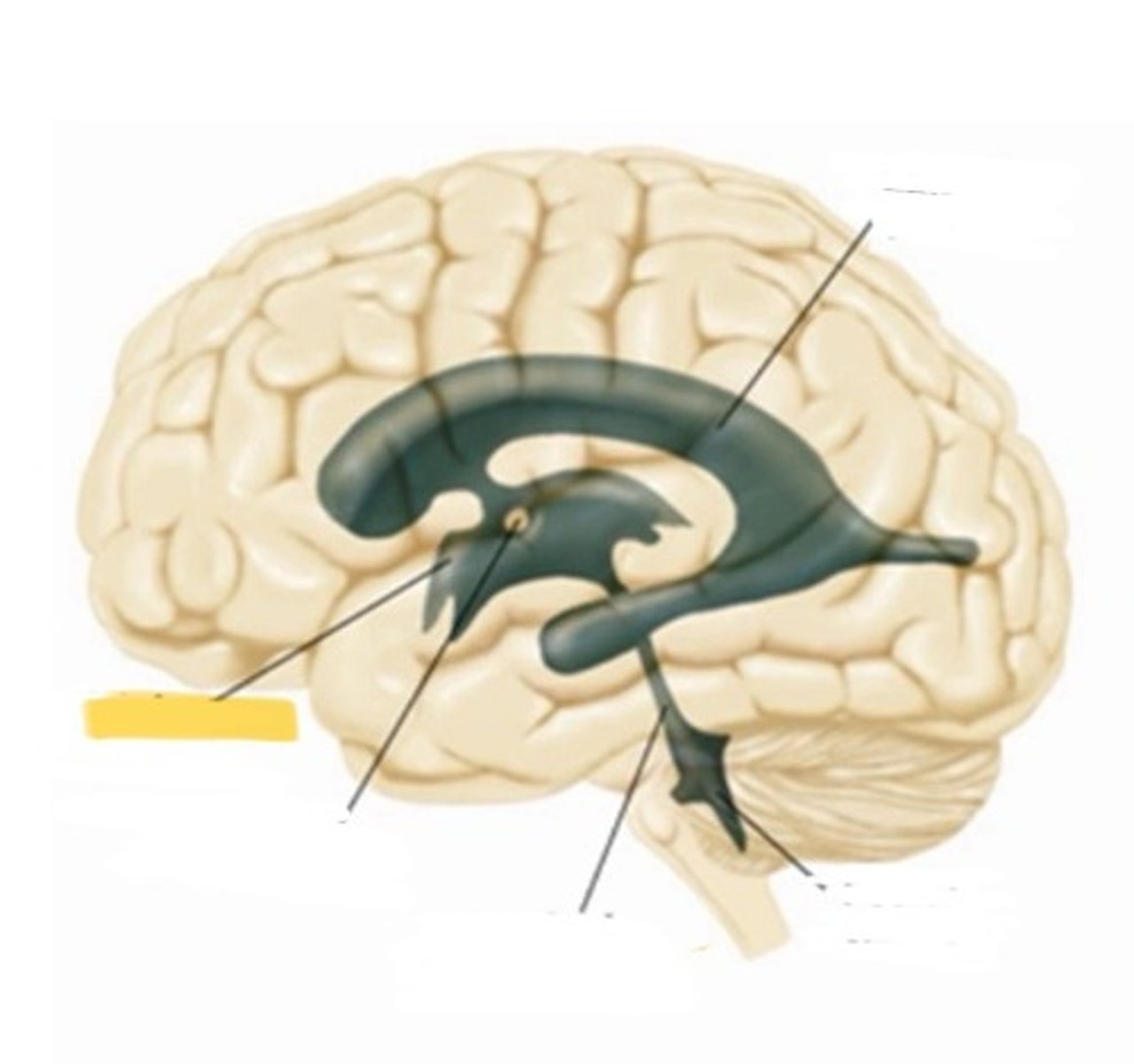
ventricle
one of the hollow spaces within the brain, filled with CSF
lateral ventricle
one of the two ventricles located in the center of the telencephalon
third ventricle
the ventricle located int he center of the diencephalon
skull
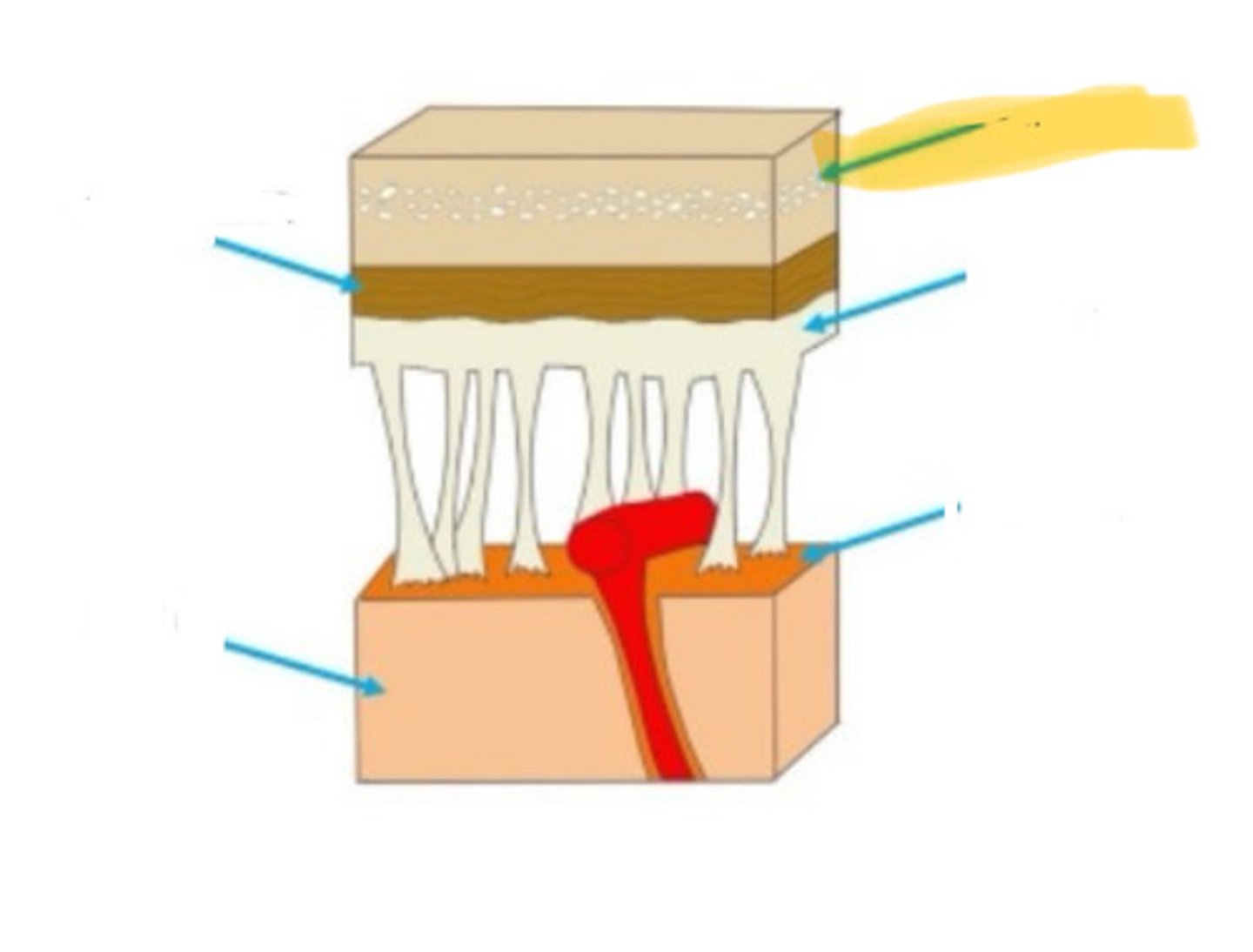
arachnoid mater
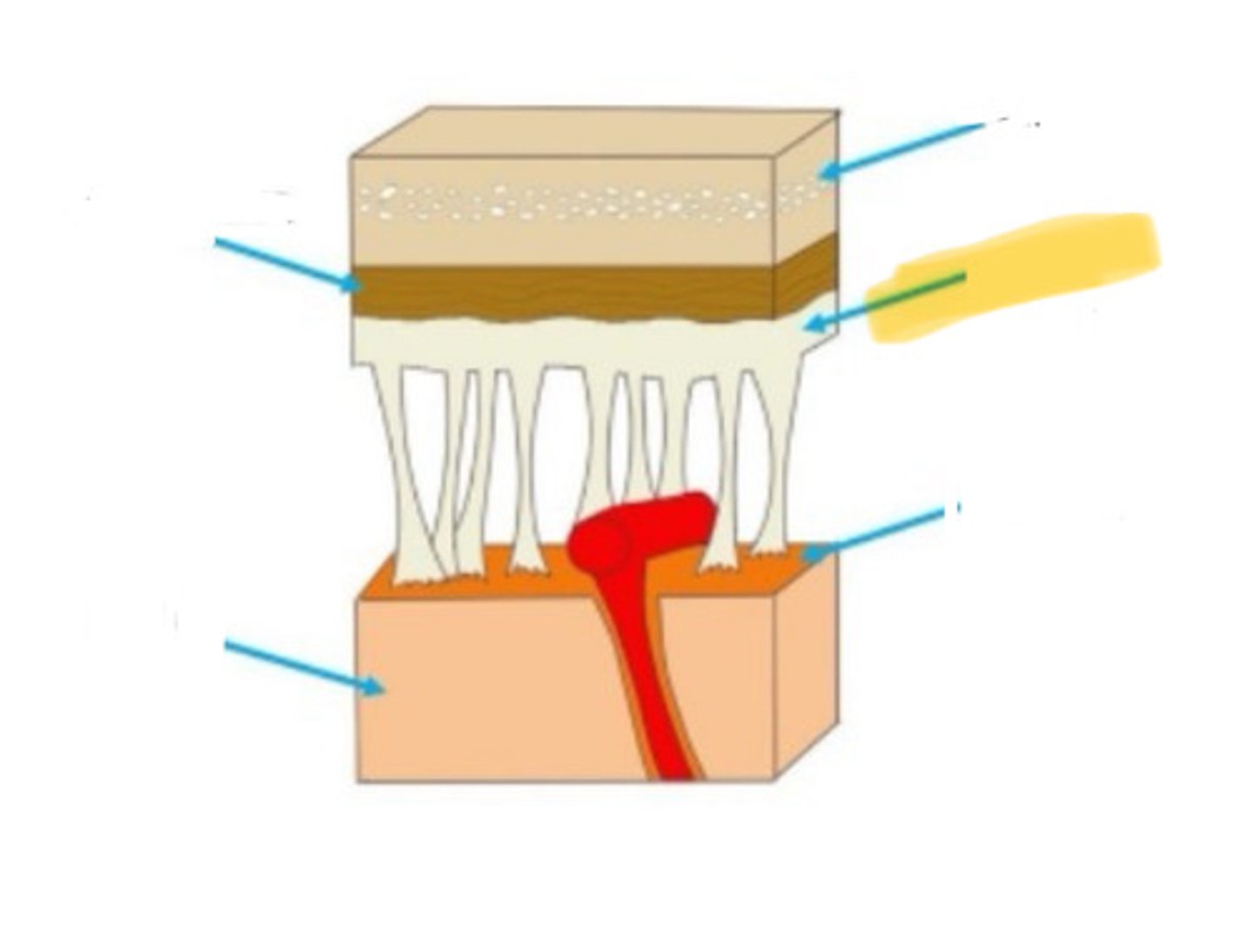
pia mater
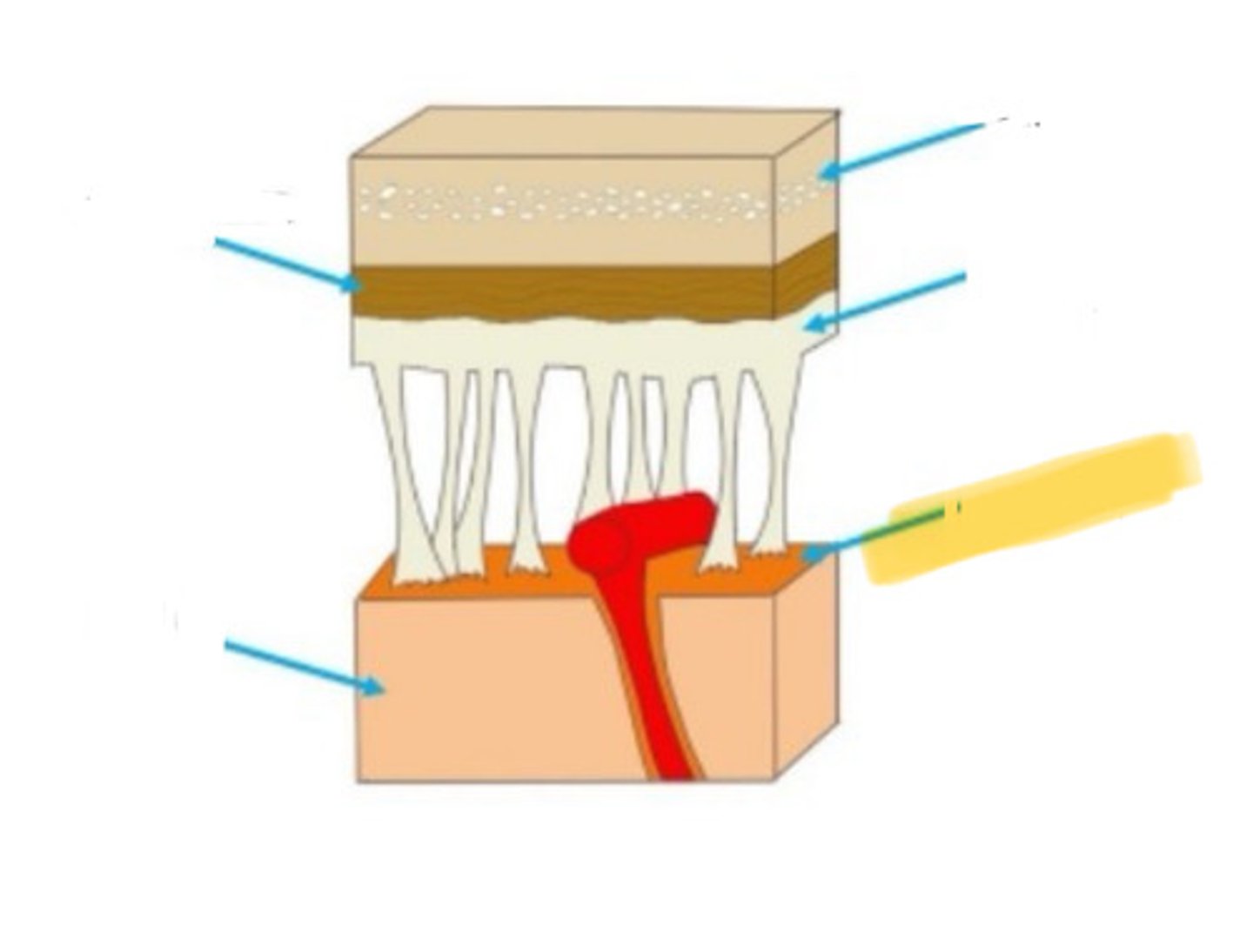
brain
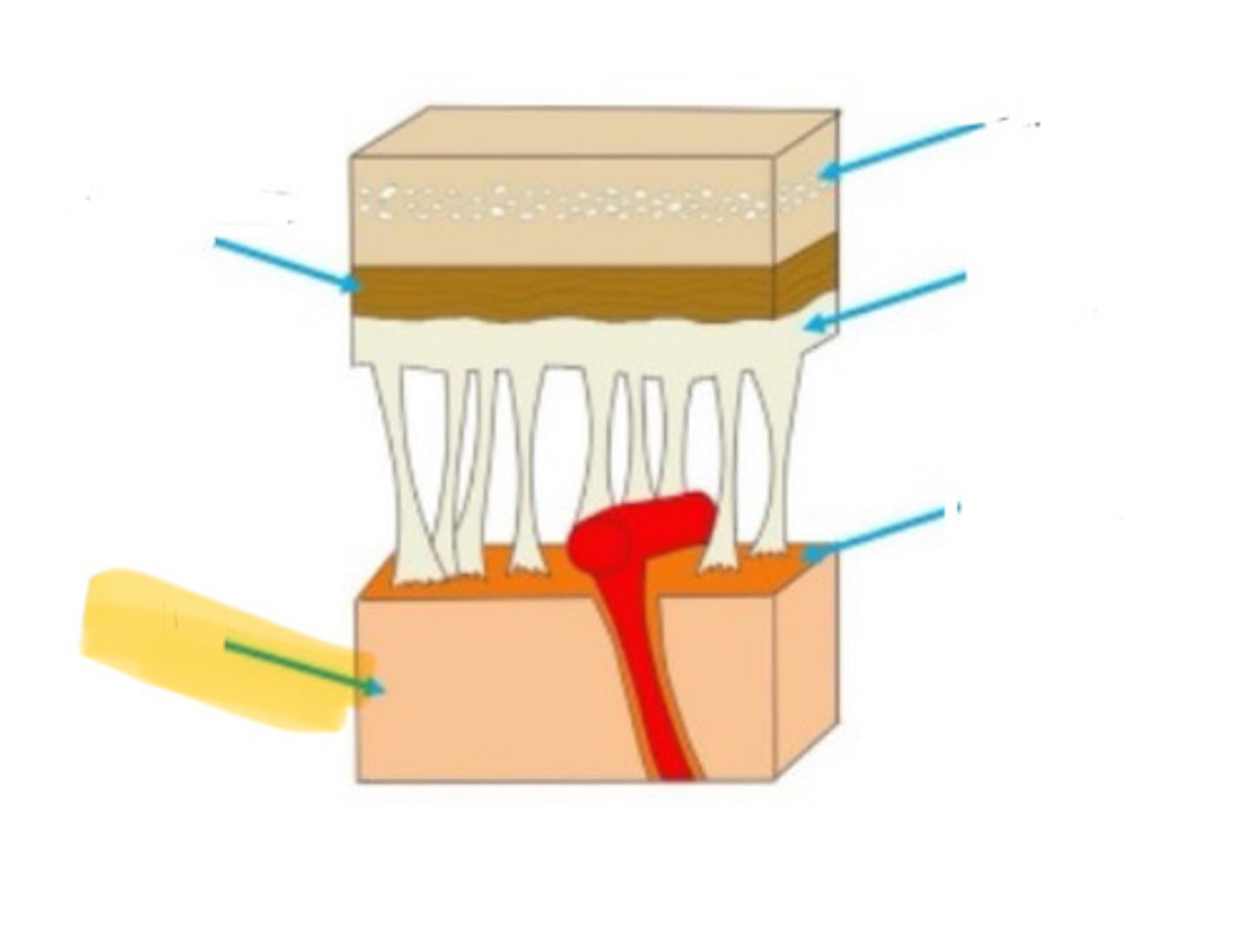
dura mater
cerebral aqueduct
a narrow tube interconnecting he third and fourth ventricles of the brain located in the center of the mesencepphalon
fourth ventricle
the ventricle located between the cerebellum and the dorsal pons, in the center of the mesencephalon
choroid plexus
the highly vascular tissue that protrudes into the ventricles and produces CSF
arachnoid granulation
small projection of the arachnoid membrane through the dura mater into the superior sagital sinus, CSF flows through the blood supply
obstructive hydrocephalus
condition in which all or some of the brain's ventricles are enlarged; caused by an obstruction that impedes the normal flow of CSF
lateral ventricle
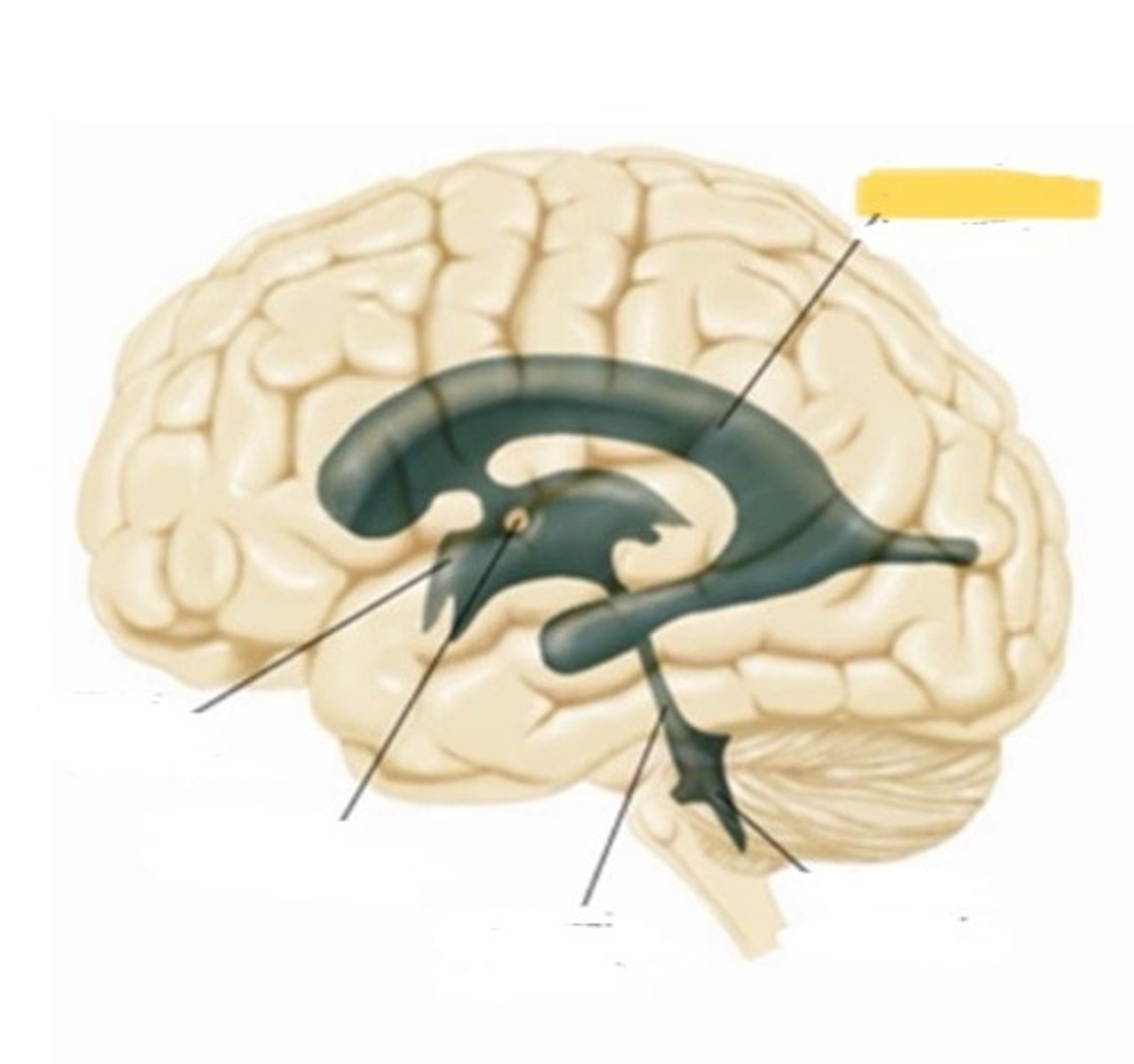
fourth ventricle
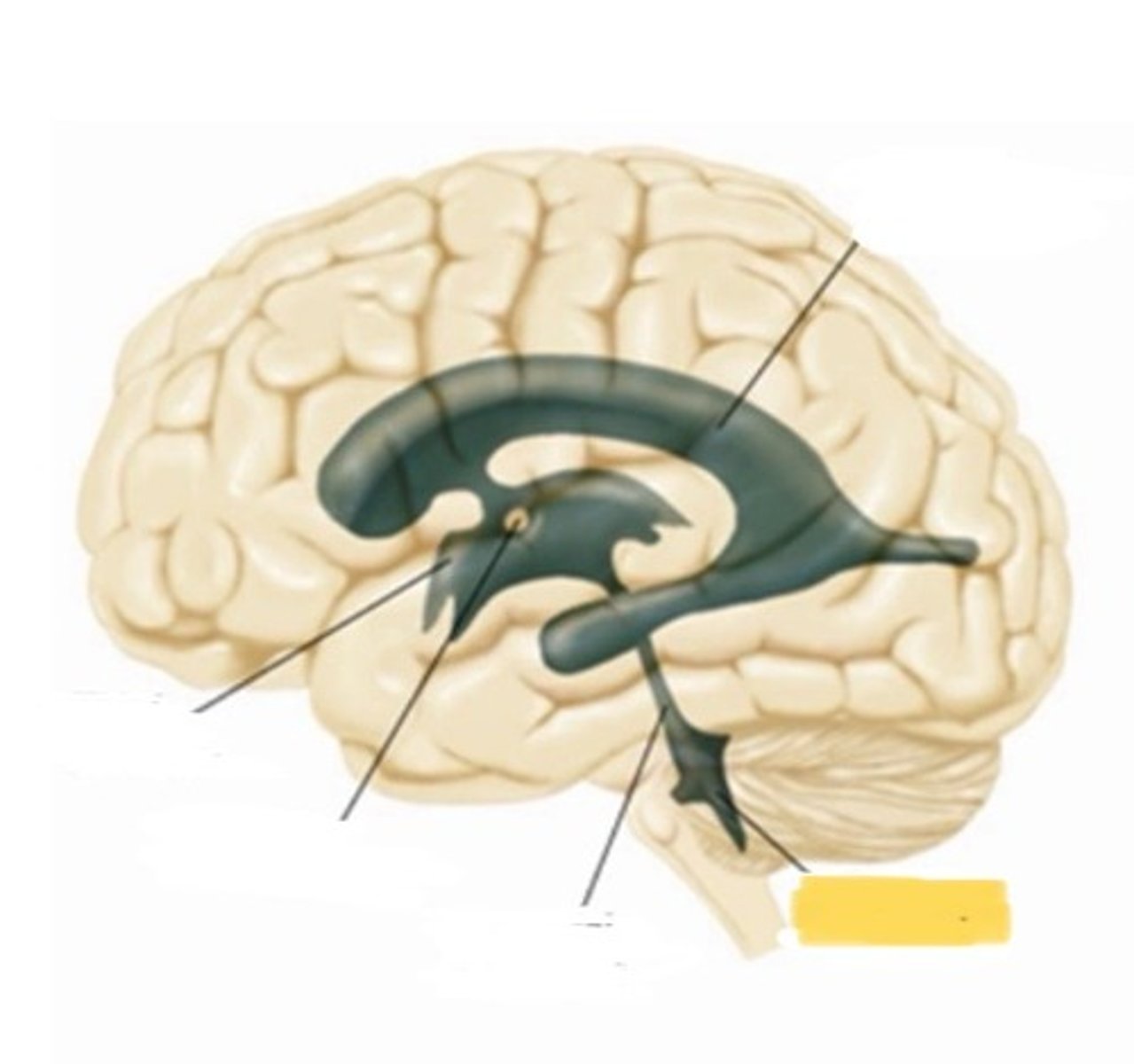
cerebral aqueduct
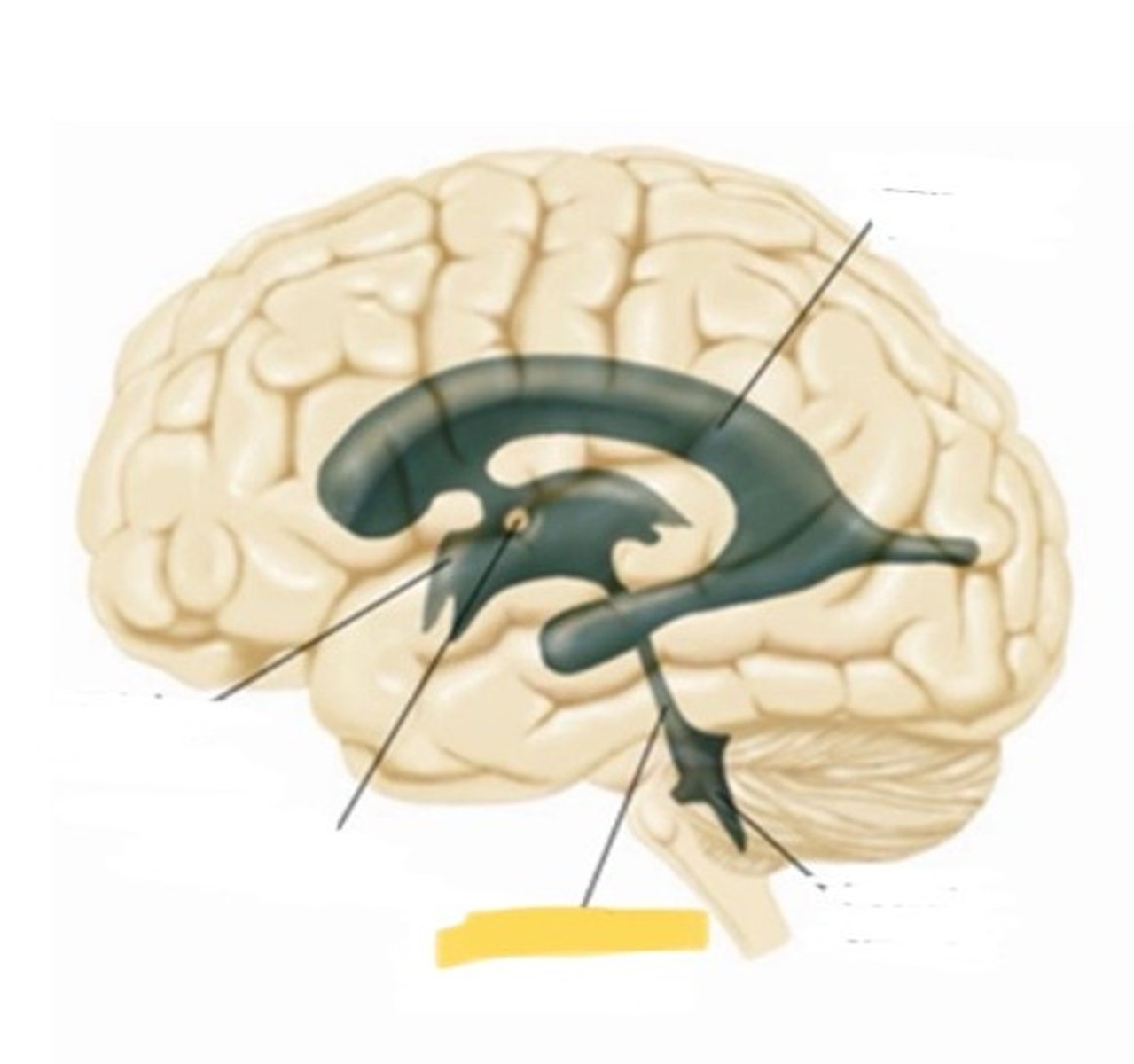
massa intermedia
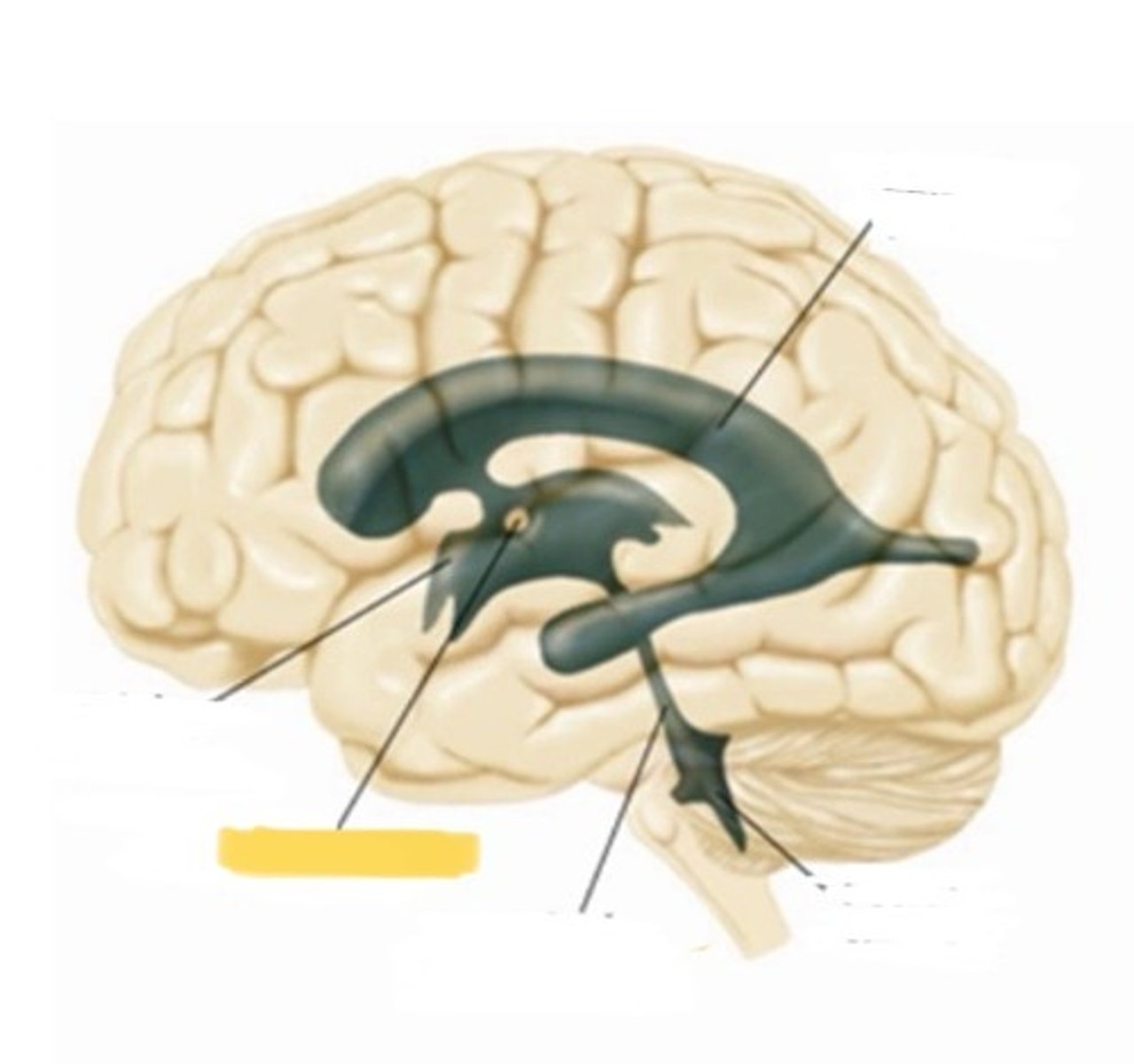
third ventricle
neural tube location
a hollow tube, closed at the rostral end
neural tube function
forms from the ectoderm tissue early in embryonic development; serves as the origin of the central nervous system
ventricular zone location
a layer of cells that line the inside of the neural tube;
cerebral cortex
the outermost layer of gray matter of the cerebral hemispheres
radial glia location
special glia with fibers that grow radially outward from the ventricular zone to the surface of the cortex
radial glia function
provides guidance for neurons migrating outward during brain development
ventricular zone function
contains founder cells that divide and give rise to the CNS
subarachnoid space location
located between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater
telencephalon
Diencephalon
mesencephalon
Metencephalon
myencephalon
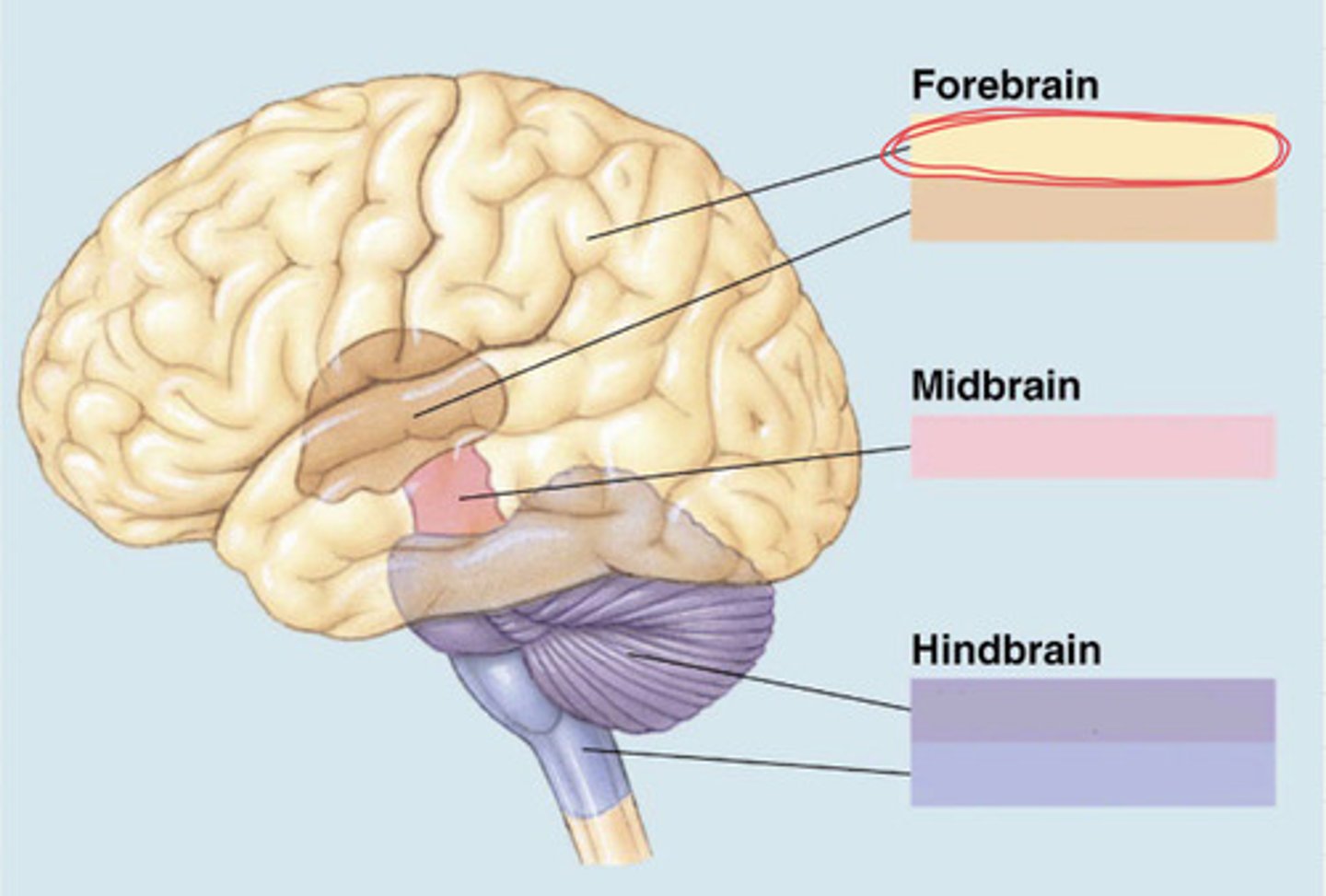
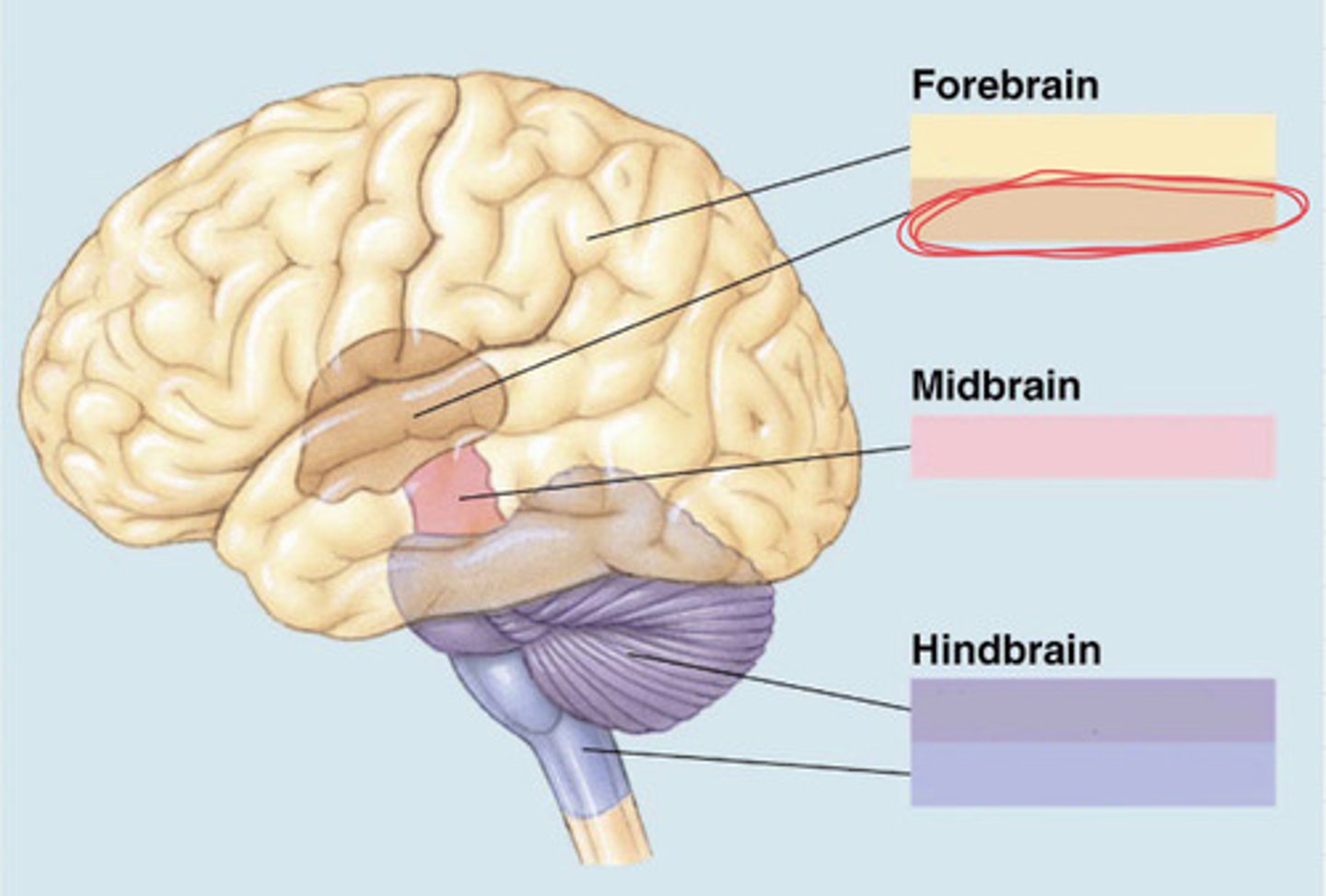
3 main subdivisions of the brain (essay)
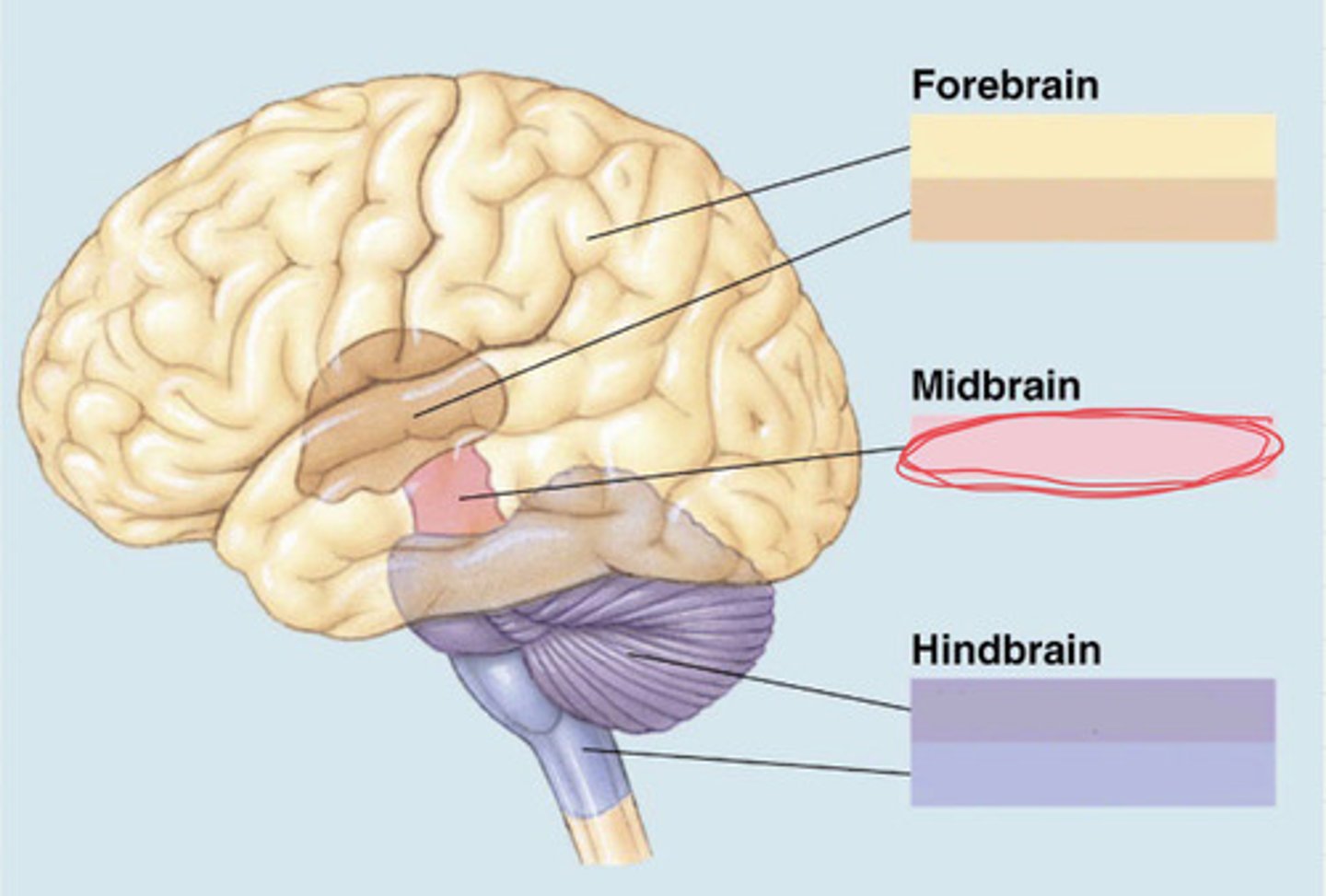
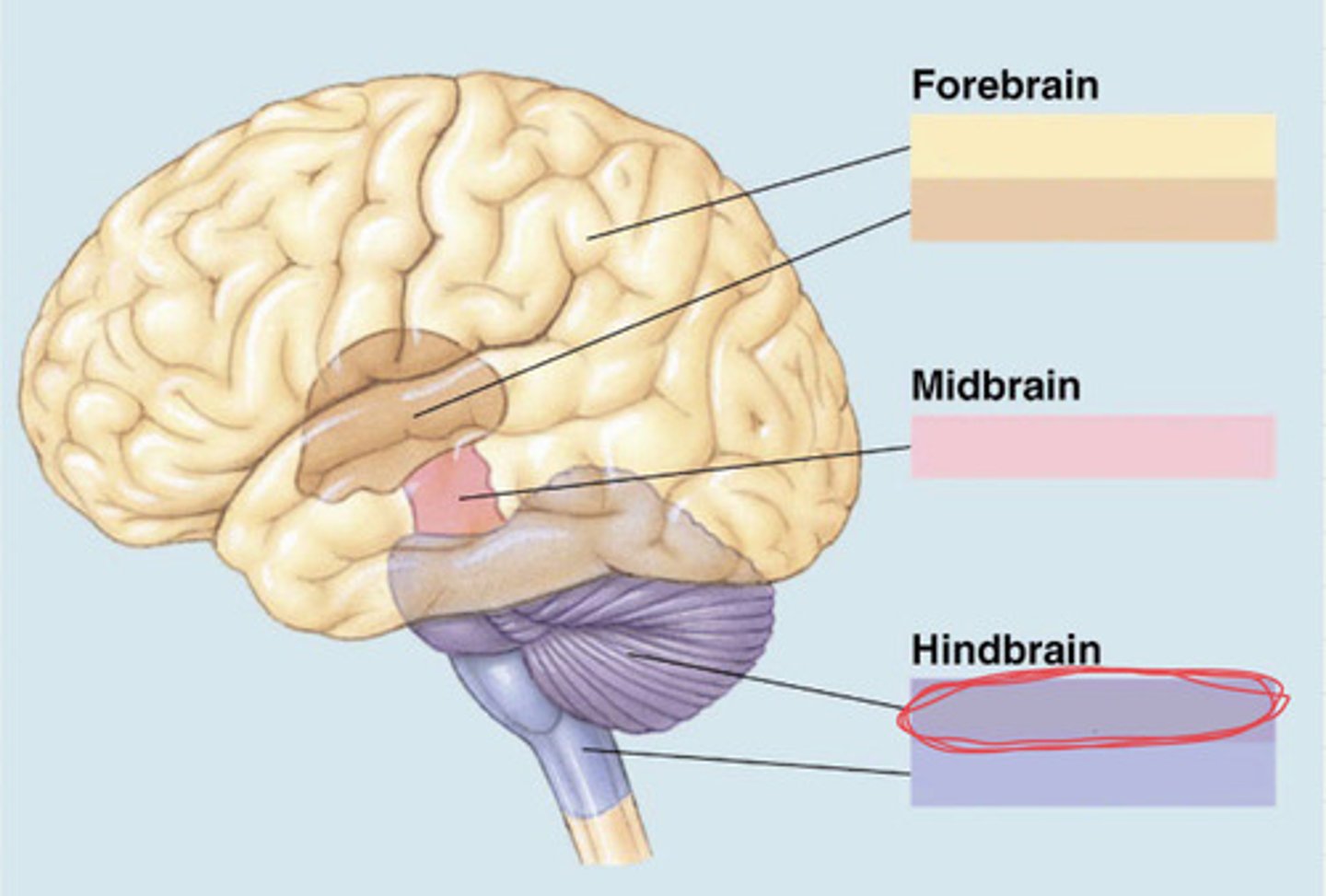
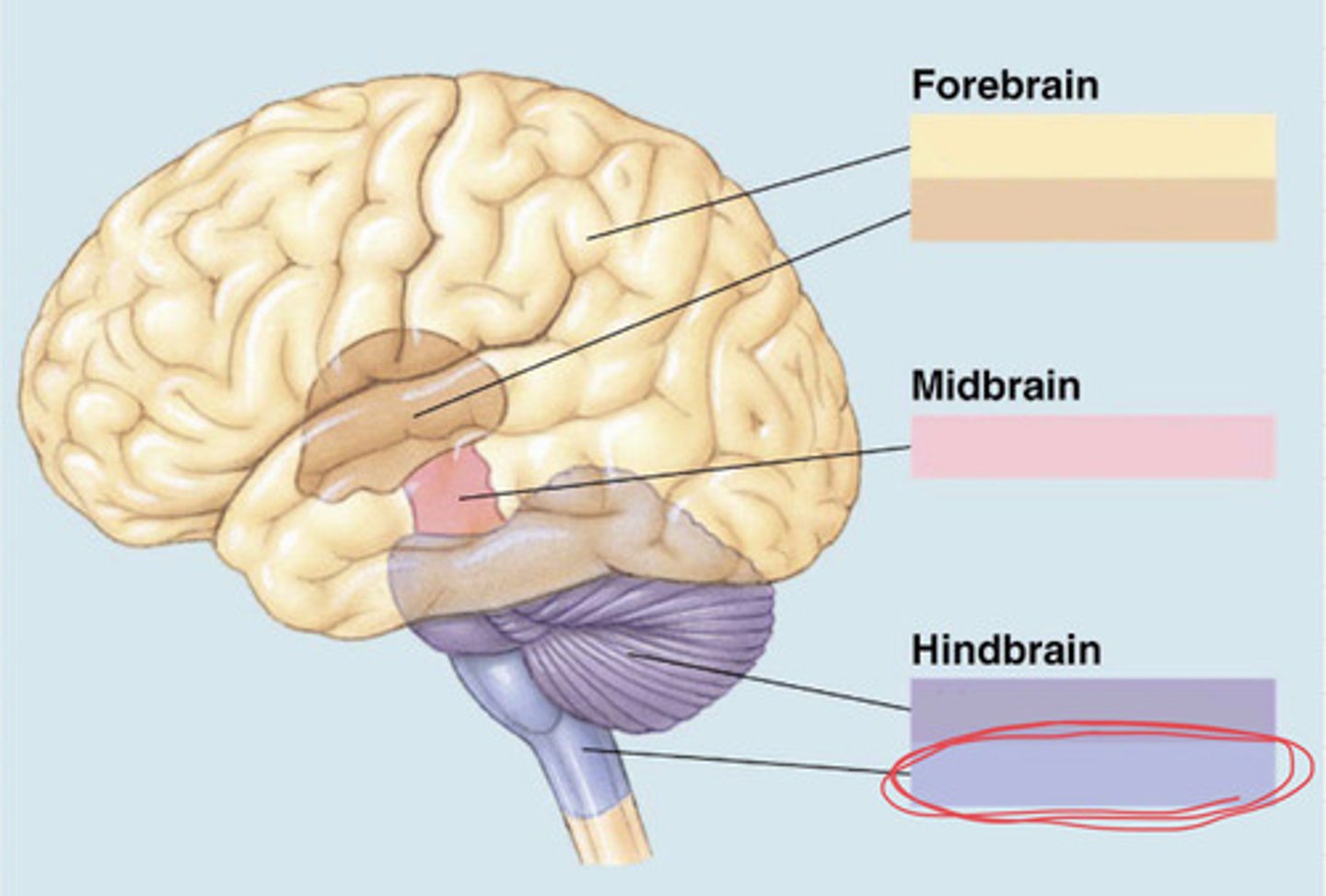
forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
Ventricle(s) in Forebrain (essay)
lateral third
ventricle(s) in the midbrain (essay)
cerebral aqueduct
ventricle(s) in the hindbrain (essay)
fourth
subdivisions of the forebrain (essay)
telencephalon and diencephalon
subdivision of the midbrain (essay)
mesencephalon
subdivision of the hindbrain (essay)
metencephalon and myelencephalon
principal structures of the telencephalon (essay)
Cerebral cortex, basal ganglia, limbic system
principle structures of the diencephalon (essay)
thalamus and hypothalamus
principle structures of the mesencephalon (essay)
tectum and tegmentum
principal structures of the metencephalon (essay)
cerebellum and pons
principle structures of the myelencephalon
medulla oblongata
forebrain
the most anterior prominent part of the mammalian brain with two cerebral hemispheres
2 hemispheres of the forebrain
telencephalon and diencephalon
cerebral cortex location
outer portion of the forebrain
longitudinal fissure
a groove that separates right and left hemispheres
corpus callosum
largest hemisphere-connecting tract
sulcus
a minor groove in the surface of the cerebral hemisphere
fissure
a major groove in the surface of the brain
gyrus
a raised part of the cortex of the cerebral hemispheres, separated by fissures or sulci
four lobes of the cerebral cortex
occipital, parietal, temporal, frontal
limbic lobe
potential fifth lobe of the cerebral cortex
primary visual cortex
the region of the posterior occipital lobe whose primary input is from the visual system
calcarine fissure
a fissure located in the occipital lobe on the medial surface of the brain; most of the primary visual cortex is located along its upper and lower banks
primary auditory cortex
the region of the superior temporal lobe whose primary input is from the auditory system
lateral fissure
the fissure that separates the temporal lobe from the overlying frontal and parietal lobes
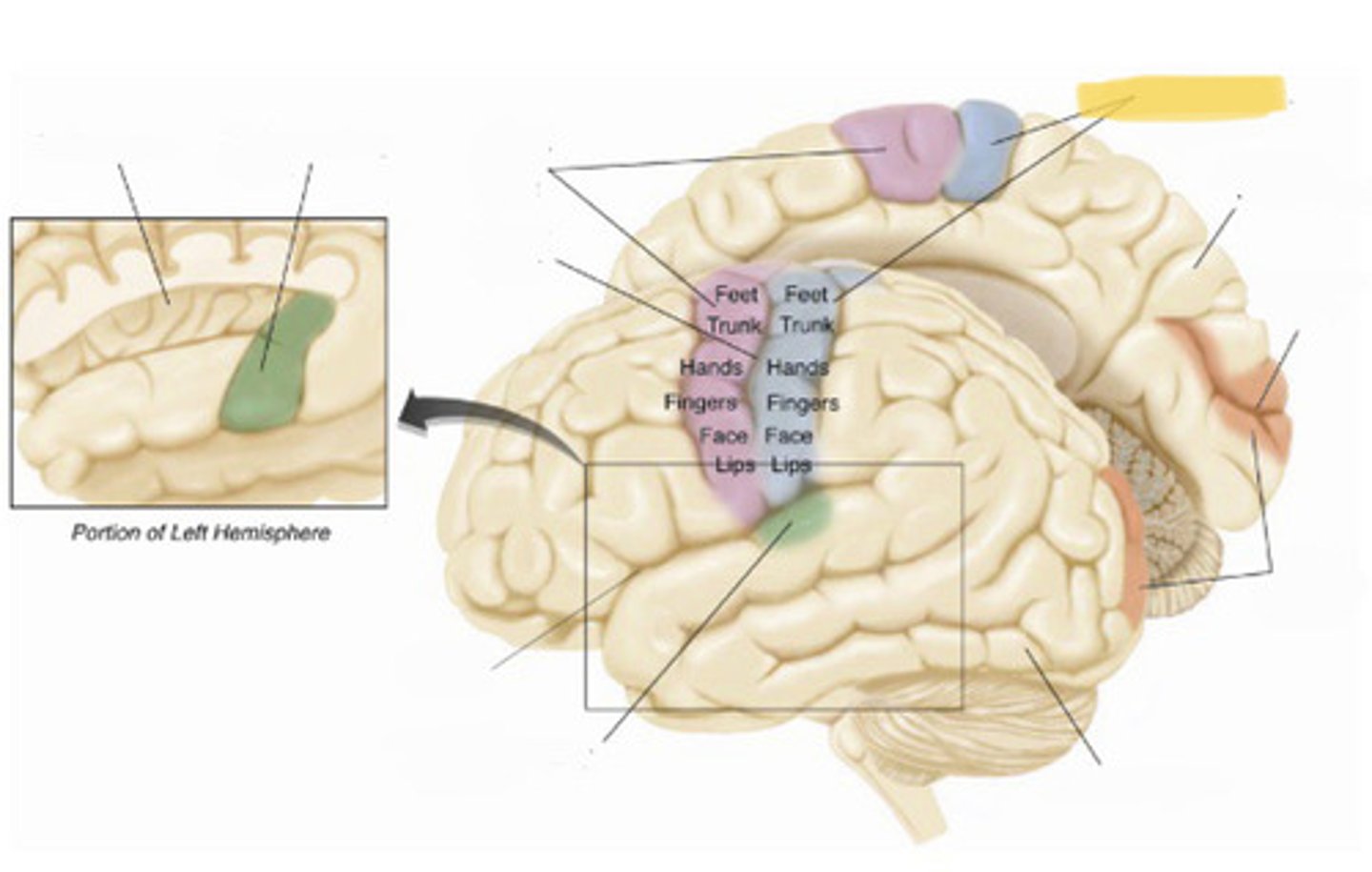
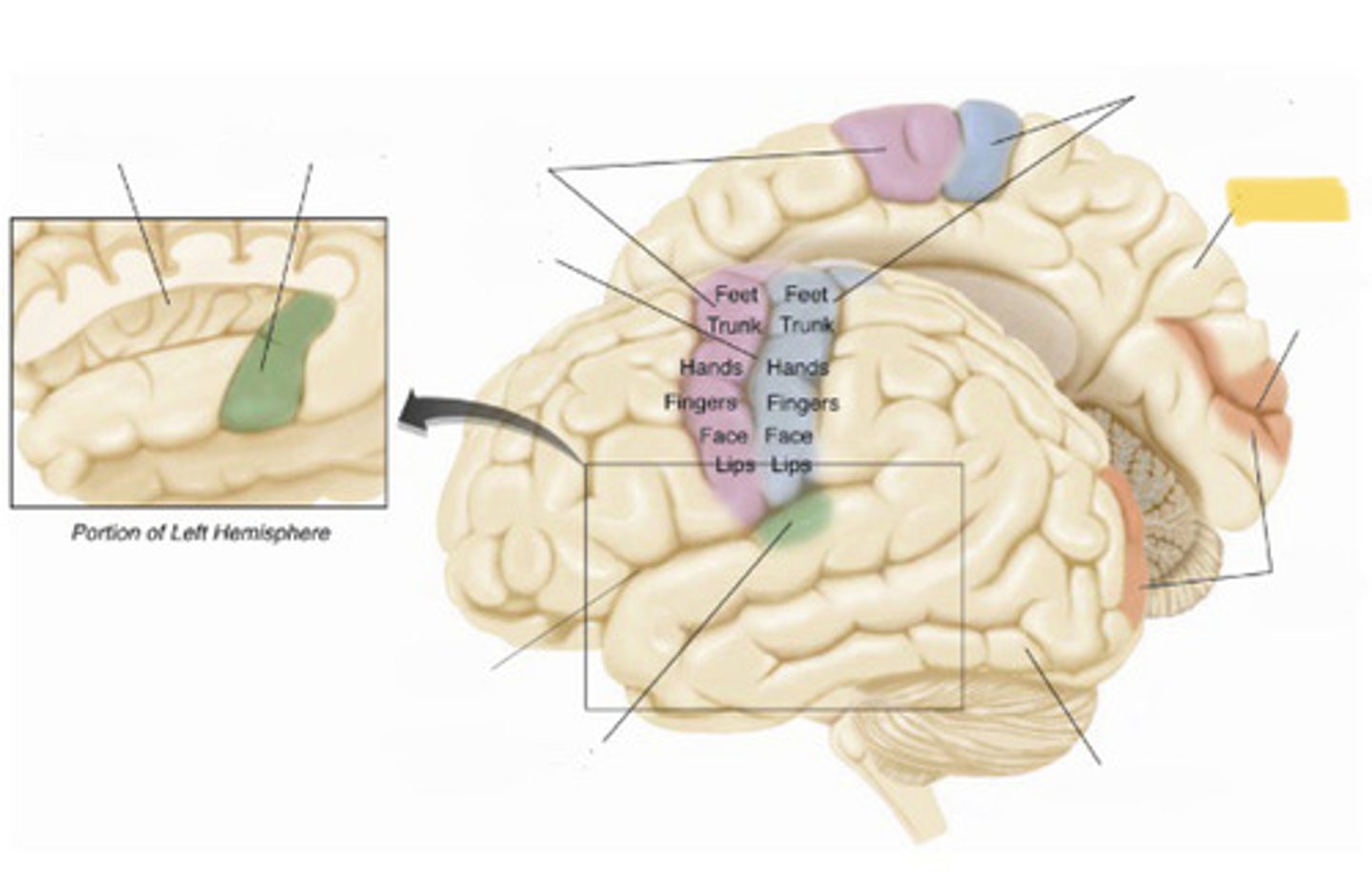
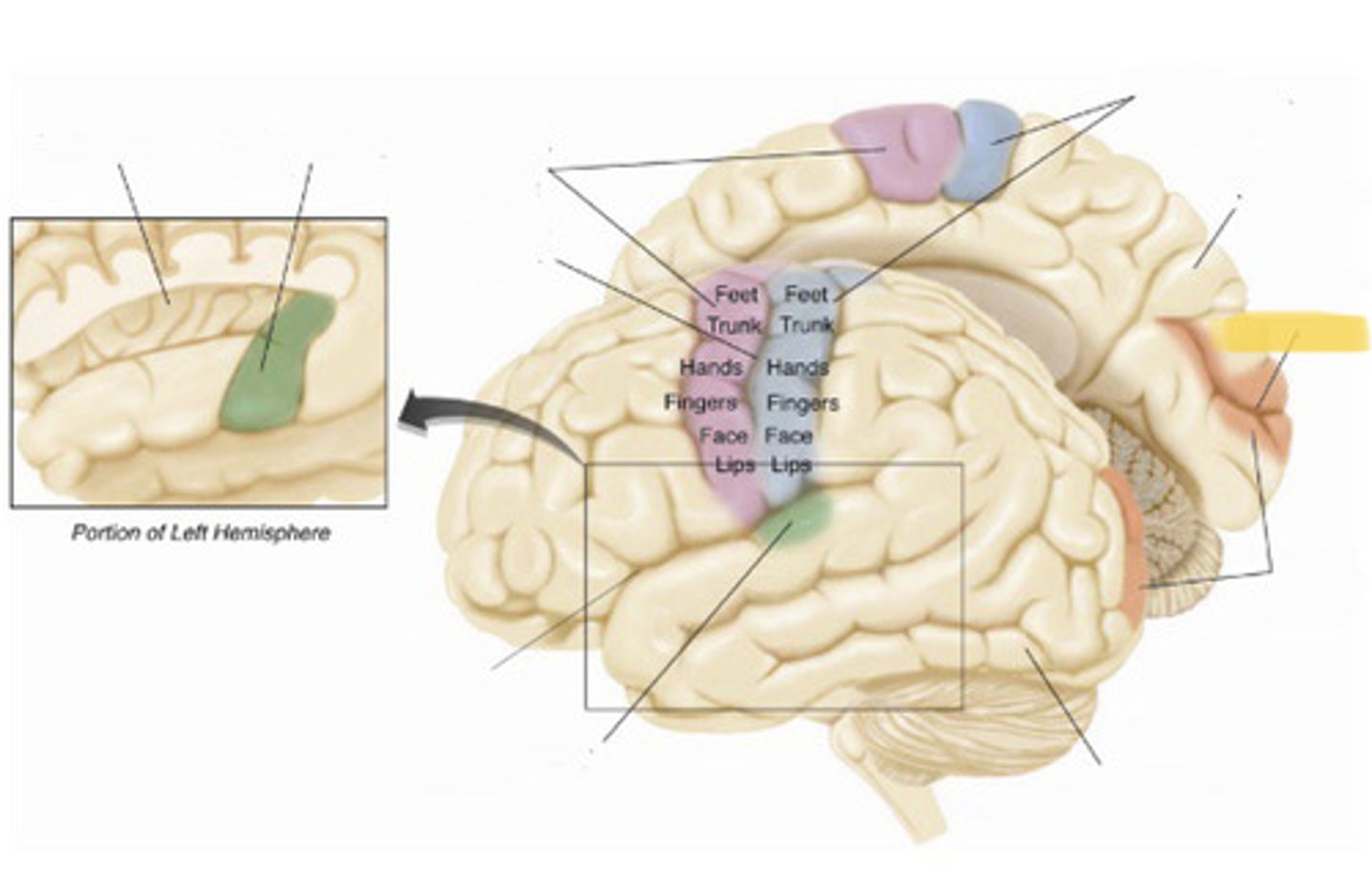
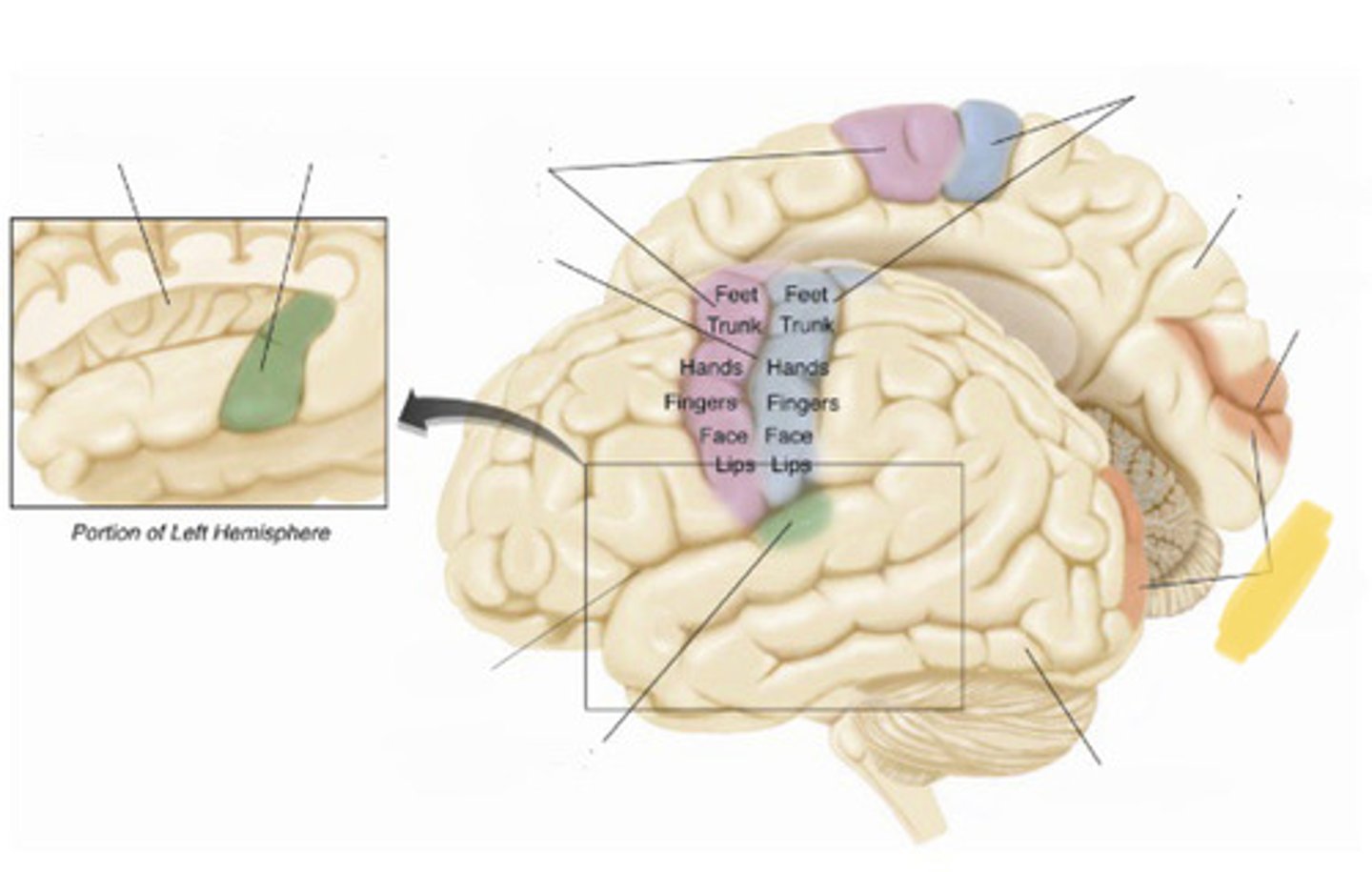
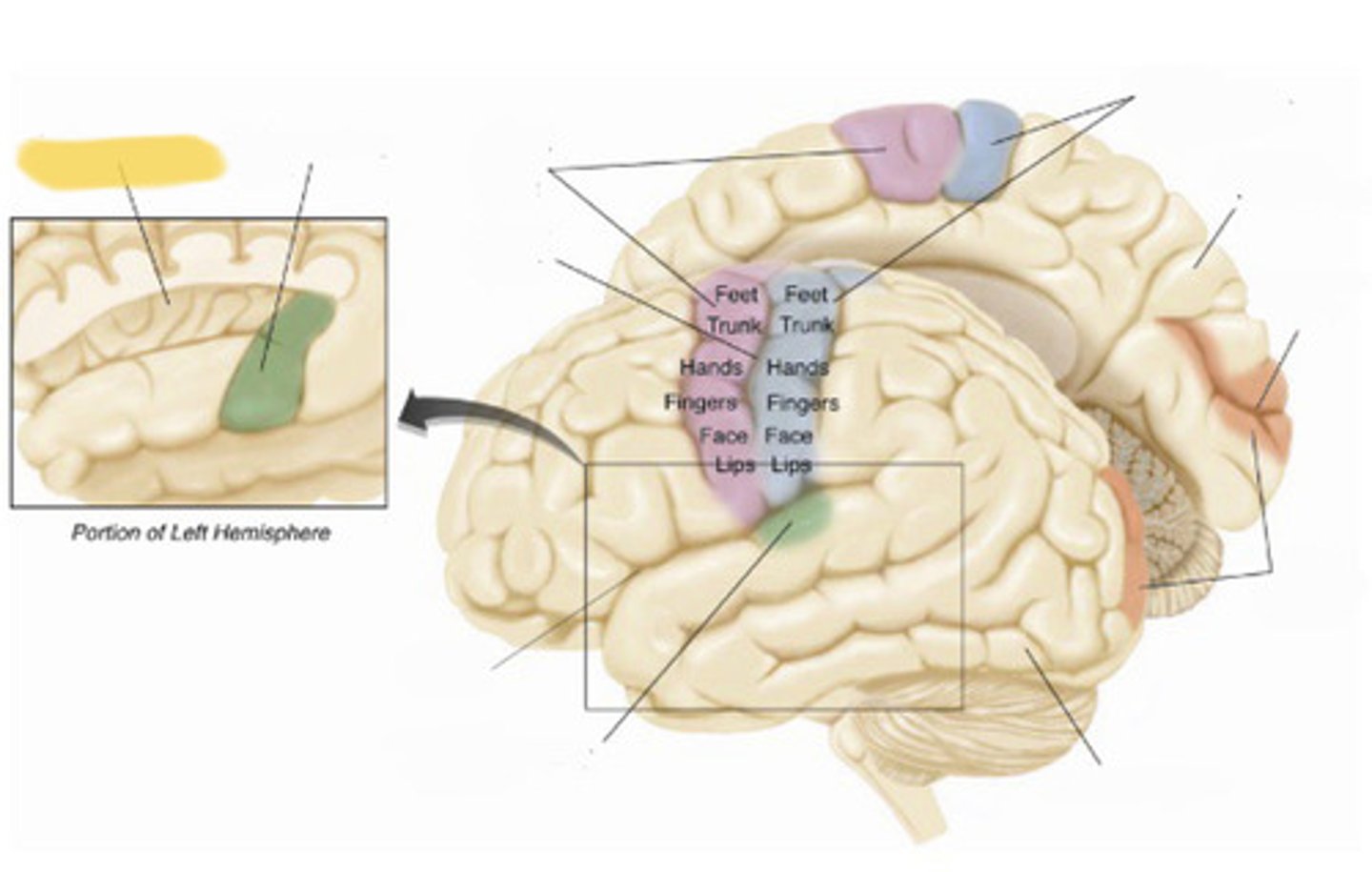
primary somatosensory cortex
the region of the anterior parietal lobe whose primary input is from the somatosensory system
central sulcus
the sulcus that separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe
primary motor cortex
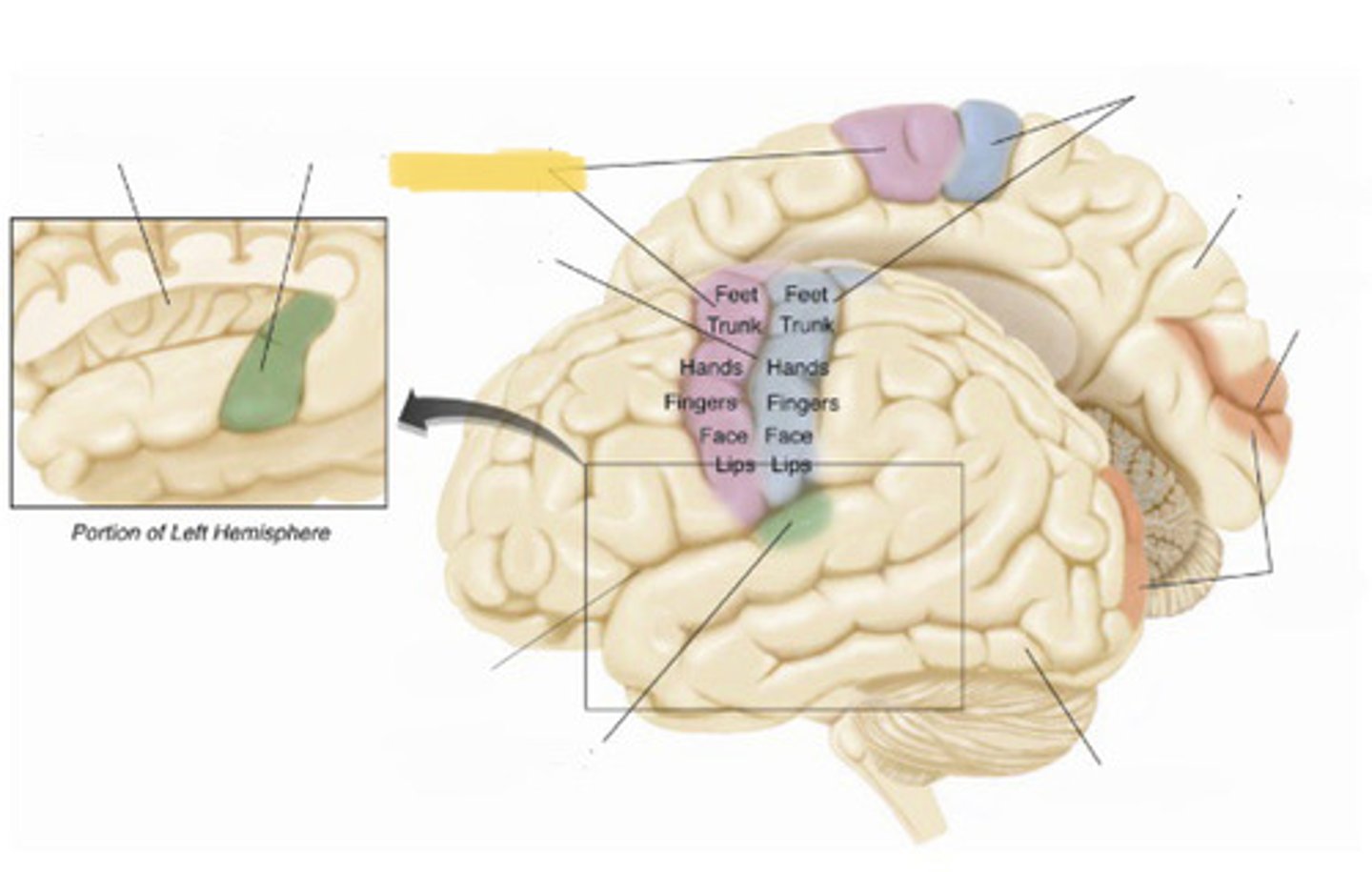
primary somatosensory cortex
right hemisphere
calcarine fissure
primary visual cortex
left hemisphere
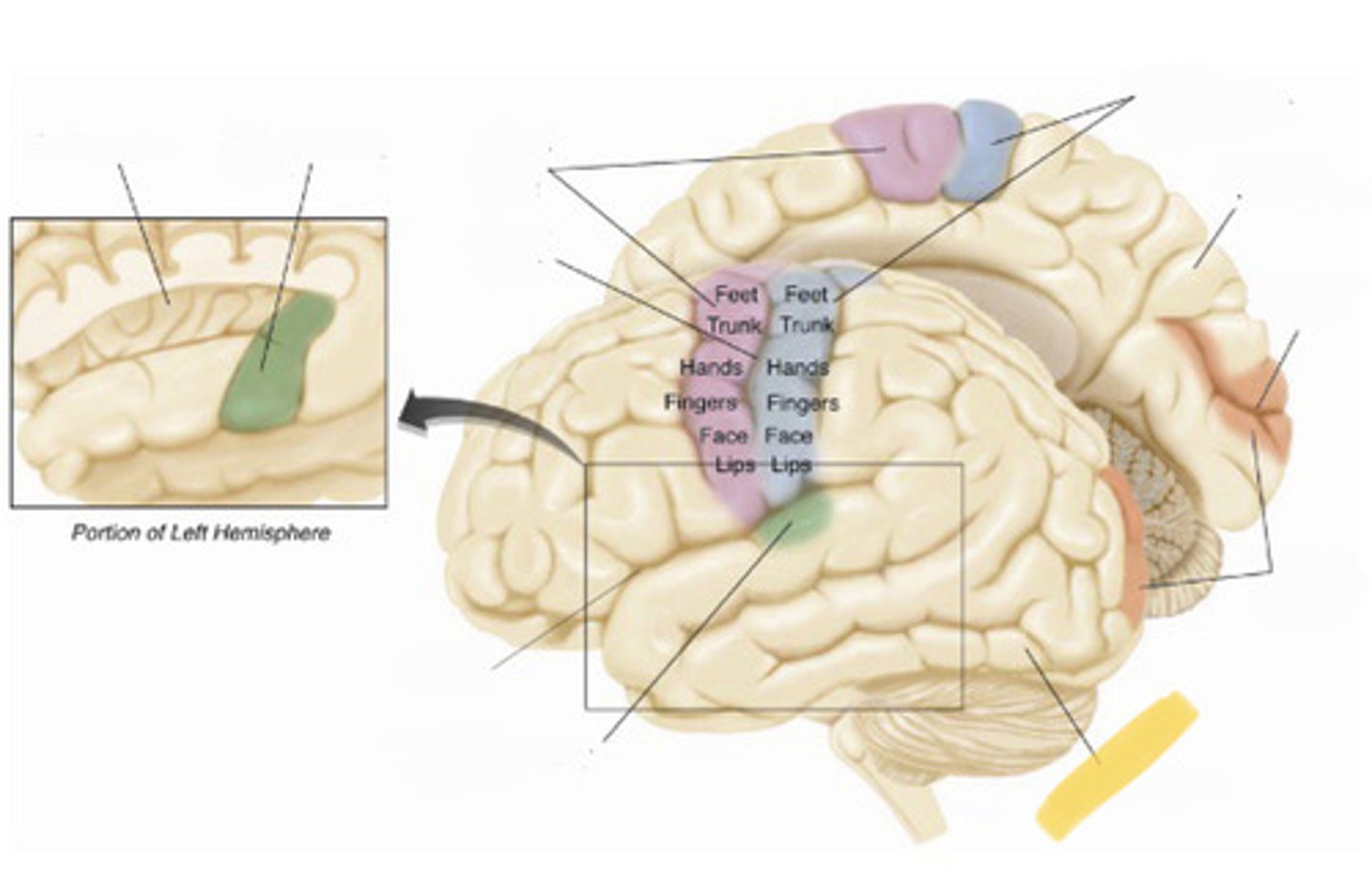
primary auditory cortex
lateral fissure
primary auditory cortex
insular cortex
sensory association cortex
those regions of the cerebral cortex that receive information from the regions of primary sensory cortex
motor association cortex
the region of the frontal lobe rostral to the primary motor cortex; also known as the premotor cortex
prefrontal cortex
the region of the frontal lobe rostral to the motor association cortex; complex cognitive behvaior
parts of the limbic system
olfactory bulb, hypothalamus, hippocampus, amygdala, cingulate gyrus of the cerebral cortex
functions associated with limbic system
motivation emotions: eating drinking sexual activity, anxiety, and aggression
structure underneath the cortex
thalamus and hypothalamus
thalamus
relay station from the sensory organs; main source of input tot he cortex
hypothalamus location
small area near the base
hypothalamus function
conveys messages to the pituitary gland to alter the release of hormones
pituitary gland
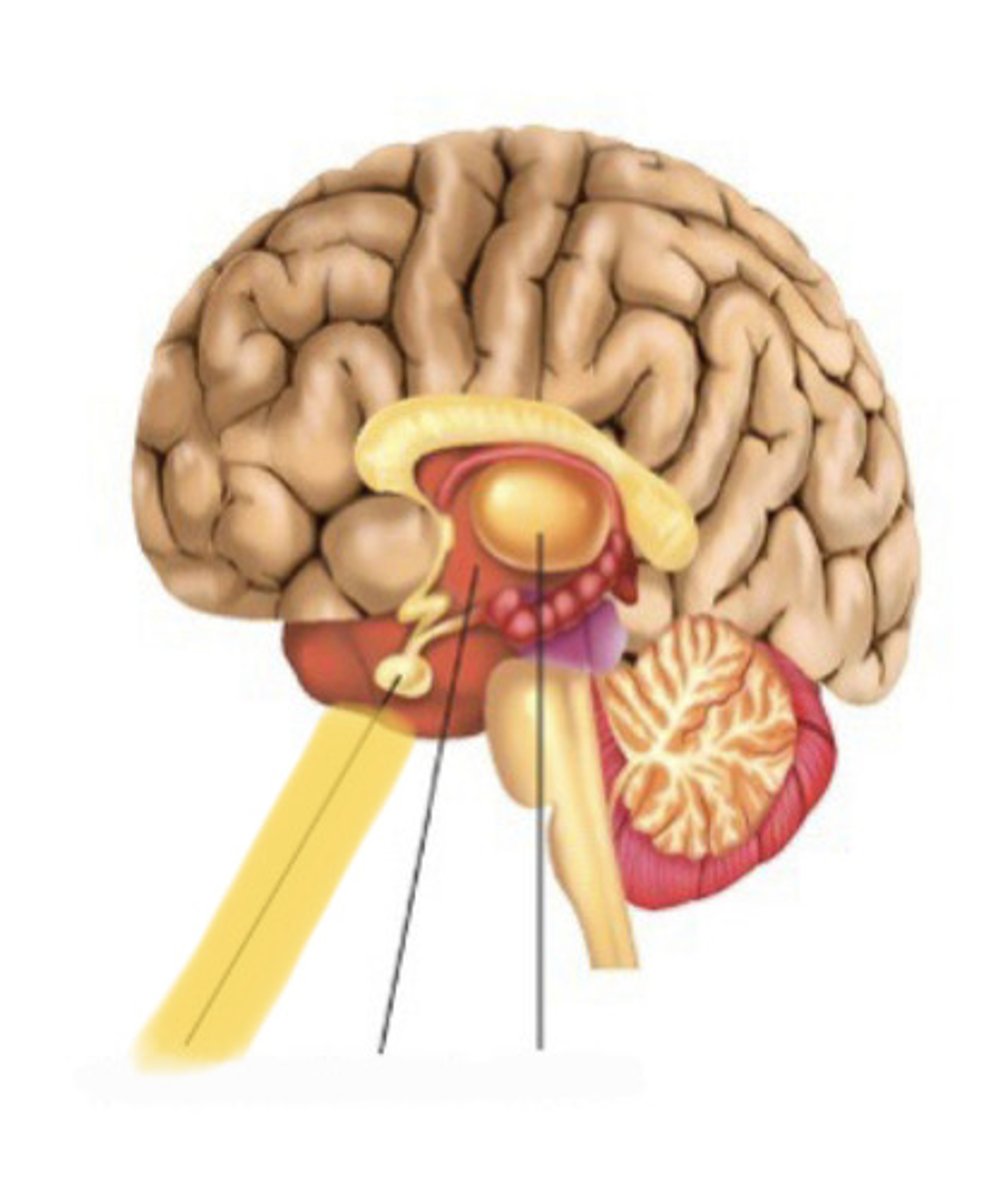
hypotahalamus
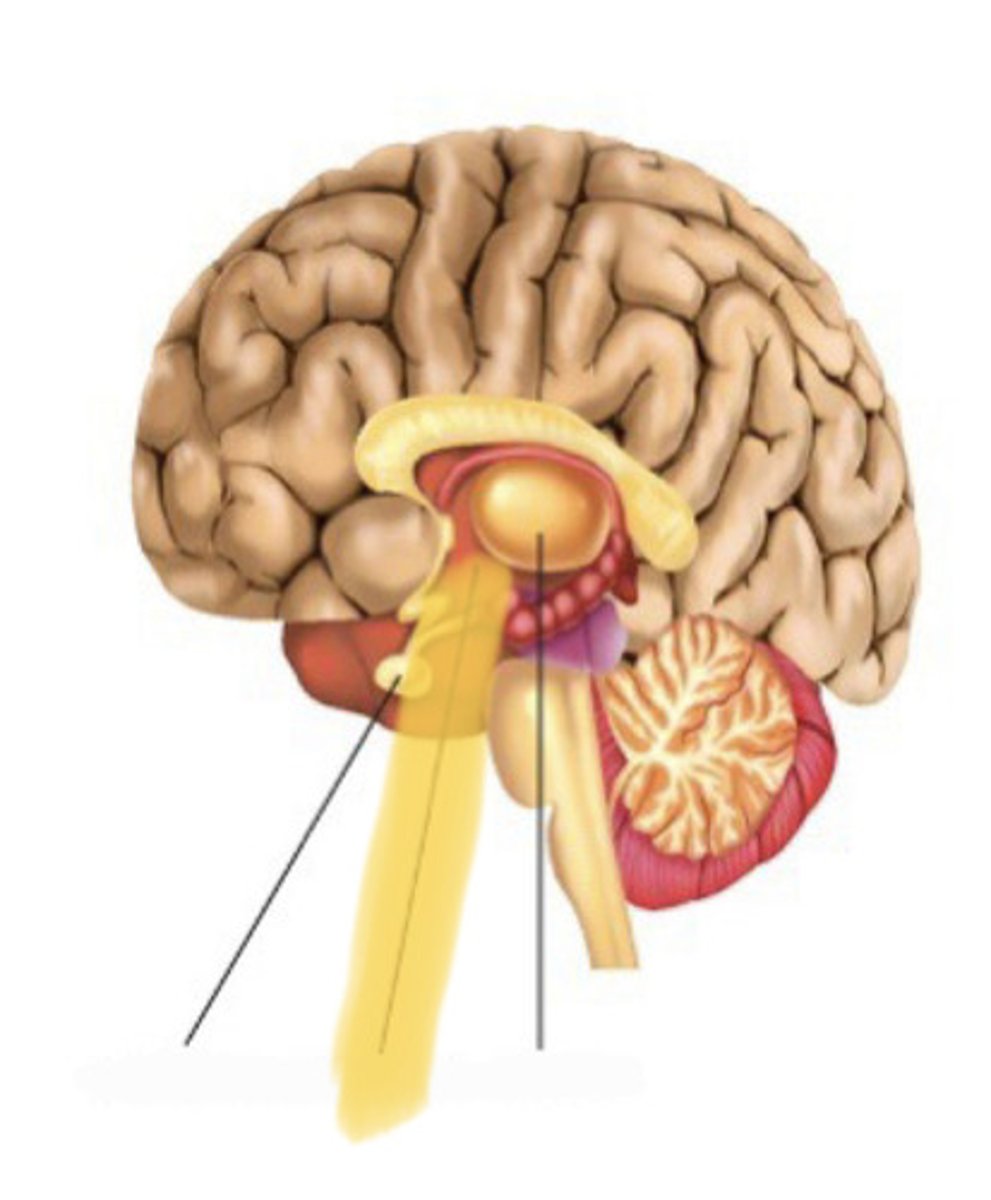
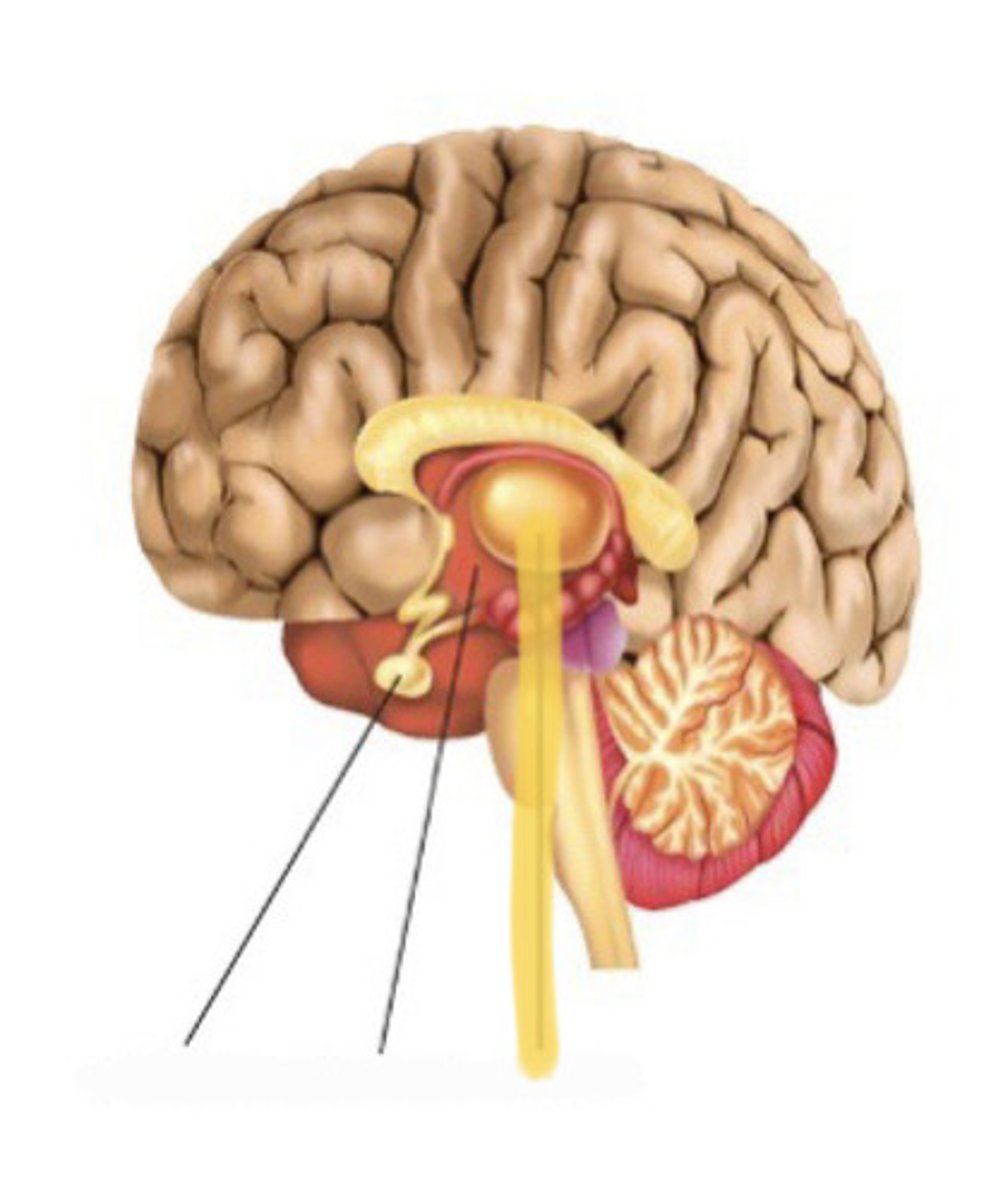
pituitary gland
hormone producing gland found at the base of the hypothalamus