Human Phys Blood
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
granulocytes
spotted, neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
agranulocytes
no spots, lymphocytes, monocytes
neutrophils
sausage links, big cell, most common, 40-70%, short term infections
eosinophils
red and blue, 1-4%, kill worms, numbers go up in response to allergic reaction
basophils
0-1%, just dots, contain histomine
lymphocyte
2nd most numerous, most of cell is nucleus, 20-45%, immune system, B+T cells
monocytes
biggest, plumber crack, 4-8%, eat things, chronic infections
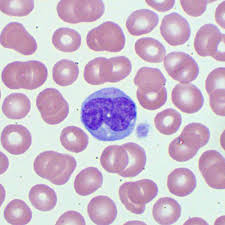
monocyte
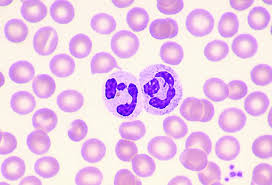
neutrophil
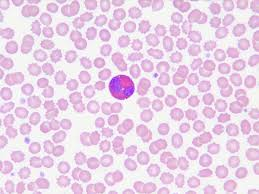
eosinophil
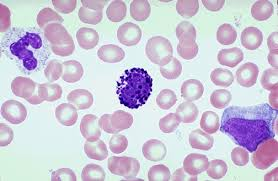
basophil
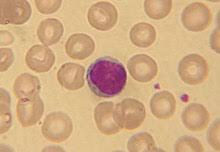
lymphocytes
lematocrit
red blood cells
buffy coat
white bload cells and platelets
plasma includes
proteins and substances
erythrocytes
RBCs, oxygen transport, no nucleus, no mitochondria, contain hemoglobin
how much hemoglobin does each cell have
250 million
what do platelets form from
megakaryocyte explosion
blue triangle
A antigen
black circle
B antigen
green thing
Rh antigen
antibodies
Y-shaped proteins that attach to antigens
agglutination
antibodies sticking cells together
hemolysis
blood starts to burst, releasing hemoglobin
why are blood transfusions dangerous
agglutination
hemolysis
kidney failure
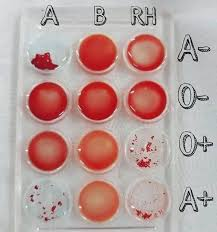
how to determine blood type using a tray
if its not a black hole, it will have that type of blood
hi
anemia
oxygen carrying ability decreases
causes of anemia
lower number of RBCs and defiecient hemoglobin
sickle-cell anemia
RBCs rupture easily, clog small blood vessels
Cause of sickle-cell anemia
single-gene mutation
polycytnemia
abnormal increase in RBCs
causes of polycythemia
bone marrow cancer and living at high altitudes
leukemia
cancer of bone marrow, huge numbers of WBCs that don’t function properly, decreased immune system
thrombus
clot that develops and persists in an unbroken blood vessel
embolus
thrombus that breaks away from the vessel wall
thrombocytopenia
insufficient number of platelets
hemophelia
hereditary disorder lack of clotting factors