AP BIO 1.4 - 1.5
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Carbohydrates
found in grains, fruits, and vegetables
Function: energy, structure, recognition, signaling
contains no nitrogen and phosphorus
What are the 3 sub-types of carbohydrates?
monosaccharide, disaccharide, polysaccharide
monosaccharides
simple sugars
building blocks
In clude hexoses: all have C6H12O6 with different isomers
Glucose - energy
Galactose - lactose
Fructose - fruit
dissaccharides
2 monosaccharides covalently bonded during condensation reaction
forms glycosidic linkage
i.e sucrose (glucose fructose) + maltose (glucose glucose)
polysaccharides
long chain of monosaccharides
may be branched/unbranched
starch
type of polysaccharide
stores plants’ energy
branched
limits the number of H-Bonds that can form
less compact
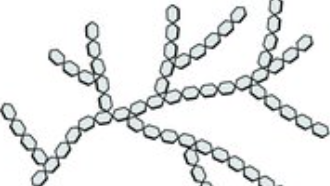
Glycogen
type of polysaccharide
stores animals’s energy (liver and muscles)
highly branched
makes solid deposits more compact than starch
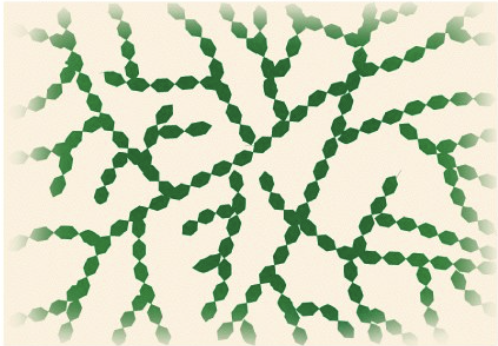
Cellulose
structures in plants (cell wall)
linear
parallel cellulose molecules form hydrogen bonds
creates thin fibers
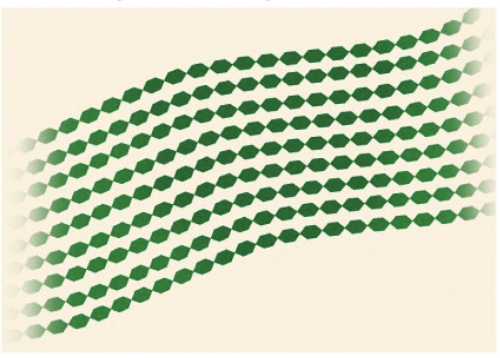
Chitin
structure fungal cell walls, insect exoskeletons, and crustacean shells
hard exoskeleton of arthropods
Also contains Nitrogen
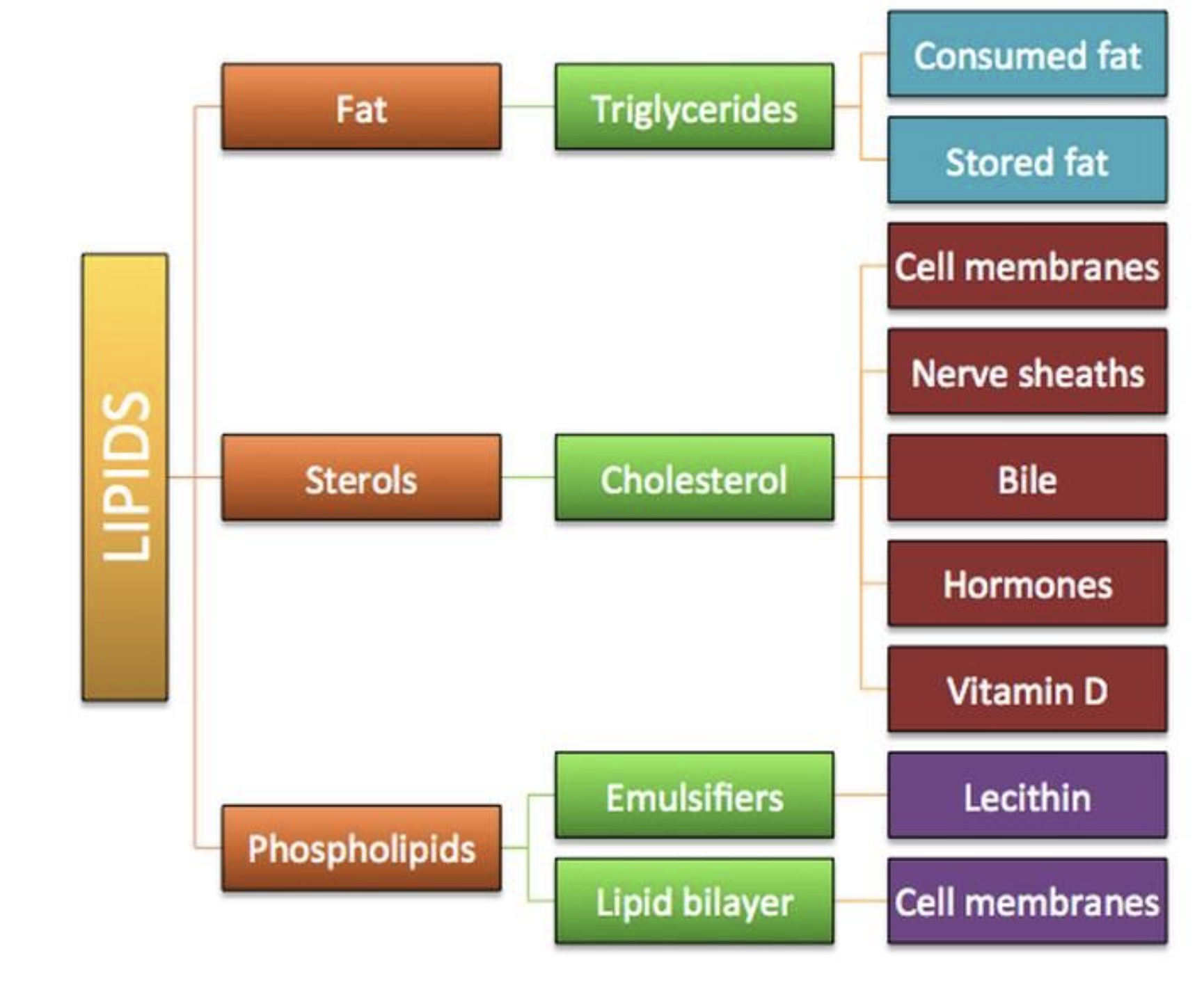
Lipids
diverse group of non-polar hydrocarbons
stores energy, provides insulation, cushioning, protection, serves as building blocks, in cellular membranes
Triglyceride
3 fatty acids (nonpolar hydrocarbon chain attached to a polar carboxyl group COOH) + 1 glycerol (an alcohol with 3 hydroxyl)
involves three condensation reactions forming three covalent bonds known as ester bonds, releasing 3 water molecules.
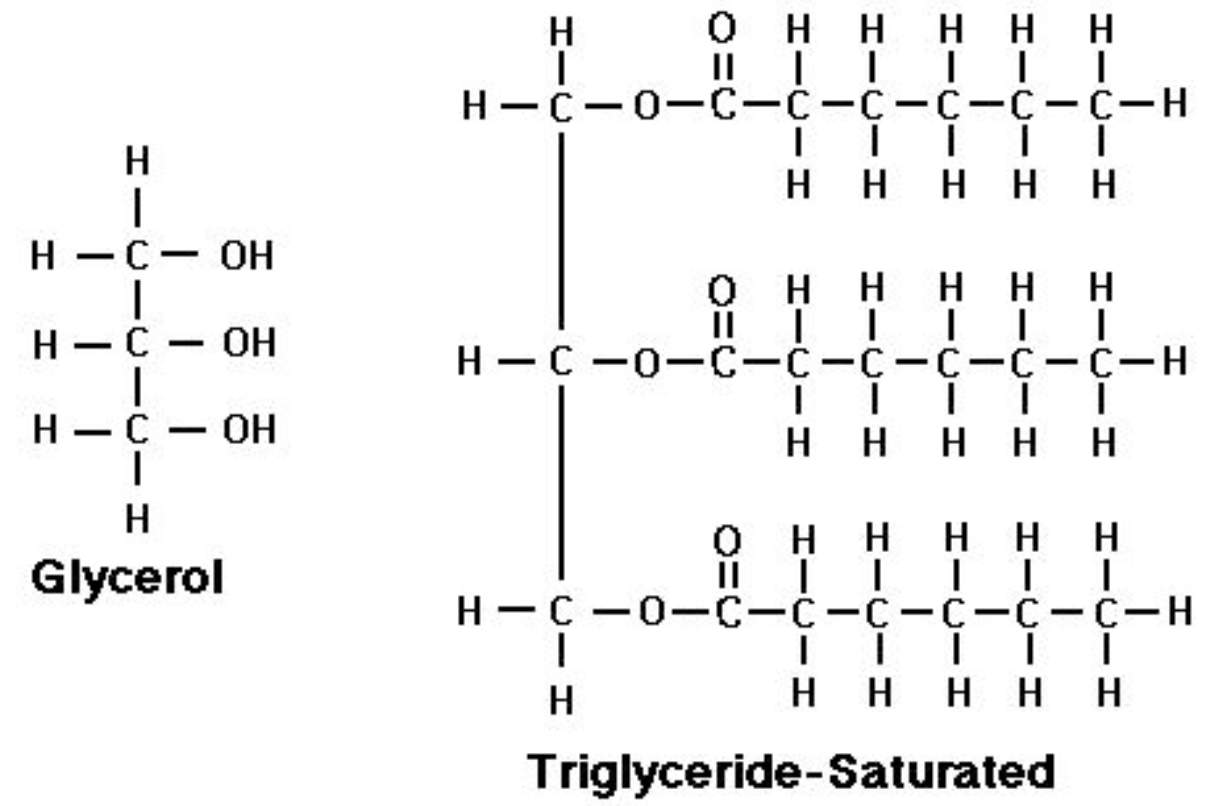
Saturated fat
“saturated” because it is saturated with H
no carbon carbon double bond
dense, pack tightly
exist as solid in room temperature
can cause cardiovascular diseases
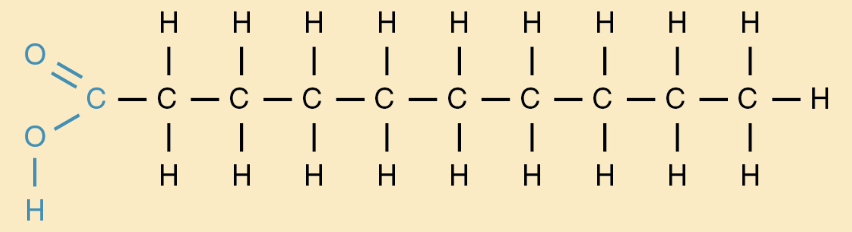
Unsaturated fat
contains at least 1 carbon carbon double bond
monounsaturated: 1 double bond
polyunsaturated: more than 1
liquids @ room temp
have a kink keeping them from being dense
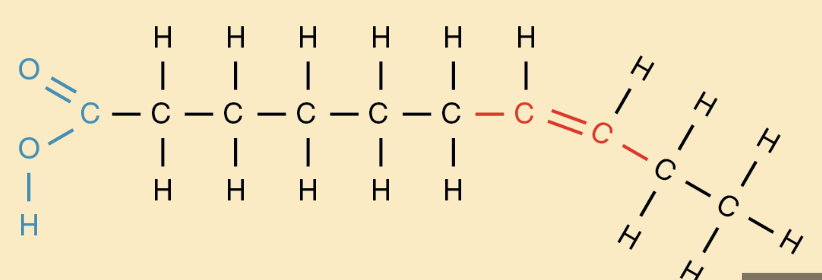
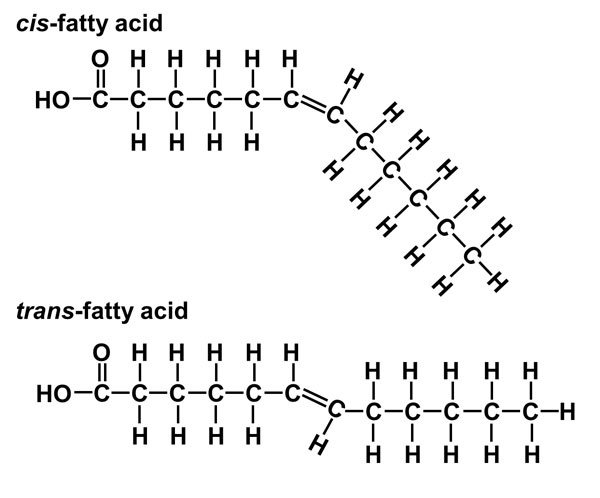
cis vs trans fat
cis fat has H on the same chain liquid, making the fat more bent → less dense
liquid
trans fat has H on opposite chains, meaning it has no bends and kinks
solids, very very unhealthy
essential fatty acids
Essential fatty acids – required but not synthesized by the body – must be part of diet
Omega-3 fatty acid (found in salmon, trout, tuna, and plants)
Omega 6-fatty acid
These fats are heart healthy
waxes
Long fatty acid chains esterified to long chain alcohols
Hydrophobic and prevent water from sticking to surface
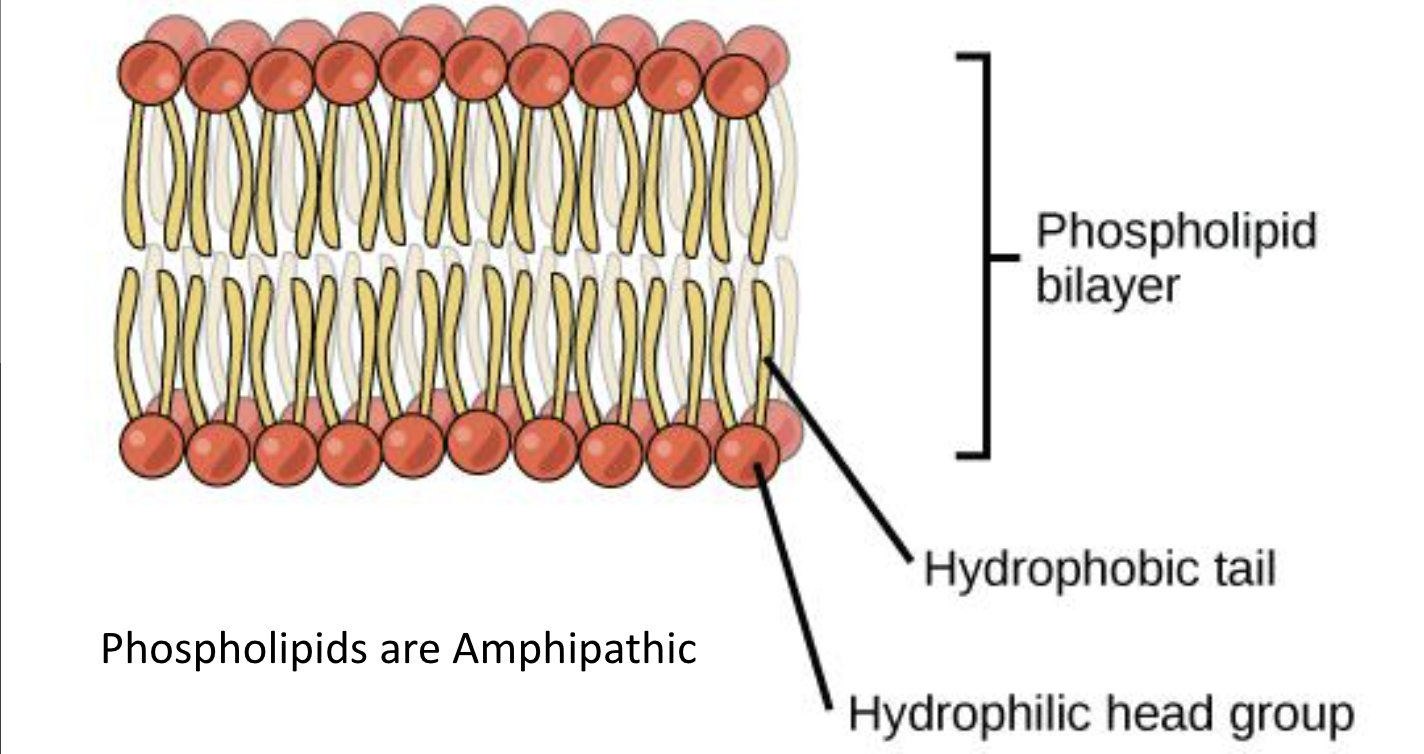
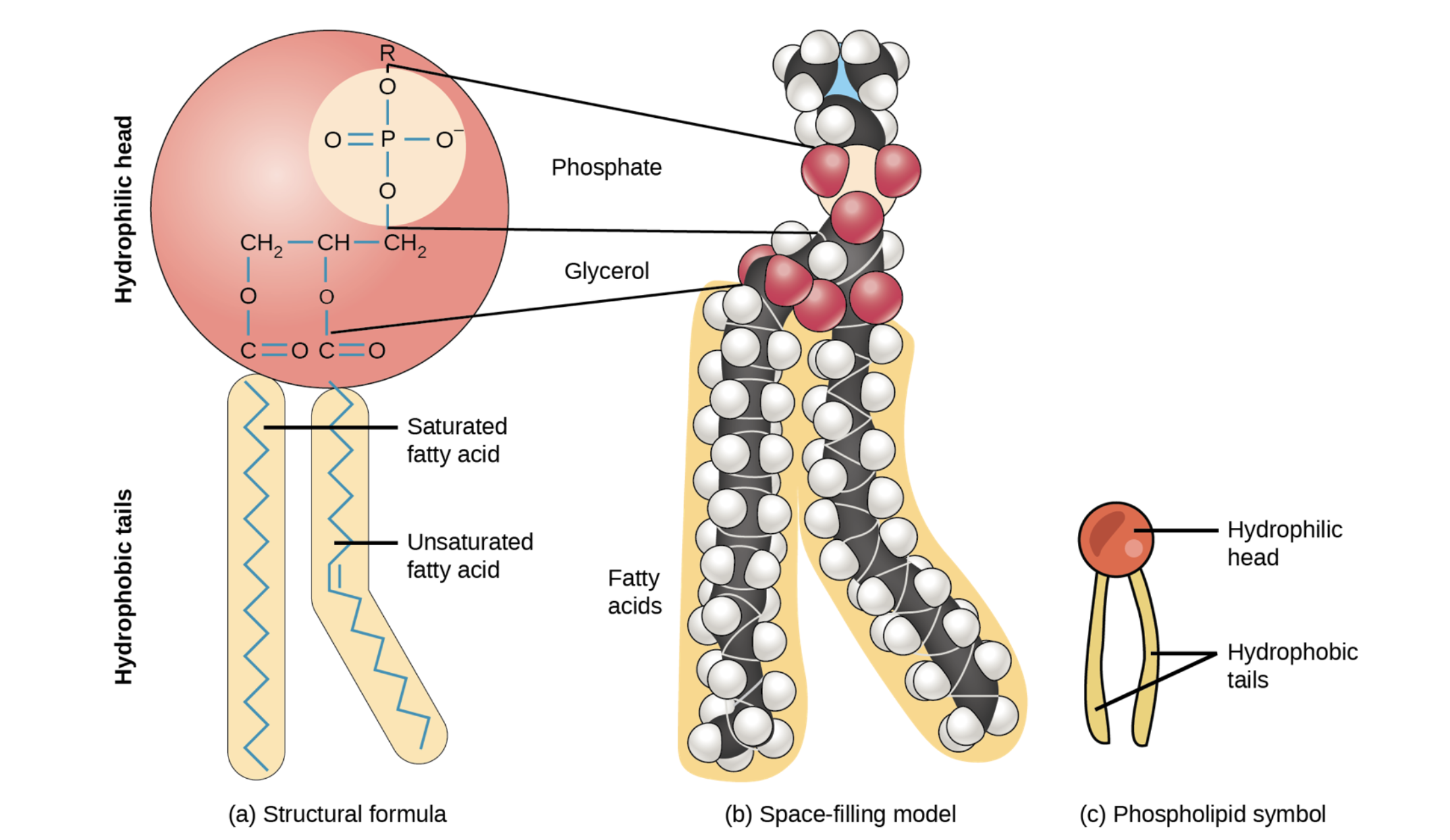
Phospholipid
2 fatty acids + a modified phosphate group attached to glycerol backbone
modified by adding a charged/polar chemical group
The hydrophilic head groups of the phospholipids face the aqueous solution
The hydrophobic tails are sequestered in the middle of the bilayer
Phospholipids contribute to dynamic nature of plasma membrane
Steroids
closed ring structure
4 linked carbon rings
short tail + hydrophobic
Precursor, “exigence”, to other hormones such as testosterone and estradiol, cholesterol, bile salts