Health Justice in Action: Role of SODH in PAD
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
causes of disparities in PAD/CLIL
-lack of awareness
-differences in risk factors and comorbidities
-high prevalence of risk factors and undertreatment
-clinical presentation variation
-social-political determinants of health/structural racism
-amputation lottery
-lack of screening “at-risk” population by USPSTF
-disparities in clinical trials
-statistical determinatino
-specialty deserts/variation by specialty-deliver of care
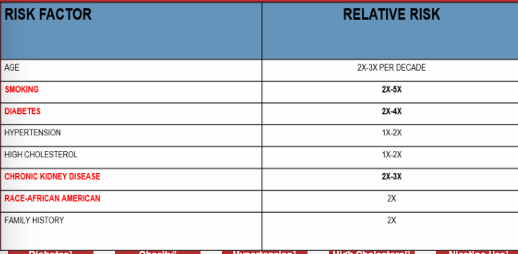
modifiable PAD risk factors
-often neglected in black americans
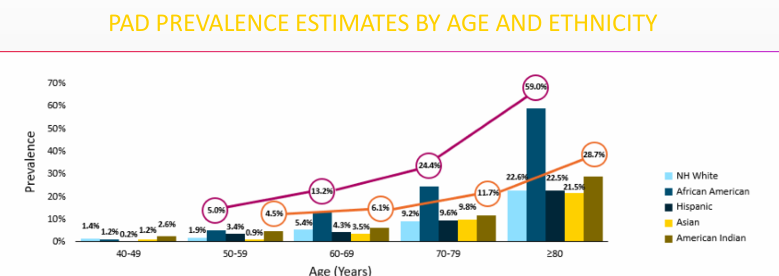
PAD prevalence disproportionately higher in
-African American & Native American populations
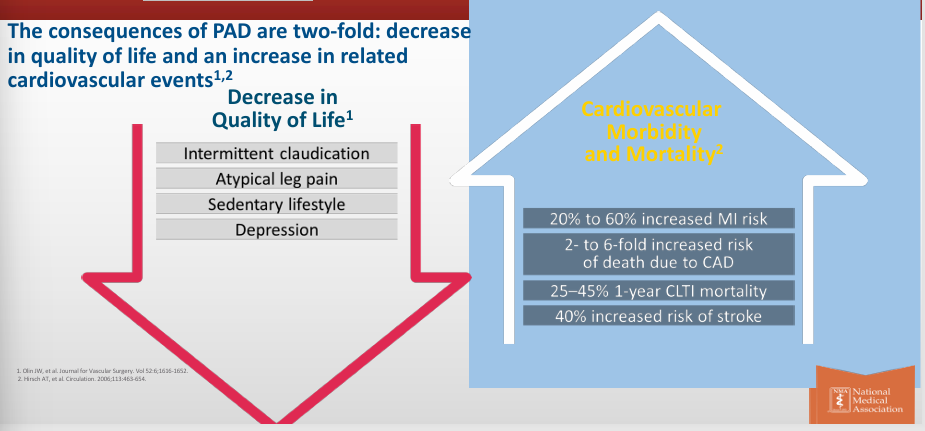
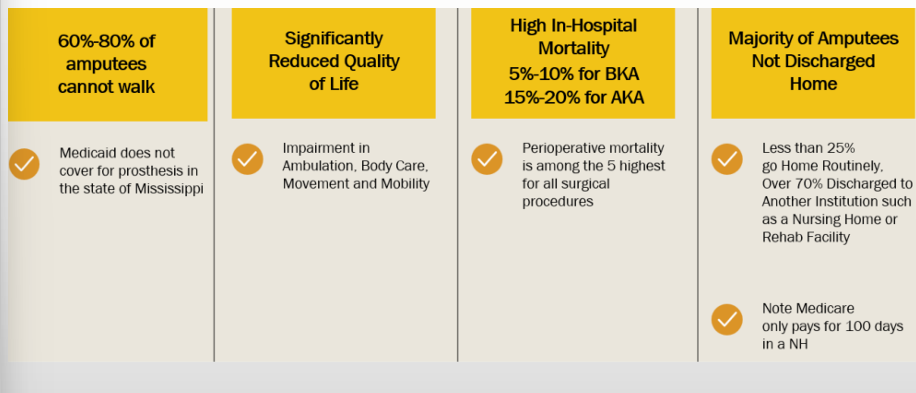
impact of PAD on patients
statins underused in
-high-risk Black Americans
opportunities for amputation prevention
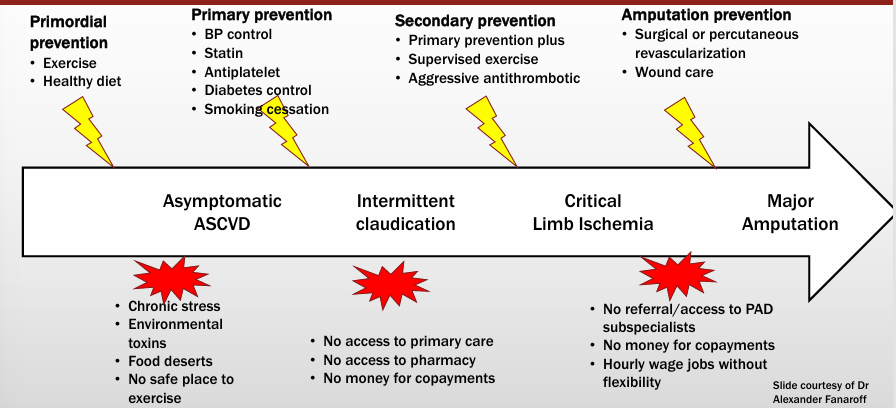
impact of SDOH

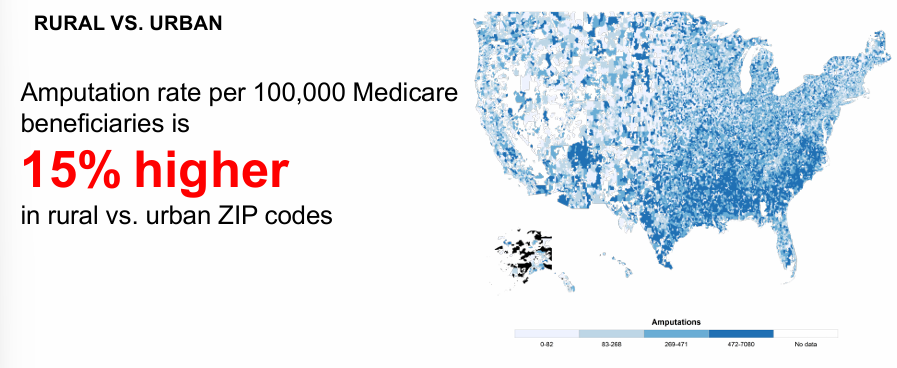
disparities in amputations
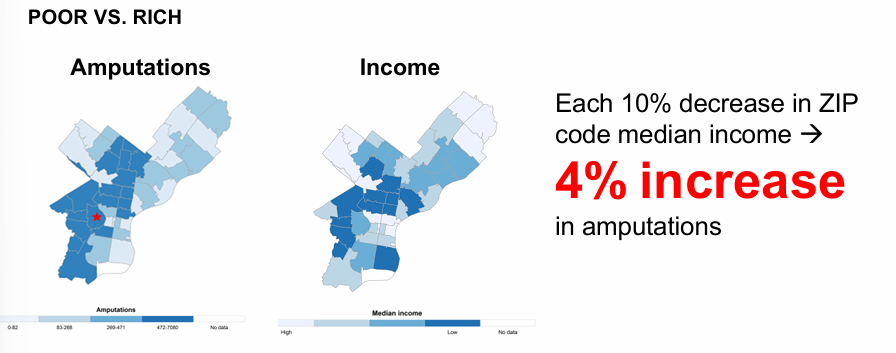
income disparities in amputations
probability of major amputation depends on
-who you are and where you live
-race/ethnicity/age/sex
-SES, hospital vascular program (majority undergoing amputations are Medicare/Medicaid recipients)
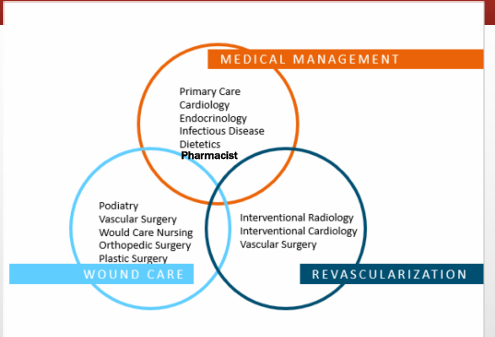
multispecialty team approach
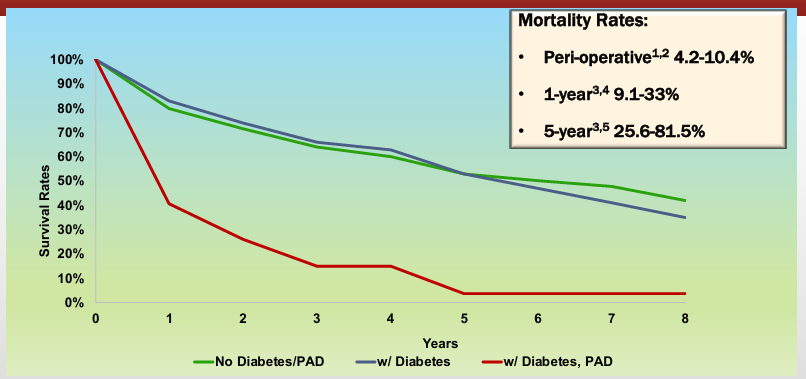
how diabetes impacts critical limb ischemia

why PAD amputations matter in diabetic patients
-poor outcomes post-amputation
evils of amputation
angiography
-underutilized before amputation
barriers related to social determinants have significant CLTI implications
-addressing poor literacy level/lack of educational awareness
-addressing financial burdens
-transportation
-prior authorization barriers
-optimization of home-based exercise interventions, monitoring, and lack of reimbursement
-chronic disease management with a limited/aging workforce
-racism in healthcare
Get a Pulse on PAD Campaign overview- call to action

amputation reduction and compassion (ARC) act

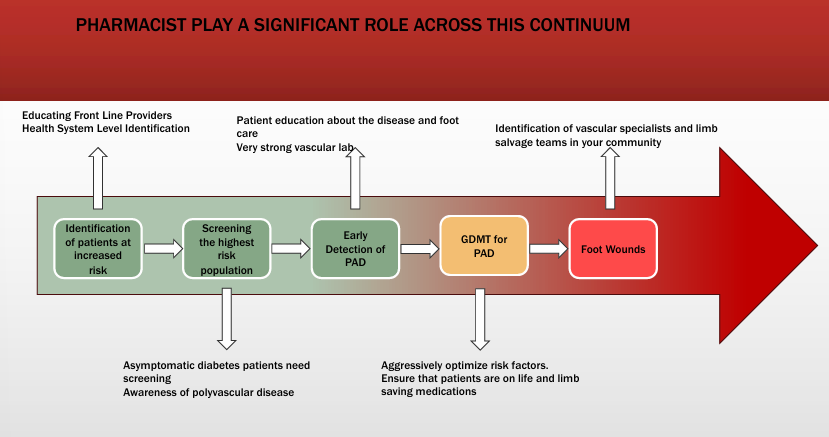
advanced practitioners play a role
-valuable in medical-specialty deserts
-clinical skills can be learned
-used in hospital/ASC/OBL settings
-chronic care disease Rx gatekeepers
-assist in community outreach and education
key SODH problem
-20% rural patients lack broadband access compared to 1% of Urban patients

call to action- stakeholder collaboration

racism in healthcare
-structural racism exists
-racism is a system
-racism saps the strength of the whole society, leading to a waste of human resources
-racism can be dismantled
key factors to organizational success
-find a champion
-build effective leadership
-effective communication
-clinical excellence/publish data
-foster life long learning (bring them to conferences)
-patient-centered care/shared decision making
-community engagement
-efficient operations
-multi-societal stakeholder collaboration
-continuous quality improvement
-financial management